Human Risk from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Arsenic in Water from Rivers with Mining Influence in the Central Andes of Peru
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling, Analytical Determination, and Quality Control
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Human Health Risk Assessment
2.4.1. Exposure Dose
2.4.2. Non-Carcinogenic Risk Assessment
2.4.3. Carcinogenic Risk Assessment
3. Results
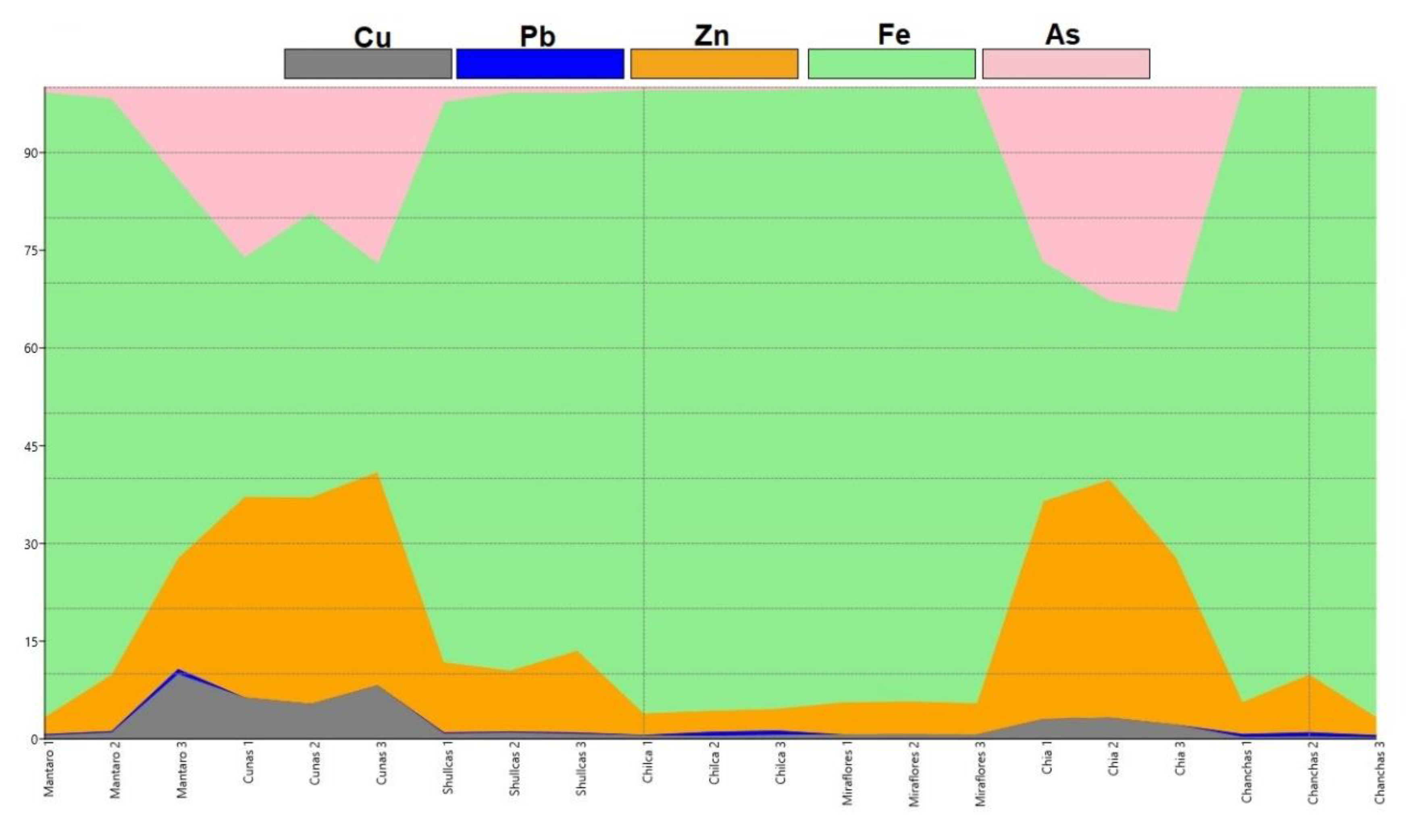
3.1. Analysis of Heavy Metals and Arsenic in River Water Subject to Mining Influence
3.2. Human Health Risk Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Assessment of Heavy Metals and Arsenic in River Water Subject to Mining Influence
4.2. Human Health Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lintern, A.; Leahy, P.J.; Heijnis, H.; Zawadzki, A.; Gadd, P.; Jacobsen, G.; Deletic, A.; Mccarthy, D.T. Identifying heavy metal levels in historical flood water deposits using sediment cores. Water Res. 2016, 105, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assubaie, F.N. Assessment of the levels of some heavy metals in water in Alahsa Oasis farms, Saudi Arabia, with analysis by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emenike, P.G.; Tenebe, I.; Ogarekpe, N.; Omole, D.; Nnaji, C. Probabilistic risk assessment and spatial distribution of potentially toxic elements in groundwater sources in Southwestern Nigeria. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Kumar Thukral, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Assessment of heavy-metal pollution in three different Indian water bodies by combination of multivariate analysis and water pollution indices. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. An Int. J. 2018, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M. Arsenic and trace metals in a large reservoir: Seasonal and spatial variations, source identification and risk assessment for both residential and recreational users. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Han, W.; Tang, J.; Bian, J.; Sun, S.; Song, T. Pollution characteristics and human health risks of elements in road dust in Changchun, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2018, 15, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Lin, L.; Ye, S.; Li, H.; Fan, J. Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in the seawater and sediment of Yalujiang Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezemonye, L.I.; Adebayo, P.O.; Enuneku, A.A.; Tongo, I.; Ogbomida, E. Potential health risk consequences of heavy metal concentrations in surface water, shrimp (Macrobrachium macrobrachion) and fish (Brycinus longipinnis) from Benin River, Nigeria. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Lu, Y.; Khan, H.; Zakir, S.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.A.; Wei, L.; Wang, T. Health risks associated with heavy metals in the drinking water of Swat, northern Pakistan. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.J.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zhai, R.H.; Chen, D.Y.; Huang, Y.Z.; Qiu, Y.; Liang, J.Z. Transfer of metals from soil to vegetables in an area near a smelter in Nanning, China. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Cui, B.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H. Assessment of river water quality in Pearl River Delta using multivariate statistical techniques. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Satar, A.M.; Ali, M.H.; Goher, M.E. Indices of water quality and metal pollution of Nile River, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2017, 43, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, F.; Chowdhury, M.S.U.; Wan Jaafar, W.Z.; Faresh, E.M.M.; Shirazi, S.M. Assessing risk and sources of heavy metals in a tropical river basin: A case study of the Selangor river, Malaysia. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Industrial metal pollution in water and probabilistic assessment of human health risk. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 185, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, C.M.; Del Angel, E.; Frías, D.M.; Gómez, A.L. Evaluation of physicochemical parameters and heavy metals in water and surface sediment in the illusions Lagoon, Tabasco, Mexico. Tecnol. Ciencias Agua 2018, 9, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Lugo, R.; Vargas, A.; Moreno, C.; Centeno, L.; Astudillo, H.; Lemus, M.; Astudillo, L.R. Blood parameters and heavy metals in tissue of the fish Pterygoplycthys multiradiatus from the Orinoco River, Venezuela. Rev. Cient. 2014, 24, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Barra-Rocha, C.H.; Fernandes-Costa, H.; Pimenta-Azevedo, L. Heavy metals in the São Mateus Stream Basin, Peixe River Basin, Paraiba do Sul River Basin, Brazil. Ambient Agua Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2019, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gammons, C.H.; Slotton, D.G.; Gerbrandt, B.; Weight, W.; Young, C.A.; McNearny, R.L.; Cámac, E.; Calderón, R.; Tapia, H. Mercury concentrations of fish, river water, and sediment in the Río Ramis-Lake Titicaca watershed, Peru. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, M.; Maceda-Veiga, A.; de Sostoa, A. Metal concentration in water, sediment and four fish species from Lake Titicaca reveals a large-scale environmental concern. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guittard, A.; Baraer, M.; McKenzie, J.M.; Mark, B.G.; Wigmore, O.; Fernandez, A.; Rapre, A.C.; Walsh, E.; Bury, J.; Carey, M.; et al. Trace-metal contamination in the glacierized Rio Santa watershed, Peru. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Yan, Y.; Dai, Y.Y.; Deng, B.; Ding, S.; Su, S.; Sun, W.; Li, Z.; Gan, Z. Distribution and risk assessment of metals in water, sediments, and wild fish from Jinjiang River in Chengdu, China. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, E.; Etuk, B. Human Health Risk Assessment of Trace metals in Water from Qua Iboe River Estuary, Ibeno, Nigeria. J. Environ. Occup. Sci. 2015, 4, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Hua, X. Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzabeygi, M.; Abbasnia, A.; Yunesian, M.; Nodehi, R.N.; Yousefi, N.; Hadi, M.; Mahvi, A.H. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in drinking water of Sistan and Baluchistan, Southeastern Iran. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2017, 23, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Shah, I.A.; Muhammad, S.; Malik, R.N.; Shah, M.T. Arsenic and Heavy Metal Concentrations in Drinking Water in Pakistan and Risk Assessment: A Case Study. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2015, 21, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petus, C.; Marieu, V.; Novoa, S.; Chust, G.; Bruneau, N.; Froidefond, J.M. Monitoring spatio-temporal variability of the Adour River turbid plume (Bay of Biscay, France) with MODIS 250-m imagery. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 74, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, P.; Paul, B. Assessment of heavy metal toxicity related with human health risk in the surface water of an industrialized area by a novel technique. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 966–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalos, G.; Orla, C.; Jácome, G.; Acuña, D.; Llacza, A.; Cubas, F. Climate Change in the Mantaro River Basin; MINEN: Lima, Peru, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Reuer, M.; Bower, N.; Koball, J.; Hinostroza, E.; De la Torre, M.; Hurtado, S.J.A.; Echevarria, S. Lead, arsenic and cadmium contamination and its impact on childrens health in La Oroya, Perú. Int. Sch. Res. Netw. 2012, 2012, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yilma, M.; Kiflie, Z.; Windsperger, A.; Gessese, N. Assessment and interpretation of river water quality in Little Akaki River using multivariate statistical techniques. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 3707–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguerne, A.; Boudoukha, A.; Benkhaled, A.; Mebarkia, A.H. Assessment of surface water quality of Ain Zada dam (Algeria) using multivariate statistical techniques. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2017, 15, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamunda, C.; Mathuthu, M.; Madhuku, M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from witwatersrand gold mining basin, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karri, V.; Schuhmacher, M.; Kumar, V. Heavy metals (Pb, Cd, As and MeHg) as risk factors for cognitive dysfunction: A general review of metal mixture mechanism in brain. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- US EPA. Risk assessment guidance for superfund (RAGS). In Human Health Evaluation Manual (HHEM). Part E: Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Yang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, M.; Wu, Z. xian. Trace elements spatial distribution characteristics, risk assessment and potential source identification in surface water from Honghu Lake, China. J. Cent. South Univ. 2018, 25, 1598–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortey-Sam, N.; Nakayama, S.M.M.; Ikenaka, Y.; Akoto, O.; Baidoo, E.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Mizukawa, H.; Ishizuka, M. Human health risks from metals and metalloid via consumption of food animals near gold mines in Tarkwa, Ghana: Estimation of the daily intakes and target hazard quotients (THQs). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 111, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Sediment of the Main Tributaries of Dongting Lake, China. Water 2018, 10, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez, A.V. Cadmium pollution in La Oroya, Peru. PAHO Bull. 1986, 20, 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Ayeni, O.; Soneye, A.S.O. Interpretation of surface water quality using principal components analysis and cluster analysis. J. Geogr. Reg. Plan. 2013, 6, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iticescu, C.; Georgescu, L.P.; Murariu, G.; Topa, C.; Timofti, M.; Pintilie, V.; Arseni, M. Lower danube water quality quantified through WQI and multivariate analysis. Water 2019, 11, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wongsasuluk, P.; Chotpantarat, S.; Siriwong, W.; Robson, M. Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Tanvir Rahman, M.A.T.M.; Saha, B.; Kamal, A.K.I. Status of heavy metals in water and sediment of the Meghna River, Bangladesh. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 11, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shil, S.; Singh, U.K. Health risk assessment and spatial variations of dissolved heavy metals and metalloids in a tropical river basin system. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantaro Water Management Authority. Participatory Water Quality Monitoring in the Mantaro River Basin; MINEN: Lima, Peru, 2015; p. 556. [Google Scholar]
- MINEN. Approve Environmental Quality Standards for Air and establish complementary provisions. Peruano Off. Newsp. 2017, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; p. 398.
- USEPA. National Recommended Water Quality Criteria; Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; p. 21.
- National Water Authority. Participatory Monitoring of Water Quality in Lake Chinchaycocha (Flood Season) Junin-Pasco; National Water Authority: Lima, Peru, 2014; p. 78.
- Sojka, M.; Jaskula, J.; Siepak, M. Heavy metals in bottom sediments of reservoirs in the lowland area of western Poland: Concentrations, distribution, sources and ecological risk. Water 2018, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, U. Regional geology and major ore deposits of central Peru. Econ. Geol. 1965, 60, 407–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goher, M.E.; Hassan, A.M.; Abdel-moniem, I.A.; Fahmy, A.H.; El-sayed, S.M. Evaluation of surface water quality and heavy metal indices of Ismailia Canal, Nile River, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, J.R.; Lechler, P.J.; Mackin, G.; Germanoski, D.; Villarroel, L.F. Evaluation of particle dispersal from mining and milling operations using lead isotopic fingerprinting techniques, Rio Pilcomayo Basin, Bolivia. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 384, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson-Edwards, K.A. Sources, mineralogy, chemistry and fate ofheavy metal-bearing particles in mining-affected river systems. Mineral. Mag. 2003, 67, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Rauf, R.; Muhammad, S.; Qasim, M.; Din, I. Arsenic and heavy metals health risk assessment through drinking water consumption in the Peshawar District, Pakistan. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016, 22, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.A.; González-Horta, C.; Sánchez-Ramírez, B.; Ballinas-Casarrubias, L.; Cerón, R.H.; Morales, D.V.; Ishida, M.C.; Gutiérrez-Torres, D.; Saunders, R.J.; Drobná, Z.; et al. Chronic exposure to arsenic and markers of cardiometabolic risk: A cross-sectional study in Chihuahua, Mexico. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naujokas, M.F.; Anderson, B.; Ahsan, H.; Vasken Aposhian, H.; Graziano, J.H.; Thompson, C.; Suk, W.A. The broad scope of health effects from chronic arsenic exposure: Update on a worldwide public health problem. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, A.M.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Cantoral-Preciado, A.; Claus Henn, B.; Leon Hsu, H.H.; Sanders, A.P.; Svensson, K.; Tamayo-Ortíz, M.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M.; Wright, R.O.; et al. Maternal blood arsenic levels and associations with birth weight-for-gestational age. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalov, R.; Jarsjö, J.; Kasimov, N.S.; Romanchenko, O.; Pietroń, J.; Thorslund, J.; Promakhova, E.V. Spatio-temporal variation of sediment transport in the Selenga River Basin, Mongolia and Russia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 663–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; McCullough, L.E.; Tzeng, J.Y.; Darrah, T.; Vengosh, A.; Maguire, R.L.; Maity, A.; SamuelHodge, C.; Murphy, S.K.; Mendez, M.A.; et al. Maternal blood cadmium, lead and arsenic levels, nutrient combinations, and offspring birthweight. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dórea, J.G. Environmental exposure to low-level lead (Pb) co-occurring with other neurotoxicants in early life and neurodevelopment of children. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Myers, R.; Wei, T.; Bind, E.; Kassim, P.; Wang, G.; Ji1, Y.; Hong, X.; Caruso, D.; Bartell, T.; et al. Placental transfer and concentrations of cadmium, mercury, lead, and selenium in mothers, newborns, and young children. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Claus, H.B.; Ettinger, A.S.; Hopkins, M.R.; Jim, R.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Christiani, D.C.; Coull, B.A.; Bellinger, D.C.; Wright, R.O. Prenatal arsenic exposure and birth outcomes among a population residing near a mining-related superfund site. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanders, A.P.; Svensson, K.; Gennings, C.; Burris, H.H.; Oken, E.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Priyanka Basnet, P.; Pizano-Zarate, M.L.; Schnaas, L.; Tamayo-Ortiz, M.; et al. Prenatal lead exposure modifies the effect of shorter gestation on increased blood pressure in children. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizullah, A.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Richter, P.; Häder, D.P. Water pollution in Pakistan and its impact on public health—A review. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, T.E.; Liang, C.L.; Morisset, A.S.; Fisher, M.; Weiler, H.; Cirtiu, C.M.; Legrand, M.; Davis, K.; Ettinger, A.S.; Fraser, W.D. Maternal and fetal exposure to cadmium, lead, manganese and mercury: The MIREC study. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pebe, G.; Villa, H.; Escate, L.; Cervantes, G. Blood lead levels in newborns in La Oroya, 2004–2005. Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud Pública 2008, 25, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Thayer, K.A.; Heindel, J.J.; Bucher, J.R.; Gallo, M.A. Role of Environmental Chemicals in Diabetes and Obesity: A National Toxicology Program Workshop Review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamas, G.A.; Navas-Acien, A.; Mark, D.B.; Lee, K.L. Heavy metals, cardiovascular disease, and the unexpected benefits of chelation therapy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2411–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chao, H.H.; Guo, C.H.; Huang, C.B.; Chen, P.C.; Li, H.C.; Hsiung, D.Y.; Chou, Y.K. Arsenic, cadmium, lead, and aluminium concentrations in human milk at early stages of lactation. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2014, 55, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plum, L.M.; Rink, L.; Hajo, H. The essential toxin: Impact of zinc on human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1342–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stern, B.R.; Solioz, M.; Krewski, D.; Aggett, P.; Aw, T.C.; Baker, S.; Crump, K.; Dourson, M.; Haber, L.; Hertzberg, R.; et al. Copper and human health: Biochemistry, genetics, and strategies for modeling dose-response relationships. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2007, 10, 157–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L.; Friedland, R.; Petanceska, S.; Schreurs, B.G.; Shi, J.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Sharma, A.; Derosa, S.; Stankovic, G. Trace copper levels in the drinking water, but not zinc or aluminum influence CNS Alzheimer-like pathology. J. Nutr. Heal. Aging 2006, 10, 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Stelmashook, E.V.; Isaev, N.K.; Genrikhs, E.E.; Amelkina, G.A.; Khaspekov, L.G.; Skrebitsky, V.G.; Illarioshkin, S.N. Role of zinc and copper ions in the pathogenetic mechanisms of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Biochemistry 2014, 79, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.; Moon, K.A.; Wang, S.; Silbergeld, E.; Navas-acien, A. The Association of Arsenic Metabolism with Cancer, Cardiovascular Disease, and Diabetes: A Systematic Review of the Epidemiological Evidence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 128, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Simcox, J.; McClain, D. Iron and Diabetes Risk. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X. Iron overload and its association with cancer risk in humans: Evidence for iron as a carcinogenic metal. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2003, 533, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C. Can excess iron increase the risk for coronary heart disease and cancer? Nutr. Bull. 2002, 27, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alissa, E.M.; Ahmed, W.H.; Al-ama, N.; Ferns, G.A.A. Relationship between indices of iron status and coronary risk factors including diabetes and the metabolic syndrome in Saudi subjects without overt coronary disease. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2007, 21, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, H.; Luczkowski, M.; Remelli, M.; Valensin, D. Copper, zinc and iron in neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and prion diseases). Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, H.M.; Abd-Elmegied, A.; Ghareeb, D.A.; Hafez, H.S.; Ahmed, H.E.A.; El-moneam, N.A. Neuroprotective effect of berberine against environmental heavy metals-induced neurotoxicity and Alzheimer’s-like disease in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Reichman, S.M.; Lim, R.P.; Naidu, R. Heavy metals in Australian grown and imported rice and vegetables on sale in Australia: Health hazard. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 100, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, F. Accumulation characteristics and potential risk of heavy metals in soil-vegetable system under greenhouse cultivation condition in Northern China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Rivers | Cu | Pb | Zn | Fe | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD Max − Min | Mean ± SD Max − Min | Mean ± SD Max − Min | Mean ± SD Max − Min | Mean ± SD Max − Min | |
| Chanchas | 0.99 ± 0.12 | 4.00 ± 0.10 | 13.20 ± 3.50 | 217.00 ± 72.00 | |
| 8.70 − 1.00 | 4.10 − 3.90 | 16.70 − 9.70 | 289.00 − 145.00 | nd | |
| Chía | 1.37 ± 0.06 | nd | 15.30 ± 0.30 | 14.40 ± 4.40 | 17.67 * ± 4.73 |
| 1.40 − 1.30 | 15.60 − 15.00 | 18.80 − 10.00 | 23.00 − 14.00 | ||
| Chilca | 1.20 ± 0.20 | 2.80 ± 2.14 | 6.30 ± 50 | 157.10 ± 10.10 | 0.70 ± 0.01 |
| 1.40 − 1.00 | 4.50 − 0.40 | 6.80 − 5.80 | 167.20 − 147.00 | 0.71 − 0.69 | |
| Cunas | 1.90 ± 0.20 | nd | 9.30 ± 0.80 | 9.50 ± 2.40 | 8.00 ± 1.00 |
| 2.10 − 1.70 | 10.10 − 8.50 | 11.90 − 7.10 | 9.00 − 7.00 | ||
| Mantaro | 14.60 ± 7.37 | 9.50 ± 9.10 | 58.30 ± 32.10 | 1140 * ± 1488.0 | 21.10 * ± 7.82 |
| 21.60 − 6.90 | 20.0 − 4.0 | 90.7 − 26.6 | 2841.0 − 502.5 | 26.2 − 12.1 | |
| Miraflores | 1.70 ± 0.10 1.80 − 1.60 | nd | 11.20 ± 0.60 11.80 − 10.60 | 183.20 ± 5.20 188.40 − 178.00 | nd |
| Shullcas | 1.13 ± 0.15 | 0.73 ± 0.06 | 13.30 ± 1.50 | 91.00 ± 4.70 | 1.67 ± 1.16 |
| 1.30 − 1.00 | 0.80 − 0.70 | 14.80 − 11.80 | 91.00 − 86.30 | 1.00 − 0.70 | |
| WHO Drinking water guidelines | 2 × 103 | 10 | 3 × 103 | 300 | 10 |
| US EPA Drinking Water Standards | 1 × 103 | 0.0 | 5 × 103 | 300 | 0.0 |
| Peruvian Drinking water EQS | 2 × 103 | 10 | 3 × 103 | 300 | 10 |
| Recreational water | 3.1 | 8.1 | 81 | na | 50 |
| Water for fish | 200 | 2.5 | 1 × 103 | na | 100 farming |
| Water | 200 | 50 | 2 × 103 | 5 × 103 | 100 irrigation |
| Response Variable | As | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expected distribution | Gaussian | with identity link function | ||
| Fitted model deviance | 607.74 | with 16 residual DFs | ||
| Null model deviance | 1610.70 | with 20 residual DFs | ||
| Parsimony (AIC-like) | 148.27 | |||
| F statistic | 6.60 | (DF = 4.16) | ||
| p(F) | 0.00246 | |||
| Term | b | SE | T | p(T) |
| (Intercept) | 1.416 | 2.228 | 0.640 | 0.534 |
| Cu | 1.519 | 0.534 | 2.840 | 0.012 |
| Pb | −0.902 | 0.956 | −0.940 | 0.360 |
| Zn | 0.219 | 0.176 | 1.250 | 0.230 |
| Fe | −0.004 | 0.008 | −0.580 | 0.573 |
| River | Sector | Cu | Pb | Zn | Fe | As | HQing-children | Cu | Pb | Zn | Fe | As | HQing-adults |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mantaro | S1 S2 | 0.06 0.02 | 1.64 0.37 | 0.03 0.02 | 0.47 0.08 | 10.05 4.64 | 12.26 5.14 | 0.02 0.01 | 0.43 0.10 | 0.78 0.50 | 0.12 0.02 | 2.63 1.22 | 3.98 1.83 |
| S3 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 9.59 | 9.98 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 0.00 | 2.51 | 2.83 | |
| Cunas | S1 S2 | 0.01 0.00 | nd nd | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 3.45 2.68 | 3.46 2.70 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.08 0.09 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.90 0.70 | 0.98 0.79 |
| S3 | 0.01 | nd | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.07 | 3.08 | 0.00 | nd | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 0.88 | |
| Shullcas | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.06 0.06 | 0.01 0.00 | 0.01 0.02 | 1.15 0.38 | 1.23 0.47 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.02 0.02 | 0.11 0.10 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.30 0.10 | 0.43 0.22 |
| S3 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.38 | 0.47 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.25 | |
| Chilca | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.03 0.29 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.03 0.02 | 0.27 0.26 | 0.33 0.58 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.01 0.08 | 0.05 0.05 | 0.01 0.01 | 0.07 0.07 | 0.14 0.20 |
| S3 | 0.00 | 0.37 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.68 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.23 | |
| Miraflores | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.01 | nd nd | 0.00 0.00 | 0.03 0.03 | nd nd | 0.04 0.04 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.10 0.10 | 0.01 0.01 | nd nd | 0.10 0.11 |
| S3 | 0.00 | nd | 0.00 | 0.03 | nd | 0.04 | 0.00 | nd | 0.09 | 0.01 | nd | 0.10 | |
| Chía | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.01 0.01 | 0.00 0.00 | 5.37 6.14 | 5.38 6.15 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.13 0.13 | 0.00 0.00 | 1.41 1.61 | 1.54 1.74 |
| S3 | 0.00 | nd | 0.01 | 0.00 | 8.82 | 8.83 | 0.00 | nd | 0.13 | 0.00 | 2.31 | 2.44 | |
| Chanchas | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.03 | 0.33 0.32 | 0.01 0.01 | 0.04 0.02 | nd nd | 0.37 0.38 | 0.00 0.01 | 0.09 0.08 | 0.11 0.14 | 0.01 0.01 | nd nd | 0.21 0.23 |
| S3 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.05 | nd | 0.39 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.01 | nd | 0.18 |
| River | Sector | Cu | Pb | Zn | Fe | As | HIderm-children | Cu | Pb | Zn | Fe | As | HIderm-adults |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mantaro | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.08 0.02 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.01 0.00 | 0.04 0.02 | 0.13 0.04 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.03 0.01 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.01 0.01 | 0.04 0.01 |
| S3 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| Cunas | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.01 0.01 | 0.01 0.01 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 |
| S3 | 0.00 | nd | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | nd | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Shullcas | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.01 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 |
| S3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Chilca | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.01 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.02 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.01 |
| S3 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |
| Miraflores | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.00 0.00 |
| S3 | 0.00 | nd | 0.00 | 0.00 | nd | 0.00 | 0.00 | nd | 0.00 | 0.00 | nd | 0.00 | |
| Chía | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.02 0.02 | 0.02 0.02 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.01 0.01 | 0.01 0.01 |
| S3 | 0.00 | nd | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.00 | nd | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Chanchas | S1 S2 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.02 0.02 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.02 0.02 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.01 0.01 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | nd nd | 0.01 0.01 |
| S3 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | nd | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | nd | 0.01 |
| River | Sector | As | Pb | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Adults | Children | Adults | ||
| Mantaro | S1 S2 | 2.63 1.22 | 1.12 5.20 | 1.14 2.56 | 6.73 1.51 |
| S3 | 2.51 | 1.07 | 2.28 | 1.35 | |
| Cunas | S1 S2 | 9.05 7.04 | 3.86 3.00 | nd nd | nd nd |
| S3 | 8.04 | 3.43 | nd | nd | |
| Shullcas | S1 S2 | 3.02 1.01 | 1.29 4.29 | 3.99 3.99 | 2.36 2.36 |
| S3 | 1.01 | 4.29 | 4.56 | 2.69 | |
| Chilca | S1 S2 | 7.04 6.94 | 3.00 2.96 | 2.28 1.99 | 1.35 1.18 |
| S3 | 7.14 | 3.05 | 2.56 | 1.51 | |
| Chía | S1 S2 | 1.41 1.61 | 6.01 6.86 | nd nd | nd nd |
| S3 | 2.31 | 9.87 | nd | nd | |
| Chanchas | S1 S2 | nd nd | nd nd | 2.28 2.22 | 1.35 1.31 |
| S3 | nd | nd | 2.34 | 1.38 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Custodio, M.; Cuadrado, W.; Peñaloza, R.; Montalvo, R.; Ochoa, S.; Quispe, J. Human Risk from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Arsenic in Water from Rivers with Mining Influence in the Central Andes of Peru. Water 2020, 12, 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071946
Custodio M, Cuadrado W, Peñaloza R, Montalvo R, Ochoa S, Quispe J. Human Risk from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Arsenic in Water from Rivers with Mining Influence in the Central Andes of Peru. Water. 2020; 12(7):1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071946
Chicago/Turabian StyleCustodio, María, Walter Cuadrado, Richard Peñaloza, Raúl Montalvo, Salomé Ochoa, and Jocelyn Quispe. 2020. "Human Risk from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Arsenic in Water from Rivers with Mining Influence in the Central Andes of Peru" Water 12, no. 7: 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071946
APA StyleCustodio, M., Cuadrado, W., Peñaloza, R., Montalvo, R., Ochoa, S., & Quispe, J. (2020). Human Risk from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Arsenic in Water from Rivers with Mining Influence in the Central Andes of Peru. Water, 12(7), 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071946







