Simple-Yet-Effective SRTM DEM Improvement Scheme for Dense Urban Cities Using ANN and Remote Sensing Data: Application to Flood Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. SRTM DEM
2.2. High-Accuracy and High-Resolution Surveyed DEM (Ground Truth)
2.3. Sentinel 2 Multispectral Imagery
2.4. Artificial Neural Network
3. Methodology
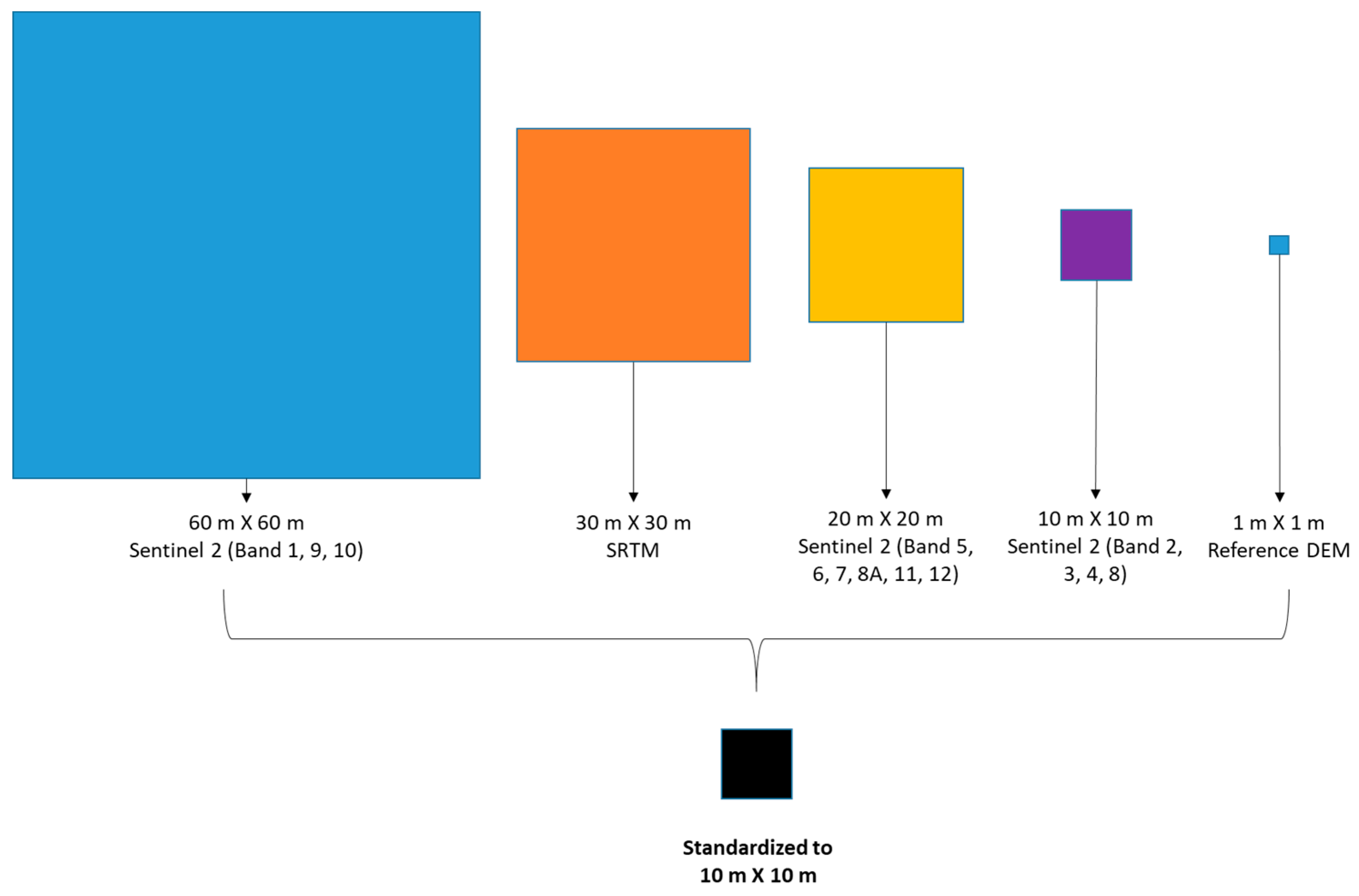
3.1. Data Pre-Processing
3.2. Artificial Neural Network Setup
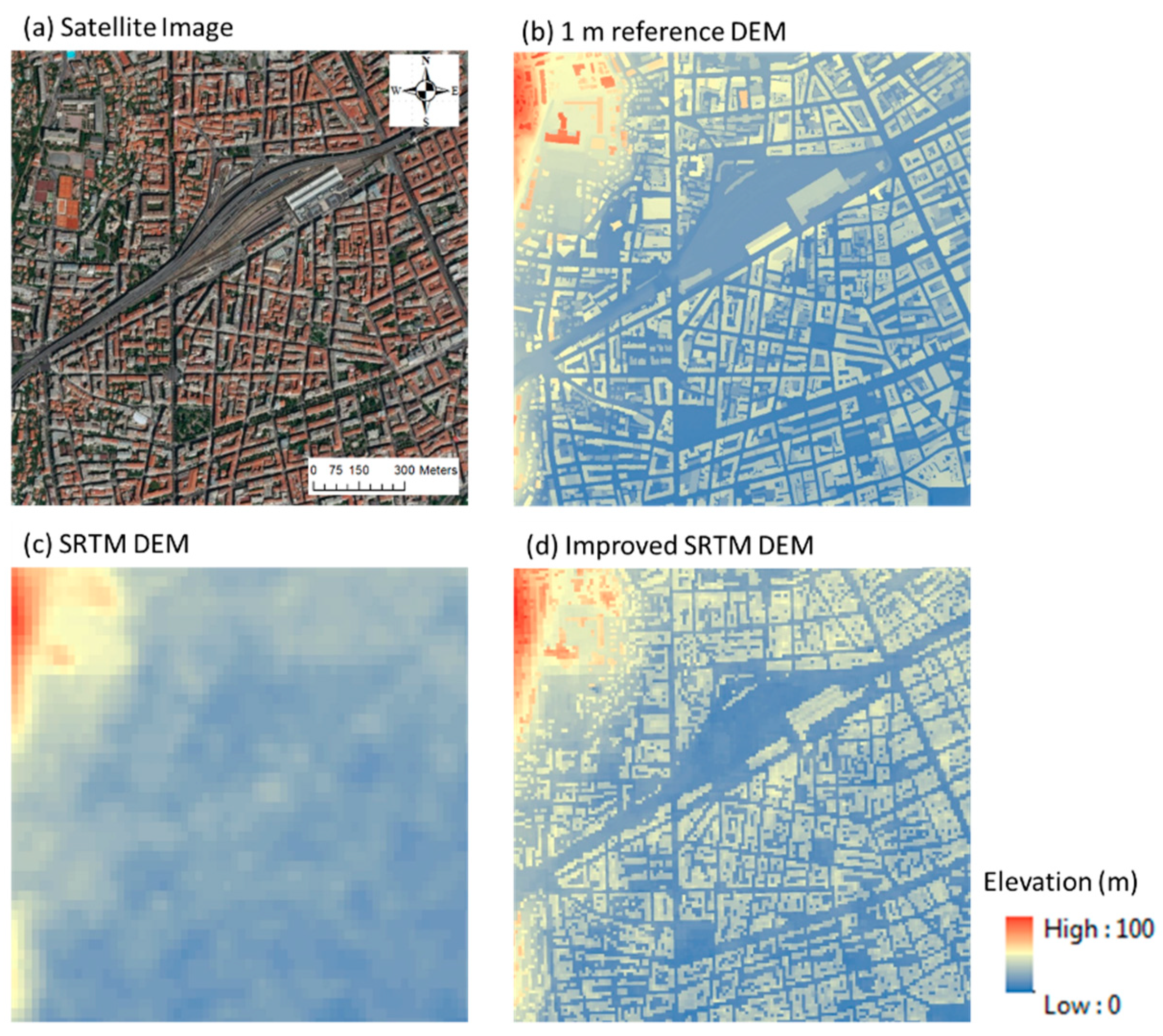
4. Proof of Concept and Application of the Approach
5. Discussion
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moudrý, V.; Lecours, V.; Gdulová, K.; Gábor, L.; Moudrá, L.; Kropáček, J.; Wild, J. On the use of global DEMs in ecological modelling and the accuracy of new bare-earth DEMs. Ecol. Model. 2018, 383, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favalli, M.; Fornaciai, A. Visualization and comparison of DEM-derived parameters. Application to volcanic areas. Geomorphology 2017, 290, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Kääb, A. Modeling Glacier Elevation Change from DEM Time Series. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10117–10142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirosław-Świątek, D.; Szporak-Wasilewska, S.; Michalowski, R.; Kardel, I.; Grygoruk, M. Developing an algorithm for enhancement of a digital terrain model for a densely vegetated floodplain wetland. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 36013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, E.; Morris, C.S.; Belz, J.E. A Global Assessment of the SRTM Performance. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Montgomery, D.R. Digital elevation model grid size, landscape representation, and hydrologic simulations. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.D.; Grayson, R.B.; Ladson, A. Digital terrain modelling: A review of hydrological, geomorphological, and biological applications. Hydrol. Process. 1991, 5, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Sun, Y.; Wendi, D.; Jiang, Z.; Liong, S.-Y.; Gourbesville, P. Flood Modelling Framework for Kuching City, Malaysia: Overcoming the Lack of Data. In Water Resources Quality and Management in Baltic Sea Countries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 559–568. [Google Scholar]
- Wendi, D.; Liong, S.; Sun, Y.; Doan, C.D. An innovative approach to improve SRTM DEM using multispectral imagery and artificial neural network. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2016, 8, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carabajal, C.C.; Harding, D.J. SRTM C-Band and ICESat Laser Altimetry Elevation Comparisons as a Function of Tree Cover and Relief. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misra, P.; Avtar, R.; Takeuchi, W. Comparison of Digital Building Height Models Extracted from AW3D, TanDEM-X, ASTER, and SRTM Digital Surface Models over Yangon City. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gamba, P.D.A.; Houshmand, F.B. SRTM data characterization in urban areas. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2002, 34, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, M.; Malvarosa, F.; Minati, E.; Zappitelli, E. A Data Fusion Algorithm for DEM Mosaicking: Building a Global DEM with SRTM-X and ERS Data. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006; pp. 3861–3864. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, D.; Ikeshima, D.; Tawatari, R.; Yamaguchi, T.; O’Loughlin, F.E.; Neal, J.C.; Sampson, C.; Kanae, S.; Bates, P.D. A high-accuracy map of global terrain elevations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5844–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, L.; Shen, H.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, L. A Global Seamless DEM Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion (GSDEM-30): Product Generation and Evaluation. Preprints 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhadi, N.A.; Kassim, M.S.M.; Abdullah, A.F. Improvement of Digital Elevation Model (DEM) using data fusion technique for oil palm replanting phase. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2018, 10, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulp, S.A.; Strauss, B.H. CoastalDEM: A global coastal digital elevation model improved from SRTM using a neural network. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X. Fusion of TanDEM-X and Cartosat-1 elevation data supported by neural network-predicted weight maps. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawker, L.; Bates, P.; Neal, J.; Rougier, J. Perspectives on Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Simulation for Flood Modeling in the Absence of a High-Accuracy Open Access Global DEM. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fewtrell, T.J.; Bates, P.D.; Horritt, M.; Hunter, N.M. Evaluating the effect of scale in flood inundation modelling in urban environments. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 5107–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, N.M.; Bates, P.D.; Néelz, S.; Pender, G.; Villanueva, I.; Wright, N.; Liang, D.; Falconer, R.A.; Lin, B.; Waller, S.; et al. Benchmarking 2D hydraulic models for urban flooding. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2008, 161, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radiomobile. Background on DEM. Available online: radiomobile.pe1mew.nl/?Geodata:Background_on_DEM (accessed on 3 March 2020).
- Goetz, A.F.; Vane, G.; Solomon, J.E.; Rock, B.N. Imaging Spectrometry for Earth Remote Sensing. Science 1985, 228, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rencz, A.N.; Bowie, C.; Ward, B.C. Application of thermal imagery from LANDSAT data to locate kimberlites, Lac de Gras area, district of Mackenzie, N.W.T. In Searching for Diamonds in Canada: Geological Survey of Canada, Open File 3228; Geological Survey of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1996; pp. 255–257. [Google Scholar]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascón, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, A.; Bertolini, A. Sentinel-2 Products Specification Document. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/document-library/content/-/article/sentinel-2-level-1-to-level-1c-product-specifications (accessed on 3 March 2020).
- U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/eros/science/usgs-eros-archive-digital-elevation-shuttle-radar-topography-mission-srtm-1-arc?qt-science_center_objects=0#qt-science_center_objects (accessed on 3 March 2020).
- Roy, D.P.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.K.; Yan, L.; Huang, H.; Li, Z. Examination of Sentinel-2A multi-spectral instrument (MSI) reflectance anisotropy and the suitability of a general method to normalize MSI reflectance to nadir BRDF adjusted reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, L.; Salas, W.A.; Skole, D. Fourier analysis of multi-temporal AVHRR data applied to a land cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashish, D.; McClendon, R.W.; Hoogenboom, G. Land-use classification of multispectral aerial images using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 1989–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, D.; Brumby, S.P.; Rowland, J.C.; Altmann, G.L. Land cover classification in multispectral imagery using clustering of sparse approximations over learned feature dictionaries. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 84793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pande, C.B.; Moharir, K.N.; Khadri, S.F.R.; Patil, S. Study of land use classification in an arid region using multispectral satellite images. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurney, K. An Introduction to Neural Networks; UCL Press: London, UK, 1997; ISBN 978-1-85728-673-1. [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert, U. Multiple Layer Perceptron Training Using Genetic Algorithms; ESANN: Bruges, Belgium, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, M. Accuracy of digital elevation model according to spatial resolution. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1998, 32, 613–617. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Moraga, C. The influence of the sigmoid function parameters on the speed of backpropagation learning. In From Natural to Artificial Neural Computation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Levenberg, K. A method for the solution of certain non-linear problems in least squares. Q. Appl. Math. 1944, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marquardt, D.W. An Algorithm for Least-Squares Estimation of Nonlinear Parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawker, L.; Rougier, J.; Neal, J.C.; Bates, P.D.; Archer, L.; Yamazaki, D. Implications of Simulating Global Digital Elevation Models for Flood Inundation Studies. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 7910–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DHI, MIKE FLOOD. Available online: https://www.mikepoweredbydhi.com/download/product-documentation (accessed on 3 March 2020).
- Brovelli, M.A.; Zamboni, G. A New Method for the Assessment of Spatial Accuracy and Completeness of OpenStreetMap Building Footprints. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Information 2018, 7, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, H.; Zipf, A.; Fu, Q.; Neis, P. Quality assessment for building footprints data on OpenStreetMap. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 700–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Property | Nice, France | Singapore |
|---|---|---|
| Entity ID | L1C_T32TLP_A016836_20180912T103308 | L1C_T48NUG_A004863_20180210T033204 |
| Acquisition Date | 2018-09-12 | 2018-02-10 |
| Tile Number | T32TLP | T48NUG |
| Cloud Cover (%) | 1.5258 | 5.6381 |
| Platform | SENTINEL-2A | SENTINEL-2B |
| Processing Level | LEVEL-1C | LEVEL-1C |
| Input Layer | Target Layer | Output Layer |
|---|---|---|
| Reflectance values of Sentinel 2, multispectral imagery SRTM DEM elevations | Surveyed DEM elevations | Improved (Rectified) elevations |
| Study Areas | RMSE of SRTM DEM (m) | RMSE of iSRTM DEM (m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire | Impervious | Pervious | Buildings | Entire | Impervious | Pervious | Buildings | |
| Nice, France | 8.36 | 9.19 | 5.98 | 12.18 | 5.18 | 5.08 | 5.52 | 6.86 |
| Singapore | 10.70 | 11.49 | 9.46 | 16.45 | 6.93 | 7.42 | 6.16 | 9.53 |
| Study Areas | Impervious Area (%) | Building Density (%) | Mean Building Height (m) | Percentage of Building Height in Different Ranges (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–30 m | 30–60 m | 60–100 m | ||||
| Nice, France | 64.7 | 34.0 | 19.1 | 93.0 | 6.9 | 0.1 |
| Singapore | 62.5 | 28.0 | 18.8 | 84.1 | 11.9 | 4.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.E.; Liong, S.-Y.; Gourbesville, P.; Andres, L.; Liu, J. Simple-Yet-Effective SRTM DEM Improvement Scheme for Dense Urban Cities Using ANN and Remote Sensing Data: Application to Flood Modeling. Water 2020, 12, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030816
Kim DE, Liong S-Y, Gourbesville P, Andres L, Liu J. Simple-Yet-Effective SRTM DEM Improvement Scheme for Dense Urban Cities Using ANN and Remote Sensing Data: Application to Flood Modeling. Water. 2020; 12(3):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030816
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dong Eon, Shie-Yui Liong, Philippe Gourbesville, Ludovic Andres, and Jiandong Liu. 2020. "Simple-Yet-Effective SRTM DEM Improvement Scheme for Dense Urban Cities Using ANN and Remote Sensing Data: Application to Flood Modeling" Water 12, no. 3: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030816
APA StyleKim, D. E., Liong, S.-Y., Gourbesville, P., Andres, L., & Liu, J. (2020). Simple-Yet-Effective SRTM DEM Improvement Scheme for Dense Urban Cities Using ANN and Remote Sensing Data: Application to Flood Modeling. Water, 12(3), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030816






