Evaluation of LNAPL Behavior in Water Table Inter-Fluctuate Zone under Groundwater Drawdown Condition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
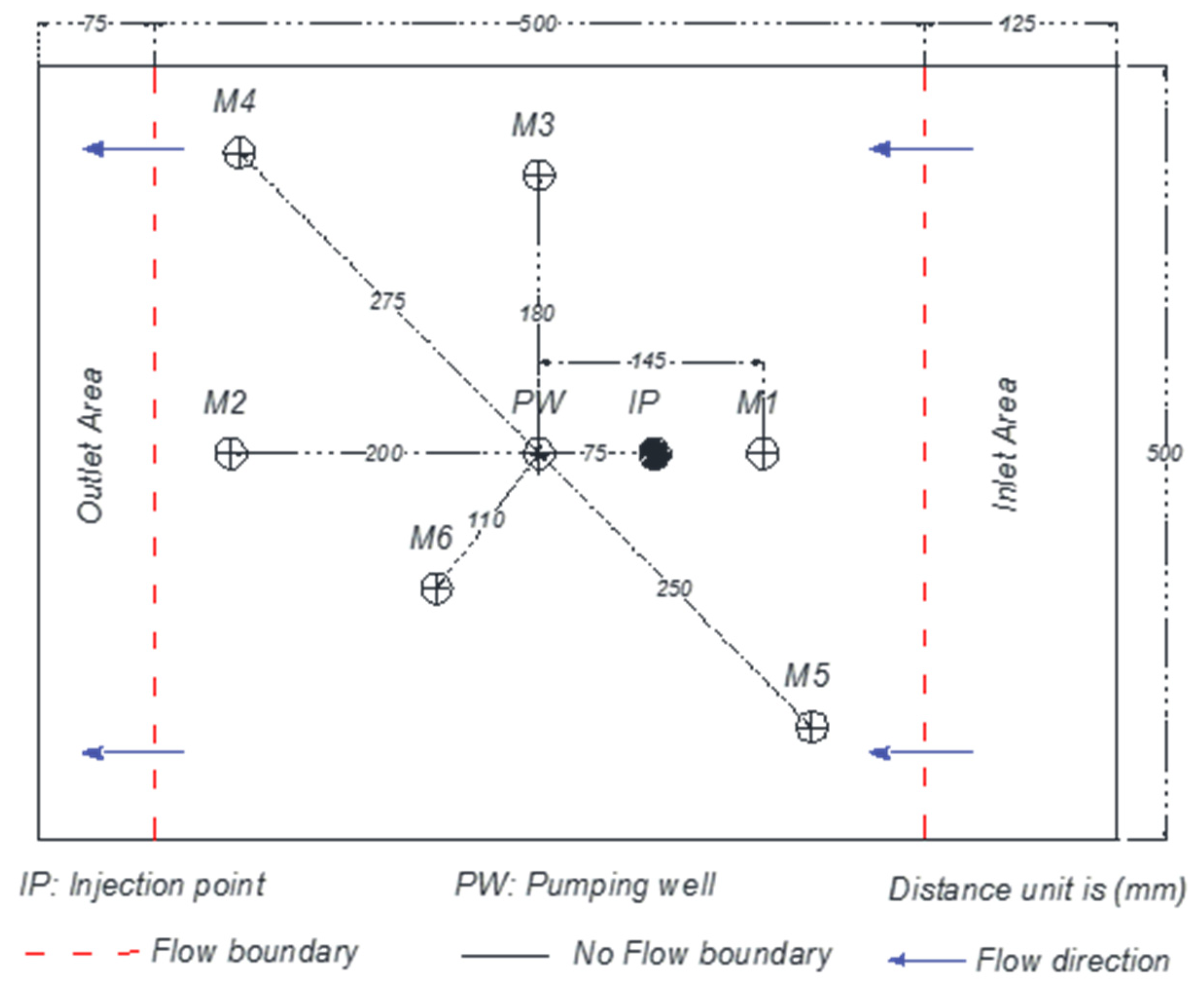
2.1. Tank Description
2.2. Aquifer Material
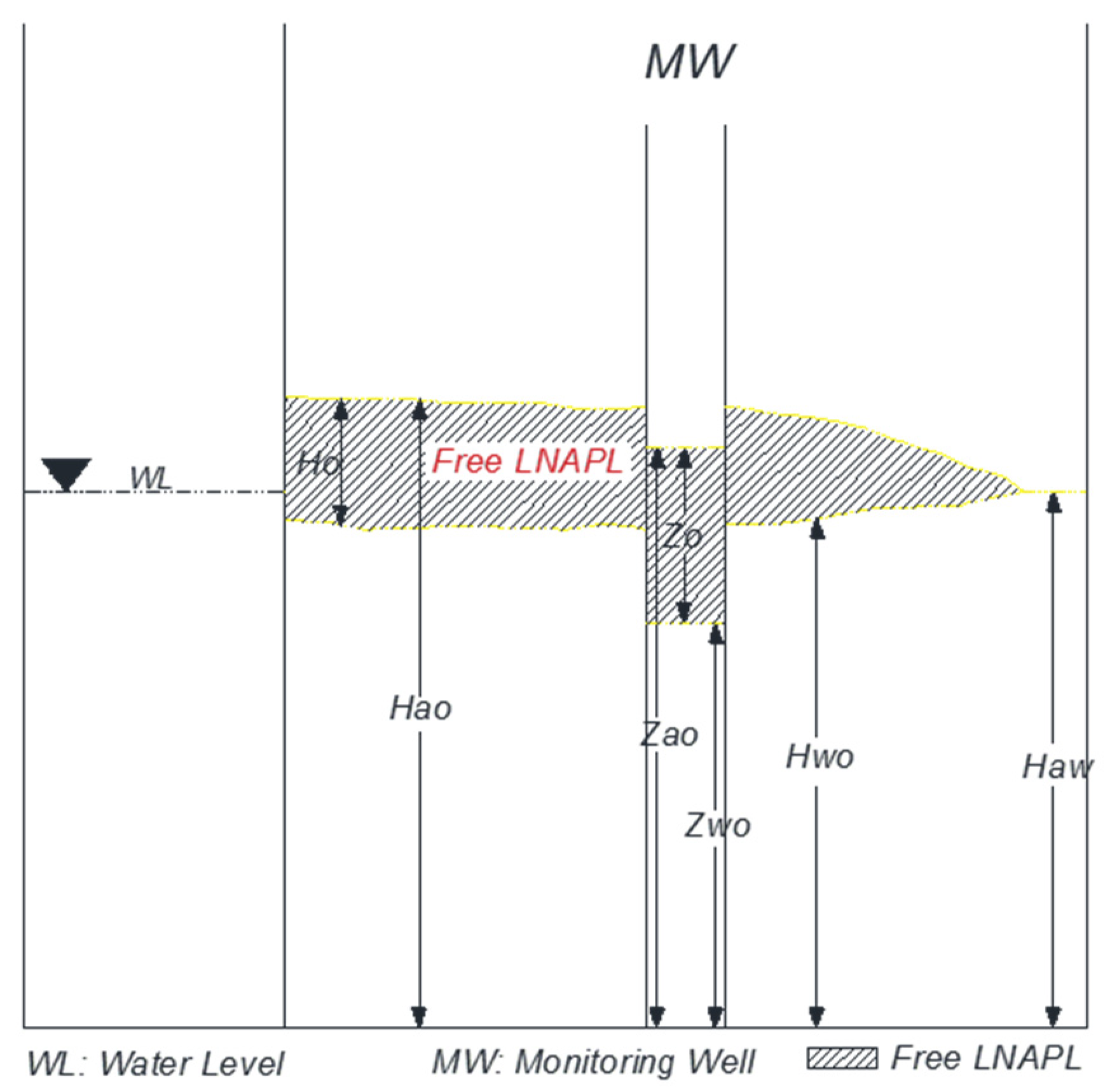
2.3. LNAPL Properties
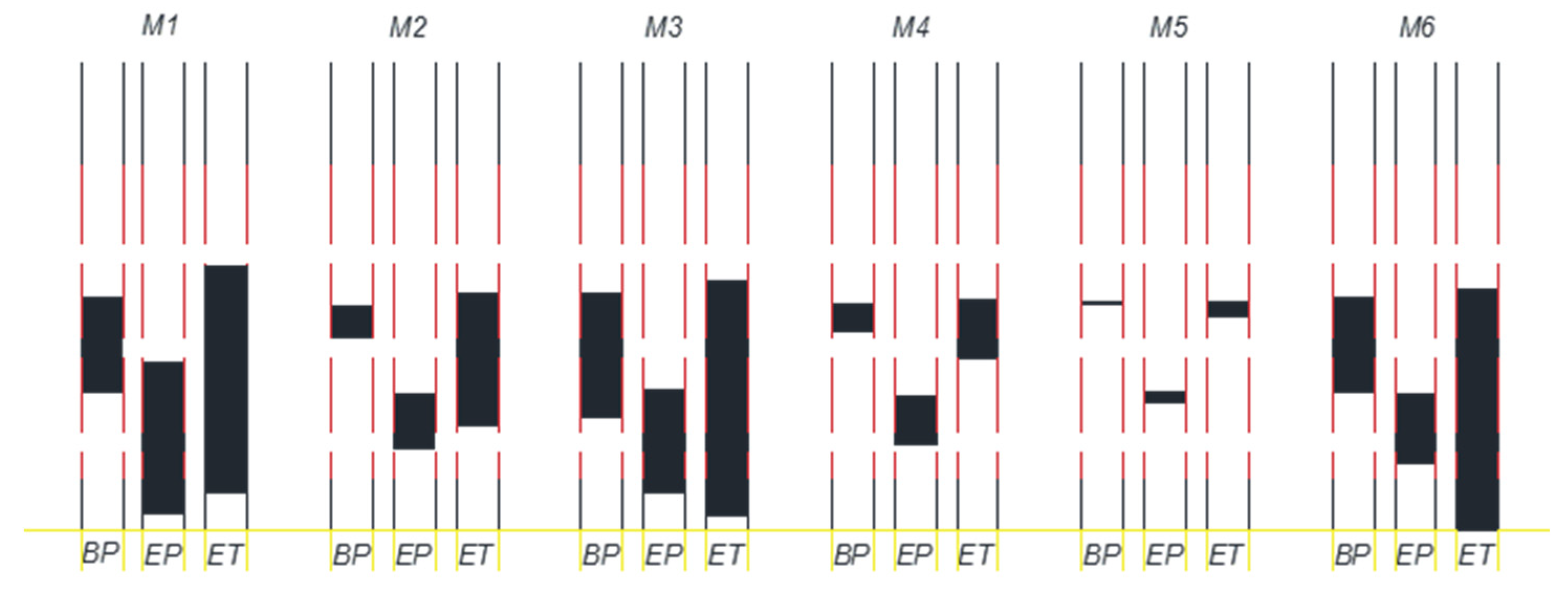
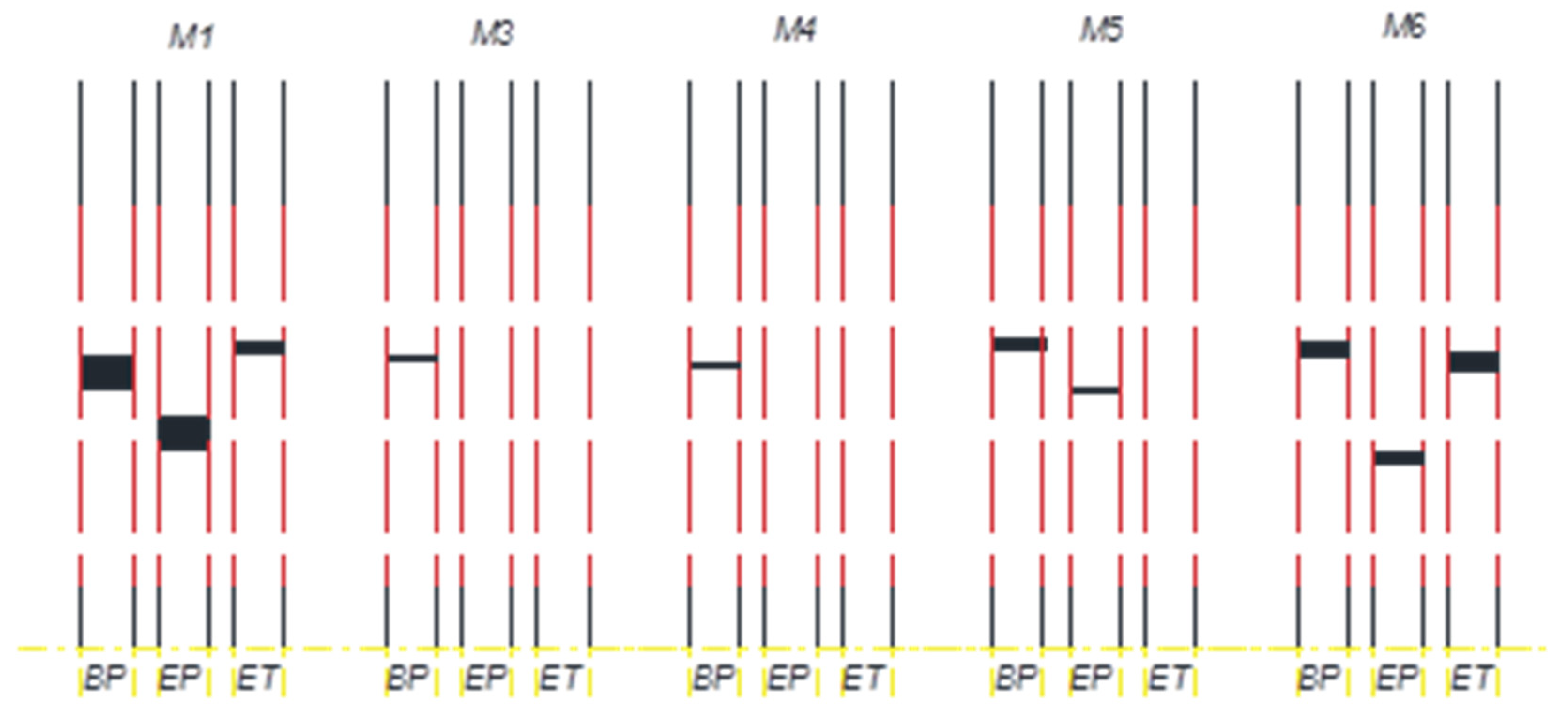
2.4. Injection of LNAPLs
3. Experiments
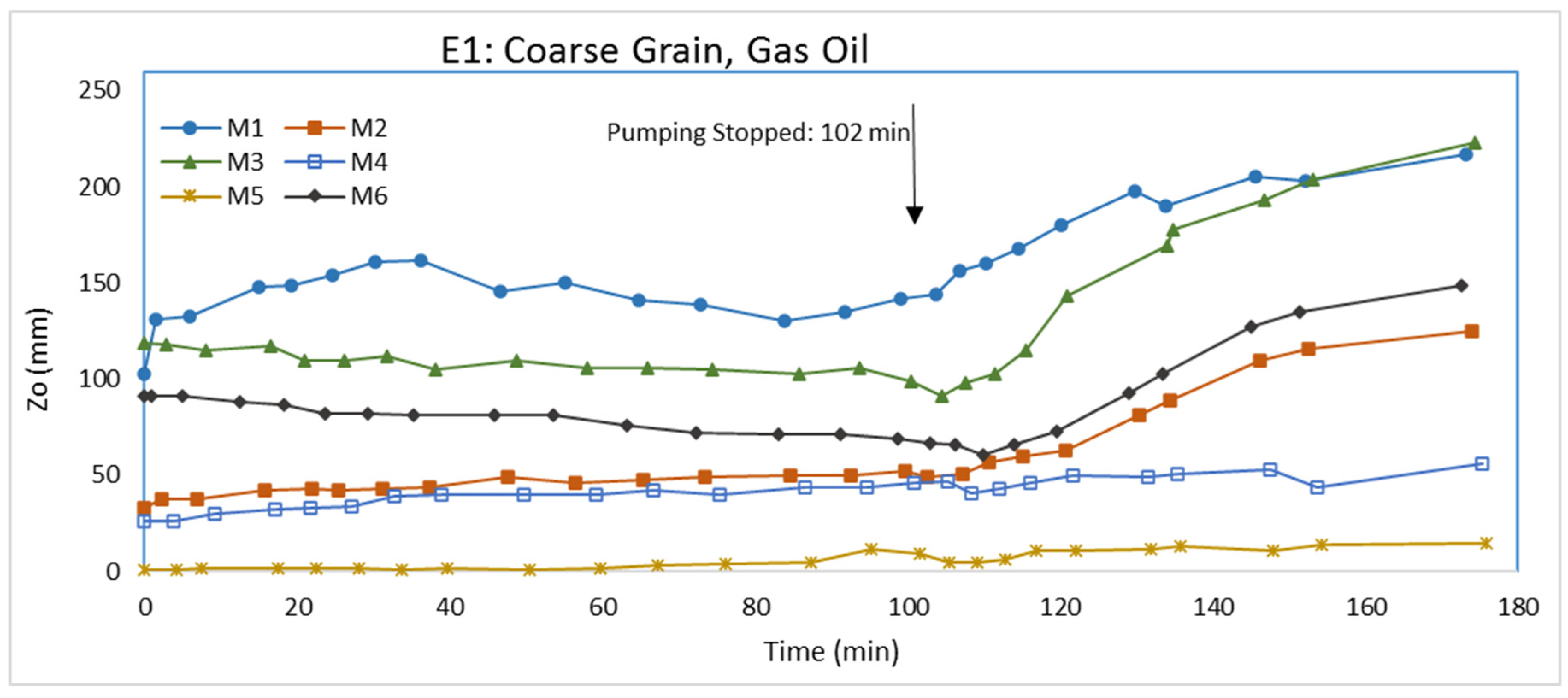
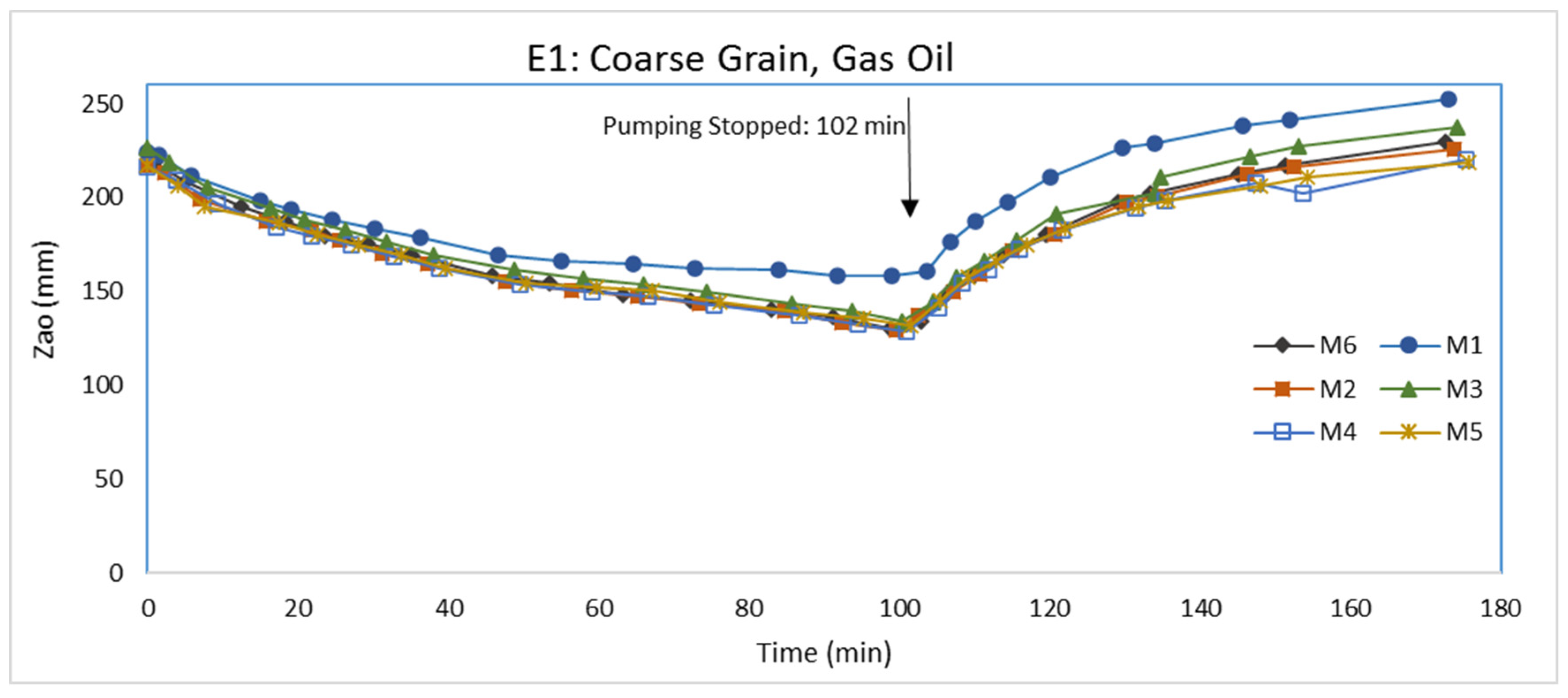
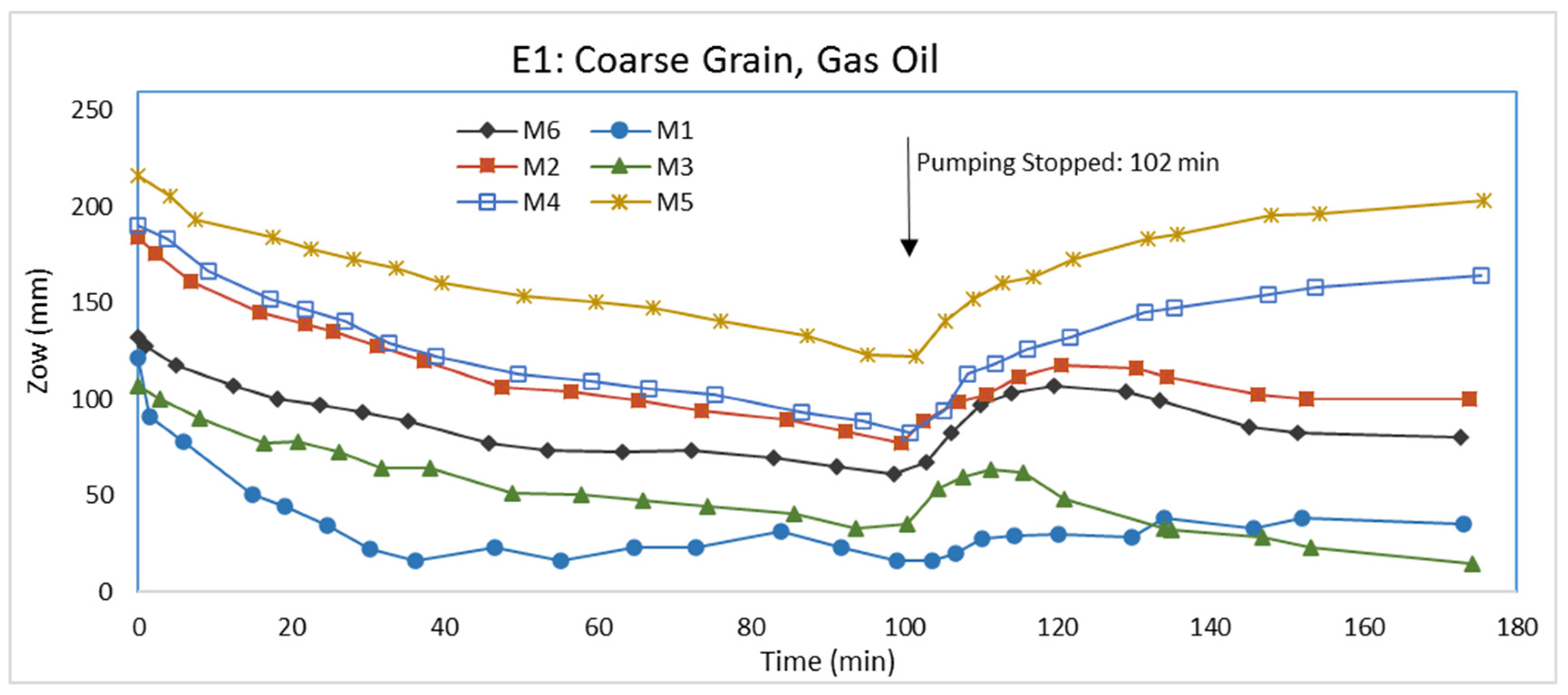
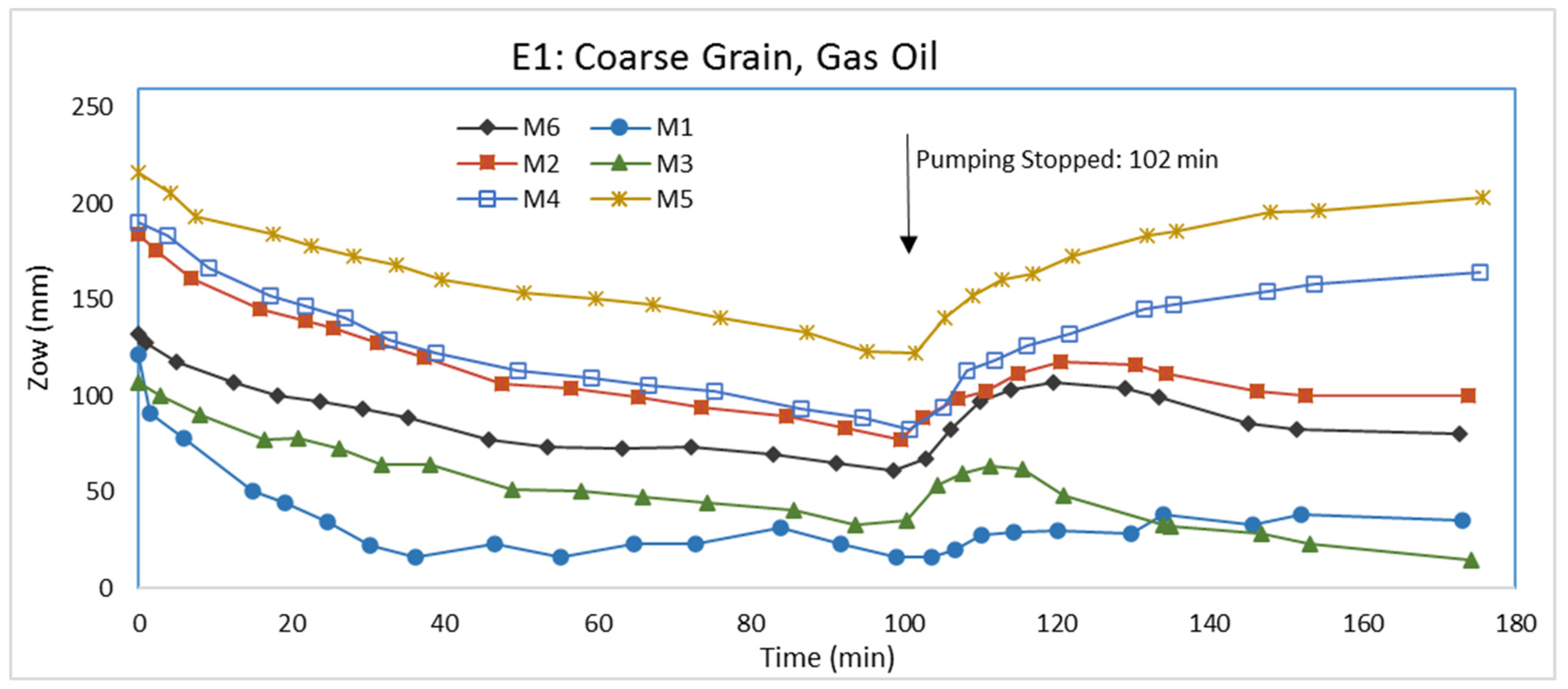
3.1. Experiment E1: Coarse Grain, Gas Oil
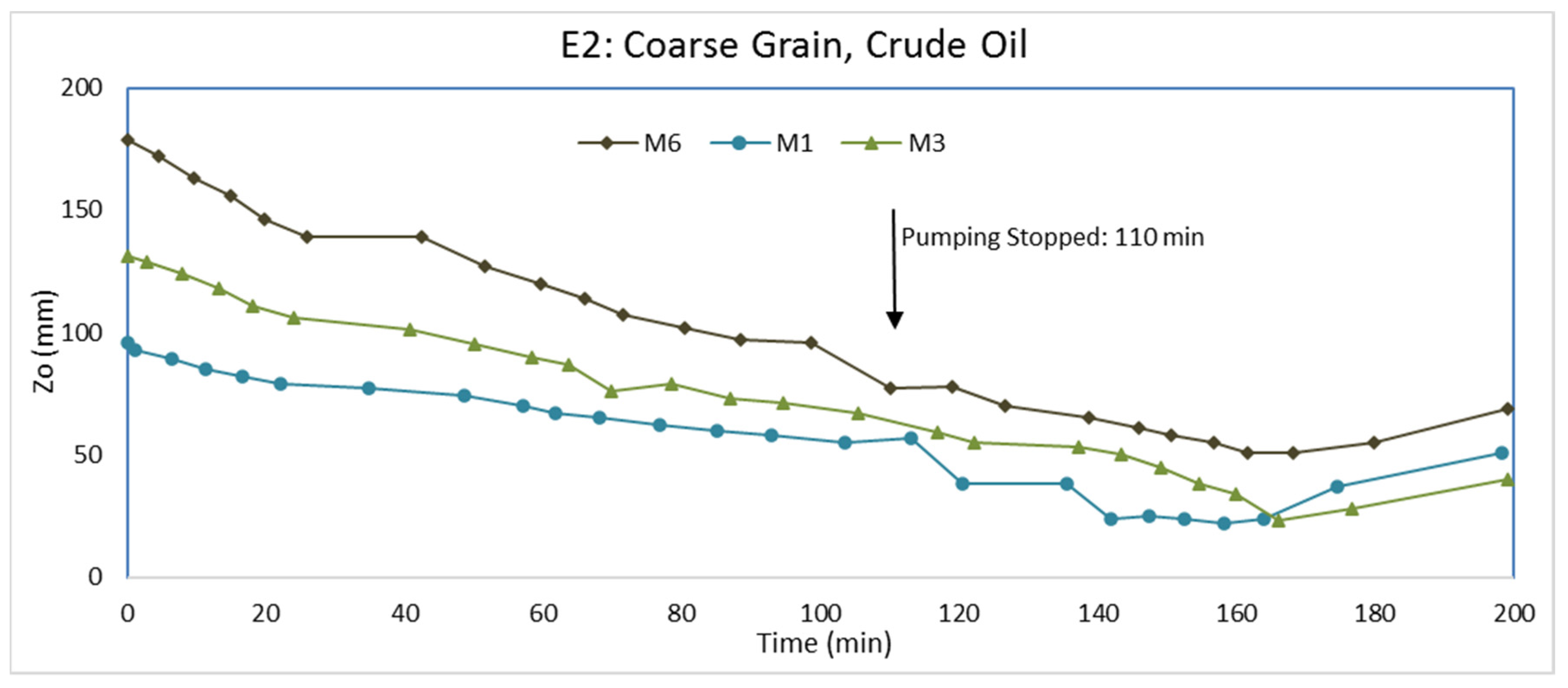
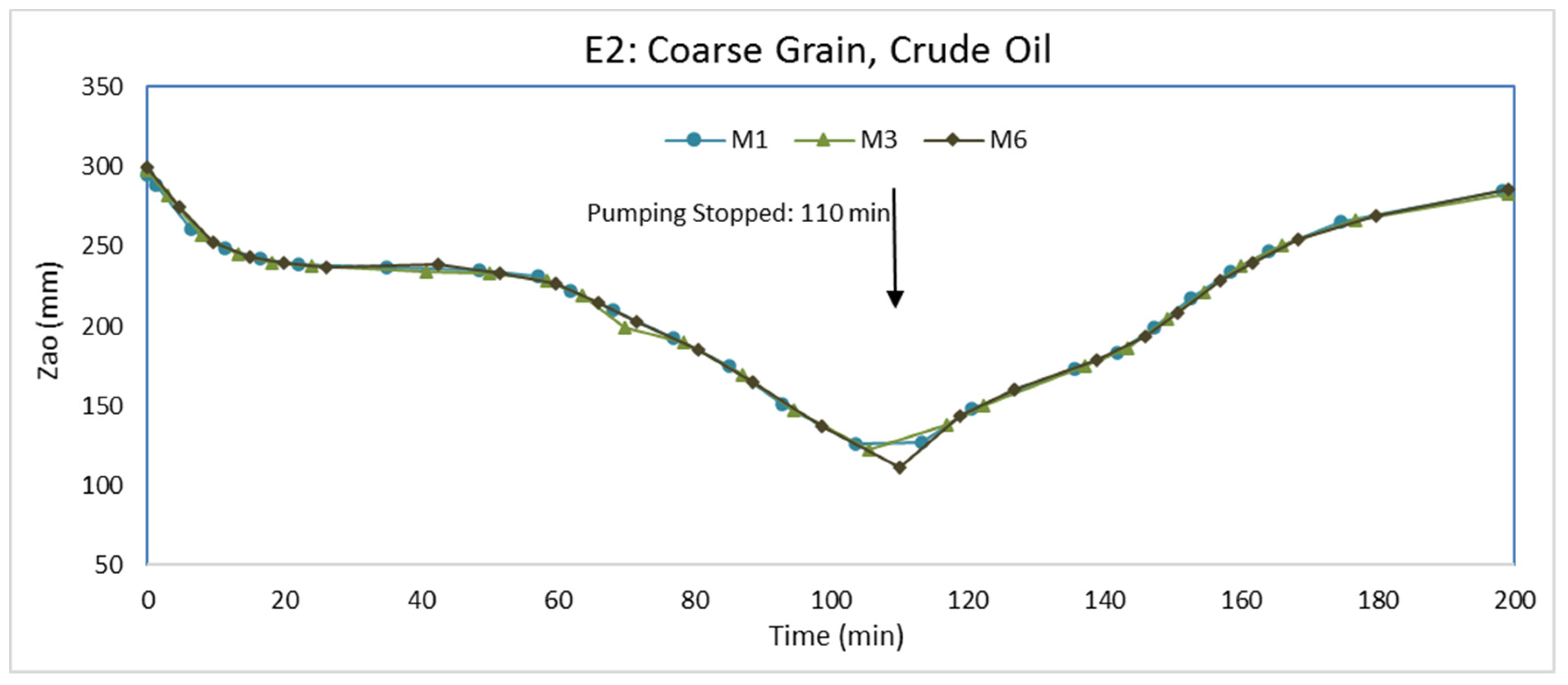
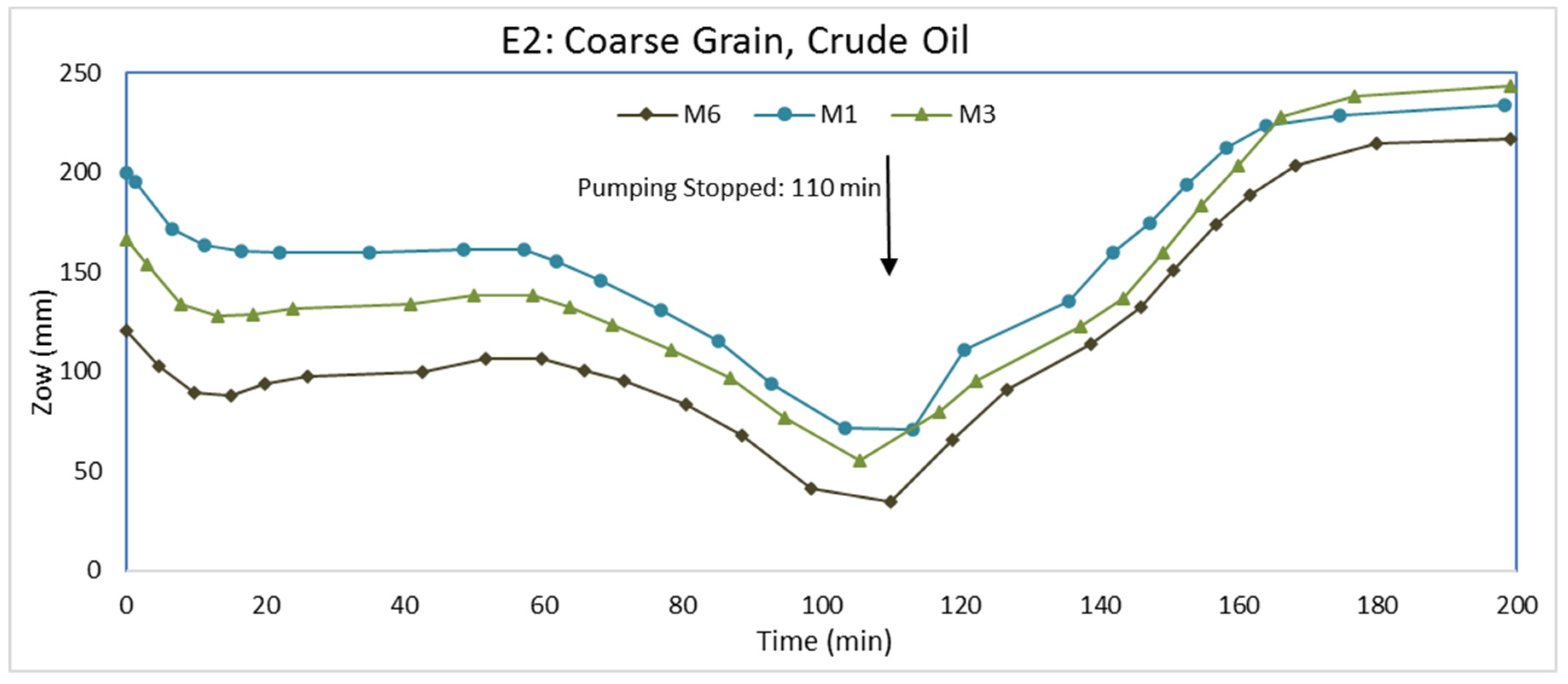
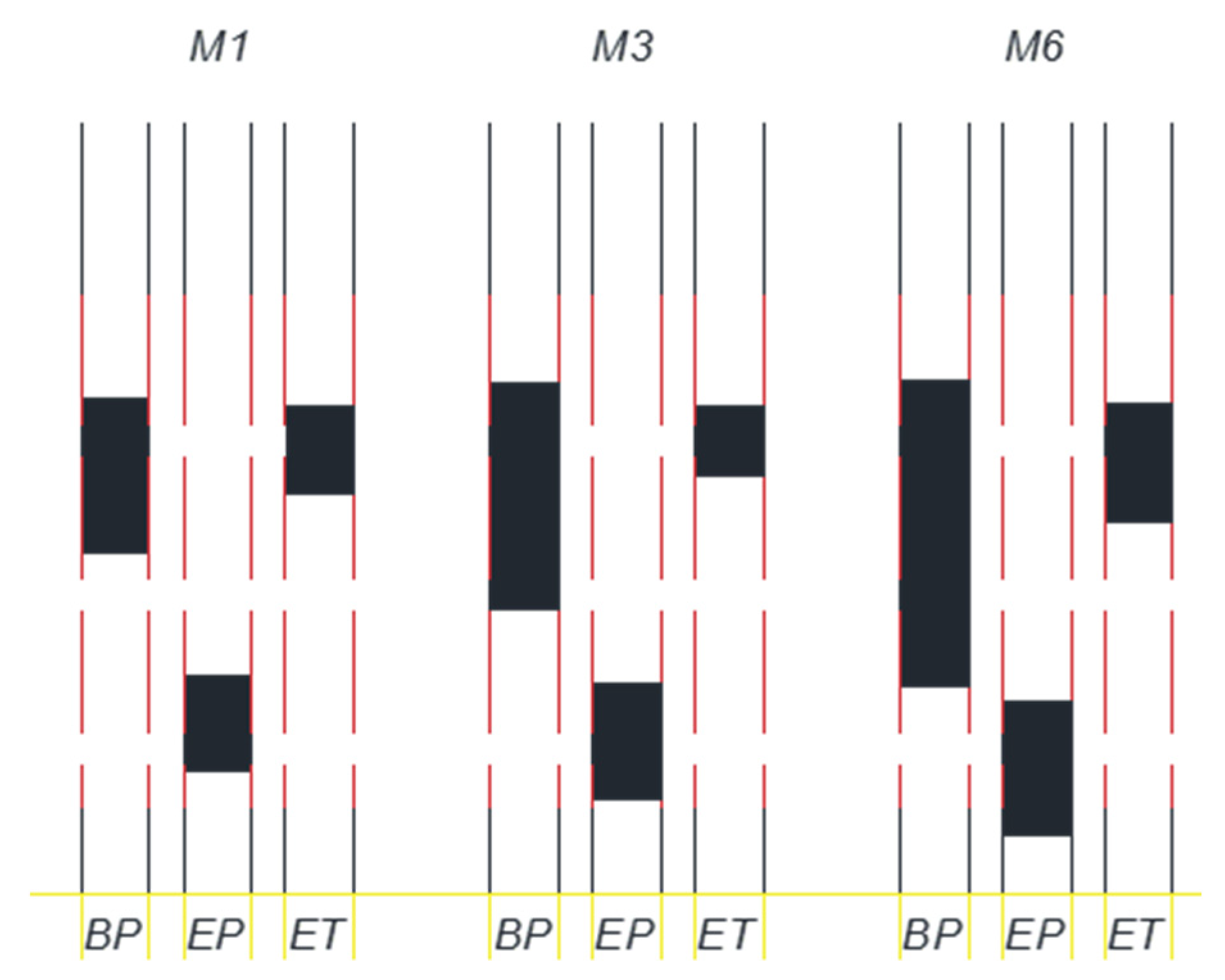
3.2. Experiment E2: Coarse Grain, Crude Oil
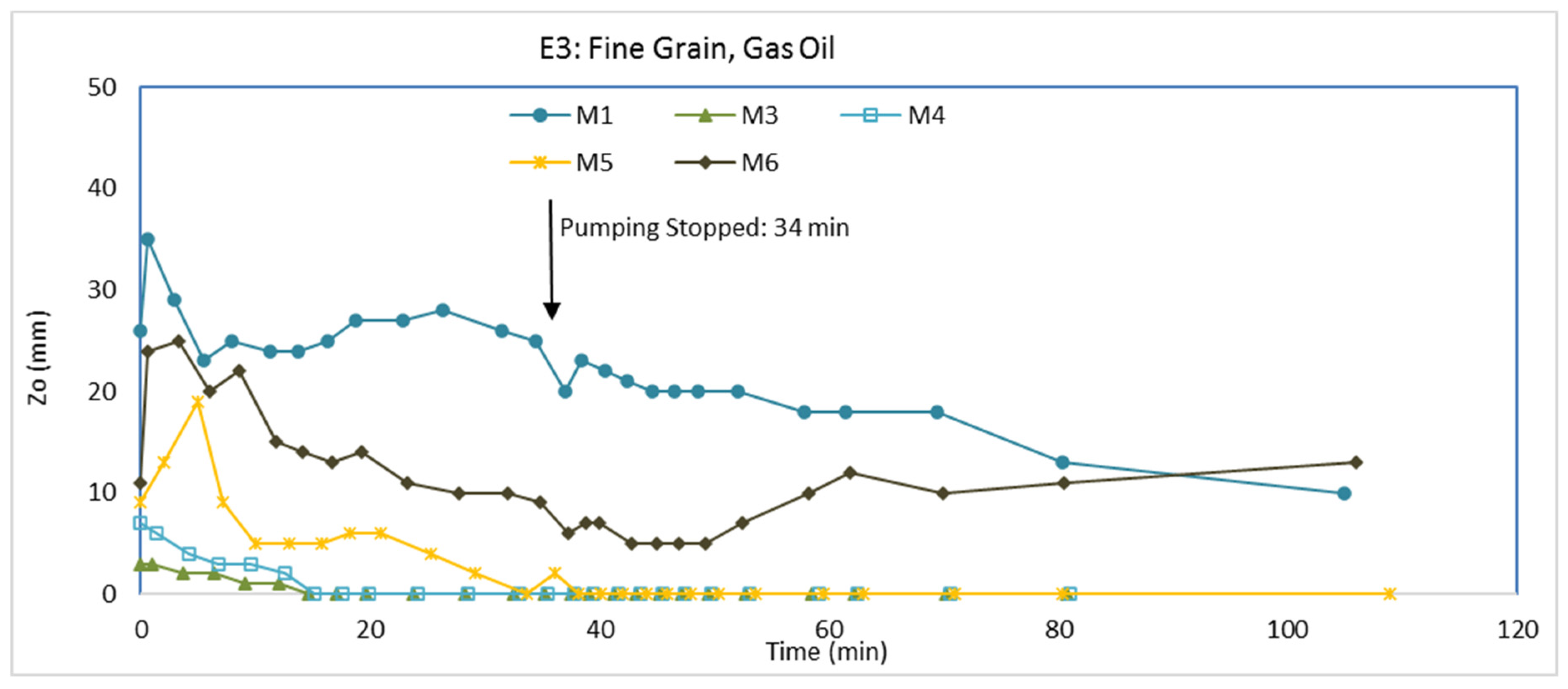
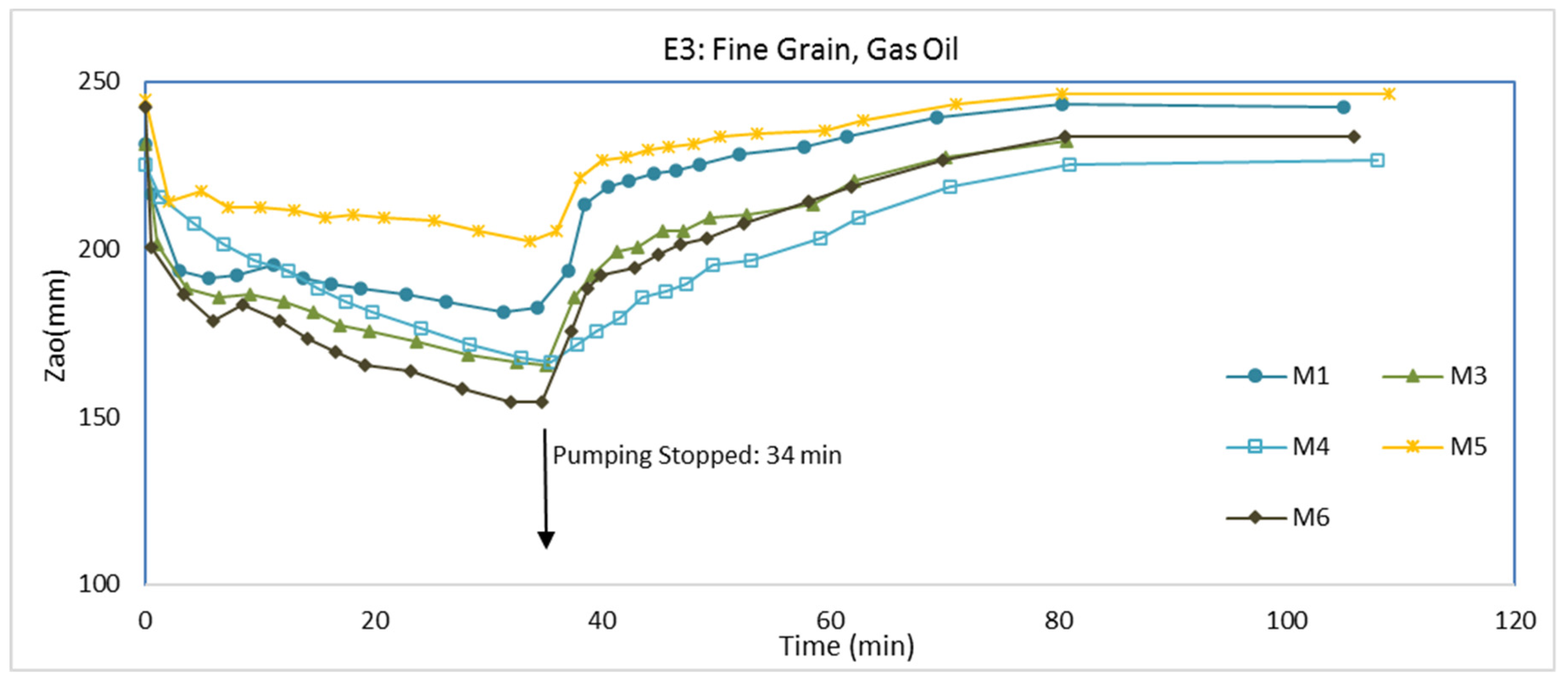
3.3. Experiment E3: Fine Grain, Gas Oil
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ASTM E2531-06(2014). In Standard Guide for Development of Conceptual Site Models and Remediation Strategies for Light Nonaqueous-Phase Liquids Released to the Subsurface; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- CL: AIRE. An Illustrated Handbook of Lnapl Transport and Fate in the Subsurface; CL: AIRE: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-1-905046-24-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fetter, C.W.; Thomas, B.; Boving, T.B.; Kreamer, D. Contaminant Hydrogeology, 3rd ed.; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 1997; 647p. [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard, R.J.; Sookhak Lari, K.; Rayner, J.L.; Davis, G.B. Evaluating an Analytical Model to Predict Subsurface LNAPL Distributions and Transmissivity from Current and Historic Fluid Levels in Groundwater Wells: Comparing Results to Numerical Simulations. Groundw. Monitor. Remed. 2018, 38, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. A Decision-Making Framework for Cleanup of Sites Impacted with Light Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids (LNAPL). EPA 542-R-04-011. 2004. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/remedytech/decisionmaking-framework-cleanup-sites-impacted-light-non-aqueousphase-liquids-lnapl (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- CRC CARE. A Practitioner’s Guide for the Analysis, Management and Remediation of LNAPL; CRC CARE Technical Report 34; CRC for Contamination Assessment and Remediation of the Environment: Adelaide, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Atteia, O.; Palmier, C.; Schäfer, G. On the influence of groundwater table fluctuations on oil thickness in a well related to an LNAPL contaminated aquifer. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 223, 103476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatsios, E.; García-Rincón, J.; Rayner, J.L.; McLaughlan, R.G.; Davis, G.B. LNAPL transmissivity as a remediation metric in complex sites under water table fluctuations. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 215, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenhard, R.J.; Rayner, J.L.; Davis, G.B. A practical tool for estimating subsurface LNAPL distributions and transmissivity using current and historical fluid levels in groundwater wells: Effects of entrapped and residual LNAPL. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2017, 205, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemblowski, M.W.; Chiang, C.Y. Hydrocarbon Thickness Fluctuations in Monitoring Wells. Ground Water 1990, 28, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestero, T.P.; Fiedler, F.R.; Kinner, N.E. An investigation of the relationship between actual and apparent gasoline thickness in a uniform sand aquifer. Ground Water 1994, 32, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pastrovich, T.L.; Baradat, Y.; Barthel, R.; Chiarelli, A.; Fussell, D.R. Protection of groundwater from oil pollution. In CONCAWE Report 3/79; CONCAWE: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1979; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, R.A.; Blake, S.B.; Champlin, S.C., Jr. Determination of hydrocarbon thicknesses in sediments using borehole data. In The Fourth National Symposium and Exposition on Aquifer Restoration and Ground Water Monitoring; National Ground Water Association: Dublin, OH, USA, 1984; pp. 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- Hampton, D.R.; Miller, P.D.G. Laboratory Investigation of the Relationship between Actual and Apparent Product Thickness in Sands; National Ground Water Association: Dublin, OH, USA, 1988; pp. 157–181. [Google Scholar]
- Schwille, F. Petroleum contamination of the subsoil: A hydrological problem. In The Joint Problems of the Oil and Water Industries: Proceedings of a Symposium Held at the Hotel Metropole, Brighton, UK, 18–20 January 1967; Institute of Petroleum: London, UK, 1967; pp. 23–54. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dam, J. The migration of hydrocarbons in a water-bearing stratum. In The Joint Problems of the Oil and Water Industries: Proceedings of a Symposium; Institute of Petroleum: London, UK, 1967; pp. 55–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zilliox, L.; Muntzer, P. Effects of hydrodynamic processes on the development of ground-water pollution: Study on physical models in a saturated porous medium. Prog. Water Technol. 1975, 7, 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, A.M.; Houghtalen, R.J.; McWhorter, D.B. Volume estimation of light nonaqueous phase liquids in porous media. Ground Water 1990, 28, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhard, R.J.; Parker, J.C. Estimation of free hydrocarbon volume from fluid levels in monitoring wells. Ground Water 1990, 28, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.C.; Lenhard, R.J.; Kuppusamy, T. A parametric model for constitutive properties governing multiphase flow in porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1987, 23, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.C.; Lenhard, R.J. Vertical integration of three-phase flow equations for analysis of light hydrocarbon plume movement. Trans. Porous Media 1989, 5, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.C.; Lenhard, R.J. A model for hysteretic constitutive relations governing multiphase flow. 1. Saturation-pressure relations. Water Resour. Res. 1987, 23, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhard, R.J.; Parker, J.C. A model for hysteretic constitutive relations governing multiphase flow. 2. Permeability-saturation relations. Water Resour. Res. 1987, 23, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.C.; Kaluarachchi, J.J.; Kremesec, V.J.; Hockman, E.L. Modeling free product recovery at hydrocarbon spill sites. In Conference Petroleum Hydrocarbons and Organic Chemicals in Ground Water: Prevention, Detection and Restoration; National Water Well Association: Dublin, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 641–655. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, J.C.; Zhu, J.L.; Johnson, T.G.; Kremesec, V.J.; Hockman, E.L. Modeling free product migration and recovery at hydrocarbon spill sites. Ground Water 1994, 32, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddill, D.W.; Parker, J.C. Simulated recovery of light, nonaqueous phase liquid from unconfined heterogeneous aquifers. Ground Water 1997, 35, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhard, R.J.; Oostrom, M.; Dane, J.H. A constitutive model for air-NAPL-water flow in the vadose zone accounting for immobile, non-occluded (residual) NAPL in strongly water-wet porous media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 73, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbeneau, R.J. LNAPL distribution and recovery model (LDRM). In Volume 1: Distribution and Recovery of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Liquids in Porous Media; API Publ. No. 4760; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Charbeneau, R.J.; Johns, R.T.; Lake, R.W.; McAdams, M.J. Free-product recovery of petroleum hydrocarbon liquids. Ground. Water Monit. Rem. 2000, 20, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Charbeneau, R.J. An analytical model for predicting LNAPL distribution and recovery from multi-layered soils. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2014, 156, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aral, M.M.; Liao, B. Effect of groundwater table fluctuations on LNAPL thickness in monitoring wells. Environ. Geol. 2002, 42, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deska, I.; Ociepa, E. Impact of the Water Table Fluctuations on the Apparent Thickness of Light Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2013, 20, 771–778. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, C.D.; Adamski, M. Relationship between Initial and Residual LNAPL Saturation for Different Soil Types; National Ground Water Association: Dublin, OH, USA, 2005; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard, R.J.; Parker, J.C. Measurement and prediction of saturation-pressure relationships in three phase-porous media systems. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1987, 1, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Aral, M. Interpretation of LNAPL Thickness Measurements Under Unsteady Conditions. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, F.; Durnford, D.S. LNAPL thickness in monitoring wells considering hysteresis and entrapment. Ground Water 1996, 34, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, J.L.; Johnston, C.D.; Rao, P.S.C. Characterising residual NAPL using partitioning and interfacial tracers and implications for interphase mass transfer. In Contaminated Site Remediation: From Source Zones to Ecosystems, Proceedings of the 2000 Contaminated Site Remediation Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 4–8 December 2000; Johnston, C.D., Ed.; CSIRO Land and Water: Wembley, Australia, 2000; pp. 613–620. [Google Scholar]
- Steffy, D.A.; Johnston, C.D.; Barry, D.A. A field study of the vertical immiscible displacement of LNAPL associated with a fluctuating water table. In Groundwater Quality: Remediation and Protection; IAHS: Wallingford, UK, 1995; pp. 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Steffy, D.A.; Johnston, C.D.; Barry, D.A. Numerical simulations and long-column tests of LNAPL displacement and trapping by a fluctuating water table. J. Soil Contam. 1998, 7, 325–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezihir, A.; Bayanlou, M.B.; Ahmadnezhad, Z.; Barzegari, G. Remediation of BTEX plume in a continuous flow model using zeolite-PRB. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2020, 230, 103604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos de Souza, M.; Oostrom, M.; White, M.D.; da Silva, G.C., Jr.; Barbosa, M.C. Simulation of subsurface multiphase contaminant extraction using a bioslurping well model. Trans. Porous Media 2016, 114, 649–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookhak Lari, K.; Johnston, C.D.; Davis, G.B. Gasoline multi-phase and multicomponent partitioning in the vadose zone: Dynamics and risk longevity. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.D.; Oostrom, M.; Lenhard, R.J. Apractical model for mobile, residual and entrapped NAPL in water-wet porous media. Ground Water 2004, 42, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, M.; Andrisani, A.; Lopez, L.; Vurro, M. A new data assimilation technique based on ememble Kalman filter and Brownian bridges: An application to Richards’ equation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2016, 208, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, L.; Holzman, M.; Ye, M.; Wang, Y.; Carmona, F.; Zha, Y. A dynamic data-driven method for dealing with model structural error in soil moisture data assimilation. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 132, 103407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LNAPL | API | Viscosity (Pa·s) | Specific Weight (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crude Oil | 31.5 | 0.0230 at 10 °C 0.0140 at 20 °C | 868.2 |
| Gas Oil | 39.2 | 0.0017 at 50 °C | 829.0 |
| Exp. No. | LNAPL | Grain Size (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| E1 | Gas Oil | Coarse grain (400–750) |
| E2 | Crude Oil | Coarse grain (400–750) |
| E3 | Gas Oil | Fine grain (<125) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azimi, R.; Vaezihir, A.; Lenhard, R.J.; Hassanizadeh, S.M. Evaluation of LNAPL Behavior in Water Table Inter-Fluctuate Zone under Groundwater Drawdown Condition. Water 2020, 12, 2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092337
Azimi R, Vaezihir A, Lenhard RJ, Hassanizadeh SM. Evaluation of LNAPL Behavior in Water Table Inter-Fluctuate Zone under Groundwater Drawdown Condition. Water. 2020; 12(9):2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092337
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzimi, Reza, Abdorreza Vaezihir, Robert J. Lenhard, and S. Majid Hassanizadeh. 2020. "Evaluation of LNAPL Behavior in Water Table Inter-Fluctuate Zone under Groundwater Drawdown Condition" Water 12, no. 9: 2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092337
APA StyleAzimi, R., Vaezihir, A., Lenhard, R. J., & Hassanizadeh, S. M. (2020). Evaluation of LNAPL Behavior in Water Table Inter-Fluctuate Zone under Groundwater Drawdown Condition. Water, 12(9), 2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092337







