Effects of Changing Fertilization since the 1980s on Nitrogen Runoff and Leaching in Rice–Wheat Rotation Systems, Taihu Lake Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Treatments
2.2. Sampling and Measurements
2.3. DNDC Model
2.4. DNDC Calibration and Validation
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
2.6. Fertilization Changes and Scenario Settings
3. Results
3.1. DNDC Model Validation
3.1.1. N in Soil Water
3.1.2. N Loss in Runoff
3.1.3. Crop Growth Biomass
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
3.3. Annual Dynamics of N Loss
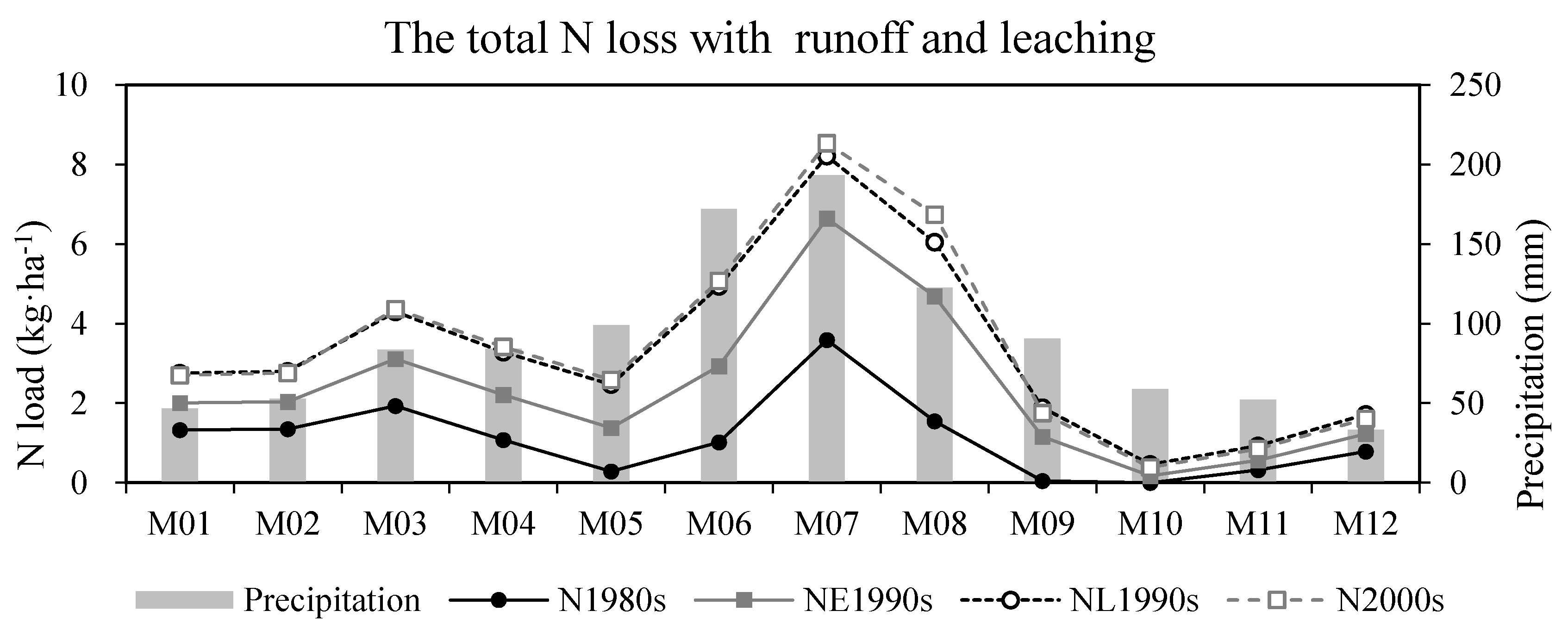
3.4. Seasonal Dynamics of N Loss
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Fertilization and Rainfall on N Loss in Runoff and Leaching
4.2. The Changes of Fertilization Rate, N Loss Loading and Water Quality in Taihu Lake since the 1980s
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.B.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yin, Z.G.; Koenig, A. Nitrogen flow analysis in Huizhou, South China. Environ. Manag. 2008, 41, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Chen, Y.X.; Jilani, G.; Shamsi, I.H.; Yu, Q.G. Model AVSWAT apropos of simulating non-point source pollution in Taihu lake basin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.S. Nitrogen pollution from agricultural non-point sources and its control in water system of Taihu Lake. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1992, 3, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.R.; Li, J.Y. Fertilizer proper use and sustainable development of soil environment in China. Adv. Environ. Sci. 1999, 7, 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Li, P.W. Studies on rainfall process, flow-making and nitrogen and phosphorus losses. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 1996, 16, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.L.; Wu, S.X.; Ji, H.J.; Kolbe, H. Estimation of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in China and the Alleviating Strategies, I. Estimation of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in China in Early 21 Century. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2004, 37, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhu, Z.L. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. PNAS 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.H.; Yin, B.; Yang, L.Z.; Yin, S.X.; Zhu, Z.L. Nitrogen Runoff and Leaching Losses during Rice-Wheat Rotations in Taihu Lake Region, China. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zheng, J.C.; Chen, L.G.; Xue, X.H. Effects of straw-returning on annual overland runoff NPK loss in farmland. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 21, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Cherobima, V.F.; Huang, C.H.; Favaretto, N. Tillage system and time post-liquid dairy manure: Effects on runoff, sediment and nutrients losses. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 184, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.S.; Tian, Y.H.; Yin, B.; Zhu, Z.L. Improving agronomic practices to reduce nitrate leaching from the rice-wheat rotation system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Yang, L.Z.; Yan, T.M.; Xue, F.; Zhao, D. Nitrogen fertilizer reduction in rice production for two consecutive years in the Taihu Lake area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.K. Improving nitrogen fertilizer efficiency in lowland rice in tropical Asia. In Nitrogen Economy of Flooded Rice Soils; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; Volume 26, ISBN 978-94-010-8471-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.M.; Park, S.W.; Lee, J.J.; Benham, B.L. Modelling and assessing the impact of reclaimed wastewater irrigation on the nutrient load from an agricultural watershed containing rice paddy fields. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2007, 42, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.O.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.S. Model development for nutrient loading from paddy rice fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 62, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschonitis, V.G.; Lekakis, E.H.; Petridou, Ν.C.; Koukouli, S.G.; Pavlatou-Ve, A. Nutrients fixation by algae and limiting factors of algal growth in flooded rice fields under semi-arid Mediterranean conditions: Case study in Thessaloniki plain in Greece. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2013, 96, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournebize, J.; Watanabe, H.; Takagi, K.; Nishimura, T. The development of a coupled model (PCPF-SWMS) to simulate water flow and pollutant transport in Japanese paddy fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2006, 4, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, V.Z. Modeling of water and nitrogen balance in the ponded water of rice field. Paddy Water Environ. 2008, 6, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.N.; Nishida, K. A nitrogen cycle model in paddy fields to improve material flow analysis: The Day-Nhue River Basin case study. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2014, 100, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.R.; Dong, B.; Qin, D.Y.; Sun, N.N.; Zhang, Z.Y. Simulation of drainage process and nitrogen loss in paddy field using DrainMOD. Trans. CSAE 2011, 27, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Congreves, K.A.; Grant, B.B.; Dutta, B.; Smith, W.N.; Chantigny, M.H.; Rochette, P.; Desjardins, R.L. Predicting ammonia volatilization after field application of swine slurry: DNDC model development. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 219, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Niu, H.S. The development of the DNDC plant growth sub-model and the application of DNDC in agriculture: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 230, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Sun, B.; Xie, X.L.; Zhuang, S.Y. Simulating the effects of chemical and non-chemical fertilization practices on carbon sequestration and nitrogen loss in subtropical paddy soils using the DNDC model. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 13, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, L.G.; Qiu, J.J.; Li, C.S.; Gao, M.F.; Gao, C.Y. Calibration of DNDC model for nitrate leaching from an intensively cultivated region of Northern China. Geoderma 2014, 223, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilhespy, S.L.; Anthony, S.; Cardenas, L.; Chadwick, D.; Prado, A.; Li, C.S.; Misselbrook, T.; Rees, R.M.; Salas, W.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; et al. First 20 years of DNDC (DeNitrification DeComposition): Model evolution. Ecol. Model. 2014, 292, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Farahbakhshazad, N.; Jaynes, D.B.; Dinnes, D.L.; Salas, W.; McLaughlin, D. Modeling nitrate leaching with a biogeochemical model modified based on observations in a row-crop field in Iowa. Ecol. Model. 2006, 196, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, B.; Zheng, X.; Li, C.; Jian, Z. Modeling nitrogen loading in a small watershed in southwest China using a DNDC model with hydrological enhancements. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 2999–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.L.; Li, C.S.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, L.K. Quantifying nitrogen loading from a paddy field in Shanhai, China with modified DNDC model. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 1997, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cao, L.K.; Sha, Z.M.; Deng, J.; Lv, W.G. Impacts of fertilization optimization on N loss from paddy fields: Observations and DNDC modeling case study in Shanghai, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, L. The Kjeldahl Method for Nitrogen. In Origins of Clinical Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; ISBN 978-0-12-597580-3. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Armstrong Black, I. An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, L.G.; Li, J.Z.; Gao, M.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, J.; Deng, J.; Li, C.; Frolking, S. The development of China-DNDC and review of its applications for sustaining Chinese agriculture. Ecol. Model. 2017, 348, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.S.; Frolking, S.; Harriss, R.; Butterbach, K. Carbon sequestration in arable soils is likely to increase nitrous oxide emissions, offsetting reductions in climate radiative forcing. Clim. Chang. 2005, 72, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qiu, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, L. Advance in a terrestrial biogeochemical model-DNDC model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Salas, W.; Zhang, R.; Krauter, C.; Rotz, A.; Mitloehner, F. Manure-DNDC: A biogeochemical process model for quantifying greenhouse gas and ammo-nia emissions from livestock manure systems. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 93, 163–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Frolking, S.; Frolking, T.A. A model of nitrous-oxide evolution from soil driven by rainfall events: 1 model structure and sensitivity. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 9759–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Frolking, S.; Harriss, R. Modling carbon biogeochemistry in agricultural soils. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1994, 8, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S. Modeling trace gas emissions from agricultural ecosystems. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2000, 58, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.C.; Shen, Q.R. Influence of longterm combined application of manure and chemical fertilizer on supplying characteristics of nitrogen on soil and soil particle fractions. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2004, 41, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmeier, M.; Roelcke, M.; Han, Y.; Lan, T.; Bergmann, H.; Böhm, D.; Cai, Z.C.; Nieder, R. Nitrogen management in a rice-wheat system in the Taihu Region: Recommendations based on field experiments and surveys. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 209, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.F.; Zou, X.Z.; Yang, S.H.; Wei, L.; Wu, J.L. Effects of combined application of organic and inorganic nitrogen fertilizer on the soil nitrogn leaching and the growth of leaf-used lettuce. Trans. CSAE 2007, 23, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, U. Integrated nitrogen fertilization for intensive and sustainable agriculture. J. Crop. Improv. 2006, 15, 259–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ambasht, R.S.; Srivastava, A.; Srivastava, N.K.; Sinhab, A. Reduction of nitrogen losses through erosion by Leonotis nepetaefolia and Sida acuta in simulated rain intensities. Ecol. Eng. 1997, 8, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.C.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, Z.F.; Yu, Z.M.; Zhu, S. Effect of sloping land use pattern on nitrogen and phosphorus loss in Qiandaohu Watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 16, 91–92. [Google Scholar]
- Pruski, F.F.; Nearing, M.A. Climate-induced changes in erosion during the 21st century for eight US locations. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Simulation of nitrate leaching under varying drip system uniformities and precipitation patterns during the growing season of maize in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 142, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrom, L.; Brink, N. Effects of differentiated applications of fertilizer N on leaching losses and distribution of inorganic N in the soil. Plant Soil 1986, 93, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, F.; Cayuela, J.A.; Fermandez-Boy, J.E.; Fernández-Boy, E.; Murillo, J.M.; Cabrera, F. Water balance and nitrate leaching in an irrigation maize crop in SW Spain. Agric. Water Manag. 1996, 32, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Min, J.; Wang, S.Q.; Shi, W.M.; Xing, G.X. Nitrogen runoff dominates water nitrogen pollution from rice-wheat rotation in the Taihu Lake region of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 156, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Qian, P.Q.; Ye, L.; Song, T. Changes in nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in Lake Taihu, 1985–2015. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 935–943. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.P.; Yang, G.Y. On Some Physical and Chemical properties of the Water in the northern part of the Lake Taihu. Oceanol. Limnol. Sci. 1959, 2, 146–162. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.S.; Liu, S.K.; He, S.L. Water quality management in Tai Lake. Shuili Xuebao 1992, 11, 22–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M. Variational trend and protection steps of water quality in Taihu Lake. J. Lake Sci. 1996, 8, 133–138. [Google Scholar]






| Crop Season | Activity | Date | Crop Season | Activity | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011/2012 Wheat | Plowing | 7 November 2011 | 2012/2013 Wheat | Plowing | 7 November 2012 |
| Sowing | 9 November 2011 | Sowing | 7 November 2012 | ||
| Basal fertilization | 9 November 2011 | Basal fertilization | 7 November 2012 | ||
| First top-dressing | 4 December 2011 | First top-dressing | 7 January 2013 | ||
| Second top-dressing | 24 February 2012 | Second top-dressing | 10 March 2013 | ||
| Harvesting | 4 June 2012 | Harvesting | 2 June 2013 | ||
| 2012Rice | Ploughing | 10 June 2012 | 2013Rice | Plouwing | 10 June 2013 |
| Pre-flooding | 20 June 2012 | Pre-flooding | 20 June 2013 | ||
| Basal fertilization | 25 June 2012 | Basal fertilization | 25 June 2013 | ||
| Rice transplanting | 25 June 2012 | Rice transplanting | 25 June 2013 | ||
| First top-dressing | 6 July 2012 | First top-dressing | 10 July 2013 | ||
| Mid-season aeration | 30 July to 5 August 2012 | Mid-season aeration | 1 to 8 August 2013 | ||
| Second-top dressing | 10 August 2012 | Second-top dressing | 15 August 2013 | ||
| Harvesting | 25 October 2012 | Harvesting | 25 October 2013 |
| Crops | Parameters | Grain | Leaf | Stem | Root |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter wheat | Max biomass production (kg C·ha−1) | 2200 | |||
| Biomass fraction | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.29 | ||
| Biomass C/N ratio | 22 | 21 | 62 | 19 | |
| Paddy rice | Max biomass production (kg C·ha−1) | 4500 | |||
| Biomass fraction | 0.37 | 0.16 | 0.3 | ||
| Biomass C/N ratio | 39 | 35 | 50 | 85 |
| Fertilizer Regimes | Paddy Rice Seasons (kg N·ha−1·yr−1) | Winter Wheat Seasons (kg N·ha−1·yr−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Fertilizer | Manure Fertilizer | Total Fertilizer | Chemical Fertilizer | Manure Fertilizer | Total Fertilizer | |
| N1980s | 140 | 60 | 200 | 105 | 45 | 150 |
| NE1990s | 265 | 35 | 300 | 175 | 25 | 200 |
| NL1990s | 315 | 35 | 350 | 225 | 25 | 250 |
| N2000s | 300 | 0 | 300 | 250 | 0 | 250 |
| Farmland Practices | Season | Stem | Leaf | Grain | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observation | Simulation | Observation | Simulation | Observation | Simulation | ||
| N2000s | 2011/2012 wheat | 1225 | 1149 | 300 | 634 | 2344 | 2505 |
| 2012 rice | 3441 | 2521 | 1774 | 1345 | 3465 | 3110 | |
| 2012/2013 wheat | 1700 | 1115 | 758 | 615 | 2513 | 2432 | |
| N1980s | 2011/2012 wheat | 1129 | 767 | 346 | 423 | 2076 | 1672 |
| 2012 rice | 2098 | 1771 | 1149 | 944 | 2631 | 2184 | |
| 2012/2013 wheat | 1077 | 757 | 484 | 418 | 1978 | 1651 | |
| Input Parameters | Range | Sensitivity Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N Runoff | N Leaching | Crop Uptake | ||
| Precipitation (mm) | 843–1436 | 1.35 | 0.96 | 0.57 |
| Fertilization rate (kg N·ha−1) | 350–500 | 1.88 | 1.87 | 0.27 |
| Fertilization rate (kg N·ha−1) | 500–600 | 1.65 | 1.76 | 0.05 |
| Ratio of manure fertilizer | 0–30% | −0.40 | −0.17 | 0.06 |
| SOC content (g C·ha−1) | 0.8–4.8 | 0.26 | 0.35 | 0.10 |
| Soil bulk density(g·cm−3) | 0.94–1.40 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.04 |
| Soil clay fraction | 0.08–0.38 | 0.17 | −3.86 | 0.05 |
| Soil pH | 5.0–8.0 | −0.04 | −0.04 | 0.00 |
| Leaching Load | Runoff Load | Crop Uptake | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenarios | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| N1980s | 5.2 | 2.1 | 7.9 | 3.9 | 259.1 | 13.2 |
| NE1990s | 9.4 | 3.2 | 18.3 | 7.2 | 295.3 | 26.4 |
| NL1990s | 14.4 | 4.6 | 25.4 | 10.2 | 299.3 | 27.2 |
| N2000s | 13.5 | 4.6 | 26.5 | 10.6 | 298.1 | 28.3 |
| Period | Fertilizer Rate (kg N·ha−1·year−1) | Water Quality | Eutrophication Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950s | <100 | <0.54–0.58 mg·L−1 [51] | Oligotrophic |
| Around the 1980s | <354 | 0.9–2.57 mg·L−1, average 1.54 mg·L−1 | Mesotrophic |
| Around the 1990s | 440–584 | 1.47–1.83 mg·L−1 in 1987–1988 [52]; 1.73–2.87 mg·L−1 in 1992–1994 [53] | Mesotrophic-Eutrophic |
| Around the 2000s | 586–640 | >2.5 mg·L−1 [48] | Eutrophic |
| After 2000 | 513–560 | Average 2.34 mg·L−1 (1.92–2.72 mg·L−1) during 2002–2006 [50] | Eutrophic |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diao, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, S.; Li, X. Effects of Changing Fertilization since the 1980s on Nitrogen Runoff and Leaching in Rice–Wheat Rotation Systems, Taihu Lake Basin. Water 2020, 12, 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030886
Diao Y, Li H, Jiang S, Li X. Effects of Changing Fertilization since the 1980s on Nitrogen Runoff and Leaching in Rice–Wheat Rotation Systems, Taihu Lake Basin. Water. 2020; 12(3):886. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030886
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiao, Yaqin, Hengpeng Li, Sanyuan Jiang, and Xinyan Li. 2020. "Effects of Changing Fertilization since the 1980s on Nitrogen Runoff and Leaching in Rice–Wheat Rotation Systems, Taihu Lake Basin" Water 12, no. 3: 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030886
APA StyleDiao, Y., Li, H., Jiang, S., & Li, X. (2020). Effects of Changing Fertilization since the 1980s on Nitrogen Runoff and Leaching in Rice–Wheat Rotation Systems, Taihu Lake Basin. Water, 12(3), 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030886





