Nitrogen Mass Balance and Pressure Impact Model Applied to an Urban Aquifer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Nitrogen Mass Balance and Pressure Impact Model
2.2.1. Nitrogen Load from the Leaky Sewer System
Exfiltration Rate (Losses) from the Sewer System
Mass of Nitrogen in Wastewater
Spatial Distribution of Sewer Exfiltration
2.2.2. Nitrogen Load from Agriculture
2.2.3. Groundwater Transport Model
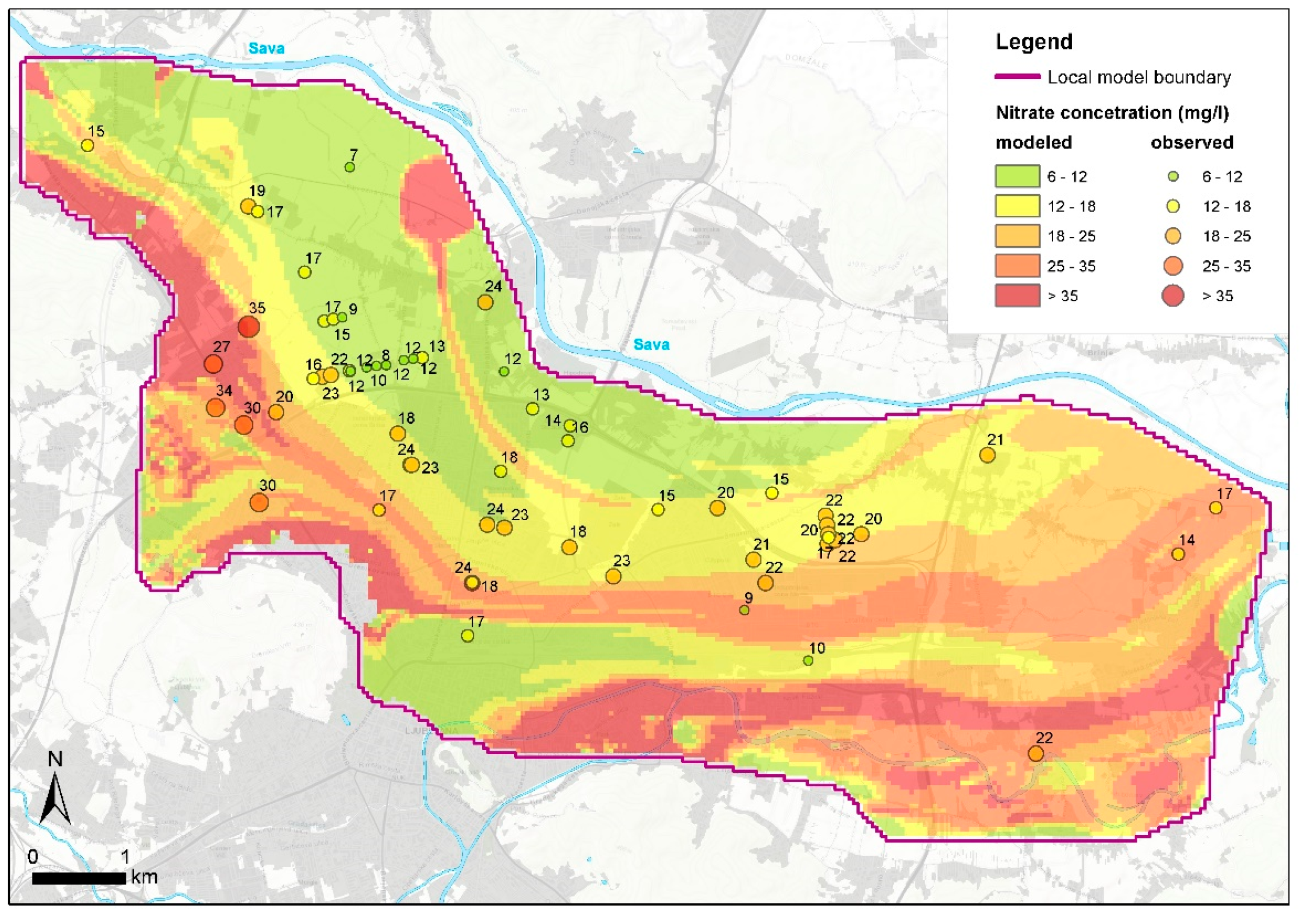
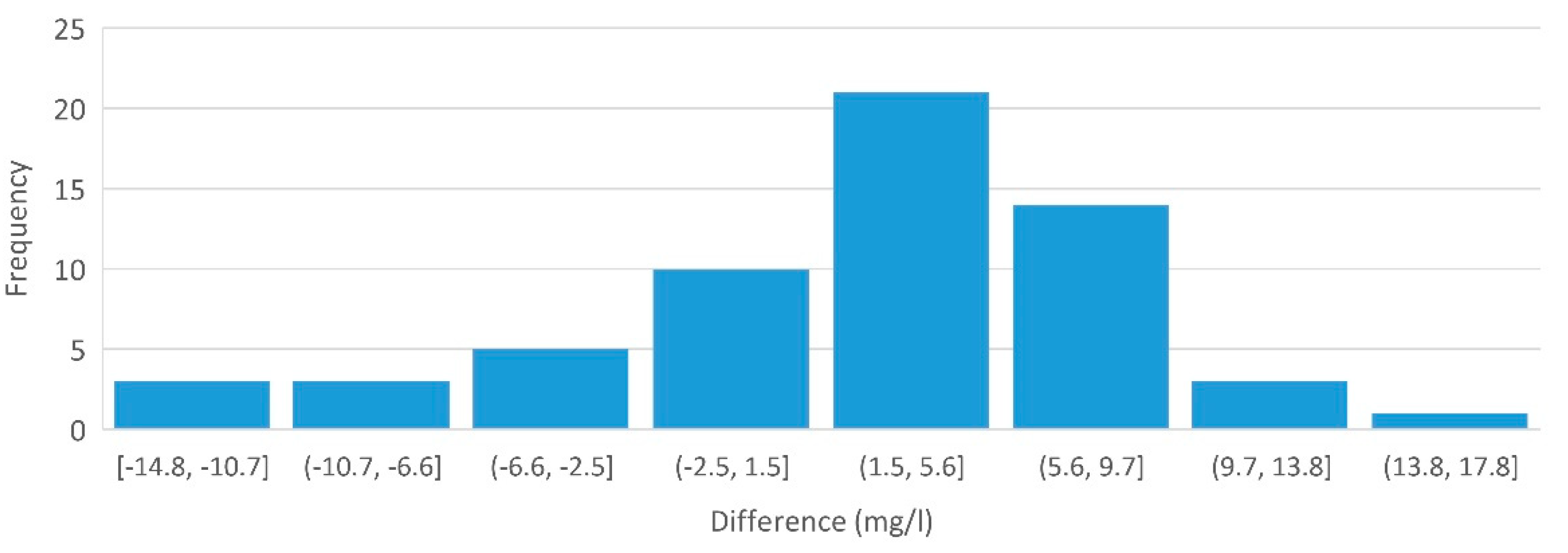
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN. World Urbanization Prospects 2018: Highlights; United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (ST/ESA/SER.A/421); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- WBG. Climate Change Action Plan; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, K.W.F. Sustainable cities and the groundwater governance challenge. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhemacha, M.A.; Gogu, C.R.; Serpescu, I.; Gaitanaru, D.; Bica, I. A hydrogeological conceptual approach to study urban groundwater flow in Bucharest city, Romania. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, M.L.; Hodge, E. Urban contaminant dynamics: From source to effect. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3796–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gogu, C.R.; Campbell, D.; de Beer, J. PREFACE: The Urban Subsurface – from Geoscience and Engineering to Spatial Planning and Management. Procedia Eng. 2017, 209, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jago-on, K.A.B.; Kaneko, S.; Fujikura, R.; Fujiwara, A.; Imai, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Zhang, J.; Tanikawa, H.; Tanaka, K.; Lee, B.; et al. Urbanization and subsurface environmental issues: An attempt at DPSIR model application in Asian cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3089–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, A.S.; Welty, C.; Maxwell, R.M.; Miller, A.J. Untangling the effects of urban development on subsurface storage in Baltimore. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 1158–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, L.; Alberti, L.; Mazzon, P.; Formentin, G. Transient Flow and Transport Modelling of an Historical CHC Source in North-West Milano. Water 2019, 11, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, S.S.D. The interdependence of groundwater and urbanisation in rapidly developing cities. Urban Water 2001, 3, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Reinstorf, F.; Leschik, S.; Musolff, A.; Krieg, R.; Strauch, G.; Molson, J.W.; Martienssen, M.; Schirmer, K. Mass fluxes of xenobiotics below cities: Challenges in urban hydrogeology. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, J.; Wolf, L.; Hoetzl, H. Leaky sewers-measurements under operating conditions. In Proceedings of the 4th World Wide Workshop for Young Environmental Scientists (WWW-YES), Vitry sur Seine, France, 10–13 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Peche, A.; Graf, T.; Fuchs, L.; Neuweiler, I. Physically based modeling of stormwater pipe leakage in an urban catchment. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 778–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, L.; Klinger, J.; Held, I.; Hötzl, H. Integrating groundwater into urban water management. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutsch, M.; Rieckermann, J.; Cullmann, J.; Ellis, J.B.; Vollertsen, J.; Krebs, P. Towards a better understanding of sewer exfiltration. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhan, J. Data-driven modelling of groundwater vulnerability to nitrate pollution in Slovenia (Podatkovno vodeno modeliranje ranljivosti podzemne vode na nitratno onesnaženje v Sloveniji). RMZ—Mater. Geoenviron. 2012, 59, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Mihorko, P.; Gacin, M. Environmental Indicators in Slovenia, Nitrates in Groundwater [VD05]; Slovenian Environment Agency: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Andjelov, M.; Kunkel, R.; Uhan, J.; Wendland, F. Determination of nitrogen reduction levels necessary to reach groundwater quality targets in Slovenia. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakida, F.T.; Lerner, D.N. Non-agricultural sources of groundwater nitrate: A review and case study. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.P.; Polizzotto, M.L. Pit latrines and their impacts on groundwater quality: A systematic review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koda, E.; Sieczka, A.; Osinski, P. Ammonium Concentration and Migration in Groundwater in the Vicinity of Waste Management Site Located in the Neighborhood of Protected Areas of Warsaw, Poland. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kringel, R.; Rechenburg, A.; Kuitcha, D.; Fouepe, A.; Bellenberg, S.; Kengne, I.M.; Fomo, M.A. Mass balance of nitrogen and potassium in urban groundwater in Central Africa, Yaounde/Cameroon. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soldatova, E.; Guseva, N.; Sun, Z.; Bychinsky, V.; Boeckx, P.; Gao, B. Sources and behaviour of nitrogen compounds in the shallow groundwater of agricultural areas (Poyang Lake basin, China). J. Contam. Hydrol. 2017, 202, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, G.; Bessenyei, É.; Karancsi, G.; Balla, D.; Mester, T. Effects of nitrogen loading from domestic wastewater on groundwater quality. Water SA 2019, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Hiscock, K.M. Modelling the effect of forest cover in mitigating nitrate contamination of groundwater: A case study of the Sherwood Sandstone aquifer in the East Midlands, UK. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arauzo, M. Vulnerability of groundwater resources to nitrate pollution: A simple and effective procedure for delimiting Nitrate Vulnerable Zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, B.T.; Hitt, K.J. Vulnerability of Shallow Groundwater and Drinking-Water Wells to Nitrate in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7834–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla, F.M.; Gallardo, M.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Global trends in nitrate leaching research in the 1960–2017 period. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalehzari, R.; Tabatabaei, S.H.; Kholghi, M. Simulation of nitrate transport and wastewater seepage in groundwater flow system. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Podlasek, A.; Bujakowski, F.; Koda, E. The spread of nitrogen compounds in an active groundwater exchange zone within a valuable natural ecosystem. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 146, 105746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, R.; Jin, S.; Chen, M.; Guan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhai, Y.; Teng, Y.; Guo, X. In-situ study of migration and transformation of nitrogen in groundwater based on continuous observations at a contaminated desert site. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 211, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieczka, A.; Bujakowski, F.; Koda, E. Modelling groundwater flow and nitrate transport: A case study of an area used for precision agriculture in the middle part of the Vistula River valley, Poland. Geologos 2018, 24, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valivand, F.; Katibeh, H. Prediction of Nitrate Distribution Process in the Groundwater via 3D Modeling. Environ. Model. Assess. 2020, 25, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bračič Železnik, B.; Jamnik, B. Javna oskrba s pitno vodo. In Podtalnica Ljubljanskega Polja; Rejec Brancelj, I., Smrekar, A., Kladnik, D., Eds.; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2005; pp. 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Vižintin, G.; Souvent, P.; Veselič, M.; ČenČur Curk, B. Determination of urban groundwater pollution in alluvial aquifer using linked process models considering urban water cycle. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestor, J.; Pestotnik, S.; Meglič, P.; Janža, M. Model of Environmental Pressures and Impacts; A.3.3 Final Report of INCOME Project (LIFE+ Programme); Geological Survey of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Prestor, J.; Pestotnik, S.; Meglič, P.; Janža, M. Načrtovanje zaščitnih ukrepov na podlagi modela obremenitev in vplivov na podzemno vodo Ljubljanskega polja. In Skrb za Pitno Vodo; Jamnik, B., Janža, M., Smrekar, A., Eds.; Skrb za pitno vodo: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2014; Volume GEOGRAFIJA SLOVENIJE 31, pp. 79–93. [Google Scholar]
- Janža, M.; Meglič, P.; Prestor, J.; Jamnik, B.; Pestotnik, S.D. T2.2.3—Report on the Improved Transport and Surface-Groundwater Interactions Model, Version 2. Project AMIIGA (Interreg, Central Europe); Geological Survey of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Meglič, P.; Janža, M.; Prestor, J.; Pestotnik, S.; Jamnik, B.D. T2.2.7—Report on the Results of the Most Probable Scenarios Threatening Groundwater, Version 2. Project AMIIGA (Interreg, Central Europe); Geological Survey of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pestotnik, S.; Prestor, J.; Meglič, P.; Janža, M.; Šram, D.D. T2.2.4—Report on Actualized Contaminants Mass Balance and Pressures-Impacts Model, Version 2. Project AMIIGA (Interreg, Central Europe); Geological Survey of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Pintar, M.; Sluga, G.; Bremec, U. Določitev Obremenitev iz Kmetijstva za Izbrane Prostorske Enote; Inštitut za vode Republike Slovenije: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- EEA. Corine Land Cover 2012 Seamless Vector Data (Version 18); Agency, E.E., Ed.; EEA: Kopenhagen, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Janža, M.; Lapanje, A.; Šram, D.; Rajver, D.; Novak, M. Research of the geological and geothermal conditions for the assessment of the shallow geothermal potential in the area of Ljubljana, Slovenia. Geologija 2017, 60, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjan, J. Količinske in Kakovostne Lastnosti Voda: Študijsko Gradivo; FGG, Inštitut za zdravstveno hidrotehniko: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Smrekar, A.; Bole, D.; Breg Valjavec, M.; Gabrovec, M.; Gašperič, P.; Ciglič, R.; Pavšek, M.; Topole, M. Register and Evaluation of the Active and the Potential Sources of Pollution, Project INCOME Action A.2.1 Report; Anton Melik Geographical Institute, ZRC SAZU: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, L.; Klinger, J.; Hoetzl, H.; Mohrlok, U. Quantifying Mass Fluxes from Urban Drainage Systems to the Urban Soil-Aquifer System (11 pp). J. Soils Sediments 2007, 7, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIKE SHE, Integrated Catchment Modelling. Available online: https://www.mikepoweredbydhi.com/products/mike-she (accessed on 6 April 2020).
- Janža, M. A decision support system for emergency response to groundwater resource pollution in an urban area (Ljubljana, Slovenia). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3763–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janža, M.; Prestor, J.; Urbanc, J.; Jamnik, B. TCE contamination plume spreading in highly productive aquifer of Ljubljansko polje. In Abstracts of the Contributions of the EGU General Assembly 2005; EGU: Vienna, Austria, 2005; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanc, J.; Jamnik, B. Distribution and origin of nitrates in the groundwater of Ljubljansko polje. Geologija 2007, 50, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Šimůnek, J.; Glöckler, D.; Stumpp, C. Handling model complexity with parsimony: Numerical analysis of the nitrogen turnover in a controlled aquifer model setup. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höge, M.; Wöhling, T.; Nowak, W. A Primer for Model Selection: The Decisive Role of Model Complexity. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 1688–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducommun, P.; Boutsiadou, X.; Hunkeler, D. Direct-push multilevel sampling system for unconsolidated aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Water Balance Component | (m3/s) |
|---|---|
| Recharge from Sava River | +3.80 |
| Recharge from precipitation | +1.51 |
| Subsurface inflow | +0.27 |
| Exfiltration from water supply system | +0.16 |
| Abstraction from wells | −1.13 |
| Discharge to Sava River | −4.63 |
| Material | Time of Construction | Exfiltration (L/s/km) | Length (km) | Exfiltration Sum (L/s) | Nitrogen Load (ton/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1975 | 0.34 | 277.24 | 95.20 | 121.07 | |
| Concrete | 1975–1995 | 0.23 | 255.00 | 58.80 | 74.78 |
| >1995 | 0.12 | 11.20 | 1.29 | 1.64 | |
| <1975 | 0.11 | 22.37 | 2.39 | 3.04 | |
| Plastic | 1975–1995 | 0.07 | 48.92 | 3.49 | 4.44 |
| >1995 | 0.04 | 186.22 | 6.65 | 8.45 | |
| Total | 800.93 | 167.82 | 213.42 |
| N Source | No. of Cells | Mean (g/day) | Median (g/day) | Min (g/day) | Max (g/day) | SD (g/day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sewer system | 11,125 | 45.26 | 41.00 | 0.10 | 223.10 | 33.36 |
| Agriculture | 7936 | 51.75 | 43.59 | 0.07 | 118.63 | 29.43 |
| Statistics | Modeled Concentration (mg/L) | Observed Concentration (mg/L) | Difference ** (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Sewer System | Total * | |||
| Mean | 4.15 | 5.48 | 15.63 | 18.36 | 2.73 |
| SD | 2.85 | 5.54 | 6.63 | 6.07 | 6.32 |
| Max | 14.79 | 26.09 | 41.49 | 35.10 | 17.83 |
| Min | 0.00 | 0.15 | 6.37 | 7.20 | −14.76 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janža, M.; Prestor, J.; Pestotnik, S.; Jamnik, B. Nitrogen Mass Balance and Pressure Impact Model Applied to an Urban Aquifer. Water 2020, 12, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041171
Janža M, Prestor J, Pestotnik S, Jamnik B. Nitrogen Mass Balance and Pressure Impact Model Applied to an Urban Aquifer. Water. 2020; 12(4):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041171
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanža, Mitja, Joerg Prestor, Simona Pestotnik, and Brigita Jamnik. 2020. "Nitrogen Mass Balance and Pressure Impact Model Applied to an Urban Aquifer" Water 12, no. 4: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041171
APA StyleJanža, M., Prestor, J., Pestotnik, S., & Jamnik, B. (2020). Nitrogen Mass Balance and Pressure Impact Model Applied to an Urban Aquifer. Water, 12(4), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041171





