Adsorption of Mixed Dye System with Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide Modified Sepiolite: Characterization, Performance, Kinetics and Thermodynamics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method and Material
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Organically Modified Sepiolite
2.3. Dye Concentration Determination and Adsorption Test
2.4. Adsorption Kinetics and Thermodynamics
2.5. Characterization
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Modified Sepiolite
3.2. Effect of the Operation Condition on Adsorption Performance
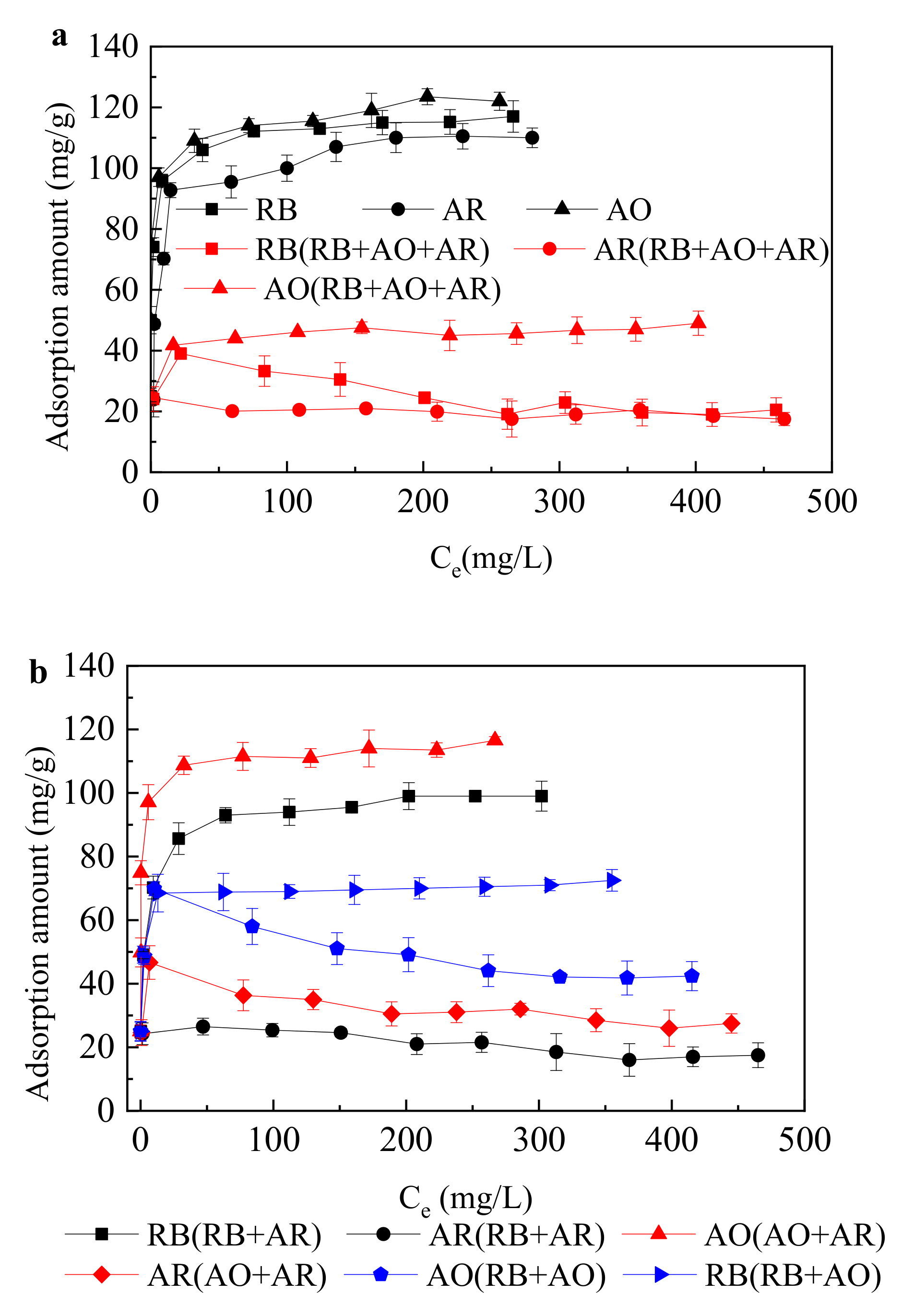
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics and Thermodynamics
4. Conclusions
- The adsorption amounts of Acid Orange II, Reactive Blue and Acid Fuchsin improved after CTMAB modification process, which confirmed the applicability of the modified sepiolite in industrial dye wastewater treatment.
- The specific surface area of modified sepiolite was obviously decreased, but the adsorption capacity was enhanced. The SEM image shows that the modified sepiolite has a dispersible morphology and the gaps were clean and smooth. The characterization indicate the modification does not deform the sepiolite structure and the CTMAB was successfully loaded.
- Acid Orange II had the characteristics of preferential adsorption in the two-component system. The electrostatic attraction of positively charged adsorption sites on the adsorbent surface with the negatively charged anionic dye could enhance the adsorption amount under acid condition.
- The adsorption performance of one-component, two-component and three-component dye system was in accordance with the quasi-second-order reaction kinetics and the adsorption equilibrium time was all around 120 min.
- The adsorption equilibrium were fitted very well to the Langmuir model and extended Langmuir isotherm.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolmakov, K.; Hebisch, E.; Wolfram, T.; Nordwig, L.A.; Wurm, C.A.; Ta, H.; Westphal, V.; Belov, V.N.; Hell, S.W. Far-Red Emitting Fluorescent Dyes for Optical Nanoscopy: Fluorinated Silicon-Rhodamines (SiRF Dyes) and Phosphorylated Oxazines. Chem. A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 13344–13356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.L.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, R.P. Enzymatic decolorization and degradation of azo dyes–A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 104, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, A.A.; Gazi, M.; Yilmaz, E. Single and binary adsorption of azo and anthraquinone dyes by chitosan-based hydrogel: Selectivity factor and Box-Behnken process design. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 104, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, M.S.; Indig, G.L. Effect of BSA Binding on Photophysical and Photochemical Properties of Triarylmethane Dyes. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 4678–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P.; McMullan, G. Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: A critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, S.; Haghighi, R. Chemical catalytic reaction and biological oxidation for treatment of non-biodegradable textile effluent. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 95, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Agricultural based activated carbons for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Fu, W.; Li, X.; Shi, D.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Gong, T.; Li, X. Membrane fouling by the aggregations formed from oppositely charged organic foulants. Water Res. 2019, 159, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, D.; Ren, W.; Liu, B. Transport of Enterococcus faecalis in granular activated carbon column: Potential energy, migration, and release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Z.; Meng, X.; Li, L.; Liu, B. Electrochemical degradation of ciprofloxacin on BDD anode using a differential column batch reactor: Mechanisms, kinetics and pathways. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 17740–17750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Liu, B.; Bai, L.; Shi, Z.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Improving the performance of loose nanofiltration membranes by poly-dopamine/zwitterionic polymer coating with hydroxyl radical activation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Gupta, R.; Yadav, A.B.; Kumar, R. Dye removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on treated sawdust. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 89, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Al-Amer, A.M.; Laoui, T.; Al-Marri, M.J.; Nasser, M.S.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution by advanced carbon nanotubes: Critical review of adsorption applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 141–161. [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson, M.J.; Brett, P.; Bennett, R.; Grau-Crespo, R. Adsorption of organic molecules at the TiO2(110) surface: The effect of van der Waals interactions. Surf. Sci. 2015, 632, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xu, T.; Gordin, M.L.; Wang, D. Nitrogen-Doped Mesoporous Carbon Promoted Chemical Adsorption of Sulfur and Fabrication of High-Areal-Capacity Sulfur Cathode with Exceptional Cycling Stability for Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, M.; Rizzo, L.; Farina, A. Endocrine disruptors compounds, pharmaceuticals and personal care products in urban wastewater: Implications for agricultural reuse and their removal by adsorption process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 3616–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liao, L.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Song, N.; Ren, B. Sepiolite-Based Adsorbents for the Removal of Potentially Toxic Elements from Water: A Strategic Review for the Case of Environmental Contamination in Hunan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayazi, M.; Afzali, D.; Ghanei-Motlagh, R.; Iraji, A. Synthesis of novel sepiolite-iron oxide-manganese dioxide nanocomposite and application for lead(II) removal from aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18893–18903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini, N.A.M.; Ismail, H.; Rusli, A. Short Review on Sepiolite-Filled Polymer Nanocomposites. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 1665–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.; Yuzer, H.; Sabah, E.; Çelik, M.S. Adsorption of cobalt from aqueous solutions onto sepiolite. Water Res. 2003, 37, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, R.; Liu, S.; Wu, D.; Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; He, H. Self-templating synthesis of silicon nanorods from natural sepiolite for high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 6356–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, C.; Vanscoyoc, G. Infrared study of sepiolite and palygorskite surfaces. In Developments in Sedimentology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Alkan, M.; Demirbas, O.; Çelikçapa, S.; Doğan, M. Sorption of acid red 57 from aqueous solution onto sepiolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 116, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G.; Guo, Y.; Liu, J. Adsorption of rhodamine B from aqueous solution onto heat-activated sepiolite. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2013, 18, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armağan, B.; Ozdemir, O.; Turan, M.; Celik, M.S. Adsorption of Negatively Charged Azo Dyes onto Surfactant-Modified Sepiolite. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; He, W.; Liu, B. Adsorption of Acid Orange Ⅱ with Two Step Modified Sepiolite: Optimization, Adsorption Performance, Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Regeneration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Guo, X.; Song, X.; Liu, X. Investigation on the degradation of acid fuchsin induced oxidation by MgFe2O4 under microwave irradiation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 335, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, A.; Ömeroğlu, Ç.; Erdoğan, Y.; Özcan, A.S. Modification of bentonite with a cationic surfactant: An adsorption study of textile dye Reactive Blue 19. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 140, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yi, H.; Tang, X.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Feng, T.; Cui, X. Behaviors and kinetics of toluene adsorption-desorption on activated carbons with varying pore structure. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, A.; Sutiono, H.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Removal of basic dyes in binary system by adsorption using rarasaponin–bentonite: Revisited of extended Langmuir model. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Bian, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.-J. Adsorption behavior of modified Iron stick yam skin with Polyethyleneimine as a potential biosorbent for the removal of anionic dyes in single and ternary systems at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.C.; Petkowicz, D.I.; Smaniotto, A.; Pergher, S. Magnetic zeolites: A new adsorbent for removal of metallic contaminants from water. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3699–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, P.S.; Singh, B.K. Instrumental characterization of clay by XRF, XRD and FTIR. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2007, 30, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B. Adsorption of Malachite Green with Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate Modified Sepiolite: Characterization, Adsorption Performance and Regeneration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Qu, F.; Yu, H.; Tian, J.; Chen, W.; Liang, H.; Li, G.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Membrane Fouling and Rejection of Organics during Algae-Laden Water Treatment Using Ultrafiltration: A Comparison between in Situ Pretreatment with Fe(II)/Persulfate and Ozone. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Liang, H.; Qu, F.; Li, K.; Chang, H.; Yu, H.; Li, G. Combined influence by humic acid (HA) and powdered activated carbon (PAC) particles on ultrafiltration membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 500, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunç, S.; Duman, O.; Çetinkaya, A. Electrokinetic and rheological properties of sepiolite suspensions in the presence of hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 377, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Qin, L.-L.; Yu, H.-Q.; Li, S.; Shan, R.-R.; Du, B. Adsorption of acid dyes from aqueous solution by CTMAB modified bentonite: Kinetic and isotherm modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 211, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habish, A.J.; Lazarević, S.; Janković-Častvan, I.; Jokić, B.; Kovač, J.; Rogan, J.; Janaćković, Đ.; Petrović, R. Nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI) supported by natural and acid-activated sepiolites: The effect of the nZVI/support ratio on the composite properties and Cd2+ adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 24, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashamiri, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Zare, F.; Wang, S. Multi-response optimization of ultrasound assisted competitive adsorption of dyes onto Cu (OH)2-nanoparticle loaded activated carbon: Central composite design. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




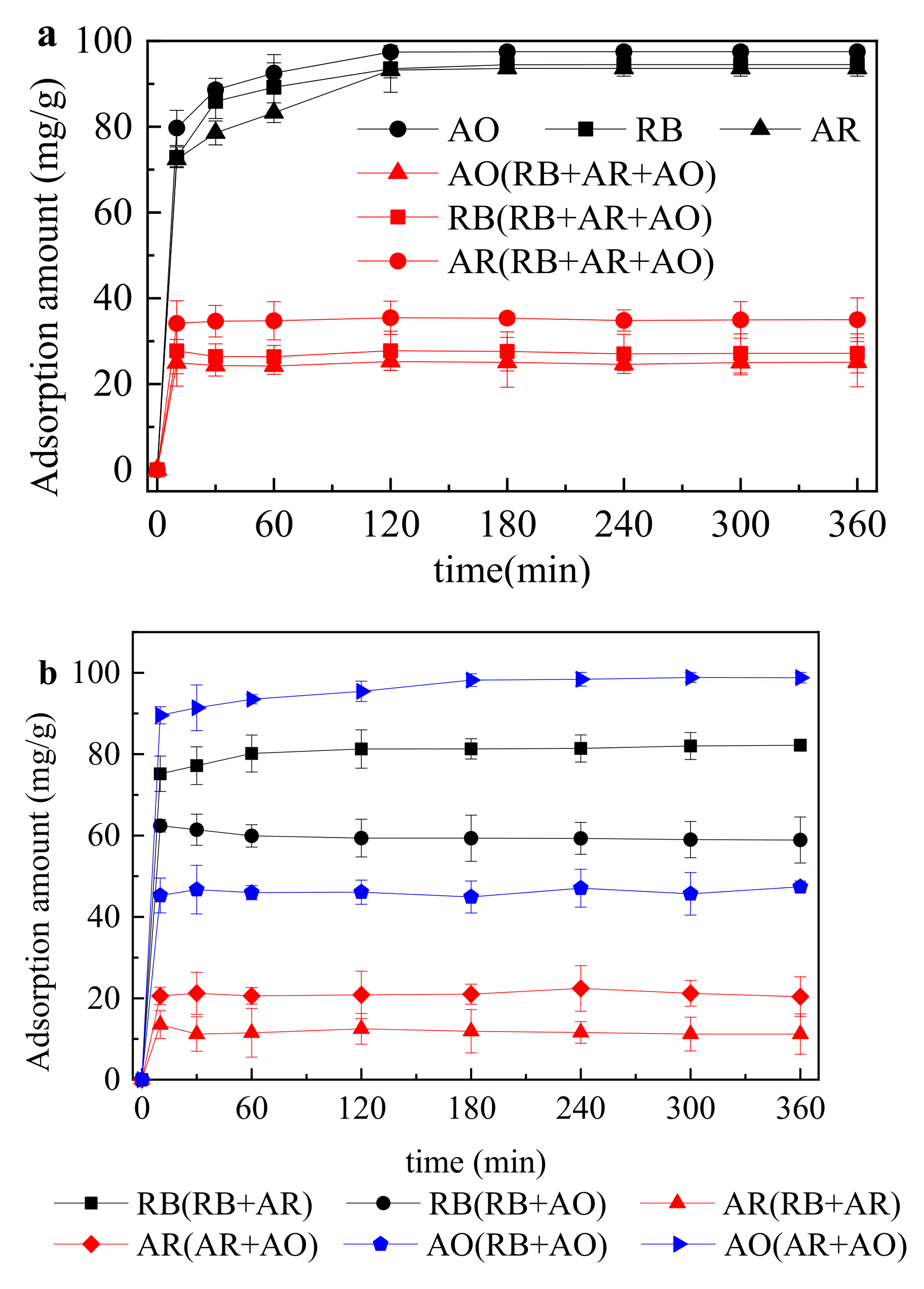

| Solution | Quasi-First-Order Reaction Kinetics Model | Quasi-Secondary Reaction Kinetics Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q1e (mg/g) | k1 (1/min) | R12 | q2e (mg/g) | k2 (1/min) | R12 | |
| RB | 21.62 | 2.42 × 10−2 | 0.85 | 95.24 | 4.53 × 10−3 | 0.99 |
| AO | 14.65 | 2.61 × 10−2 | 0.79 | 98.14 | 5.36 × 10−3 | 0.99 |
| AR | 22.01 | 1.93 × 10−2 | 0.80 | 94.70 | 2.91 × 10−3 | 0.99 |
| RB + AR | 79.46 | 1.61 × 10−2 | 0.61 | 107.30 | 8.6 × 10−2 | 0.97 |
| RB + AO | 1.84 | 1.59 × 10−3 | 0.23 | 104.17 | 1.10 × 10−2 | 0.99 |
| AO + AR | 22.53 | 1.00 × 10−2 | 0.28 | 115.61 | 7.09 × 10−2 | 0.99 |
| RB + AO + AR | 3.39 | 5.09 × 10−3 | 0.56 | 87.18 | 1.42 × 10−1 | 0.99 |
| Solution | Langmuir Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R12 | |
| RB | 115.0 | 0.32 | 0.99 |
| AO | 119.0 | 0.50 | 0.99 |
| AR | 110.0 | 0.16 | 0.99 |
| RB + AR | 129.9 | 0.34 | 0.99 |
| RB in RB + AR | 107.5 | 0.86 | 0.99 |
| AR in RB + AR | 26.5 | 0.28 | 0.99 |
| RB + AO | 134.9 | 1.55 | 0.99 |
| RB in RB + AO | 72.5 | 2.19 | 0.99 |
| AO in RB + AO | 69.9 | 1.99 | 0.99 |
| AO + AR | 144.9 | 1.00 | 0.99 |
| AO in AO + AR | 116.5 | 3.73 | 0.99 |
| AR in AO + AR | 46.7 | 3.70 | 0.99 |
| RB + AO + AR | 96.2 | 1.85 | 0.99 |
| RB in RB + AO + AR | 39.0 | 0.05 | 0.99 |
| AO in RB + AO + AR | 49.0 | 0.17 | 0.99 |
| AR in RB + AO + AR | 22.7 | 0.04 | 0.99 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Zou, A.; He, W.; Liu, B. Adsorption of Mixed Dye System with Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide Modified Sepiolite: Characterization, Performance, Kinetics and Thermodynamics. Water 2020, 12, 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040981
Yu J, Zou A, He W, Liu B. Adsorption of Mixed Dye System with Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide Modified Sepiolite: Characterization, Performance, Kinetics and Thermodynamics. Water. 2020; 12(4):981. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040981
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jian, Aiyi Zou, Wenting He, and Bin Liu. 2020. "Adsorption of Mixed Dye System with Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide Modified Sepiolite: Characterization, Performance, Kinetics and Thermodynamics" Water 12, no. 4: 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040981
APA StyleYu, J., Zou, A., He, W., & Liu, B. (2020). Adsorption of Mixed Dye System with Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide Modified Sepiolite: Characterization, Performance, Kinetics and Thermodynamics. Water, 12(4), 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040981






