Geochemical Composition of the Lomé Lagoon Sediments, Togo: Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Major, Trace and Rare Earth Element Concentrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
- to characterize the micro-granulometry of the sediments to assess the particle size distribution,
- to evaluate the spatio-temporal variability of major, trace, and rare earth element concentrations,
- to determine the Ce and Eu anomalies and La/Yb ratios to evaluate the Rare Earth Element (REE) fractionation and its controlling factors,
- to assess the sediment quality using enrichment factors calculated using different normalizing elements (Al, Cs, Fe, Ti) and a local reference material,
- to assess the potential ecotoxicological risks for aquatic ecosystems by comparing TE concentrations with Sediment Quality Guidelines (SQG) and by determining the percentage of a non-residual fraction or labile fraction of TE.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling and Processing
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Data Processing
2.4.1. Enrichment Factor
2.4.2. Sediment Quality Assessment Based on Sediment Quality Guidelines (SQG)
2.4.3. Calculation of Ce and Eu Anomalies and (La/Yb)N Ratio in Rare Earth Elements (REE)
with N = normalized.
2.5. Statistical Analyses and Data Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Granulometry and Micro-Granulometry of the Lomé Lagoon Sediments
3.2. Major Element Composition of the Lomé Lagoon Sediments
3.3. Rare Earth Element (REE) Content and Seasonal Variability
3.4. Trace Element (TE) Composition of the Lomé Lagoon Sediments
3.4.1. Seasonal Variability
3.4.2. Enrichment Factors (EF)
Choice of Reference Material
Choice of the Normalizing Element
Enrichment Factors of Trace Elements
3.4.3. Distribution of TE between the Residual and Non-Residual (labile) Phases
3.4.4. Comparison with the Sediment Quality Guidelines (SQGs)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marthe, Y.K.; Lanciné, G.D.; Bamory, K.; Aristide, D.G.; Ardjouma, D. Seasonal and Spatial Variations in Water Physicochemical Quality of Coastal Potou Lagoon (Côte d’Ivoire, Western Africa). J. Water Resour. Prot. 2015, 7, 748. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, J.; Saleem, M.; Munir, H.S. Spatial distribution, environmental assessment and source identification of metals content in surface sediments of freshwater reservoir, Pakistan. Geochemistry 2016, 76, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, Q.; Meng, F.; Lin, Y.; Du, Y. Integrated toxicity evaluation of metals in sediments of Jiaozhou Bay (China): Based on biomarkers responses in clam Ruditapes philippinarum exposed to sediment extracts. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, V.; Nithya, B.; Magesh, N.S.; Jayaprakash, M. Seasonal variations and environmental risk assessment of trace elements in the sediments of Uppanar River estuary, southern India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabakaran, K.; Nagarajan, R.; Eswaramoorthi, S.; Anandkumar, A.; Merlin, F. Environmental significance and geochemical speciation of trace elements in Lower Baram River sediments. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 933–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Walker, T.R.; Davis, E.; Ma, G. Spatiotemporal characterization of metals in small craft harbour sediments in Nova Scotia, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Ni, S. Metal contamination in sediment of one of the upper reaches of the Yangtze River: Mianyuan River in Longmenshan Region, Southwest of China. Soil Sediment Contam. 2015, 24, 368–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, Z.; Shi, Y.; Ni, S.; Wang, R.; Xu, W.; Xu, J. Distribution of potentially toxic elements in sediment of the Anning River near the REE and V-Ti magnetite mines in the Panxi Rift, SW China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonathan, M.P.; Sarkar, S.K.; Roy, P.D.; Alam, M.A.; Chatterjee, M.; Bhattacharya, B.D.; Bhattacharya, A.; Satpathy, K.K. Acid leachable trace metals in sediment cores from Sunderban mangrove wetland, India: An approach towards regular monitoring. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, S.; Ramasamy, S.; Chandrasekar, N.; Simon Peter, T.; Gopal, V.; Godson, P.S.; Magesh, N.S. Trace element concentrations in reef associated sediments of Koswari Island, Gulf of Mannar biosphere reserve, southeast coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rousan, S.; Al-Taani, A.A.; Rashdan, M. Effects of pollution on the geochemical properties of marine sediments across the fringing reef of Aqaba, Red Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myung, C.J. Heavy metal contamination of soils and waters in and around the Imcheon Au-Ag mine, Korea. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 1661, 369–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.D.; Mahmood, K.; Sultan, M.J.; Khan, A.S.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Sagintayev, Z. Trace element geochemistry of groundwater from Quetta Valley, Western Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J. Geochemistry of trace elements and water quality assessment of natural water within the Tarim River Bassin in the extreme arid region, NW China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 136, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.; Di Martino, V. Trace element compartmentation in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica and biomonitoring applications. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwesigye, A.R.; Tumwebaze, S.B. Water contamination with heavy metals and trace elements from Kilembe copper mine and tailing sites in Western Uganda; implications for domestic water quality. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Ternengo, S.; Marengo, M.; El Idrissi, O.; Yepka, J.; Pasqualini, V.; Gobert, S. Spatial variations in trace element concentrations of the sea urchin, Paracentrotus lividus, a first reference study in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, I.; Yang, Z. Inputting history of heavy metals into the inland Lake recorded in sediment profiles: Poyang lake in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-X.; Li, M.; Zhao, C.; Yang, K.; Li, K.; Peng, M.; Yang, Z.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Bai, R.; et al. Concentrations of toxic metals and ecological risk assessment for sediments of major freshwater lakes in China. J. Geochem. Exp. 2015, 157, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbie, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danovaro, R. Pollution threats in the Mediterranean Sea: An overview. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 19, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, C.K. Assessing the impact of human activities on British Columbia’s estuaries. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coynel, A.; Gorse, L.; Curti, C.; Schafer, J.; Grosbois, C.; Morelli, G.; Ducassou, E.; Blanc, G.; Maillet, G.M.; Mojtahid, M. Spatial distribution of trace elements in the surface sediments of a major European estuary (Loire Estuary, France): Source identification and evaluation of anthropogenic contribution. J. Sea Res. 2016, 118, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, L.M.; Djaneye-Boundjou, G.; Boyode, B.P.; Assih, B.T. Water quality evaluation from Lomé’s lagoon: Effects on heavy metals contamination on fishes. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2007, 11, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gnandi, K.; Han, S.; Rezaie-Boroon, M.H.; Porrachia, M.; Deheyn, D. Increased Bioavailability of Mercury in the Lagoons of Lomé, Togo: The Possible Role of Dredging. AMBIO 2011, 40, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayah, M. Contribution des Apports Anthropiques dans la Pollution d’un Hydrosystème Lagunaire Subtropical: Hydrogéochimie du Système Lagunaire de Lomé. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lomé, Lomé, Togo, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mimikou, M.A.; Baltas, E.; Varanou, E.; Pantazis, K. Regional impacts of climate change on water resources quantity and quality indicators. J. Hydrol. 2000, 234, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardta, K.; Ulbrichb, U. Potential impacts of climate change on groundwater recharge and stream flow in a central European low mountain range. J. Hydrol. 2003, 284, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Jain, S.K. Trends in seasonal and annual rainfall and rainy days in Kashmir valley in the last century. Quatern. Int. 2010, 212, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuseppe, S.; Sibel, E.; Flavia, F.; Lukuba, N.S.; Giulia, L. Effects of seasonal change and seawater intrusion on water quality for drinking and irrigation purposes, in coastal aquifers of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 64–84. [Google Scholar]
- Bharathi, M.D.; Patra, S.; Sundaramoorthy, S.; Madeswaran, P.; Sundaramanickam, A. Elucidation of seasonal variations of physicochemical and biological parameters with statistical analysis methods in Puducherry coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayah, M.; Malgorzata, G.; Lallébila, T.; Bawa, L.M.; Bril, H.; Djaneye-Boundjou, G. Qualité et pollution des eaux d’un hydrosytème littoral tropical: Cas du système lagunaire de Lomé, Togo. Eur. Sci. J. 2015, 11, 95–119. [Google Scholar]
- Adjoussi, P. Changement Climatique Global: Évaluation de L’évolution des Paramètres Climatiques au Togo. Master’s Thesis, University of Lomé, Lomé, Togo, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Salomons, W.; Förstner, U. Trace metal analysis on polluted sediments. I: Assessment of Sources and Intensities. Environ. Technol. Lett. 1980, 1, 494–505. [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz, A.J.; Elrick, K.A. The relation of stream sediment surface area, grain size and composition to trace element chemistry. Appl. Geochem. 1987, 2, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, J.L.; Messaïtfa, A.; Krempp, G.; Behra, P. Fluvial transports of mercury pollution in the Ill river basin (Northeastern France): Partitioning into aqueous phases, suspended matter and bottom sediments. In Mercury Contaminated Site; Ebinghaus, R., Ed.; Environmental Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 501–520. [Google Scholar]
- Mahvi, A.H.; Mesdaghinia, A.R.; Naghipoor, D. Comparison of heavy metal extraction efficiency in contamined soil by various concentration of EDTA. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2005, 8, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Baize, D.; Saby, N.; Walter, C. Le cuivre extrait à l’EDTA dans les sols de France Probabilités de carences et de toxicités selon la BDAT. Etude Gest. Sols 2006, 13, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Leleyter, L.; Rousseau, C.; Biree, L.; Baraud, F. Comparison of EDTA, HCl and sequential extraction procedures, for selected metals (Cu, Mn, Pb, Zn), in soils, riverine and marine sediments. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 116, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaker, A. Hydrologie et Biogéochimie du Bassin Versant du Fleuve Ibrahim: Un Observatoire du Fonctionnement de la Zone Critique au Liban. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toulouse, Toulouse INP, Toulouse, France, 2016; 256p. [Google Scholar]
- Benabdelkader, A.; Taleb, A.; Probst, J.L.; Belaidi, N.; Probst, A. Anthropogenic contribution and influencing factors on metal features in fluvial sediments from a semi-arid Mediterranean river basin (Tafna River, Algeria): A multi-indices approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, M.A.; Payre-Suc, V.; Julien, F.; Camara, M.; Baque, D.; Probst, A.; Sidibe, K.; Probst, J.L. Geochemical composition of fluvial sediments in the Milo River basin (Guinea): Is there any impact of artisanal mining and of a big African city, Kankan? J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 145, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, R.; Stoner, J.H. Pb in particulates from the lower atmosphere of the eastern Atlantic. Nature 1973, 245, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, B.; Nombela, M.A.; Vilas, F. Geochemistry of Major and Trace Elements in Sediments of the Ria de Vigo (NW Spain): An Assessment of Metal Pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, L.; Probst, A.; Probst, J.L.; Erwin, U. Heavy metal distribution in some French forest soils: Evidence for atmospheric contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 312, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Azzi, D.; Viers, J.; Guiresse, M.; Probst, A.; Aubert, D.; Caparros, J.; Charles, F.; Guizien, K.; Probst, J.L. Origin and fate of copper in a small Mediterranean vineyard catchment: New insights from combined chemical extraction and δ65Cu isotopic composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celis-Hernandez, O.; Rosales, L.; Cundy, A.B.; Carranza-Edwards, A.; Croudace, I.W.; Hernandez-Hernandez, H. Historical trace element accumulation in marine sediments from the Tamaulipas shelf, Gulf of Mexico: An assessment of natural vs anthropogenic inputs. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, P.; Pradhap, D.; Krishnakumar, S.; Silva, J.D.; Vidyasakar, A.; Sackaria, M.; Godson, P.S.; Arumugam, K.; Magesh, N.S. A baseline study on trace element based sediment pollution and potential ecological risk of reef sediments of Musal, Manoli and Manoli putti Islands, Gulf of Mannar, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’guessan, Y.M. Dynamique des Éléments Traces Dans les Eaux de Surfaces des Bassins Versant Agricoles de Gascogne. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paul Sabatier—Toulouse III, Toulouse, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- N’guessan, Y.M.; Probst, J.L.; Bur, T.; Probst, A. Trace elements in stream bed sediments from agricultural catchments (Gascogne region, S-W France): Where do they come from? Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2939–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; Mc Lennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1985; 321p. [Google Scholar]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leleyter, L.; Probst, J.L.; Depretris, P.; Haida, S.; Mortatti, J.; Rouault, R.; Samuel, J. REE distribution pattern in river sediments: Partitioning into residual and labile. Comptes Rendus Académie Sci. Ser. IIA Earth Planet. Sci. 1999, 329, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussiez, V.; Ludwig, W.; Probst, J.L.; Monaco, A. Background levels of heavy metals in surficial sediments of the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean): An approach based on 133Cs normalization and lead isotope measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 26, 1843–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; De Caritat, P. Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: Regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Sci Total Environ. 2005, 337, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupré, B.; Allègre, C.J. A global geochemical mass budget applied to the Congo Basin Rivers: Erosion rates and continental crust composition. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 3469–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celis-Hernandez, O.; Rosales-Hoz, L.; Carranza-Edwards, A. Heavy metal enrichment in surface sediments from the SW Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8891–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bur, T.; Probst, J.L.; N’guessan, Y.M.; Probst, A. Distribution and origin of lead in stream sediments from small agricultural catchments draining Miocene molassic deposits (SW France). Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avumadi, A.; Gnandi, K.; Probst, J.L. Trace element distribution and enrichment in the stream sediments of the Lake Togo watersheds (South of Togo). Adv. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 4, 87–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol. 2000, 39, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windom, H.L.; Schropp, S.J.; Calder, F.D.; Ryan, J.D.; Smith, R.G.; Burney, L.C. Natural trace metal concentrations in estuarine and coastal marine sediments of the southeastern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Weijden, C.H. Pitfalls of mormalization of marine geochemical data using a common divisor. Mar. Geol. 2002, 184, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinex, S.A.; Wright, D.A. Distribution of trace metals in the sediments and biota of Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1988, 19, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loring, D.H. Lithium a new approach for the granulometric normalization of trace metal data. Mar. Chem. 1990, 29, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hissler, C.; Probst, J.L. Impact of mercury atmospheric deposition on soils and streamsin a mountainous catchment (Vosges, France) polluted by chlor-alkali industrial activity: The important trapping role of the organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 361, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, F. A procedure for correcting the grain size effect in heavy metal analyses of estuarine and coastal sediments. Environ. Technol. Lett. 1980, 1, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloundi, M.K.; Duplay, J.; Quaranta, G. Heavy metal contamination of coastal lagoon sediments by anthropogenic activities: The case of Nador (East Morocco). Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deely, J.M.; Fergusson, J.E. Heavy metal and organic matter concentrations and distributions in dated sediments of a small estuary adjacent to a small urban area. Sci. Total Environ. 1994, 153, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, N.F.Y.; Yao, M.W.Y. Normalization and heavy metal contamination in mangrove sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 216, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Morgan, L.J. The potential for biological effects of sediment-sorbed contaminants tested in the National Status and Trends Program. In NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS OMA 52; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Seattle, WA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- MENVIQ/EC. Critères Intérimaires pour L’évaluation de la Qualité des Sédiments du Saint-Laurent; Environnment Canada—Centre Saint-Laurent et Ministère de l’Environnement du Québec: Montréal, QC, Canada, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Persaud, D.; Jaagumagi, R. Guidelines for the Protection and Management of Aquatic Sediment Quality in Ontario; Water Resources Branch; Ontario Ministry of the Environment: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1993; p. 27. ISBN 0-7778-9248-7. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.I.; MacDonnald, D.D.; Keenleyside, K.A.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Field, J. A preliminary evaluation of sediment quality assessment values for freshwater ecosystems. J. Great Lake. Res. 1996, 22, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonnald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T.A. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binelli, A.; Sarkar, S.K.; Chatterjee, M.; Riva, C.; Parolin, M.; Bhattacharya, B.D.; Bhattacharya, A.K.; Satpathy, K.K. A comparison of sediment quality guidelines for toxicity assessment in the Sunderban wetlands (Bay of Bengal, India). Chemosphere 2008, 78, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, A.; Yang, G.; Liu, J. Assessing metal toxicity in sediments of Yellow River wetland and its surrounding coastal areas, China. Estuar. Coastal Shelf Sci. 2014, 151, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Chen, J.; Ru, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Wei, C. Heavy metals in river surface sediments affected with multiple pollution sources, South China: Distribution, enrichment and source apportionment. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 176, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhong, W. Toxicities and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake, China, based on sediment quality guidelines. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 62, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwell, S.I.; Apeti, A.D.; Pait, A.S.; Radenbaugh, T.; Britton, R. Benthic habitat contaminant status and sediment toxicity in Bristol Bay, Alaska. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 24, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.F. A review of chemical-based sediment quality assessment methodologies for the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merhaby, D.; Ouddane, B.; Net, S.; Halwani, J. Assessment of trace metals contamination in surficial sediments along Lebanese Coastal Zone. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehler, W.T.; Gagliardi, B.; Keough, M.J.; Pettigrove, V. Evaluating freshwater mining sediment toxicity in Tasmania: Achieving strong multiple lines of evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kechiched, R.; Laouar, R.; Bruguier, O.; Salmi-Laouar, S.; Kocsis, K.; Bosch, D.; Foufou, A.; Ameur-Zaimeche, O.; Larit, H. Glauconite-bearing sedimentary phosphorites from the Tébessa region (eastern Algeria): Evidence of REE enrichment and geochemical constraints on their origin. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 145, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, A.V. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the ocean. Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2004, 39, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifuoggi, M.; Donadio, C.; Ferrara, L.; Stanislao, C.; Toscanesi, M.; Arienzo, M. Levels of pollution of rare earth elements in the surface sediments from the Gulf of Pozzuoli (Campania, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Liu, S.; Kandasamy, S.; Jin, A.; Lou, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, B.; Wang, X.; Mohamed, C.A.; Shi, X. Grain-size effect on rare earth elements in Pahang River and Kelantan River, Peninsular Malaysia: Implications for sediment provenance in the southern South China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 189, 103977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan S, M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Geochem. Mineral. Rare Earth Elem. Rev. Mineral. 1989, 21, 169–200. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Trace Elements in Soil and Plants, 2nd ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992; p. 365. [Google Scholar]
- Laveuf, C.; Cornu, S.; Juillot, F. Rare earth elements as tracers of pedogenetic processes. C. R. Geosci. 2008, 340, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leleyter, L. Spéciation Chimique des Éléments Majeurs, Traces et des Terres Rares dans les Matières en Suspension et dans les Sédiments de fond des Cours d’eau: Application aux Fleuves de Patagonie (Argentine) à la Piracicaba (Brésil) à l’Oued Sebou (Maroc) et à l’Ile (France). Ph.D. Thesis, Université Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Horbe, A.M.C.; Da Costa, M.L. Geochemical evolution of a lateritic Sn-Zr-Th-Nb-Y-REE-bearing ore body derived from apogranite: The case of Pitinga, Amazonas—Brazil. J. Geochem. Explor. 1999, 66, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoratos, T.; Martini, G. Brake wear particle emissions: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2491–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peikertova, P.; Filip, P. Influence of the Automotive Brake Wear Debris on the Environment—A Review of Recent Research. SAE Int. J. Mat. Manuf. 2016, 9, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leleyter, L.; Probst, J.L. A new sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace elements in river sediments. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1999, 73, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiero, D.M.; Probst, J.-L.; Depetris, P.J.; Bidart, S.M.; Leleyter, L. Iron and other transition metals in Patagonian riverborne and windborne materials: Geochemical control and transport to the southern South Atlantic Ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 3603–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquery, M.; Welbourm, P.M. The relationship between metal concentration and organic matter in sediments and metal concentration in aquatic macrophyte eriocaulon septangulare. Water Res. 1995, 29, 2094–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriano, D.C.; Wenzel, W.W.; Vangronsveld, J.; Bolan, N.S. Role of assisted natural remediation in environmental cleanup. Geoderma 2004, 122, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Mohan, D.; Singh, V.K.; Malik, A. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediment—A tributaryon the Ganges, India. J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; MacDonald, D.D. Recommended Uses of Empirically Derived, Sediment Quality Guidelines for Marine and Estuarine Ecosystems. Human Ecol. Risk Assess. 1998, 4, 1019–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Field, L.J.; MacDonald, D.D. Predicting toxicity in marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, R.C.; Ditsworth, G.R.; Schults, D.W.; Lamberson, J.O. Sediment toxicity to a marine infaunal amphipod: Cadmium and its interaction with sewage sludge. Mar. Environ. Res. 1986, 18, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Toro, D.M.; Mahony, J.D.; Hansen, D.J.; Scott, K.J.; Hicks, M.B.; Mayr, S.M.; Redmond, M.S. Toxicity of cadmium in sediments: The role of acid volatile sulfide. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1990, 9, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, J.P.M. Measurement of heavy metal speciation over redox gradients in natural water-sediment interfaces and implications for uptake by benthic organisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 5130–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, H.; Pan, K.; Yan, Y.; Wang, W.X. Mercury distribution, speciation and bioavailability in sediments from the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campana, O.; Blasco, J.; Simpson, S.L. Demonstrating the appropriateness of developing sediment quality guidelines based on sediment geochemical properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7483–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
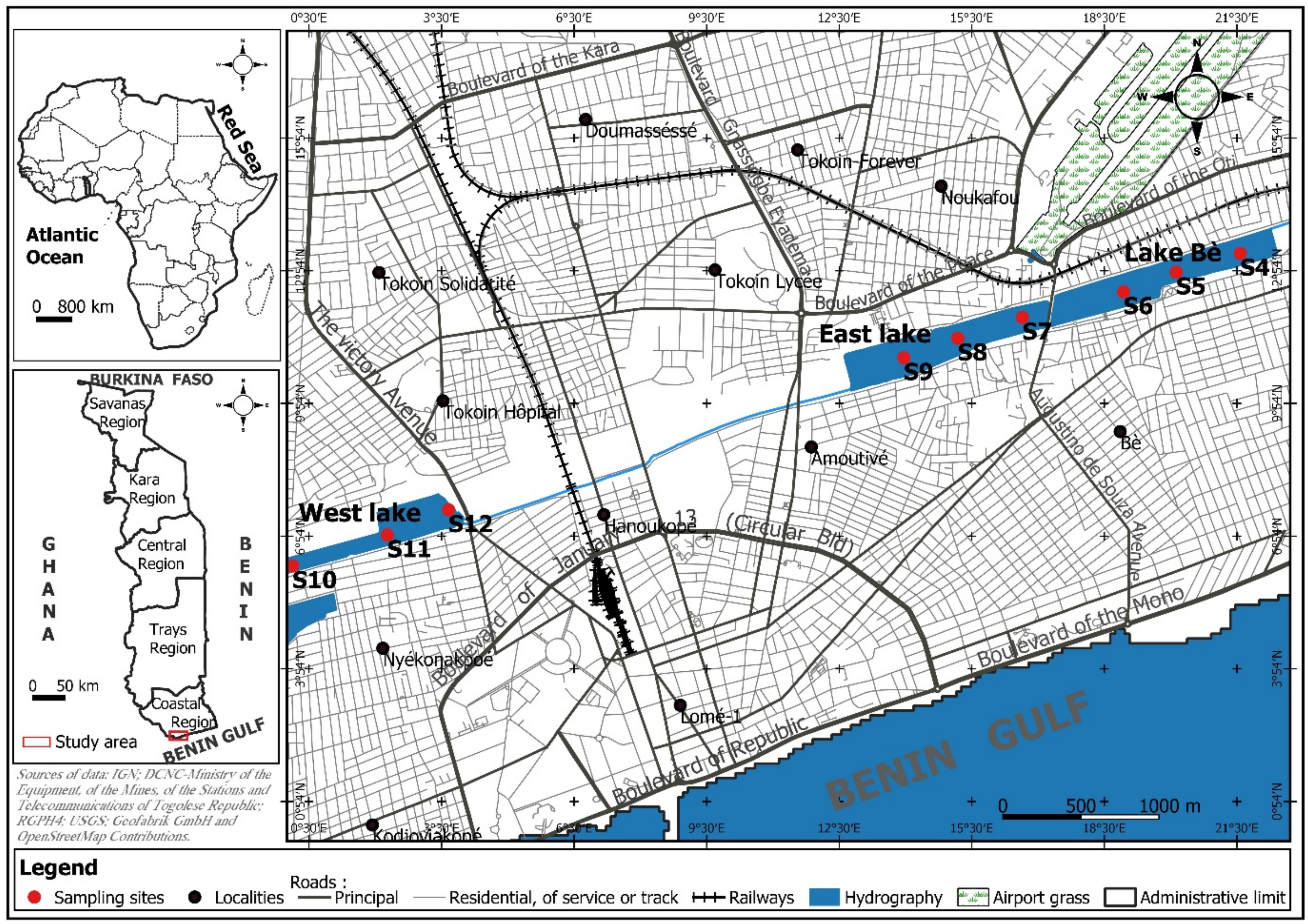









| Lakes | Sampling Sites | Geographical Coordinates (UTM) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lake Bè | S4 | X = 1.25543, Y = 6.15295 | 4 |
| S5 | X = 1.25173, Y = 6.15187 | 4 | |
| S6 | X = 1.24868, Y = 6.15073 | 4 | |
| East Lake | S7 | X = 1.24283, Y = 6.14925 | 2 |
| S8 | X = 1.23909, Y = 6.14805 | 2 | |
| S9 | X = 1.23597, Y = 6.14692 | 2 | |
| West Lake | S10 | X = 1.20060, Y = 6.13489 | 2 |
| S11 | X = 1.20609, Y = 6.13668 | 2 | |
| S12 | X = 1.20963, Y = 6.13133 | 2 |
| REE (µg·g−1) | Sediments of the Lomé Lagoon (n = 9) | PAAS | Sed_R | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Season (DS) | Wet Season (WS) | |||||||||
| Min | Max | Mean | Med | Min | Max | Mean | Med | |||
| La | 29.8 | 61.8 | 46.9 | 47.2 | 21.6 | 49.0 | 35.1 | 35.3 | 38.2 | 63.7 |
| Ce | 65.5 | 127.8 | 100.4 | 103.6 | 48.6 | 105.4 | 78.3 | 78.8 | 79.6 | 131.3 |
| Pr | 6.9 | 13.0 | 10.2 | 10.3 | 5.0 | 10.8 | 8.0 | 8.1 | 8.8 | 15.0 |
| Nd | 26.8 | 45.1 | 37.2 | 38.0 | 19.0 | 39.3 | 29.8 | 29.6 | 33.9 | 56.1 |
| Sm | 5.2 | 8.5 | 7.1 | 7.3 | 3.8 | 7.8 | 5.9 | 5.9 | 5.5 | 10.9 |
| Eu | 1.1 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 2.2 |
| Gd | 4.1 | 6.6 | 5.5 | 5.7 | 3.2 | 5.9 | 4.6 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 8.9 |
| Tb | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.3 |
| Dy | 3.6 | 5.8 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 3.3 | 5.2 | 4.2 | 4.1 | 4.7 | 8.0 |
| Ho | 0.7 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.7 |
| Er | 2.0 | 3.1 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 3.0 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 4.5 |
| Tm | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.7 |
| Yb | 1.9 | 3.1 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 3.2 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 4.6 |
| Lu | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.7 |
| PAAS Normalization | Season | Min | Max | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eu* | Dry season | 1.08 | 1.25 | 1.16 |
| Wet season | 0.98 | 1.13 | 1.07 | |
| Ce* | Dry season | 1.01 | 1.03 | 1.02 |
| Wet season | 1.02 | 1.04 | 1.03 | |
| (La/Yb)N | Dry season | 1.10 | 2.12 | 1.48 |
| Wet season | 0.53 | 1.44 | 1.00 |
| As | Cd | Co | Cr | Cu | Mo | Ni | Pb | Sb | Sn | Th | U | Zn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Wet season | 0.54 | −0.26 | −0.03 | 0.83 | −0.55 | −0.31 | 0.18 | −0.46 | −0.40 | −0.82 | 0.58 | −0.16 | −0.75 |
| Dry season | −0.04 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 0.13 | −0.67 | 0.66 | −0.11 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.76 | −0.71 | 0.27 | |
| Fe | Wet season | 0.40 | −0.15 | −0.24 | 0.36 | −0.43 | −0.09 | −0.28 | −0.55 | −0.24 | −0.52 | 0.26 | 0.18 | −0.66 |
| Dry season | 0.10 | −0.02 | −0.11 | 0.50 | 0.06 | −0.35 | 0.41 | −0.03 | −0.05 | 0.03 | 0.31 | −0.40 | 0.03 | |
| Cs | Wet season | −0.30 | −0.86 | 0.88 | 0.54 | −0.65 | 0.15 | 0.94 | −0.49 | −0.73 | −0.64 | 0.74 | −0.87 | −0.34 |
| Dry season | −0.33 | 0.53 | 0.59 | 0.31 | 0.41 | −0.68 | 0.76 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.48 | 0.96 | −0.52 | 0.64 | |
| Ti | Wet season | −0.51 | −0.59 | 0.85 | 0.26 | −0.21 | 0.15 | 0.83 | −0.07 | −0.31 | −0.27 | 0.68 | −0.76 | 0.14 |
| Dry season | −0.48 | 0.30 | 0.20 | −0.54 | 0.33 | 0.12 | −0.38 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 0.28 | −0.04 | 0.61 | 0.17 |
| NRF (%) | <1% | 1–5% | 5–15% | 15–25% | 25–40% | 40–60% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry season | Al, Ba, Be, Cr, Cs, Ga, Ge, Nb, Rb, Sn, Ta, Th, Zr, Ti, W | Sb, Cs, Hf, U, Fe, | As, Bi, Ni, V, Mo, Sc | Co, Cu, Y, Sr | Pb, Zn | Cd |
| Wet season | Al, Be, Cr, Cs, Hf, Nb, Rb, Sn, Ta, Th, U, Zr, Ti, W | Sb, Cs, Ba, Ga, Fe, Ge | As, Bi, Ni, V, Mo, Sc | Co, Cu, Y | Pb, Zn, Sr | Cd |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badassan, T.E.-E.; Avumadi, A.M.D.; Ouro-Sama, K.; Gnandi, K.; Jean-Dupuy, S.; Probst, J.-L. Geochemical Composition of the Lomé Lagoon Sediments, Togo: Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Major, Trace and Rare Earth Element Concentrations. Water 2020, 12, 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113026
Badassan TE-E, Avumadi AMD, Ouro-Sama K, Gnandi K, Jean-Dupuy S, Probst J-L. Geochemical Composition of the Lomé Lagoon Sediments, Togo: Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Major, Trace and Rare Earth Element Concentrations. Water. 2020; 12(11):3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113026
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadassan, Tchaa Esso-Essinam, Akouvi Massan Duanyawo Avumadi, Kamilou Ouro-Sama, Kissao Gnandi, Séverine Jean-Dupuy, and Jean-Luc Probst. 2020. "Geochemical Composition of the Lomé Lagoon Sediments, Togo: Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Major, Trace and Rare Earth Element Concentrations" Water 12, no. 11: 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113026
APA StyleBadassan, T. E.-E., Avumadi, A. M. D., Ouro-Sama, K., Gnandi, K., Jean-Dupuy, S., & Probst, J.-L. (2020). Geochemical Composition of the Lomé Lagoon Sediments, Togo: Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Major, Trace and Rare Earth Element Concentrations. Water, 12(11), 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113026







