Abstract
Nine per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs), including six perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs) and three perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids (PFSAs), were tested to find their adsorption selectivity from surface water and the feasibility of the powder activated carbon (PAC) process between the perchlorination and coagulation processes by operating parameters such as mixing intensity, dosage, contact time, initial pH, and concentration of perchlorination. The removal efficiency of four types of PAC revealed that the coal-based activated carbon was clearly advanced for all of the PFASs, and the thermal regenerated PAC did not exhibit a significant reduction in adsorption capacity. The longer carbon chain or the higher molecular weight (MW) obtained a higher adsorption capacity and the MW exhibited a more proportional relationship with the removal efficiency than the carbon chain number, regardless of the PFCA and PFSA species. Approximately 80% and 90% equilibria were accomplished within 60 and 120 min for the long chain carbon PFAS, respectively, while for the short chain PFAS, 240 min was required to reach 85% equilibrium. The effect of mixing intensity (rpm) was not considered for the removal of the PFAS, although it was relatively influenced in the short PFAS species. Due to the surface charge of the PAC and the properties of protonation of the PFASs, the acid condition increased the PFASs’ adsorption capacity. The prechlorination decreased the removal efficiency, and the reduction rate was more significantly influenced for the short chain PFAS than for the long chain PFAS.
1. Introduction
Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are one class of fluorinated substances that contain at least one fluorine atom (-F) replacing one or all of the hydrogen atoms on the carbon skeleton and a terminal functional group on the organic and inorganic compound [1]. Buck et al. (2011) divided them into polymeric and non-polymeric PFASs, and each PFAS includes three sub-groups and four sub-families, respectively [1]. Polymeric PFASs are fluoropolymers, sidechain fluorinated polymers, and perfluoropolyethers and non-polymeric PFASs are perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs), fluorotelomers (FT), per- and polyfluroalkyl ethers, and perfluoroalkane sulfonlyl fluorides [2]. In general, current target PFASs belong either to perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs) or perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids (PFSAs), and these are the most significant of the PFAAs.
Due to a PFAS containing one or more carbon atoms, it can usually be sorted with long and short carbon chains depending on the carbon length (number). The USEPA (2017) defined a long chain PFAS with eight or more as a PFCA and six or more as a PFSA [3], i.e., less than eight and six carbon chains for PFCAs and PFSAs, respectively, referring to them as short chains [2].
Among PFASs, perfluorooctane sulfonic acid, C8F17SO3H (PFOS), was first identified in 2001 by Giesy and Kannan [4] and, simultaneously, the presence of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA, C7F15COOH) was also recognized in numerous samples of human blood [5]. PFASs have been widely used in various industries worldwide since 1950 due to their chemical and thermal stability (536 kJ/mol of C–F bond energy), high redox potential (F to F-, E0 = 3.6 V), perfect orbital overlap (2s and 2p), low molecular polarity, high surface activity, low surface tension, strong biological resistance, and amphiphilic nature, as they contain a hydrophilic functional group and a hydrophobic fluorinated tail [2,6,7]. Widespread application in industries such as electroplating, surface coating, and aqueous film-forming foams has resulted in their frequent occurrence in air, soil, and water, and an accumulation in the environment and in humans [8,9].
Various technologies have been studied to satisfy the increasing concern for and reinforcing regulation of PFAS concentrations in water. Due to the strong biological resistance of PFASs, the technologies for their removal or remediation from solution have focused on physical and chemical treatment. For example, these include coagulation using alum, ferric chloride, and polyaluminum chloride (PACl) [10], oxidation using electrochemicals [11] and photocatalytics [12], and adsorption using activated carbon (AC) [13] and ion exchange (IX) [13,14]. Among these technologies, the application of granular activated carbon (GAC) and IX is now widely used and are known accessible technologies. Commercial GAC was first employed by the 3M company to remove PFBS from effluent and it was reported to have achieved 98.4% removal [15]; the application of powder activated carbon (PAC) showed a higher capacity due to its greater surface area, shorter internal diffusion, better site accessibility, and faster adsorption kinetics than GAC [16,17]. Some studies using IX concluded that IX can adsorb more than GAC [13,17,18] depending on the operating condition of the initial experiment. Furthermore, it was concluded that the adsorption process involving long carbon chain PFASs exhibited a greater removal capacity than that of short carbon chain PFASs, and it easily met the USEPA regulation [19].
The application of PAC is still favored in water treatment plants (WTPs) for the removal of micropollutants and to affect the coagulation process despite costly and complicated operation [20]. However, PAC has not been widely applied to PFAS study. Recent studies on PFAS removal were mostly carried out for PFOS and PFOA; these are referred to as long chain PFASs, showing an easy high removal efficiency at a higher level than expected in the environment (mg/L or ug/L) [21], and in the simulated synthesis of water. Therefore, the present study aims to examine the removal efficiency using PAC in different physical and chemical conditions for nine species of PFASs, including short and long carbon chains from surface water that is raw water for drinking at the WTP.
The specific objectives are to (1) find the removal efficiency of different PAC types, (2) determine the effective concentration of the PAC, the contact reaction time, the mixing intensity, the initial solution pH, and the prechlorination to optimize the operating system, and (3) compare the effect of carbon chain length and the selectivity of each PFAS on the adsorption process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
A standard solution containing six PFCAs and three PFSAs among PFASs was purchased from Wellington Laboratories (Guelph, ON, Canada) and was used without further purification. The physicochemical properties of each PFAS, such as the full name, abbreviation, chemical formula, and Kow and pKa values, are summarized in Table 1. For PFOA, different pKa values were reported to be −0.1, −3.8, and 2.8 by Burns et al. (2008) and Goss (2008), respectively [22,23]. Coal and coconut GACs were purchased from Singi Chemical (Yangsan, Korea). Other chemicals used in this study were analytical reagent grade or better.

Table 1.
Name, abbreviations, number of carbons, chemical formula, and physicochemical properties of six perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs) and three perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids (PFSAs).
2.2. Preparation of the PACs
Two PACs were originated from virgin coal and coconut GAC and two other PACs were also tested to estimate the availability of the used coal GAC through a fixed bed column; these were prepared from first and third regenerations followed by drying at 200 °C~300 °C, pyrolysis at 400 °C–600 °C, and activation at ~800 °C. Each GAC was crushed with a mortar and pestle and sieved using 18–32 mesh. After that, the GACs were washed with DI and dried at 110 °C for 24 h; they are referred to as PCO-0, PCO-1, PCO-3, and PCC-0 for the fresh coal first and third regenerations, and the fresh coconut PAC, respectively. The physical characteristics of each PAC, including surface area, pore volume, mean pore diameter, and pore size distribution, were tested by the BET method and are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Properties of four types of powder activated carbons (PACs).
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
Batch experiment tests were conducted using the surface water and the primary water quality parameters, including pH: 8.3 ± 2.1, dissolved organic matter (DOM): 3.53 ± 3.2 mgC/L, alkalinity: 55 ± 12 mgCaCO3/L, hardness: 105 ± 26 mgCaCO3/L, and turbidity: 5.1 ± 1.6 NTU. The primary mixed stock solutions for nine PFASs were first prepared with 1 µg/L of each. From the stock solution, a certain amount containing nine PFASs was spiked into the raw water samples to obtain a desired concentration (~100 ng/L) for all the batch experiments, and then a desired mass of PACs was added. All of the individual batch tests were carried out using a 1 L glass jar with a controlled mixer speed. After the batch test, the aliquot of the sample was taken out and filtered with a 0.22 µm polyethersulfone (PES) syringe filter (Millipore, Germany). Blank experiments were also conducted for a 1 L glass jar and a syringe filter confirming that there was no change of PFAS concentration. To determine the removal efficiency for the four types of PACs, a series of batch tests was carried out at 50 mg/L of PAC, 0.5 h of contact time, and an initial pH of ~8.3 without pH adjustment during the experiments. The PFAS sorption rate was estimated for PCO-0 at a concentration of 10 mg/L and the samples were collected at intervals of 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 6 h. The effect of the mixing intensity was tested by experiments conducted at 30, 60, 90, and 120 rpm for the nine PFASs under the following conditions: 50 mg/L of PCO-0, 0.5 h of contact time, and initial pH of 8.2. The initial pH of the solution was set at 5.5, 7.0, 8.5, or 10 and the removal efficiency for PFPeA (5), PFHxA (6), PFHpA (7), and PFBS (4) was tested. To find the feasibility of the PAC process that occurred just after the prechlorination and before the coagulation process, the effect of prechlorination was tested at a concentration of Cl2 from 0 to 50 mg/L in the same manner as described above. All of the experiments conducted were duplicated.
2.4. Analysis
The concentration of the nine PFASs was analyzed using an ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS, Waldbronn, Germanuy) equipped with a poroshell EC-C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm, 2.7 µm). An Agilent 6490 MS/MS system with triple quadrupole was used to measure a single fragment. The BET surface area (SA), pore size distribution, and pore volume were determined using an N2 gas adsorption analyzer (model: Autosorb iQ3, Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of PACs
The physical properties of the four types of PACs in this study are presented in Table 2. The average effective size of all the PACs is approximately 0.74 mm. The BET SA and mean pore size were 1014 and 1133 m2/g, and 1.90 and 2.15 nm for PCO-0 and PCC-0, respectively, indicating that PCC-0 has a ~10% higher BET SA but a ~13% lower mean pore size than PCO-0. The thermal regenerations (PCO-1 and PCO-3) significantly reduced the BET SA by 10% and 34%, while increasing the mean pore width by 20% and 54% for the first and third time, respectively. Similarly, although the total pore volume (<50 nm cm3/g) was changed by less than 10%, increasing the thermal regeneration significantly increased the mesopore volume from 0.192 to 0.379 cm3/g (increased by 97%) and considerably decreased the primary micropore volume from 0.151 to 0.027 cm3/g (decreased by 84%), considering the pore structure was destroyed.
3.2. Removal Efficiency of the PFASs
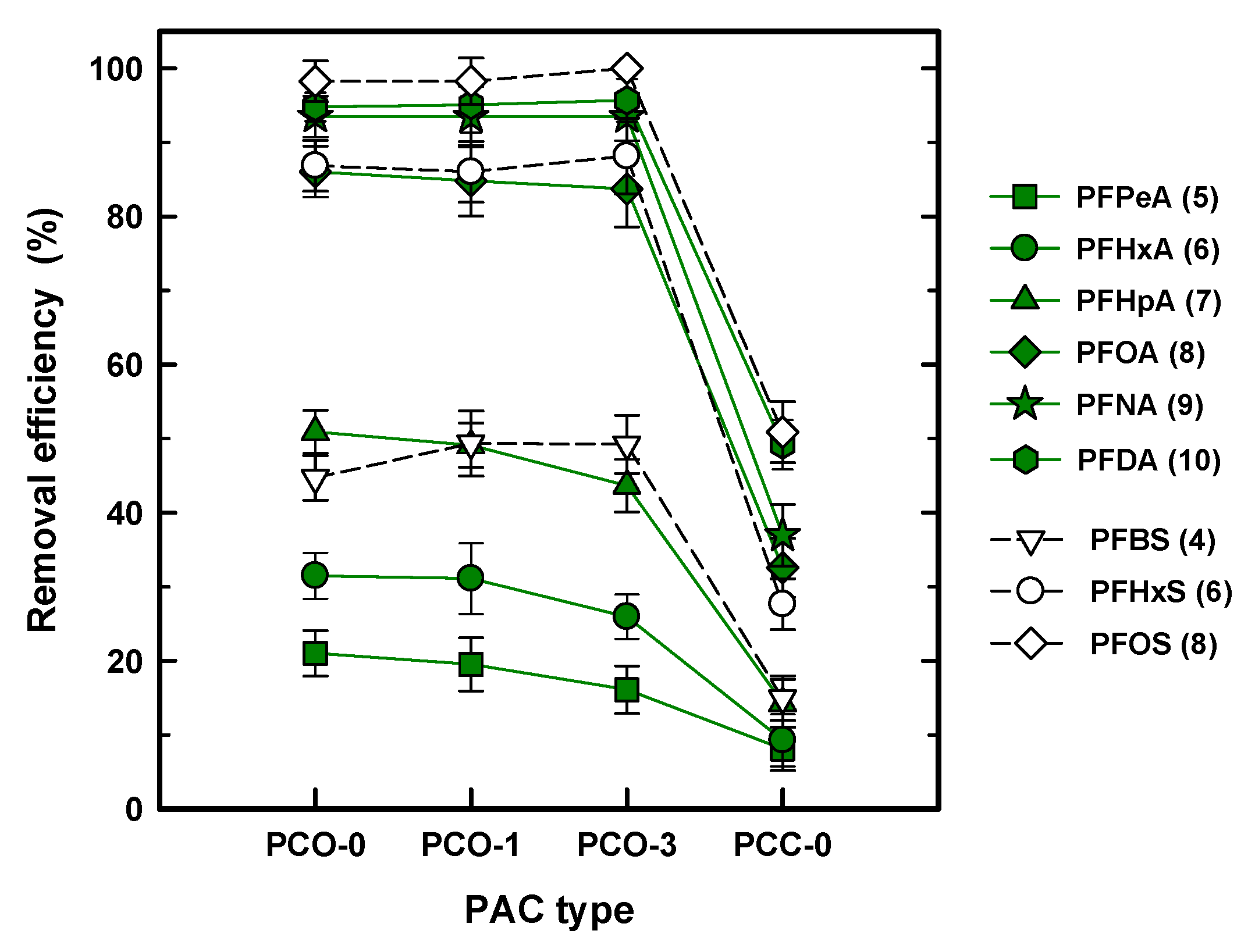
Figure 1 shows the removal efficiency of all the PFASs for different PAC adsorbents at 50 mg/L PAC and 0.5 h of contact time. Regardless of the species of PFAS, the removal efficiency for the coal-based PACs (PCO-0, PCO-1, and PCO-3) and the coconut shell-based PAC (PCC-0) ranged from 100% to 20% and ~50% to 10%, respectively, indicating that the PCOs exhibited at least two or three times higher removal efficiency than PCC-0. The significant decrease for PCC-0 can be attributed to the physical property of the coconut shell GAC. Typically, coconut shell GAC was developed to increase the adsorption capacity by increasing the BET SA and the micropore distribution [24]. As shown in Table 2, PCC-0 shows the highest BET SA and the primary micropore volume was distributed by 54%. As a result, the increased micropore volume led to a loss of adsorption capacity for all the PFASs tested. Similarly, most research has used coal-based GAC in PFAS removal from a solution [13,17,25]. Liu et al. (2019) compared four types of commercial GACs for removal of 10 PFAS species using a fixed column and concluded that the higher removal efficiency of the PFAS was determined by the higher volume of meso- or macropores and not the BET SA [26].
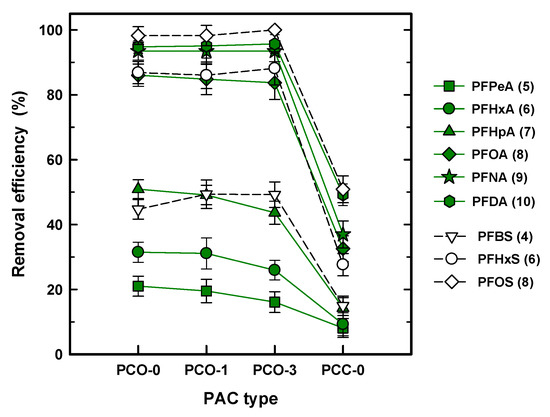
Figure 1.
Removal efficiency (%) of the per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) with different PAC types. The number in the legend denotes the carbon chain length.
In the drinking WTPs (DWTPs), the GAC process occurs after the filtration process to remove a variety of DOC as advanced treatment. The saturated GAC was regenerated with thermal treatment, resulting in a reduction of the SA and an increase in the pore size by destroying the inner pore structure [27,28]. Therefore, it is noteworthy to compare the capability of fresh GAC and first and third regenerated GAC for PFAS removal. Considering that the reduction of the removal efficiency for the regenerated PAC was less than 5%, which is within a standard deviation (SD), the effect of the first and third thermal regenerations can be negligible on adsorption for all of the PFASs in spite of reducing the BET SA and increasing the mean pore width. The previous study using commercial GAC reported the stationary removal efficiency of DOC in spite of the loss of BET SA after thermal regeneration of the GAC [29]. Therefore, it is anticipated that decreased adsorption capacity by a reduced BET SA can be recovered by enlarging the pore size. Comparing the species of PFASs in terms of removal efficiency, which is from 20% for PFPeA (5) to ~100% for PFOS (8) using PCO-0 (similar to PCO-1 and PCO-3), it is obvious that the adsorption capacity is strongly determined by the species of PFAS or the carbon chain length, i.e., a longer carbon chain improves the adsorption capacity for the PAC.
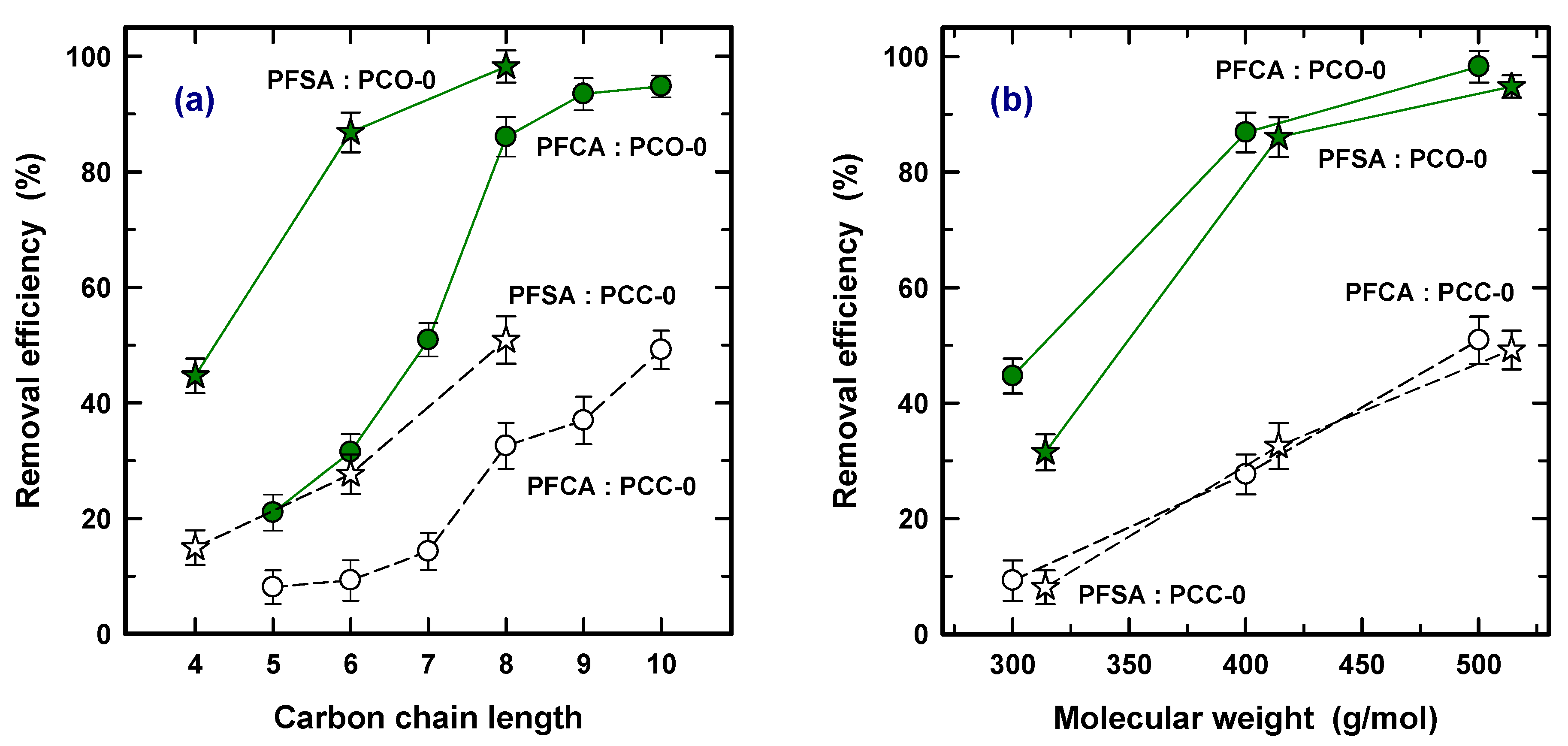
Various adsorption interaction mechanisms have been discussed for carbonaceous adsorbents for ionic and ionizable organic compounds, such as hydrophobicity, H-bonds, electro donor–acceptor interactions, electrostatic interaction, ligand exchange, Lewis acid–base reactions, covalent bond formation, and oxidative coupling [30]. Among them, both electrostatic interaction and hydrophobicity are strongly considered to be main driving forces for the adsorption of PFOAs and PFOSs on AC [23,31,32]. The enhanced adsorption capacity for longer carbon chains using commercial GAC has also been also observed for river water in DWTPs [33,34]. The enhanced adsorption was attributed to this since the hydrophobic GAC surface prefers to interact strongly with the hydrophobic PFAS, corresponding to the higher hydrophobicity of the longer carbon chain [19]. Figure 2 was drawn to show carbon chain length (a) and MW (b) for PCO-0 and PCC-0. According to Figure 2a, it was found that PFSA is more adsorptive than PFCA for both types of PACs with the same carbon chain length. For example, PFHxS (6, PFSA) and PFHxA (6, PFCA) achieved 87% and 32% for PAC-0 and 27% and 9% for PCC-0 in removal efficiency, respectively. This is in accordance with the previous results. Park et al. (2020) obtained a longer breakthrough Bed Volume (BV) for PFBS (4) and PFOS (8) over PFBA (4) and PFOA (8) using GAC in fixed column tests, respectively [19].
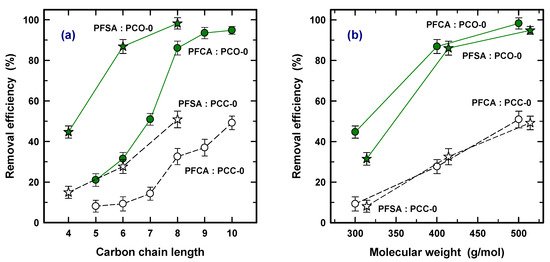
Figure 2.
Comparison of removal efficiency (%) as a function of carbon chain length (a) and molecular weight (b) using PCO-0 (solid line) and PCC-0 (dash line).
Based on Table 2, PFHxA (6), PFOA (8), and PFDA (10) have very similar MWs to PFBS (4), PFHxS (6), and PFOS (8) (less than 5% difference in MW), respectively. Figure 2b, showing the MW, confirms that a very similar removal efficiency was obtained at similar MWs for both of the PACs. Therefore, this clearly concluded that (1) a longer carbon chain increases the adsorption capacity on the PAC because of the higher hydrophobicity interaction, (2) the species of PFSAs obtain a higher adsorption capacity than PFCAs with the same carbon chain length, and (3) similar MWs lead to similar levels of PFAS adsorption regardless of the type of sulfonate and carboxyl. In addition, the similar trend of removal efficiency with higher removal efficiency with longer carbon chains for PCO and PCC confirms that the effective difference in PFAS removal between PAC and PCC was mainly derived from a physical property, i.e., pore volume.
3.3. PAC Dosage
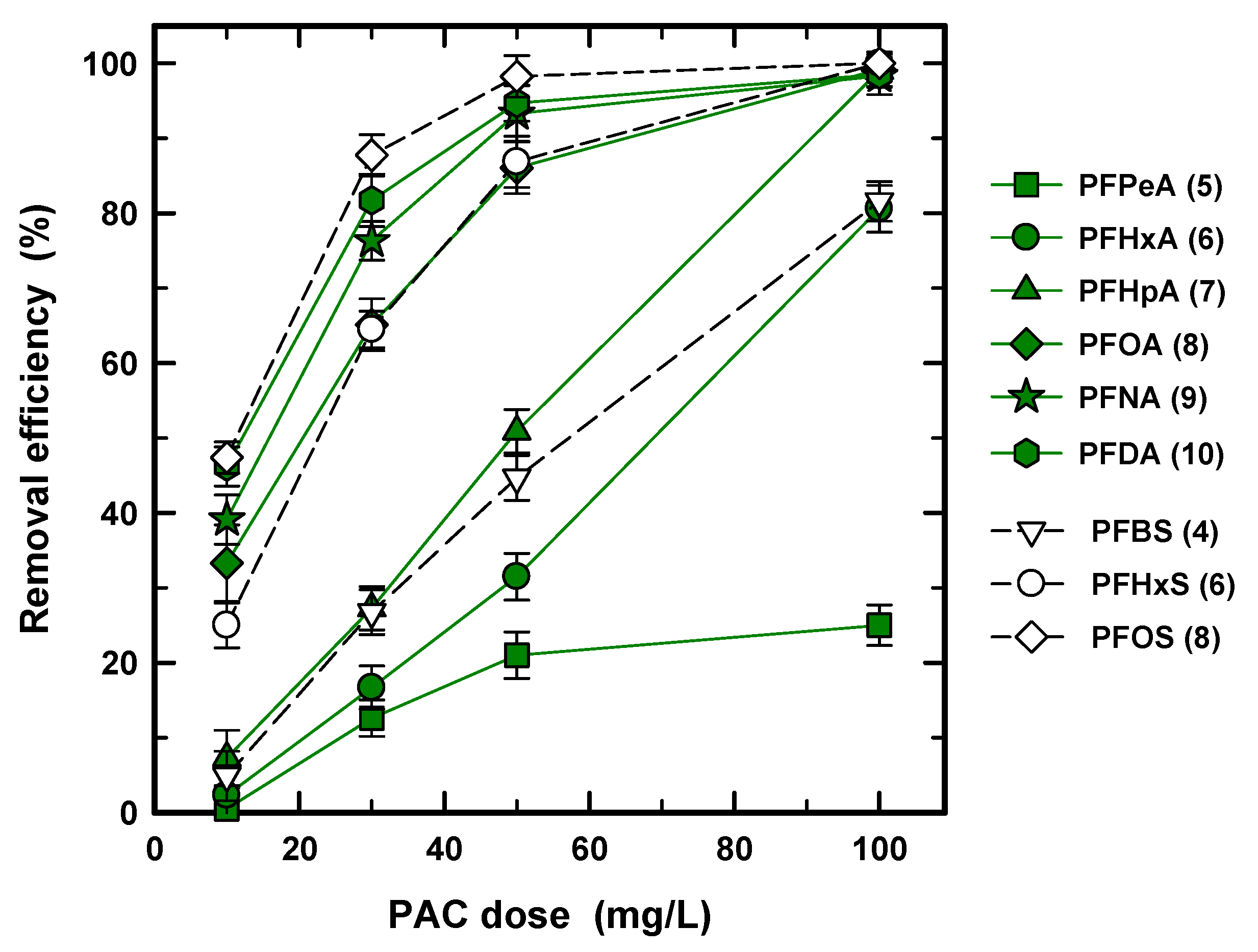
To determine the optimized PAC concentration, the removal efficiency for nine PFASs was obtained at 10, 30, 50, and 100 mg/L of PAC concentration with 30 min of contact time, as shown in Figure 3. At the lowest concentration of 10 mg/L, the removal efficiency for PFPeA (5), PFHxA (6), PFHpA (7), and PFBS (4) was only less than 10%, and the other PFASs showed 20–50% efficiency. To accomplish over 80% removal, 50 mg/L and 100 mg/L concentrations are required for long and short chains, respectively, except for PFPeA (5). The big difference in Figure 3 again clearly occurs between the short and long carbon chains at 10, 30, and 50 mg/L of PAC. Meanwhile, the short chains of PFHxA (6), PFHpA (7), and PFBS (4) proportionally increased with the increase in PAC concentration and reached 100% and 70% removal efficiency, respectively; the increasing rate of removal efficiency of PFPeA (5) is reduced with the increasing PAC concentration. This phenomenon is due to the slow rate of adsorption for PFPeA (5). For long carbon chains, the slope was decreased from 10–30 and 30–50 mg/L of PAC due to the limited adsorption site and high concentration gradient [35]. Accordingly, the USEPA regulation (70 ng/L for PFOA and PFOS), for all long chain PFASs, was easy to satisfy at 30 mg/L of PAC and 30 min of contact time. However, the short chain PFASs needed a higher dosage and PFPeA (5) did not meet the regulation at 100 mg/L of PAC in that condition.
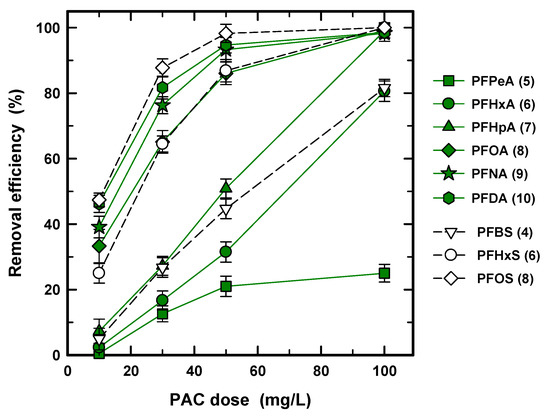
Figure 3.
Removal efficiency (%) of PFASs at different dosages of PCO-0 with a condition of 30 min of contact time.
3.4. Kinetic
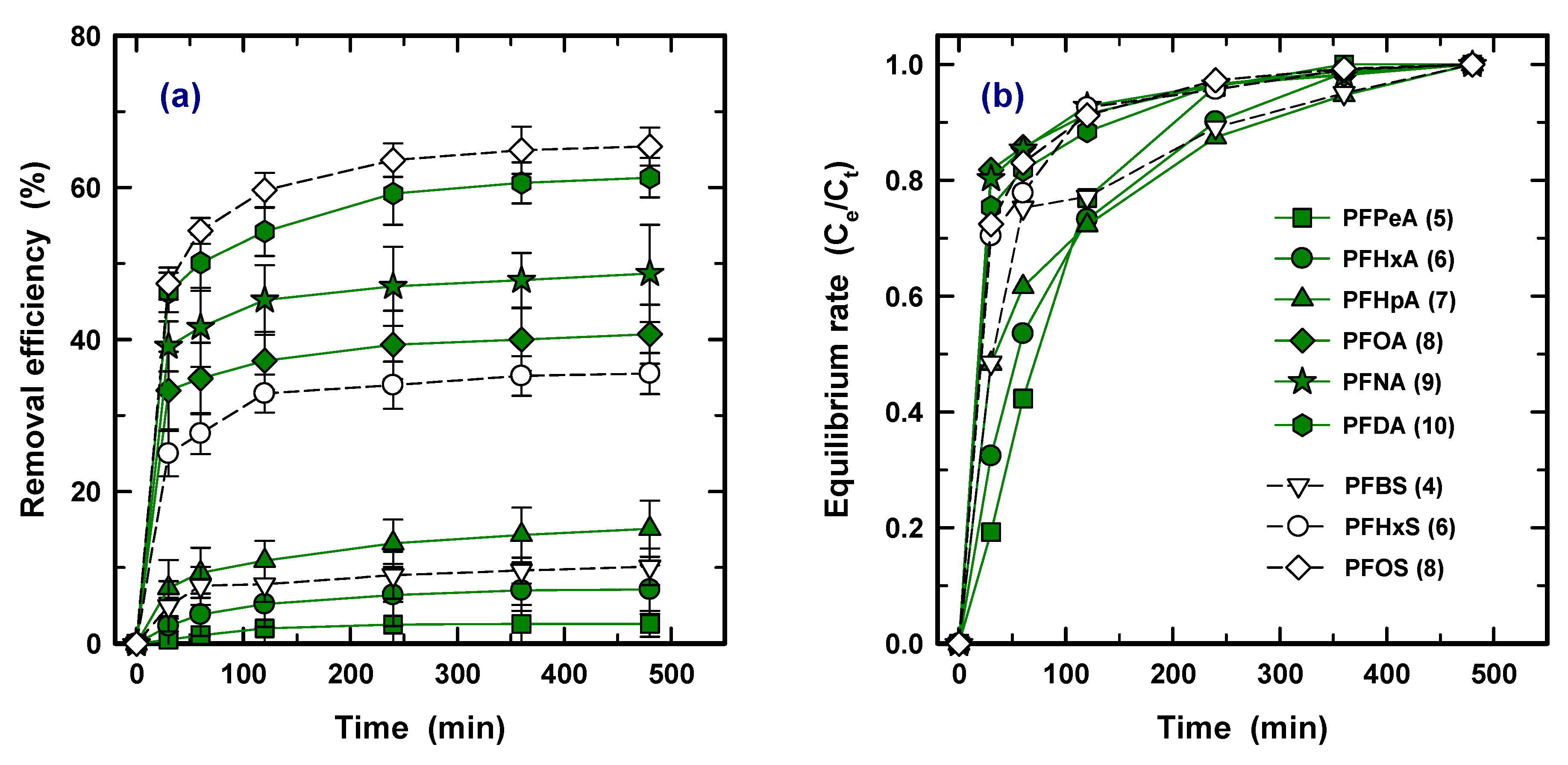
The sorption kinetics for nine PFASs are shown in Figure 4a as plots of removal efficiency versus time (30, 60, 120, 240, 360, 480 min) at 10 mg/L of PAC. It was found that the adsorption rate of all the PFASs was initially fast, indicating that ~70% of removal was accomplished within 30 min, and constant efficiency was observed at ~240 min; this is similar to the other PAC results for PFOA and PFOS [17]. To determine the initial rate, Figure 4b shows time versus rate of equilibrium concentration (Ce) to concentration at a specific time (Ct). For PFOA (8), PFNA (9), PFDA (10), PFHxS (6), and PFOS (8), which obtained over 80% removal efficiency in Figure 1, 70–80% and 90% of the adsorption process was accomplished within 30 and 60 min, respectively. The others required 360 min to reach 90% adsorption. Due to strong competition at the beginning, the adsorption rate for the lower hydrophobicity PFAS species was retarded. Therefore, this result confirms that the species exhibited stronger interaction with PAC influence on not only higher adsorption capacity but also on rapid initial kinetic rate.
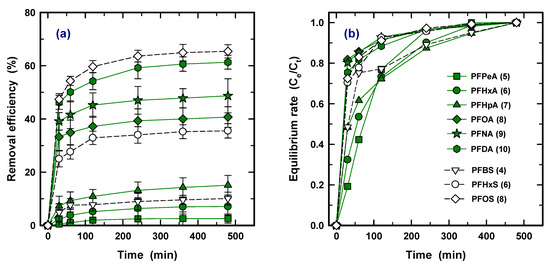
Figure 4.
Removal efficiency (a) and equilibrium rate (Ce/Ct) (b) as a function of time with a condition of 10 mg/L of PCO-0 and initial concentration of 100 ng/L (Ce and Ct are concentration at equilibrium and a desired time, respectively).
Pseudo first order (PFO) and pseudo second order (PSO) kinetic models are used to describe the interaction and follow Equations (1) and (2), respectively [36,37]. The calculated sorption parameters are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Kinetic parameters of the pseudo first order (PFO) and pseudo second order (PSO) models for nine PFASs.
Compared with R2, PSO shows higher accuracy than PFO for all PFASs, except for PFPeA (5), indicating that the interaction between PAC and PFASs was followed by a chemical reaction [17].
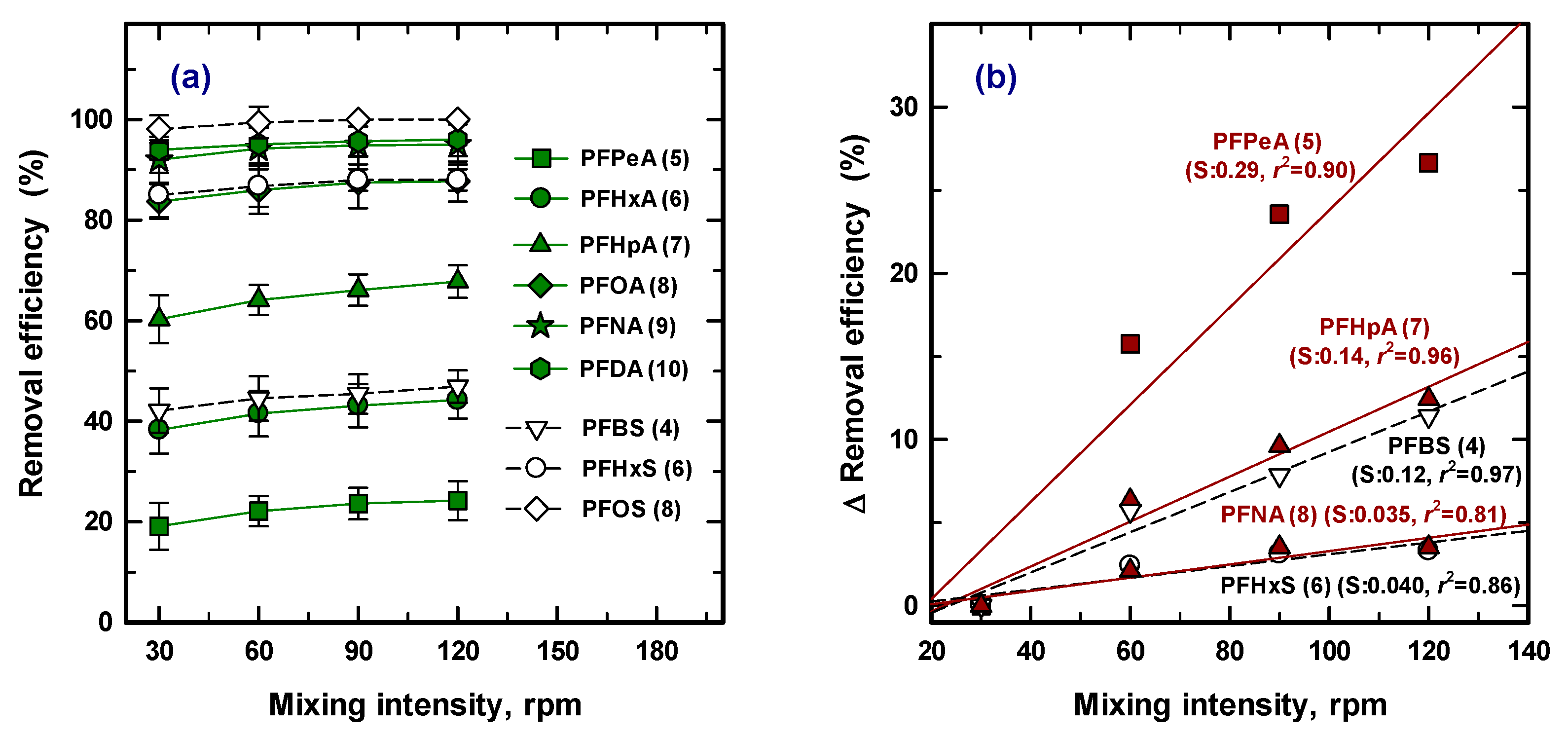
3.5. Mixing Intensity
The effect of mixing intensity was also required as an optimized operation parameter. Agitation speed is one of the physical parameters used to evaluate the distribution of the adsorbate ions and the PAC from solution. Figure 5a shows the adsorption removal at 30, 60, 90, and 120 rpm with 50 mg/L of PAC for 30 min, and compares the variation of removal efficiency for nine species of PFASs. At a glance, the removal efficiency for each PFAS was slightly increased with the increased mixing intensity. To assess the detailed effect for removal, Figure 4b, including only five PFASs (PFPeA (5), PFHpA (7), PFBS (4), PFNA (8), and PFHxS (6)) was redrawn to estimate the rate of change by removal efficiency. Less than a 5% increase was shown for PFNA (8) and PFHxS (6) with four times higher mixing intensity, while PFPeA (5) was enhanced up to ~25% at 120 rpm. Therefore, physical treatment can improve the removal efficiency, leading to rapid mass transfer by reducing film diffusion for the low removal efficiency condition [38]. High removal efficiency (over 80%) means that only 20% of the target contaminant remains available for removal, and the concentration gradient was relatively low. Therefore, intensified physical treatment is not considered and chemical treatment needs to achieve greater removal efficiency.
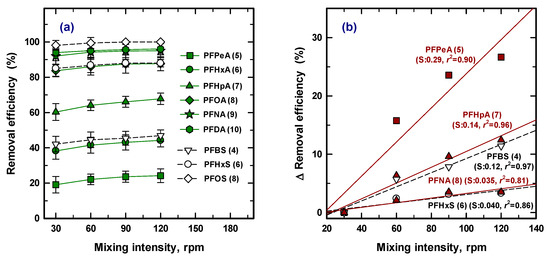
Figure 5.
Removal efficiency of nine PFASs at an intensity of mixing (a) and the change of removal efficiency for five PFASs (b).
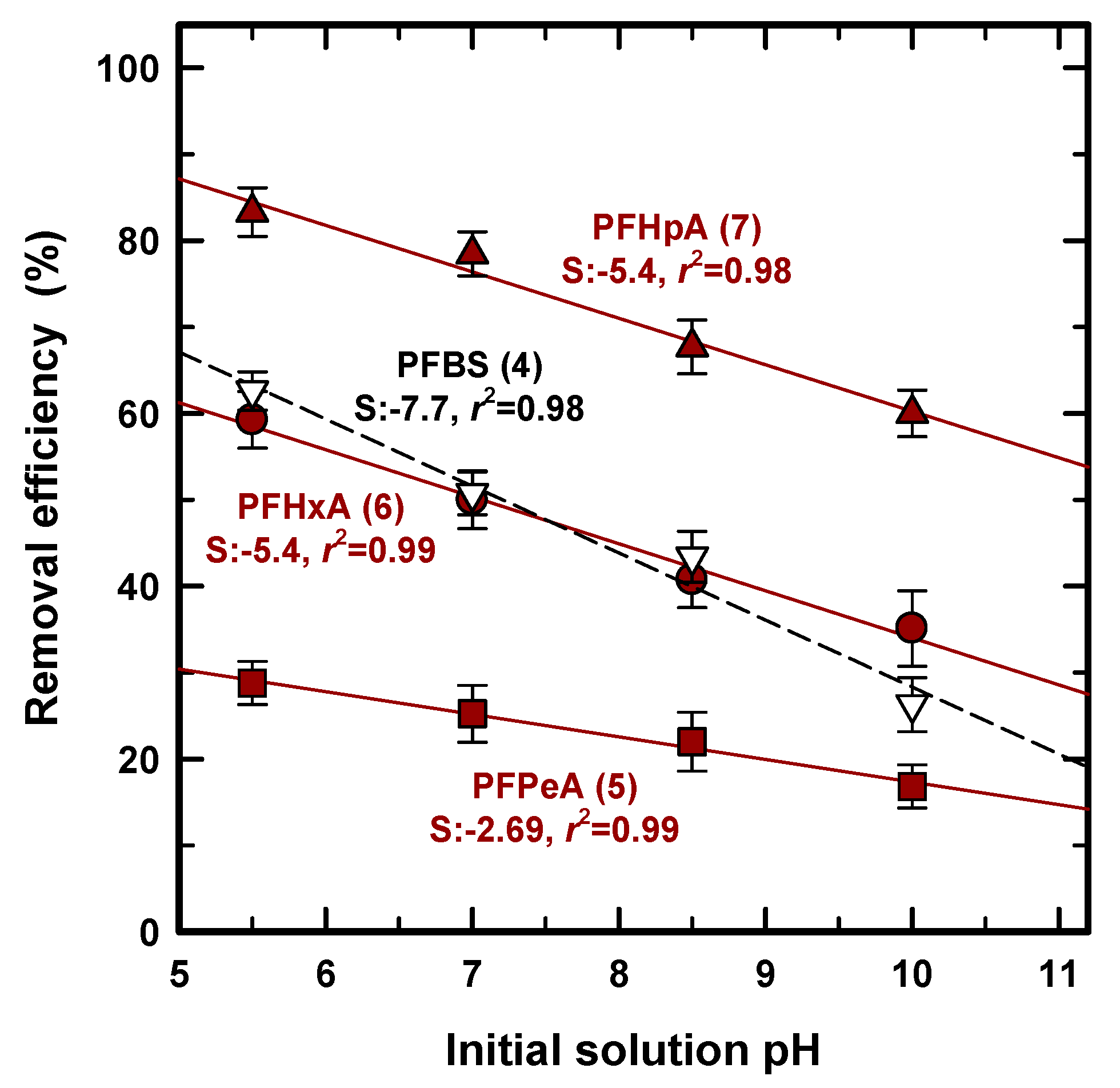
3.6. Effect of Solution pH
As for PFAS adsorption, the solution pH was crucially taken into consideration and was a significant parameter in determining the adsorption capacity [39] because it can determine the surface charge of the adsorbent and the adsorbated speciation [39,40]. In general, the speciation of an inorganic anion, such as phosphate or arsenic, is determined by protonation/deprotoantion near its pKa [41,42], and PFASs as organic acids can exist in either protonated or deprotonated forms based on the pKa value, shown in Table 1. Since the value of pKa was less than 1 for all of the PFASs except for PFOA in Table 1, this study does not need to consider the protonation/deprotonation effect for adsorption. Figure 6 shows the removal efficiency for PFPeA (5), PFHxA (6), PFHpA (7), and PFBS (4) at an initial pH of 5.5, 7.0, 8.5, and 10, and regression lines (solid line) including slope and R2 were added to find the quantitative effect. Removal efficiency was decreased with the increase in solution pH, regardless of the use of PFCA or PFSA. This corresponds to other research studies using GAC [43] and porous graphite for PFCS [44], i.e., the electrostatic force can occur between the negatively charged PFAS and the positively charged surface charge. On the other hand, Krippner et al. (2014) obtained the opposite result using a plant root known for weak acids [45]. PFBA (4), PFPeA (5), PFHxA (6), and PFBS (4), which are considered as relatively short chains, showed an increased uptake with an increase in solution pH, whereas PFDA (10) uptake was significantly decreased with an increased pH. Most studies have demonstrated, or used, a very low pKa that was usually applied as less than 1 for all of the PFAS species, as shown in Table 1, but Prevedouros et al. (2006) and Moroi et al. (2001) found 2.0~3.0 for PFOA and ~2.66 for PFDA, respectively [46,47]. However, according to our results, there was less removal efficiency at a higher pH for all samples, strengthening the less than 1 value of pKa, and the protonation was not the primary parameter by which to decide the PFAS uptake for PAC.
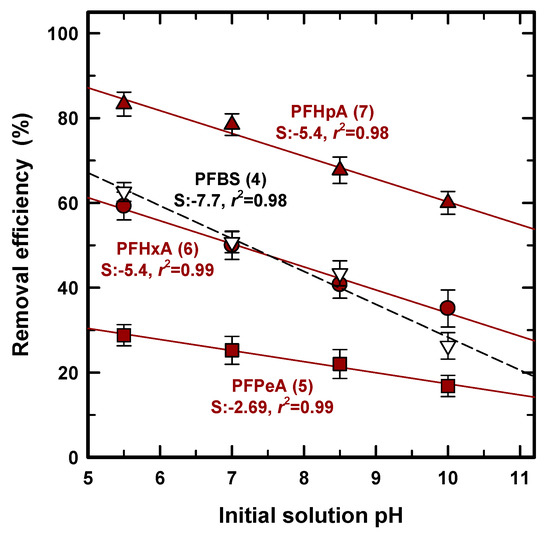
Figure 6.
Removal efficiency of pH at 5.5, 7.0, 8.5, and 10.0.
We attempted to verify the quantitative pH effect from four regression lines calculated with a very high R2 (>0.98) regardless of the PFAS species. A high R2 value indicates that the decrease in removal efficiency occurs proportionally and quantitatively with the increase in pH. Therefore, the presence of a hydroxide ion competes with the PFASs that are constantly affected at the pH range from 5.5–10.
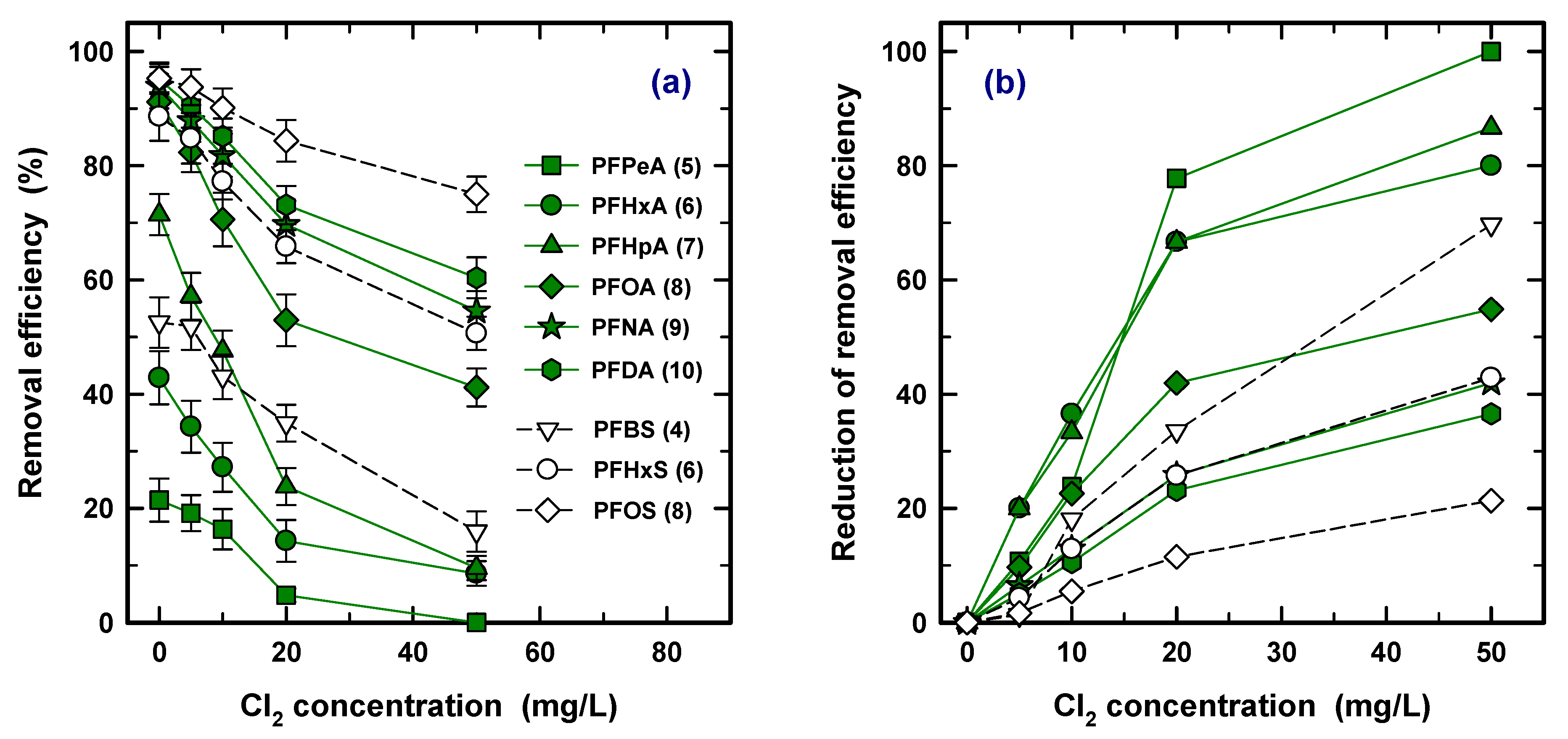
3.7. Effect of Chlorination
In the advanced water treatment process, prechlorination took place immediately before coagulation/flocculation to remove the organic matter and NH3-N [48,49]. Therefore, the effect of prechlorination should be considered because the PAC process would be considered to have taken place before the coagulation/flocculation. The removal efficiency of nine PFASs was obtained at 0, 5, 10, 30, and 50 mg/L of Cl2, as shown in Figure 7. Removal efficiency was decreased with increasing concentration of Cl2 for all the PFAS species in Figure 7a. Chemical oxidation also refers to destruction technologies such as thermal treatment and biological treatment for PFAS removal or separation from water. However, a strong bond between C–F and a high melting point of the PFAS led to a low removal restriction of the application in the lab and the field [50]. Therefore, the effect of chlorination is ignorable in the oxidation of PFASs.
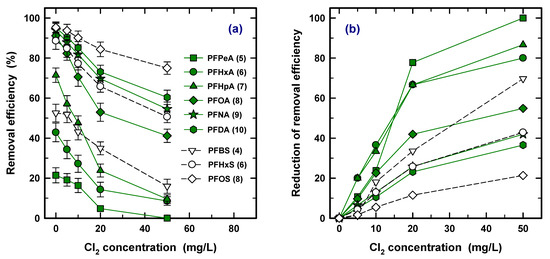
Figure 7.
The effect of prechlorination at different concentrations (a) and reduction rates of removal efficiency (b).
The rate of reduction is also shown to find the effect of the concentration of Cl2 in Figure 7b. The rate of reduction ranges from 1% to 20% at 5 mg/L and from 20% to 100% at 50 mg/L of Cl2. Clearly, the higher reduction rate was observed in a short carbon chain PFAS species, resulting in a lower removal efficiency for PAC, and the order of the reduction rate is the reverse of the order of removal efficiency of PAC. However, since the concentration of Cl2 during prechlorination generally operated under ~3 mg/L [51,52], in the operation system, the shift of removal efficiency is considered for 5 mg/L of Cl2.
3.8. Selectivity of Each PFAS
The condition of the experiment is that nine PFAS species were simultaneously mixed and tested using PAC. Therefore, we attempted to estimate the effect of each species on the adsorption uptake for PCO-0. The binary separation factor (SF) was used to compare the relative affinity of PAC for the various PFASs.
where q and C represent the uptake in the solid (μg/g) and the concentration of A in the solid (ng/L), respectively. A and B in the subscripts denote species of PFASs. The calculated SF is shown in Table 4. In general, a value of αA/B of greater than 1 indicates that A has a higher preference than B for the adsorbent. According to Table 3, the values of αA/B of PFPeA (5) (third raw) are greater than 1, indicating that PFPeA (5) has the lowest affinity for PAC. The highest affinity, 70.8, occurs between PFPeA (5) and PFOS (8). By comparison with increasing the number of one and two carbon chain lengths, the value of the affinity was proportionally increased 1.4–3.9 and 2.3–8.9 times, respectively. The increasing value is decreased with an increase in carbon chain length, indicating that the adsorption uptake is more influenced in shorter carbon chain PFAS species.

Table 4.
The separation factor for nine PFASs.
4. Conclusions
Four types of PACs were investigated to determine the feasibility in WTPs by comparing the removal of various PFAS species in different conditions, such as PAC dosage, mixing contact time, mixing intensity, pH, and concentration of chlorination. Overall, the use of PAC based on coal shows high removal efficiency even for short carbon chains. Even very low initial concentration of PFASs in raw water containing a relatively high concentration of DOC, which reduces the PFAS adsorption capacity, can meet the current PFOA and PFOS regulations (70 ng/L) set by the USEPA. The fact that the coal-based PAC showed a higher removal efficiency proves that the structure of PAC was first considered when it was applied in PFAS removal. The behavior of removal by adsorption was mainly determined by the number of carbon chains and the MW of PFAS species, corresponding to a higher number of carbons or the MW enhancing the removal efficiency. By comparing the time to reach equilibrium, higher removal efficiency was found to reduce the equilibrium time. As predicted, the solution pH reduced the removal efficiency with an increase in pH as a significant parameter.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.S. and B.A.; methodology, T.K. and H.-S.Y.; formal analysis, T.K. and H.-S.Y.; investigation, D.Z.; writing the manuscript, H.S. and B.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Research Foundation of Korea, funding: NRF-2019R1A2C1009129.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Duan, J.; Tian, S.; Ji, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, D. Short-chain per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in aquatic systems: Occurrence, impacts and treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122506. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Risk Management for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) under TSCA. 2017. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/assessing-and-managing-chemicals-under-tsca/risk-management-and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfass (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Giesy, J.P.; Kannan, K. Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.J.; Clemen, L.A.; Ellefson, M.E.; Johnson, H.O. Compound-specific, quantitative characterization of organic fluorochemicals in biological matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oyetade, A.; Varadwaj, G.B.B.; Nyamori, V.O.; Jonnalagadda, S.B.; Martincigh, B.S. A critical review of the occurrence of perfluoroalkyl acids in aqueous environments and their removal by adsorption onto carbon nanotubes. Rev. Environ Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 17, 603–635. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, C.A.; Field, J.A. Perfluorinated surfactants and the environmental implications of their use in fire-fighting foams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3864–3870. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrens, L. Polyfluoroalkyl compounds in the aquatic environment: A review of their occurrence and fate. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kotthoff, M.; Müller, J.; Jürling, H.; Schlummer, M.; Fiedler, D. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in consumer products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14546–14559. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik, B.K.; Pramanik, S.K.; Suja, F. A comparative study of coagulation, granular- and powdered-activated carbon for the removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate in drinking water treatment. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2610–2617. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, Q.; Wang, J.; Niu, J.; Yang, B.; Yang, Y. Electrochemical oxidation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) substitute by modified boron doped diamond (BDD) anodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122280. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Ruiz, B.; Ribao, P.; Diban, N.; Rivero, M.J.; Ortiz, I.; Urtiaga, A. Photocatalytic degradation and mineralization of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) using a composite TiO2 -rGO catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCleaf, P.; Englund, S.; Ostlund, A.; Lindegren, K.; Wiberg, K.; Ahrens, L. Removal efficiency of multiple poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water using granular activated carbon (GAC) and anion exchange (AE) column tests. Water Res. 2017, 120, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woodard, S.; Berry, J.; Newman, B. Ion exchange resin for PFAS removal and pilot test comparison to GAC. Remediation 2017, 27, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. 3M Cottage Grove Site Proposed Cleanup Plan for PFCs; Minnesota Pollution Control Agency: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2009; Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/pfc3-04.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Hansen, M.C.; Børresen, M.H.; Schlabach, M.; Cornelissen, G. Sorption of perfluorinated compounds from contaminated water to activated carbon. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Deng, S.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Sorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate on activated carbons and resin: Kinetic and isotherm study. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Zaggia, A.; Conte, L.; Falletti, L.; Fant, M.; Chiorboli, A. Use of strong anion exchange resins for the removal of perfluoroalkylated substances from contaminated drinking water in batch and continuous pilot plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.; Wu, S.; Lopez, I.J.; Chang, J.Y.; Karanfil, T.; Snyder, S.A. Adsorption of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in groundwater by granular activated carbons: Roles of hydrophobicity of PFAS and carbon characteristics. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115364. [Google Scholar]
- Boehler, M.; Zwickenpflug, B.; Hollender, J.; Ternes, T.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H. Removal of micropollutants in municipal wastewater treatment plants by powder-activated carbon. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar]
- Stebel, E.K.; Pike, K.A.; Nguyen, H.; Hartmann, H.A.; Klonowski, M.J.; Lawrence, M.G.; Collins, R.M.; Hefner, C.E.; Edmiston, P.L. Absorption of short-chain to long-chain perfluoroalkyl substances using swellable organically modified silica. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 11, 1854–1866. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, D.C.; Ellis, D.A.; Li, H.; McMurdo, C.J.; Webster, E. Experimental pKa determination for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and the potential impact of pKa concentration dependence on laboratory-measured partitioning phenomena and environmental modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9283–9288. [Google Scholar]
- Goss, K.-U. The pKa values of PFOA and other highly fluorinated carboxylic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 456–458. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.; Samal, D.P.; Meikap, B.C. Preparation of activated carbon from green coconut shell and its characterization. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Senevirathna, S.T.M.L.D.; Tanaka, S.; Fujii, S.; Kunacheva, C.; Harada, H.; Shivakoti, B.R.; Okamoto, B. A comparative study of adsorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) onto granular activated carbon, ion-exchange polymers and non-ion-exchange polymers. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.J.; Werner, D.; Bellona, C. Removal of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) from contaminated groundwater using granular activated carbon: A pilot-scale study with breakthrough modeling. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 11, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar]
- Son, H.J.; Ryu, D.C.; Jang, S.H. Effect of pore structure change on the adsorption of NOM and THMs in water due to the increase of reactivation number of coal-based activated carbon. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2010, 32, 965–972. [Google Scholar]
- San Miguel, G.; Lambert, S.D.; Graham, N.J. The regeneration of field-spent granular-activated carbons. Environ. Technol. 2002, 31, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-G.; Son, H.-J.; Jung, J.-M.; Ryu, D.-C.; Yoo, P.-J. Evaluation of drinking water treatment efficiency according to regeneration temperatures of granular activated carbon (GAC). J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2015, 24, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Kah, M.; Sigmund, G.; Xiao, F.; Hofmann, T. Sorption of ionizable and ionic organic compounds to biochar, activated carbon and other carbonaceous materials. Water Res. 2017, 124, 673–692. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliano, E.; Sgroi, M.; Falciglia, P.P.; Vagliasindi, F.G.A.; Roccaro, P. Removal of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water by adsorption: Role of PFAS chain length, effect of organic matter and challenges in adsorbent regeneration. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115381. [Google Scholar]
- Saeidi, N.; Kopinke, F.-D.; Georgi, A. Understanding the effect of carbon surface chemistry on adsorption of perfluorinated alkyl substances. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122689. [Google Scholar]
- Eschauzier, C.; Beerendonk, E.; Scholte-Veenendaal, P.; De Voogt, P. Impact of treatment processes on the removal of perfluoroalkyl acids from the drinking water production chain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flores, C.; Ventura, F.; Martin-Alonso, J.; Caixach, J. Occurrence of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in NE spanish surface waters and their removal in a drinking water treatment plant that combines conventional and advanced treatments in parallel lines. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vadivelan, V.; Kumar, K.V. Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2005, 286, 90–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergreen, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Zeitschrift fur Chemie und Industrie der Kolloide 1907, 2, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem. Eng. J. 1998, 70, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Low, K.; Chung, L. Removal of some organic dyes by hexane-extracted spent bleaching earth. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 1997, 69, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.W.; Deng, S.B.; Chen, Y.G.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Yu, G. Removal of perfluorinated carboxylates from washing wastewater of perfluorooctanesulfonyl fluoride using activated carbons and resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.X.; Deng, S.B.; Du, Z.W.; Liu, K.; Yu, G. Adsorptive removal of emerging polyfluoroalky substances F-53B and PFOS by anion-exchange resin: A comparative study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 550–557. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-G.; He, F.; An, B. The application of alginate coated iron hydroxide for the removal of Cu(II) and Phosphate. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3835. [Google Scholar]
- An, B.; Kim, H.; Park, C.; Lee, S.-P.; Choi, J.-W. Preparation and characterization of an organic/inorganic hybrid sorbent (PLE) to enhance selectivity for As(V). J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 289, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Maimaiti, A.; Shi, H.; Wu, R.; Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Qi, D.; Yu, G.; Deng, S. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of emerging perfluoro-2-propoxypropanoic acid (GenX) on activated carbons and resins. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Wu, Z.; Ma, D.; Xiang, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Deng, Y.; Tan, S.; Cai, X. Fabrication of few-layered porous graphite for removing fluorosurfactant from aqueous solution. Langmuir 2018, 34, 15181–15188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krippner, J.; Brunn, H.; Falk, S.; Georgii, S.; Schubert, S.; Stahl, T. Effects of chain length and pH on the uptake and distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances in maize (Zea mays). Chemosphere 2014, 94, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prevedouros, K.; Cousins, I.T.; Buck, R.C.; Korzeniowski, S.H. Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Moroi, Y.; Yano, H.; Shibata, O.; Yonemitsu, T. Determination of acidity constants of perfluoroalkanoic acids. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 74, 667–672. [Google Scholar]
- Tobiason, J.E.; Nabi bidhendi, G.H.R.; Torabian, A.; Ghadimkhani, A.A.; Etemadi, H. Preozonation and prechlorination effects on TOC removal by nanofiltration in water treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2008, 2, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Blatchley, E.R.; Wang, X.; Ren, P. UV/chlorine process for ammonia removal and disinfection by-product reduction: Comparison with chlorination. Water Res. 2015, 68, 804–811. [Google Scholar]
- Mahinroosta, R.; Senevirathana, L. A review of the emerging treatment technologies for PFAS contaminated soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109896. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wu, R.; Duan, J.; Saint, C.P.; van Leeuwen, J. Impact of prechlorination on organophosphorus pesticides during drinking water treatment: Removal and transformation to toxic oxon byproducts. Water Res. 2016, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-K.; Son, H.-J.; Kim, S.-G.; Hwang, Y.-D.; Ryu, D.-C. Effect of pH control, ozonation and coagulation on THMs formation in drinking water treatment process of the downstream of nakdong river. J. Koran Soc. Environ. Eng. 2017, 39, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).