Abstract
Adsorption has been regarded as one of the most efficient and economic methods for the removal of antibiotics from aqueous solutions. In this work, different graphene-based magnetic nanocomposites using a modified solvothermal method were synthesized and employed to remove sulfadiazine (SDZ) from water. The adsorption capacity of the optimal magnetic reduced graphene oxide (MrGO) was approximately 3.24 times that of pure Fe3O4. After five repeated adsorption cycles, the removal rate of SDZ (100 μg/L) by MrGO nanocomposites was still around 89.3%, which was only about a 3% decrease compared to that in the first cycle. Mechanism investigations showed that both chemical and physical adsorption contributed to the removal of SDZ. The excellent adsorption performance and recyclability of MrGO nanocomposites could be attributed to their wonderful 3D interconnected petal-like structures. The MrGO with SDZ could be easily recollected by magnetic separation. The MrGO also exhibited excellent adsorption performance in the purification of real polluted water.
1. Introduction
Antibiotics, an important group of pharmaceuticals used in humans and animals, have caused significant concern in recent years due to their wide occurrence and resistance. Most antibiotics are partially metabolized in organisms and excreted to the environment through urine and feces in the form of their parent compounds or metabolites [1]. The concentration of some antibiotics has been measured to reach a ppm level in hospitals or sewage effluents [2]. Sulfadiazine (SDZ, the total usage was 1260 t/yr in 2013), the second most widely used pharmaceutical of 13 kinds of common sulfonamides in China [3], has been widely detected in different environments, such as wastewater treatment plants [4], hospitals [5], groundwater [6], and livestock farms [7]. Exposure to low concentrations of antibiotics, such as SDZ, could lead to the accumulation and spread of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) and antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB), which are expected to impact the ecosystem and human health [1,2].
To remove antibiotics, large numbers of studies have been carried out to develop treatment technologies. Among the technologies investigated, adsorption is regarded as one of the most efficient and economic approaches for the removal of antibiotics from aqueous solutions [8,9]. Mesoporous materials are used as adsorbents because of their high surface area and versatile surface functional groups, which have attracted increasing attention [10,11]. Reduced graphene oxide (rGO), a derivative of graphene, shows great promise as an effective adsorbent because of its large specific surface area and abundant pore structures [12,13]. During the past few years, many studies have been carried out to investigate the removal of heavy metal ions and dyes using rGO and very promising results have been achieved. Some reports show that the maximum adsorption capacities for methylene blue and Pb2+ could reach to 433 and 416 mg/g [14,15], respectively. However, few investigations on the interaction between antibiotic contaminants and graphene-based materials have been conducted. The structure of different kinds of antibiotics may vary greatly, and different driving forces are generated in the adsorption process. Some zwitterionic antibiotics carry cations or anions and are readily adsorbed by anionic or cationic adsorbents. Some antibiotics are rich in aromatic ring structures, producing π–π electron in the forms of a donor-acceptor with rGO [16,17]. SDZ is used in large quantities and contains an aromatic ring in its structure. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the adsorption process of SDZ on graphene-based materials.
Due to the van der Waals force and π–π interactions between layers [18], free-standing rGO nanosheets are easy to stack and agglomerate, which decreases the specific surface area and adsorption capacity. It is difficult for pollutants to acquire paths into the inner layers of the stacked graphene. To retain the inherent property of graphene, three-dimensional (3D) graphene was constructed [19,20]. Although this kind of structure improved the performance of graphene to some extent, the separation and recycle of rGO emerges to be another important issue. Recently, magnetization-introduced Fe3O4 nanoparticles have been focused and developed benefiting from the rapid and facile separation using a magnet [21,22]. However, although magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles have good biocompatibility and stability, their weak adsorption capacity is an issue. As a result, it is urgent to fabricate rGO-integrated magnetic Fe3O4 nanocomposites with 3D interconnected porous structures.
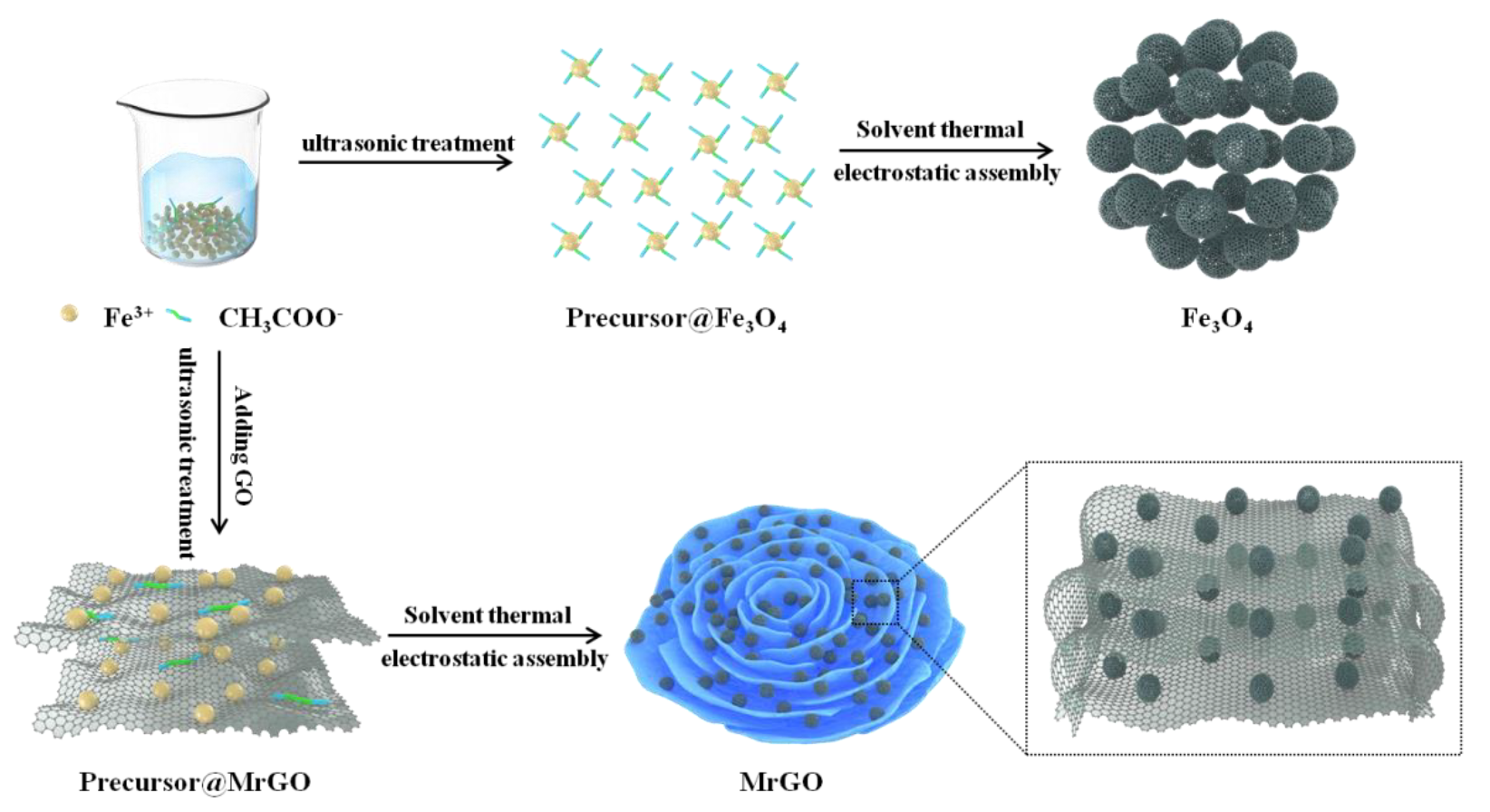
Herein, we prepared a series of magnetic material using a modified solvothermal method. Materials were synthesized via the reduction of FeCl3 using an ethylene glycol solvent with sodium acetate as an electrostatic stabilizer and alkali source. By controlling the content of rGO, the MrGO magnetic nanocomposites with different porous structures were synthesized. To evaluate the adsorption performance, SDZ was selected as the target contaminant. Batch experiments and different analysis methods were carried out. The results from this work could help find an effective method to obtain magnetic nanocomposites with porous structures, avoiding the stacking and aggregation of rGO nanosheets.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
Flake graphite, ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O), sodium acetate (CH3COONa), and ethylene glycol (EG) were purchased from Guangzhou Chemical Regent Company (Guangzhou, China). SDZ (purity 99.1%) was purchased from Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH (Augsburg, Germany). All chemicals used in this study were of analytical grade. Ultrapure water (≥18 MΩ cm) was used to prepare experimental solutions throughout this study.
2.2. Preparation of MrGO
Graphene oxide (GO) was prepared using natural flake graphite with a modified Hummer method. The details can be found in our previous work [23]. For the preparation of MrGO, 1.05 g FeCl3·6H2O and 1.8 g CH3COONa were dissolved in a 100-mL EG solution. Then, 0.1 g GO was added and the resulting suspension was stripped by ultrasonic treatment for 2 h to obtain a homogeneous colloidal solution. The solution was stirred continually for 1 h. Next, 50 mL of the colloidal solution was transferred into a teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave (100 mL) and heated at 200 °C for 10 h. When the autoclave naturally cooled to the room temperature, the magnetic nanocomposite was prepared. The nanocomposite was washed several times with deionized water, recollected magnetically, and freeze-dried for 12 h. The resulting magnetic nanocomposite was named as MrGO-1.
A pure Fe3O4 sample, used as a benchmark, was prepared using the same procedure as described above, except that no GO was added. Similarly, MrGO-2 (0.2 g GO) and MrGO-3 (0.3 g GO) were prepared by controlling the amount of GO. Moreover, rGO was synthesized using the same approach as stated above. The schematic illustration of preparing the MrGO nanocomposites is shown in Figure 1.
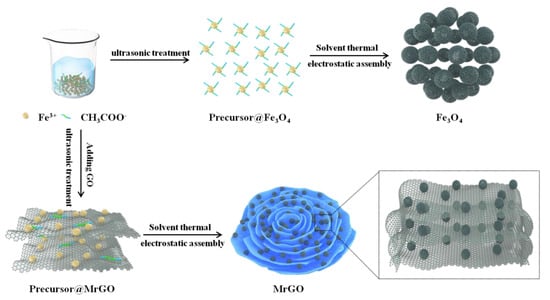
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of preparing the MrGO nanocomposite.
2.3. Material Characterizations
Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD, D/MAX 2200 VPC, Rigaku, Japan) was used to characterize the crystalline structures with Cu K α (λ = 1.5406 Å) radiation at a scan step of 0.2 s−1 from 5° to 80°. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR, Spectrum two, Perkin-Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA) was used to study the functional groups on the material surfaces. The magnetic properties (VSM) were investigated using a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometer (MPMS3). Thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA, STA409PC, Netzsch, Germany) was used to confirm the content of the composite under air in the temperature range of 30–800 °C. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET, ASAP-2020, Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA) was conducted to measure the specific surface area and pore size distribution under N2 adsorption/desorption. The particle size properties were measured using a particle size analyzer (Zetasizer Nano ZS90, Malvern, England). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, ESCALab250, ThermoFisher, Dreieich, Germany) was applied to determine the surface chemical compositions and electronic structures. The morphologies and microstructures were observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, ZEISS Ultra-55, Oberkochen, Germany) and a transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEM-1600HR, JEOL, Toyko, Japan).
2.4. Adsorption and Recyclability Experiments
To study the adsorption kinetics of SDZ, batch experiments were conducted. A standard SDZ solution with a concentration of 400 μg/L was prepared in advance. Then, five types of the as-prepared absorbents (5 mg) were added respectively into centrifuge tubes (50 mL) containing the SDZ standard aqueous solution (20 mL). The samples were stirred in a rotating shaker (WSZ-100A, Shanghai Yiheng, Shanghai, China) with a speed of 180 rpm at 25 °C. The solution pH was not controlled because no obvious variation (<0.2) occurred after the adsorption. At the preselected adsorption time (0.5–24 h), a series of samples (1 mL) were withdrawn with syringes and filtered through 0.22-μm PES filter membranes (The recovery was about 98.5%). The residual concentrations of SDZ were measured using LC-MS. Control experiments were also conducted simultaneously through the same procedures without adding an adsorbent. The adsorption isotherms were studied with a series of different initial concentrations of SDZ (50–2000 μg/L) using the same procedure stated above and the adsorption time was fixed at 3 h. All the batch adsorption experiments were performed in duplicate.
The recyclability experiments were conducted as follows. A standard SDZ solution with a concentration of 100 μg/L was prepared. Next, 5 mg of the as-prepared adsorbent was added, and adsorption reactions were performed with the same procedures as mentioned above, but the adsorption time was changed to 3 h. After the supernatant was quickly separated by a magnet, the precipitates were recollected and re-dispersed in a 20 mL NaOH solution (0.1 M) for the desorption of SDZ. The experimental parameters of the desorption process were in accord with those of the adsorption. Next, the recollected adsorbent was washed with deionized water until the pH value reached to near 7. After that, the adsorbent was reused for SDZ adsorption. These procedures were repeated five times.
Different water samples were collected to evaluate the practical application potential of the adsorbents. Lake water (LW), river water (RW), and waste water (WW) were collected from the Liuxi Lake, East River, and the effluent of Guangzhou Liede Waste Water Treatment Plant, respectively, which are all located in the Pearl River Basin, Guangdong, China. The water samples were filtered through 0.45-μm PES filter membranes within 24 h and then stored at 4 °C until use. These real water samples were characterized, and the results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Properties of real water samples.
The adsorption capacity (Qt, μg/mg, Equation (1)) of adsorbent and removal efficiency (w, %, Equation (2)) of SDZ were calculated as follows:
where C0 and Ce (μg/L) are the initial and equilibrium concentrations of SDZ, respectively, m (mg) is the mass of the adsorbent, and V (L) is the volume of SDZ solution.
The pseudo-first-order model (Equation (3)) and pseudo-second-order model (Equation (4)) were used to investigate the adsorption kinetic:
If Qe is measured in the experiments, the fractional uptake (F) with respect to the equilibrium can be calculated via Equation (5):
F(t) = Qt/Qe
Substituting Equation (3) into Equation (5) yielded:
When Equation (4) was substituted into Equation (5), the fractional uptake could be expressed:
where Qe (μg/mg) is the adsorption capacity at the equilibrium state, t (h) is the predetermined time, k1 (h−1) is the pseudo-first-order adsorption rate constant, and k2 (mg/(μg·h)) is the pseudo-second-order adsorption rate constant.
The Langmuir (Equation (8)) and Freundlich (Equation (9)) models were used to analyze the adsorption isotherm data:
where KL (L/μg) is the Langmuir isotherm constant, Qm (μg/mg) is the maximum adsorption capacity, KF (μg/mg (L/μg)1/n) is the Freundlich isotherm constant, and n is the measure of adsorption intensity.
Qe = KFCe1/n
2.5. Chemical Analysis
The concentration of SDZ in the residual solution was analyzed using an ACQUITY UPLC-Xevo TQ MS system (Waters, Milford, MA, USA). The mobile phase consisted of methanol and ultrapure water (0.1% formic acid) at a volume ratio of 60:40, and a BEH-C18 column (1.7 μm, 2.1 mm × 100 mm) was used for the separation. The flow rate was set at 0.3 mL/min and the column temperature 40 °C. An injection volume of 10 μL was used for all samples. Calibration curves were established using a series of standard SDZ solutions in the range of 10 to 400 μg/L.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
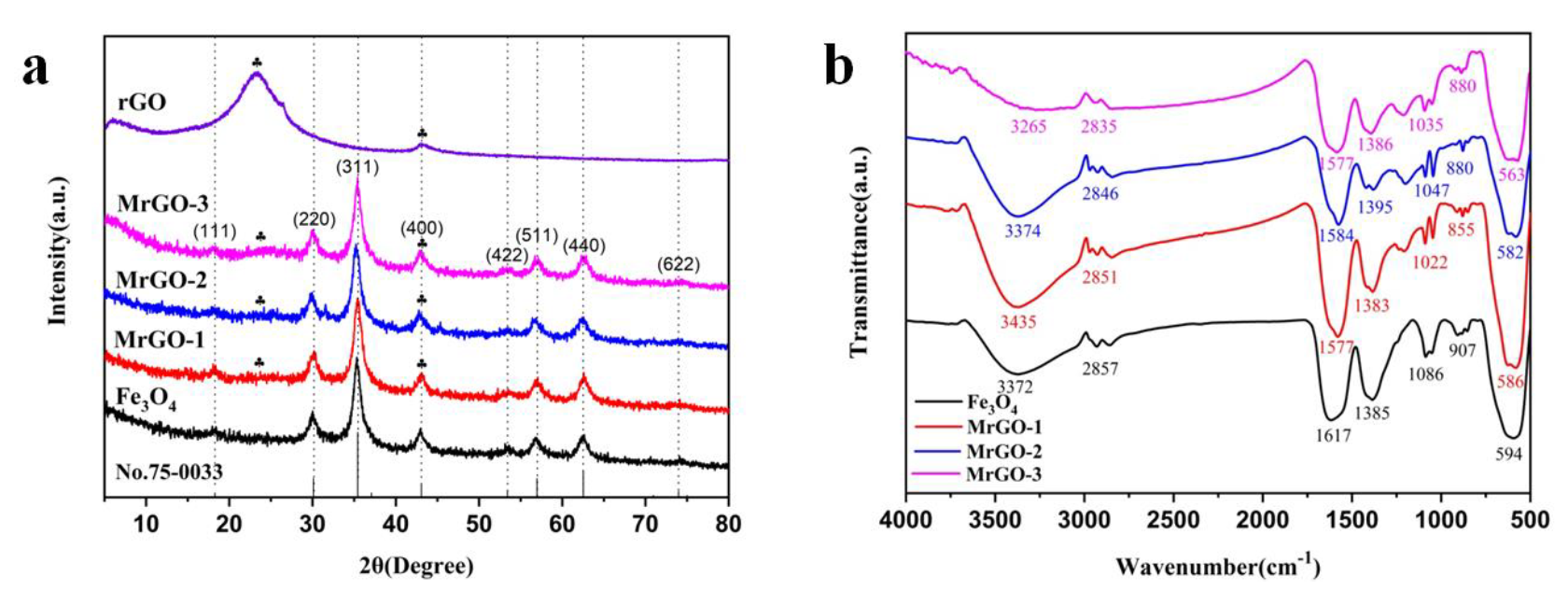
The XRD spectra of Fe3O4, MrGO-1, MrGO-2, MrGO-3, and rGO were shown in Figure 2a. In the spectrum of the Fe3O4 sample, diffraction peaks were observed at 2θ = 18.3°, 30.1°, 35.5°, 43.1°, 53.5°, 57.0°, 62.6°, and 75.1°, which can be indexed to the (111), (220), (311), (400), (422), (511), (440), and (662) planes of Fe3O4 (JCPDS No.75-0033), respectively. These diffraction peaks were also observed in the spectra of MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3. The peaks were sharp and intense, which demonstrates a well-crystallized form of magnetic materials. In the 2θ range of 20–25°, the rGO sample shows a broad diffraction peak, which corresponds to the (002) plane of rGO amorphous carbon [23]. As shown in the spectra of MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 samples, the weak signals of rGO could also be tracked [24]. With increasing content of rGO, the corresponding peaks of the nanocomposites became increasingly obvious. These results reveal that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles in the MrGO nanocomposites were successfully deposited onto the rGO nanosheet. The FTIR spectra data are shown in Figure 2b. The characteristic band near 600 cm−1 is intense, owing to the bending vibration of the Fe-O bonds [25]. Meanwhile, six peaks at around 3400 cm−1, 2850 cm−1, 1600 cm−1, 1385 cm−1, 1050 cm−1, and 900 cm−1 were observed in all of the four types of samples, which may be ascribed to the functional groups introduced by ethylene glycol and sodium acetate during the reaction [26]. A broad stretching band at around 3400 cm−1 represents the stretching vibration of -OH and H-OH, probably due to the presence of residual water. The bands at 2850 cm−1 and 1050 cm−1 are assigned to the stretching and bending vibration of -CH2, respectively. The other bands at 1600 cm−1, 1385 cm−1, and 900 cm−1 can be ascribed to the stretching and bending vibration of C=O, C-H, and C-C bonds, respectively [27]. The FTIR results show that many oxygen-containing functional groups were present on the surface of the as-prepared materials.
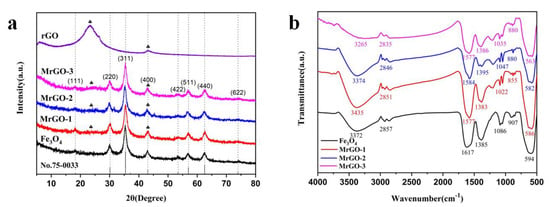
Figure 2.
(a) XRD patterns of materials; and (b) FTIR spectra of materials.
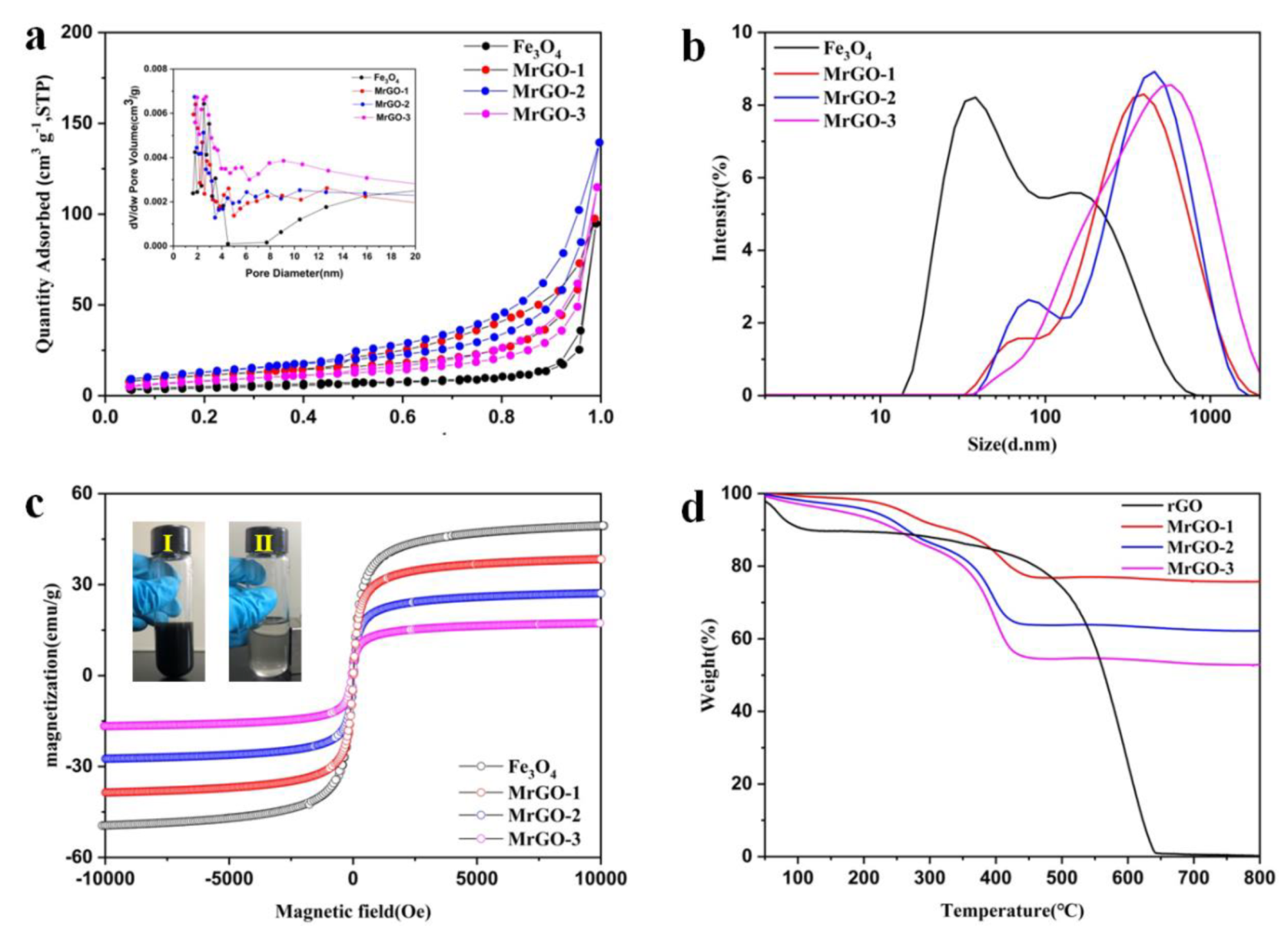
The porous properties of the four types of magnetic materials were tested (Figure 3a). The BET-specific surface areas of Fe3O4, MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 are 15.28 m2/g, 30.08 m2/g, 47.62 m2/g, and 38.44 m2/g, respectively. After incorporating rGO, the specific surface areas of magnetic materials were greater than that of pure Fe3O4. The pore size distribution of the materials shows that they are mesopore materials. The Fe3O4, MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 magnetic materials show two scope pore sizes centered at 2–4 nm and 8–50 nm, respectively. The smaller one may be attributed to the mesopore rGO and the larger one may be resulted from the aggregation and staking of Fe3O4 [28]. In general, improvement of specific surface areas and abundant pore structures of MrGO are closely related to the adsorption capacity. The average sizes of Fe3O4, MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 magnetic materials were 55.1 nm, 260.9 nm, 249.3 nm, and 319.9 nm, respectively (Figure 3b). To investigate the magnetism, the hysteresis loops of the as-prepared materials were recorded at room temperature (Figure 3c). All these samples show ferromagnetic behavior [29]. The corresponding saturation magnetizations (Ms) of Fe3O4, MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 are 51.2 emu/g, 38.5 emu/g, 22.7 emu/g, and 14.1 emu/g, respectively. This may be beneficial for chain formation due to the magnetic dipole interaction in the adsorption process. With the increase of rGO content, the saturation magnetization of MrGO nanocomposites decreases gradually.
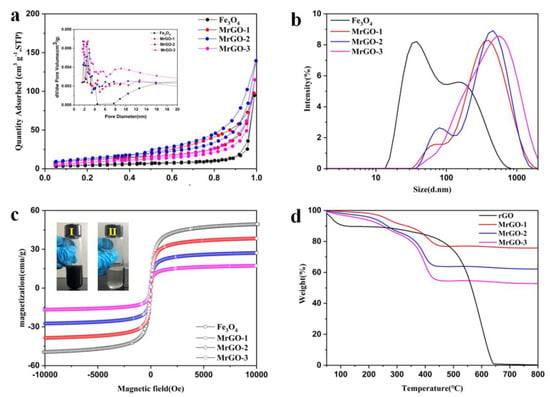
Figure 3.
(a) N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms of four types magnetic materials (the inset is BJH pore distribution data); (b) size distribution of four types magnetic materials; (c) the magnetic hysteresis loops of four types magnetic materials (digital image of separation of MrGO-0.2 in water, (Ⅰ) before and (Ⅱ) after magnetic separation); (d) TGA curve of magnetic materials.
The thermo gravimetric analysis of MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 was measured under an air atmosphere to reveal the compositions of MrGO nanocomposites (Figure 3d). The nanocomposites mainly display two stages of weight loss. The first stage of the slight weight loss (about 2–6 wt %) is ascribed to the evaporation of surface-adsorbed water and solvent molecules under 200 °C. The second stage of the major weight loss is mainly resulted from the decomposition of the rGO skeleton and the removal of the oxygen-containing functional groups at 200–430 °C [30,31]. The residual mass percentages of the prepared MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 nanocomposites are about 75.7%, 62.3%, and 52.9%, respectively. These values are the weight percentages of Fe3O4 in the MrGO nanocomposites.
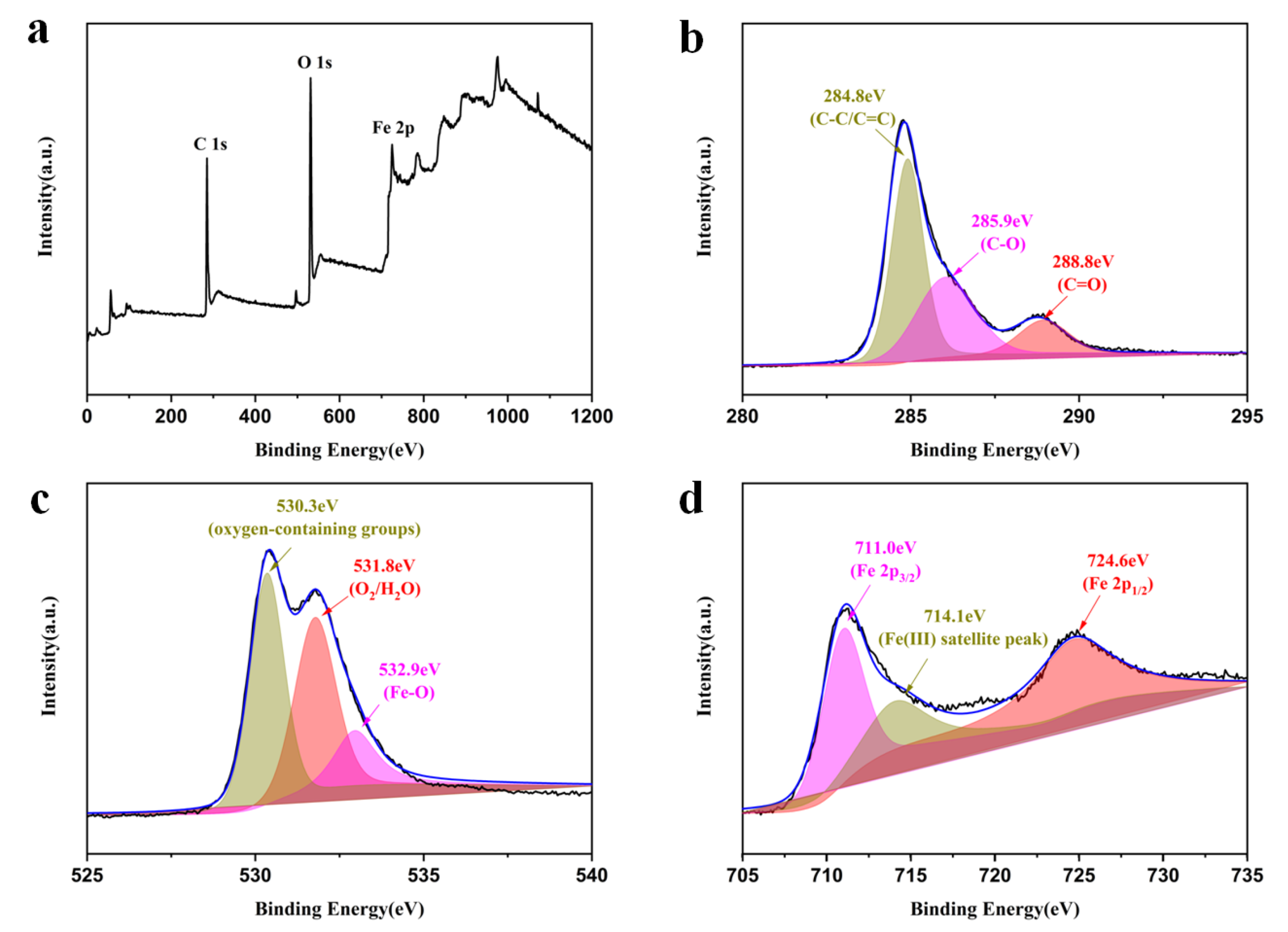
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was used to further study the surface chemical composition and electronic structure. The XPS survey results show the presence of C, O, and Fe elements in MrGO-2 (Figure 4a). The high-resolution XPS spectra of C 1 s, O 1 s, and Fe 2p were recorded as shown in Figure 4b–d. The C 1s XPS spectrum of the MrGO-2 (Figure 4b) contained three main components including the C-C/C=C (284.8 eV), C-O (285.9 eV), and C=O (288.8 eV) functional groups, which are in great agreement with previously reported work. Additionally, the highest peak value is at 284.8 eV, proving that the sp2 bonding of carbon atoms is the main species [32,33]. It can be seen from the spectrum of O 1s (Figure 4c) that the three peaks at 532.9 eV, 531.8 eV, and 530.3 eV belong to Fe-O, H2O molecules, and oxygen-containing groups (-OH and -COOH) [34], respectively. In Figure 4d, the Fe 2p3/2 and the Fe 2p1/2 XPS spectrums demonstrate that the peaks of binding energies are around 711.0 eV and 724.6 eV. The satellite peak indicates the characteristic peaks of γ-Fe2O3, which suggests the presence of Fe (Ⅲ) on the rGO surface [35].
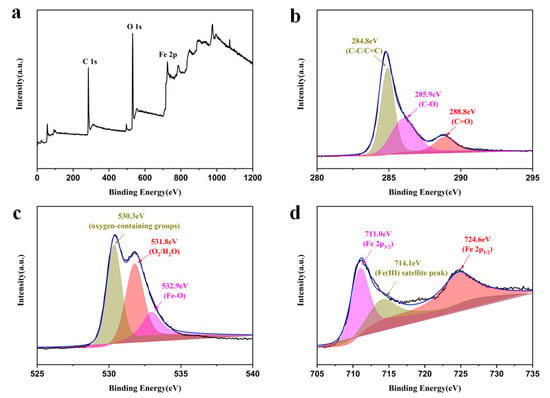
Figure 4.
XPS spectra: (a) survey scan, (b) C 1s spectrum, (c) O 1s spectrum, and (d) Fe 2p spectrum of MrGO-2.
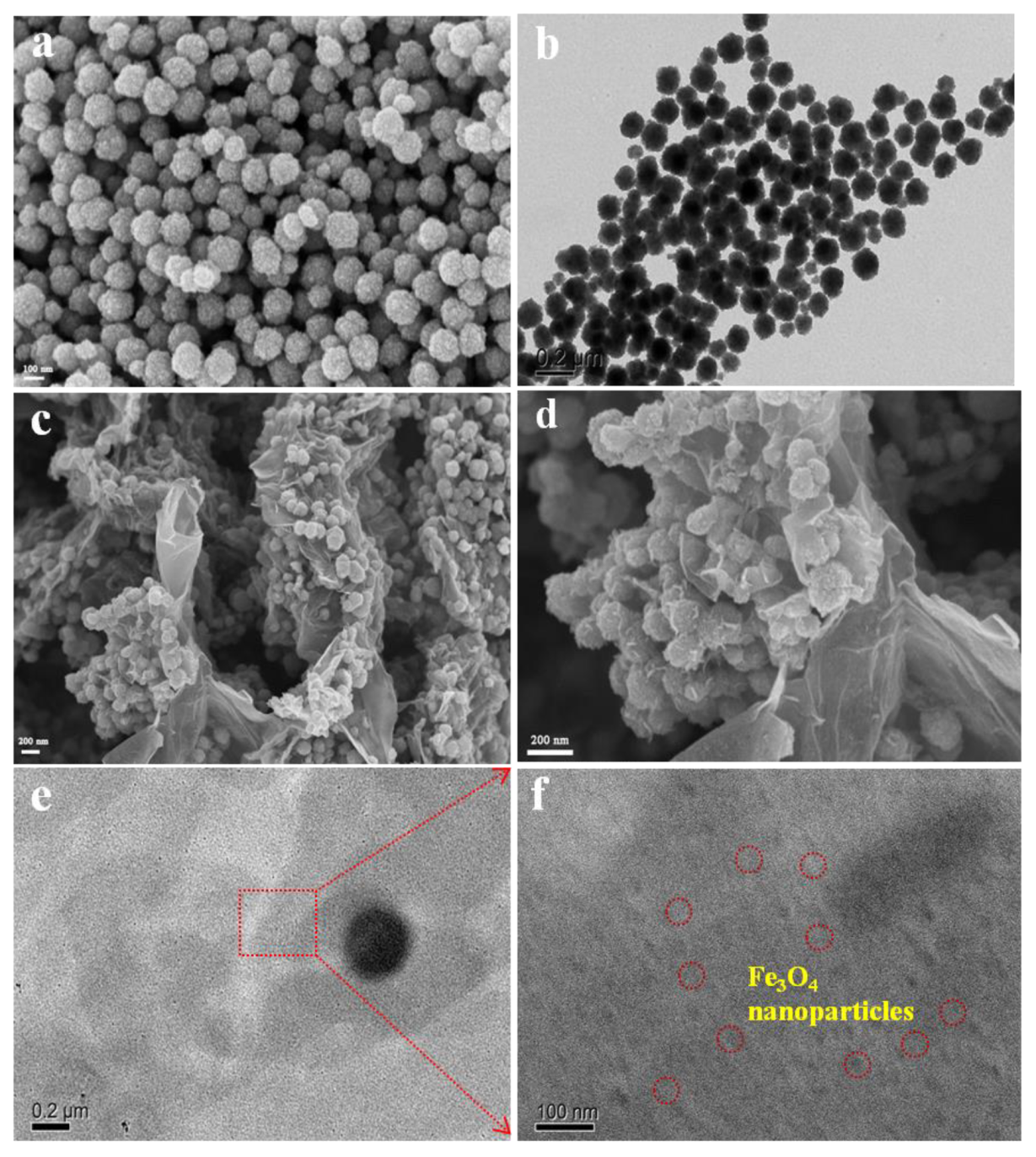
To investigate the morphologies and microstructures of magnetic materials, their SEM and TEM images were recorded (Figure 5). It can be observed that the Fe3O4 exhibits a regular and homogeneous nanoparticle structure (Figure 5a,b). The diameters of most nanoparticles are less than 100 nm without obvious agglomeration, which exhibits good crystallinity after reaction. Interestingly, the MrGO-2 presents a wonderful 3D petal-like structure (Figure 5c,d). This is because the rGO nanosheets were curled and entangled together layer by layer and performed bottom-up electrostatic assembly to form the unique petal-like structure during the reaction. The rGO spread outward so that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles could anchor onto the petal. On one hand, this rGO nanosheet outside could bring large numbers of active sites and target contaminants may be adsorbed from multiple directions, producing π−π electron donor-acceptors combined with rGO. On the other hand, the Fe3O4 on the petal could serve as a magnetic core, aggregating contaminants preventing them from desorption. Figure 5e,f displays the TEM images of MrGO-2 in different magnifications. The MrGO-2 is thin and transparent without restacking and agglomeration. Large numbers of Fe3O4 nanoparticles are uniformly distributed onto the rGO nanosheet and the diameter of the nanoparticle is about 30–50 nm. There seems to be good adhesion between Fe3O4 and rGO, which may greatly affect the adsorption performance.
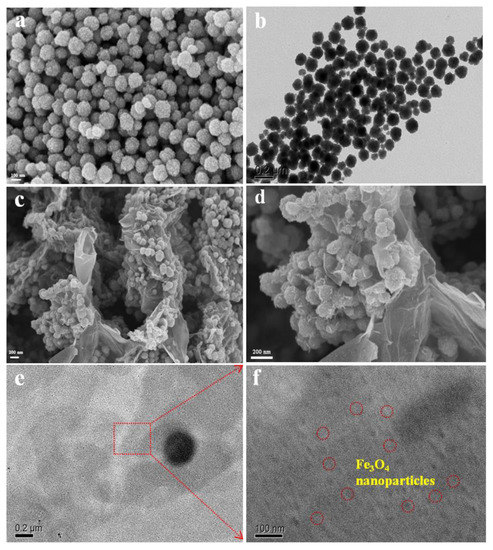
Figure 5.
(a) SEM; (b) TEM images of Fe3O4; (c,d) SEM; (e,f) TEM images of MrGO-2.
3.2. Adsorption
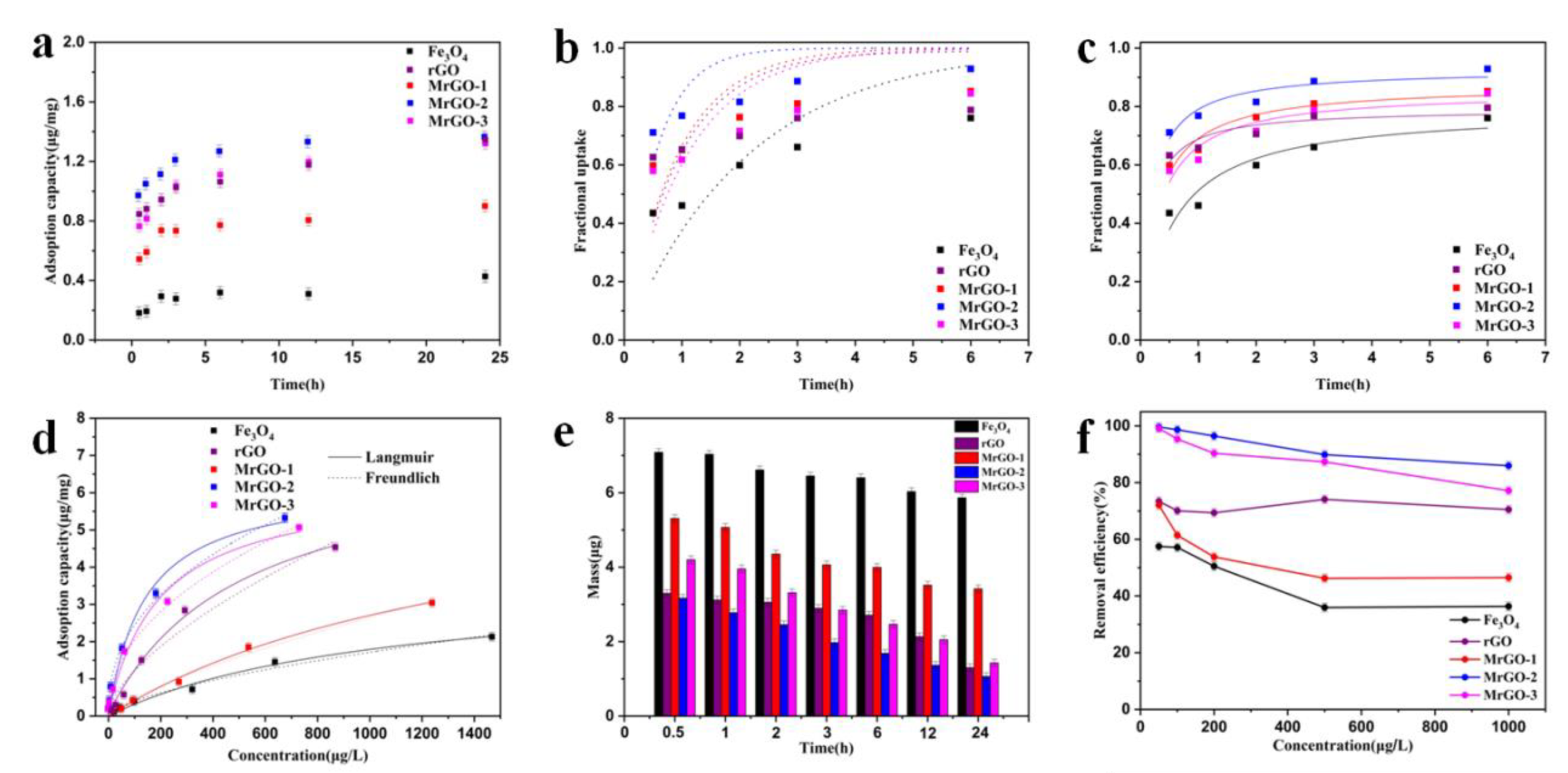
The adsorption kinetics of SDZ was investigated to understand the adsorption behavior of different types of magnetic materials (Figure 6a). As the adsorption time increases, the adsorption capacities of MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 show an obvious increase relative to Fe3O4. According to the Formulae (1), the adsorption capacities of MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 were calculated to be 0.90μg/mg, 1.36 μg/mg, and 1.31 μg/mg, respectively after reaction for 24 h, but that of Fe3O4 was only 0.42 μg/mg. This meant that the introduction of rGO into the material can greatly enhance the adsorption capacity. The magnetic materials of MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 had about 2.14, 3.24, and 3.12 times improvement, respectively. The adsorption capacity of rGO was 1.34 μg/mg, which meant that the MrGO-2 and MrGO-3 samples after the magnetizing modification still maintained their adsorption capacity. Furthermore, these data were taken to fit the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order model using Equations (6) and (7) (Figure 6b,c) [36]. According to the correlation coefficient (R2), the data tends to fit better the pseudo-second-order model than the pseudo-first-order model (Table 2), which indicates that the chemical adsorption of SDZ may exist in the adsorption process [37,38]. This result could be ascribed to the abundant functional groups on the surface of magnetic materials. Among these magnetic materials, the MrGO-2 sample had the greatest rate constant for SDZ adsorption (5.79 mg/(μg/h)). The equilibrium adsorption capacity and the adsorption rate constant results indicate that there were some differences in magnetic materials for removing SDZ. Besides, the adsorption of SDZ on these five adsorbents changed very slowly after 3 h. The kinetic process demonstrates that the adsorption after reaction for 3h approaches to equilibrium, which suggests that the reaction time is sufficient to remove SDZ from these adsorbents.
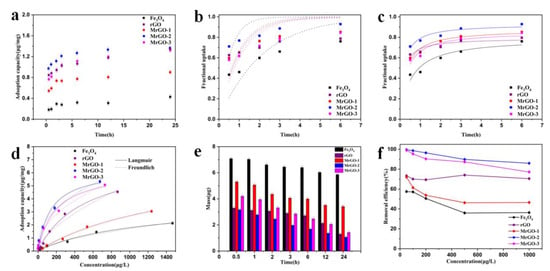
Figure 6.
Adsorption behavior of the five types of magnetic materials: (a) adsorption kinetics, (b) pseudo-first-order fit for t ≤ 6 h, (c) pseudo-second-order fit for t ≤ 6 h, (d) adsorption isotherms, (e) SDZ mass variation, (f) SDZ removal efficiency. Reaction conditions: T0 = 25 °C, C0, SDZ = (a,c) = 400 μg/L, C0, SDZ = (b,d) = 50–2000 μg/L, (adsorbents) = 0.25 g/L and pH with no adjustment.

Table 2.
Relevant parameters of the adsorption experiments.
The adsorption isotherms of SDZ for the five adsorbents were measured (Figure 6d). These materials showed an obvious increase in the adsorption capacity, with the increase of the initial concentration of SDZ. At the initial concentration of 2000 μg/L, the adsorption capacities of Fe3O4, rGO, MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 were 2.13μg/mg, 4.51 μg/mg, 3.05 μg/mg, 5.31 μg/mg, and 5.07 μg/mg, respectively, in the adsorption equilibrium state. Both Langmuir and Freundlich models were used to study the adsorption [39,40]. The materials exhibited a better correlation with the Langmuir adsorption model than that of the Freundlich model (Table 2). Using the Langmuir model, the maximum adsorption capacities of MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 were calculated to be 6.74 μg/mg, 6.27 μg/mg, and 6.26 μg/mg, respectively, which was an improvement on that of Fe3O4 (3.67 μg/mg). The isotherm constants of the adsorbents were consistent with the adsorption kinetics result. The MrGO-2 sample was the most efficient of the five types of materials.
The SDZ mass variation of these adsorbents were investigated in the adsorption process (Figure 6e). The total mass of SDZ in the aqueous solution was 8 μg. In the presence of MrGO-2, the mass of SDZ decreased rapidly within 0.5 h, and further decreased to 1.06 μg after 24 h. In the case of Fe3O4, the mass did not decrease significantly and still remained at 5.86 μg after reaction for 24 h. The mass of MrGO-1 and MrGO-3 were 3.52 μg and 1.42 μg, respectively, indicating the better adsorption capacity of these two adsorbents than pure Fe3O4. In other words, rGO played an important role influencing the adsorption performance of the magnetic materials.
The removal of SDZ with different initial concentrations was shown in Figure 6f. MrGO-2 exhibited the highest removal efficiency among the five types of materials. The removal efficiencies of SDZ by Fe3O4, rGO, MrGO-1, MrGO-2, and MrGO-3 were 57.6%, 73.4%, 72.1%, 99.6%, and 99.1%, respectively, at the initial concentration of 50 μg/L. When the concentration of SDZ was increased to 1000 μg/L, the removal efficiencies of SDZ by these five materials changed to 36.3%, 70.5%, 46.5%, 85.9%, and 77.1%, respectively. The pure Fe3O4 sample showed the lowest removal efficiency toward both low and high concentrations of SDZ. First, this phenomenon may be due to the serious agglomeration of magnetic Fe3O4. Second, an appropriate content of rGO brought functional groups, and these groups could serve as the active sites for improving the absorption capacity of the materials. Third, target contaminants were prone to desorption without magnetism. Comparing the results presented above, it can be concluded that MrGO-2 is the most reactive material for SDZ removal.
3.3. Recyclability
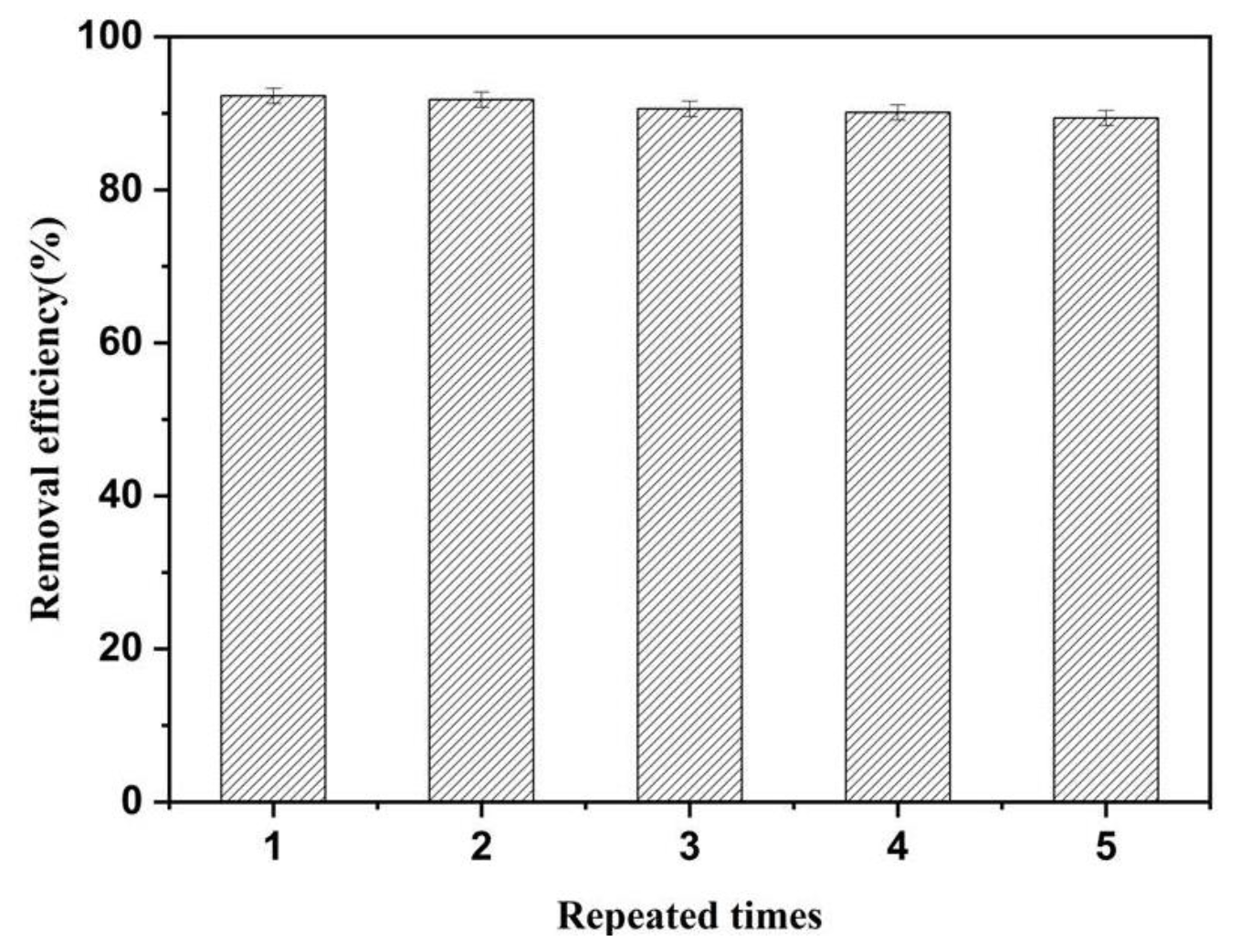
The recyclability of adsorbent is a vital factor for evaluating its practical applications in the environment. Therefore, the recyclability of MrGO-2 was further investigated and the results are shown in Figure 7. After five repeated adsorption cycles, the removal efficiency still remained at 89.3%. Compared to the first adsorption, the removal efficiency showed only about a 3% decrease after five cycles. This result suggests that the adsorbent has remarkable recyclability and it has the potential for removing SDZ from aqueous solutions.
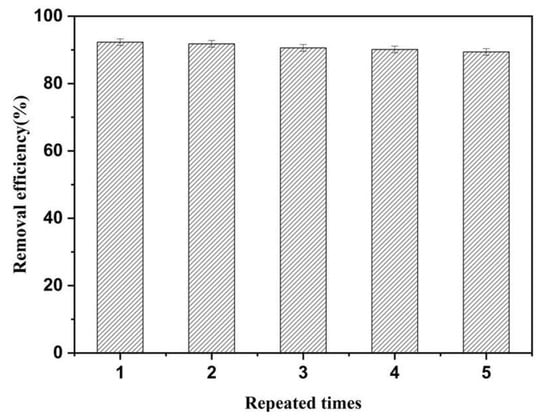
Figure 7.
Recyclability of MrGO-2. Reaction conditions: T0 = 25 °C, C0, SDZ = 100 μg/L, (MrGO-2) = 0.25 g/L and pH with no adjustment.
3.4. Applications
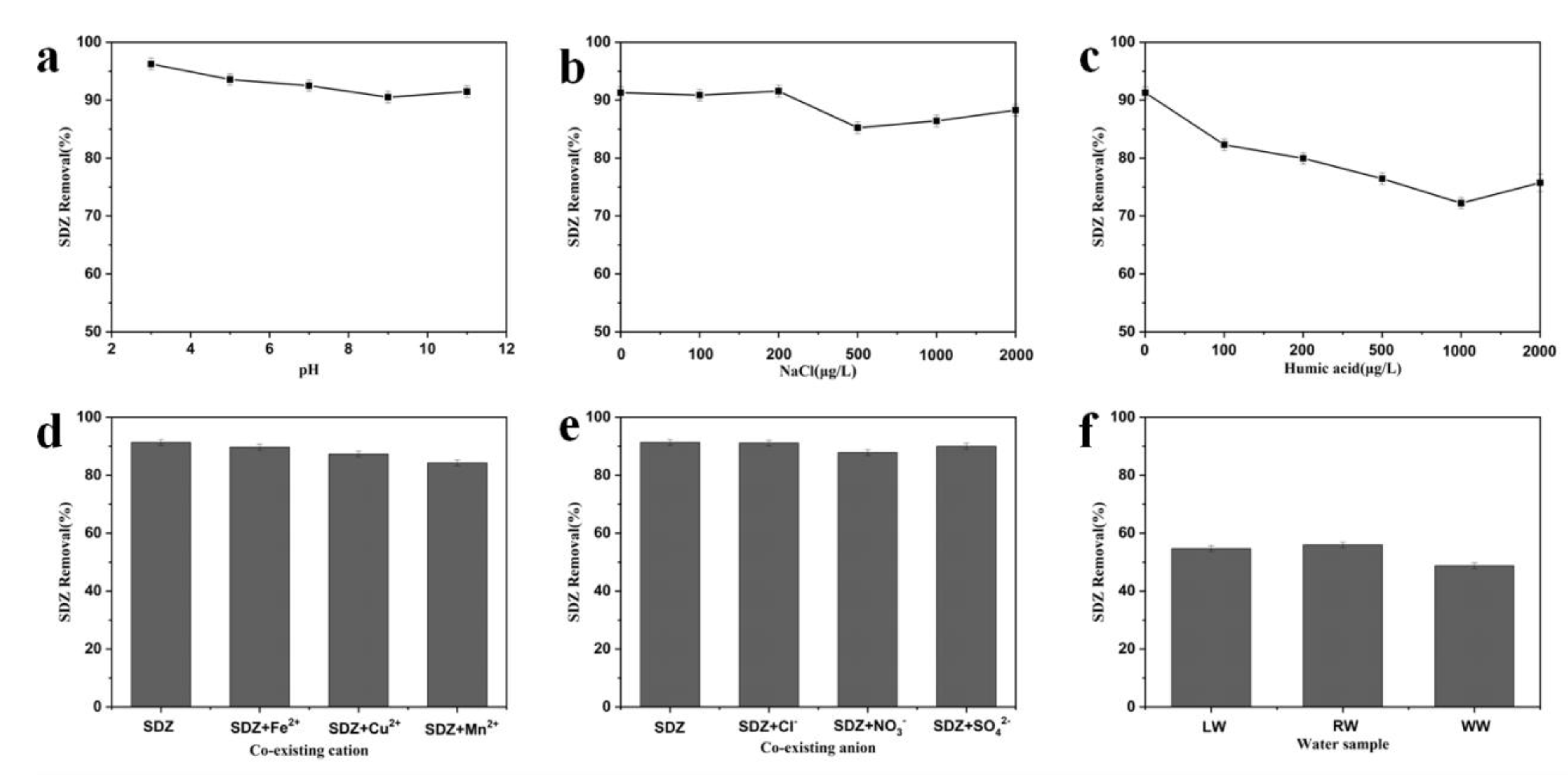
To demonstrate the application capability of MrGO-2 in real water environments, batch adsorption experiments were conducted to investigate the influence of various parameters including solution pH (3–11), natural organic matters (0–2000 μg/L as humic acid (HA)), ion strength (0–2000 μg/L as NaCl), common co-existing cations/anions (1000 μg/L), and the three real water samples collected. The adsorption experiments in real water detail were conducted using the same procedures specified at the experimental section. The initial spiked concentration of SDZ was 100 μg/L and the solutions were placed on a rotating shaker with a speed of 180 rpm for 3 h. The results of adsorption were displayed in Figure 8. The pH value was a vital parameter that affects most solid–liquid systems. The removal of SDZ under different pH values showed that a better result was achieved under acidic conditions (Figure 8a). This is probably because the adsorbent with oxygen-containing functional groups possesses faint acidity, which makes it easy for the target contaminant to approach in the adsorption process. When the initial pH value of the solution was increased to 11, the removal of SDZ decreased slightly. Humic acid is a common natural organic matter in water and wastewater. With the increase of HA concentrations from 0 to 1000 μg/L, the removal efficiency of SDZ declined from 91.3% to 72.2% (Figure 8b). This decline may be resulted from the strong competition from HA, which could be adsorbed onto the surface of MrGO-2 via π-π interactions. The effect of ionic strength on the removal of SDZ by MrGO-2 was investigated with NaCl as the auxiliary electrolyte (Figure 8c). The removal of SDZ increased when, NaCl with concentrations in the range of 0 to 200 μg/L, was added. It is generally believed that an appropriate electrolyte can improve the electric double layer surface and weaken the electrostatic repulsion between SDZ and MrGO-2. Various common co-existing cations and anions (Fe2+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Cl−, NO3−, and SO42−) were observed to affect the removal of SDZ by MrGO-2 (Figure 8d,e). The removal rate of SDZ was 91.3% without the presence of cations. After the addition of Fe2+, Cu2+, and Mn2+, the removal of SDZ decreased to 89.6%, 87.3%, and 84.2%, respectively. This may be because these cations have certain affinities for the adsorption sites of MrGO-2. The co-existing anions added had no significant effect on the removal of SDZ. The effectiveness of MrGO-2 was further evaluated using three different real water samples (Figure 8f). It showed that the removal rates of SDZ in SW, RW, and WW were 54.6%, 55.9%, and 48.8%, respectively. The comparatively ordinary removal efficiencies with these real waters could be probably ascribed to the presence of relatively high concentrations of dissolved organic compounds (2.3 mg/L in LW, 2.5 mg/L in RW, and 6.7 mg/L in WW). Besides, the co-existing cations/anions and the ionic strength in real waters could also affect the removal efficiency.
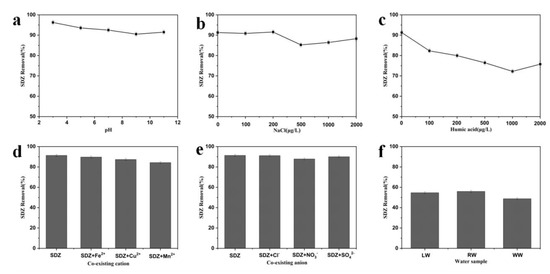
Figure 8.
Effects of various water parameters and components on the removal of SDZ by MrGO-2: (a) pH, (b) natural organic matter, (c) ionic strength, (d) co-existing cation, (e) co-existing anion, (f) three real waters. Reaction conditions: T0 = 25 °C, C0, SDZ = 100 μg/L, (adsorbents) = 0.25 g/L and pH with no adjustment.
4. Conclusions
The MrGO nanocomposites were synthesized via a modified solvothermal method. Different graphene-based magnetic nanocomposites were employed to remove SDZ from water. The adsorption capacity of MrGO-2 showed approximately 3.24 times that of pure Fe3O4. After five repeated adsorption cycles, the removal rate of SDZ by MrGO-2 still remained at 89.3%, which was only about a 3% decrease compared to that in the first cycle. This excellent adsorption performance and recyclability of MrGO could be attributed to the wonderful 3D interconnected petal-like structure. With the assistance of material characterization and balance analysis, the removal of SDZ was found to be mediated probably by both chemical and physical adsorption. The relative contents of rGO and Fe3O4 seem to play an important role in the construction of their 3D structures and adsorption performance. The MrGO after the adsorption experiments can be easily recycled via magnetic separation. Moreover, the MrGO-2 also exhibited excellent adsorption performance in real water environments. The initial concentration of SDZ was at trace levels, which was close to the concentration in the actual environments. This work proposes a novel material with unique 3D-interconnected structures for promoting the adsorption capacity, which has certain application prospects in practical water treatment.
Author Contributions
J.Z.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Data curation, Writing—original draft preparation; Y.F.: Methodology, Analysis, Writing—review and editing; J.-L.L.: Analysis; B.Y.: Resources; G.-G.Y.: Resources, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Key R & D program of Guangxi Province, China (2018AB36018), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC U1701242).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest or competing financial relationships.
References
- Le Page, G.; Gunnarsson, L.; Snape, J.; Tyler, C.R. Integrating human and environmental health in antibiotic risk assessment: A critical analysis of protection goals, species sensitivity and antimicrobial resistance. Environ. Int. 2017, 109, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Ying, G.-G.; Singer, A.C.; Zhu, Y.-G. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Ying, G.-G.; Pan, C.-G.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhao, J.-L. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of china: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.-D.; Zou, S.; Li, P.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. Occurrence and elimination of antibiotics at four sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), South China. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4526–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Meyer, M.T.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.-A.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, L.; Cao, J.; Shu, W. Determination of antibiotics in sewage from hospitals, nursery and slaughter house, wastewater treatment plant and source water in Chongqing region of Three Gorge Reservoir in China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Galán, M.J.; Garrido, T.; Fraile, J.; Ginebreda, A.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, J.; Ginebreda, A. Simultaneous occurrence of nitrates and sulfonamide antibiotics in two ground water bodies of Catalonia (Spain). J. Hydrol. 2010, 383, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Guo, X.; Xu, J.; Kong, X.; Gao, S.; Shan, Z. Pollution characteristics and environmental risk assessment of typical veterinary antibiotics in livestock farms in Southeastern China. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2014, 49, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Johir, A.H.; Belhaj, D. Competitive sorption affinity of sulfonamides and chloramphenicol antibiotics toward functionalized biochar for water and wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Hu, J.; Shah, S.M.; Su, X. Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 368, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yu, C.; Gao, F.; Lei, J.; Tian, B.; Wang, L.; Luo, Q.; Tu, B.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, D. Cubic mesoporous silica with large controllable entrance sizes and advanced adsorption properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3146–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yue, Q.; Yu, L.; Yang, X.; Hou, X.; Zhao, D.; Cheng, X.; Deng, Y. Amphiphilic block copolymers directed interface coassembly to construct multifunctional microspheres with magnetic core and monolayer mesoporous aluminosilicate shell. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1800345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, D.; Deng, S.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; He, C.; Cagnetta, G.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Preparation of porous graphene oxide by chemically intercalating a rigid molecule for enhanced removal of typical pharmaceuticals. Carbon 2017, 119, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Zhuo, N.; Tian, Z.; Xu, P.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W. Interactions between antibiotics and graphene-based materials in water: A Comparative experimental and theoretical investigation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24273–24280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Lu, F.; Qiu, H.; Sun, M. Fabrication of novel magnetic chitosan grafted with graphene oxide to enhance adsorption properties for methyl blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, C.-X.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Hao, S.-M.; Qu, J.; Huang, P.-P.; Cao, C.; Song, W.; Yu, Z.-Z. Sandwichlike magnesium silicate/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for enhanced Pb2+ and methylene blue adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14653–14659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhu, D. Adsorption of tetracycline and sulfamethoxazole on crop residue-derived ashes: Implication for the relative importance of black carbon to soil sorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5580–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Ai, J.; Fu, H.; Chen, W.; Zheng, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D. Enhanced removal of sulfonamide antibiotics by KOH-activated anthracite coal: Batch and fixed-bed studies. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zou, L.; Pan, L.; Sun, Z. Novel graphene-like electrodes for capacitive deionization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8692–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, R.; Arsalani, N.; Panahian, Y. One-pot synthesis of novel magnetic three-dimensional graphene/chitosan/nickel ferrite nanocomposite for lead ions removal from aqueous solution: RSM modelling design. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.; Li, Y.; Salvatierra, R.V.; Wang, T.; Dong, P.; Ji, Y.; Lee, S.-K.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Smith, R.H.; et al. Three-dimensional printed graphene foams. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6860–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Fan, J.T.; Ma, N.; Zhang, L.; Leung, C.; Chan, H.L.; Leung, C.W. The attachment of Fe3O4 nanoparticles to graphene oxide by covalent bonding. Carbon 2010, 48, 3139–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, H.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Li, A.-M.; Cheng, R. Flocculation performance and mechanism of graphene oxide for removal of various contaminants from water. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3037–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Yi, F.; Gao, A.; Shu, D.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, W.; He, C.; Meng, T.; Zhao, S. Preparation of 3D reduced graphene Oxide/MnO2 nanocomposites through a vacuum-impregnation method and their electrochemical capacitive behavior. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touqeer, T.; Mumtaz, M.W.; Mukhtar, H.; Irfan, A.; Akram, S.; Shabbir, A.; Rashid, U.; Nehdi, I.; Yaw, T.C.S. Fe3O4-PDA-Lipase as surface functionalized nano biocatalyst for the production of biodiesel using waste cooking oil as feedstock: Characterization and process optimization. Energies 2019, 13, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Solvothermal self-assembly of magnetic Fe3O4 nanochains by ethylenediamine functionalized nanoparticles for chromium (VI) removal. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4270–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Yang, H. TEM and EBSD study of Fe3O4 particle chains grown and assembled in external magnetic field. Microsc. Microanal. 2010, 16, 1790–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastami, T.R.; Entezari, M.; Hu, Q.H.; Hartono, S.B.; Qiao, S. Role of polymeric surfactants on the growth of manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Wang, Z.; Lin, R.; Wang, D.; Chen, C.; Li, Y. An efficientfficient, controllable and facile two-step synthesis strategy: Fe3O4@RGO composites with various Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their supercapacitance properties. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3303–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Lou, S.; Yuan, L.; Gao, T.; Wu, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, K. Synthesis of high saturation magnetization superparamagnetic Fe3O4 hollow microspheres for swift chromium removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4913–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulego, P.; Laca, A.; Calvo, S.; Díaz, M. Eggshell-supported catalysts for the advanced oxidation treatment of humic acid polluted wastewaters. Water 2019, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Shen, W.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, W. 3D CoFe2O4 nanorod/flower-like MoS2 nanosheet heterojunctions as recyclable visible light-driven photocatalysts for the degradation of organic dyes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 447, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ruan, G.; Li, X.; Cong, Y.; Du, F.; Li, J. Reduced graphene oxide-hybridized polymeric high-internal phase emulsions for highly efficient removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water matrix. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3661–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, Y.; Zong, M.; Ding, X.; Li, S.; Wang, M. Synthesis of ZnS quantum dots and CoFe2O4 nanoparticles co-loaded with graphene nanosheets as an efficient broad band EM wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-H.; Wu, M.-F.; Tang, T.; Xing, Q.-J.; Peng, C.-Q.; Li, F.; Liu, H.; Luo, X.-B.; Zou, J.-P.; Min, X.-B.; et al. Mechanism investigation of anoxic Cr(VI) removal by nano zero-valent iron based on XPS analysis in time scale. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Liu, Y.; He, W.; Tang, X.; Jin, W.; Zhao, Y. A novel graphene oxide-carbon nanotubes anchored α-FeOOH hybrid activated persulfate system for enhanced degradation of Orange II. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 83, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, J.-P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, L.; Zhan, F.; Cai, D.; Wu, Z. Waste carton-derived nanocomposites for efficient removal of hexavalent chromium. Langmuir 2018, 34, 5955–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Tu, G.; Zhao, D.; Tsang, P.E.; Fang, Z. Biomass waste components significantly influence the removal of Cr(VI) using magnetic biochar derived from four types of feedstocks and steel pickling waste liquor. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Xu, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S. Properties of biomass-derived biochars: Combined effects of operating conditions and biomass types. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Kumar, A.; Sarswat, A.; Franco, M.A.; Pittman, C.U. Cadmium and lead remediation using magnetic oak wood and oak bark fast pyrolysis bio-chars. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).