The Improvement Effects of Different Treatment Methods of Soil Wastewater Washing on Environmental Pollution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. BC Sample Preparation and Characterization
2.2. Soil Characteristics and the Soil Washing Effluents
2.3. Heavy Metals Removal from the Washing Wastewater by Ca(OH)2 Addition
2.4. Adsorption of Heavy Metals by BCs in the Wastewater
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. BC Characterization
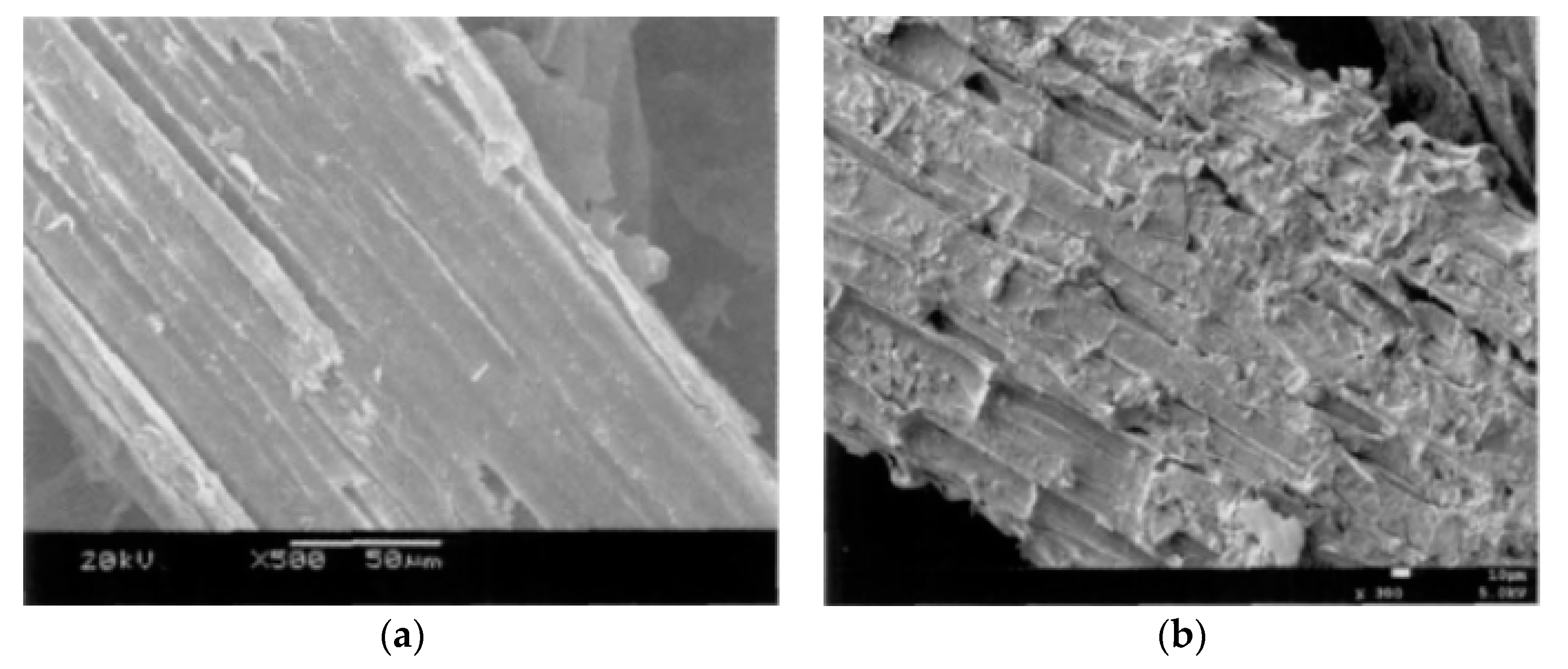
3.1.1. SEM Analysis
3.1.2. BET Analysis
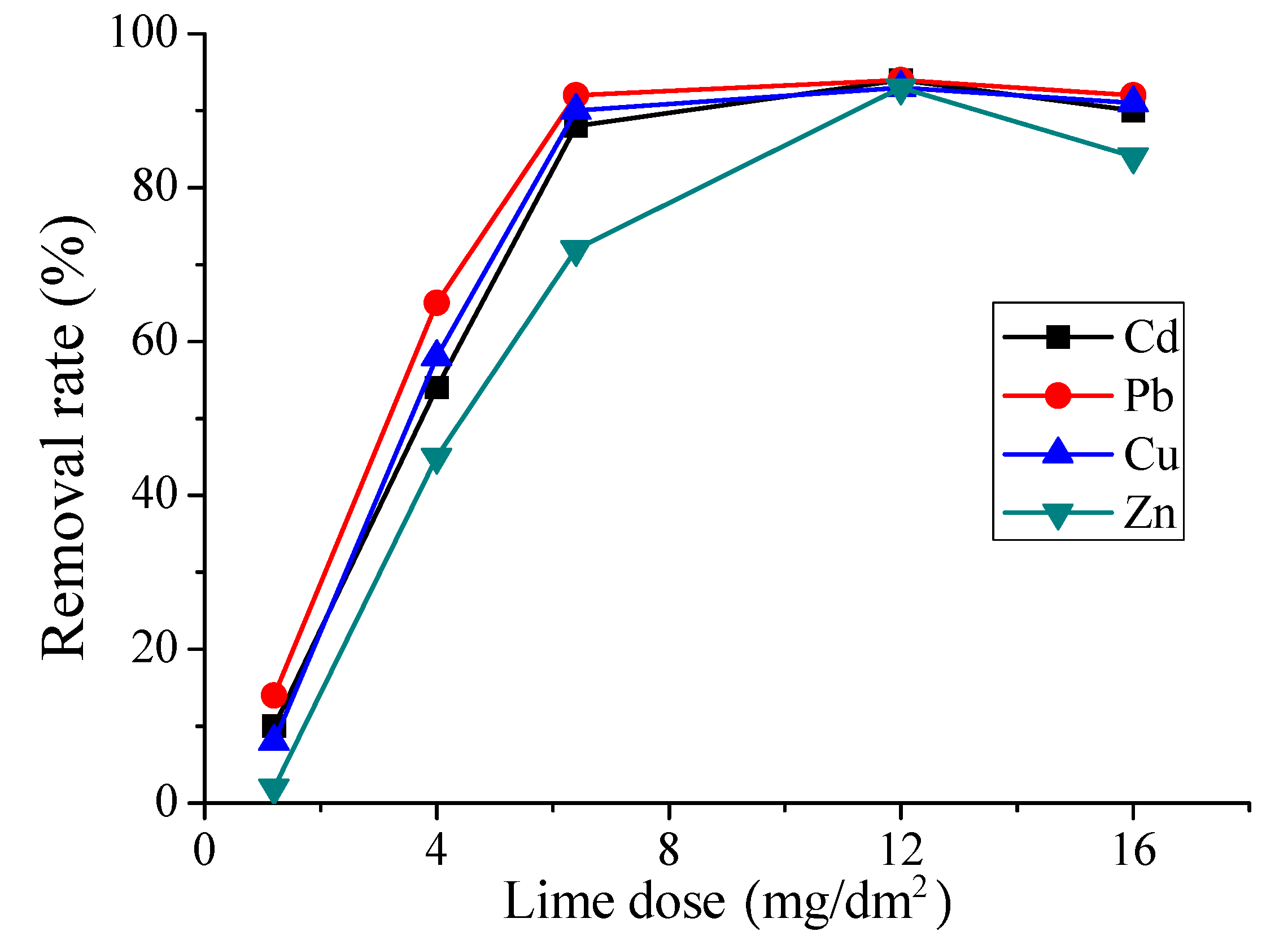
3.2. Heavy Metals Removal by Ca(OH)2 Addition
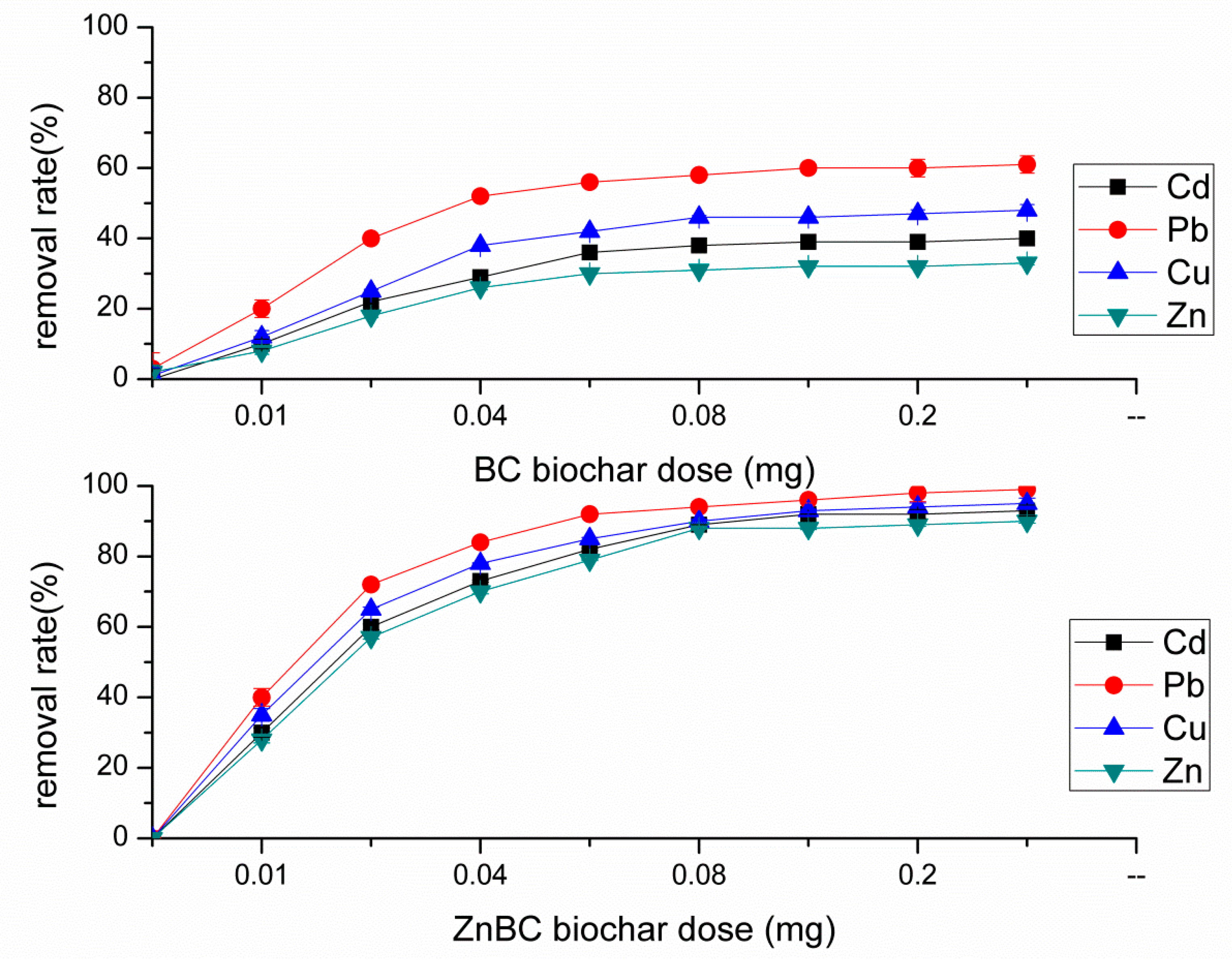
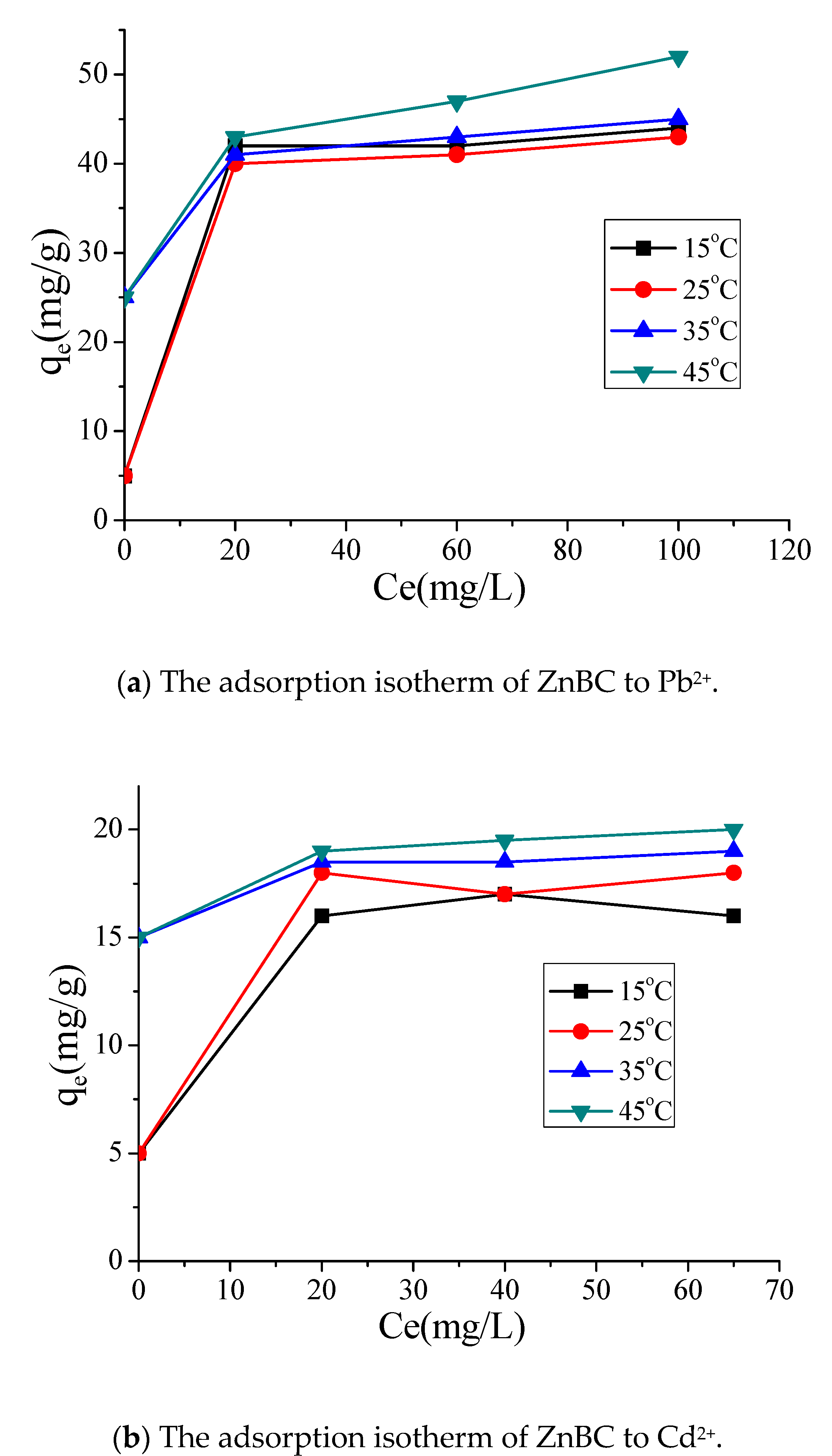
3.3. BC Sorption of Heavy Metals
3.4. Comparison of Ca(OH)2 and BC Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, F.-J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Tang, Z.; McGrath, S.P. Soil Contamination in China: Current Status and Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viard, B.; Pihan, F.; Promeyrat, S.; Pihan, J.-C. Integrated assessment of heavy metal (Pb, Zn, Cd) highway pollution: Bioaccumulation in soil, Graminaceae and land snails. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiyuan, J.; Lau, A.Y.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhang, W.; Kao, C.-M.; Baek, K.; Ok, Y.S.; Li, X. Chelant-enhanced washing of CCA-contaminated soil: Coupled with selective dissolution or soil stabilization. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 612, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, N.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Thangarajan, R.; Kumpiene, J.; Park, J.; Makino, T.; Kirkham, M.B.; Scheckel, K.G. Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils–To mobilize or to immobilize. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 266, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, L.; Li, N.; Luo, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Christie, P. Effects of multiple heavy metal contamination and repeated phytoextraction by Sedum plumbizincicola on soil microbial properties. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2010, 46, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.; Li, Y. Reliability and stability of immobilization remediation of Cd polluted soils using sepiolite under pot and field trials. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, T.; Sugahara, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Takano, H.; Kamiya, T.; Sasaki, K.; Itou, T.; Sekiya, N. Remediation of cadmium contamination in paddy soils by washing with chemicals: Selection of washing chemicals. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wei, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.; Qian, T.; Zheng, W. Effect of soil washing with only chelators or combining with ferric chloride on soil heavy metal removal and phytoavailability: Field experiments. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Takano, H.; Kamiya, T.; Itou, T.; Sekiya, N.; Inahara, M.; Sakurai, Y. Restoration of cadmium-contaminated paddy soils by washing with ferric chloride: Cd extraction mechanism and bench-scale verification. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermont, G.; Bergeron, M.; Mercier, G.; Richer-LaFLèche, M. Soil washing for metal removal: A review of physical/chemical technologies and field applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Maejima, Y.; Akahane, I.; Kamiya, T.; Takano, H.; Fujitomi, S.; Ibaraki, T.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Bolan, N. A practical soil washing method for use in a Cd-contaminated paddy field, with simple on-site wastewater treatment. Geoderma 2016, 270, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, A.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Huguenot, D.; Fabbricino, M.; Esposito, G. Application of an electrochemical treatment for EDDS soil washing solution regeneration and reuse in a multi-step soil washing process: Case of a Cu contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 163, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satyro, S.; Race, M.; Di Natale, F.; Erto, A.; Guida, M.; Marotta, R. Simultaneous removal of heavy metals from field-polluted soils and treatment of soil washing effluents through combined adsorption and artificial sunlight-driven photocatalytic processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, M.; Chen, M.-Y. Coupling and Coordination Development of Australian Energy, Economy, and Ecological Environment Systems from 2007 to 2016. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.L.; Schouten, G.; Schultz, C. Biologically produced sulphide for purification of process streams, effluent treatment and recovery of metals in the metal and mining industry. Hydrometall 2006, 83, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Luo, Z.; Hills, C.; Xue, G.; Tyrer, M. Precipitation of heavy metals from wastewater using simulated flue gas: Sequent additions of fly ash, lime and carbon dioxide. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2605–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Samanta, A.N.; Ray, S. Reduction of COD and removal of Zn2+ from rayon industry wastewater by combined electro-Fenton treatment and chemical precipitation. Desalination 2011, 266, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadirvelu, K. Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from an agricultural solid waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 76, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Dong, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, C.-H.; Xia, P. Influence of different kinds of BC on Cd and Pb forms in soil. J. Agro. Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 892–898. [Google Scholar]
- Khorram, M.S.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, D.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, H.; Yuet, Y. Dissipation of fomesafen in BC-amended soil and its availability to corn (Zea mays L.) and earthworm (Eisenia fetida). J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.; Syed, T.A.B. Potential of sawdust and corn cobs derived BC to improve soil aggregate stability, water retention, and crop yield of degraded sandy loam soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudrahem, F.; Soualah, A.; Aissani-Benissad, F. Pb(II) and Cd(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Activated Carbon Developed from Coffee Residue Activated with Phosphoric Acid and Zinc Chloride. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Tan, F.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Zhenga, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. ZnCl2-activated BC from biogas residue facilitates aqueous As(III) removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 377, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Removal of arsenic and cadmium with sequential soil washing techniques using Na 2 EDTA, oxalic and phosphoric acid: Optimization conditions, removal effectiveness and ecological risks. Chemosphere 2016, 156, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Du, X.; Li, S.; Zeng, J.; Yi, Y.; Zeng, G. Simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0 from simulated flue gas over CoOx-CeO2 loaded biomass activated carbon derived from maize straw at low temperatures. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Guo, L.; Nie, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, G. Adsorption characteristics of Cu and Zn onto various size fractions of aggregates from red paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Huang, B.; Luo, N.; Long, L.; Huang, M.; Zhai, X.; Zeng, G. Effect of land use pattern change from paddy soil to vegetable soil on the adsorption-desorption of cadmium by soil aggregates. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 24, 2734–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.D. Agricultural chemical analysis of soil. Chin. Agric. Press 2000, 6, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, D.F. Loss-on-ignition as an estimate of organic matter and organic carbon in non-calcareous soils. J. Soil Sci. 1964, 15, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-W.; Huang, B.; Huang, J.-Q.; Chen, G.; Xiong, W.-P.; Nie, X.-D.; Ma, W.-M.; Zeng, G.-M. Influence of different phosphates on adsorption and leaching of Cu and Zn in red soil. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, B.; Luo, N.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, G. Remediation of multiple heavy metal-contaminated soil through the combination of soil washing and in situ immobilization. J. Total. Environ. 2018, 635, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.T.; Kameda, T.; Kumagai, S.; Yoshioka, T. Effectiveness of Mg–Al-layered double hydroxide for heavy metal removal from mine wastewater and sludge volume reduction. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, G.Z.; Li, W.G.; Ping, W. Pyrolysis Characteristics and Kinetics of the Preparation Process of Sludge-Based Activated Carbon by ZnCl2 Activation Method. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2013, 20, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, N. Reaction of Anions and Cations with Variable-Charge Soils. Adv. Agron. 1986, 38, 183–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gong, D. Discrimination of breast tumors in ultrasonic images using an ensemble classifier based on TensorFlow framework with feature selection. J. Investig. Med. 2019, 67 (Suppl. S1), A3. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Gao, B. Removal of Cu, Zn, and Cd from aqueous solutions by the dairy manure-derived BC. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.K.; Strezov, V.; Chan, K.Y.; Ziolkowski, A.; Nelson, P.F. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on production and nutrient properties of wastewater sludge BC. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Xu, C.; Sheng, G.D. Surface characteristics of crop-residue-derived black carbon and lead(II) adsorption. Water Res. 2008, 42, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Lehmann, J.; McBride, M.B.; Hay, A.G. Adsorption of copper and zinc by BCs produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.-S. Removal of lead from water using BCs prepared from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Bricka, M.; Smith, F.; Yancey, B.; Mohammad, J.; Steele, P.H.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Gómez-Serrano, V.; Gong, H.; et al. Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.J.; Pardo, R.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Cadmium(II) and zinc(II) adsorption by the aquatic moss Fontinalis antipyretica: Effect of temperature, pH and water hardness. Water Res. 2004, 38, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Lian, F.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Xing, B.; Qiu, W. Synthesis and characterization of a novel MnOx-loaded biochar and its adsorption properties for Cu2+ in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 242, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.R. The relative adsorption selectivities of Pb, Cu, Zn, Cd and Ni by soils developed on shale in New Valley, Egypt. Geoderma 2008, 144, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB18918-2002. Discharge standard of pollutants for municipal wastewater treatment plant. Stand. Press China 2003, 7, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kadirvelu, K.; Namasivayam, C. Agricutural By-Product as Metal Adsorbent: Sorption of Lead(II) from Aqueous Solution onto Coirpith Carbon. Environ. Technol. 2000, 21, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, Z.; Chaudhari, L.B. Separation of binary heavy metals from aqueous solutions by nanofiltration and characterization of the membrane using Spiegler–Kedem model. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Ghafarinazari, A.; Shirazian, S.; Khoshsima, A. Numerical modeling and optimization of wastewater treatment using porous polymeric membranes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2012, 53, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.L.; Liu, W.J.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, H. Magnesium Oxide Embedded Nitrogen Self-Doped BC Composites: Fast and High-Efficiency Adsorption of Heavy Metals in an Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10081–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Geng, Z.J.; Yang, S.S.; Sun, C.Y. Kinetics and thermodynamics for Cu2+ adsorption by modified corn straw. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 7, 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.C.; Pang, Y. Adsorption characteristics of rice husk BC on Iow-concentration Pb(Ⅱ) fromwater. Ind. Water Treat. 2020, 40, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Halim, S.; Shehata, A.; El-Shahat, M.F. Removal of lead ions from industrial waste water by different types of natural materials. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1678–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, W.E.; Johns, M.M. Agricultural by-products as metal adsorbents: Sorption properties and resistance to mechanical abrasion. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. 2010, 66, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Wang, Q. Synthesis of an efficient Pb adsorption nano-crystal under strong alkali hydrothermal environment using a gemini surfactant as directing agent. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2019, 41, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar]
| Variables/Properties and Units | Value |
|---|---|
| Clay (%) | 32.81 ± 0.04 |
| Silt (%) | 43.27 ± 3.43 |
| Sand (%) | 23.92 ± 3.48 |
| pH | 5.22 ± 0.03 |
| SOM (%) | 38.43 ± 0.59 |
| CEC (cmol/kg) | 20.50 ± 1.30 |
| Fe (g/kg) | 32.13 ± 3.18 |
| Cd (mg/kg) | 16.83 ± 0.22 |
| Pb (mg/kg) | 465.28 ± 2.36 |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 182.43 ± 2.25 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 1178.35 ± 1.58 |
| Metal Elements | Concentration (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|
| Fe | 27.1 |
| Mg | 122.6 |
| Mn | 3.8 |
| Cu | 0.006 |
| Zn | 212.5 |
| Pb | 0.3 |
| Cd | 84.4 |
| Sample. | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 59.21 | 0.17 | 2.60 |
| ZnBC | 780.23 | 0.59 | 2.57 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, L.; Chen, M. The Improvement Effects of Different Treatment Methods of Soil Wastewater Washing on Environmental Pollution. Water 2020, 12, 2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092329
Zhan L, Chen M. The Improvement Effects of Different Treatment Methods of Soil Wastewater Washing on Environmental Pollution. Water. 2020; 12(9):2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092329
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Linjie, and Minxian Chen. 2020. "The Improvement Effects of Different Treatment Methods of Soil Wastewater Washing on Environmental Pollution" Water 12, no. 9: 2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092329
APA StyleZhan, L., & Chen, M. (2020). The Improvement Effects of Different Treatment Methods of Soil Wastewater Washing on Environmental Pollution. Water, 12(9), 2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092329




