Variation in Runoff, Suspended Sediment Load, and Their Inter-Relationships in Response to Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities Over the Last 60 Years: A Case Study of the Upper Fenhe River Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Data Collection, and Methods
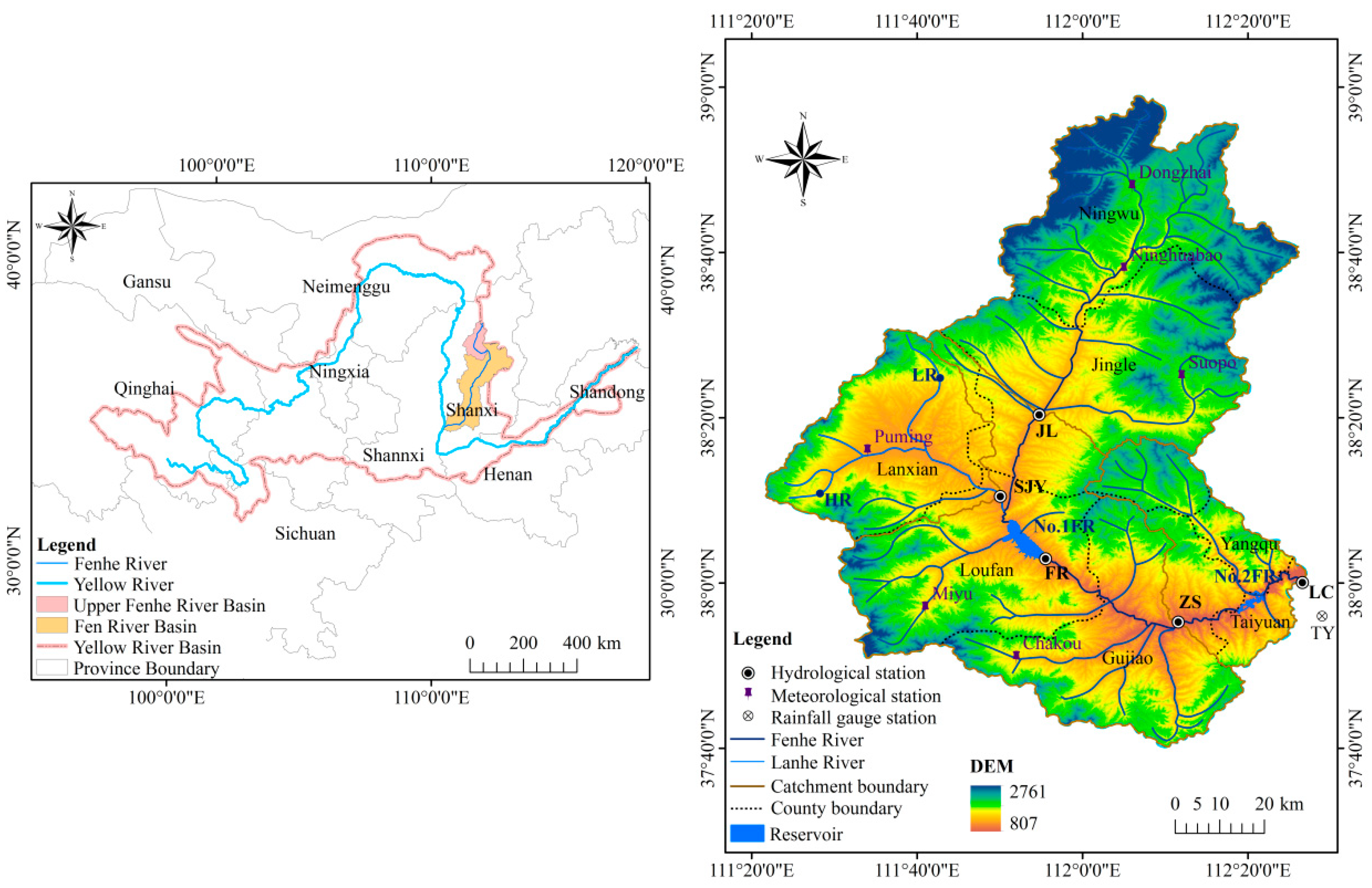
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Methods
3. Results
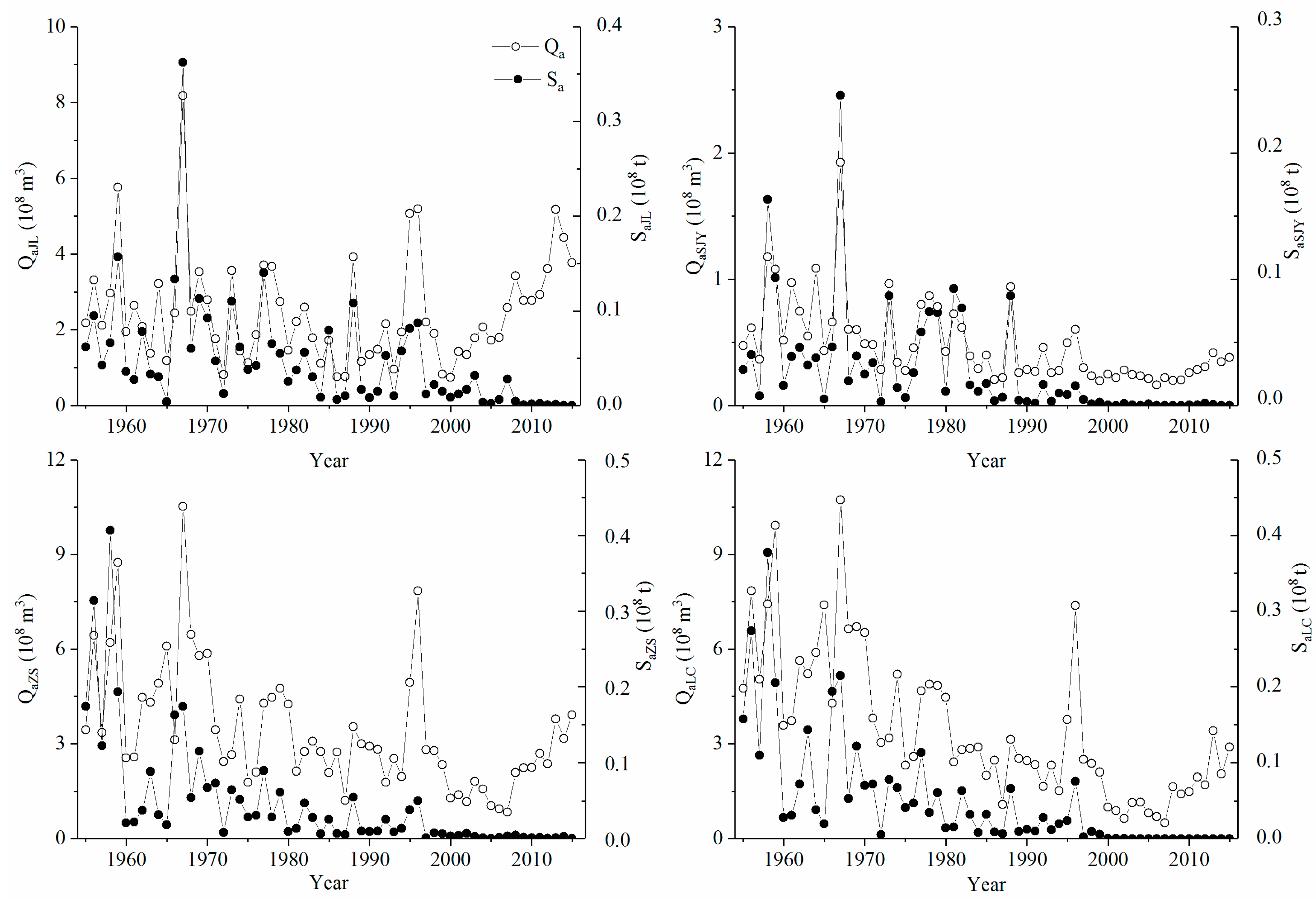
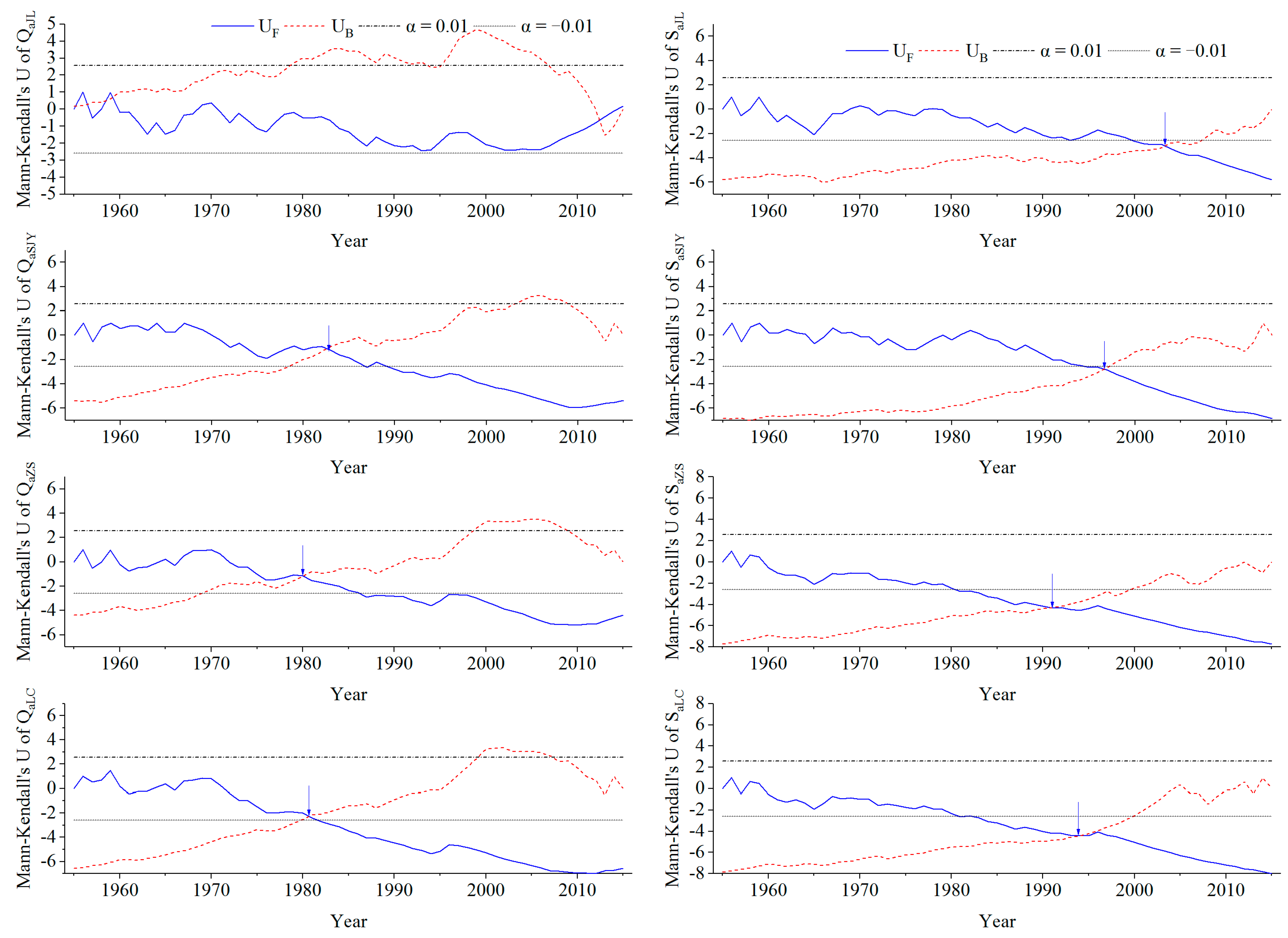
3.1. Temporal Variation in Qa and Sa Based on Mann–Kendall Tests
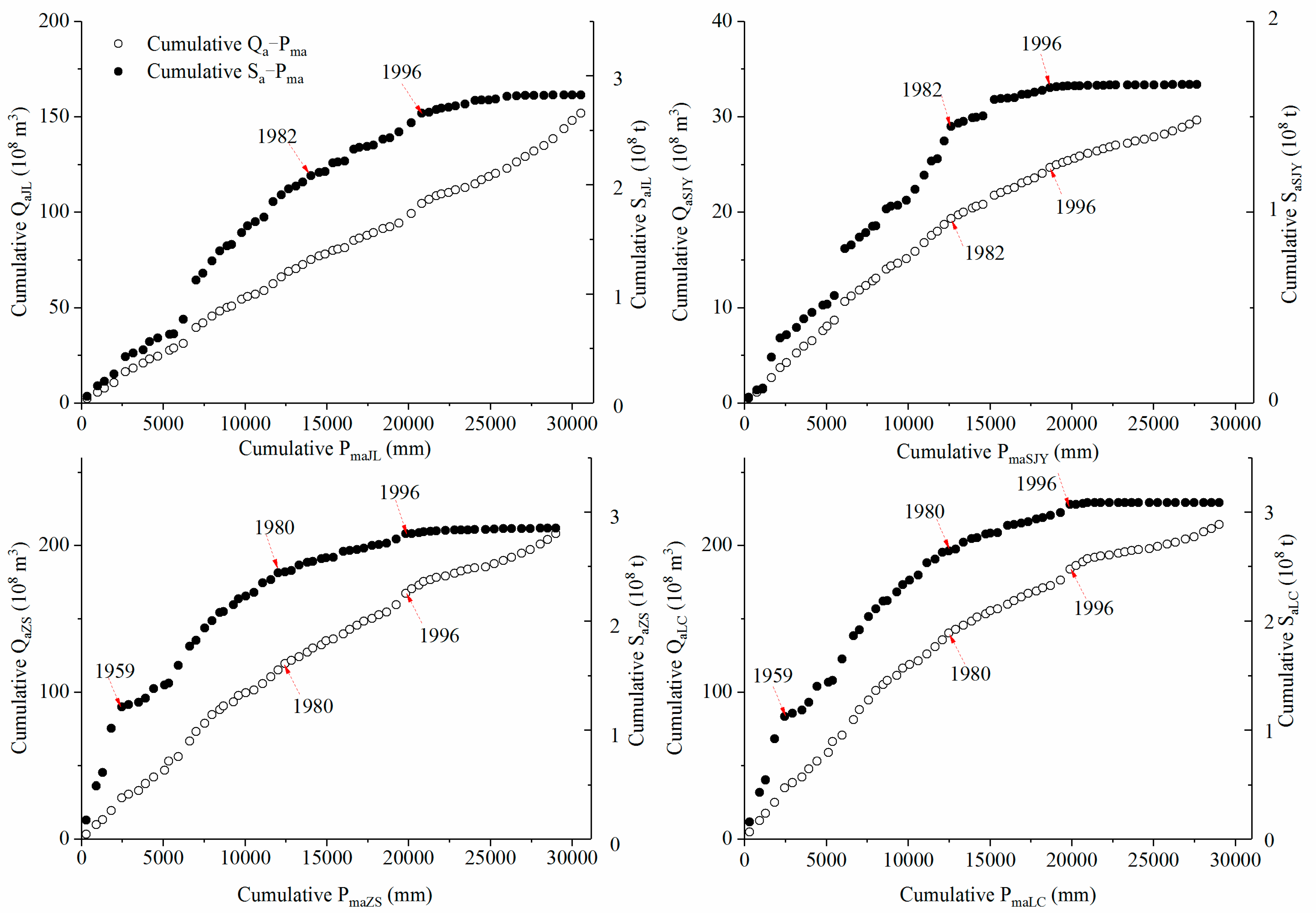
3.2. Temporal Variation of Qa–Pma and Sa–Pma Based on Double Mass Curves
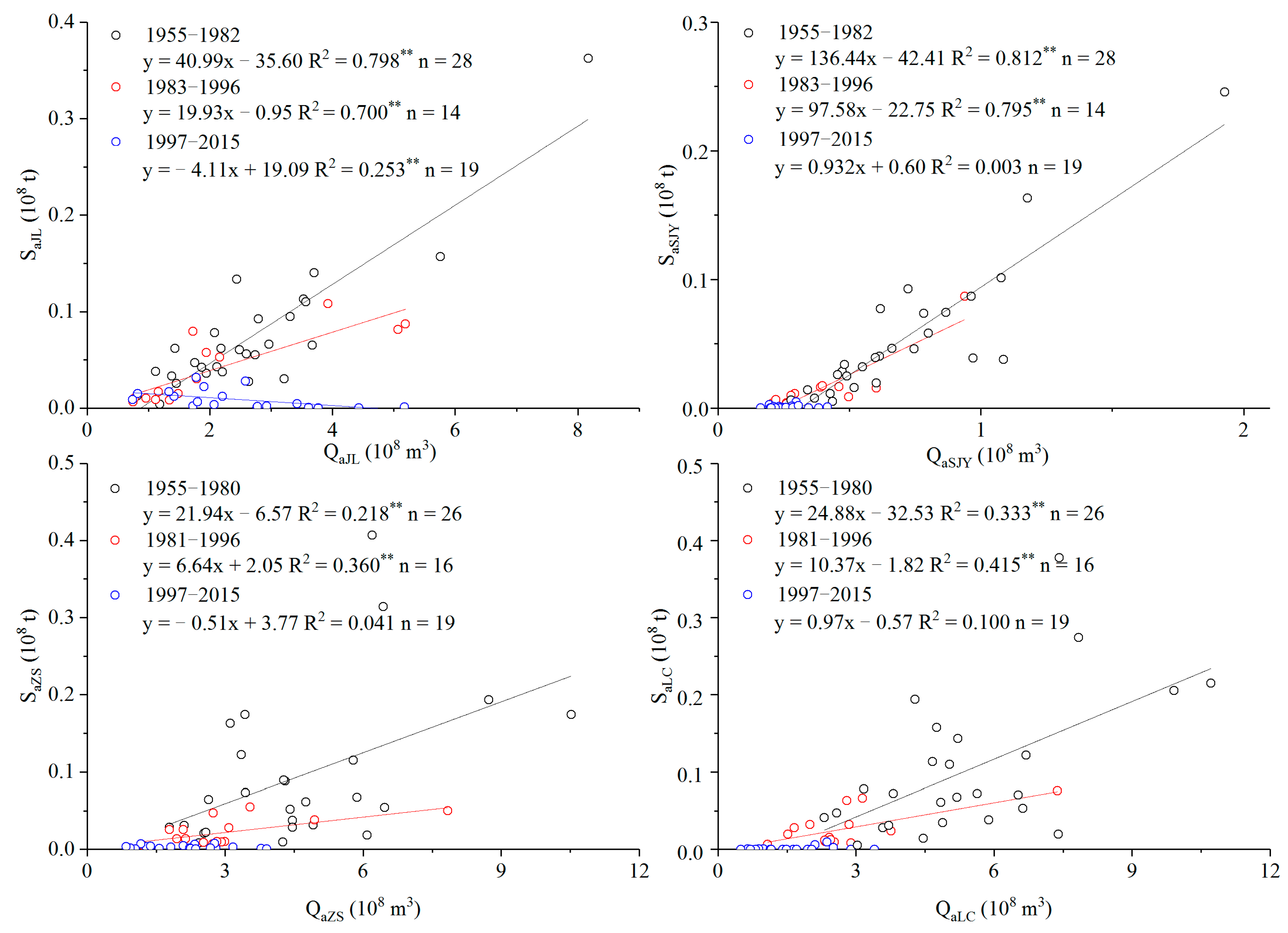
3.3. Changes in Average Qa, Sa, and the Qa–Sa Relationships during Three Separate Study Periods
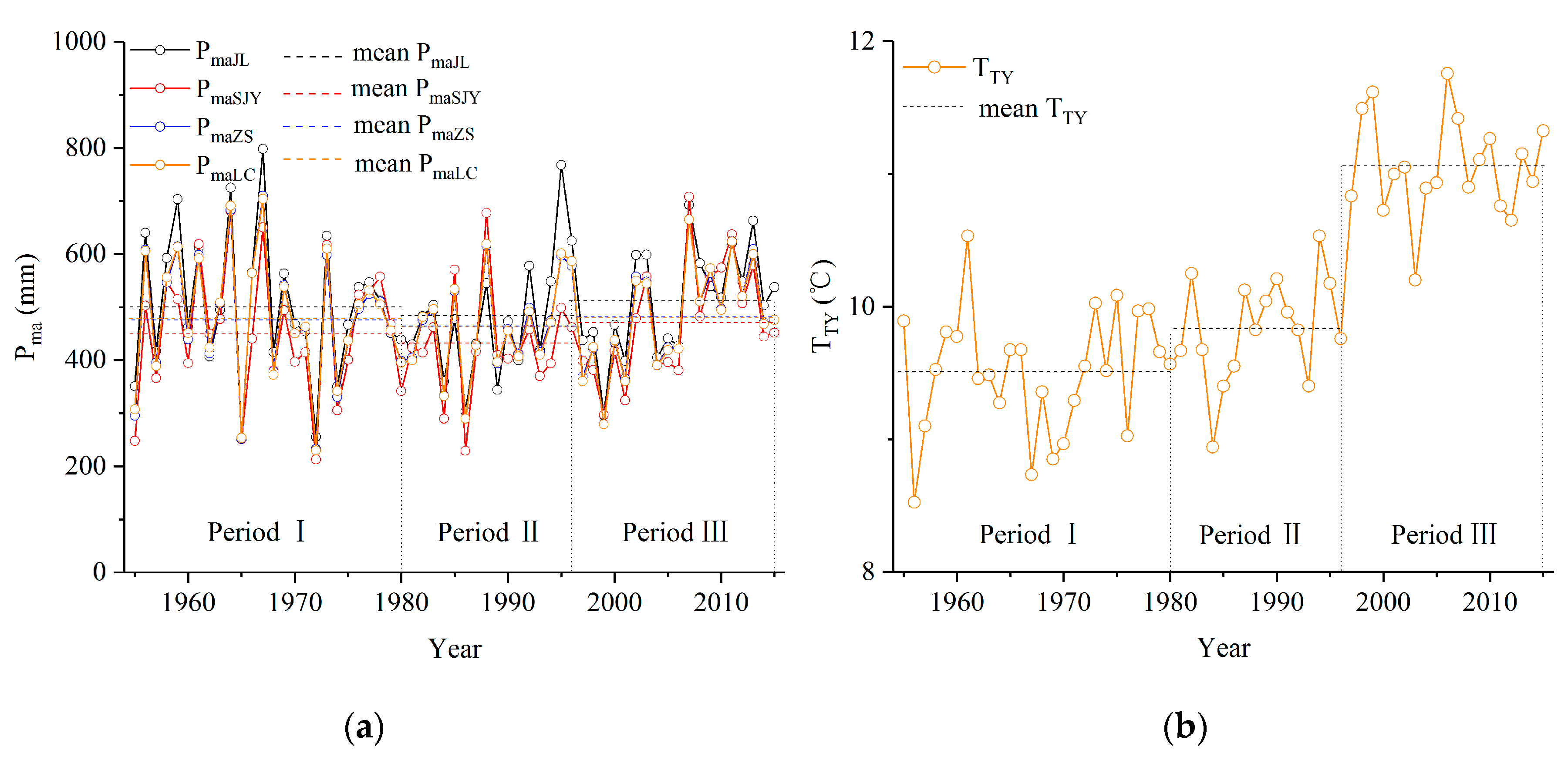
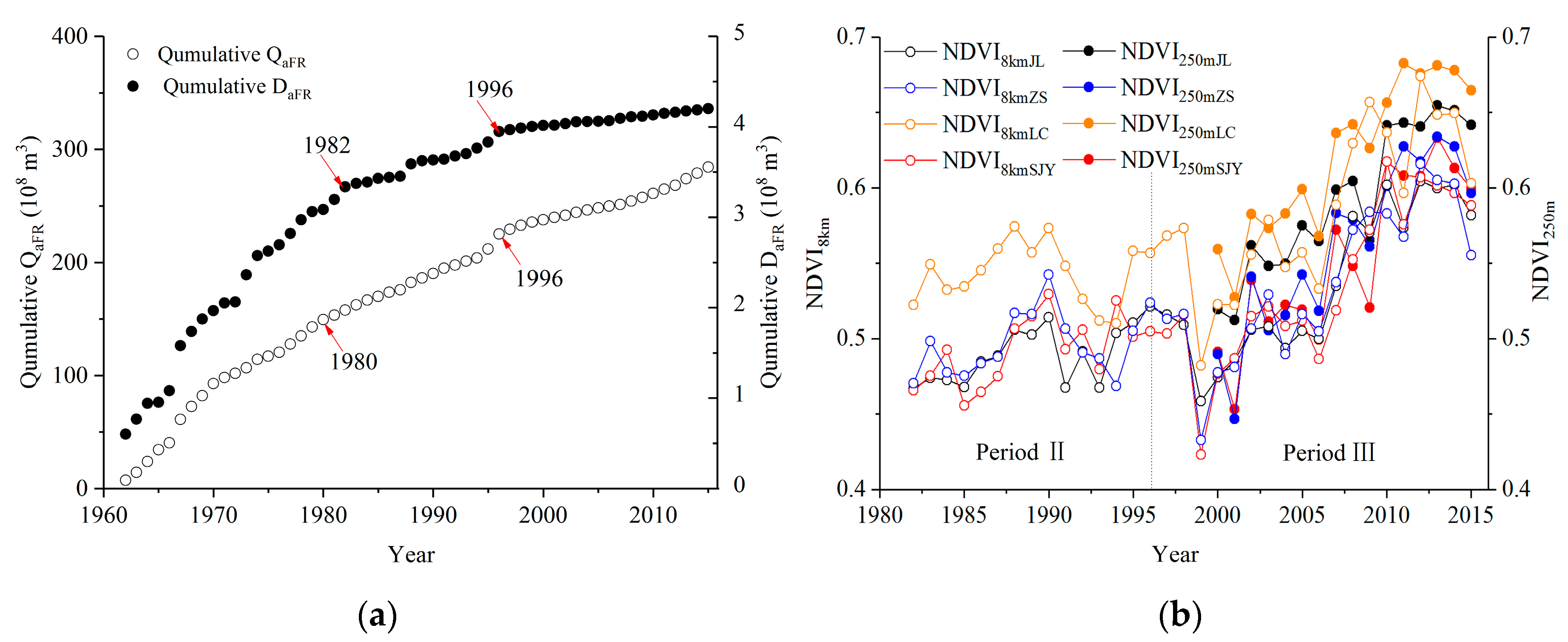
3.4. Temporal Variation in Potential Influential Variables
3.5. Pearson’s Correlations between Qa, Sa, and Potential Influencing Variables
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Tian, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, G. Responses of natural runoff to recent climatic variations in the Yellow River basin, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4471–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestir, E.L.; Schoellhamer, D.H.; Morgan-King, T.; Ustin, S.L. A step decrease in sediment concentration in a highly modified tidal river delta following the 1983 El Nino floods. Mar. Geol. 2013, 345, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Swain, D.L.; Touma, D. Anthropogenic warming has increased drought risk in California. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3931–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datsch Silveira, M.A.; Ribeiro, D.L.; Vieira, G.M.; Demarco, N.R.; Gregio d’Arce, L.P. Direct and Indirect Anthropogenic Contamination in Water Sources: Evaluation of Chromosomal Stability and Cytotoxicity Using the Allium cepa Test. Bull. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2018, 100, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Y.; Leininger, T.D.; Moran, M. Impacts of reforestation upon sediment load and water outflow in the Lower Yazoo River Watershed, Mississippi. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremicael, T.G.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Betrie, G.D.; van der Zaag, P.; Teferi, E. Trend analysis of runoff and sediment fluxes in the Upper Blue Nile basin: A combined analysis of statistical tests, physically-based models and landuse maps. J. Hydrol. 2013, 482, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Cohen, S.; Kettner, A.J.; Brakenridge, G.R. How important and different are tropical rivers?—An overview. Geomorphology 2014, 227, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusca, R.C.; Álvarez-Borrego, S.; Hastings, P.A.; Findley, L.T. Colorado River flow and biological productivity in the Northern Gulf of California, Mexico. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 164, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.J.; Fagherazzi, S.; Mei, X.F.; Gao, J.J. Decline in suspended sediment concentration delivered by the Changjiang (Yangtze) River into the East China Sea between 1956 and 2013. Geomorphology 2016, 268, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.J.; Mu, X.M.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.J.; Sun, W.Y. Changes in run-off and sediment load in the three parts of the Yellow River basin, in response to climate change and human activities. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, D.H.; Elnur, M.A.H. Detection of hydrologic trends and variability. J. Hydrol. 2002, 255, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Fang, D. Recent trends in the suspended sediment loads of the world’s rivers. Glob. Planet Chang. 2003, 39, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo Juan, D.; Escobar Heber, A. Sediment load trends in the Magdalena River basin (1980–2010): Anthropogenic and climate-induced causes. Geomorphology 2018, 302, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Chen, S.L.; Ping, D. Temporal variation of sediment load in the Yellow River basin, China, and its impacts on the lower reaches and the river delta. Catena 2010, 83, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.H.; Jiao, J.Y.; Zhao, G.J.; Zhao, H.K.; He, Z.; Mu, X.M. Spatial–temporal variation and periodic change in streamflow and suspended sediment discharge along the mainstream of the Yellow River during 1950–2013. Catena 2016, 140, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, X.P.; Rui, L.; Chen, L.L.; Lin, P.F. Did streamflow or suspended sediment concentration changes reduce sediment load in the middle reaches of the Yellow River? J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X.; Li, F.X. Response of lower Yellow River bank breachings to La Niña events since 924 CE. Catena 2019, 176, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X. Response of land accretion of the Yellow River delta to global climate change and human activity. Quatern. Int. 2008, 186, 0–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Q.; Liang, Z.M.; Bao, Z.X.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.M. Changes in streamflow and sediment for a planned large reservoir in the middle Yellow River. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 878–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Su, J.L.; Wang, Y.G.; Chen, Y. Study on water-sediment relationship in the Yellow River. J. Sediment. Res. 2019, 44, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.Y.; Fu, B.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Ma, Y.; Sivapalan, M. Multiscale temporal variability of flow-sediment relationships during the 1950s–2014 in the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.J.; Liang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.F. Driving forces of changes in the water and sediment relationship in the Yellow River. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 576, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.Q.; Gao, J.N.; Han, L. Changes and implications of the relationship between rainfall, runoff and sediment load in the Wuding River basin on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2019, 175, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E. The sediment delivery problem. J. Hydrol. 1983, 65, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.X.; Xu, J.X. A study of scale effect on specific sediment yield in the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. China 2007, 50, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.J.; Mu, X.M.; Strehmel, A.; Tian, P. Temporal variation of streamflow, sediment load and their relationship in the Yellow River basin, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.S.; Liang, S.J.; Wang, J. Analysis of discontinuous flow of the Fenhe River. Yellow River 1998, 20, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, H.F. Response of runoff in mid and upper reaches of Fenhe River to climate changes during the last 50 years. J. China Hydrol. 2006, 26, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Water Resources of Shanxi Province. Fenhe River Records; Shanxi People’s Publishing House: Taiyuan, China, 2006.
- Yao, W.X. Analysis on the sand production in the upstream basin of Fenhe reservoir. Shanxi Archit. 2007, 32, 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.Q. Vegetation in Shanxi Province; Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.J. Analysis on land-used cover change in the upper reaches of Fenhe River, China during 1976–1990. J. Shanxi Univer. Natur. Sci. Edit. 2008, 31, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.J.; Hou, Z.H.; Xu, X.L. The impact of land use change on ecology-economy harmony degree in the upper reaches of Fenhe River watershed. J. Desert Res. 2012, 32, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.P. Effect of Soil and Water Conservation on Siltation in Upper Fenhe Reservoir Reaches. Soil Water Conserv. Sci. Tec. Shanxi 2016, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.Z.; Yan, X.; Ren, G.P.; Wang, Y.Q. Summarization and application of high-tech in to Wanjiazhai Projects. Eng. Mech. 2007, 24 (Suppl. II), 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- NASA Modis Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer. Available online: https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/dataprod/mod13.php (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Holben, B. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Statistics in Shanxi Province. Shanxi Province Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1996–2015.
- Fan, X.H.; Wang, Q.X.; Wang, M.B. Changes in temperature and precipitation extremes during 1959–2008 in Shanxi, China. Appl. Clim. 2012, 109, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Measures; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric test against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. Public Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, J.M.; Pellegrino, G.Q.; Bsllrdyrt, M.V.; Martinelli, L.A.; Victoria, R.L.; Krusche, A.V. Trends in Hydrological Parameters of a Southern Brazilian Watershed and its Relation to Human Induced Changes. Water Resour. Manag. 1998, 12, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, X.M.; Liu, C.M.; Peng, B. Responses of runoff to climatic variation and human activities in the Fenhe River, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X. Trend of sediment yield in the coarser sediment producing area in the middle Yellow River basin in the period 1997–2007 and the formative cause. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Q.S.; Niu, Y.J. Effect of construction of check dams and reservoirs in Lanhe River Basin, Lanxian County. Sci. Tec. Soil Water Conserv. Shanxi Pro. 1995, 1, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Analysis on the Inflow and Outflow of Fenhe reservoir. Sci. Tech. Inf. Dev. Econ. 2010, 20, 165–167. [Google Scholar]
- History of Taiyuan. Available online: http://www.taiyuan.gov.cn/doc/2017/02/15/691195.shtml (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Rong, L.; Li, S.R. Thinking about solving the shortage of water resources in Taiyuan. Mod. Urban Res. 1995, 2, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, J.H.; Yan, S.Y.; Gu, P.; Wu, Z.N.; Hu, C.H. Application of MIKE SHE to study the impact of coal mining on river runoff in Gujiao mining area, Shanxi, China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravotta, C.A., III; Goode, D.J.; Bartles, M.D.; Risser, D.W.; Galeone, D.G. Surface water and groundwater interactions in an extensively mined watershed, upper Schuylkill River, Pennsylvania, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 3574–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M. A Brief Record of Water Consevancy Important Events in Shanxi Province (1949–2002); Shanxi Science and Technology Press: Taiyuan, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Kettner, A. Sediment flux and the Anthropocene. Philos Trans. R. Soc. A 2011, 369, 957–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.M.; Liu, Y.C.; Liang, A.Z. Influence of water resources on urban development of Taiyuan city and Countermeasures. Prod. Res. 2004, 2, 119–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.L. Analysis on the development of the depression cone of deep groundwater level in Taiyuan City in recent 25 years. Shanxi Hydrotech. 2018, 1, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, R.Q.; Zhang, W.X.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.Q. Impacts of water transfer from the Yellow River on water environment in the receiving area of the Fenhe River. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar]
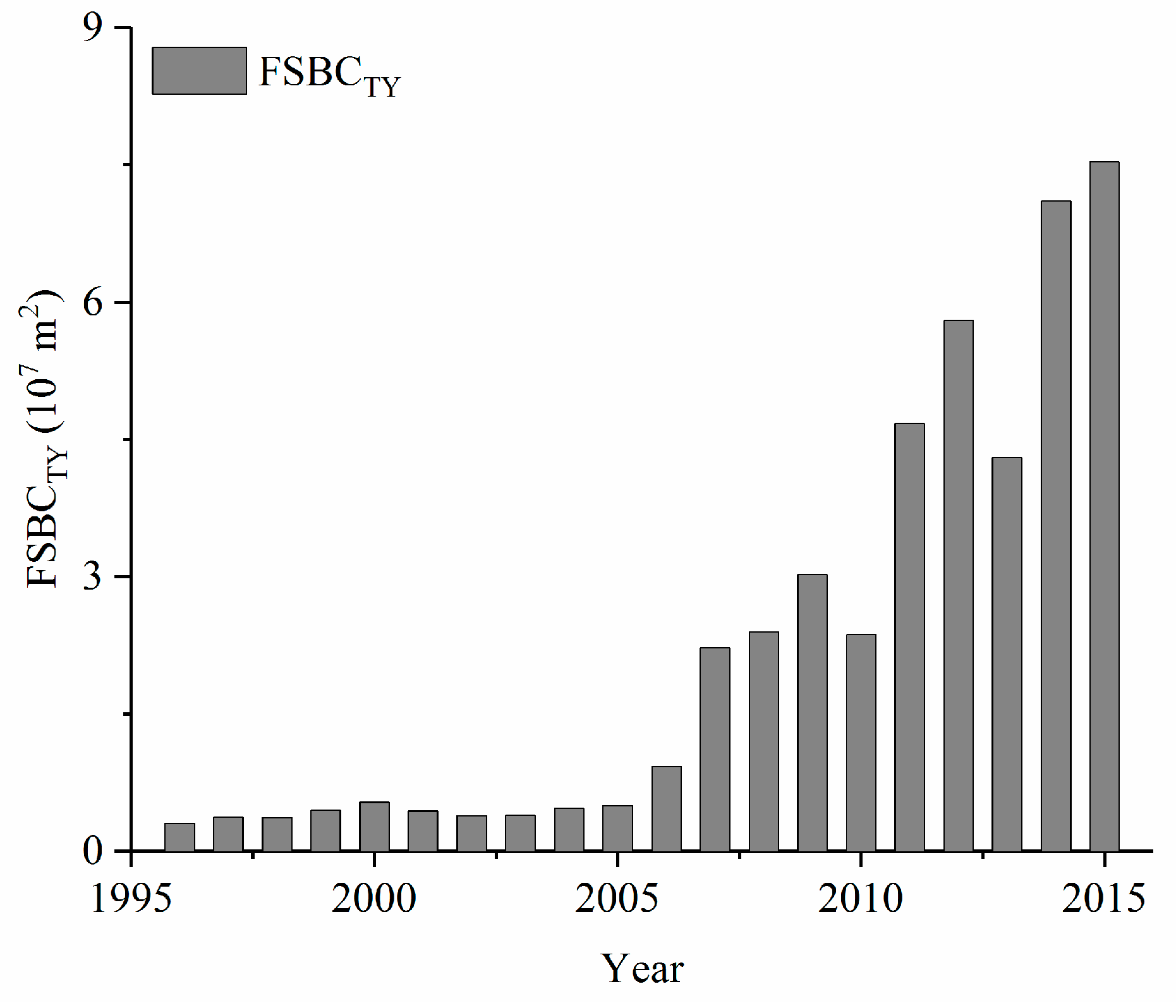
| Periods | PmaJL | PmaSJY | PmaZS | PmaLC | TTY | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (mm) | CV (%) | Mean (mm) | CV (%) | Mean (mm) | CV (%) | Mean (mm) | CV (%) | Mean (mm) | CV (%) | |
| 1955–1959 | 541 | 27.80 | 436 | 28.87 | 492 | 28.59 | 494 | 28.01 | 9.4 | 6.03 |
| 1960–1969 | 529 | 30.25 | 484 | 27.61 | 509 | 27.79 | 510 | 27.43 | 9.5 | 5.31 |
| 1970–1979 | 468 | 22.57 | 443 | 27.60 | 449 | 22.87 | 453 | 23.12 | 9.6 | 4.30 |
| 1980–1989 | 432 | 17.60 | 424 | 30.51 | 437 | 21.92 | 437 | 22.27 | 9.7 | 3.95 |
| 1990–1999 | 500 | 26.73 | 408 | 13.77 | 450 | 20.93 | 449 | 21.66 | 10.4 | 7.11 |
| 2000–2009 | 515 | 19.60 | 469 | 24.16 | 488 | 19.58 | 487 | 19.78 | 11.0 | 3.72 |
| 2010–2015 | 565 | 11.10 | 533 | 14.53 | 533 | 12.67 | 530 | 12.43 | 11.0 | 2.51 |
| Stations | Controlling Area (km2) | Qa (1955–2015) | Sa (1955–2015) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z | β | Z | β | ||
| (mm∙km−2∙a−1) | (t∙km−2∙a−1) | ||||
| JL | 2799 | 0.86 ns | 0.41 | −4.89 *** | −34.66 |
| SJY | 1140 | −5.05 *** | −0.68 | −3.17 ** | −54.39 |
| ZS | 6819 | −3.34 *** | −0.73 | −2.62 ** | −9.24 |
| LC | 7705 | −5.56 *** | −1.07 | −3.72 *** | −14.8 |
| Variable | 1955–1982 (Period I) | 1983–1996 (Period II) | 1997–2015 (Period III) | ||
| Mean (108 m3) | Mean (108 m3) | Change Rate (%) | Mean (108 m3) | Change Rate (%) | |
| QaJL | 2.68 | 2.10 | −21.77 | 2.49 | −7.25 |
| QaSJY | 0.69 | 0.38 | −44.53 | 0.26 | −62.29 |
| Variable | 1955–1982 (Period I) | 1983–1996 (Period II) | 1997–2015 (Period III) | ||
| Mean (105 t) | Mean (105 t) | Change Rate (%) | Mean (105 t) | Change Rate (%) | |
| SaJL | 74.37 | 40.88 | −45.03 | 8.87 | −88.08 |
| SaSJY | 51.73 | 14.59 | −71.79 | 0.85 | −98.36 |
| Variable | 1955–1980 (Period I) | 1981–1996 (Period II) | 1997–2015 (Period III) | ||
| Mean (108 m3) | Mean (108 m3) | Change Rate (%) | Mean (108 m3) | Change Rate (%) | |
| QaZS | 4.59 | 3.01 | −34.55 | 2.13 | −53.65 |
| QaLC | 5.39 | 2.73 | −49.46 | 1.60 | −70.35 |
| Variable | 1955–1980 (Period I) | 1981–1996 (Period II) | 1997–2015 (Period III) | ||
| Mean (105 t) | Mean (105 t) | Change Rate (%) | Mean (105 t) | Change Rate (%) | |
| SaZS | 94.20 | 22.02 | −76.62 | 2.69 | −97.14 |
| SaLC | 101.66 | 26.45 | −73.99 | 0.98 | −99.04 |
| Stations | Pma (1955–2015) | NDVI8km (1982–2015) | NDVI250m (2000–2015) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z | β (mm∙(10a)−1) | Z | β ((10a)−1) | Z | β ((10a)−1) | |
| JL | 0.13 ns | 0.90 | 2.96 ** | 0.033 | 4.36 *** | 0.097 |
| SJY | 0.33 ns | 3.13 | 3.33 *** | 0.036 | 3.56 *** | 0.101 |
| ZS | −0.15 ns | −1.13 | 2.84 ** | 0.034 | 4.01 *** | 0.108 |
| LC | −0.27 ns | −1.65 | 2.12 * | 0.026 | 4.16 *** | 0.104 |
| Correlation | JL | SJY | ZS | LC | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period I | Period II | Period III | Period I | Period II | Period III | Period I | Period II | Period III | Period I | Period II | Period III | |||||||||||||
| 1955–1982 | 1983–1996 | 1997–2015 | 1955–1982 | 1983–1996 | 1997–2015 | 1955–1980 | 1981–1996 | 1997–2015 | 1955–1980 | 1981–1996 | 1997–2015 | |||||||||||||
| r | n | r | n | r | n | r | n | r | n | r | n | r | n | r | n | r | n | r | n | r | n | r | n | |
| Qa−Pma | ★ | 28 | ★ | 14 | ◆ | 19 | ★ | 28 | ★ | 14 | ns | 19 | ns | 26 | ns | 16 | ns | 19 | ns | 26 | ns | 16 | ns | 19 |
| Qa−QaFR | ★ | 21 | ★ | 14 | ★ | 19 | ★ | 21 | ◆ | 14 | ★ | 19 | ★ | 21 | ★ | 16 | ★ | 19 | ★ | 21 | ★ | 16 | ★ | 19 |
| Qa−DaFR | ★ | 20 | ★ | 14 | ns | 19 | ★ | 20 | ★ | 14 | ns | 19 | ★ | 20 | ns | 16 | ns | 19 | ◆ | 20 | ns | 16 | ns | 19 |
| Qa−NDVI8km | -- | -- | ◆ | 14 | ★ | 19 | -- | -- | ns | 14 | ★ | 19 | -- | -- | ◆ | 15 | ◆ | 19 | -- | -- | ns | 15 | ns | 19 |
| Qa−NDVI250m | -- | -- | -- | -- | ★ | 16 | -- | -- | -- | -- | ★ | 16 | -- | -- | -- | -- | ★ | 16 | -- | -- | -- | -- | ★ | 16 |
| Qa–Sa | ★ | 28 | ★ | 14 | ◇ | 19 | ★ | 28 | ★ | 14 | ns | 19 | ◆ | 26 | ◆ | 16 | ns | 19 | ★ | 26 | ★ | 16 | ns | 19 |
| Sa−Pma | ★ | 28 | ★ | 14 | ns | 19 | ★ | 28 | ★ | 14 | ns | 19 | ns | 26 | ★ | 16 | ns | 19 | ◆ | 26 | ★ | 16 | ns | 19 |
| Sa−QaFR | ★ | 21 | ◆ | 14 | ◇ | 19 | ★ | 21 | ns | 14 | ns | 19 | ★ | 21 | ★ | 16 | ns | 19 | ◆ | 21 | ★ | 16 | ns | 19 |
| Sa−DaFR | ★ | 20 | ★ | 14 | ◆ | 19 | ★ | 20 | ★ | 14 | ns | 19 | ★ | 20 | ★ | 16 | ns | 19 | ★ | 20 | ★ | 16 | ns | 19 |
| Sa−NDVI8km | -- | -- | ns | 14 | ◇ | 19 | -- | -- | ns | 14 | ns | 19 | -- | -- | ns | 15 | ◇ | 19 | -- | -- | ns | 15 | ns | 19 |
| Sa−NDVI250m | -- | -- | -- | -- | ns | 16 | -- | -- | -- | -- | ns | 16 | -- | -- | -- | -- | ns | 16 | -- | -- | -- | -- | ◇ | 16 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Wu, Z.; Fan, X.; Li, H.; Meng, Q.; Wang, J. Variation in Runoff, Suspended Sediment Load, and Their Inter-Relationships in Response to Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities Over the Last 60 Years: A Case Study of the Upper Fenhe River Basin, China. Water 2020, 12, 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061757
Zhang L, Li S, Wu Z, Fan X, Li H, Meng Q, Wang J. Variation in Runoff, Suspended Sediment Load, and Their Inter-Relationships in Response to Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities Over the Last 60 Years: A Case Study of the Upper Fenhe River Basin, China. Water. 2020; 12(6):1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061757
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Luan, Suqing Li, Zhitao Wu, Xiaohui Fan, Hongjian Li, Qi Meng, and Jing Wang. 2020. "Variation in Runoff, Suspended Sediment Load, and Their Inter-Relationships in Response to Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities Over the Last 60 Years: A Case Study of the Upper Fenhe River Basin, China" Water 12, no. 6: 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061757
APA StyleZhang, L., Li, S., Wu, Z., Fan, X., Li, H., Meng, Q., & Wang, J. (2020). Variation in Runoff, Suspended Sediment Load, and Their Inter-Relationships in Response to Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities Over the Last 60 Years: A Case Study of the Upper Fenhe River Basin, China. Water, 12(6), 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061757





