Lessons Learnt from the Long-Term Management of a Large (Re)constructed Wetland, the Kis-Balaton Protection System (Hungary)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Doom and Adventurous Rebirth of the Kis-Balaton Wetlands
1.2. Management Context and Study Objectives
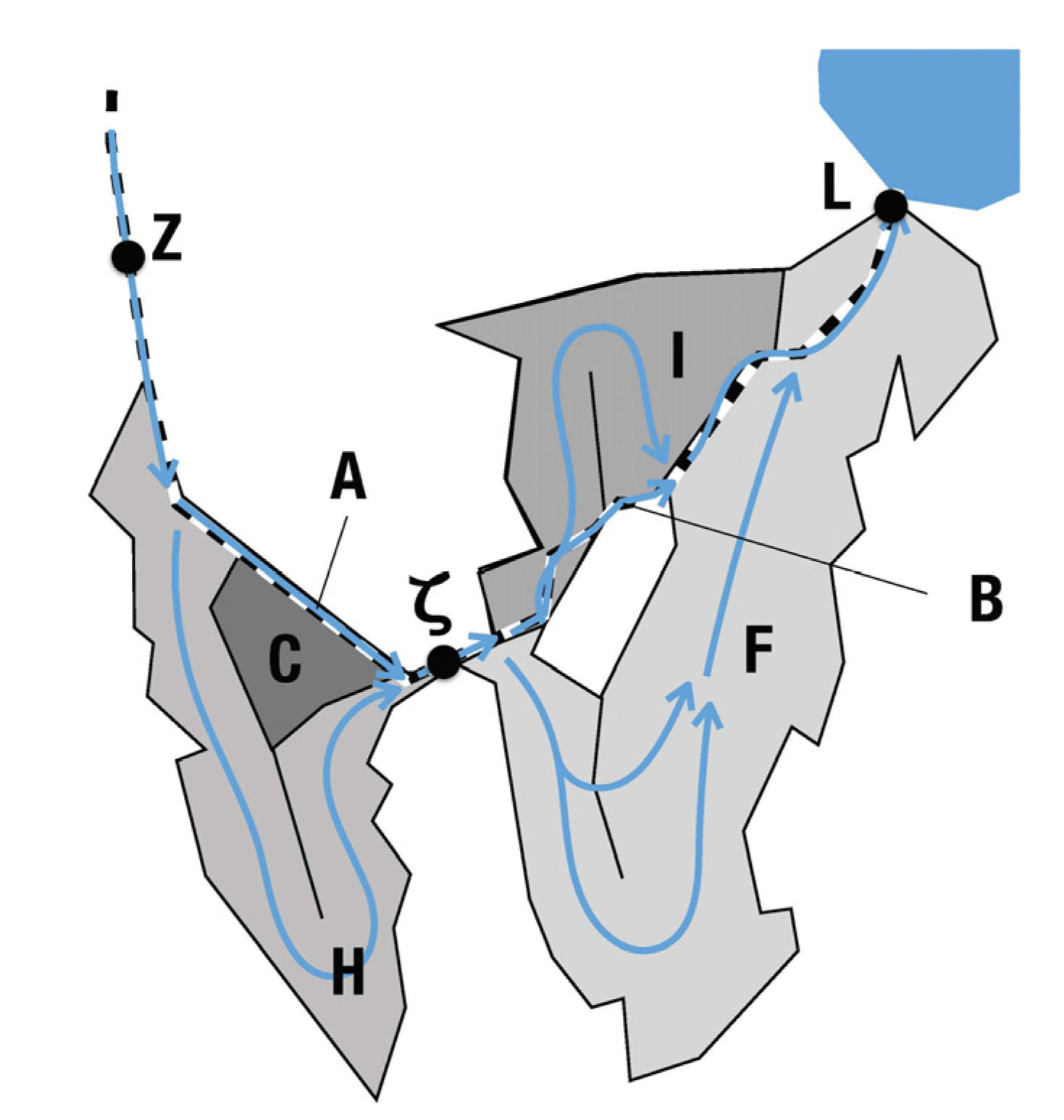
2. Materials and Methods
- Compilation of water, suspended solids (SS), and total phosphorus (TP) balances for the entire system and phases 1 and 2 separately. This included estimating non-monitored components (hydraulic, sediment, and nutrient loads from smaller tributaries) by catchment modelling.
- Calculation of retentions efficiencies of SS and TP for the entire system and for phases 1 and 2 separately. Retention in Lake H was also simulated by a dynamic model to characterize conditions when a net release of TP was likely.
- Analysis of retention and the efficiency of management with respect to the declared objectives of the Kis-Balaton system.
2.1. Balances of Water, SS, and TP
2.2. Annual and Seasonal Retention of TP and SS
3. Results and Discussion
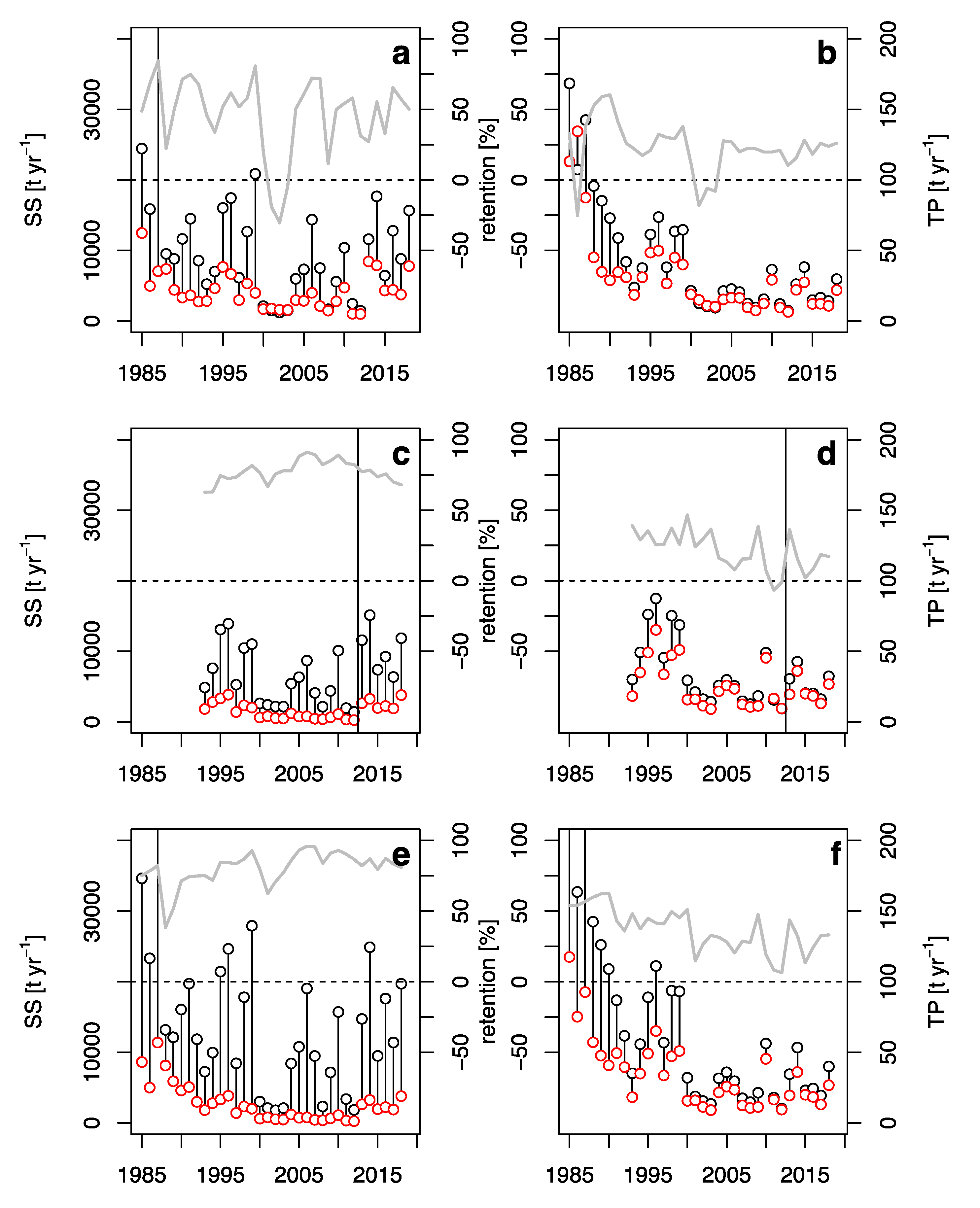
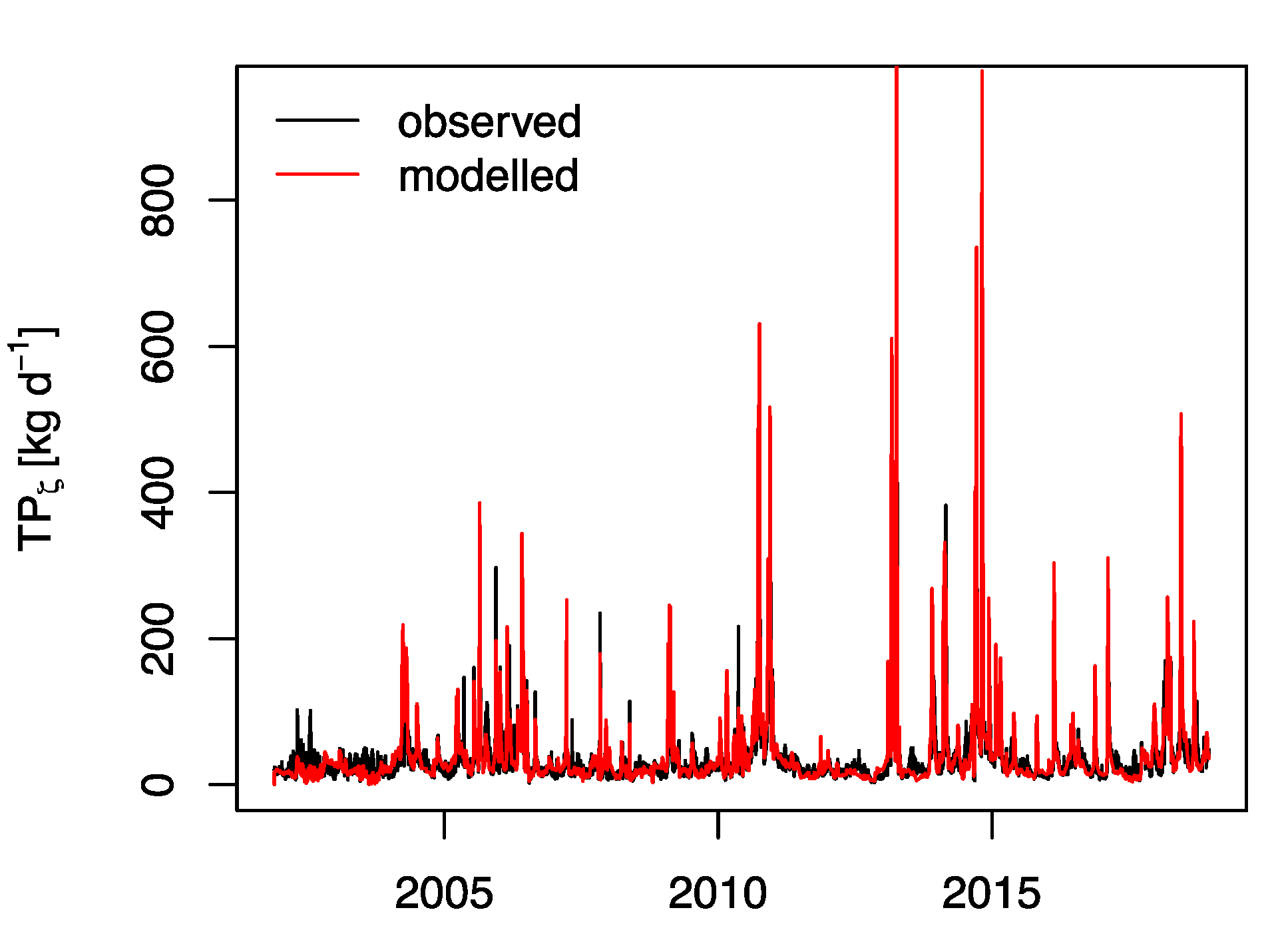
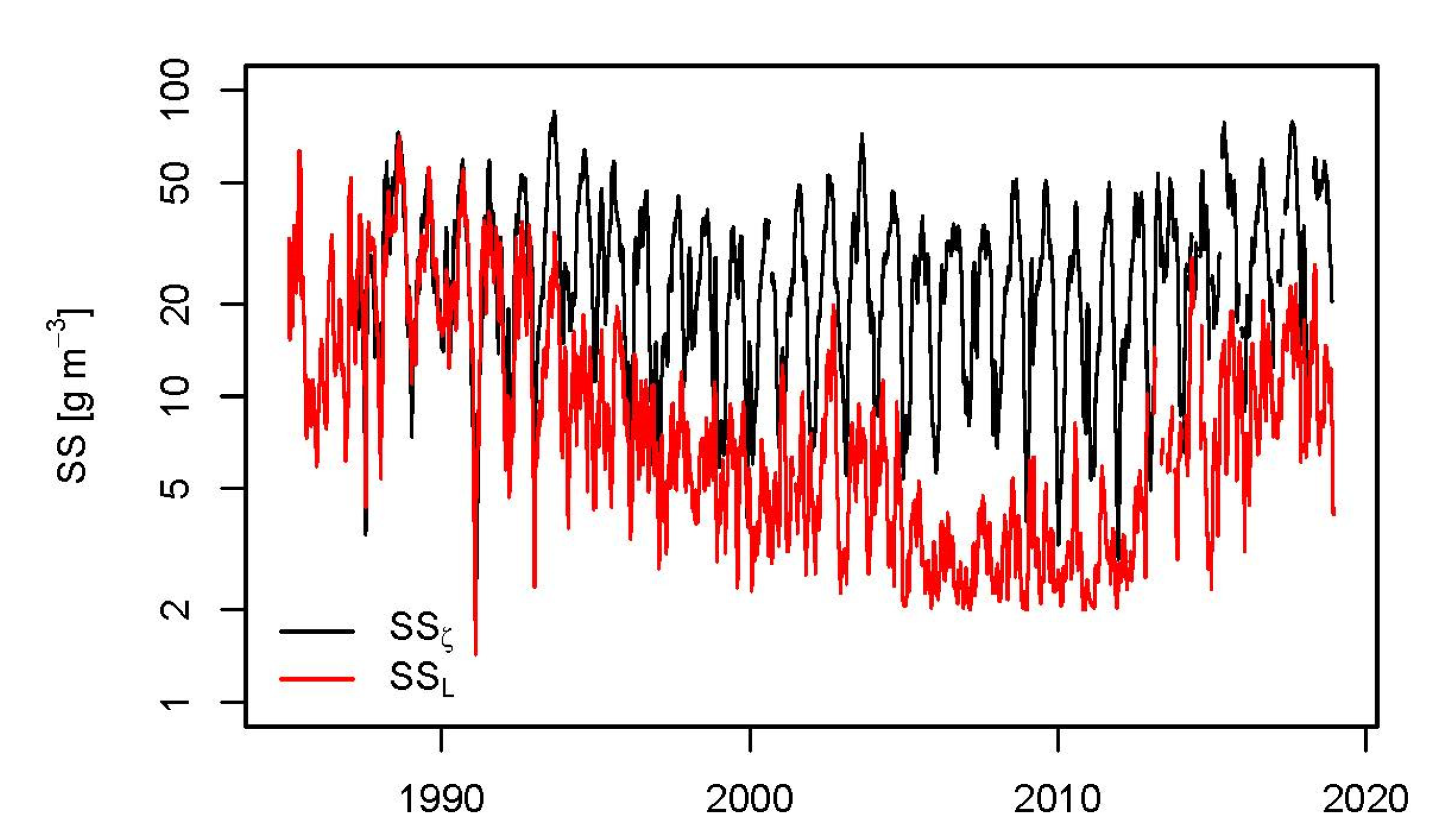
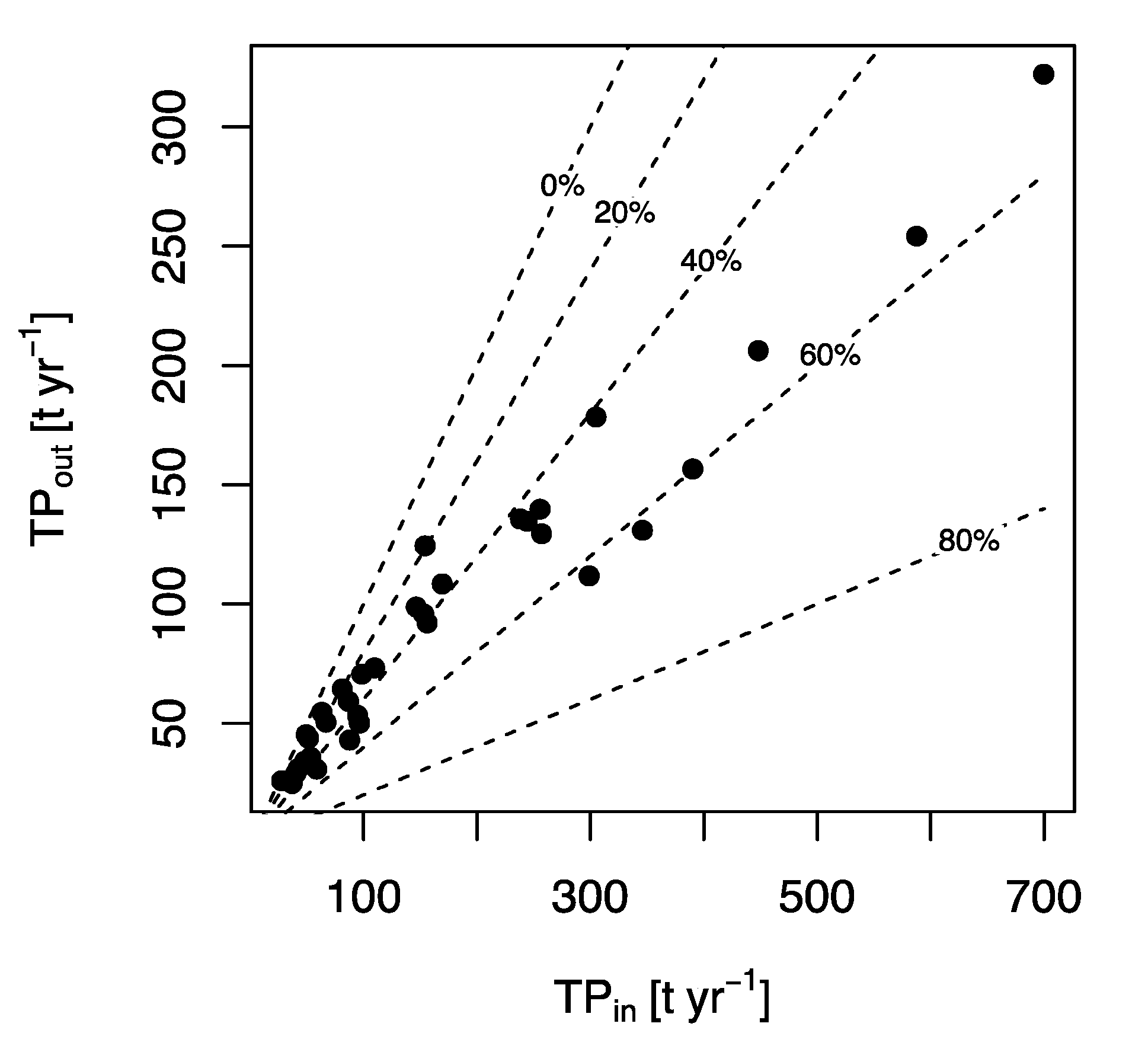
3.1. Balances of Water, SS, and TP
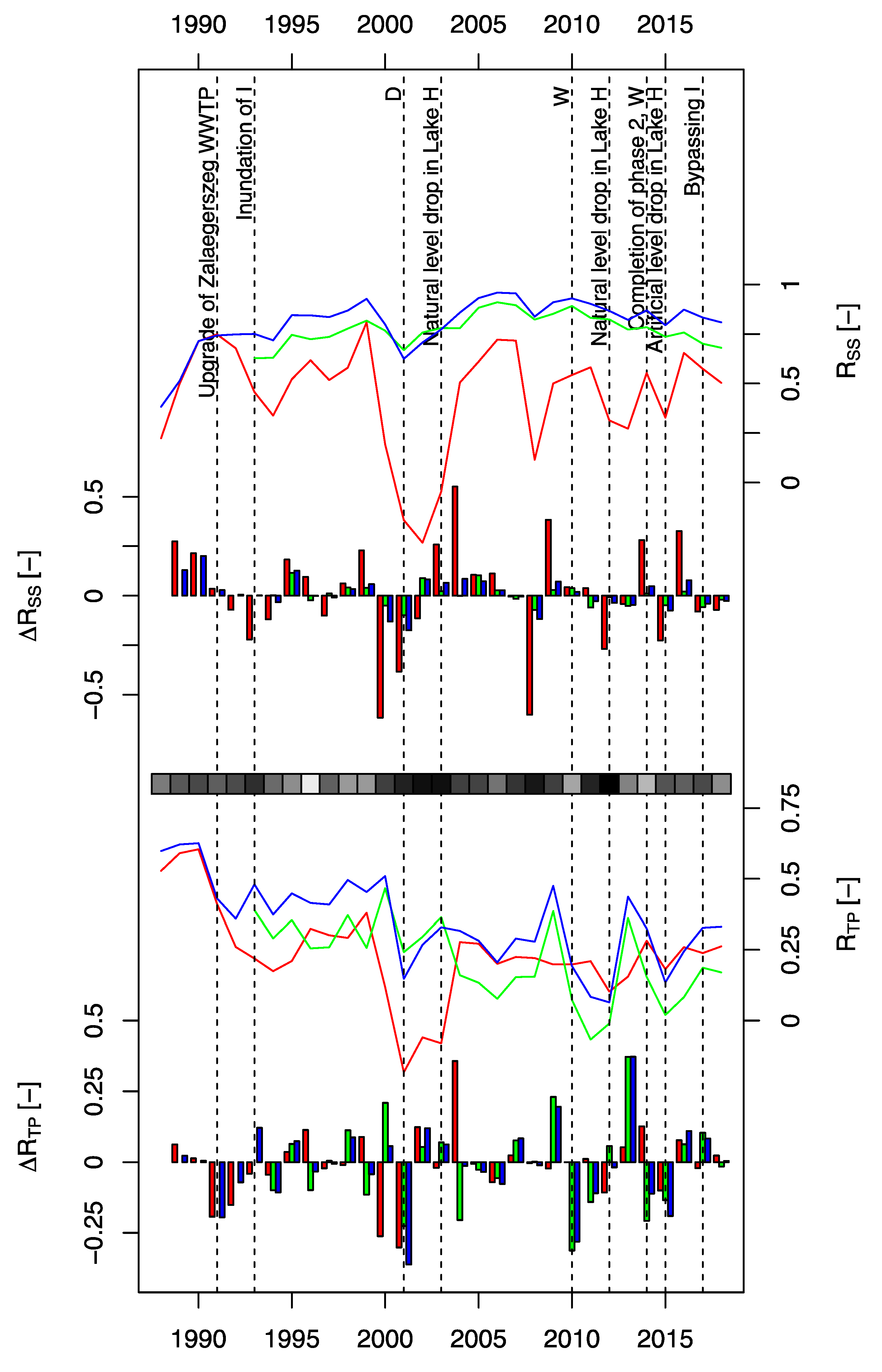
3.2. Retention and Evaluation of the Operational Success
3.3. Futile Management Actions
3.4. Climate as the Chief Manager
3.5. Does Science-Based Rational Environmental Management Exist in Practice?
- the absence of macrovegetation cover in Lake H after inundation;
- the negligible TP retention efficiency of dense reedstands when load is mostly algal P;
- TP retention efficiency of the complex habitat in the hydraulic boundary conditions of Lake F;
- the efficiency of bypass without a hydraulically well-defined upstream section.
- close the material balances and provide a solid basis for retention assessments;
- follow the behavior of the complex lake F.
3.6. Final Balance of the Kis-Balaton Project
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McIntosh, B.S.; Ascough, J.C.; Twery, M.; Chew, J.; Elmahdi, A.; Haase, D.; Harou, J.J.; Hepting, D.; Cuddy, S.; Jakeman, A.J.; et al. Environmental decision support systems (EDSS) development—Challenges and best practices. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 1389–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenführ, F.; Weber, M.; Langer, T. Rational Decision Making; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3642-028-489. [Google Scholar]
- von Winterfeldt, D. Bridging the gap between science and decision making. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110 (Suppl. S3), 14055–14061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reichert, P.; Langhans, S.D.; Lienert, J.; Schuwirth, N. The conceptual foundation of environmental decision support. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 154, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Somlyódy, L.; van Straten, G. Modeling and Managing Shallow Lake Eutrophication: With Application to Lake Balaton, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1986; ISBN 978-3-642-82709-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zlinszky, A.; Timár, G. Historic maps as a data source for socio-hydrology: A case study of the Lake Balaton wetland system, Hungary. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4589–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Virág, Á. Past and Present of Lake Balaton [A Balaton Múltja És Jelene]; Egri Press Ltd.: Eger, Hungary, 1998; (In Hungarian). ISBN 9639060216. Available online: https://library.hungaricana.hu/en/view/VizugyiKonyvek_244a/ (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Herodek, S. Phytoplankton Changes during Eutrophication and P and N Metabolism. In Modeling and Managing Shallow Lake Eutrophication: With application to Lake Balaton; Somlyódy, L., van Straten, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1986; ISBN 978-3-642-82709-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Láng, I. Impact on Policymaking: Background to a Government Dcision. In Modeling and Managing Shallow Lake Eutrophication: With Application to Lake Balaton; Somlyódy, L., van Straten, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1986; ISBN 978-3-642-82709-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Istvánovics, V.; Somlyódy, L. Factors influencing lake recovery from eutrophication—The case of Basin 1 of Lake Balaton. Water Res. 2001, 35, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somlyódy, L. Eutrophication Management Models. In Modeling and Managing Shallow Lake Eutrophication: With Application to Lake Balaton; Somlyódy, L., van Straten, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1986; ISBN 978-3-642-82709-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kárpáti, I. Biological Foundations for the Operational. Technological and Organisational Concepts of Kis-Balaton Protection System [“A Kisbalaton Védőrendszer Üzemeltetésének. Technológiai És Üzemszervezési Koncepcióinak Biológiai Megalapozása”]; Agricultural University of Keszthely: Keszthely, Hungary, 1980. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar]
- Istvánovics, V.; Kovács, A.; Vörös, L.; Herodek, S.; Pomogyi, P. Phosphorus cycling in a large, reconstructed wetland, the lower Kis-Balaton Reservoir (Hungary). SIL Proc. 1922–2010 1997, 26, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čıžková, H.; Pechar, L.; Husák, Š.; Květ, J.; Bauer, V.; Radová, J.; Edwards, K. Chemical characteristics of soils and pore waters of three wetland sites dominated by Phragmites australis: Relation to vegetation composition and reed performance. Aquat. Bot. 2001, 69, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somlyódy, L.; Herodek, S. Revision of the Lower Reservoir of Kis-Balaton—Synthesis Report [“A Kis-Balaton Alsó-Tározó Felülvizsgálata. Szintézis Jelentés”]; Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of Sanitary and Environmental Engineering: Budapest, Hungary, 1997. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar]
- Somlyódy, L. Eutrophication Modeling, Management and decision making: The Kis-Balaton Case. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioAquaPro. Proposal on the Operation Regime of the Kis Balaton Water Protection System. Biomonitoring System for the Implementation of the 2nd Phase of Kis Balaton” Project. [A Kis-Balaton Vízvédelmi Rendszer Üzemeltetéssel Kapcsolatos Előzetes Javaslatok. «Kis-Balaton Vízvédelmi Rendszer II. Ütem Megvalósítása» Projekthez Kapcsolódó Biomonitoring Rendszer Kialakítása”]; KEOP-2.2.1/2F/09-2009-0001 project report; BioAquaPro Ltd.: Debrecen, Hungary, 2018. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar]
- Kovács, Á.; Honti, M.; Clement, A. Design of best management practice applications for diffuse phosphorus pollution using interactive GIS. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, Á.; Honti, M. Estimation of diffuse phosphorus emissions at small catchment scale by GIS-based pollution potential analysis. Desalination 2008, 226, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, A.; Somlyódy, L.; Koncsos, L. Modeling the phosphorus retention of the Kis-Balaton upper reservoir. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, H. Lake Restoration and Reduction of Nutrient Loading: Expectations Experiences and Extrapolations; Academia Verlag Richarz: St. Augustin, Germany, 1989; ISBN 978-3883453798. [Google Scholar]
- Istvánovics, V.; Somlyódy, L. The role of sediments in P retention of the Kis-Balaton reservoir. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 1998, 83, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Gaál, R.; Bencsics, A.; Puskás, Z. Provisional Operational Procedures for the Kis-Balaton Water Protection System [“KBVR Ideiglenes Üzemeltetési Szabályzat”]; West Transdanubian Water Directorate, West Transdanubian Environmental and Nature Protection Authority and Balaton-felvidéki National Park: Szombathely, Hungary, 2014; p. 40. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo, M.A.; Valentín, A.; Claros, J.; Moreno, L.; Segura, M.; Lassalle, M.; Vera, P. Assessing the effect of emergent vegetation in a surface-flow constructed wetland on eutrophication reversion and biodiversity enhancement. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 113, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvánovics, V.; Clement, A.; Somlyódy, L.; Specziár, A.; G.-Tóth, L.; Padisák, J. Updating water quality targets for shallow Lake Balaton (Hungary), recovering from eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Date | Event/Action |
|---|---|
| 1970s | Eutrophication of Lake Balaton |
| 1982 | Unprecedented large bloom of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Lake Balaton |
| 1983 | Decree of the Council of Ministers |
| 1985 | Completion of Lake H (phase 1) |
| 1986 | The whole Kis-Balaton project area gets nature protection status |
| 1990 | Collapse of agriculture in relation to the change of the political system |
| 1991 | Upgrade of WWTP in the town of Zalaegerszeg |
| 1993 | Inundation of the Ingói Reeds (start of phase 2) |
| 1996 | Revision of plans of phase 2 |
| 2013 | Start of flow diversion from Ingói Reeds to Lake F |
| 2014 | Official completion of Lake F |
| 2019 | Unprecedented large bloom of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae and Ceratium furcoides in Lake Balaton |
| Type of Year | Flow | SS | TP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lake H | Average | 9% | 12% | 14% |
| Dry | 13% | |||
| Wet | 9% | |||
| Lake F | Average | 33% | 13% | 20% |
| Dry | 40% | |||
| Wet | 29% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Honti, M.; Gao, C.; Istvánovics, V.; Clement, A. Lessons Learnt from the Long-Term Management of a Large (Re)constructed Wetland, the Kis-Balaton Protection System (Hungary). Water 2020, 12, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030659
Honti M, Gao C, Istvánovics V, Clement A. Lessons Learnt from the Long-Term Management of a Large (Re)constructed Wetland, the Kis-Balaton Protection System (Hungary). Water. 2020; 12(3):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030659
Chicago/Turabian StyleHonti, Mark, Chunni Gao, Vera Istvánovics, and Adrienne Clement. 2020. "Lessons Learnt from the Long-Term Management of a Large (Re)constructed Wetland, the Kis-Balaton Protection System (Hungary)" Water 12, no. 3: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030659
APA StyleHonti, M., Gao, C., Istvánovics, V., & Clement, A. (2020). Lessons Learnt from the Long-Term Management of a Large (Re)constructed Wetland, the Kis-Balaton Protection System (Hungary). Water, 12(3), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030659





