The Use of TiO2 as a Disinfectant in Water Sanitation Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Use of Conventional Treatment Methods
1.2. The Use of TiO2 as an Alternative Disinfectant
2. Microbial Disinfection Methods and the TiO2 Mechanism
2.1. Viruses
2.2. Bacteria
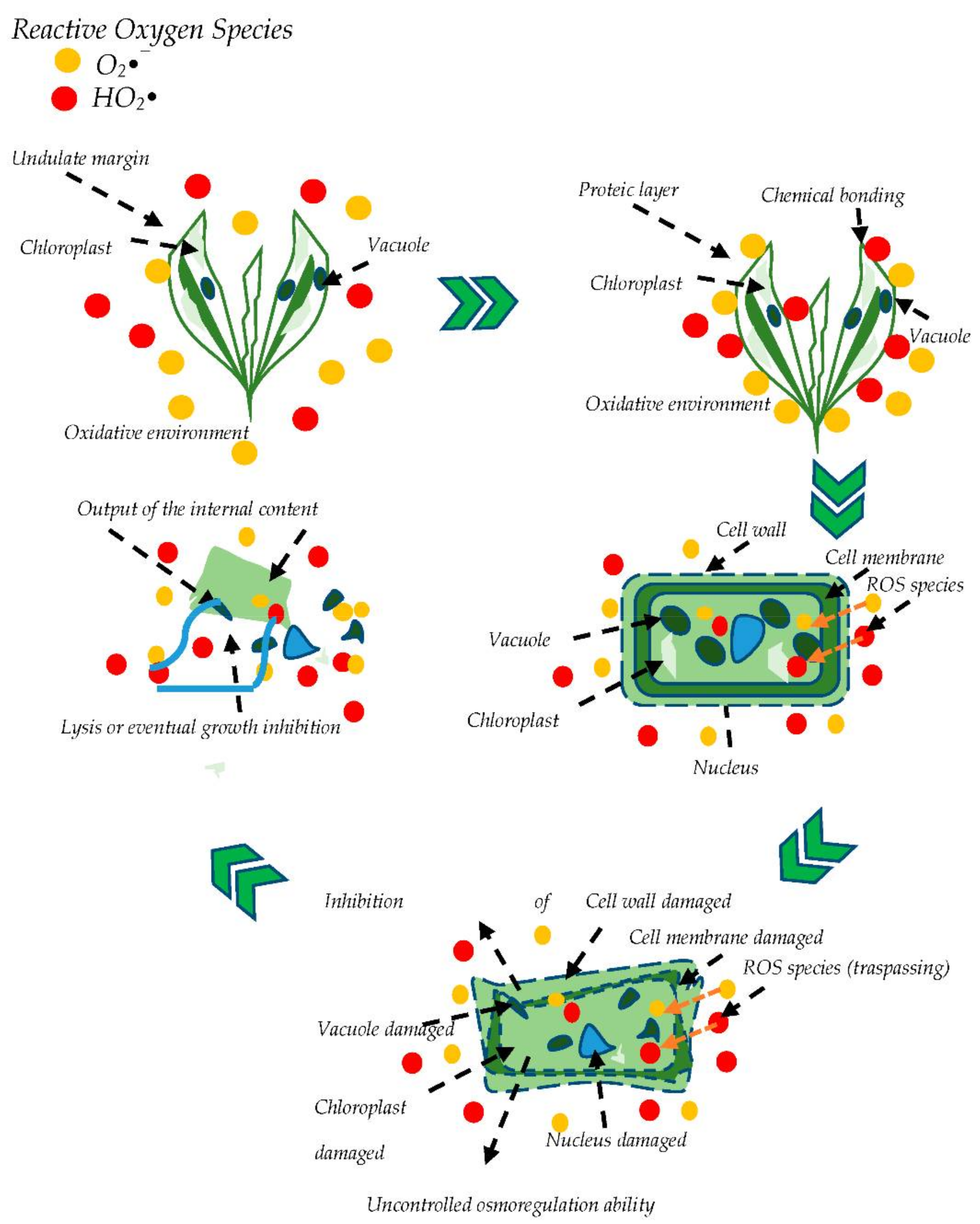
2.3. Algae
2.4. Protozoa
2.5. Fungi
3. Feasibility of Using TiO2
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalin, C.; Qiu, H.; Hanasaki, N.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Balancing water resource conservation and food security in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4588–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laxma Reddy, V.P.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.H. A review of photocatalytic treatment for various air pollutants. Asian J. Atmos Environ. 2011, 5, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraisheh, M.; Wu, L.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Photocatalytic disinfection of Escherichia coli using TiO2 P25 and Cu-doped TiO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 28, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimapilis, E.A.S.; Hsu, C.S.; Mendoza, R.M.O.; Lu, M.C. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for water disinfection. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2018, 28, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vortmann, M.; Balsari, S.; Holman, S.R.; Greenough, P.G. Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene at the World’s Largest Mass Gathering. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2015, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, J.; Chen, S.; Li, B.; Sekar, R.; Zhao, Z.; Jia, J.; Wang, Y.; Kang, P. Disentangling the drivers of diversity and distribution of fungal community composition in wastewater treatment plants across spatial scales. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, W.; Jax, K.; Berger, S. Biodegradation and Persistance. Bioremediat. Biodegrad. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Matos, A.; Gmurek, M.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Martins, R.C. Ozone and photocatalytic processes for pathogens removal from water: A review. Catalysts 2019, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajasulochana, P.; Preethy, V. Comparison on efficiency of various techniques in treatment of waste and sewage water—A comprehensive review. Resour. Effic. Technol. 2016, 2, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levantesi, C.; La Mantia, R.; Masciopinto, C.; Bockelmann, U.; Ayuso-Gabella, M.N.; Salgot, M.; Tandoi, V.; Van Houtte, E.; Wintgens, T.; Grohmann, E. Quantification of pathogenic microorganisms and microbial indicators in three wastewater reclamation and managed aquifer recharge facilities in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4923–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetta, S.; Pignata, C.; Lorenzi, E.; De Ceglia, M.; Meucci, L.; Bonetta, S.; Gilli, G.; Carraro, E. Peracetic Acid (PAA) disinfection: Inactivation of microbial indicators and pathogenic bacteria in a municipal wastewater plant. Water 2017, 9, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metcalf, L.; Eddy, H.P.; Tchobanoglous, G. Wastewater Engineering Treatment Disposal and Reuse; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hijnen, W.A.M.; Beerendonk, E.F.; Medema, G.J. Inactivation credit of UV radiation for viruses, bacteria and protozoan (oo)cysts in water: A review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Recreational Water Quality Criteria. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-10/documents/rwqc2012.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Rojas-Valencia, M.N. Research on ozone application as disinfectant and action mechanisms on wastewater microorganisms. In Science against Microbial Pathogens: Communicating Current Research and Technological Advances; Microbiology Book Series-Number 3; FORMATEX: Badajoz, Spain, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 263–271. [Google Scholar]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Carbon black, titanium dioxide and talc. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2010, 93, 1–413. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, V.C.; Phillips, P.M.; Levine, A.B.; McDaniel, K.L.; Sills, R.C.; Jortner, B.S.; Butt, M.T. Neurotoxicity produced by dibromoacetic acid in drinking water of rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 79, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guariglia, S.R.; Jenkins, E.C.; Chadman, K.K.; Wen, G.Y. Chlorination byproducts induce gender specific autistic-like behaviors in CD-1 mice. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasfi, T.; Coulomb, B.; Boudenne, J.L. Occurrence, origin, and toxicity of disinfection byproducts in chlorinated swimming pools: An overview. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-López, R.; Luna-Pabello, V.; Barrera-Godínez, J.; Orta de Velásquez, M.; Fernández-Villagómez, G. Effect of mineral aggregates on the morphology and viability of Toxocara canis eggs. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Shen, Z.-P.; Cheng, C.; Shi, L.; Cheng, R.; Yuan, D. Hai Photocatalytic disinfection performance in virus and virus/bacteria system by Cu-TiO2 nanofibers under visible light. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Chung, H.; Choi, W.; Yoon, J. Linear correlation between inactivation of E. coli and OH radical concentration in TiO2 photocatalytic disinfection. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, H.A.; Ditta, I.B.; Varghese, S.; Steele, A. Photocatalytic disinfection using titanium dioxide: Spectrum and mechanism of antimicrobial activity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2011, 90, 1847–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical Photolysis of Water at a Semiconductor Electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, T. Sterilization with particulate photosemiconductor. J. Antibact. Antifung. Agents. 1985, 13, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, T.; Tomoda, R.; Nakajima, T.; Wake, H. Photoelectrochemical sterilization of microbial cells by semiconductor powders. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1985, 29, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Tomoda, R.; Nakajima, T.; Nakamura, N.; Komine, T. Continuous-sterilization system that uses photosemiconductor powders. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sjogren, J.C.; Sierka, R.A. Inactivation of phage MS2 by iron-aided titanium dioxide photocatalysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1994, 60, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfrum, E.J.; Huang, J.; Blake, D.M.; Maness, P.C.; Huang, Z.; Fiest, J. Photocatalytic oxidation of bacteria, bacterial and fungal spores, and model biofilm components to carbon dioxide on titanium dioxide–coated surface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, A.G.; Pulgarín, C. Photocatalytic inactivation of E. coli: Effect of (continuous–intermittent) light intensity and of (suspended–fixed) TiO2 concentration. Appl. Catal. B 2003, 44, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitoraj, D.; Janczyk, A.; Strus, M.; Kisch, H.; Stochel, G.; Heczko, P.B.; Macyk, W. Visible light inactivation of bacteria and fungi by modified titanium dioxide. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2007, 6, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TatlIdil, I.; Sökmen, M.; Breen, C.; Clegg, F.; Buruk, C.K.; BacaksIz, E. Degradation of Candida albicans on TiO2 and Ag-TiO2 thin films prepared by sol-gel and nanosuspensions. J. Sol. Gel. Sci. Technol. 2011, 60, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwegmann, H.; Ruppert, J.; Frimmel, F.H. Influence of the pH-value on the photocatalytic disinfection of bacteria with TiO2—Explanation by DLVO and XDLVO theory. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assress, H.A.; Selvarajan, R.; Nyoni, H.; Ntushelo, K.; Mamba, B.B.; Msagati, T.A.M. Diversity, Co-occurrence and Implications of Fungal Communities in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dalecka, B.; Oskarsson, C.; Juhna, T.; Kuttava Rajarao, G. Isolation of Fungal Strains from Municipal Wastewater for the Removal of pharmaceutical substances. Water 2020, 12, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, J.; Yang, D.; Ng, T.W.; Wong, P.K.; Yu, J.C. Enhanced photocatalytic water disinfection properties of Bi 2MoO6-RGO nanocomposites under visible light irradiation. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6307–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxma Reddy, P.V.; Kavitha, B.; Kumar Reddy, P.A.; Kim, K.H. TiO2-based photocatalytic disinfection of microbes in aqueous media: A review. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seven, O.; Dindar, B.; Aydemir, S.; Metin, D.; Ozinel, M.A.; Icli, S. Solar photocalytic disinfection of a group of bacteria and fungi aqueous suspensions with TiO2, ZnO and sahara desert dust. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2004, 165, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Gondal, M.A.; Dastageer, A.; Bagabas, A. Disinfection of Escherichia coli Bacteria from Water by Laser Induced Photo-Catalytic Process using Pure and Doped nano-WO3. Proceedings of 2010 International Conference on Environmental Science and Development, Singapore, 26–28 February 2010; pp. 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, S.G.; Mizrahi, A.; Meyerstein, D. The Role of Carbonate in Catalytic Oxidations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2189–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.L.; Sun, D.S.; Chu, W.C.; Tseng, Y.H.; Ho, H.C.; Wang, J.B.; Chung, P.H.; Chen, J.H.; Tsai, P.J.; Lin, N.T. The effects of the bacterial interaction with visible-light responsive titania photocatalyst on the bactericidal performance. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2009, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tallósy, S.P.; Janovák, L.; Ménesi, J.; Nagy, E.; Juhász, Á.; Balázs, L.; Deme, I.; Buzás, N.; Dékány, I. Investigation of the antibacterial effects of silver-modified TiO2 and ZnO plasmonic photocatalysts embedded in polymer thin films. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 11155–11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xiang, Q.; Liao, Y.; Wen, T.; Zhang, H. Visible-light-driven CdSe quantum dots/graphene/TiO2 nanosheets composite with excellent photocatalytic activity for E. coli disinfection and organic pollutant degradation. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2018, 457, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lv, B.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, X. Bactericidal mechanisms and effector targets of TiO2 and Ag-TiO2 against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyauchi, M.; Sunada, K.; Hashimoto, K. Antiviral effect of visible light-sensitive Cuxo/TiO2 photocatalyst. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankarapillai, V.S.; Pillai, A.M.; Rahdar, A.; Sobha, A.P.; Das, S.S.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Mokarrar, M.H.; Kyzas, G.Z. On facing the SARS-cov-2 (COVID-19) with combination of nanomaterials and medicine: Possible strategies and first challenges. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Sichel, C.; Polo-López, M.I.; de Cara-García, M.; Tello, J.C. Photocatalytic disinfection of natural well water contaminated by Fusarium solani using TiO2 slurry in solar CPC photo-reactors. Catal. Today 2009, 144, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, T.; Fukuda, T.; Nakata, K.; Murakami, T.; Tryk, D.A.; Koide, Y.; Fujishima, A. Photocatalytic inactivation and removal of algae with TiO2-coated materials. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, J.; Ma, S.; Liu, G.; Yang, K.; Tong, M.; Lin, D. Toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to Escherichia coli: Effects of particle size, crystal phase and water chemistry. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Middepogu, A.; Hou, J.; Gao, X.; Lin, D. Effect and mechanism of TiO2 nanoparticles on the photosynthesis of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalon, S.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H.; Escrig, D.; Costa, V. Photocatalytic water disinfection of Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia lamblia using a fibrous ceramic TiO2 photocatalyst. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeledo-Lameiro, M.J.; Reboredo-Fernández, A.; Polo-López, M.I.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Ares-Mazás, E.; Gómez-Couso, H. Photocatalytic inactivation of the waterborne protozoan parasite Cryptosporidium parvum using TiO2/H2O2 under simulated and natural solar conditions. Catal. Today 2017, 280, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobsey, M.D. Managing Water in the Home Accelerated Gains from Improved Water Supply; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, D.M.; Maness, P.C.; Huang, Z.; Wolfrum, E.J.; Huang, J.; Jacoby, W.A. Application of the photocatalytic chemistry of titanium dioxide to disinfection and the killing of cancer cells. Sep. Purif. Methods 1999, 28, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-García, N.; Suárez, S.; Sánchez, B.; Coronado, J.M.; Malato, S.; Maldonado, M.I. Photocatalytic degradation of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plant effluents using immobilized TiO2 in a solar pilot plant. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 103, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniamerian, H.; Tsapekos, P.; Alvarado-Morales, M.; Shokrollahzadeh, S.; Safavi, M.; Angelidaki, I. Anti-algal activity of Fe2O3–TiO2 photocatalyst on Chlorella vulgaris species under visible light irradiation. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hwang, H.M.; Wang, L.; Kim, I.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, H. Solar-light photocatalytic disinfection using crystalline/amorphous low energy bandgap reduced TiO2. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Sunada, K.; Iyoda, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A. Photocatalytic bactericidal effect of TiO2 thin films: Dynamic view of the active oxygen species responsible for the effect. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 1997, 106, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orta de Veláquez, M.T.; Martínez, J.L.; Monje-Ramírez, I.; Rojas-Valencia, M.N. Destruction od helminth (Ascaris suum) eggs by Ozone. Sci Eng. 2004, 26, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Orta, M.T.; Yañez-Noguez, I.; Jiménez-Cisneros, B. Adding silver and copper to hydrogen peroxide and peracetic acid in the disinfection of advanced primary treatment effluent. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Xagoraraki, I.; Yin, Z.; Svambayev, Z. Fate of Viruses in Water Systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpuz, M.V.A.; Buonerba, A.; Vigliotta, G.; Zarra, T.; Ballesteros, F.; Campiglia, P.; Belgiorno, V.; Korshin, G.; Naddeo, V. Viruses in wastewater: Occurrence, abundance and detection methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, A.M.; Mariñas, B.J.; Lu, Y.; Shisler, J.L. Waterborne Viruses: A Barrier to Safe Drinking Water. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerba, C.P.; Betancourt, W.Q.; Kitajima, M. How much reduction of virus is needed for recycled water: A continuous changing need for assessment? Water Res. 2017, 108, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinon, A.; Vialette, M. Survival of Viruses in Water. Intervirology 2018, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumian, T.M.; Leite, J.P.G.; Castello, A.A.; Gaggero, A.; Caillou, M.S.L.; de Miagostovich, M.P. Detection of rotavirus A in sewage samples using multiplex qPCR and an evaluation ofthe ultracentrifugation and adsorption-elutionmethods for virus concentration. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 170, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddeo, V.; Liu, H. Editorial Perspectives: 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): What is its fate in urban water cycle and how can the water research community respond? Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, P.D.; Wadell, A.; Allard, A.; Hierholzer, J.C. “Adenoviruses.” Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 8th ed.; Murray, P.R., Ed.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, P.; Costa, S.; Brown, B.; Silva, S.; Rodrigues, R.; Valério, E. Quantitative PCR detection of enteric viruses in wastewater and environmental water sources by the Lisbon municipality: A case study. Water 2020, 12, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roos, W.H.; Ivanovska, I.L.; Evilevitch, A.; Wuite, G.J.L. Viral capsids: Mechanical characteristics, genome packaging and delivery mechanisms. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1484–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Z.; Di, C.; Yang, L.; Rong, C. Nano-TiO2 membrane adsorption reactor (MAR) for virus removal in drinking water. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 230, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.E.; Rodriguez, R.A.; Linden, K.G.; Hargy, T.M.; Larason, T.C.; Wright, H.B. Wavelength dependent UV inactivation and DNA damage of adenovirus as measured by cell culture infectivity and long range quantitative PCR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Wu, L.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Chung, Y.C. Inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli in water using photocatalysis with fixed TiO2. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 212, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigginton, K.R.; Kohn, T. Virus disinfection mechanisms: The role of virus composition, structure, and function. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Sharzad, K.; Mushaq, S.; Ali, I.; Rafe, M.H.; Fazal-ul-Karim, S.M. Antibacterial and antiviral potential of colloidal Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles suitable for biological applications. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Khalil, S.; Ayub, N.; Bibi, A.; Saeed, B.; Khalid, S. Prevelance of total coliforms, faecal coliforms and E. coli in Rawalpindi vegetable markets. Nat. Sci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahimi, R.; Zargari, S.; Yousefi, A.; Yaghoubi Berijani, M.; Ghaffarinejad, A.; Morsali, A. Visible light photocatalytic disinfection of E. coli with TiO2-graphene nanocomposite sensitized with tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhan, S.; Ma, S.; Zhou, Q. Fabrication of TiO2–Bi2WO6 binanosheet for enhanced solar photocatalytic disinfection of E. coli: Insights on the mechanism. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6841–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.A.; Barros, M.P.; Campos, S.C.; Pinto, E.; Rajamani, S.; Sayre, R.T.; Colepicolo, P. Biochemical biomarkers in algae and marine pollution: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellner, K.G.; Doucette, G.J.; Kirkpatrick, G.J. Harmful algal blooms: Causes, impacts and detection. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atici, T.; Tokatli, C. Algal Diversity and Water Quality Assessment with Cluster Analysis of Four Freshwater Lakes (Mogan, Abant, Karagöl and Poyrazlar) of Turkey. Wulfenia J. 2014, 21, 155–169. [Google Scholar]
- Delanka-Pedige, H.M.K.; Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.P.; Cornelius, J.; Henkanatte-Gedera, S.M.; Tchinda, D.; Zhang, Y.; Nirmalakhandan, N. Pathogen reduction in an algal-based wastewater treatment system employing Galdieria sulphuraria. Algal Res. 2019, 39, 101423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, P.; Mandotra, S.K. Application of Microalgae in Wastewater Treatment. Appl. Microalgae Wastewater Treat. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hund-Rinke, K.; Simon, M. Ecotoxic effect of photocatalytic active nanoparticles (TiO2) on algae and daphnids. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2006, 13, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Yang, D.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Cheng, F.Q. Algae removal of high algae raw water by coagulation enhanced by ozonation. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2009, 30, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, R.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tang, T. Algae removal performance of UV-radiation-enhanced coagulation for two representative algal species. Environment 2020, 745, 141013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dars, F.M.S.E.; Abdel Rahman, M.A.M.; Salem, O.M.A.; Abdel-Aal, E.S.A. Algal control and enhanced removal in drinking waters in Cairo, Egypt. J. Water Health 2015, 13, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeleye, A.S.; Keller, A.A. Interactions between Algal Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Commercial TiO2 Nanoparticles in Aqueous Media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12258–12265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walochnik, J.; Aspöck, H. Protozoan Pathogens: Identification. In Els; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanis, P.; Kourenti, C.; Smith, H. Waterborne transmission of protozoan parasites: A worldwide review of outbreaks and lessons learnt. J. Water Health 2007, 5, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, J.N.; Daniels, M.E.; Watson, F.G.; Oates, S.C.; Miller, M.A.; Conrad, P.A.; Shapiro, K.; Hardin, D.; Dominik, C.; Melli, A.; et al. Hydrologic and vegetative removal of Cryptosporidium parvum, Giardia lamblia, and Toxoplasma gondii surrogate microspheres in coastal wetlands. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomass, Z.; Kidane, D. Parasitological Contamination of Wastewater Irrigated and Raw Manure Fertilized Vegetables in Mekelle City and Its Suburb, Tigray, Ethiopia. 2009. MEJS 2012, 4, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zacharia, A.; Outwater, A.H.; Ngasala, B.; Deun, R. Van Pathogenic parasites in raw and treated wastewater in Africa: A Review. Resour. Environ. 2018, 8, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Tefese, W.; Tilhan, G.; Anberber, M. Cryptosporidiosis: An emerging food and waterborne protozoan disease of global significance. Food Beverage World 2016, 43, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Grimason, A.M.; Smith, H.V.; Young, G.; Thitai, W.N. Occurrences and removal of Ascaris sp. ova by waste stabilization ponds in Kenya. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 33, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madoni, P. Protozoa in wastewater treatment processes: A minireview. Ital. J. Zool. 2011, 78, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supha, C.; Boonto, Y.; Jindakaraked, M.; Ananpattarachai, J.; Kajitvichyanukul, P. Long-term exposure of bacterial and protozoan communities to TiO2 nanoparticles in an aerobic-sequencing batch reactor. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 34609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, R.E.; Priester, J.H.; Werlin, R.A.; Gel, J.; Horst, A.M.; Orias, E.; Holden, P.A. Differential growth of and nanoscale TiO2 accumulation in tetrahymena thermophila by direct feeding versus trophic transfer from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5616–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hageskal, G.; Lima, N.; Skaar, I. The study of fungi in drinking water. Mycol. Res. 2009, 113, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montiel, A.; Rigal, S.; Welté, B. Study of the origin of musty taste in the drinking water supply. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualotto, A.C. Aspergillosis: From Diagnosis to Prevention; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 9789048124084. [Google Scholar]
- Sankaran, S.; Khanal, S.K.; Pometto, A.L.; van Leeuwen, J. (Hans) Ozone as a selective disinfectant for nonaseptic fungal cultivation on corn-processing wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8265–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, M.N.; Sharma, A.K.; Burn, S.; Saint, C.P. Feasibility study on the application of advanced oxidation technologies for decentralised wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 35, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zeng, G.; Tang, L.; Fan, C.; Zhang, C.; He, X.; He, Y. An overview on limitations of TiO2-based particles for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants and the corresponding countermeasures. Water Res. 2015, 79, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; Li, H. Suspension Plasma Spray Fabrication of Nanocrystalline Titania Hollow Microspheres for Photocatalytic Applications. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2015, 24, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.T.; Goswami, D.Y.; Block, S.S. Simultaneous detoxification and disinfection of water by solar photocatalytic treatment. Int. Sol. Energy Conf. 1997, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Lonnen, J.; Kilvington, S.; Kehoe, S.C.; Al-Touati, F.; McGuigan, K.G. Solar and photocatalytic disinfection of protozoan, fungal and bacterial microbes in drinking water. Water Res. 2005, 39, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malato, S.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Maldonado, M.I.; Blanco, J.; Gernjak, W. Decontamination and disinfection of water by solar photocatalysis: Recent overview and trends. Catal. Today 2009, 147, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, C.; Gupta, A.K.; Pal, A. Photocatalytic Degradation of Crystal Violet (C. I. Basic Violet 3) on Silver Ion Doped TiO2. Dye. Pigm. 2005, 66, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldvari, M.; Bagonluri, M. Carbon nanotubes as functional excipients for nanomedicines: I Pharmaceutical properties. Nanomedicine 2008, 4, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsiedel, R.; Kapp, M.D.; Schulz, M.; Wiench, K.; Oesch, F. Genotoxicity investigations on nanomaterials: Methods, preparation and characterization of test material, potential artifacts and limitations-many questions, some answers. Mutat. Res. 2009, 681, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, J.; Jackowska-Tracz, A.; Zarzyńska, J.; Pławińska-Czarnak, J. Chances and limitations of nanosized titanium dioxide practical application in view of its physicochemical properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. TiO2 photocatalysis: Design and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2012, 13, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, V.R.; Sarker, S.; Yu, B.; Kar, A.; Sun, X.; Dey, S.K. TiO2 nanotubes and its composites: Photocatalytic and other photo-driven applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2013, 28, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, D. Bulk TiO2 vs Alternative Ti-Based Photocatalysts for the Mild Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, I.; Verma, A.; Örmeci, B. Mathematical modeling of E. coli inactivation in water using Fe-TiO2 composite in a fixed bed reactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 260, 118242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, A.; Lee, J.; Saianand, G.; Lee, K.; Chun, W.; Hou, Y.; Kannan, V.; Park, S.; Kim, W. Cost-Effective Production of TiO2 with 90-Fold Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity Via Facile Sequential Calcination and Ball Milling Post-Treatment Strategy. Materials 2020, 13, 5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, M.; Richaume, A.; Guyonnet, J.P.; Dubost, A.; Martins, J.M.F.; Pommier, T. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles strongly impact soil microbial function by affecting archaeal nitrifiers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffan, M.; Decome, L.; Rose, J.; Orsiere, T.; De Meo, M.; Briosis, V.; Chaneac, C.; Olivi, L.; Berge-Iefranc, J.L.; Botta, A.; et al. In vitro interactions between DMSA-coated maghemite nanoparticles and human fibroblasts: A physio- chemical and cyto-genotoxical study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4367–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, E. Toxicity of nC60 fullerenes to two aquatic species: Daphnia and largemouth bass [abstract]. In Proceedings of the 227th American Chemical Society National Meeting, Anaheim, CA, USA, 27 March–1 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
| Year | Topic | Organisms Studied | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 | Inactivation of phages | Phage MS2 (=ATCC 15597B1) grown on host lawns of E. coli ATCC 15597 | [28] |
| 2002 | Photocatalytic Oxidation of Bacteria, Bacterial and Fungal Spores | Escherichia coli, Micrococcus luteus, Bacillus subtilis (cells and spores), Aspergillus niger spores | [29] |
| 2003 | Effect of (Continuous–Intermittent) Light Intensity and of (Suspended −Fixed) TiO2 Concentration | E. coli | [30] |
| 2007 | Inactivation of Bacteria and Fungi by Modified Titanium Dioxide | E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Candida albicans, A. niger | [31] |
| 2011 | E. Degradation of Fungi on TiO2 and Ag-TiO2 Thin Films Prepared by Sol–Gel and Nanosuspensions | C. albicans | [32] |
| Spectrum and Microbial Activity | E. coli, other genera as Bacteroides, Edwardsiella, Enterobacter Legionella, Pneumophila, Proteus, and other coliforms | [23] | |
| 2012 | Explanation of Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DVLVO) and the extended version of Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (XDLVO) Theory | E. coli | [33] |
| 2015 | Disinfection of Bacteria Using TiO2 P25 and Cu-Doped TiO2 | E. coli | [3] |
| 2019 | Ozone and photocatalytic processes for Pathogens’ Removal from Water | Virus, Bacteria, and Fungi | [8] |
| Diversity, Co-occurrence, and Implications of Fungal Communities in Wastewater Treatment Plants | Fungi | [34] | |
| 2020 | Isolation of Fungal Strains from Municipal Wastewater Plants | Fungi | [35] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magaña-López, R.; Zaragoza-Sánchez, P.I.; Jiménez-Cisneros, B.E.; Chávez-Mejía, A.C. The Use of TiO2 as a Disinfectant in Water Sanitation Applications. Water 2021, 13, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121641
Magaña-López R, Zaragoza-Sánchez PI, Jiménez-Cisneros BE, Chávez-Mejía AC. The Use of TiO2 as a Disinfectant in Water Sanitation Applications. Water. 2021; 13(12):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121641
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagaña-López, Rafael, Paloma I. Zaragoza-Sánchez, Blanca E. Jiménez-Cisneros, and Alma C. Chávez-Mejía. 2021. "The Use of TiO2 as a Disinfectant in Water Sanitation Applications" Water 13, no. 12: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121641
APA StyleMagaña-López, R., Zaragoza-Sánchez, P. I., Jiménez-Cisneros, B. E., & Chávez-Mejía, A. C. (2021). The Use of TiO2 as a Disinfectant in Water Sanitation Applications. Water, 13(12), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121641