Variation of Melt Water and Rainfall Runoff and Their Impacts on Streamflow Changes during Recent Decades in Two Tibetan Plateau Basins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
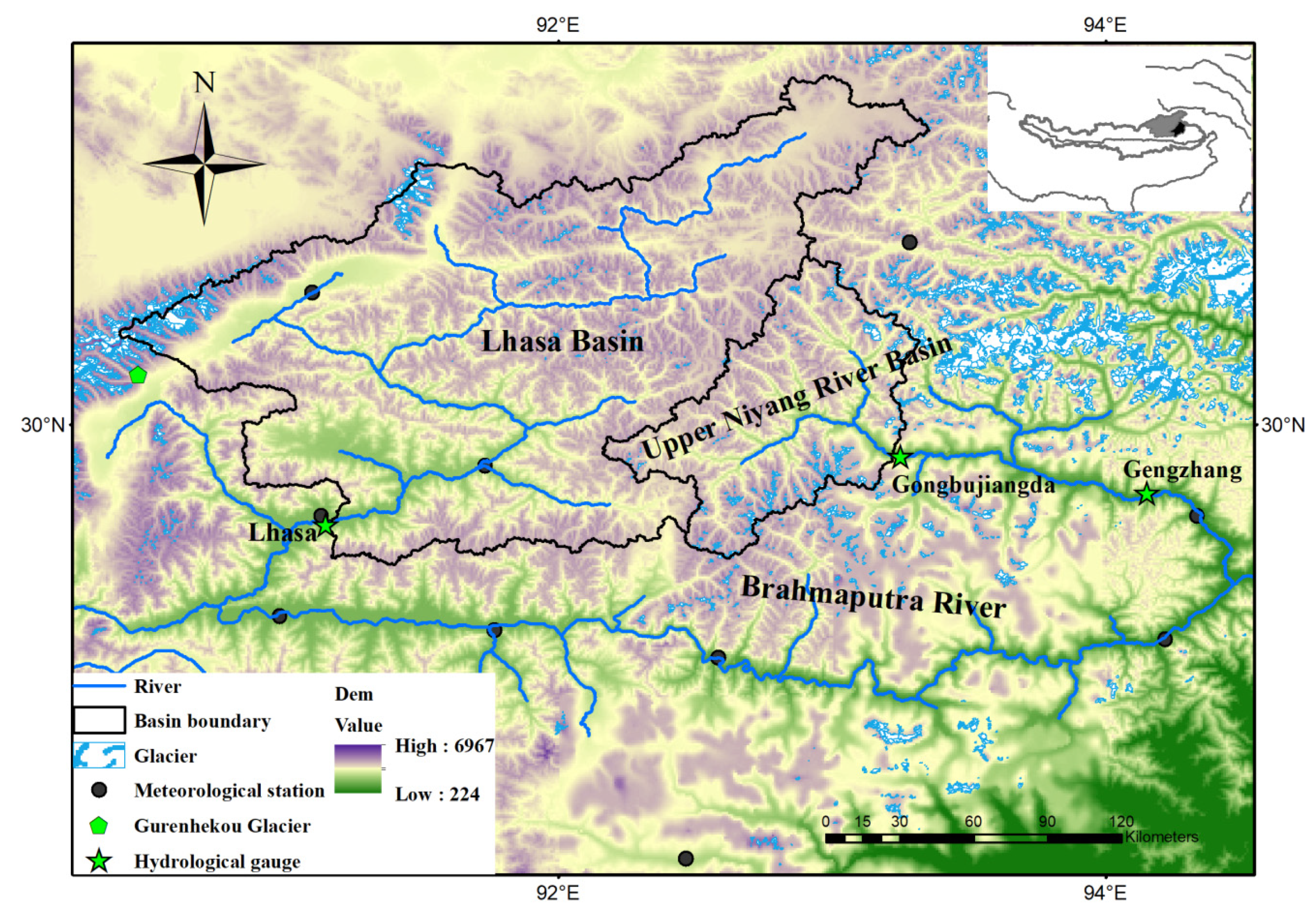
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Model Description and Parameters
2.3.2. Trend and Controlling Role Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Model Evaluations
3.2. Components and Characteristics of Streamflow
3.3. Variation of Runoff Components under Current Climate Change
3.4. Influence of the Runoff Component’s Change on River Streamflow Trend
4. Discussion
4.1. Linkage between Glacier Runoff and Climate Change
4.2. Roles of Melt Water
4.3. Ground Water and Implication of this Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bibi, S.; Wang, L.; Li, X.P.; Zhou, J.; Chen, D.L.; Yao, T.D. Climatic and associated cryospheric, biospheric, and hydrological changes on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, E1–E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Van Beek, L.P.; Bierkens, M.F. Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, R.D.; He, Y.H.; Chen, X.H. Responses of the hydrological regime to variations in meteorological factors under climate change of the Tibetan plateau. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Pang, G.J.; Yang, M.X. Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades: A review based on observations and simulations. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 1116–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, T. HYDROLOGY Asian glaciers are a reliable water source. Nature 2017, 545, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Kang, S.C.; Wang, X.M.; Pepin, N.; Wu, H. Understanding changes in the water budget driven by climate change in cryospheric-dominated watershed of the northeast Tibetan Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 1040–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.D.; Ding, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Gao, H.K.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhao, C.C.; Xu, J.L.; Han, H.D.; Shangguan, D.H. Projecting climate change impacts on hydrological processes on the Tibetan Plateau with model calibration against the glacier inventory data and observed streamflow. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 60–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.K.; Qiu, B.; Guo, W.D.; Zhu, Z.W.; Hsu, P.C. Intraseasonal variability of Tibetan Plateau snow cover. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 3451–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, D.H.; Zhou, B.T.; Xiao, C.D. Progress in studies of cryospheric changes and their impacts on climate of china. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, C.; Song, Y.; Liu, Z.; Kang, E. Effects of Cryospheric Change on Alpine Hydrology: Combining a Model With Observations in the Upper Reaches of the Hei River, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3414–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.L.; Wu, T.; Shen, L.C.; Pepin, N.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wu, Z.W.; Kang, S.C.; AghaKouchak, A. Review of snow cover variation over the Tibetan Plateau and its influence on the broad climate system. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.Y.; Ju, Q.; Yu, Z.B.; Hao, J.; Gu, H.H.; Gu, H.N.; Li, W. Simulation of snowmelt runoff and sensitivity analysis in the Nyang River Basin, southeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Nat. Hazards 2019, 99, 931–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Yang, H.B.; Gao, B.; Wang, T.H.; Qin, Y.; Yang, D.W. Frozen ground degradation may reduce future runoff in the headwaters of an inland river on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Tong, K.; Meng, F.; Kan, B. Spatiotemporal variation of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau based on MODIS snow product, 2001–2014. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 708–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.S.; Chen, F.; Gao, Y.H.; Barlage, M.; Li, J.D. Using Multisource Satellite Data to Assess Recent Snow-Cover Variability and Uncertainty in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Deng, S.F.; Zhao, Q.D.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhang, X.W. Projected glacier meltwater and river run-off changes in the Upper Reach of the Shule River Basin, north-eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, T.; Kulkarni, A.; Kaab, A.; Huggel, C.; Paul, F.; Cogley, J.G.; Frey, H.; Kargel, J.S.; Fujita, K.; Scheel, M.; et al. The State and Fate of Himalayan Glaciers. Science 2012, 336, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Pu, J.; Shen, Y.; Lu, A. Recent glacial retreat in High Asia in China and its impact on water resource in Northwest China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2004, 47, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.J.; Yuan, R.F.; Gui, J.; Lv, Y.M. Climate background, fact and hydrological effect of multiphase water transformation in cold regions of the Western China: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 190, 33–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, B.; He, K.N.; Li, R.J.; Wang, H.; Wen, J. Trends, Abrupt Changes, and Periodicity of Streamflow in Qinghai Province, the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Huang, H.; Liu, G.; Wu, S. Statistical estimation of the impacts of glaciers and climate change on river runoff in the headwaters of the Yangtze River. Quat. Int. 2014, 336, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Shangguan, D. Glacier change and glacier runoff variation in the Tuotuo River basin, the source region of Yangtze River in western China. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Qi, F.; Wang, Q.J.; Song, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Li, Y.G. The influence from the shrinking cryosphere and strengthening evopotranspiration on hydrologic process in a cold basin, Qilian Mountains. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 144, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Hao, Z.C.; Xu, C.Y.; Lai, X.D. Response of melt water and rainfall runoff to climate change and their roles in controlling streamflow changes of the two upstream basins over the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Res. 2020, 51, 272–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.F.; Ren, Q.S.; Wei, X.H.; Wang, J.S.; Yang, X.L.; Jiang, Z.S. Climate change, glacier melting and streamflow in the Niyang River Basin, Southeast Tibet, China. Ecohydrology 2011, 4, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Mei, Y.D.; Chen, J.H.; Hu, T.S.; Xiao, W.H. Attribution Analysis of Dry Season Runoff in the Lhasa River Using an Extended Hydrological Sensitivity Method and a Hydrological Model. Water 2019, 11, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasch, M.; Mauser, W.; Weber, M. Quantifying present and future glacier melt-water contribution to runoff in a central Himalayan river basin. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Hao, Z.; Tong, K. Discharge regime and simulation for the upstream of major rivers over Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 8500–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, J.; Running, S.; Nemani, R. An improved method for estimating surface humidity from daily minimum temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1997, 85, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.Y. Validation and comparison of a new gauge-based precipitation analysis over mainland China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Tang, Q.H.; Pan, M.; Tang, Y. A Long-Term Land Surface Hydrologic Fluxes and States Dataset for China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 2067–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, S.X.; Mo, X.G.; Peng, B.; Qiu, J.X.; Li, M.X.; Liu, C.M.; Wang, Z.G.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. Evaluation of Remotely Sensed Precipitation and Its Performance for Streamflow Simulations in Basins of the Southeast Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 2577–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.F.; Liu, C.H.; Kang, E. The Glacier Inventory of China. Ann. Glaciol. 2009, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, W.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; Xu, L.; Wu, L.Z.; Shangguan, D.H.; Yao, X.J.; Wei, J.F.; Bao, W.J.; Yu, P.C.; Liu, Q.; et al. The second Chinese glacier inventory: Data, methods and results. J. Glaciol. 2015, 61, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Kayastha, R.B.; Ramanathan, A.L.; Dimri, A.P. Comparison of hydrological regime of glacierized Marshyangdi and Tamor river basins of Nepal. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Yang, T.; Xu, C.Y.; Yong, B.; Shi, P.F. Understanding the discharge regime of a glacierized alpine catchment in the Tianshan Mountains using an improved HBV-D hydrological model. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 172, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duethmann, D.; Bolch, T.; Farinotti, D.; Kriegel, D.; Vorogushyn, S.; Merz, B.; Pieczonka, T.; Jiang, T.; Su, B.D.; Guntner, A. Attribution of streamflow trends in snow and glacier melt-dominated catchments of the Tarim River, Central Asia. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4727–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lutz, A.; Immerzeel, W.; Shrestha, A.; Bierkens, M. Consistent increase in High Asia’s runoff due to increasing glacier melt and precipitation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Arnold, J.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, X. Inclusion of glacier processes for distributed hydrological modeling at basin scale with application to a watershed in Tianshan Mountains, northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 477, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Long, D.; Hong, Y.; Zeng, C.; Yan, D.H. Improved modeling of snow and glacier melting by a progressive two-stage calibration strategy with GRACE and multisource data: How snow and glacier meltwater contributes to the runoff of the Upper Brahmaputra River basin? Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 2431–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.J.; Shen, Y.; Fink, M.; Kralisch, S.; Brenning, A. Unraveling the Hydrology of the Glacierized Kaidu Basin by Integrating Multisource Data in the Tianshan Mountains, Northwestern China. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Wood, E.F.; Burges, S.J. A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for general circulation models. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 14415–14428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wood, E.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Surface soil moisture parameterization of the VIC-2L model: Evaluation and modification. Glob. Planet. Chang. 1996, 13, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkauer, K.A.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Simulation of spatial variability in snow and frozen soil. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.C.; Su, F.G.; Li, Y.; Tong, K. Changes in Terrestrial Water Storage during 2003–2014 and Possible Causes in Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2909–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Su, F.G.; Xu, B.Q. Quantifying the contribution of glacier meltwater in the expansion of the largest lake in Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 11158–11173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Ding, Y. Observed degree-day factors and their spatial variation on glaciers in western China. Ann. Glaciol. 2006, 43, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, F.; Adam, J.C.; Bowling, L.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Streamflow simulations of the terrestrial Arctic domain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D08112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Griffin: London, UK, 1975; p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Merwade, V.; Kam, J.; Thurner, K. Streamflow trends in Indiana: Effects of long term persistence, precipitation and subsurface drains. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Zheng, H.X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, D.M.; Lei, L.P. Long-Term Changes of Lake Level and Water Budget in the Nam Co Lake Basin, Central Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hao, Z.; Cairang, L. The impacts of climate change and land cover/use transition on the hydrology in the upper Yellow River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 502, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, B.; Su, F.; Xu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Generation of High Mountain Precipitation and Temperature Data for a Quantitative Assessment of Flow Regime in the Upper Yarkant Basin in the Karakoram. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8462–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.R.; de Condappa, D. Opportunities for harnessing the increased contribution of glacier and snowmelt flows in the Ganges basin. Water Policy 2013, 15, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, H.; Qin, J.; Lin, C.G.; Tang, W.J.; Chen, Y.Y. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: A review. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 112, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Yang, K.; Liang, S.L.; Guo, X.F. The altitudinal dependence of recent rapid warming over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Chang. 2009, 97, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; He, Y.Q.; An, W.L.; Song, L.L.; Zhang, W.; Catto, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.J.; Liu, H.C.; Cao, W.H.; et al. Climate and glacier change in southwestern China during the past several decades. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookhagen, B.; Burbank, D.W. Toward a complete Himalayan hydrological budget: Spatiotemporal distribution of snowmelt and rainfall and their impact on river discharge. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritchard, H.D. Asia’s shrinking glaciers protect large populations from drought stress. Nature 2019, 569, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Basin | Gauge | Gauge Location | Drainage Area (km2) | Glacier Area (km2) | Percent of Drainage Area for Glacier (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | |||||
| LRB | Lhasa | 29.63 | 91.15 | 26,235 | 356.0 | 1.36 |
| UNRB | Gongbujiangda | 29.88 | 93.25 | 6417 | 231.0 | 3.60 |
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tlaps | −3.6 | −4.1 | −4.9 | −5.7 | −6.4 | −5.6 | −5.1 | −5.2 | −5.8 | −3.8 | −4.4 | −3.8 |
| R | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.84 |
| Model Parameter | Unit | Range | LRB | UNRB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degree-day factor for ice-melt (DDFice) | mm °C−1 day−1 | 3.4–11.8 | 9.0 | 9.0 |
| Degree-day factor for snowmelt (DDFsnow) | mm °C−1 day−1 | 3.0–7.9 | 4.1 | 4.1 |
| Fraction of Dsmax where non-linear baseflow begins (Ds) | None | 0–1 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Maximum velocity of baseflow(Dsmax) | mm/d | 0–50 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| Fraction of maximum soil moisture where non-linear baseflow occurs (Ws) | None | 0–1 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Variable infiltration curve parameter (binfilt) | None | 0–0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Thickness of the second soil moisture layer (d2) | m | 0–3 | 1.1 | 1.3 |
| Basin | Overall | Calibration | Validation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSE | PBIAS (%) | NSE | PBIAS (%) | NSE | PBIAS (%) | |
| LRB | 0.87 | 3.38 | 0.87 | −2.81 | 0.86 | 6.82 |
| UNRB | 0.85 | −0.98 | 0.87 | −5.22 | 0.84 | 3.5 |
| Basin | Total Runoff | Rainfall Runoff | Glacial Runoff | Snowmelt Runoff |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRB | 4.62 × 107 m3/year | 4.08 × 107 m3/year | 0.73 × 107 m3/year * | −0.19 × 107 m3/year |
| UNRB | 1.53 × 107 m3/year * | 0.974 × 107 m3/year | 0.626 × 107 m3/year * | −0.07 × 107 m3/year |
| Basin | Trend of Total Runoff (m3/Year) | Contribution from Rainfall Runoff (%) | Contribution from Glacial Runoff (%) | Contribution from Snowmelt Runoff (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRB | 4.62 × 107 | 88.31 | 15.80 | −4.11 |
| UNRB | 1.53 × 107 | 63.66 | 40.92 | −4.58 |
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRB | 91.3 | 87.8 | 64.7 | 26.2 | 8.9 | 4.9 | 8.2 | 13.0 | 19.7 | 40.9 | 74.9 | 90.8 |
| UNRB | 90.5 | 77.6 | 41.0 | 15.0 | 5.8 | 3.6 | 4.5 | 6.1 | 9.0 | 26.9 | 64.1 | 90.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.-Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ju, Q.; Lai, X. Variation of Melt Water and Rainfall Runoff and Their Impacts on Streamflow Changes during Recent Decades in Two Tibetan Plateau Basins. Water 2020, 12, 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113112
Zhang Y, Xu C-Y, Hao Z, Zhang L, Ju Q, Lai X. Variation of Melt Water and Rainfall Runoff and Their Impacts on Streamflow Changes during Recent Decades in Two Tibetan Plateau Basins. Water. 2020; 12(11):3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113112
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yueguan, Chong-Yu Xu, Zhenchun Hao, Leilei Zhang, Qin Ju, and Xide Lai. 2020. "Variation of Melt Water and Rainfall Runoff and Their Impacts on Streamflow Changes during Recent Decades in Two Tibetan Plateau Basins" Water 12, no. 11: 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113112






