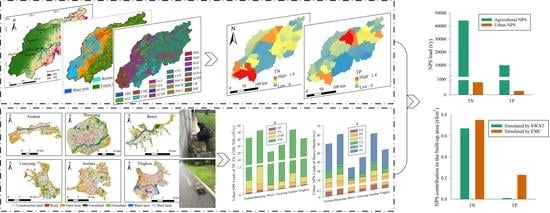
Quantifying the Contribution of Agricultural and Urban Non-Point Source Pollutant Loads in Watershed with Urban Agglomeration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Data Collection
2.2.1. Sampling and Analyses
- 1.
- Water quality sampling in the Hun-Taizi River watershed
- 2.
- Rainfall runoff samplings in different urban functional zones
2.2.2. Data Collection
- 1.
- Geographic dataset
- 2.
- Weather and hydrological dataset
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Agricultural NPS Pollution
2.3.2. Urban NPS Pollution
2.3.3. Schematic of the Integrated Method Framework
3. Results
3.1. Agricultural NPS Pollution in the Hun-Taizi River Watershed
3.2. Characteristics of the EMC in Urban NPS Monitoring
3.3. Urban NPS Pollutant Loads
3.4. Contribution of Agricultural and Urban NPS Pollution Loads
4. Discussion
4.1. Estimating the Characteristic Pollutants of Urban NPS Pollution in an Urban Agglomeration
4.2. Integrated Approach for Estimating Agricultural and Urban NPS Pollutant Loads
4.3. Uncertainty Analysis and Implication
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bian, B.; Cheng, X.J.; Li, L. Investigation of urban water quality using simulated rainfall in a medium size city of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 183, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Song, K.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Hao, F.H. Non-point source pollution dynamics under long-term agricultural development and relationship with landscape dynamics. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Y.; Huang, G.R. Monitoring of Non-Point Source Pollutions from an Agriculture Watershed in South China. Water 2014, 6, 3828–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.Y.; Dong, R.Z.; Jiang, C.S.; Ni, M.F. Influences of land use metrics at multi-spatial scales on seasonal water quality: A case study of river systems in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 206, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.U.; Sanin, M.; Lian, Q.; Zappi, M.; Gang, D.D. Nonpoint Source Pollution; Water Environment Federation: Virginia Beach, VA, USA, 2017; Volume 89, pp. 1580–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ongley, E.D.; Zhang, X.L.; Yu, T. Current status of agricultural and rural non-point source Pollution assessment in China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.L.; Li, W.C.; Zhai, L.M.; Yen, H.; Lei, Q.L.; Liu, H.B.; Ren, T.Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, F.L.; Fan, X.P. An innovative approach to identifying agricultural pollution sources and loads by using nutrient export coefficients in watershed modeling. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dai, Y.; Zhi, X.S.; Xie, H.; Shen, Z.Y. Quantifying nonpoint source emissions and their water quality responses in a complex catchment: A case study of a typical urban-rural mixed catchment. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bian, J.M.; Lao, W.M.; Zhao, Y.S.; Hou, Z.Y.; Sun, X.Q. Assessing the Impacts of Best Management Practices on Nonpoint Source Pollution Considering Cost-Effectiveness in the Source Area of the Liao River, China. Water 2019, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UN. World Urbanization Prospects 2018: Highlights; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.L. Important progress and future direction of studies on China’s urban agglomerations. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 1003–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.N. Will urban expansion lead to an increase in future water pollution loads?—A preliminary investigation of the Haihe River Basin in northeastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7024–7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Liu, J.; Aini, G.; Gong, Y.W. A comparative study of the grain-size distribution of surface dust and stormwater runoff quality on typical urban roads and roofs in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.M.; Shi, T.; Zong, M.; Walter, M.T. Assessing the Impact of Urbanization on Direct Runoff Using Improved Composite CN Method in a Large Urban Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angrill, S.; Petit-Boix, A.; Morales-Pinzon, T.; Josa, A.; Rieradevall, J.; Gabarrell, X. Urban rainwater runoff quantity and quality—A potential endogenous resource in cities? J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 189, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Andrieu, H.; Hamel, P. Understanding, management and modelling of urban hydrology and its consequences for receiving waters: A state of the art. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.M.; Shi, T.; Qu, X.Q.; Walter, M.T. Effects of urbanization on direct runoff characteristics in urban functional zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhi, X.S.; Shen, Z.Y.; Dai, Y.; Aini, G. Comparison between snowmelt-runoff and rainfall-runoff nonpoint source pollution in a typical urban catchment in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.M.; Gong, J.P.; Sun, F.Y.; Xu, Y.Y. Characterization and first flush analysis in road and roof runoff in Shenyang, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, G.B.; Zhong, Y.C.; Shen, Z.Y. Evaluating the impacts of soil data on hydrological and nonpoint source pollution prediction. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heathman, G.C.; Flanagan, D.C.; Larose, M.; Zuercher, B.W. Application of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool and Annualized Agricultural Non-Point Source models in the St. Joseph River watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 63, 552–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, S.T.Y.; Chen, W.L. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.I.; Shen, Z.Y.; Chen, L.; Qiu, J.L.; Dong, J.W. Time-varying sensitivity analysis of hydrologic and sediment parameters at multiple timescales: Implications for conservation practices. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, J.; Wong, K.M.; Stenstrom, M.K. Automatic calibration of the US EPA SWMM model for a large urban catchment. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 134, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment—Part 1: Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, B.; Pachel, K.; Loigu, E. Modelling stormwater runoff, quality, and pollutant loads in a large urban catchment. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. 2017, 66, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelde, A.M.; Cerro, I.; Sanchez-Perez, J.M.; Sauvage, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Antiguedad, I. Application of the SWAT model to assess the impact of changes in agricultural management practices on water quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.; Clinciu, I.; Tudose, N.C.; Ungurean, C.; Adorjani, A.; Mihalache, A.L.; Davidescu, A.A.; Davidescu, S.O.; Dinca, L.; Cacovean, H. Assessing the vulnerability of water resources in the context of climate changes in a small forested watershed using SWAT: A review. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.T.; Li, H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y. Development of EMC-based empirical model for estimating spatial distribution of pollutant loads and its application in rural areas of Korea. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.T.Y.; Liu, A.J.; Goodrich, J.A. Assessing the water quality impacts of future land-use changes in an urbanising watershed. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2009, 26, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttles, K.M.; Singh, N.K.; Vose, J.M.; Martin, K.L.; Emanuel, R.E.; Coulston, J.W.; Saia, S.M.; Crump, M.T. Assessment of hydrologic vulnerability to urbanization and climate change in a rapidly changing watershed in the Southeast US. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, R.Y.; Guo, T.; Engel, B.A.; Flanagan, D.C.; Lee, J.G.; Li, S.Y.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Collingsworth, P.D.; Wallace, C.W. Evaluating efficiencies and cost-effectiveness of best management practices in improving agricultural water quality using integrated SWAT and cost evaluation tool. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; He, Q.; Ai, H.N.; Wang, Z.T.; Zhang, Q.Q. Pollutant concentrations and pollution loads in stormwater runoff from different land uses in Chongqing. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motew, M.; Chen, X.; Carpenter, S.R.; Booth, E.G.; Seifert, J.; Qiu, J.X.; Loheide, S.P.; Turner, M.G.; Zipper, S.C.; Kucharik, C.J. Comparing the effects of climate and land use on surface water quality using future watershed scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Guo, B.B.; Hao, F.H.; Huang, H.B.; Li, J.Q.; Gong, Y.W. Modeling urban storm rainfall runoff from diverse underlying surfaces and application for control design in Beijing. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.Z.; Yang, S.T.; Hao, F.H.; Ren, X.Y.; Zhao, C.S.; Wang, Y.; Lei, T.J.; Sun, F. Evolution and Driving Forces of Non-Point Source Pollution in a Developing Megacity: Beijing as a Long-Term Case Study. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-w.; Shan, B.-q.; Yin, C.-q. Pollutant loads of surface runoff in Wuhan City Zoo, an urban tourist area. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation: Denver, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Hu, Y.M.; Li, C.L. Landscape metrics for three-dimensional urban building pattern recognition. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 87, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, L.S. Liaoning Statistical Yearbook 2020; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Yang, J.; Maximov, I.; Siber, R.; Bogner, K.; Mieleitner, J.; Zobrist, J.; Srinivasan, R. Modelling hydrology and water quality in the pre-alpine/alpine Thur watershed using SWAT. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEPA. Analyses Methods for Monitoring Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; van Griensven, A.; Van Liew, M.W.; et al. SWAT: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. Asabe 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busico, G.; Colombani, N.; Fronzi, D.; Pellegrini, M.; Tazioli, A.; Mastrocicco, M. Evaluating SWAT model performance, considering different soils data input, to quantify actual and future runoff susceptibility in a highly urbanized basin. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 266, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MHURD. Technical Guide for Sponge Cities—Water System Construction of Low Impact Development; China Building Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Palla, A.; Gnecco, I. Hydrologic modeling of Low Impact Development systems at the urban catchment scale. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gironas, J.; Roesner, L.A.; Rossman, L.A.; Davis, J. A new applications manual for the Storm Water Management Model (SWMM). Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.S.; Chen, L.; Shen, Z.Y. Impacts of urbanization on regional nonpoint source pollution: Case study for Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9849–9860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.L.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.M.; Gong, J.P.; Xu, Y.Y. Modeling the Quality and Quantity of Runoff in a Highly Urbanized Catchment Using Storm Water Management Model. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Xia, J.; Liang, T. Non-point source pollution modelling using Soil and Water Assessment Tool and its parameter sensitivity analysis in Xin’anjiang catchment, China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, S.Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, X.R.; Wang, Z.; Qin, C.H.; Hao, R.X.; Lu, J.; Gao, J.J. Assessing the Effects of Land Use Changes on Non-Point Source Pollution Reduction for the Three Gorges Watershed Using the SWAT Model. J. Environ. Inform. 2013, 22, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Qiu, J.L.; Hong, Q.; Chen, L. Simulation of spatial and temporal distributions of non-point source pollution load in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.C.; Wang, G.Q.; Wang, L.J.; Zheng, B.H. Impact of land use changes on water quality in headwaters of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11448–11460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, P.W.; Lei, M.; Yang, S.C.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.Y.; Dong, N.; Guo, G.H. Development of a model to simulate soil heavy metals lateral migration quantity based on SWAT in Huanjiang watershed, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 77, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, F.H.; Huang, H.B.; Shan, Y.S.; Geng, X.J. Combine the soil water assessment tool (SWAT) with sediment geochemistry to evaluate diffuse heavy metal loadings at watershed scale. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.Z.; Shrestha, N.K.; Wang, J. Incorporating a non-reactive heavy metal simulation module into SWAT model and its application in the Athabasca oil sands region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 20879–20892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.B.; Zhou, L.F.; He, S.L.; Lu, C.; Wu, G.L.; Ye, W.; Ji, P.X. A heavy metalmodule coupled with the SWATmodel and its preliminary application in a mine-impacted watershed in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Blanco, M.L.; Taboada-Castro, M.M.; Taboada-Castro, M.T. Rainfall-runoff response and event-based runoff coefficients in a humid area (northwest Spain). Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.C.; Wang, G.Q.; Yang, Y.; Xue, B.L.; Wu, B.B. Assessment of the Impacts of Land Use Changes on Nonpoint Source Pollution Inputs Upstream of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci. World J. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.J.; Miller, S.N. Using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to assess land use impact on water resources in an East African watershed. J. Hydrol. 2013, 486, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.W.; Won, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.E.; Jeong, J. Hydrological Impacts of Urban Imperviousness in White Rock Creek Watershed. Trans. Asabe 2011, 54, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Lakshmi, V.; Patra, K.C. Evaluating the Uncertainties in the SWAT Model Outputs due to DEM Grid Size and Resampling Techniques in a Large Himalayan River Basin. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2017, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Source | TN | TP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load (t/y) | Contribution (t/km2) | Load (t/y) | Contribution (t/km2) | |
| Dry farm land NPS by SWAT | 21,600 | 3.38 | 8690 | 1.36 |
| Paddy field NPS by SWAT | 22,600 | 6.28 | 1220 | 0.34 |
| Forestland NPS by SWAT | 3840 | 0.29 | 95.1 | 0.01 |
| Grassland NPS by SWAT | 8.44 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.00 |
| Wetland NPS by SWAT | 2.32 | 0.02 | 1.18 | 0.01 |
| Urban NPS by SWAT | 2100 | 0.67 | 27.5 | 0.01 |
| Urban NPS by EMC | 853 | 0.75 | 266 | 0.23 |
| Study Area | Pb | Cu | Cr | Ni | Cd | Zn | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central Liaoning Urban Agglomeration | 227 | 346 | 248 | 87 | 3.05 | 1220 | This study |
| Northeast corner of China bordering Russia | 20.21 | 21.75 | 47.35 | 47.35 | - | - | [56] |
| Muskeg River Watershed | 0–0.7 | 0–8.2 | - | - | - | - | [57] |
| Liuyang River | - | - | - | - | - | 0–500 | [58] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zong, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, J. Quantifying the Contribution of Agricultural and Urban Non-Point Source Pollutant Loads in Watershed with Urban Agglomeration. Water 2021, 13, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101385
Zong M, Hu Y, Liu M, Li C, Wang C, Liu J. Quantifying the Contribution of Agricultural and Urban Non-Point Source Pollutant Loads in Watershed with Urban Agglomeration. Water. 2021; 13(10):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101385
Chicago/Turabian StyleZong, Min, Yuanman Hu, Miao Liu, Chunlin Li, Cong Wang, and Jianxin Liu. 2021. "Quantifying the Contribution of Agricultural and Urban Non-Point Source Pollutant Loads in Watershed with Urban Agglomeration" Water 13, no. 10: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101385
APA StyleZong, M., Hu, Y., Liu, M., Li, C., Wang, C., & Liu, J. (2021). Quantifying the Contribution of Agricultural and Urban Non-Point Source Pollutant Loads in Watershed with Urban Agglomeration. Water, 13(10), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101385