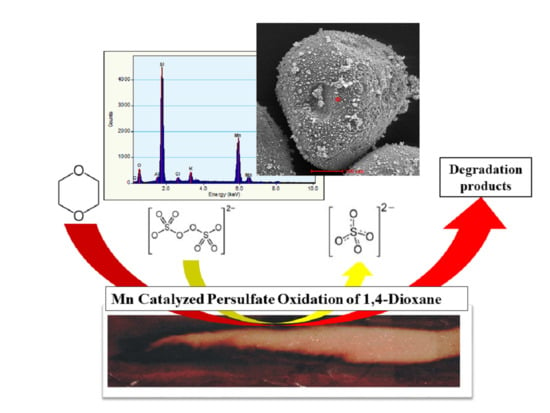
Comparison of Manganese Dioxide and Permanganate as Amendments with Persulfate for Aqueous 1,4-Dioxane Oxidation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. 1,4-Dioxane Degradation Batch Experiments
2.3. Gas Chromatography—Time of Flight—Mass Spectrometry
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5. Persulfate and Sulfate Anion Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
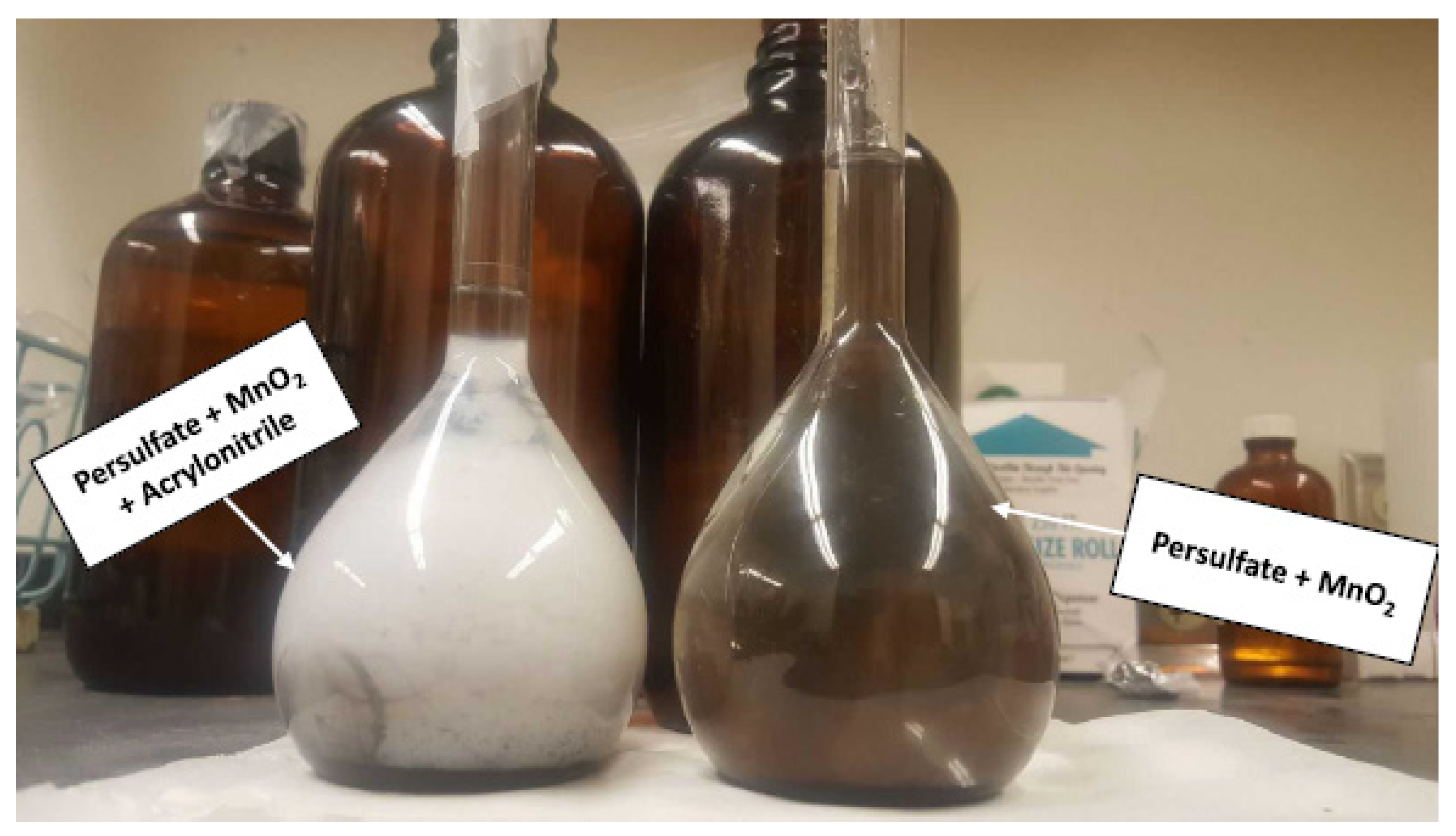
3.1. Activation of Persulfate
3.2. 1,4-Dioxane Degradation
3.3. Rate Constant Versus Oxidant Content
3.4. Rate Constant Versus Manganese Content
3.5. Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy Characterization of Manganese Dioxide
4. Summary and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zenker, M.J.; Borden, R.C.; Barlaz, M.A. Occurrence and Treatment of 1,4-Dioxane in Aqueous Environments. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2003, 20, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.H.; Anderson, J.K.; Bower, P.A. Co-occurrence of 1,4-dioxane with trichloroethylene in chlorinated solvent groundwater plumes at US Air Force installations: Fact or fiction. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2012, 8, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, D.T.; Anderson, R.H.; Mahendra, S.; Newell, C.J. Evidence of 1,4-Dioxane Attenuation at Groundwater Sites Contaminated with Chlorinated Solvents and 1,4-Dioxane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6510–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Re-Evaluation of Some Organic Chemicals, Hydrazine and Hydrogen Peroxide; L. International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, H.M.; Vimonses, V.; Leslie, G.; Amal, R. Degradation of 1,4-dioxane in water using TiO2 based photocatalytic and H2O2/UV processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, T.K.G.; Stickney, J.A.; DiGuiseppi, W.H. Environmental Investigation and Remediation: 1,4-Dioxane and other Solvent Stabilizers; CRC Press Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- U.S.EPA. Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) on 1,4-Dioxane; National Center for Environmental Assessment, Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- DiGuiseppi, W.H.; Whitesides, C. Treatment Options for Remediation of 1,4-Dioxane in Groundwater. Environ. Eng. Am. Acad. Environ. Eng. 2007, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- DiGuiseppi, W.; Walecka-Hutchinson, C.; Hatton, J. 1,4-Dioxane Treatment Technologies. Remediat. J. 2016, 27, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gedalanga, P.B.; Mahendra, S. Advances in bioremediation of 1,4-dioxane-contaminated waters. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamson, D.T.; Mahendra, S.; Walker, K.L., Jr.; Rauch, S.R.; Sengupta, S.; Newell, C.J. A Multisite Survey to Identify the Scale of the 1,4-Dioxane Problem at Contaminated Groundwater Sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollitt, K.J.G.; Kim, J.H.; Peccia, J.; Elimelech, M.; Zhang, Y.; Charkoftaki, G.; Hodges, B.; Zucker, I.; Huang, H.; Deziel, N.C.; et al. 1,4-Dioxane as an emerging water contaminant: State of the science and evaluation of research needs. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Johnson, M.D.; Kubicki, J.D.; Holguin, F.O.; Dungan, B.; Carroll, K.C. Cyclodextrin-enhanced 1,4-dioxane treatment kinetics with TCE and 1,1,1-TCA using aqueous ozone. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, R.J.; Teel, A.L. Treatment of Contaminated Soils and Groundwater Using ISCO. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2006, 10, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolthoff, I.M.; Miller, I.K. The Chemistry of Persulfate. I. The Kinetics and Mechanism of the Decomposition of the Persulfate Ion in Aqueous Medium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 3055–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huling, S.; Pivetz, B. Engineering Issue Paper: In-Situ Chemical Oxidation. Engineering Issue, EPA/600/R-06/072. 2007. Available online: https://clu-in.org/download/contaminantfocus/pcb/ISCO-600R06072.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Cuypers, C.; Grotenhuis, T.; Joziasse, J.; Rulkens, W. Rapid persulfate oxidation predicts PAH bioavailability in soils and sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitonaki, A.; Petri, B.; Crimi, M.; Mosbæk, H.; Siegrist, R.L.; Bjerg, P.L. In Situ Chemical Oxidation of Contaminated Soil and Groundwater Using Persulfate: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 55–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Sun, K.; Lin, C.; Ma, J.; He, M.; Ouyang, W. Persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for organic-contaminated soil remediation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronholm, J.; Metsälä, H.; Hartonen, K.; Riekkola, M.L. Oxidation of 4-Chloro-3-methylphenol in Pressurized Hot Water/Supercritical Water with Potassium Persulfate as Oxidant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3247–3251. [Google Scholar]
- Anipsitakis, G.; Dionysiou, D.D. Degradation of Organic Contaminants in Water with Sulfate Radicals Generated by the Conjunction of Peroxymonosulfate with Cobalt. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.; Dionysiou, D.D. Radical Generation by the Interaction of Transition Metals with Common Oxidants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronk, G. Case study comparison of multiple activation methods for sodium persulfate ISCO treatment. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds, Monterey, CA, USA, 19–22 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Pignatello, J.J.; Ma, J.; Mitch, W.A. Comparison of Halide Impacts on the Efficiency of Contaminant Degradation by Sulfate and Hydroxyl Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Brusseau, M.L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, N.; Quig, L.; Johnson, G.R. In-situ activation of persulfate by iron filings and degradation of 1,4-dioxane. Water Res. 2015, 83, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Persulfate activation by subsurface minerals. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2010, 115, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teel, A.L.; Ahmad, M.; Watts, R.J. Persulfate activation by naturally occurring trace minerals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Subsurface Minerals. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2016, 191, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, G.; Chen, X.; Wu, W.; Liu, C.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Fan, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, D. Mechanisms of Interaction between Persulfate and Soil Constituents: Activation, Free Radical Formation, Conversion, and Identification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 14352–14361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Li, X.; Kang, J.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Persulfate Activation on Crystallographic Manganese Oxides: Mechanism of Singlet Oxygen Evolution for Nonradical Selective Degradation of Aqueous Contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Z.; Zhang, H.C. Mn-based catalysts for sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes: A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; von Gunten, U.; Kim, J.H. Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation: Critical Assessment of Opportunities and Roadblocks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3064–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bruton, T.A.; Doyle, F.M.; Sedlak, D.L. In Situ Chemical Oxidation of Contaminated Groundwater by Persulfate: Decomposition by Fe(III)- and Mn(IV)-Containing Oxides and Aquifer Materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10330–10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Liu, F.; Xue, Q.; Brusseau, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Degradation of trichloroethene by siderite-catalyzed hydrogen peroxide and persulfate: Investigation of reaction mechanisms and degradation products. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 274, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Orozco, R.; Camargos, N.; Liu, H. Mechanisms on the Impacts of Alkalinity, pH, and Chloride on Persulfate-Based Groundwater Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3948–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Zhong, H.; Brusseau, M.L. The natural activation ability of subsurface media to promote in-situ chemical oxidation of 1,4-dioxane. Water Res. 2019, 149, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urynowicz, M.A.; Siegrist, R.L. Chemical degradation of TCE DNAPL by Permanganate. In Chemical Oxidation and Reactive Barriers: Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds; Wickramanayake, G.B., Gavaskar, A.R., Chen, A.S.C., Eds.; Battelle Press: Columbus, OH, USA, 2000; pp. 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma, S.; Marshall, M. Experimental study of oxidation of pooled NAPL. In Chemical Oxidation and Reactive Barriers: Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds; Wickramanayake, G.B., Gavaskar, A.R., Chen, A.S.C., Eds.; Battelle Press: Columbus, OH, USA, 2000; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, S.H.; Glass, R.J.; Peplinski, W.J. Bench-scale visualization of DNAPL remediation processes in analog heterogeneous aquifers: Surfactant floods and in situ oxidation using permanganate. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2002, 58, 13–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, L.K.; Thomson, N.R. Laboratory-scale in situ chemical oxidation of a perchloroethylene pool using permanganate. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2002, 56, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Schwartz, F.W. DNAPL mass transfer and permeability reduction during in situ chemical oxidation with permanganate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Schwartz, F.W. DNAPL remediation with in situ chemical oxidation using potassium permanganate. II. Increasing removal efficiency by dissolving Mn oxide precipitates. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 68, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiderscheidt, J.L.; Siegrist, R.L.; Illangasekare, H. Intermediate-scale 2D experimental investigation of in situ chemical oxidation using potassium permanganate for remediation of complex DNAPL source zones. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2008, 102, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marble, J.C.; Carroll, K.C.; Janousek, H.; Brusseau, M.L. In situ oxidation and associated mass-flux-reduction/mass-removal behavior for systems with organic liquid located in lower-permeability sediments. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2010, 117, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusseau, M.L.; Carroll, K.C.; Allen, T.; Baker, J.; DiGuiseppi, W.; Hatton, J.; Morrison, C.; Russo, A.; Berkompas, J. Impact of In Situ Chemical Oxidation on Contaminant Mass Discharge: Linking Source-Zone and Plume-Scale Characterizations of Remediation Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5352–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marble, J.C.; Brusseau, M.L.; Carroll, K.C.; Plaschke, M.; Fuhrig, L.; Brinker, F. Application of a Persistent Dissolved-Phase Reactive Treatment Zone for Mitigation of Mass Discharge from Sources Located in Lower-Permeability Sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Hornstein, B.J. The kinetics and mechanism of the ferrate(VI) oxidation of hydroxylamines. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 6923–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, R.G. Kinetics and Mechanism of Reactions of Transition Metal Complexes; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Huang, C.F.; Mohanty, N.; Kurakalva, R.M. A rapid spectrophotometric determination of persulfate anion in ISCO. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1540–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethna, S.M. The ELBS Persulfate Oxidation. Chem. Rev. 1951, 49, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, D.; Ball, R.; Boving, T.B. Peroxone activated persulfate treatment of 1,4-dioxane in the presence of chlorinated solvent co-contaminants. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Carroll, K.C. Natural attenuation method for contaminant remediation reagent delivery assessment for in situ chemical oxidation using aqueous ozone. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.-C.J.; Khaleel, R.; Carroll, K.C. Flow through Heterogeneous Geologic Media; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Post, J.E. Manganese oxide minerals: Crystal structures and economic and environmental significance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3447–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Carroll, K.C. Metal-free catalysis of persulfate activation and organic-pollutant degradation by nitrogen-doped graphene and aminated graphene. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Contaminant (mM) | Oxidants | Manganese | pH | mM | Oxidant: Contaminant | Rate Constant | Rate Constant | Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,4-D | Sodium Persulfate (mM) | Potassium Permanganate (mM) | Dioxide (g/L) | Start | End | Total Oxidants | (Mole Ratio) | k (h−1) | 95% C.I. | R2 |
| Sodium Persulfate Only | ||||||||||
| 0.5 | 5 | 0 | 0.0 | 5.2 | 4.0 | 5 | 10 | 0.0003 | ±0.0012 | 0.03 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 0 | 0.0 | 4.6 | 2.8 | 49 | 98 | 0.0124 | ±0.0010 | 0.98 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 0 | 0.0 | 4.6 | 2.7 | 49 | 98 | 0.0112 | ±0.0007 | 0.99 |
| 0.5 | 250 | 0 | 0.0 | 4.0 | 2.3 | 250 | 500 | 0.0352 | ±0.0338 | 0.92 |
| Sodium Persulfate and Manganese Dioxide | ||||||||||
| 0.5 | 5 | 0 | 100.0 | 5.2 | 3.1 | 5 | 10 | 0.0017 | ±0.0007 | 0.57 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 0 | 4.3 | 4.6 | 2.5 | 49 | 98 | 0.0127 | ±0.0014 | 0.97 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 0 | 7.9 | 4.5 | 2.5 | 49 | 98 | 0.0109 | ±0.0005 | 0.99 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 0 | 11.0 | 4.5 | 2.4 | 49 | 98 | 0.0129 | ±0.0008 | 0.99 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 0 | 17.4 | 4.5 | 2.4 | 49 | 98 | 0.0154 | ±0.0012 | 0.99 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 0 | 100.0 | 4.4 | 2.4 | 49 | 98 | 0.0083 | ±0.0010 | 0.97 |
| 0.5 | 250 | 0 | 17.4 | 4.0 | 2.3 | 250 | 500 | 0.0432 | ±0.0194 | 0.95 |
| Sodium Persulfate and Potassium Permanganate | ||||||||||
| 0.5 | 49 | 49 | 0.0 | 6.1 | 6.6 | 98 | 196 | 0.0092 | ±0.0041 | 0.94 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 91 | 0.0 | 7.8 | 6.7 | 140 | 280 | 0.0115 | ±0.0011 | 0.98 |
| 0.5 | 49 | 200 | 0.0 | 8.6 | 7.0 | 249 | 498 | 0.0192 | ±0.0033 | 0.96 |
| Potassium Permanganate without Sodium Persulfate | ||||||||||
| 0.5 | 0 | 49 | 0.0 | 8.1 | 7.8 | 49 | 98 | 0.0059 | ±0.0006 | 0.98 |
| 0.5 | 0 | 49 | 100.0 | 6.5 | 7.6 | 49 | 98 | 0.0053 | ±0.0006 | 0.98 |
| Sodium Persulfate, Potassium Permanganate, and Manganese Dioxide | ||||||||||
| 0.5 | 49 | 49 | 100.0 | 6.1 | 6.9 | 98 | 196 | 0.007 | ±0.0012 | 0.96 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bridges, L.; Mohamed, R.A.M.; Khan, N.A.; Brusseau, M.L.; Carroll, K.C. Comparison of Manganese Dioxide and Permanganate as Amendments with Persulfate for Aqueous 1,4-Dioxane Oxidation. Water 2020, 12, 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113061
Bridges L, Mohamed RAM, Khan NA, Brusseau ML, Carroll KC. Comparison of Manganese Dioxide and Permanganate as Amendments with Persulfate for Aqueous 1,4-Dioxane Oxidation. Water. 2020; 12(11):3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113061
Chicago/Turabian StyleBridges, Logan, Ruba A. M. Mohamed, Naima A. Khan, Mark L. Brusseau, and Kenneth C. Carroll. 2020. "Comparison of Manganese Dioxide and Permanganate as Amendments with Persulfate for Aqueous 1,4-Dioxane Oxidation" Water 12, no. 11: 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113061
APA StyleBridges, L., Mohamed, R. A. M., Khan, N. A., Brusseau, M. L., & Carroll, K. C. (2020). Comparison of Manganese Dioxide and Permanganate as Amendments with Persulfate for Aqueous 1,4-Dioxane Oxidation. Water, 12(11), 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113061