Discovering Water Quality Changes and Patterns of the Endangered Thi Vai Estuary in Southern Vietnam through Trend and Multivariate Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
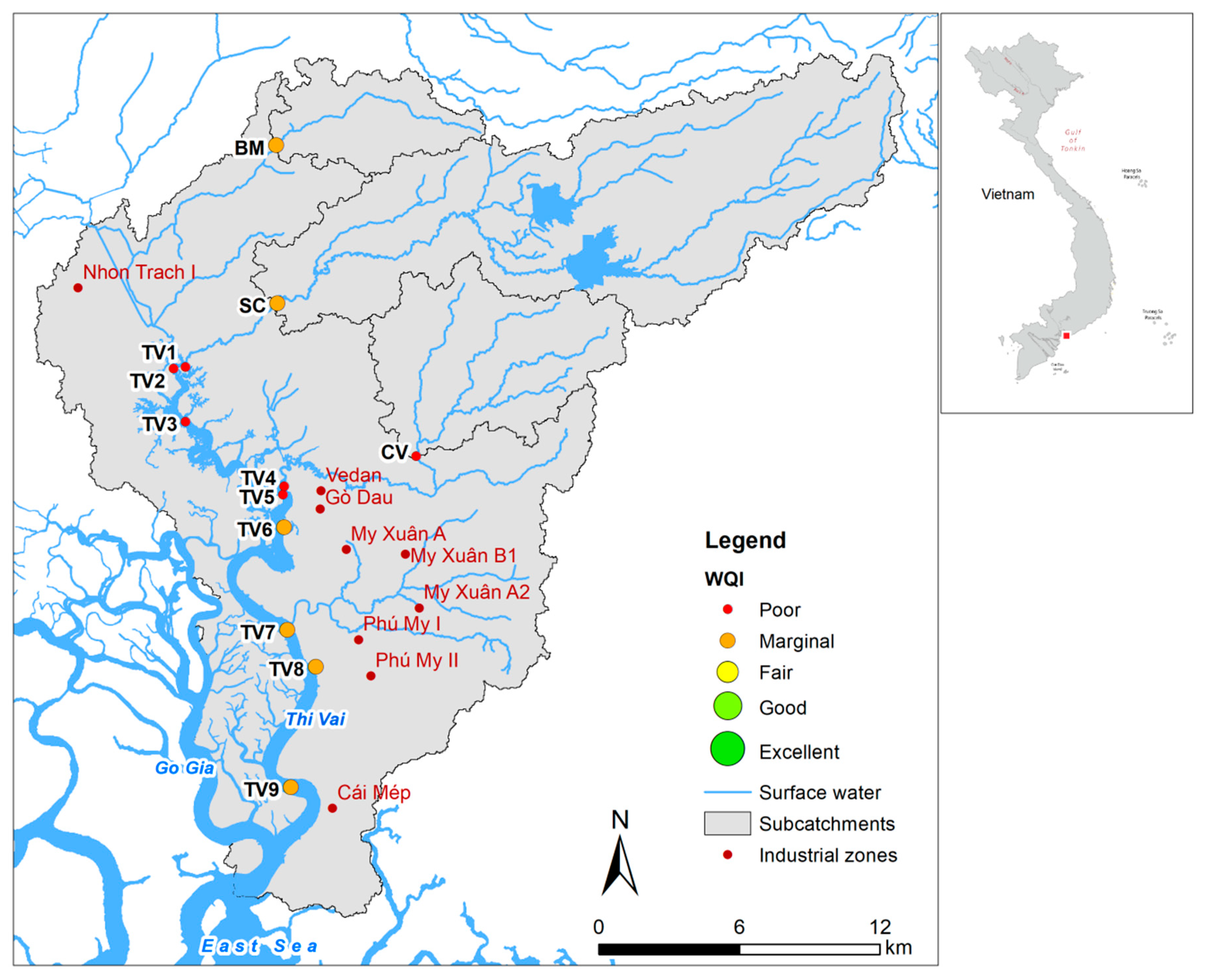
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Trend Analysis
2.3.2. Cluster Analysis
2.3.3. Principal Component Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Quarterly and Long-Term (1999–2013) Evolution of Water Quality
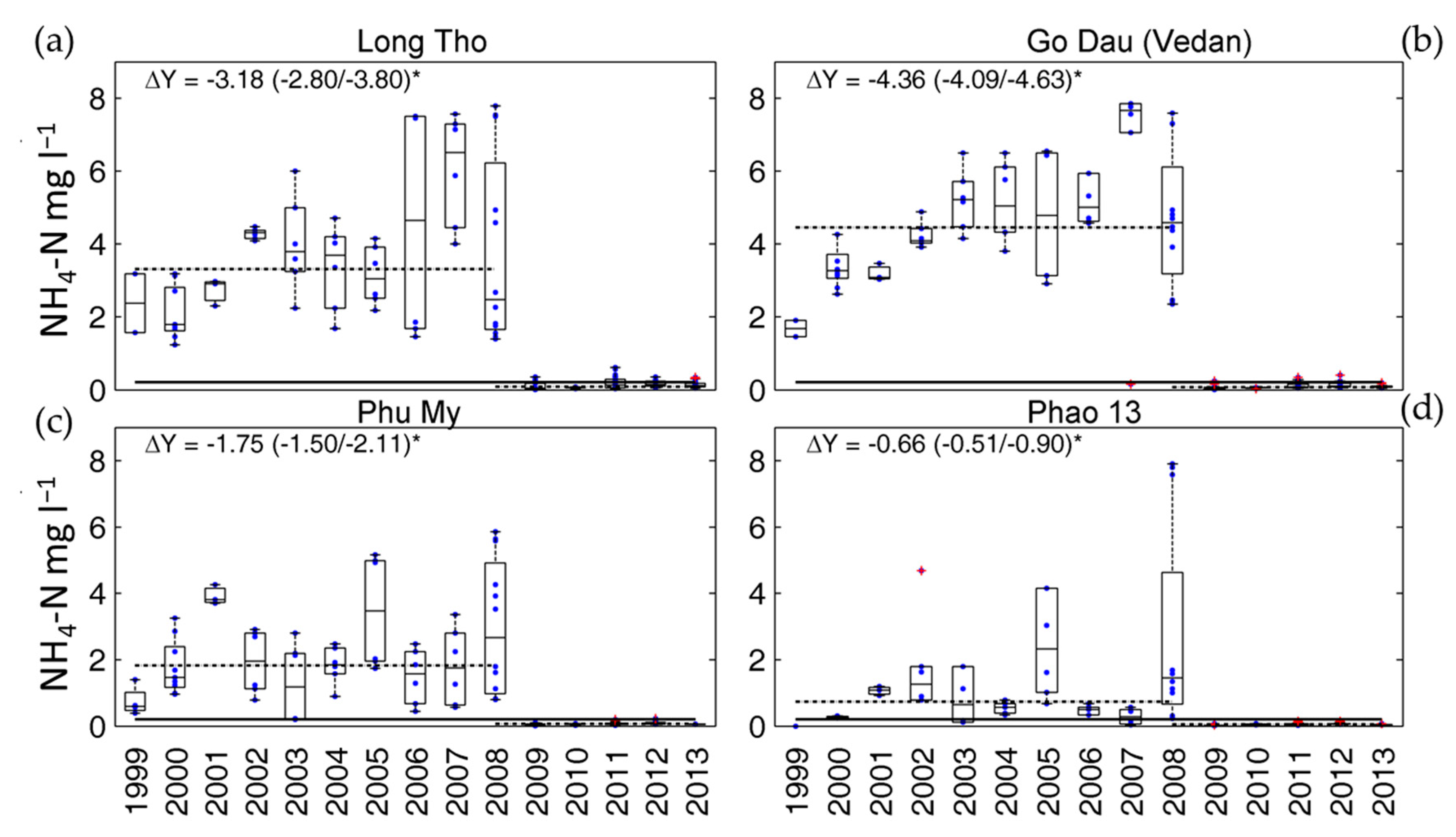
3.1.1. Period before the Vedan Scandal (1999–2008)
3.1.2. Recovery Period after the Vedan Scandal (2009–2013)
3.2. Temporal and Spatial Analysis—Short Term
3.2.1. Descriptive Statistics of Short-Term Water Parameters
3.2.2. Cluster Analysis of Short-Term Temporal and Spatial Variations in Water Quality
3.2.3. Principal Component Analysis on Current Drivers of Pollution in the Thi Vai River
3.2.4. Implications for Water Quality Management
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, W.; Yang, M. Urbanization, economic growth and environmental pollution: Evidence from China. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2019, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinia, N.J.; Kroeze, C. Future trends in urbanization and coastal water pollution in the Bay of Bengal: The lived experience. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2015, 17, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeze, C.; Gabbert, S.; Hofstra, N.; A Koelmans, A.; Li, A.; Löhr, A.; Ludwig, F.; Strokal, M.; Verburg, C.; Vermeulen, L.; et al. Global modelling of surface water quality: A multi-pollutant approach. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2016, 23, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarczuk, A.; Jelonkiewicz, L.; Lenart-Boroń, A. The effect of anthropogenic and natural factors on the prevalence of physicochemical parameters of water and bacterial water quality indicators along the river Białka, southern Poland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10102–10114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soares, A.L.C.; Pinto, C.C.; Oliveira, S.C. Impacts of anthropogenic activities and calculation of the relative risk of violating surface water quality standards established by environmental legislation: A case study from the Piracicaba and Paraopeba river basins, Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.-J.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M. Lost in translation: The German literature on freshwater salinization. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziemann, H.; Schulz, C.-J. Methods for biological assessment of salt-loaded running waters–fundamentals, current positions and perspectives. Limnologica 2011, 41, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malaj, E.; Von Der Ohe, P.C.; Grote, M.; Kuehne, R.; Mondy, C.P.; Usseglio-Polatera, P.; Brack, W.; Schaefer, R.B. Organic chemicals jeopardize the health of freshwater ecosystems on the continental scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9549–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stehle, S.; Schulz, R. Pesticide authorization in the EU—Environment unprotected? Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 19632–19647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, J.; Masiá, A.; Blasco, C.; Picó, Y. Occurrence and removal efficiency of pesticides in sewage treatment plants of four Mediterranean River Basins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerecke, A.C.; Schärer, M.; Singer, H.P.; Müller, S.R.; Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Sägesser, M.; Ochsenbein, U.; Popow, G. Sources of pesticides in surface waters in Switzerland: Pesticide load through waste water treatment plants—Current situation and reduction potential. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisner, M. Surface Water Pollution by Untreated Municipal Wastewater Discharge Due to a Sewer Failure. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling Eutrophication: Nitrogen and Phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braukmann, U.; Böhme, D. Salt pollution of the middle and lower sections of the river Werra (Germany) and its impact on benthic macroinvertebrates. Limnologica 2011, 41, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kefford, B.J.; Buchwalter, D.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Davis, J.; Duncan, R.P.; Hoffmann, A.; Thompson, R. Salinized rivers: Degraded systems or new habitats for salt-tolerant faunas? Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20151072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beketov, M.A.; Liess, M. Acute and delayed effects of the neonicotinoid insecticide thiacloprid on seven freshwater arthropods. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2008, 27, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, A.; Hayashi, T.I.; Ohnishi, H.; Suzuki, K.; Hayasaka, D.; Goka, K. Fipronil application on rice paddy fields reduces densities of common skimmer and scarlet skimmer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roessink, I.; Merga, L.B.; Zweers, H.J.; Brink, P.J.V.D. The neonicotinoid imidacloprid shows high chronic toxicity to mayfly nymphs. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, T.C.; Van Staalduinen, M.A.; Van Der Sluijs, J.P. Macro-invertebrate decline in surface water polluted with imidacloprid. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- UN-Water. United Nations UN World Water Development Report 2003; Unesco: Fontenoy, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chabba, A.P.S. Water-Borne Diseases in India 2013. Available online: https://en.reset.org/blog/water-borne-diseases-india (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Meon, G.; Pätsch, M.; Van Phuoc, N.; Hong Quan, N. EWATEC-COAST: Technologies for environmental and water protection of coastal regions in vietnam. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference for Environment and Natural Resources–ICENR, Ho-Chi-Minh City, Vietnam, 17–18 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.Q. Modeling of Nutrient Dynamics during Flood Events at Catchment Scale in Tropical Regions, in Leichtweiß-Institute for Hydraulics and Water Resources (LWI). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Braunschweig, Braunschweig, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.S. Water Quality Component. Sub-Project from Vietnam Water Sector Review Project; Institute of Environmental Technology, VAST: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- CEM. Current Environmental Monitoring Status in Vietnam (Thực trạng hệ thống quan trắc Môi trường ở Việt Nam). 2018. Available online: http://cem.gov.vn/mang-luoi-quan-trac-moi-truong/thuc-trang-he-thong-quan-trac-moi-truong-o-viet-nam (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Prilop, K.; Quan, N.H.; Lorenz, M.; Le, H.; Hien, L.T.; Meon, G. Integrated water quality monitoring of the Thi Vai River: An assessment of historical and current situation. EWATEC-COAST: Technologies for Environmental and Water Protection of Coastal Zones in Vietnam. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference for Environment and Natural Resources, ICENR 2014, Hochiminh, Vietnam, 17–18 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, N.H.; Hieu, N.Q.; Nga, D.T.Q.; Lorenz, M. Long-Term Water Quality Assessment of the Thi Vai River, Vietnam: Impacts of Pollution Management. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environment and Climate Change—Challenge and Response, and Lession Learnt, Hochiminh, Vietnam, 17–18 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Pham, H.T. The dark side of development in Vietnam: Lessons from the killing of the Thi Vai River. J. Macromarket. 2012, 32, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Nguyen, T.H.; Bui, T.L. Method on estimating damages to economy and environment from polluted catchment catchment—A case study of Thi Vai river (Phương pháp tính toán thiệt hại về kinh tế và môi trường đối với một lưu vực sông bị ônhiễm—Trường hợp điển hình: Lưu vực sông Thị Vải). VNU-HCM J. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2011, M1, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.T.H.; Zeunert, S.; Lorenz, M.; Meon, G. Multivariate statistical assessment of a polluted river under nitrification inhibition in the tropics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13845–13862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-W.; Lin, K.-H.; Kuo, Y.-M. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci. Total. Environ. 2003, 313, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, P.; Haque, M.Z.; Rahim, S.A.; Embi, A.F.; Elfithri, R.; Lihan, T.; Khali, W.W.M.; Khan, F.; Mokhtar, M. Multivariate Chemometric Approach on the Surface Water Quality in Langat Upstream Tributaries, Peninsular Malaysia. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.R. Predicting combined effects of land use and climate change on river and stream salinity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2018, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hesse, C.; Krysanova, V. Modelling Climate and Management Change Impacts on Water Quality and In-Stream Processes in the Elbe River Basin. Water 2016, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenz, M.; Zeunert, S.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Meon, G. Eco-hydrological modeling of a tropical catchment exposed to anthropogenic pressure and climate impact. Hydrol. Wasserbewirtsch. 2017, 61, 408–423. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.P.; Li, G.N.; Zhang, C. Modeling the effects of point and non-point source pollution on a diversion channel from Yellow River to an artificial lake in China. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 1806–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Salles, C.; Cernesson, F.; Perrin, J.; Tournoud, M. Nutrient load modelling during floods in intermittent rivers: An operational approach. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 768–781. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, N.H.; Meon, G. Nutrient Dynamics During Flood Events in Tropical Catchments: A Case Study in Southern Vietnam. Clean Soil Air Water 2014, 43, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapra, S.C. MCGraw-Hill Sries in Water Resources and Environmental Engineering. In Surface Water-Quality Modelling; MCGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- O’Flynn, B.; O’Flynn, B.; Regan, F.; Lawlor, A.; Wallace, J.; Torres, J.; O′mathuna, C. Experiencesand recommendations in deploying a real-time, water quality monitoring system. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, F.; Lupu, R.G.; Stan, A.; Craciun, I.; Teodosiu, C. Towards real time mon-itoring of water quality in river basins. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2010, 9, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Shore, M.; Murphy, S.; Mellander, P.E.; Shortle, G.; Melland, A.R.; Crockford, L.; O’Flaherty, V.; Williams, L.; Morgan, G.; Jordan, P. Influence of stormflow and baseflowphosphorus pressures on stream ecology in agricultural catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boёnne, W.; Desmet, N.; Van Looy, S.; Seuntjens, P. Use of online water qualitymonitoring for assessing the effects of WWTP overflows in rivers. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, M.J.; Loewenthal, M.; Read, D.S.; Hutchins, M.G.; Prudhomme, C.; Armstrong, L.K.; Harman, S.A.; Wickham, H.D.; Gozzard, E.; Carvalho, L. Identifying multiplestressor controls on phytoplankton dynamics in the River Thames (UK) using high-frequency water quality data. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helsel, D.R.; Hirsch, R.M.; Ryberg, K.R.; Archfield, S.A.; Gilroy, E.J. Statistical Methods in Water Resources: US Geological Survey Techniques and Methods; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; Book 4, Chapter A3.
- Le, T.T.H.; Lorenz, M.; Zeunert, S.; Nguyen, C.V.; Meon, G. Spatial and temporal variability of water quantity and water quality of the Thi Vai catchment in southern Vietnam-Data analysis of a monitoring program. Hydrol. Wasserbewirtsch. 2017, 61, 370–382. [Google Scholar]
- Canada Council of Ministers of the Environment. Canadian Environmental Quality Guidlines for the Protection of Aquatic Life; Environment and Climate Change Canada: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2001.
- ASTM International. ASTM D2007 19 Standard Test. Method for Characteristic Groups in Rubber Extender and Processing Oils and Other Petroleum-Derived Oils by the Clay-Gel Absorption Chromatographic Method; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- CCME. Synthesis of Research and Application of the CCME Water Quality Index; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME): Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2012; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- MONRE. QCVN 08-2008 BTNMT National Technical Regulation on Surface Water Quality; MONRE: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2008.
- IER. Báo cáo kết quả thực hiện Nhiệm vụ "Kết quả xác định phạm vi, mức độ ô nhiễm và ảnh hưởng đến môi trường do hành vi gây ô nhiễm của Công ty Vedan đối với sông Thị Vải" (Report on Identification of Areas, Pollution Levels and Impacts of Vedan Company to Thi Vai river); Institute for Environment and Natural Resources (IER), Vietnam National University—Ho Chi Minh City (VNU—HCM): Hochiminh, Vietnam, 2009.
- Ballantine, D.J.; Davies-Colley, R.J. Water quality trends in New Zealand rivers: 1989–2009. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 186, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, V.; Lefebvre, R.; Therrien, R.; Savard, M.M. Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. J. Hydrol. 2008, 353, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, C.; Thyne, G.D.; McCray, J.E.; Turner, A.K. Evaluation of graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wan, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Chen, Y. Stormwater Runoff Pollutant Loading Distributions and Their Correlation with Rainfall and Catchment Characteristics in a Rapidly Industrialized City. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118776. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matlab. MATLAB Runtime. 2013. Available online: https://jp.mathworks.com/products/compiler/matlab-runtime.html (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Thanh Nien News. Pollution Soon to Render Dong Nai River Unusable; Thanhnien: Hochiminh, Vietnam, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, M.K. Nitrification in natural streams. J. Water Pollut. Control. Fed. 1976, 48, 2380–2393. [Google Scholar]
- Wheaton, F.W.H.; Hochheimer, J.N.; Kaiser, G.E.; Krones, M.J.; Libey, G.S.; Easter, C.C. Nitrification filter principles, in Aquaculture reuse systems: Engineering design and management. In Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 101–126. [Google Scholar]
- Dong Nai Statistic Office. Statistcal Yearbook; Gerneral Statistics Offiice of Vietnam: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2013.
- Joseph, S.; Ouseph, P.P. Assessment of nutrients using multivariate statistical techniques in estuarine systems and its management implications: A case study from Cochin Estuary, India. Water Environ. J. 2010, 24, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, I.; Westrich, B. Processes governing river water quality identified by principal component analysis. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 3113–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A. Assessment of water quality using principal component analysis: A case study of the river Ganges. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2010, 32, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkarkhi, A.F.M.; Ahmad, A.; Easa, A.M. Assessment of surface water quality of selected estuaries of Malaysia: Multivariate statistical techniques. Environment 2008, 29, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.N. Assessment of Spatial and Temporal Fluctuations in Water Quality of a Tropical Permanent Estuarine System—Tapi, West Coast India. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2009, 7, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Ghosh, S.; Satpathy, K.K.; Bhattacharya, B.D.; Sarkar, S.K.; Mishra, P.; Raja, P. Water quality assessment of the ecologically stressed Hooghly River Estuary, India: A multivariate approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallard, R.; Edmond, J. Geochemistry of the Amazon.: 2. The influence of geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1983, 88, 9671–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.; Jeison, D.; Rubilar, O.; Ciudad, G.; Chamy, R. Nitrification–denitrification via nitrite accumulation for nitrogen removal from wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shortle, J.S.; Mihelcic, J.R.; Zhang, Q.; Arabi, M. Nutrient control in water bodies: A systems approach. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perlman, H. Why Is the Ocean Salty? US Geological Survey. 2013. Available online: http://ga.water.usgs. gov/edu/whyoceansalty. html (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Nave, R. Resistance and Resistivity. Available online: http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/resis.html#c1 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- López-Vicente, M.; Calvo-Seas, E.; Álvarez, S.; Cerdà, A. Effectiveness of Cover Crops to Reduce Loss of Soil Organic Matter in a Rainfed Vineyard. Land 2020, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| BOD5 (kg d−1) | TN (kg d−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before 2008 | 2009 | Before 2008 | 2009 | |
| Go Dau | 205 | 41 | 45 | 5 |
| Vedan | 75,862 | 102 | 15,745 | 25 |
| NhonTrach 1 | 132 | 217 | 147 | 37 |
| NhonTrach 2 | 2400 | 131 | 115 | 21 |
| NhonTrach 3—Tin Nghia | 960 | 47 | 113 | 5 |
| NhonTrach 3—Formosa | 266 | 106 | 369 | 2 |
| NhonTrach 5 | 38 | 101 | 17 | 84 |
| Det may NhonTrach | 42 | 72 | 3 | 17 |
| My Xuan A | 4068 | 159 | 707 | 5 |
| My Xuan A2 | 130 | 106 | 59 | 23 |
| My Xuan B1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Phu My I | 672 | 80 | 2284 | 35 |
| Phu My II | - | 193 | - | 47 |
| CaiMep | 22 | 22 | 14 | 6 |
| Total | 84,799 | 1379 | 19,619 | 313 |
| Station | Percentile | 1999–2008 | 2009–2013 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO | BOD5 | NH4 | NO2 | NO3 | DO | BOD5 | NH4 | NO2 | NO3 | ||
| Long Tho (TV2) | 5 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 1.46 | 0.004 | 0.05 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 0.03 | 0.004 | 0.02 |
| N1 = 62 | 25 | 2.1 | 5.0 | 1.93 | 0.011 | 0.10 | 4.1 | 4.0 | 0.05 | 0.054 | 0.13 |
| N2 = 174 | Median | 2.9 | 6.6 | 3.31 | 0.020 | 0.24 | 4.6 | 5.0 | 0.09 | 0.170 | 0.25 |
| 75 | 4.3 | 10.0 | 4.47 | 0.030 | 0.43 | 5.3 | 7.5 | 0.20 | 0.248 | 0.44 | |
| 95 | 5.5 | 20.9 | 7.51 | 0.199 | 2.16 | 6.8 | 9.0 | 0.34 | 0.310 | 0.58 | |
| Go Dau (TV4) | 5 | 0.4 | 3.0 | 2.35 | 0.002 | 0.05 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 0.03 | 0.036 | 0.06 |
| N1 = 62 | 25 | 1.1 | 5.3 | 3.28 | 0.005 | 0.05 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 0.06 | 0.110 | 0.13 |
| N2 = 174 | Median | 2.2 | 7.1 | 4.46 | 0.010 | 0.12 | 4.5 | 5.0 | 0.07 | 0.190 | 0.22 |
| 75 | 2.6 | 10.2 | 5.94 | 0.016 | 0.24 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 0.11 | 0.250 | 0.40 | |
| 95 | 4.2 | 15.0 | 7.75 | 0.110 | 2.73 | 5.9 | 9.0 | 0.24 | 0.320 | 0.52 | |
| Phu My (TV8) | 5 | 2.0 | 2.2 | 0.40 | 0.010 | 0.05 | 4.2 | 3.0 | 0.03 | 0.019 | 0.02 |
| N1 = 64 | 25 | 3.0 | 3.7 | 0.98 | 0.050 | 0.15 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 0.05 | 0.044 | 0.12 |
| N2 = 144 | Median | 3.7 | 6.0 | 1.82 | 0.215 | 0.36 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 0.06 | 0.079 | 0.20 |
| 75 | 4.7 | 8.9 | 2.82 | 0.300 | 0.72 | 5.8 | 7.0 | 0.08 | 0.143 | 0.27 | |
| 95 | 5.7 | 12.9 | 5.13 | 0.399 | 2.44 | 6.3 | 9.0 | 0.17 | 0.200 | 0.44 | |
| Phao 13 (TV9) | 5 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 0.11 | 0.011 | 0.09 | 4.3 | 3.0 | 0.01 | 0.012 | 0.02 |
| N1 = 54 | 25 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 0.34 | 0.050 | 0.31 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 0.03 | 0.026 | 0.11 |
| N2 = 144 | Median | 5.2 | 5.0 | 0.73 | 0.140 | 0.42 | 5.4 | 6.0 | 0.05 | 0.050 | 0.18 |
| 75 | 5.7 | 7.0 | 1.57 | 0.190 | 0.48 | 5.9 | 7.0 | 0.07 | 0.080 | 0.24 | |
| 95 | 6.1 | 9.6 | 7.65 | 0.295 | 1.32 | 6.5 | 9.8 | 0.10 | 0.120 | 0.40 | |
| Vietnamese Water Quality Standards | A1 | ≥6 | 4 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 2 | |||||
| A2 | ≥5 | 6 | 0.2 | 0.02 | 5 | ||||||
| B1 | ≥4 | 15 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 10 | ||||||
| B2 | ≥2 | 25 | 1 | 0.05 | 15 | ||||||
| Sampling Site | T | pH | EC | DO | TSS | NH4 | NO2 | NO3 | PO4 | Fetotal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM (Bung Mon) | 29.8 (1.2) | 6.4 (0.7) | 0.07 (0.02) | 6.3 (1.4) | 121 (298) | 0.29 (0.13) | 0.02 (0.01) | 1.45 (0.37) | 0.05 (0.03) | 1.09 (0.73) |
| SC (Suoi Ca) | 29.9 (1.3) | 7.3 (0.2) | 0.11 (0.05) | 6.3 (0.9) | 58 (90) | 0.25 (0.27) | 0.03 (0.02) | 1.04 (0.56) | 0.07 (0.07) | 1.38 (0.83) |
| CV (Cau Vac) | 28.8 (1.9) | 6.9 (0.7) | 0.13 (0.05) | 6.4 (0.9) | 90 (162) | 0.29 (0.22) | 0.12 (0.10) | 1.51 (0.53) | 0.12 (0.10) | 2.84 (3.99) |
| TV1 | 30.6 (1.5) | 7.0 (0.1) | 18.1 (13.5) | 5.2 (1.0) | 39 (83) | 0.21 (0.10) | 0.14 (0.09) | 0.52 (0.29) | 0.06 (0.05) | 3.60 (7.65) |
| TV2 (Long Tho) | 29.8 (1.0) | 7.0 (0.5) | 23.8 (9.8) | 4.3 (1.4) | 39 (38) | 0.52 (0.48) | 0.09 (0.06) | 0.26 (0.19) | 0.03 (0.02) | 1.30 (1.10) |
| TV3 | 31.0 (1.0) | 7.1 (0.1) | 30.3 (12.9) | 4.7 (1.2) | 13 (7) | 0.15 (0.09) | 0.20 (0.09) | 0.40 (0.18) | 0.04 (0.04) | 0.98 (0.62) |
| TV4 (Go Dau) | 30.8 (1.2) | 7.2 (0.14) | 38.7 (9.6) | 4.6 (0.9) | 18 (14) | 0.11 (0.05) | 0.21 (0.08) | 0.38 (0.18) | 0.03 (0.01) | 0.84 (0.45) |
| TV5 (Vedan) | 30.5 (0.9) | 7.0 (0.5) | 38.9 (8.5) | 4.6 (1.1) | 32 (26) | 0.10 (0.12) | 0.20 (0.07) | 0.19 (0.13) | 0.03 (0.03) | 0.54 (0.70) |
| TV6 | 30.9 (1.1) | 7.3 (0.2) | 41.8 (7.2) | 4.6 (0.9) | 17 (12) | 0.09 (0.04) | 0.21 (0.09) | 0.36 (0.16) | 0.03 (0.01) | 0.74 (0.44) |
| TV7 | 31.3 (1.2) | 7.5 (0.2) | 45.9 (6.3) | 5.4 (0.7) | 21 (36) | 0.08 (0.03) | 0.15 (0.08) | 0.35 (0.16) | 0.03 (0.01) | 0.91 (0.92) |
| TV8 (Phu My) | 31.0 (1.1) | 7.2 (0.5) | 43.2 (6.3) | 5.1 (0.8) | 31 (27) | 0.07 (0.08) | 0.09 (0.05) | 0.19 (0.14) | 0.03 (0.02) | 0.61 (0.53) |
| VN-Standard A1 | 6–8.5 | ≥6 | 20 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | ||
| VN-Standard A2 | 6–8.5 | ≥5 | 30 | 0.2 | 0.02 | 5 | 0.2 | 1 | ||
| VN-Standard B1 | 5–5.9 | ≥4 | 50 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 10 | 0.3 | 1.5 | ||
| VN-Standard B2 | 5–5.9 | ≥2 | 100 | 1.0 | 0.05 | 15 | 0.5 | 2 | ||
| Number of samples | 743 | 523 | 509 | 502 | 522 | 555 | 556 | 555 | 556 | 581 |
| Parameters | Entire Period | Dry Season | Rainy Season | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| pH | 0.038 | −0.087 | 0.640 | −0.409 | 0.318 | −0.549 | 0.034 | 0.158 | 0.775 |
| DO | 0.099 | 0.819 | 0.167 | 0.828 | 0.018 | −0.178 | 0.163 | 0.759 | 0.178 |
| TSS | 0.780 | 0.076 | −0.239 | 0.050 | 0.801 | 0.079 | 0.688 | 0.150 | −0.386 |
| NH4 | 0.191 | 0.000 | −0.719 | −0.114 | 0.293 | 0.818 | 0.202 | 0.196 | −0.543 |
| NO2 | 0.032 | −0.684 | 0.348 | −0.577 | −0.152 | −0.098 | 0.060 | −0.794 | 0.387 |
| NO3 | 0.302 | 0.654 | −0.107 | 0.823 | 0.029 | 0.255 | 0.434 | 0.515 | 0.028 |
| PO4 | 0.603 | 0.304 | 0.166 | 0.529 | 0.381 | −0.130 | 0.737 | 0.123 | 0.169 |
| Fetotal | 0.867 | 0.034 | −0.078 | 0.196 | 0.830 | 0.078 | 0.809 | 0.042 | −0.200 |
| Eigenvalue | 1.86 | 1.67 | 1.18 | 2.20 | 1.69 | 1.11 | 1.93 | 1.58 | 1.30 |
| Total variance [%] | 23.3 | 20.9 | 14.7 | 27.5 | 21.1 | 13.8 | 24.1 | 19.7 | 16.2 |
| Cumulative variance [%] | 23.3 | 44.2 | 58.9 | 27.5 | 48.6 | 62.4 | 24.1 | 43.8 | 60.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorenz, M.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Le, T.D.H.; Zeunert, S.; Dang, D.H.; Le, Q.D.; Le, H.; Meon, G. Discovering Water Quality Changes and Patterns of the Endangered Thi Vai Estuary in Southern Vietnam through Trend and Multivariate Analysis. Water 2021, 13, 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101330
Lorenz M, Nguyen HQ, Le TDH, Zeunert S, Dang DH, Le QD, Le H, Meon G. Discovering Water Quality Changes and Patterns of the Endangered Thi Vai Estuary in Southern Vietnam through Trend and Multivariate Analysis. Water. 2021; 13(10):1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101330
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorenz, Malte, Hong Quan Nguyen, Trong Dieu Hien Le, Stephanie Zeunert, Duc Huy Dang, Quang Dung Le, Huyen Le, and Günter Meon. 2021. "Discovering Water Quality Changes and Patterns of the Endangered Thi Vai Estuary in Southern Vietnam through Trend and Multivariate Analysis" Water 13, no. 10: 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101330
APA StyleLorenz, M., Nguyen, H. Q., Le, T. D. H., Zeunert, S., Dang, D. H., Le, Q. D., Le, H., & Meon, G. (2021). Discovering Water Quality Changes and Patterns of the Endangered Thi Vai Estuary in Southern Vietnam through Trend and Multivariate Analysis. Water, 13(10), 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101330






