Removal of AOX in Activated Sludge of Industrial Chemical Dyestuff with Bimetallic Pd/Fe Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Activated Sludge and Chemical Reagents
2.2. Pd/Fe Preparation and Characterization
2.3. Batch Experiment Procedure
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Pd/Fe
3.2. Effect of Some Experimental Parameters on the Removal of AOX in Activated Sludge
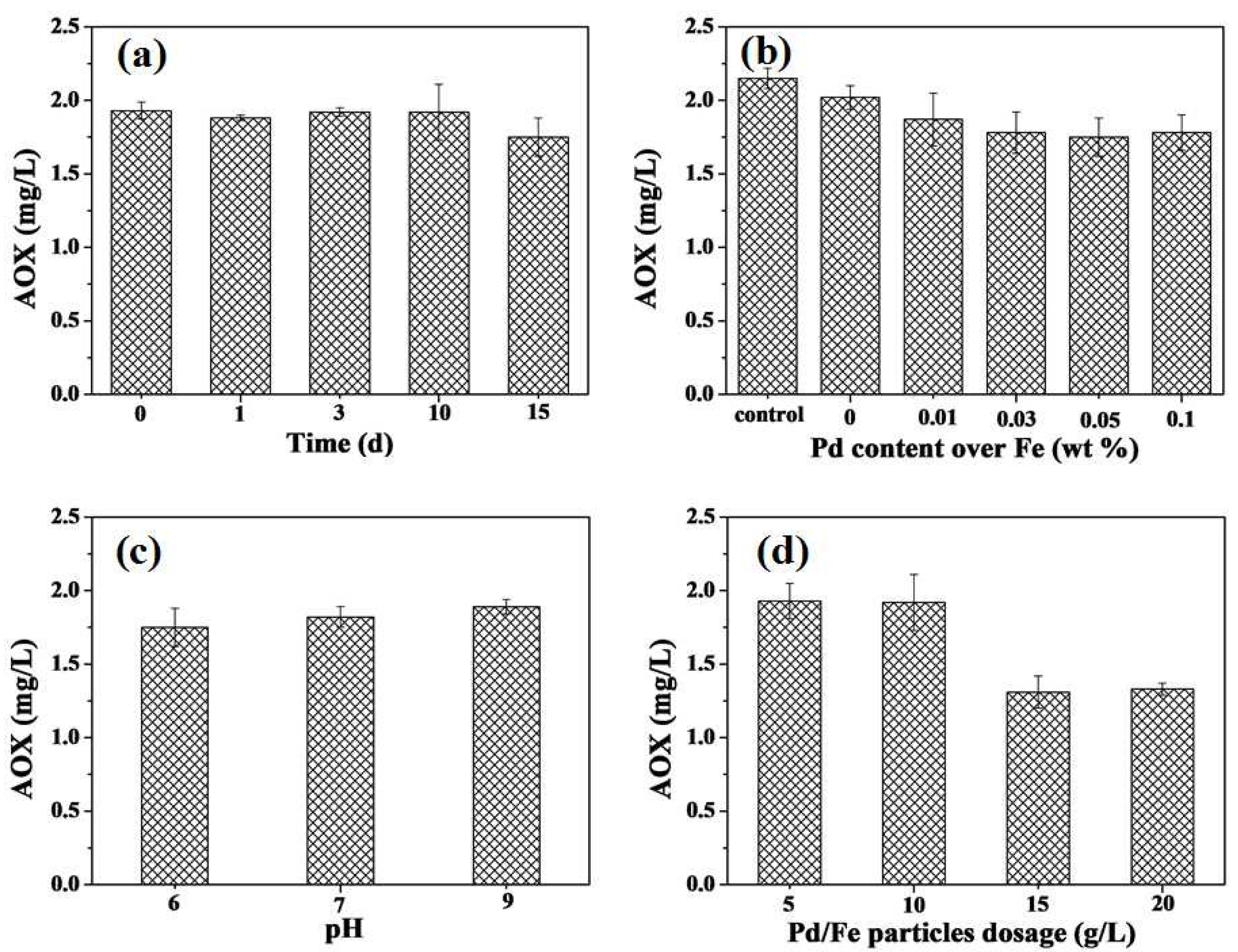
3.2.1. Effect of Pd Loading on the Removal of AOX
3.2.2. Effect of Initial pH
3.2.3. Effect of Reaction Time
3.2.4. Effect of Pd/Fe Bimetallic Particle Added Amounts
3.2.5. Concentration Changes of AOX in Supernatant
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meharg, A.; Wright, J.; Osborn, D. Chlorobenzenes in rivers draining industrial catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 251, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milh, H.; Eyck, K.V.; Bastiaens, B.; Laet, S.D.; Dewil, R. Predicting Residual Adsorbable Organic Halides Concentrations in Industrial Wastewater Using Typical Wastewater Parameters. Water 2020, 12, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Deng, S.; Chen, G.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Cheng, X.; Shi, L. Pd/Al bimetallic nanoparticles for complete hydrodechlorination of 3-chlorophenol in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, W.X. Comparison of reductive dechlorination of p-chlorophenol using Fe0 and nanosized Fe0. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 334–339. [Google Scholar]
- Tunçal, T.; Uslu, O. Industrial sludge remediation with photonic treatment using Ti-Ag nano-composite thin films: Persistent organic pollutant removal from sludge matrix. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 149, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.W.; Chen, L.J.; Liu, R. AOX contamination status and genotoxicity of AOX-bearing pharmaceutical wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 52, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneghem, J.V.; Brems, A.; Lievens, P.; Block, C.; Billen, P.; Vermeulen, I.; Dewil, R.; Baeyens, J.; Vandecasteele, C. Fluidized bed waste incinerators: Design, operational and environmental issues. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 551–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barret, M.; Barcia, G.C.; Guillon, A.; Carrère, H.; Patureau, D. Influence of feed characteristics on the removal of micropollutants during the anaerobic digestion of contaminated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapanen, A.; Vikman, M.; Rajasaerkkae, J.; Virta, M.; Itaevaara, M. Biotests for environmental quality assessment of composted sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Chu, W.H.; Wei, H.B.; Zhao, H.Y.; Xu, B.; Gao, N.Y.; Yin, D.Q. Reductive dechlorination of haloacetamides in drinking water by Cu/Fe bimetal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 203, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, U.D.; Suresh, S. Effects of solvent, pH, salts and resin fatty acids on the dechlorination of pentachlorophenol using magnesium-silver and magnesium-palladium bimetallic systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anang, E.; Liu, H.; Fan, X.Y.; Zhao, D.Y.; Gong, X. Compositional evolution of nanoscale zero valent iron and 2,4-dichlorophenol during dechlorination by attapulgite supported Fe/Ni nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moujahid, A.; Bang, J.J.; Yan, F. Effect of mixing on reductive dechlorination of persistent organic pollutants by Fe/Pd nanoparticles. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Xu, X.; Yong, L.; Wang, D. Catalytic hydrodechlorination of 2, 4-dichlorophenol over nanoscale Pd/Fe: Reaction pathway and some experimental parameters. Water Res. 2006, 40, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Qian, T.T.; Jiang, H. Bimetallic Fe nanoparticles: Recent advances in synthesis and application in catalytic elimination of environmental pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Rui, L.; Chen, L.; Tang, L. Enhanced dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol by recoverable Ni/Fe–Fe3O4 nanocomposites. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 48, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Li, P.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, W.; Fan, S.; Verkhozina, V.A. Catalytic dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls in soil by palladium-iron bimetallic catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Zheng, Z.; Meng, X.Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, L. Surfactant mediated HCB dechlorination in contaminated soils and sediments by micro and nanoscale Cu/Fe Particles. Geoderma 2010, 159, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grittini, C.; Malcomson, M.; Fernando, Q.; Korte, N. Rapid dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls on the surface of a Pd/Fe bimetallic system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2898–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Ramjaun, S.N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Photocatalytic degradation and chlorination of azo dye in saline wastewater: Kinetics and AOX formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 192, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Ben, W.; Qu, J.; Zhang, H. Degradation of endocrine-disrupting chemicals during activated sludge reduction by ozone. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, A.; Jeong, S.W.; Jang, A.; Choi, H. Reduction of highly concentrated nitrate using nanoscale zero-valent iron: Effects of aggregation and catalyst on reactivity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 105, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, Q.; Cissoko, N.; Wo, J.; Xu, X. Catalytic dechlorination of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by Pd/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles in the presence of humic acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.J.; Jovanovic, G. Dechlorination of p-chlorophenol on a Pd/Fe catalyst in a magnetically stabilized fluidized bed; Implications for sludge and liquid remediation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 3085–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ling, X.Y.; Su, X.; Lee, J.Y. Carbon-supported Pt and PtRu nanoparticles as catalysts for a direct methanol fuel cell. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 8234–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chao, C.; Liu, H.; Ma, J. Preparation and characterization of PAA/PVDF membrane-immobilized Pd/Fe nanoparticles for dechlorination of trichloroacetic acid. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4656–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Hu, Y.; Luo, G.S.; Dai, Y.Y. Candida rugosa lipase immobilized by a specially designed microstructure in the PVA/PTFE composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, Y.; Lim, T.T. Catalytic hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols by Pd/Fe nanoparticles: Comparisons with other bimetallic systems, kinetics and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 76, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Min, W.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Gang, Y. Highly active and stable Ni-Fe bimetal prepared by ball milling for catalytic hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4576–4582. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, H.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Shin, H.J.; Yang, J.W. Degradation of trichloroethylene by zero-valent iron immobilized in cationic exchange membrane. Desalination 2008, 223, 212–220. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Liu, R.; Zheng, W.; Lin, L.; Chen, L. Removal of AOX in Activated Sludge of Industrial Chemical Dyestuff with Bimetallic Pd/Fe Particles. Water 2021, 13, 1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13111543
Xu C, Liu R, Zheng W, Lin L, Chen L. Removal of AOX in Activated Sludge of Industrial Chemical Dyestuff with Bimetallic Pd/Fe Particles. Water. 2021; 13(11):1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13111543
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Cancan, Rui Liu, Wei Zheng, Lichu Lin, and Lvjun Chen. 2021. "Removal of AOX in Activated Sludge of Industrial Chemical Dyestuff with Bimetallic Pd/Fe Particles" Water 13, no. 11: 1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13111543
APA StyleXu, C., Liu, R., Zheng, W., Lin, L., & Chen, L. (2021). Removal of AOX in Activated Sludge of Industrial Chemical Dyestuff with Bimetallic Pd/Fe Particles. Water, 13(11), 1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13111543




