Exploring the Clustering Property and Network Structure of a Large-Scale Basin’s Precipitation Network: A Complex Network Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Network Methodology
2.1. Degree and Degree Distribution
2.2. Clustering Coefficient
2.3. The Average Path Length
2.4. Small-World Network
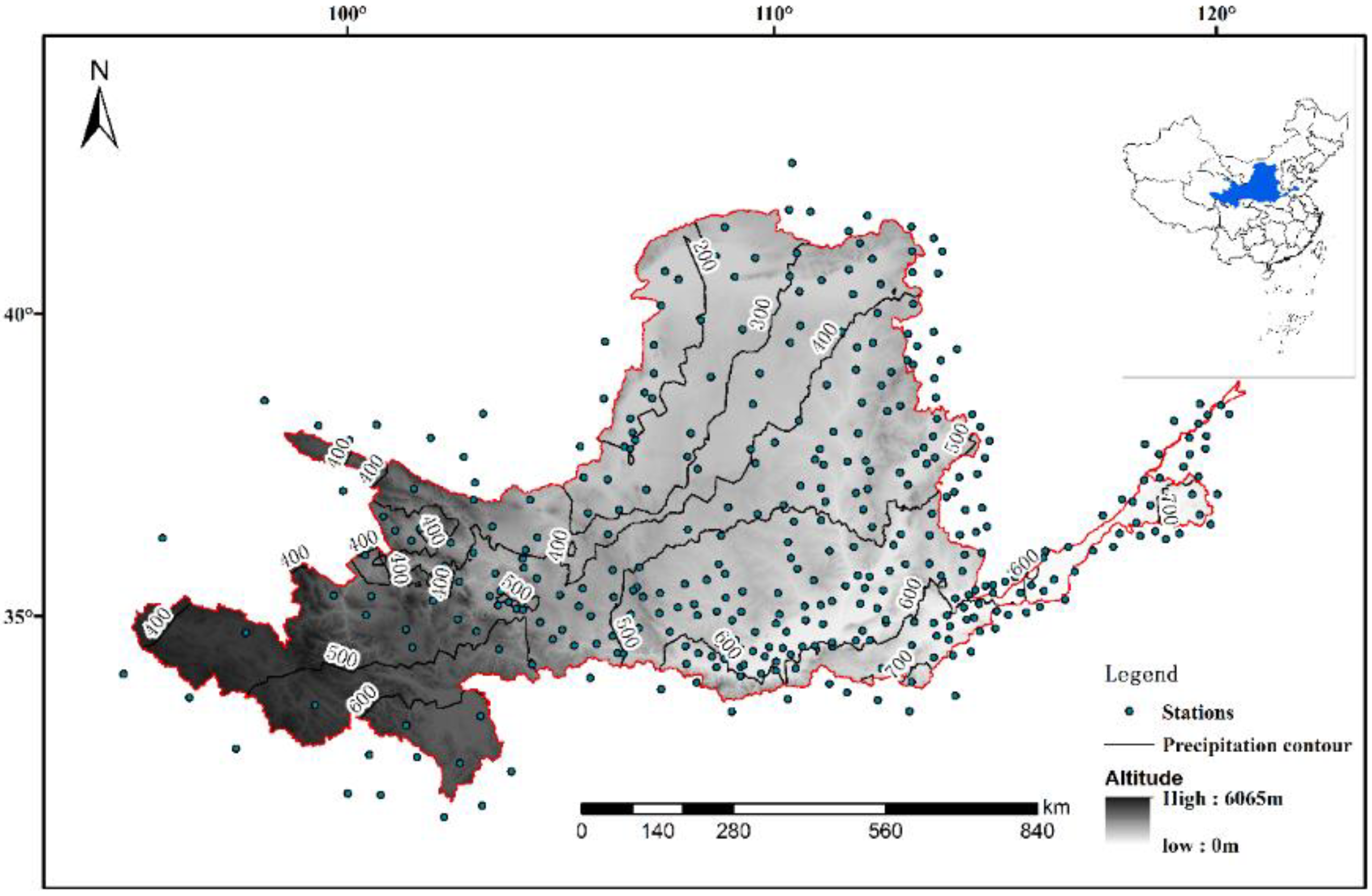
3. Study Area and Data
4. Analysis and Results
4.1. Network Construction
4.2. Descriptive Analysis of Network Graph Characteristics
4.3. Network Architecture
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Qin, D.; Zhou, Z.; Over, T.M. Theory and practice of runoff space-time distribution. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2004, 47, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Kundu, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Rainfall Trend Analysis by Mann-Kendell Test: A Case Study of North-Eastern Part of Cuttack District, Orissa. Int. J. Geol. Earth Environ. Sci. 2012, 2, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sa’adi, Z.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Chung, E.S.; Wang, X.J. Trends analysis of rainfall and rainfall extremes in Sarawak, Malaysia using modified Mann–Kendall test. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2017, 131, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, L.; López, L.; Merino, A.; Berthet, C.; García-Ortega, E.; Sánchez, J.L.; Dessens, J. Hailfall in southwest France: Relationship with precipitation, trends and wavelet analysis. Atmos. Res. 2015, 156, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrésani, B. An overview of wavelet analysis and time-frequency analysis (a minicourse). In International Workshop on Self-Similar Systems; Joint Institute for Nuclear Research: Dubna, Russia, July 1998; pp. 9–34. [Google Scholar]
- Westra, S.; Sharma, A. Dominant modes of interannual variability in Australian rainfall analyzed using wavelets. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donges, J.F.; Zou, Y.; Marwan, N.; Kurths, J. Complex networks in climate dynamics. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2009, 174, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinhaeuser, K.; Chawla, N.V.; Ganguly, A.R. An exploration of climate data using complex networks. ACM Sigkdd Explor. Newsl. 2010, 12, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellingeri, M.; Lu, Z.M.; Cassi, D.; Scotognella, F. Analyses of the response of a complex weighted network to vertices removal strategies considering edges weight: The case of the Beijing urban road system. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 32, 1850067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.; Yu, X.; Sokolowski, P. Identifying vulnerable lines in a power network using complex network theory. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Seoul, South Korea, 5–8 July 2009; Volume 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W. Lag synchronization of complex networks via pinning control. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2011, 12, 2579–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Q.H.; Liang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, T. Coevolution spreading in complex networks. Phys. Rep. 2019, 820, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Shen, H. Dynamical analysis of a discrete-time SIS epidemic model on complex networks. Appl. Math. Lett. 2019, 94, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, L. Complex networks and fundamental urban processes. Mansueto Inst. Urban. Innov. Res. Pap. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.; Bookhagen, B.; Marwan, N.; Kurths, J. Analysis of spatial and temporal extreme monsoonal rainfall over South Asia using complex networks. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, N.; Rheinwalt, A.; Bookhagen, B.; Barbosa, H.M.; Marwan, N.; Marengo, J.; Kurths, J. The South American rainfall dipole: A complex network analysis of extreme events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 7397–7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konapala, G.; Mishra, A. Review of complex networks application in hydroclimatic extremes with an implementation to characterize spatio-temporal drought propagation in continental USA. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 600–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, U.; Malik, N.; Cheung, K.; Marwan, N.; Kurths, J. A network-based comparative study of extreme tropical and frontal storm rainfall over Japan. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, C.; Mineo, C.; Moccia, B. Setting a methodology to detect main directions of synchronous heavy daily rainfall events for Lazio region using complex networks. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2116, p. 210003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, N.; Goswami, B.; Rheinwalt, A.; Bookhagen, B.; Hoskins, B.; Kurths, J. Complex networks reveal, global pattern of extreme-rainfall teleconnections. Nature 2019, 566, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Donner, R.V.; Marwan, N.; Donges, J.F.; Kurths, J. Complex network approaches to nonlinear time series analysis. Phys. Rep. 2019, 787, 1–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Xu, J.H.; Li, W.H. Complex network analysis of climate change in the Tarim River Basin, Northwest China. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2017, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsonis, A.A.; Roebber, P.J. The architecture of the climate network. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2004, 333, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarsoglio, S.; Laio, F.; Ridolfi, L. Climate dynamics: A network-based approach for the analysis of global precipitation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivakumar, B.; Woldemeskel, F.M. A network-based analysis of spatial rainfall connections. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 69, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Zhao, H.; Woldemeskel, F.M.; Sivakumar, B. Network theory and spatial rainfall connections: An interpretation. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halverson, M.J.; Fleming, S.W. Complex network theory, streamflow, and hydrometric monitoring system design. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3301–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivakumar, B.; Woldemeskel, F.M. Complex networks for streamflow dynamics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4565–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braga, A.C.; Alves, L.G.A.; Costa, L.S.; Ribeiro, A.A.; De Jesus, M.M.A.; Tateishi, A.A.; Ribeiro, H.V. Characterization of river flow fluctuations via horizontal visibility graphs. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 444, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serinaldi, F.; Kilsby, C.G. Irreversibility and complex network behavior of stream flow fluctuations. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 450, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albert, R.; Barabási, A. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 47–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chirgui, Z.M. Small-word or scale-free phenomena in Internet. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Management of Innovation and Technology, Singapore, June 2010; pp. 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsonis, A.A.; Swanson, K.L.; Roebber, P.J. What Do Networks Have to Do with Climate? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolaczyk, E.D.; Csárdi, G. Mathematical Models for Network Graphs; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdős, P.; Rényi, A. On the evolution of random graphs. Publ. Math. Inst. Hung. Acad. 1960, 5, 17–61. [Google Scholar]
- Erdős, P.; Rényi, A. On random graphs. Publ. Math. 1959, 6, 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- Erdős, P.; Rényi, A. On the strength of connectedness of a random graph. Acta Math. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1964, 12, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of small-world networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J. Characteristics of Climate Change of Precipitation and Rain Days in the Yellow River Basin during Recent 50 Years. Plateau Meterol. 2014, 33, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- China Meteorological Data Service Center. Available online: http://data.cma.cn (accessed on 2 January 2020).
- Liu, T.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.R. A Brief Review of Complex Networks and Its Application. Syst. Eng. 2005, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, M.E. Assortative mixing in networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 208701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, M.E.J.; Park, J. Why social networks are different from other types of networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2003, 68, 036122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De, N.S.; Leoncini, X. Critical behavior of the XY-rotor model on regular and small-world networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2013, 88, 012131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Z. A geometric growth model interpolating between regular and small-world networks. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2007, 40, 11863–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juher, D.; Kiss, I.Z.; Saldaña, J. Analysis of an epidemic model with awareness decay on regular random networks. J. Theor. Biol. 2014, 365, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, D.J. A Simple Model of Global Cascades on Random Networks. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, Washington, DC, USA, 30 April 2002; Volume 99, pp. 5766–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitney, D.E. Dynamic Model of Cascades on Random Networks with a Threshold Rule. In Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London, London, UK, 8 December 2009; Volume 20, pp. 103–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wu, Y. A unified model for Sierpinski networks with scale-free scaling and small-world effect. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2009, 388, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klemm, K.; Eguíluz, V.M. Growing scale-free networks with small-world behavior. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2002, 65, 057102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sallaberry, A.; Zaidi, F.; Melançon, G. Model for generating artificial social networks having community structures with small-world and scale-free properties. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2013, 3, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Du, F.; Dai, H.P.; Sun, Y.X. Random pseudofractal scale-free networks with small-world effect. Eur. Phys. J. B Condens. Matter Complex. Syst. 2006, 53, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

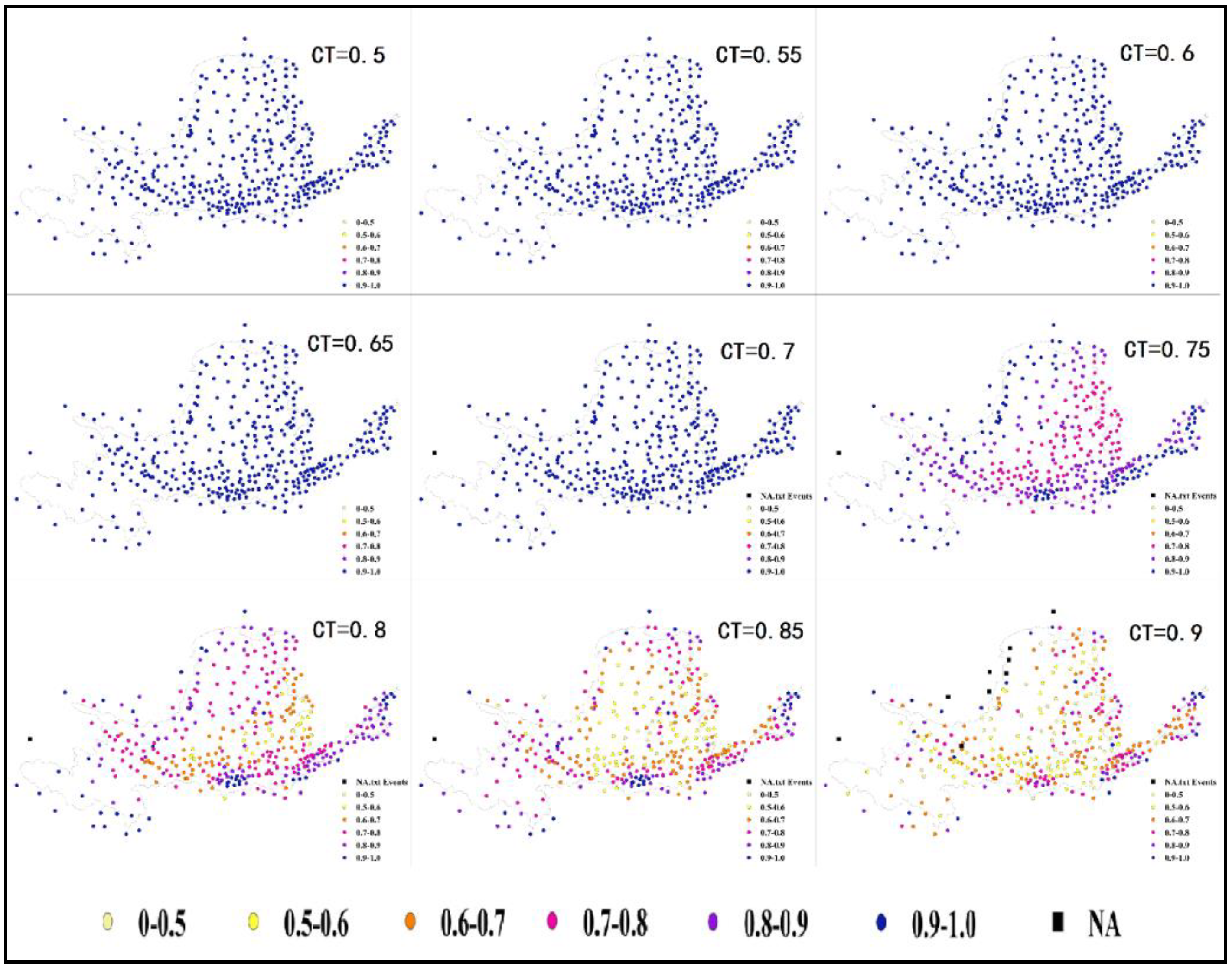
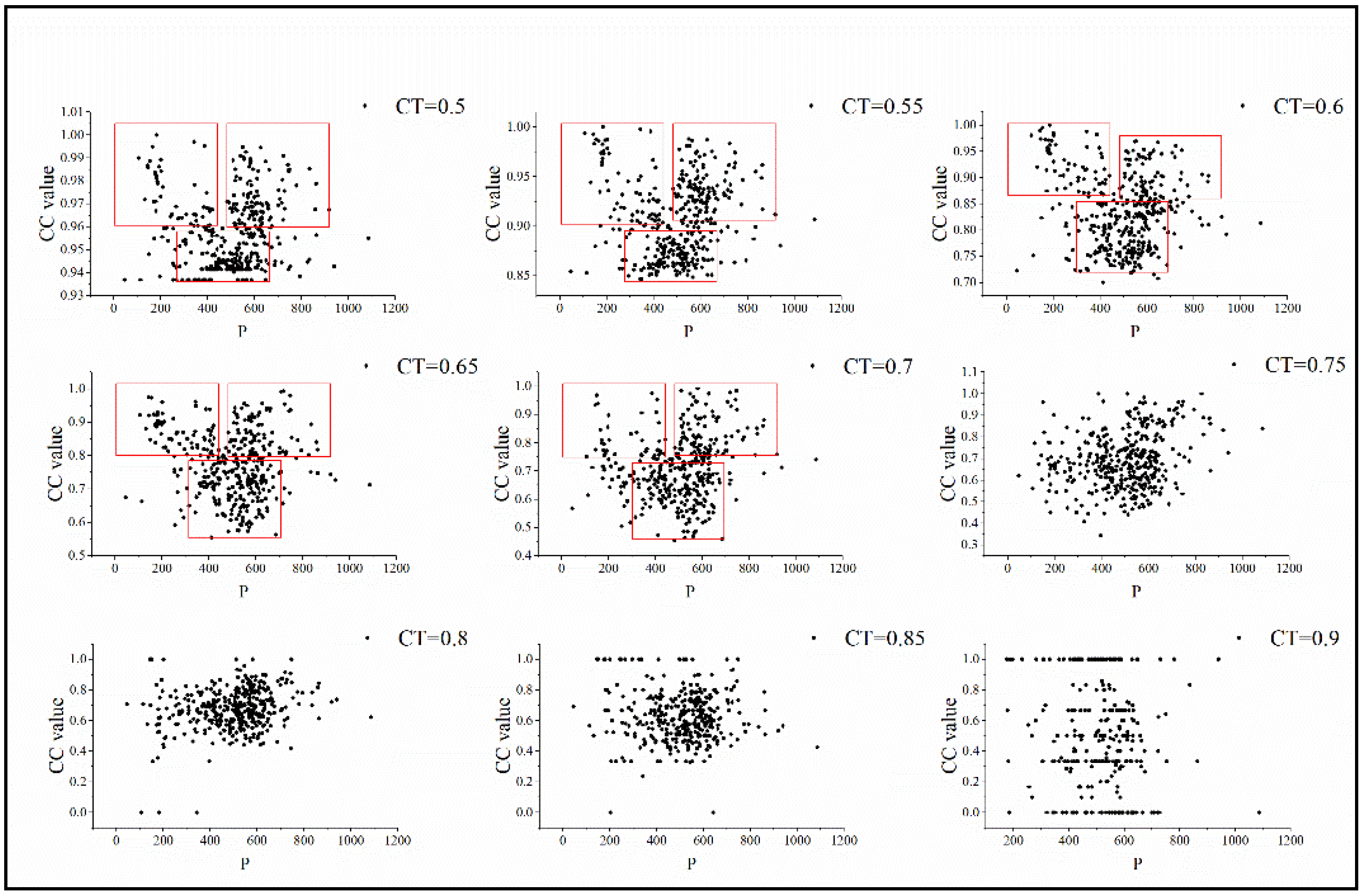
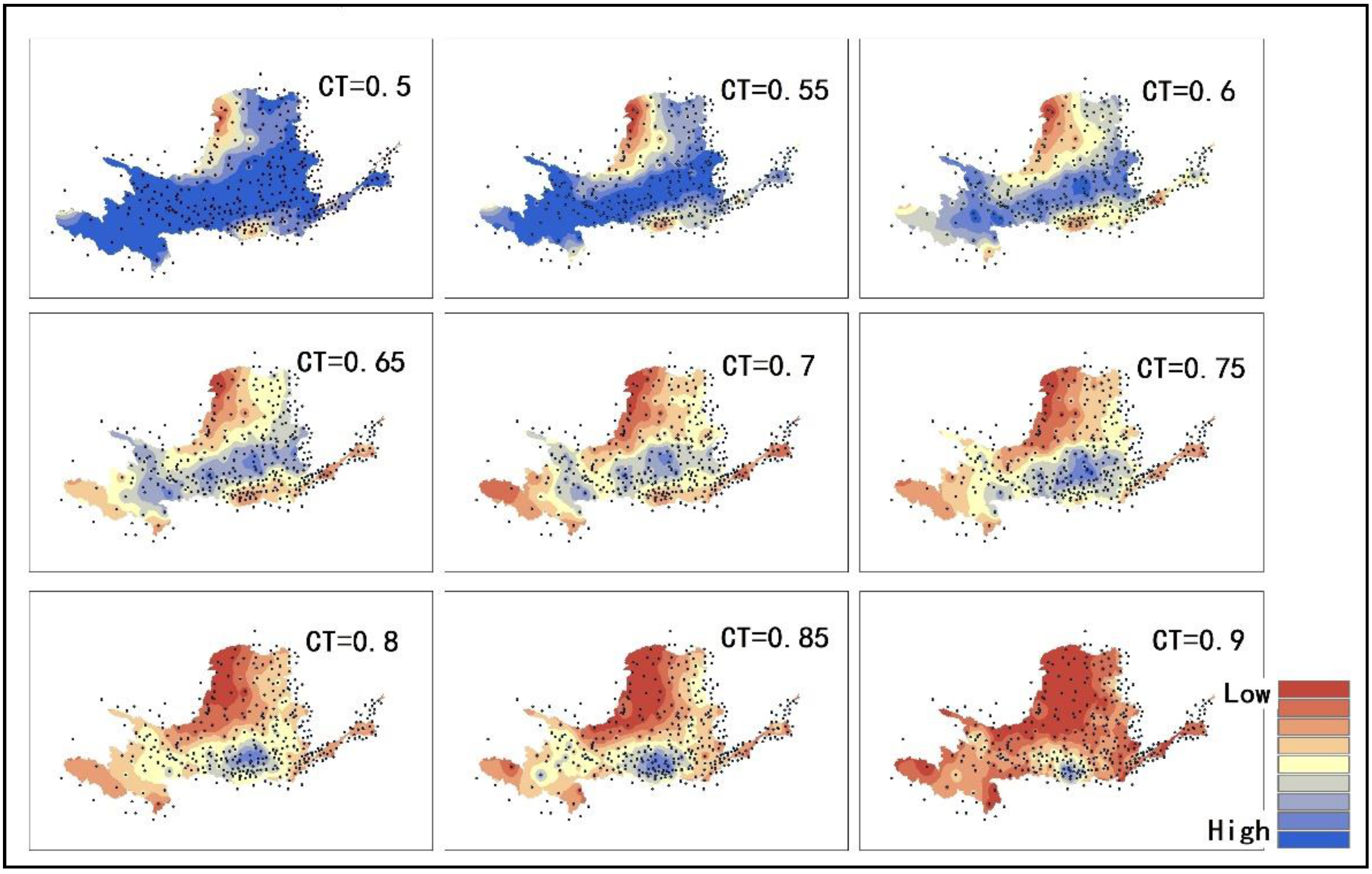
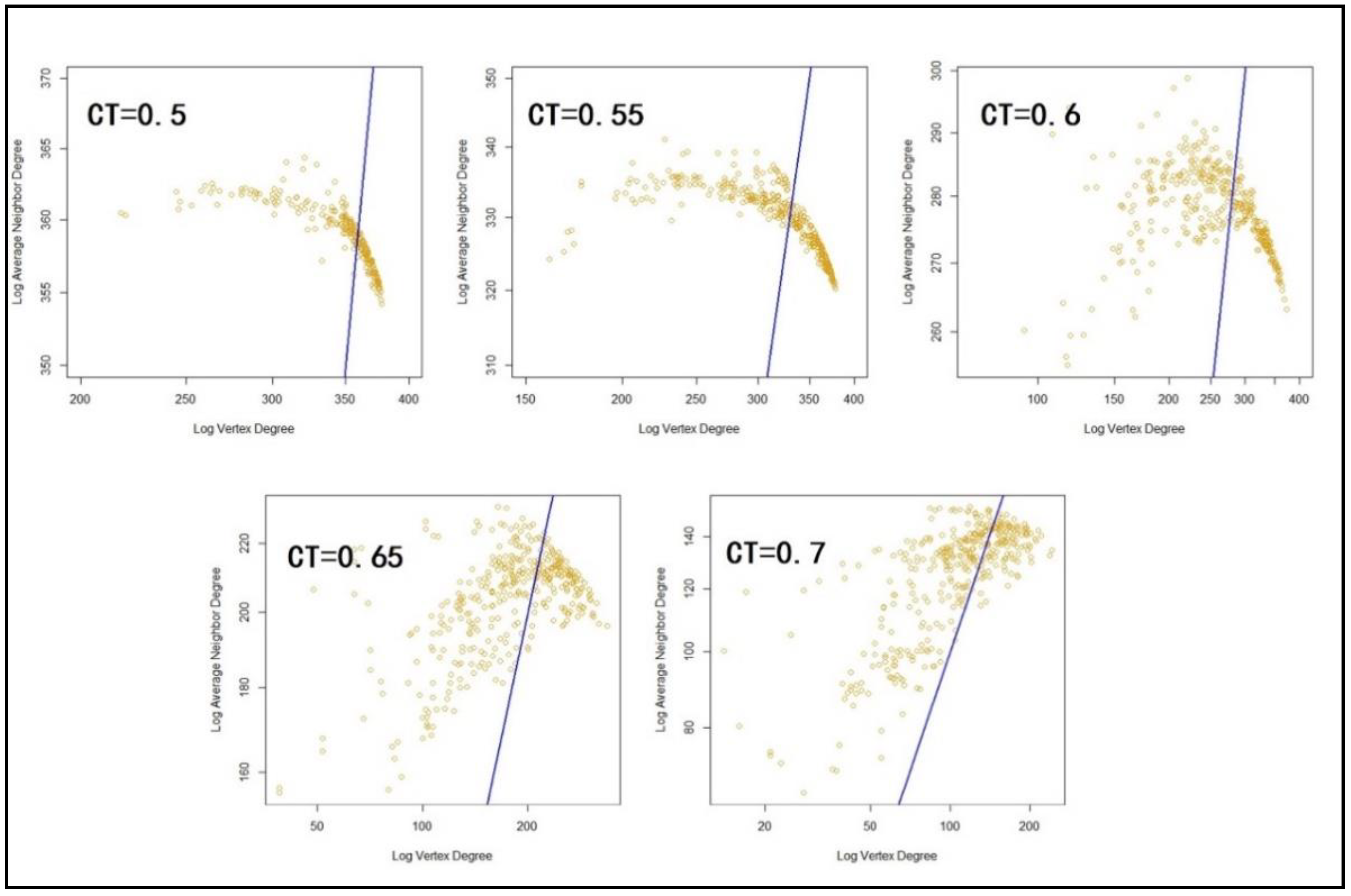
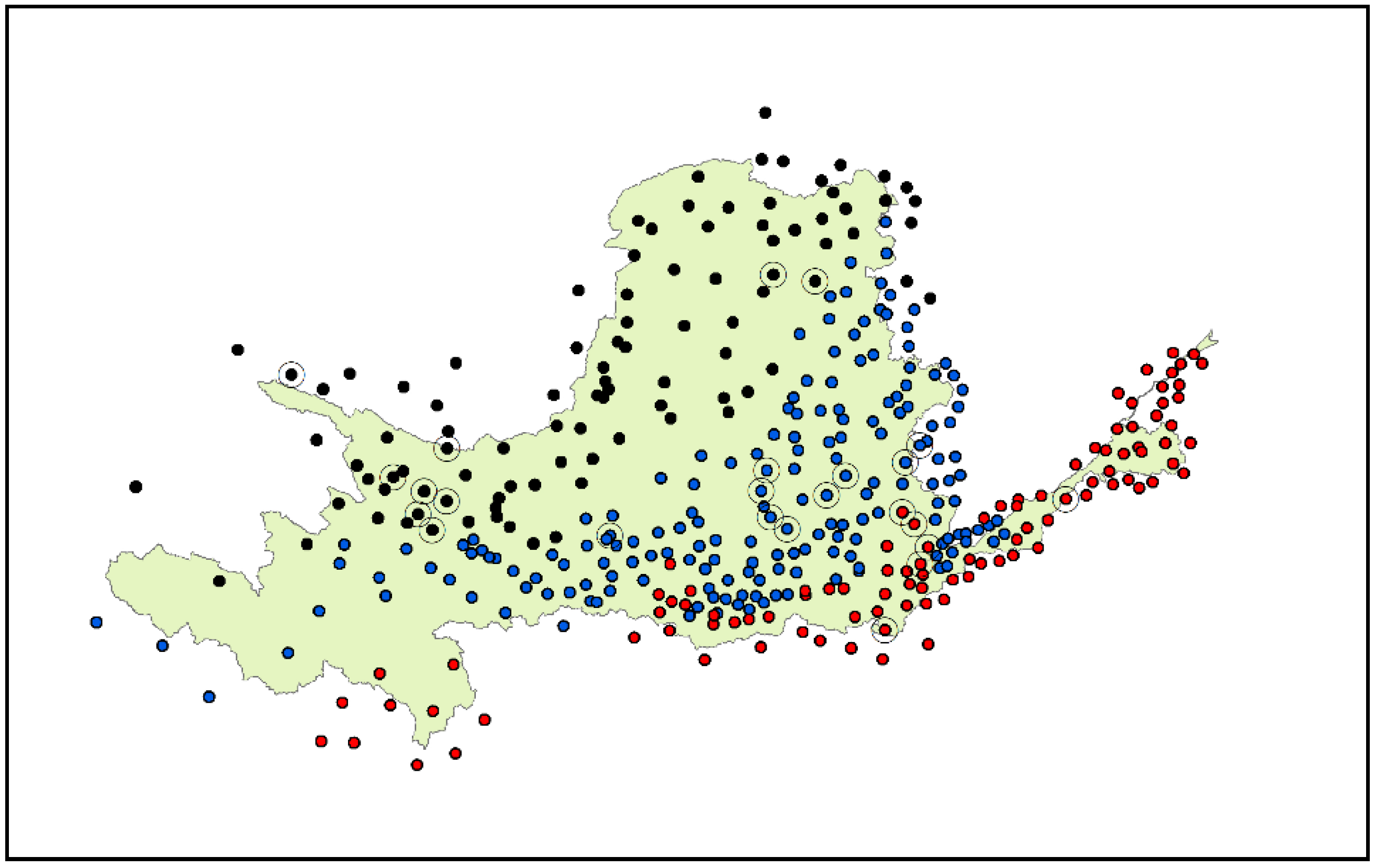
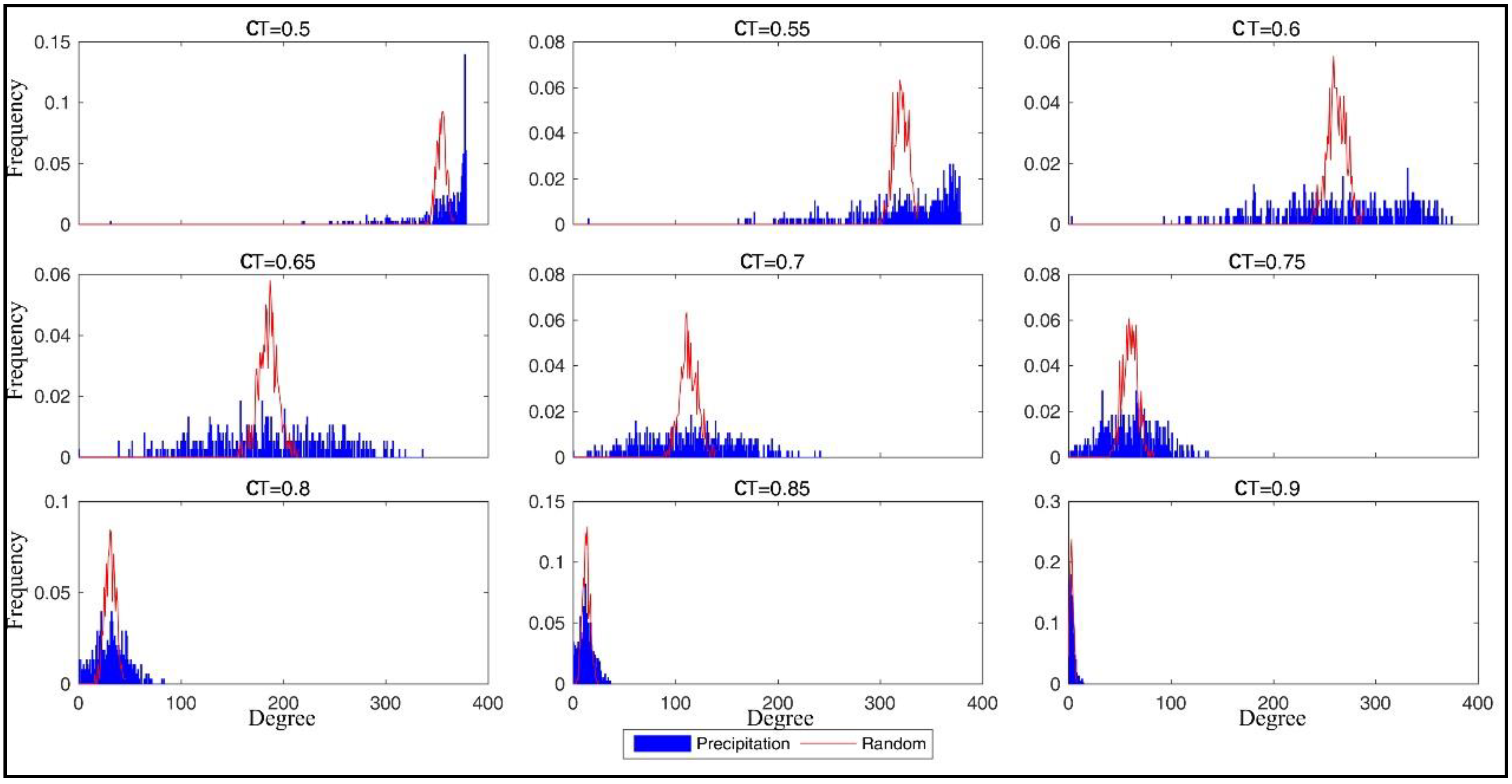

| CC Range | Percentage of Stations within Each Clustering Coefficient Range for Different CT (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.6 | 0.65 | 0.7 | 0.75 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | |
| 0–0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.37 | 5.54 | 7.65 | 18.21 | 36.41 |
| 0.5–0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.17 | 13.72 | 18.73 | 17.68 | 25.07 | 7.39 |
| 0.6–0.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19.00 | 31.13 | 31.93 | 31.66 | 22.96 | 8.71 |
| 0.7–0.8 | 0 | 0 | 32.19 | 35.36 | 32.19 | 22.16 | 24.80 | 15.57 | 1.58 |
| 0.8–0.9 | 0 | 44.85 | 45.91 | 30.08 | 13.72 | 14.78 | 13.72 | 6.07 | 3.17 |
| 0.9–1 | 100 | 55.15 | 21.90 | 12.14 | 6.60 | 6.60 | 3.17 | 6.33 | 11.61 |
| Na | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 1.32 | 5.80 | 31.13 |
| CC Range | Percentage of Stations within Each Clustering Coefficient Range for Different CT (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.6 | 0.65 | 0.7 | 0.75 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | |
| 0–0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.37 | 10.82 |
| 0.5–0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6.33 | 15.83 | 19.79 |
| 0.6–0.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19.79 | 29.02 | 30.61 |
| 0.7–0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.70 | 34.04 | 25.59 | 19.79 |
| 0.8–0.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41.95 | 27.97 | 19.00 | 10.29 |
| 0.9–1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.74 | 30.08 | 11.61 | 7.92 | 6.33 |
| Na | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 2.37 |
| Sub-Network 1 | Sub-Network 2 | Sub-Network 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station | Frequency | Station | Frequency | Station | Frequency |
| 52877 | 5 | 53848 | 4 | 53970 | 5 |
| 52787 | 4 | 53845 | 3 | 53975 | 5 |
| 52645 | 3 | 53859 | 3 | 57077 | 4 |
| 52866 | 3 | 53864 | 3 | 53978 | 3 |
| 52874 | 3 | 53872 | 3 | 54904 | 3 |
| 52876 | 3 | 53875 | 3 | 57071 | 3 |
| 52972 | 3 | 53910 | 3 | ||
| 53543 | 3 | 53942 | 3 | ||
| 53553 | 3 | 53946 | 3 | ||
| CT | P-network | |
|---|---|---|
| Apath | CC | |
| 0.5 | 1.0628 | 0.9549 |
| 0.55 | 1.1525 | 0.8976 |
| 0.6 | 1.3079 | 0.8090 |
| 0.65 | 1.5178 | 0.7241 |
| 0.7 | 1.8325 | 0.6468 |
| 0.75 | 2.4349 | 0.6380 |
| 0.8 | 3.7052 | 0.6408 |
| 0.85 | 6.6712 | 0.5826 |
| 0.9 | 8.8586 | 0.4719 |
| CT | P-random Network Apath | P-random Network CC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Mean | Max | Min | Mean | Max | |
| 0.5 | 1.0628 | 1.0628 | 1.0628 | 0.9371 | 0.9372 | 0.9373 |
| 0.55 | 1.1525 | 1.1525 | 1.1525 | 0.8473 | 0.8475 | 0.8477 |
| 0.6 | 1.3072 | 1.3072 | 1.3072 | 0.6924 | 0.6928 | 0.6932 |
| 0.65 | 1.5099 | 1.5099 | 1.5099 | 0.4891 | 0.49 | 0.491 |
| 0.7 | 1.7006 | 1.7006 | 1.7006 | 0.298 | 0.2994 | 0.3008 |
| 0.75 | 1.8406 | 1.8407 | 1.8408 | 0.1568 | 0.1594 | 0.1616 |
| 0.8 | 1.9849 | 1.9882 | 1.9923 | 0.0785 | 0.0823 | 0.0862 |
| 0.85 | 2.5963 | 2.6023 | 2.6087 | 0.0284 | 0.0341 | 0.0401 |
| 0.9 | 5.0019 | 5.2504 | 5.5338 | 0 | 0.008 | 0.0204 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Lu, F.; Zhu, K.; Song, X.; Dai, Y. Exploring the Clustering Property and Network Structure of a Large-Scale Basin’s Precipitation Network: A Complex Network Approach. Water 2020, 12, 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061739
Xu Y, Lu F, Zhu K, Song X, Dai Y. Exploring the Clustering Property and Network Structure of a Large-Scale Basin’s Precipitation Network: A Complex Network Approach. Water. 2020; 12(6):1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061739
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yiran, Fan Lu, Kui Zhu, Xinyi Song, and Yanyu Dai. 2020. "Exploring the Clustering Property and Network Structure of a Large-Scale Basin’s Precipitation Network: A Complex Network Approach" Water 12, no. 6: 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061739
APA StyleXu, Y., Lu, F., Zhu, K., Song, X., & Dai, Y. (2020). Exploring the Clustering Property and Network Structure of a Large-Scale Basin’s Precipitation Network: A Complex Network Approach. Water, 12(6), 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061739






