Coupled Microbiological–Isotopic Approach for Studying Hydrodynamics in Deep Reservoirs: The Case of the Val d’Agri Oilfield (Southern Italy)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
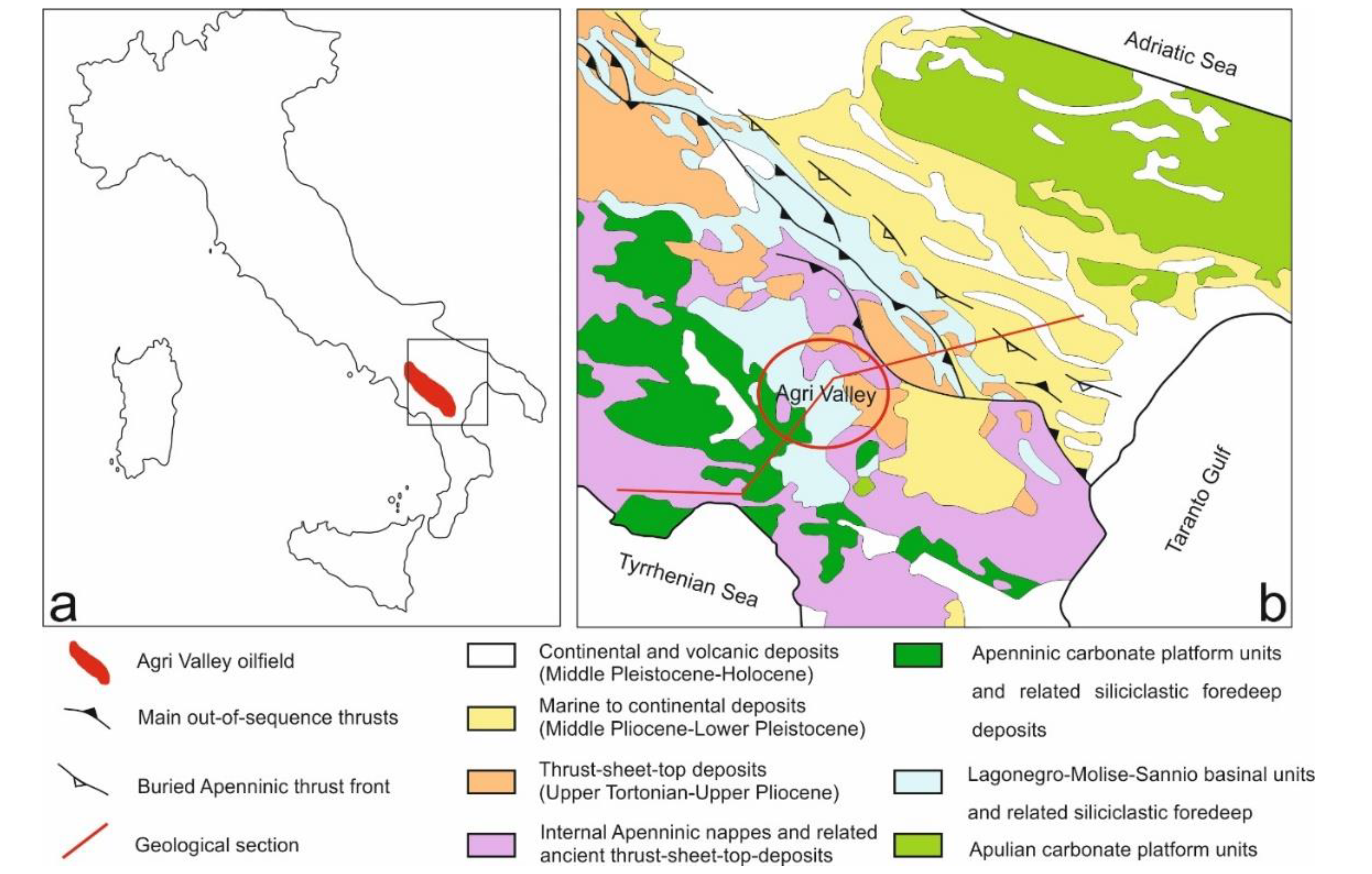
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Hydrogeological Investigations
2.3. Water Sampling and Analyses
2.4. Chemical Analyses
2.5. Microbiological Analyses: 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
3. Results
3.1. Hydrogeological Settings
3.2. Isotope Investigations
3.3. Chemical Analyses
3.4. Next-Generation Sequencing Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Satter, A.; Iqbal, G.M. Oil and gas recovery methods in low permeability and unconventional reservoirs. In Reservoir Engineering-The Fundamentals, Simulation, and Management of Conventional and Unconventional Recoveries; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2016; pp. 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Djuraev, U.; Jufar, S.R.; Vasant, P. A review on conceptual and practical oil and gas reservoir monitoring methods. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2017, 152, 586–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanchi, J.R. Introduction to Reservoir Simulation. In Principles of Applied Reservoir Simulation, 4th ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Agosta, F.; Alessandroni, M.; Antonellini, M.; Tondi, E.; Giorgioni, M. From fractures to flow: A field-based quantitative analysis of an outcropping carbonate reservoir. Tectonophysics 2010, 490, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, J.; Neilson, J.E.; Laubach, S.E.; Whidden, K.J. Advances in carbonate exploration and reservoir analysis. In Advances in Carbonate Exploration and Reservoir Analysis; Garland, J., Neilson, J.E., Laubach, S.E., Whidden, K.J., Eds.; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2012; Volume 370, pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lavenu, A.P.C.; Lamarche, J.; Gallois, A.; Gauthier, B.D.M. Tectonic versus diagenetic origin of fractures in a naturally fractured carbonate reservoir analog (Nerthe anticline, southeastern France). AAPG Bull. 2013, 97, 2207–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, O.; Ascione, A.; Mazzoli, S.; Virieux, J.; Zollo, A. Seismic imaging of a fluid storage in the actively extending Apennine mountain belt, southern Italy. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3802–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneva, I.; Cilona, A.; Tondi, E.; Agosta, F.; Giorgioni, M. Characterisation of the permeability anisotropy of Cretaceous platform carbonates by using 3D fracture modeling: The case study of Agri Valley fault zones (southern Italy). Ital. J. Geosci. 2015, 134, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Feng, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Wen, X.; Si, J.; Xi, H.; Guo, R.; Jia, B. Stable isotopic and geochemical identification of groundwater evolution and recharge sources in the arid Shule River Basin of Northwestern China. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4703–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, E.; Bucci, A.; Ogata, K.; Zanini, A.; Naclerio, G.; Chelli, A.; Francese, R.; Boschetti, T.; Pittalis, D.; Celico, F. Hydrodynamics in Evaporate-Bearing Fine-Grained Successions Investigated through an Interdisciplinary Approach: A Test Study in Southern Italy—Hydrogeological Behaviour of Heterogeneous Low-Permeability Media. Geofluids 2018, 2018, 5978597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanini, A.; Petrella, E.; Sanangelantoni, A.M.; Angelo, L.; Ventosi, B.; Viani, L.; Rizzo, P.; Remelli, S.; Bartoli, M.; Bolpagni, R.; et al. Groundwater characterisation from an ecological and human perspective: An interdisciplinary approach in the Functional Urban Area of Parma, Italy. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2019, 30, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.T.; Lee, I.M.; Schiff, K.C. Inactivation of indicator micro-organisms from various sources of faecal contamination in seawater and freshwater. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 1st Addendum to, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, R.W.; George, L.H.; Smith, R.L.; LeBlanc, D.R. Transport of microspheres and indigenous bacteria through a sandy aquifer: Results of natural-and forced-gradient tracer experiments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, A.; Petrella, E.; Celico, F.; Naclerio, G. Use of molecular approaches in hydrogeological studies: The case of carbonate aquifers in southern Italy. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapelle, F.H. Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated ground water: The perspectives of history and hydrology. Groundwater 1999, 37, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.K.; Singh, O.V.; Jain, R.K. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Environmental pollution and bioremediation. Trends Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez-Vega, D.; Gallego, J.L.R.; Pelaez, A.I.; de Cordoba, G.F.; Moreno, J.; Muñoz, D.; Sanchez, J. Engineered in situ bioremediation of soil and groundwater polluted with weathered hydrocarbons. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2007, 43, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Tian, S.; Wang, W.; Qi, Q.; Jiang, P.; Gao, X.; Li, F.; Li, H.; Yu, H. Petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria for the remediation of oil pollution under aerobic conditions: A perspective analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X.; Mbadinga, S.M.; Liu, J.-F.; Zhou, L.; Yang, S.-Z.; Gu, J.-D.; Mu, B.-Z. Microbiota and their affiliation with physiochemical characteristics of different subsurface petroleum reservoirs. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 2017, 120, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, W.R.; Schmitz, R.A. Metagenomics–the key to the uncultured microbes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, L.-Y.; Liu, S.-J.; Hu, J.-Y.; He, Y.; Zhou, H.-W.; Zhang, X.-H. Profiling of microbial community during in situ remediation of volatile sulfide compounds in river sediment with nitrate by high throughput sequencing. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzyk, K.H.; Rectanus, H.V.; Bartling, C.M.; Rosansky, S.; Minard-Smith, A.; Mullins, L.A.; Neil, K. Use of omic tools to assess methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) degradation in groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giano, S.I.; Maschio, L.; Alessio, M.; Ferranti, L.; Improta, S.; Schiattarella, M. Radiocarbon dating of active faulting in the Agri high valley, southern Italy. J. Geodyn. 2000, 29, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Addezio, G.; Karner, D.B.; Burrato, P.; Insinga, D.; Maschio, L.; Ferranti, L.; Renne, P.R. Tephrochronology in faulted Middle Pleistocene tephra layer in the Val d’Agri area (Southern Italy). Ann. Geophys. 2006, 49, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Giocoli, A.; Stabile, T.A.; Adurno, I.; Perrone, A.; Gallipoli, M.R.; Gueguen, E.; Norelli, E.; Piscitelli, S. Geological and geophysical characterisation of the southeastern side of the High Agri Valley (southern Apennines, Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patacca, E.; Scandone, P.; Bellatalla, M.; Perilli, N.; Santini, U. The Numidian-sand event in the Southern Apennines. Mem. Sci. Geol. Padova 1992, 43, 297–337. [Google Scholar]
- Merlini, S.; Mostardini, F. Appennino centro-meridionale: Sezioni geologiche e proposta di modello strutturale. Mem. Soc. Geol. It. 1986, 35, 177–202. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, R.W.H.; Corrado, S.; Mazzoli, S.; De Donatis, M.; Di Bucci, D.; Naso, G.; Scrocca, D.; Nicolai, C.; Zucconi, V. Time and space variability of «thin-skinned» and «thick-skinned» thrust tectonics in the Apennines (Italy). Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2000, 11, 5–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menardi Noguera, A.; Rea, G. Deep structure of the Campanian–Lucanian arc (southern Apennine, Italy). Tectonophysics 2000, 324, 239–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wavrek, D.A.; Mosca, F. Compositional grading in the oil column: Advances from a mass balance and quantitative molecular analysis. In Understanding Petroleum Reservoirs: Towards an Integrated Reservoir Engineering and Geochemical Approach; Cubitt, J.M., England, W.A., Larter, S.R., Eds.; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2004; Volume 237, pp. 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Cazzini, F.F. The history of the upstream oil and gas industry in Italy. In History of the European Oil and Gas Industry; Craig, J., Gerali, F., MacAulay, F., Sorkhabi, R., Eds.; Geological Society Special Publications: London, UK, 2018; Volume 465, pp. 243–274. [Google Scholar]
- Olita, F. Investigation of the natural hydrocarbon manifestations and 3D reconstruction of the reservoir in the Tramutola area (Basilicata). Master’s thesis, University of Basilicata, Potenza, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Scandone, P.; Sgrosso, I. Flysch con Inocerami nella valle del Cavolo presso Tramutola (Lucania). Boll. Soc. Nat. Napoli 1964, 73, 166–175. [Google Scholar]
- Mattioni, L.; Tondi, E.; Shiner, P.; Renda, P.; Vitale, S.; Cello, G. The Argille Varicolori unit in Lucania (Italy): A record of tectonic offscraping and gravity sliding in the Mesozoic-Tertiary Lagonegro Basin, southern Apennines. In Tectonics of the Western Mediterranean and North Africa; Moratti, G., Chalouan, A., Eds.; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2006; Volume 262, pp. 277–288. [Google Scholar]
- Scandone, P. Studi di geologia lucana: La serie calcareo-silico-marnosa e i suoi rapporti con l’Appennino calcareo. Boll. Soc. Nat. Napoli 1967, 76, 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- Scandone, P. Studi di geologia lucana: Note illustrative della carta dei terreni della serie calcareo–silico–marnosa. Boll. Soc. Nat. Napoli 1972, 81, 225–300. [Google Scholar]
- De Vita, P.; Allocca, V.; Celico, F.; Fabbrocino, S.; Cesaria, M.; Monacelli, G.; Musilli, I.; Piscopo, V.; Scalise, A.R.; Summa, G.; et al. Hydrogeology of continental Southern Italy. J. Maps 2018, 14, 230–241. [Google Scholar]
- Berserzio, R.; Felletti, F.; Giudici, M.; Miceli, A.; Zembo, I. Aquifer analogues to assist modeling of groundwater flow: The Pleistocene aquifer complex of the Agri Valley (Basilicata). In Proceedings Italian National Workshop “Developments in Aquifer Sedimentology and Ground Water Flow Studies in Italy; Ist. Poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato: Roma, Italy, 2007; pp. 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Petrella, E.; Celico, F. Heterogeneous aquitard properties in sedimentary successions in the Apennine chain: Case studies in southern Italy. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 3365–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, E.; Celico, F. Mixing of water in a carbonate aquifer, southern Italy, analysed through stable isotope investigations. Int. J. Speleol. 2013, 42, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vita, P.; Allocca, V.; Manna, F.; Fabbrocino, S. Coupled decadal variability of the North Atlantic Oscillation, regional rainfall and karst spring discharges in the Campania region (southern Italy). Hydrol. Earth Sys. Sci. 2012, 16, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allocca, V.; De Vita, P.; Manna, F.; Nimmo, J.R. Groundwater recharge assessment at local and episodic scale in a soil mantled perched karst aquifer in southern Italy. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Esposito, L.; Testa, G.; Ciarcia, S.; Pagnozzi, M. The upwelling water flux feeding springs: Hydrogeological and hydraulic features. Water 2018, 10, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorillo, F.; Leone, G.; Pagnozzi, M.; Catani, V.; Testa, G.; Esposito, L. The upwelling groundwater flow in the karst area of Grassano-Telese springs (Southern Italy). Water 2019, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paternoster, M.; Scarfiglieri, A.; Mongelli, G. Groundwater chemistry in the high Agri Valley (Southern Apennines, Italy). GeoActa 2005, 4, 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. In Water and Environment News; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, April 1998.
- U.S. EPA. Method 3510C (SW-846): Separatory Funnel Liquid-Liquid Extraction; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. EPA. Method 5030C (SW-846): Purge-and-Trap for Aqueous Samples Revision 3; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. EPA. Method 8015D (SW-846): Nonhalogenated Organics Using GC/FID Revision 4; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. EPA. Method 8270E (SW-846): Semivolatile Organic Compounds by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Milani, C.; Hevia, A.; Foroni, E.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Lugli, G.A.; Sanchez, B.; Martín, R.; Gueimonde, M.; van Sinderen, D.; et al. Assessing the fecal microbiota: An optimised ion torrent 16S rRNA gene-based analysis protocol. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Gonzalez Peña, A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Optimising taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longinelli, A.; Selmo, E. Isotopic composition of precipitation in Italy: A first overall map. J. Hydrol. 2003, 270, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Petrella, E.; Naclerio, G.; Falasca, A.; Bucci, A.; Capuano, P.; De Felice, V.; Celico, F. Non-permanent shallow halocline in a fractured carbonate aquifer, southern Italy. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajcar Bronić, I.; Barešić, J.; Borković, D.; Sironić, A.; Mikelić, I.L.; Vreča, P. Long-Term Isotope Records of Precipitation in Zagreb, Croatia. Water 2020, 12, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auling, G.; Busse, H.-J.; Egli, T.; El-Banna, T.; Stackebrandt, E. Description of the Gram-negative, obligately aerobic, nitrilotriacetate (NTA)-utilizing bacteria as Chelatobacter heintzii, gen. nov., sp. nov., and Chelatococcus asaccharovorans, gen. nov., sp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1993, 16, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahe, Y.F.; Perez, M.J.; Tacheau, C.; Fanchon, C.; Martin, R.; Rousset, F.; Seite, S. A new Vitreoscilla filiformis extract grown on spa water-enriched medium activates endogenous cutaneous antioxidant and antimicrobial defenses through a potential Toll-like receptor 2/protein kinase C, zeta transduction pathway. Clin. Cosmet. Investig Dermatol. 2013, 6, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Palleroni, N.J. New species of the genus Actinoplanes, Actinoplanes ferrugineus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1979, 29, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pellegrin, V.; Juretschko, S.; Wagner, M.; Cottenceau, G. Morphological and biochemical properties of a Sphaerotilus sp. isolated from paper mill slimes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willems, A.; Busse, J.; Goor, M.; Pot, B.; Falsen, E.; Jantzen, E.; Hoste, B.; Gillis, M.; Kersters, K.; Auling, G.; et al. Hydrogenophaga, a new genus of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria that includes Hydrogenophaga flava comb. nov.(formerly Pseudomonas flava), Hydrogenophaga palleronii (formerly Pseudomonas palleronii), Hydrogenophaga pseudoflava (formerly Pseudomonas pseudoflava and “Pseudomonas carboxydoflava”), and Hydrogenophaga taeniospiralis (formerly Pseudomonas taeniospiralis). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1989, 39, 319–333. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-Q.; Chen, Y.-G.; Li, W.-J.; Tian, X.-P.; Xu, L.-H.; Jiang, C.-L. Sphingomonas yunnanensis sp. nov., a novel Gram-negative bacterium from a contaminated plate. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 2361–2364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Niel, C.B. On the morphology and physiology of the purple and green sulphur bacteria. Archiv. Mikrobiol. 1932, 3, 1–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, G.N.; Patel, B.K.; Grassia, G.S.; Sheehy, A.J. Anaerobaculum thermoterrenum gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel, thermophilic bacterium which ferments citrate. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevenieau, F.; Fardeau, M.L.; Ollivier, B.; Joulian, C.; Baena, S. Desulfomicrobium thermophilum sp. nov., a novel thermophilic sulphate-reducing bacterium isolated from a terrestrial hot spring in Colombia. Extremophiles 2007, 11, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimtong, S.; Tachaapaikoon, C.; Pason, P.; Kyu, K.L.; Kosugi, A.; Mori, Y.; Ratanakhanokchai, K. Isolation and characterization of endocellulase-free multienzyme complex from newly isolated Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum strain NOI-1. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegel, J.; Ljungdahl, L.G. Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus gen. nov., spec. nov., a new, extreme thermophilic, anaerobic bacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 1981, 128, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knøchel, S. Growth characteristics of motile Aeromonas spp. isolated from different environments. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1990, 10, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, M.A.; Ihssen, J.; Matthies, C.; Schramm, A.; Acker, G.; Drake, H.L. Dechloromonas denitrificans sp. nov., Flavobacterium denitrificans sp. nov., Paenibacillus anaericanus sp. nov. and Paenibacillus terrae strain MH72, N2O-producing bacteria isolated from the gut of the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardet, J.-F.; Bowman, J.P. Flavobacterium. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Whitman, W.B., Rainey, F., Kämpfer, P., Trujillo, M., Chun, J., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Dedysh, S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., in association with Bergey’s Manual Trust: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Spring, S.; Kampfer, P.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.-H. Polyphasic characterization of the genus Leptothrix: New descriptions of Leptothrix mobilis sp. nov. and Leptothrix discophora sp. nov. nom. rev. and emended description of Leptothrix cholodnii emend. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 19, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyuzhnaya, M.G.; Bowerman, S.; Lara, J.C.; Lidstrom, M.E.; Chistoserdova, L. Methylotenera mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., an obligately methylamine-utilising bacterium within the family Methylophilaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2819–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Song, F.; Xin, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Fang, C. Microvirga guangxiensis sp. nov., a novel alphaproteobacterium from soil, and emended description of the genus Microvirga. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1997–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kodama, Y.; Watanabe, K. Sulfuricurvum kujiense gen. nov., sp. nov., a facultatively anaerobic, chemolithoautotrophic, sulfur-oxidising bacterium isolated from an underground crude-oil storage cavity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 2297–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kojima, H.; Fukui, M. Sulfuritalea hydrogenivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a facultative autotroph isolated from a freshwater lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 1651–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inagaki, F.; Takai, K.; Nealson, K.H.; Horikoshi, K. Sulfurovum lithotrophicum gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel sulfur-oxidising chemolithoautotroph within the ε-Proteobacteria isolated from Okinawa Trough hydrothermal sediments. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Sugita, K.; Yumoto, I.; Nodasaka, Y.; Okabe, S. Thiovirga sulfuroxydans gen. nov., sp. nov., a chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidising bacterium isolated from a microaerobic waste-water biofilm. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aruga, S.; Kamagata, Y.; Kohno, T.; Hanada, S.; Nakamura, K.; Kanagawa, T. Characterisation of filamentous Eikelboom type 021N bacteria and description of Thiothrix disciformis sp. nov. and Thiothrix flexilis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Storti, F.; Billi, A.; Salvini, F. Particle size distributions in natural carbonate fault rocks: Insights for non-self-similar cataclasis. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 206, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, F.; Grieco, D.S.; Agosta, F.; Prosser, G. Space-time evolution of cataclasis in carbonate fault zones. J. Struct. Geol. 2018, 110, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, A.; La Bruna, V.; Castelluccio, P.; Panza, E.; Rustichelli, A.; Tondi, E.; Giorgioni, M.; Agosta, F. Fracture simulation parameters of fractured reservoirs: Analogy with outcropping carbonates of the Inner Apulian Platform, southern Italy. J. Struct. Geol. 2019, 123, 18–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodini, G.; Avino, R.; Brombach, T.; Caliro, S.; Cardellini, C.; De Vita, S.; Frondini, F.; Granirei, D.; Marotta, E.; Ventura, G. Fumarolic and diffuse soil degassing west of Mount Epomeo, Ischia, Italy. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 133, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celico, F.; Petrella, E.; Celico, P. Hydrogeological behaviour of some fault zones in a carbonate aquifer of Southern Italy: An experimentally based model. Terra Nova 2006, 18, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, E.; Capuano, P.; Carcione, M.; Celico, F. A high-altitude temporary spring in a compartmentalised carbonate aquifer: The role of low-permeability faults and karst conduits. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, A.; Naclerio, G.; Allocca, V.; Celico, P.; Celico, F. Potential use of microbial community investigations to analyse hydrothermal systems behaviour: The case of Ischia Island, Southern Italy. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, A.; Petrella, E.; Naclerio, G.; Gambatese, S.; Celico, F. Bacterial migration through low-permeability fault zones in compartmentalised aquifer systems: A case study in Southern Italy. Int. J. Speleol. 2014, 43, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aquino, D.; Petrella, E.; Florio, M.; Celico, P.; Celico, F. Complex hydraulic interactions between compartmentalised carbonate aquifers and heterogeneous siliciclastic successions: A case study in southern Italy. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4252–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, E.; Aquino, D.; Fiorillo, F.; Celico, F. The effect of low-permeability fault zones on groundwater flow in a compartmentalised system. Experimental evidence from a carbonate aquifer (Southern Italy). Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca, V.; Marzano, E.; Tramontano, M.; Celico, F. Environmental impact of cattle grazing on a karst aquifer in the southern Apennines (Italy): Quantification through the grey water footprint. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekdeger, A.; Matthess, G. Factors of bacteria and virus transport in groundwater. Environ. Geol. 1983, 5, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurry, S.W.; Coyne, M.S.; Perfect, E. Fecal coliform transport through intact soil blocks amended with poultry manure. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naclerio, G.; Fardella, G.; Marzullo, G.; Celico, F. Filtration of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus cereus spores in a pyroclastic topsoil, carbonate Apennines, southern Italy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 70, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, A.; Petrella, E.; Naclerio, G.; Allocca, V.; Celico, F. Microorganisms as contaminants and natural tracers: A 10-year research in some carbonate aquifers (southern Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, S.; Mazzoli, S.; Megna, A.; Santini, S. Finite element modelling of stress field perturbations and interseismic crustal deformation in the Val d’Agri region, southern Apennines, Italy. Tectonophysics 2015, 657, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Name | Latitude N | Longitude E | Altitude (m a.s.l.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RWS1 | 40.3247 | 15.9897 | 1047 |
| RWS2 | 40.3411 | 16.0003 | 1290 |
| S1 | 40.3225 | 15.7597 | 636 |
| S2 | 40.3228 | 15.7586 | 643 |
| S3 | 40.3175 | 15.7594 | 643 |
| Part | 40.3225 | 15.7592 | 643 |
| Sample | Final Read Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling Campaigns | |||
| 19 July 2018 | 29 October 2018 | 18 March 2019 | |
| S1 | 73,995 | 59,369 | 49,512 |
| S2 | 93,820 | 57,630 | 61,065 |
| Part | n.a. | 44,730 | 53,341 |
| Deep reservoir | 101,690 | 60,563 | 77,931 |
| Taxonomy | Growth Temperature (°C) | Citations |
|---|---|---|
| Actinoplanes | 10–35 | [63] |
| Aeromonas | 5–25 | [72] |
| Chlorobium | 25–30 | [67] |
| Dechloromonas | 25 | [73] |
| Flavobacterium | 15–30 | [74] |
| Hydrogenophaga | 30 | [65] |
| Leptothrix | 10–37 | [75] |
| Methylotenera | 10–34 | [76] |
| Microvirga | 37 | [77] |
| Sphaerotilus | 25–40 | [64] |
| Sphingomonas | 28 | [66] |
| Sulfuricurvum | 25 | [78] |
| Sulfuritalea | 10–32 | [79] |
| Sulfurovum | 10–40 | [80] |
| Thiovirga | 30 | [81] |
| Thiothrix | 20–37 | [82] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizzo, P.; Bucci, A.; Sanangelantoni, A.M.; Iacumin, P.; Celico, F. Coupled Microbiological–Isotopic Approach for Studying Hydrodynamics in Deep Reservoirs: The Case of the Val d’Agri Oilfield (Southern Italy). Water 2020, 12, 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051483
Rizzo P, Bucci A, Sanangelantoni AM, Iacumin P, Celico F. Coupled Microbiological–Isotopic Approach for Studying Hydrodynamics in Deep Reservoirs: The Case of the Val d’Agri Oilfield (Southern Italy). Water. 2020; 12(5):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051483
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizzo, Pietro, Antonio Bucci, Anna Maria Sanangelantoni, Paola Iacumin, and Fulvio Celico. 2020. "Coupled Microbiological–Isotopic Approach for Studying Hydrodynamics in Deep Reservoirs: The Case of the Val d’Agri Oilfield (Southern Italy)" Water 12, no. 5: 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051483








