Examining the Applicability of Wavelet Packet Decomposition on Different Forecasting Models in Annual Rainfall Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
2.1. Study Area
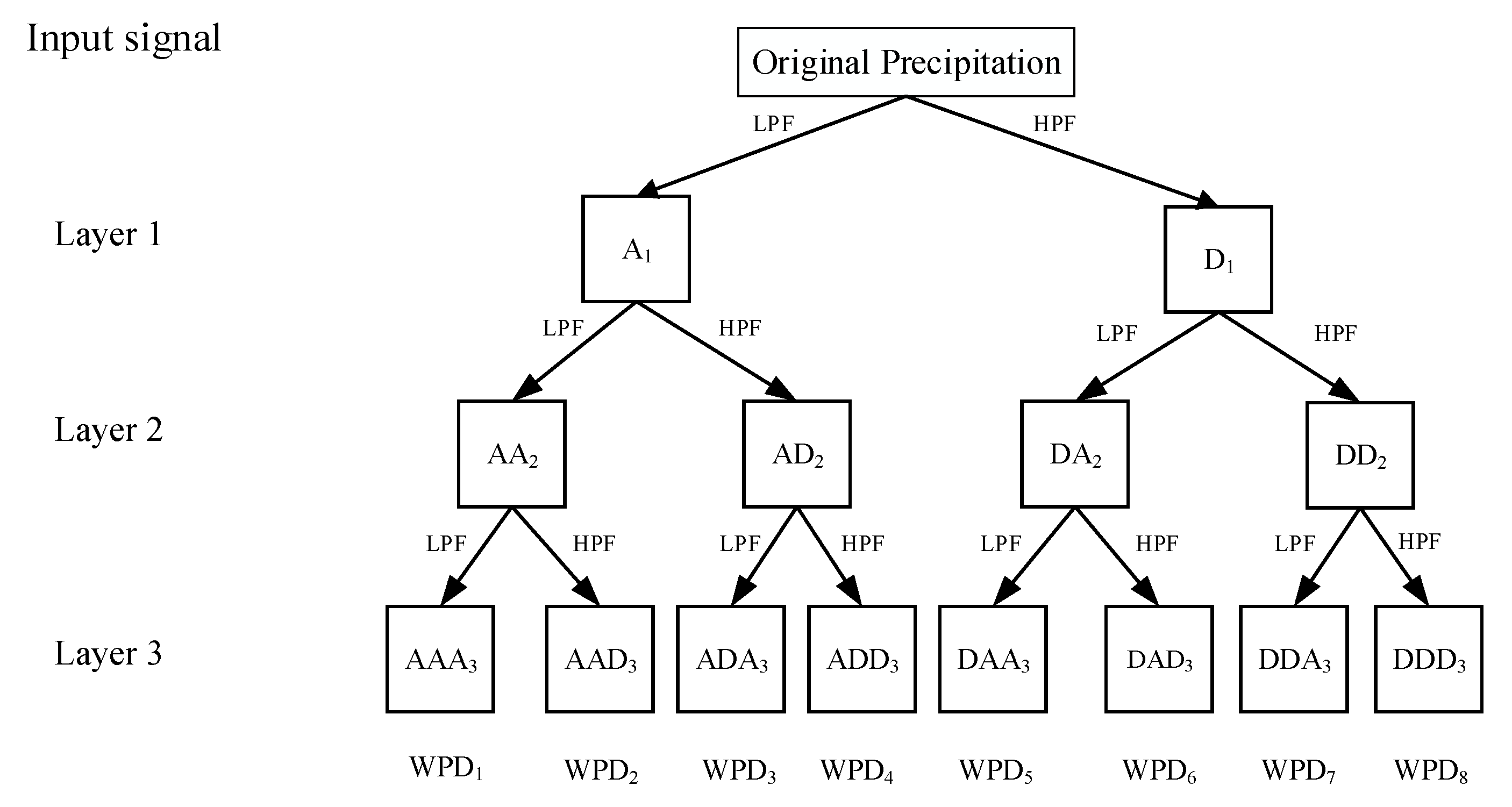
2.2. Wavelet Packet Decomposition WPD
2.3. Extreme Learning Machine (ELM)
2.4. Back-Propagation Neural Network (BPNN)
2.5. ARIMA
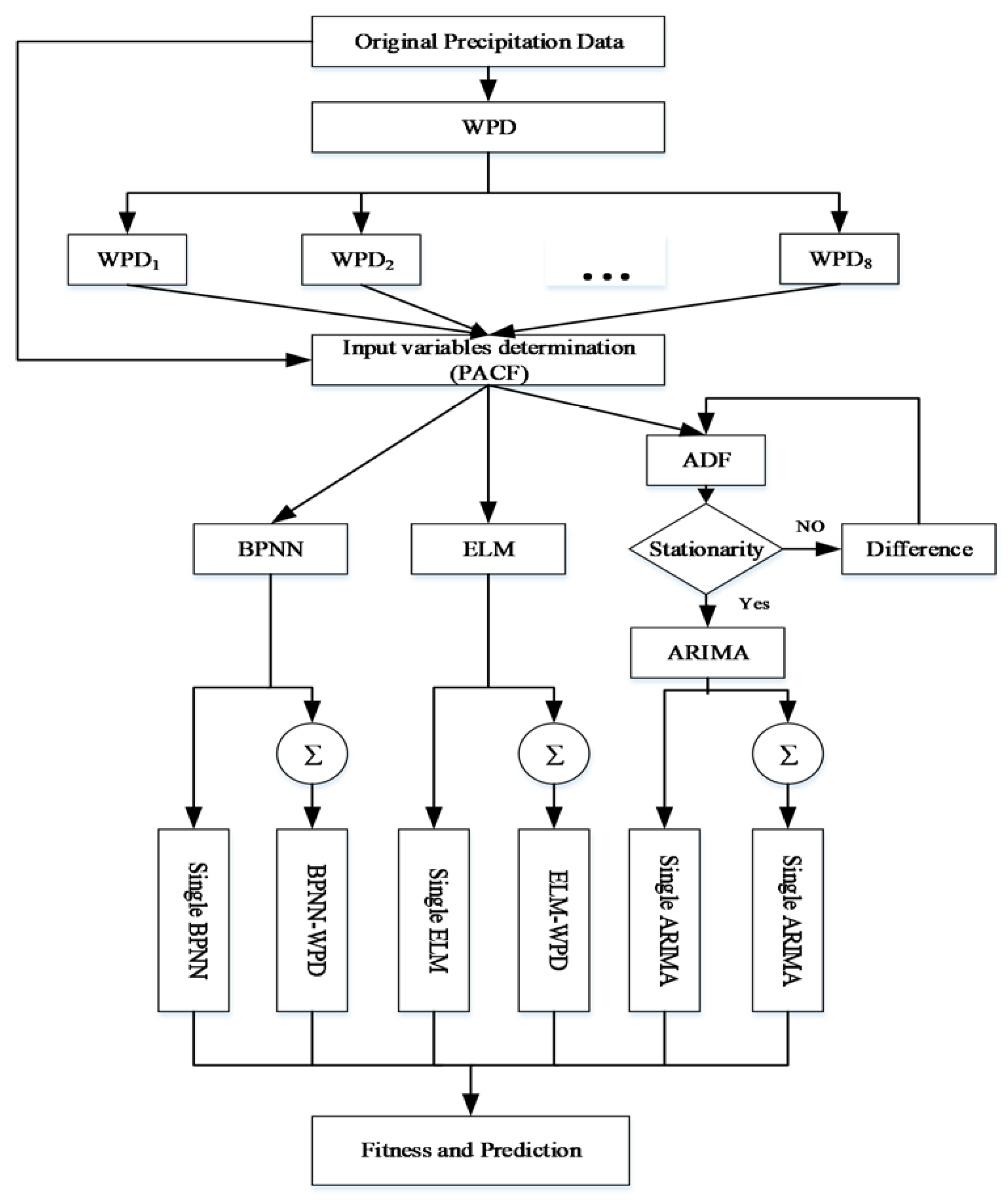
2.6. Framework of the Proposed Hybrid Model
2.7. Evaluation Indicators
3. Results
3.1. Decomposition Results
3.2. Selection of Input Variable
3.3. Model Development
- (1)
- ELM and BPNN models
- (2)
- ARIMA
- (3)
- WPD-ANN and WPD-ARIMA
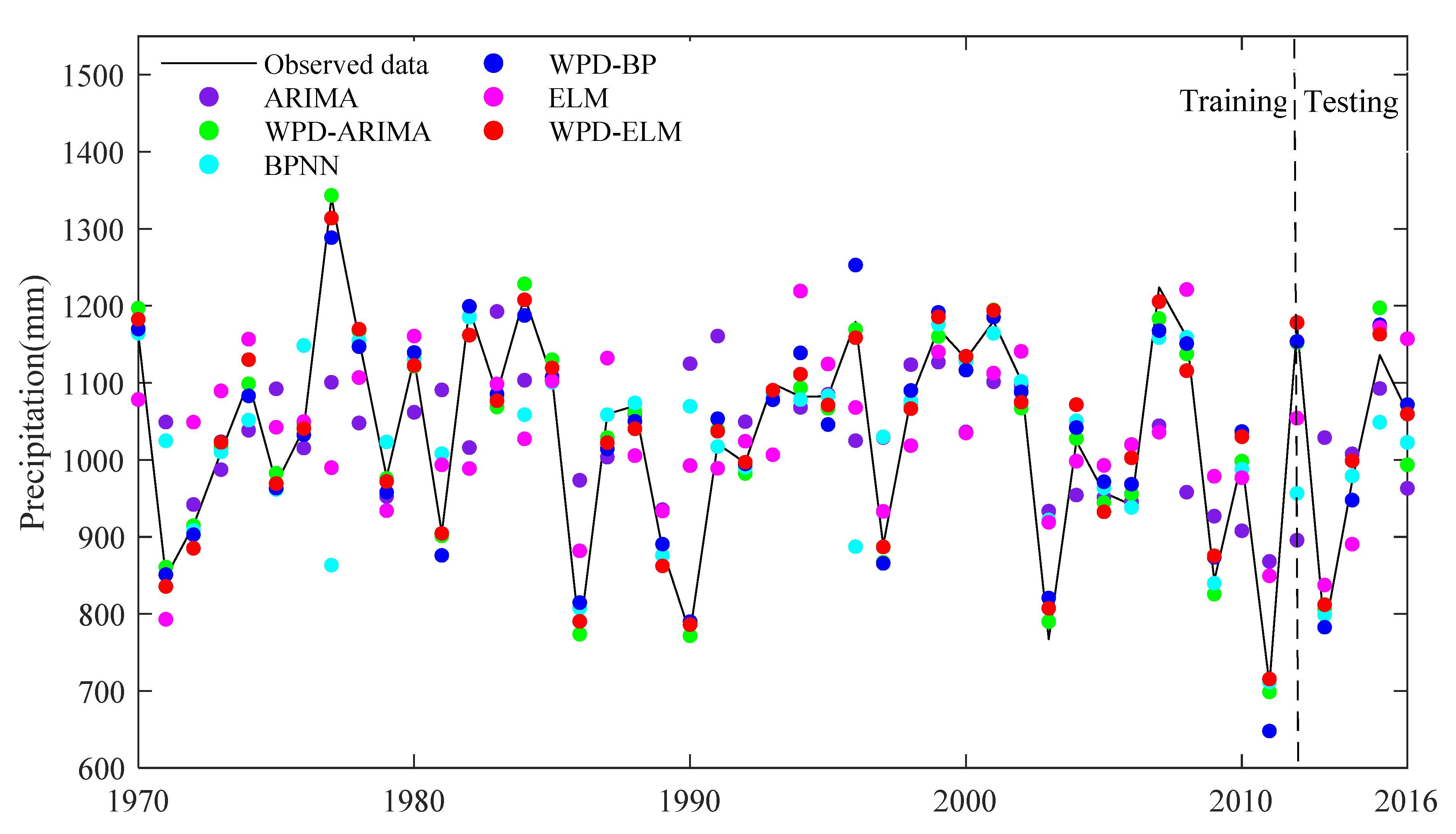
3.4. Comparative Analysis
3.5. Discussion of Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, H.; Li, J.-L.; Liang, T.-G. Study on the estimation of precipitation resources for rainwater harvesting agriculture in semi-arid land of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 71, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-C.; Xu, D.-M.; Chau, K.-W.; Chen, S. Improved annual rainfall-runoff forecasting using PSO-SVM model based on EEMD. J. Hydroinformatics 2013, 15, 1377–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Cimen, M. A wavelet-support vector machine conjunction model for monthly streamflow forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kinsland, G.; Poudel, D.; Fenech, A. Urban flood prediction under heavy precipitation. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, H.; Snow, J.A.; Su, B.; Jiang, T. Seasonal predictions of precipitation in the Aksu-Tarim River basin for improved water resources management. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 147, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Bae, D.-H. Correcting mean areal precipitation forecasts to improve urban flooding predictions by using long short-term memory network. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, A. A decision support system for the safety of airport runways: The case of heavy rainstorms. Transp. Res. Part. A Policy Pract. 2002, 36, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuligowski, R.J.; Barros, A.P. Experiments in Short-Term Precipitation Forecasting Using Artificial Neural Networks. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1998, 126, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-García, E.G.; Salcedo-Sanz, S.; Casanova-Mateo, C. Accurate precipitation prediction with support vector classifiers: A study including novel predictive variables and observational data. Atmos. Res. 2014, 139, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, K.; Eslami, H.R.; Kahawita, R. Parameter estimation of an ARMA model for river flow forecasting using goal programming. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pektaş, A.O.; Kerem Cigizoglu, H. ANN hybrid model versus ARIMA and ARIMAX models of runoff coefficient. J. Hydrol. 2013, 500, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-C.; Chau, K.-W.; Cheng, C.-T.; Qiu, L. A comparison of performance of several artificial intelligence methods for forecasting monthly discharge time series. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhote, V.; Mishra, S.; Shukla, J.P.; Pandey, S.K. Runoff prediction using Big Data analytics based on ARIMA Model. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2018, 47, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar]
- Valipour, M.; Banihabib, M.E.; Behbahani, S.M.R. Comparison of the ARMA, ARIMA, and the autoregressive artificial neural network models in forecasting the monthly inflow of Dez dam reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlando, P.; Rosso, R.; Cadavid, L.G.; Salas, J.D. Forecasting of short-term rainfall using ARMA models. J. Hydrol. 1993, 144, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Chau, K.W. Prediction of rainfall time series using modular soft computingmethods. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Q. MODWT-ARMA model for time series prediction. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalaskaris, T.; Panagiotidis, T.; Pantrakis, A. Stochastic Monthly Rainfall Time Series Analysis, Modeling and Forecasting in Kavala City, Greece, North-Eastern Mediterranean Basin. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmud, I.; Bari, S.H.; Rahman, M.T.U. Monthly rainfall forecast of Bangladesh using autoregressive integrated moving average method. Environ. Eng. Res. 2017, 22, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Balasmeh, O.; Babbar, R.; Karmaker, T. Trend analysis and ARIMA modeling for forecasting precipitation pattern in Wadi Shueib catchment area in Jordan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, N.Q.; Babel, M.S.; Weesakul, S.; Tripathi, N.K. An artificial neural network model for rainfall forecasting in Bangkok, Thailand. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nastos, P.T.; Paliatsos, A.G.; Koukouletsos, K.V.; Larissi, I.K.; Moustris, K.P. Artificial neural networks modeling for forecasting the maximum daily total precipitation at Athens, Greece. Atmos. Res. 2014, 144, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbot, J.; Marohasy, J. Input selection and optimisation for monthly rainfall forecasting in Queensland, Australia, using artificial neural networks. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbot, J.; Marohasy, J. Skilful rainfall forecasts from artificial neural networks with long duration series and single-month optimization. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Le, L.M.; Le, T.-T.; Bui, K.-T.T.; Le, V.M.; Ly, H.-B.; Prakash, I. Development of advanced artificial intelligence models for daily rainfall prediction. Atmos. Res. 2020, 237, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wen, X.H.; Li, J.G. Wavelet Analysis-Support Vector Machine Coupled Models for Monthly Rainfall Forecasting in Arid Regions. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1049–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, G.; Kanagasabai, A.; Mohan, J.; Seshadri, N.P.G. Music induced emotion using wavelet packet decomposition—An EEG study. Biomed. Signal. Process. Control. 2018, 42, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O. Wavelet regression model for short-term streamflow forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Cimen, M. Precipitation forecasting by using wavelet-support vector machine conjunction model. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2012, 25, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-C.; Peng, Y.; Liang, G.-H. The Research of Monthly Discharge Predictor-corrector Model Based on Wavelet Decomposition. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 22, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.-D.; He, B.; Peng, Y.; Ren, M.-L. Singular Spectrum Analysis and ARIMA Hybrid Model for Annual Runoff Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 2683–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, L.; Nagesh Kumar, D. Predictability of nonstationary time series using wavelet and EMD based ARMA models. J. Hydrol. 2013, 502, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkata Ramana, R.; Krishna, B.; Kumar, S.R.; Pandey, N.G. Monthly Rainfall Prediction Using Wavelet Neural Network Analysis. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3697–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Partal, T.; Cigizoglu, H.K.; Kahya, E. Daily precipitation predictions using three different wavelet neural network algorithms by meteorological data. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdourahamane, Z.S.; Acar, R.; Serkan, S. Wavelet-copula-based mutual information for rainfall forecasting applications. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.L.; Lai, S.H.; Yao, Y.; Ahmed, A.N.; Jaafar, W.Z.W.; El-Shafie, A. Performance Enhancement Model for Rainfall Forecasting Utilizing Integrated Wavelet-Convolutional Neural Network. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 2371–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben messaoud, M.a.; Bouzid, A.; Ellouze, N. Speech enhancement based on wavelet packet of an improved principal component analysis. Comput. Speech Lang. 2016, 35, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, M. Data mining-assisted short-term wind speed forecasting by wavelet packet decomposition and Elman neural network. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 175, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Mi, X.; Li, Y. Comparison of two new intelligent wind speed forecasting approaches based on Wavelet Packet Decomposition, Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise and Artificial Neural Networks. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 155, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Kim, S.; Kisi, O.; Singh, V.P.; Parasuraman, K. River Stage Forecasting Using Wavelet Packet Decomposition and Machine Learning Models. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4011–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, W.; Lu, H.; Wang, J. Multi-step forecasting for wind speed using a modified EMD-based artificial neural network model. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.-F.; Lei, X.-H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wen, X.; Ji, Y.; Kang, A.-Q. An adaptive middle and long-term runoff forecast model using EEMD-ANN hybrid approach. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alickovic, E.; Kevric, J.; Subasi, A. Performance evaluation of empirical mode decomposition, discrete wavelet transform, and wavelet packed decomposition for automated epileptic seizure detection and prediction. Biomed. Signal. Process. Control. 2018, 39, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang-Bin, H.; Qin-Yu, Z.; Chee-Kheong, S. Extreme learning machine: A new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37541), Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 July 2004; Volume 982, pp. 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, Z.M.; Sulaiman, S.O.; Deo, R.C.; Chau, K.W. An enhanced extreme learning machine model for river flow forecasting: State-of-the-art, practical applications in water resource engineering area and future research direction. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCelland, J.; Rumelhart, D. Parallel Distributed Processing; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J.; Shi, P.; Jiang, P.; Hu, J.W.; Qu, S.M.; Chen, X.Y.; Chen, Y.B.; Dai, Y.Q.; Xiao, Z.W. Application of BP Neural Network Algorithm in Traditional Hydrological Model for Flood Forecasting. Water 2017, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Box, G. Box and Jenkins: Time Series Analysis, Forecasting and Control. In A Very British Affair: Six Britons and the Development of Time Series Analysis during the 20th Century; Mills, T.C., Ed.; Palgrave Macmillan UK: London, UK, 2013; pp. 161–215. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.-c.; Chau, K.-w.; Xu, D.-m.; Chen, X.-Y. Improving Forecasting Accuracy of Annual Runoff Time Series Using ARIMA Based on EEMD Decomposition. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 2655–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilucci, M.; Materazzi, M.; Pambianchi, G.; Burt, P.; Guerriero, G. Assessment of Variations in the Temperature-Rainfall Trend in the Province of Macerata (Central Italy), Comparing the Last Three Climatological Standard Normals (1961–1990; 1971–2000; 1981–2010) for Biosustainability Studies. Environ. Process. 2019, 6, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) over the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) in Assessing Average Model Performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Keum, H.J.; Han, K.Y. Real-Time Urban Inundation Prediction Combining Hydraulic and Probabilistic Methods. Water 2019, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| No. | Series | Input Variables |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | original | q(t−1)~q(t−9) |
| 2 | WPD1 | q(t−1)~q(t−12) |
| 3 | WPD2 | q(t−1)~q(t−11) |
| 4 | WPD3 | q(t−1)~q(t−11) |
| 5 | WPD4 | q(t−1)~q(t−12) |
| 6 | WPD5 | q(t−1)~q(t−12) |
| 7 | WPD6 | q(t−1)~q(t−10) |
| 8 | WPD7 | q(t−1)~q(t−10) |
| 9 | WPD8 | q(t−1)~q(t−9) |
| No. | Series | h | p-Value | t-Statistic | Critical Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Original | 1 | 0 | −7.928 | −3.489 |
| 2 | WPD1 | 0 | 0.288 | −2.586 | −3.506 |
| 3 | Diff (WPD1) | 1 | 0.020 | −2.348 | −1.948 |
| 4 | WPD2 | 1 | 0 | −7.001 | −3.504 |
| 5 | WPD3 | 1 | 0.007 | −4.299 | −3.504 |
| 6 | WPD4 | 1 | 0 | −6.753 | −3.504 |
| 7 | WPD5 | 1 | 0.004 | −4.470 | −3.506 |
| 8 | WPD6 | 1 | 0 | −7.419 | −3.504 |
| 9 | WPD7 | 1 | 0 | −11.164 | −3.504 |
| 10 | WPD8 | 1 | 0 | −9.553 | −3.504 |
| No. | Series | ARIMA | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Original | ARIMA (12,1,2) | 11.292 |
| 2 | WPD1 | ARIMA (9,1,3) | 4.026 |
| 3 | WPD2 | ARIMA (6,0,6) | 5.63 |
| 4 | WPD3 | ARIMA (7,0,5) | 5.494 |
| 5 | WPD4 | ARIMA (5,0,8) | 6.531 |
| 6 | WPD5 | ARIMA (2,0,7) | 3.076 |
| 7 | WPD6 | ARIMA (11,0,9) | 6.535 |
| 8 | WPD7 | ARIMA (12,0,5) | 6.435 |
| 9 | WPD8 | ARIMA (6,0,6) | 6.806 |
| Model | Training | Testing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | NSEC | RMSE | MAE | R | NSEC | RMSE | MAE | |
| ARIMA | 0.415 | 0.139 | 129.978 | 101.046 | −0.304 | −0.535 | 175.136 | 141.295 |
| WPD-ARIMA | 0.991 | 0.981 | 19.399 | 14.951 | 0.951 | 0.903 | 44.127 | 37.199 |
| BPNN | 0.618 | 0.357 | 112.634 | 53.775 | 0.820 | 0.434 | 106.368 | 74.221 |
| WPD-BPNN | 0.978 | 0.957 | 29.445 | 22.924 | 0.988 | 0.973 | 23.176 | 19.947 |
| ELM | 0.628 | 0.394 | 109.308 | 85.583 | 0.819 | 0.649 | 83.698 | 78.656 |
| WPD-ELM | 0.986 | 0.9712 | 23.687 | 19.091 | 0.997 | 0.973 | 23.069 | 19.051 |
| Model | Index | Training(%) | Testing(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| WPD-ARIMA & ARIMA | R(↑) | 138.81 | 413.25 |
| NSEC(↑) | 607.65 | 268.63 | |
| RMSE(↓) | 85.08 | 74.80 | |
| MAE(↓) | 85.20 | 73.67 | |
| WPD-BPNN & BPNN | R(↑) | 58.14 | 20.43 |
| NSEC(↑) | 167.82 | 124.37 | |
| RMSE(↓) | 73.86 | 78.21 | |
| MAE(↓) | 57.37 | 73.12 | |
| WPD-ELM & ELM | R(↑) | 56.91 | 21.66 |
| NSEC(↑) | 146.35 | 49.89 | |
| RMSE(↓) | 78.33 | 72.44 | |
| MAE(↓) | 77.69 | 75.78 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Du, Y.; Xu, D. Examining the Applicability of Wavelet Packet Decomposition on Different Forecasting Models in Annual Rainfall Prediction. Water 2021, 13, 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13151997
Wang H, Wang W, Du Y, Xu D. Examining the Applicability of Wavelet Packet Decomposition on Different Forecasting Models in Annual Rainfall Prediction. Water. 2021; 13(15):1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13151997
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hua, Wenchuan Wang, Yujin Du, and Dongmei Xu. 2021. "Examining the Applicability of Wavelet Packet Decomposition on Different Forecasting Models in Annual Rainfall Prediction" Water 13, no. 15: 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13151997
APA StyleWang, H., Wang, W., Du, Y., & Xu, D. (2021). Examining the Applicability of Wavelet Packet Decomposition on Different Forecasting Models in Annual Rainfall Prediction. Water, 13(15), 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13151997







