Hydrological Processes in Eucalypt and Pine Forested Headwater Catchments within Mediterranean Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Geomorphologic Characteristics of the Study Catchments
2.1.2. Geology and Soils
2.1.3. Land Use and Vegetation
2.2. Hydro-Meteorological Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Annual Water-Balance Calculation
2.3.2. Hydrograph and Streamflow Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Rainfall Pattern over the Study Period
3.2. Annual Water Balance
3.2.1. Inter Annual Variation
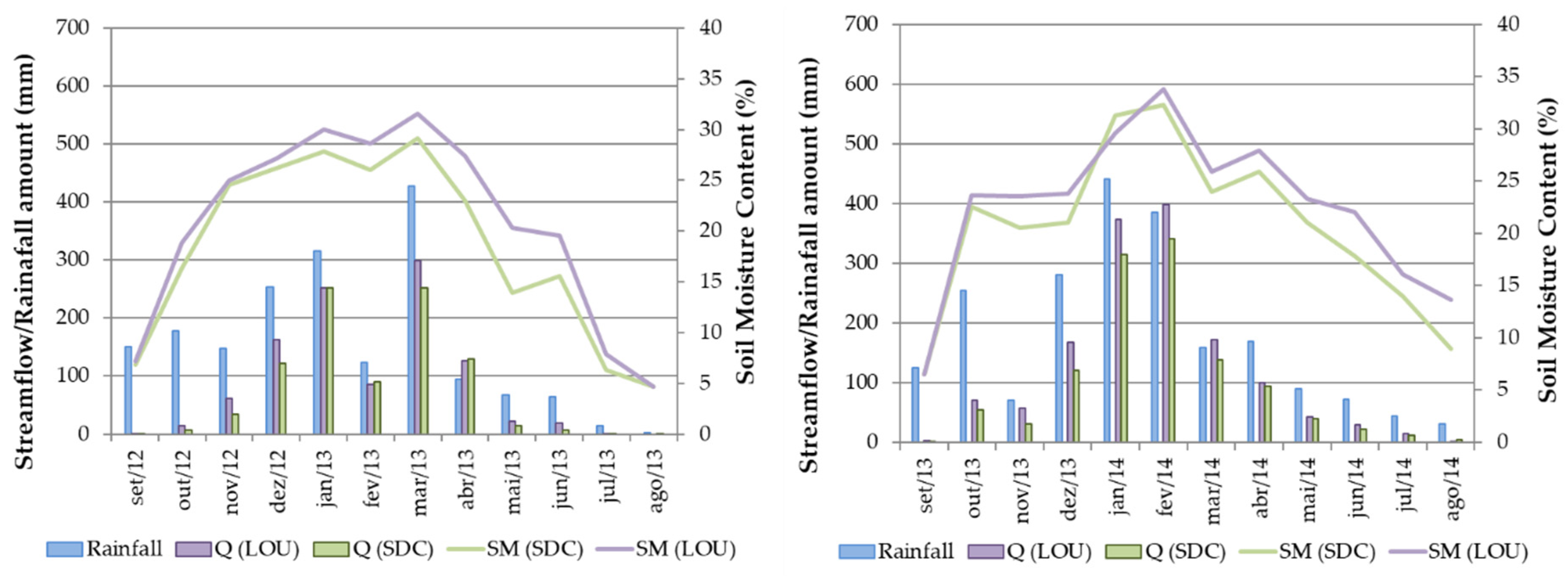
3.2.2. Seasonal Variation
3.3. Changes in Soil Moisture Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Lorente, A.; Seeger, M.; García-Ruiz, J.M. Assessing the Effect of Climate Oscillations and Land-use Changes on Streamflow in the Central Spanish Pyrenees. Ambio 2003, 32, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debussche, M.A.X.; Lepart, J.; Dervieux, A. Mediterranean landscape changes: Evidence from old postcards. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 1999, 8, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasanta-Martínez, T.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Cuadrat-Prats, J.M. Mountain Mediterranean landscape evolution caused by the abandonment of traditional primary activities: A study of the Spanish Central Pyrenees. Appl. Geogr. 2005, 25, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafleur, B.; Paré, D.; Claveau, Y.; Thiffault, É.; Bélanger, N. Influence of afforestation on soil: The case of mineral weathering. Geoderma 2013, 202–203, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO. Future Production from Forest Plantations; Forest Plantations Thematic Papers; FAO Forest Resources Development Service—Forest Resources Division: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, F.; Lionello, P. Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 63, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboni, D.; Harrison, S.P.; Bartlein, P.J.; Jalut, G.; New, M.; Prentice, I.C.; Sanchez-Goñi, M.-F.; Spessa, A.; Davis, B.; Stevenson, A.C. Relationships between plant traits and climate in the Mediterranean region: A pollen data analysis. J. Veg. Sci. 2004, 15, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Walker, G.R. Predicting the Effect of Vegetation Changes on Catchment Average Water Balance; CSIRO Land and Water- Technical Reports; Cooperative Research Centre for Catchment Hydrology: Melbourne, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantari, Z.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; Walsh, R.P.D.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Destouni, G. Urbanization development under climate change: Hydrological responses in a peri-urban Mediterranean catchment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 2207–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Walker, G.R. Response of mean annual evapotranspiration to vegetation changes at catchment scale. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.A.; Blackie, J.R.; Eeles, C.W.O. Final Report on The East African Catchment Research Project; Experimental Methods (ODMI R2532); Instiute of Hydrology: Wallingford, UK, 1976; Volume 1, p. 108.
- Tromp van Meerveld, I.; McDonnell, J.J. Comment to “Spatial correlation of soil moisture in small catchments and its relationship to dominant spatial hydrological processes, Journal of Hydrology, 286: 113–134”. J. Hydrol. 2005, 303, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latron, J.; Gallart, F. Runoff generation processes in a small Mediterranean research catchment (Vallcebre, Eastern Pyrenees). J. Hydrol. 2008, 358, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.L.; Roulet, N.T. Antecedent moisture conditions and catchment morphology as controls on spatial patterns of runoff generation in small forest catchments. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.A.; Kathuria, A. Response of streamflow to afforestation and thinning at Red Hill, Murray Darling Basin, Australia. J. Hydrol. 2010, 412–413, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, D.; Tromp-van Meerveld, H.J.; Gobbi, A.; Borga, M.; Dalla Fontana, G. The influence of soil moisture on threshold runoff generation processes in an alpine headwater catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, N.A.; Almeida, C.A.; Coelho, C.O.A. Impacts of landuse and cover type on runoff and soil erosion in a marginal area of Portugal. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 3, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, N.E.; Freer, J.; Aulenbach, B.T. Hydrological Dynamics of the Panola Mountain Research Watershed, Georgia. Ground Water 2003, 41, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ruiz, J.M.; Lana-Renault, N. Hydrological and erosive consequences of farmland abandonment in Europe, with special reference to the Mediterranean region. A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallart, F.; Llorens, P. Observations on land cover changes and water resources in the headwaters of the Ebro catchment, Iberian Peninsula. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2004, 29, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moreno, J.I.; Beniston, M.; Garcia-Ruiz, J.M. Trends in Hight flows in the Central Spanish Pyrenees: Response to climatic factors or to land-use change? Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeger, M.; Ries, J.B. Soil degradation and soil surface process intensities on abandoned fields in Mediterranean mountain environments. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda, A. Soil erosion after land abandonment in a semiarid environment of southeastern Spain. Arid. Soil Res. Rehabil. 1997, 11, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammeraat, L.H.; Imeson, A.C. The evolution and significance of soil-vegetation patterns following land abandonment and fire in Spain. Catena 1999, 37, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piegay, H.; Walling, D.E.; Landon, N.; He, Q.; Liebault, F.; Petiot, R. Contemporary changes in sediment yield in an alpine mountain basin due to afforestation (the upper Drome in France). Catena 2004, 55, 183–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.M.; Govers, G.; Doorn, A.; van Quetier, F.; Chouvardas, D.; Rounsevell, M. The response of soil erosion and sediment export to land-use change in four areas of Europe: The importance of landscape pattern. Geomorphology 2008, 98, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouri, M.; Giourga, C. Land abandonment and slope gradient as key factors of soil erosion in Mediterranean terraced lands. Catena 2007, 69, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.N.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Almeida, A.C.; Figueiredo, A. Soil erosion and hydrological response to land abandonment in a central inland area of Portugal. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.D. Processos Hidrologicos e Hidroquimicos em Povoamentos de Eucalyptus globulus Labill e Pinus Pinaster Aiton. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shakesby, R.A.; Boakes, D.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Gonçalves, A.J.B.; Walsh, R.P.D. Limiting the soil degradation impacts of wildfire in Pine and Eucalyptus forest in Portugal. Appl. Geogr. 1996, 16, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.D.; Walsh, R.P.D.; Shakesby, R.A. Post-fire forestry management and nutrient losses in eucalyptus and pine plantations, Northern Portugal. Land Degrad. Dev. 2000, 11, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.O.A.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Boulet, A.K.; Keizer, J.J. Overland flow generation processes, erosion yields and solute loss following different intensity fires. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2004, 37, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.D.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Boulet, A.K.; Leighton-Boyce, G.; Keizer, J.J.; Ritsema, C.J. Influence of burning intensity on water repellency and hydrological processes at forest and shrub sites in Portugal. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakesby, R.A.; Bento, C.P.M.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Stoof, C.R.; Urbanek, E.; Walsh, R.P.D. Impacts of prescribed fire on soil loss and soil quality: An assessment based on an experimentally-burned catchment in central Portugal. Catena 2015, 128, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoof, C.R.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Mol, W.; Van den Berg, J.; De Kort, A.; Drooger, S.; Slingerland, E.C.; Mansholt, A.U.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; Ritsema, C.J. Soil surface changes increase runoff and erosion risk after a low–moderate severity fire. Geoderma 2015, 239–240, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Keizer, J.J.; Gonzalez-Pelayo, O.; Alegre-Prats, S.; Ritsema, C.; Geissen, V. Effect of fire frequency on runoff, soil erosion, and loss of organic matter at the micro-plot scale in north-central Portugal. Geoderma 2016, 269, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.S.; Correia, A.; Borges, J.G. Floresta. In Ecossistemas e Bem-Estar Humano: Avaliação para Portugal do Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; Pereira, H.M., Domingos, T., Vicente, L., Proença, V., Eds.; Escolar Editora: Lisboa, Portugal, 2009; pp. 184–211. [Google Scholar]
- IFN6; ICNF. Inventario Florestal Nacional 6—Áreas dos Usos do Solo e das Espécies Florestais de Portugal Continental; Resultados Preliminares, 34; Instituto da Conservação da Natureza e das Florestas: Lisboa, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Baptista, F.O. A Política Agrária do Estado Novo; Edicões Afrontamento: Porto, Portugal, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, I.S. Propriedade da Terra e Política Florestal em Portugal. Silva Lusitana 2003, 11, 185–199. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, N.; Graaff, J.; de Rodrigo, I.; Duarte, F. Historical review of land-use changes in Portugal (before and after EU integration in 1986) and their implications for land degradation and conservation, with a focus on Centro and Alentejo regions. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.; Tomé, M.; Pereira, J.S. A produtividade do eucaliptal. In O Eucaliptal em Portugal: Impactes Ambientais e Investigação Científica; Alves, A.M., Pereira, J.S., Silva, J.M.N., Eds.; Technical University of Lisbon: Lisboa, Portugal, 2007; p. 398. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, K.A. The water balance of the Mbeya experimental catchments. East Afr. Agric. For. J. 1979, 43, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruijnzeel, L.A. Hydrological functions of tropical forest: Not seeing the soil for the trees? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 104, 185–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, K.A.; Jobbagy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. Effects of afforestation on water yield: A global synthesis with implications for policy. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, X.; McNulty, S.G.; Vose, J.M. Potential water yield reduction due to forestation across China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, P.; Xiong, W.; Shen, Z.; Guo, M.; Shi, Z.; Du, A.; Wang, L. Water-Yield Reduction After Afforestation and Related Processes in the Semiarid Liupan Mountains, Northwest China1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2008, 44, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Sun, G.; Liu, S.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, G.; Dai, L. The Forest-Streamflow Relationship in China: A 40-Year Retrospect1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2008, 44, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanclay, J.K. Managing water use from forest plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, A.J.D.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Walsh, R.P.D.; Shakesby, R.A.; Ceballos, A.; Doerr, S.H. Hydrological implications of soil water-repellency in Eucalyptus globulus forests, north-central Portugal. J. Hydrol. 2000, 231–232, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakesby, R.A.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Walsh, R.P.D. Ground-level changes after wildfire and ploughing in eucalyptus and pine forests, Portugal: Implications for soil microtopographical development and soil longevity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2002, 13, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton-Boyce, G.; Doerr, S.H.; Shakesby, R.A.; Walsh, R.P.D.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Boulet, A.K.; Coelho, C.O.A. Temporal Dynamics of water repellency and soil moisture in Eucalypt plantations, Portugal. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente—ARH Centro. PGRH do Vouga, Mondego, Lis—RH4—Relatório Base—P2—Climatologia—Temperatura Média Annual; Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente—ARH Centro: Coimbra, Portugal, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Weijden, C.H.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Hydrogeochemistry in the Vouga River basin (central Portugal): Pollution and chemical weathering. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 580–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014—International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports 106; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Roma, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Veur, J. Soil Survey of The Sites Near Lourizela and Falgorosa: Soil Descriptions and Particle Analysis; IBERLIM Interim Report; University of Aveiro: Aveiro, Portugal, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A.D. The Effects of Fire and Different Logging Practices on Nutrient Losses in Overland Flow from Eucalyptus and Pine Forests, Northern Portugal; University of Wales: Swansea, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Boulet, A.K. Escoamento Superficial nos Eucaliptais da Serra do Caramulo. Master’s Thesis, University of Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gosch, L. Einfluss Unterschiedlicher Forstmanagementstrategien auf Bodenhydraulische Parameter zur Standortswassermodellierung im Águeda Einzugsgebiet Zentralportugal; Dresden University of Technology: Dresden, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, C.O.A.; Laouina, A.; Regaya, K.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Carvalho, T.M.M.; Chaker, M.; Naafa, R.; Naciri, R.; Boulet, A.K.; Keizer, J.J. The impact of soil water repellency on soil hydrological and erosional processes under Eucalyptus and evergreen Quercus forests in the Western Mediterranean. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2005, 3, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, J.J.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Shakesby, R.A.; Domingues, C.S.P.; Malvar, M.C.; Perez, I.M.B.; Matias, M.J.S.; Ferreira, A.J.D. The role of soil water repellency in overland flow generation in pine and eucalypt forest stands in coastal Portugal. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton-Boyce, G.; Doerr, S.H.; Shakesby, R.A.; Walsh, R.P.D. Quantifying the impact of soil water repellency on overland flow generation and erosion: A new approach using rainfall simulation and wetting agent on in situ soil. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 2337–2345. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.M.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; Wahren, F.T.; Wahren, A.; Feger, K.-H.; Bernard-Jannin, L.; Rial-Rivas, M.E.; Keizer, J.J.; Nunes, J.P. Soil water repellency dynamics in pine and eucalypt plantations in Portugal—A high-resolution time series. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 27, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, A.-K.; Prats, S.A.; Malvar, M.C.; González-Pelayo, O.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Keizer, J.J. Surface and subsurface flow in eucalyptus plantations in north-central Portugal. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2015, 63, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skogerboe, G.V. Cutthroat Flumes for Water Measurement; Office of Agriculture, Bureau for Technical Assistance: Ft. Collins, CO, USA, 1974; p. 22.
- Chow, V.T. Handbook of Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1964; 1495p. [Google Scholar]
- ARHC. Parte 2—Caracterização Geral e Diagnóstico. Caracterização das Massas de Águas Subterrâneas. In Plano de Gestão das Bacias Hidrográficas dos Rios Vouga, Mondego e Lis Integradas na Região Hidrografica 4; Final Revision. Administração da Região Hidrografica do Centro I.P.; Administração da Região Hidrografica do Centro: Coimbra, Portugal, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; Melching, C.S. Modelling the dependence and internal structure of storm events for continuous rainfall simulation. J. Hydrol. 2012, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.J.; McMahon, T.A. Evaluation of automated techniques for base flow and recession analyses. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, T.; Ju, C.; He, C. Effect of reforestation on annual water yield in a large watershed in northeast China. J. For. Res. 2015, 26, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; White, D.A.; Xiang, D.; Short, T.M.; Xiao, W.; Chen, J.; Deng, Z.; Yang, Z. Simple model of evapotranspiration by Eucalyptus plantations for data poor areas and tested using water balance data from a small catchment in Guangxi, China. Aust. For. 2019, 82, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lane, P.N.J.; Morris, J.; Ningnan, Z.; Guangyi, Z.; Guoyi, Z.; Daping, X. Water balance of tropical eucalypt plantations in south-eastern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 124, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Hanjra, M.; Mu, J. Water management and crop production for food security in China: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, N.; Harper, R.; Li, Q.; Liu, K.; Wei, X.; Ning, D.; Hou, Y.; Liu, S. A global review on hydrological responses to forest change across multiple spatial scales: Importance of scale, climate, forest type and hydrological regime. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fahey, B.; Jackson, R. Hydrological impacts of converting native forests and grasslands to pine plantations, South Island, New Zealand. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1997, 84, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.E.; Zhang, L.; McMahon, T.A.; Western, A.W.; Vertessy, R.A. A review of paired catchment studies for determining changes in water yield resulting from alterations in vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2005, 310, 28–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, P.N.J.; Best, A.E.; Hickel, K.; Zhang, L. The response of flow duration curves to afforestation. J. Hydrol. 2005, 310, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.D.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Ritsema, C.J.; Boulet, A.K.; Keizer, J.J. Soil and water degradation processes in burned areas: Lessons learned from a nested approach. Catena 2008, 74, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, T.H. Eucalypt plantations and climate change. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 301, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.D.; Prats, S.A.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Shakesby, R.A.; Páscoa, F.M.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; Keizer, J.J.; Ritsema, C. Strategies to prevent forest fires and techniques to reverse degradation processes in burned areas. Catena 2015, 128, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, T.H.; Broadhurst, L.M.; Pinkard, E.; Prober, S.M.; Dillon, S.K.; Bush, D.; Pinyopusarerk, K.; Doran, J.C.; Ivkovich, M.; Young, A.G. Native forests and climate change: Lessons from eucalypts. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 347, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bart, R.; Hope, A. Streamflow response to fire in large catchments of a Mediterranean-climate region using paired-catchment experiments. J. Hydrol. 2010, 388, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.D. As alterações climáticas e a floresta. In Floresta Viva: Património de Futuro; Baptista, F., Jacinto, R., Mendes, T., Eds.; Centro de Ciência Viva: Proença-a-Nova, Portugal, 2009; pp. 9–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.J.D.; Silva, J.S.; Rodrigues, D.; Gomes, F.; Bingre, P.; Leitão, I.; Pinto, L.; Boulet, A.-K.; Monteiro, A.; Ferreira, C. A floresta da Região Centro num contexto de alterações climáticas: Subsídios para aumentar a adaptação e a resiliência. In Livro Verde Para o Desenvolvimento Rural da Região Centro; Ferreira, A.J.D., Ed.; CERNAS: Coimbra, Portugal, 2017; pp. 234–256. [Google Scholar]




| P (m) | A (km2) | Hmax (m) | Hmin (m) | ΔH (m) | S (%) | O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIN | 4150 | 0.65 | 455 | 200 | 255 | 32 | S-N |
| EUC | 4020 | 0.52 | 485 | 273 | 212 | 28 | E-W |
| Tc (min) | L (m) | LFP (m) | Lk (m) | Sc (m/m) | DD | Or | |
| PIN | 31 | 1140 | 1342 | 835 | 0.171 | 1.29 | 2 |
| EUC | 34 | 1123 | 1434 | 921 | 0.142 | 1.78 | 2 |
| Catchment Name | Soil Type | Horizon | Mean Depth (cm) | BD (g/cm3) | OM (%) | Particle Size Distribution (%) | Ksat (mm/h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse | Sand | Silt | Clay | |||||||
| PIN | Umbric Regosol | 1 | 25 | 0.98 | 8 | 43 | 36 | 52 | 12 | 70 |
| EUC | Humic Cambisol | 1 | 30 | 0.89 | 13 | 18 | 21 | 56 | 23 | 70 |
| EUC | Humic Cambisol | 2 | 65 | 1.03 | 5 | 14 | 26 | 55 | 19 | - |
| EUC | Umbric Regosol | 1 | 35 | 0.98 | 13 | 50 | 23 | 59 | 18 | 70 |
| Total Rainfall | Rainfall Duration | Average Rainfall Intensity | Average Event Duration | Average I30max | Total Rainfall | Rainfall Duration | Average Rainfall Intensity | Average Event Duration | Average I30max | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010/2011 | n | mm | days | mm/day | day/event | mm/h | 2013/2014 | n | mm | days | mm/day | day/event | Av I30max |
| Total > 10 mm | 31 | 1026 | 35.8 | 28.7 | 1.2 | 9.9 | Total > 10 mm | 42 | 1821 | 60.5 | 30.1 | 1.4 | 10.2 |
| >120 mm | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | >120 mm | 4 | 562 | 17.0 | 33.0 | 4.3 | 15.2 |
| 120–60 mm | 4 | 343 | 10.4 | 33.0 | 2.6 | 17.8 | 120–60 mm | 7 | 478 | 16.4 | 29.1 | 2.3 | 9.6 |
| 60–30 mm | 8 | 332 | 12.2 | 27.1 | 1.5 | 11.2 | 60–30 mm | 9 | 398 | 12.8 | 31.2 | 1.4 | 11.6 |
| 30–10 mm | 19 | 351 | 13.2 | 26.7 | 0.7 | 7.6 | 30–10 mm | 22 | 383 | 14.3 | 26.9 | 0.6 | 8.9 |
| 2011/2012 | 2014/2015 | ||||||||||||
| Total > 10 mm | 31 | 790 | 27.9 | 28.3 | 0.9 | 8.7 | Total > 10 mm | 33 | 1261 | 40.4 | 31.2 | 1.2 | 13.3 |
| >120mm | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | >120 mm | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 120–60 mm | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 120–60 mm | 6 | 551 | 13.9 | 39.5 | 2.3 | 19.6 |
| 60–30 mm | 9 | 369 | 10.7 | 34.4 | 1.2 | 11.4 | 60–30 mm | 10 | 394 | 15.7 | 25.1 | 1.6 | 13.3 |
| 30–10 mm | 22 | 421 | 17.2 | 24.5 | 0.8 | 7.6 | 30–10 mm | 17 | 317 | 10.8 | 29.4 | 0.6 | 11.1 |
| 2012/2013 | 2015/2016 | ||||||||||||
| Total > 10 mm | 35 | 1278 | 37.9 | 33.7 | 1.1 | 7.9 | Total > 10 mm | 44 | 2102 | 55.3 | 38.0 | 1.3 | 12.0 |
| >120 mm | 2 | 347 | 6.4 | 54.1 | 3.2 | 13.4 | >120 mm | 4 | 946 | 17.0 | 55.8 | 4.2 | 19.3 |
| 120–60 mm | 1 | 90 | 2.1 | 42.8 | 2.1 | 12.0 | 120–60 mm | 3 | 223 | 4.8 | 46.4 | 1.6 | 19.0 |
| 60–30 mm | 10 | 420 | 12.3 | 34.3 | 1.2 | 10.7 | 60–30 mm | 13 | 517 | 15.5 | 33.3 | 1.2 | 15.1 |
| 30–10 mm | 22 | 421 | 17.2 | 24.5 | 0.8 | 8.7 | 30–10 mm | 24 | 416 | 18.0 | 23.1 | 0.8 | 8.2 |
| Year | PIN R | PIN Q | PIN BT | PIN SR | PIN ET | PIN Gs | EUC R | EUC Q | EUC BT | EUC SR | EUC ET | EUC Gs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | |
| 2010/2011 | 1520 | 361 | 190 | 172 | 1082 | 76 | 1259 | 463 | 262 | 200 | 734 | 63 |
| 2011/2012 | 1192 | 208 | 119 | 90 | 924 | 60 | 984 | 217 | 104 | 113 | 718 | 49 |
| 2012/2013 | 2049 | 1045 | 655 | 390 | 901 | 102 | 1839 | 909 | 475 | 433 | 838 | 92 |
| 2013/2014 | 2465 | 1428 | 901 | 527 | 914 | 123 | 2121 | 1175 | 641 | 533 | 840 | 106 |
| 2014/2015 | 1554 | 807 | 528 | 279 | 670 | 78 | 1372 | 731 | 394 | 330 | 579 | 69 |
| 2015/2016 | 2504 | 1430 | 795 | 635 | 949 | 125 | 2127 | 1291 | 618 | 680 | 723 | 106 |
| Correlation/R | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.09 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.52 | 1.00 |
| (a) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sep-oct-nov | dec-jan-feb | mar-apr-may | jun-jul-aug | ||||||||||||||||||
| Year | R | Rs/R | Qs/Qt | Qs/Rs | Rs/R | Qs/Qt | Qs/Rs | Rs/R | Qs/Qt | Qs/Rs | Rs/R | Qs/Qt | Qs/Rs | ||||||||
| mm | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |||||||||
| PIN | EUC | PIN | EUC | PIN | EUC | PIN | EUC | PIN | EUC | PIN | EUC | PIN | EUC | PIN | EUC | ||||||
| 2010/2011 | 1256 | 34 | 14 | 11 | 10 | 12 | 42 | 77 | 72 | 44 | 63 | 17 | 7 | 17 | 10 | 36 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| 2011/2012 | 984 | 32 | 10 | 11 | 6 | 8 | 16 | 27 | 25 | 29 | 35 | 42 | 62 | 60 | 26 | 32 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 7 |
| 2012/2013 | 1763 | 26 | 8 | 5 | 15 | 9 | 38 | 48 | 51 | 64 | 67 | 32 | 43 | 44 | 69 | 67 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 24 | 9 |
| 2013/2014 | 2121 | 21 | 9 | 7 | 27 | 20 | 52 | 66 | 66 | 69 | 70 | 20 | 22 | 23 | 66 | 65 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 29 | 27 |
| 2014/2015 | 1372 | 55 | 45 | 46 | 43 | 45 | 25 | 37 | 31 | 76 | 66 | 15 | 15 | 17 | 51 | 60 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 33 | 62 |
| 2015/2016 | 2127 | 22 | 12 | 8 | 31 | 22 | 50 | 61 | 62 | 70 | 75 | 26 | 24 | 28 | 54 | 65 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 70 | 72 |
| correlation/Rs | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.59 | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.48 | −0.50 | −0.52 | |||||||||||||
| (b) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ALL YEARS | PIN | EUC | |||||||||||||||||||
| R | Rs/R | Qt | Qs/Qt | Qt/R | R | Rs/R | Qt | Qs/Qt | Qt/R | ||||||||||||
| mm | % | mm | % | % | mm | % | mm | % | % | ||||||||||||
| sep-oct-nov | 3347 | 30 | 825 | 16 | 25 | 2893 | 30 | 647 | 14 | 22 | |||||||||||
| dec-jan-feb | 4596 | 41 | 2946 | 56 | 64 | 3878 | 40 | 2649 | 55 | 68 | |||||||||||
| mar-apr-may | 2760 | 24 | 1383 | 26 | 50 | 2395 | 25 | 1358 | 28 | 57 | |||||||||||
| jun-jul-aug | 581 | 5 | 126 | 2 | 22 | 533 | 5 | 132 | 3 | 25 | |||||||||||
| Monthly Data Set | Daily Data Set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIN | EUC | PIN | EUC | ||
| R (mm)/SM (%) | 0.67 | 0.66 | R (mm)/SM (%) | 0.43 | 0.41 |
| BT (mm)/SM (%) | 0.75 | 0.72 | R-3days (mm)/SM (%) | 0.56 | 0.55 |
| SR (mm)/SM (%) | 0.62 | 0.59 | |||
| Q (%)/SM (%) | 0.81 | 0.71 | |||
| Q (mm)/SM (%) | 0.72 | 0.68 | Q (mm)/SM (%) | 0.53 | 0.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boulet, A.-K.; Rial-Rivas, M.E.; Ferreira, C.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Kalantari, Z.; Keizer, J.J.; Ferreira, A.J.D. Hydrological Processes in Eucalypt and Pine Forested Headwater Catchments within Mediterranean Region. Water 2021, 13, 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101418
Boulet A-K, Rial-Rivas ME, Ferreira C, Coelho COA, Kalantari Z, Keizer JJ, Ferreira AJD. Hydrological Processes in Eucalypt and Pine Forested Headwater Catchments within Mediterranean Region. Water. 2021; 13(10):1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101418
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoulet, Anne-Karine, Mitas E. Rial-Rivas, Carla Ferreira, Celeste O. A. Coelho, Zahra Kalantari, Jan Jacob Keizer, and António J. D. Ferreira. 2021. "Hydrological Processes in Eucalypt and Pine Forested Headwater Catchments within Mediterranean Region" Water 13, no. 10: 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101418
APA StyleBoulet, A.-K., Rial-Rivas, M. E., Ferreira, C., Coelho, C. O. A., Kalantari, Z., Keizer, J. J., & Ferreira, A. J. D. (2021). Hydrological Processes in Eucalypt and Pine Forested Headwater Catchments within Mediterranean Region. Water, 13(10), 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101418









