Tsunami-Related Data: A Review of Available Repositories Used in Scientific Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Issue Description
3. Methodology
3.1. Process of Selection
3.2. Evaluation of Data Repositories
3.2.1. Repository Content
3.2.2. General Availability
3.2.3. Filter/Search Options
3.3. Ontological Contribution into the Data Repositories and Datasets
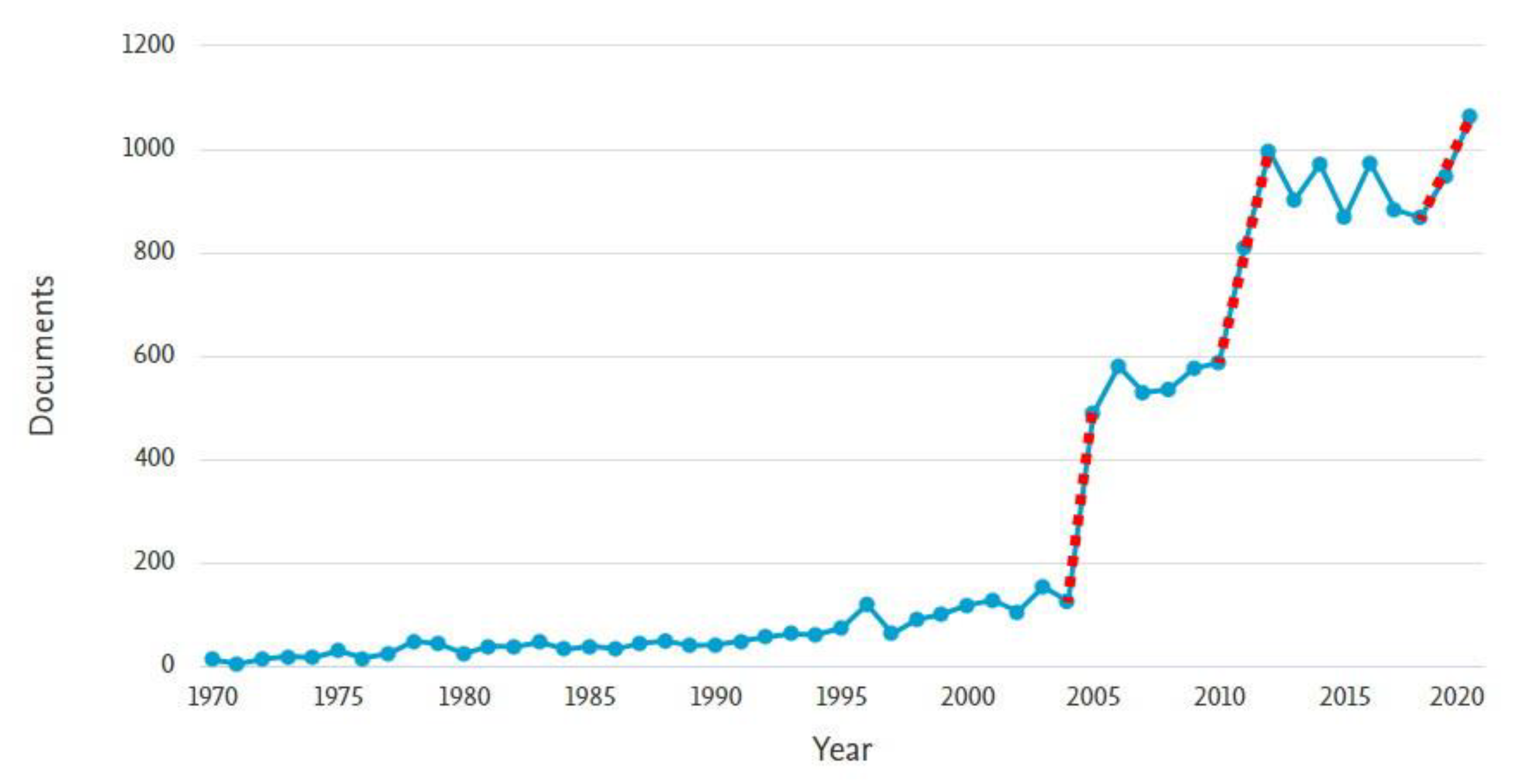
4. Results
4.1. Repositories
4.2. Data Formats
4.2.1. General Formats
NetCDF
HTML
CSV
ZIP
4.2.2. Mapping Formats
KML
WMS
WCS
Esri REST
5. Discussion
5.1. Identified Issues and Perspectives
- Data resources are heterogeneous and poorly arranged, which prevents automatic machine processing. Moreover, in some cases, even searching or filtering tools are missing, which significantly reduces the effectiveness of manual work with the source repository.
- Even the most significant actors in the field, such as NOAA or data.gov, change the form of presentation or search in their repositories from time to time [31]. Although this issue seems minor, user interface or interface usability plays a significant role when a huge volume of data needs to be searched and processed.
- Research papers and studies refer to datasets that are not directly associated with tsunamis (e.g., general geography), but their data can be used, and it is impossible to identify them when searching with relevant search terms. This reveals that the demarcation line between the tsunami and non-tsunami fields of study is difficult to define. The multidisciplinary nature of tsunami-oriented research makes the analysis of datasets and repositories more complicated.
- The semantic differences among concepts of datasets, data, resources, and repositories generate confusion. These concepts are used in various contexts. The development of a virtual data collection system can help improve the organization of tsunami-related datasets.
- There are many deactivated, nonfunctional, or unavailable files, even found during the search in the dataset. This issue is typical of the outcomes of research projects. Project documents or data are available only within the sustainability period, after which websites or interfaces are not managed or maintained.
- Although there are datasets offering one or more formats of the same data, there are specific formats of data associated with specific software applications unreadable for standard available SW solutions. Typically, old data prepared for obsolete applications are impossible to run in existing operating systems.
- Noise is often present in the data that must be filtered out, and void data that need to be dealt with (at least from the modeling side).
- Not all datasets are the primary resources and only contain a reference. However, their features can be used as catalogs or guideposts as they work with datasets more appropriately than pages in which datasets are originally uploaded.
5.2. Demonstration of Ontology-Engineering Help
- The first line of research is focused on the usage of ontologies for categorization of concepts related to the above-mentioned domains, sharing of these ontological structures between interested parties (humans, humans and computers, or between computers), and system interoperability.
- The second line illustrates how ontologies can be directly integrated or connected to the designed system.
- To receive fundamental insights into tsunami-related and tsunami-not-directly related data repositories.
- To discover which characteristics are shared by more data repositories.
- To explore the backbone of the ontology consisting of core ontological classes together with the relationships between them.
- To ask concrete questions on data repositories and related facts.
- hasDomain; MeteorologyAndAtmosphericSciences, EnvironmentalSciences, or Oceanography.
- hasOwner; U.S.GeneralServicesAdministration.
- hasAccess; free.
- providesFormatOfDataset; PDF, XML, HTML, or TIFF (most cited data formats).
- providesLanguageOfDataset; English.
- SELECT ?repository ?countOfTsunamiDatasets
- WHERE {
- ? Repository rdf:type dronto:WebBasedDatasetRepository.
- ? repository dronto:hasTsunamiDataset ?countOfTsunamiDatasets
- }
- ORDER BY DESC (?countOfTsunamiDatasets)
- LIMIT 3
- Data.gov Catalog: 871.
- Data World: 639.
- OSF Share: 432.
- PREFIX rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#>
- PREFIX rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#>
- PREFIX dronto: <http://www.semanticweb.org/husáková/ontologies/2021/DROntology#>
- SELECT ?repository
- WHERE
- {? Repository rdf:type dronto:WebBasedDatasetRepository.
- ?repository dronto:hasDomain dronto:MeteorologyAndAtmosphericSciences.}
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| # | Name | Organization | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Data.gov Catalog | U.S. General Services Administration | https://catalog.data.gov/dataset |
| Note: Data.gov Catalog was launched in 2009 and is managed and hosted by the U.S. General Services Administration, Technology Transformation Service. It is an online repository of policies, tools, case studies, and other resources to support data governance, management, exchange, and use throughout the federal government. Data.gov follows the DCAT-US Schema v1.1. | |||
| 2. | Data.gov Dataset | U.S. General Services Administration | https://data.doi.gov/dataset |
| Note: was launched in 2009 and is managed and hosted by the U.S. General Services Administration, Technology Transformation Service, and includes data from several U.S. departments and services. This database contains more than 28,000 datasets. The majority of these datasets are geospatial types. The dataset finder offers filtering based on tags of datasets, dataset formats, origin organization, publisher, and bureaus. | |||
| 3. | OSF Home | Center for Open Science | https://osf.io/ |
| Note: OSF Home is a free, open platform to support your research and enable collaboration. Part of OFS called OSF Share. | |||
| 4. | OSF Share | Center for Open Science | https://share.osf.io/ |
| Note: OSF Share was founded in 2013 by the Association of American Universities and the Association of Public and Land-grant Universities. It is a community open-source initiative developing tools and services to connect related, yet distributed, research outputs, enabling new kinds of scholarly discovery. The National Endowment for the Humanities (NEH) is currently supporting SHARE in a project to integrate digital humanities into the scholarly web. | |||
| 5. | Japan Tsunami Trace database | IRIDeS | https://tsunami3.civil.tohoku.ac.jp/ |
| Note: Japan Tsunami Trace database contains information about destroyed buildings and drifting objects, traces indicating the inundation limit. This database includes more than 30,000 records. The majority of data in this database are collected from Japan. This database also contains a Japan map with tsunami incidents and pictures from these incidents. | |||
| 6. | National Centers for Environmental Information | National Centers for Environmental Information | https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/hazard/ |
| Note: NCEI (formerly NGDC)—Natural Hazards Data, Images, and Education is part of NOAA. NCEI archives and assimilates tsunami, earthquake, and volcano data to support research, planning, response, and mitigation. Long-term data, including photographs, can be used to establish the history of natural hazard occurrences and help mitigate against future events. Related groups of datasets to a tsunami are Hazards Data: Map Search, Tsunami Events, Tsunami Runups, and Recent/Significant Tsunami Events. | |||
| 7. | Queensland Goverment—Open Data Portal | The State of Queensland | https://www.data.qld.gov.au/dataset |
| Note: Queensland Government offers Open Data Portal with more than 2700 datasets and 11,200 resources across all fields related to Queensland under the Right to Information Act 2009 (RTI Act) and the Information Privacy Act 2009 (IP Act). Six of these datasets are related to tsunamis. | |||
| 8. | EM-DAT Public | EM-DAT | https://public.emdat.be/ |
| Note: EM-DAT (Emergency Events Database) Public was launched in 1988 by the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED) with the initial support of the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Belgian Government. The main objective of the database is to serve the purposes of humanitarian action at national and international levels. The initiative aims to rationalize decision making for disaster preparedness, as well as provide an objective base for vulnerability assessment and priority setting. EM-DAT contains essential core data on the occurrence and effects of over 22,000 mass disasters in the world from 1900 to the present day. | |||
| 9. | Figshare | Figshare | https://figshare.com/ |
| Note: Figshare was launched at the beginning of the year 2012. It is an online open-access repository with aim of preserving and share research outputs, including datasets, figures, and videos. Figshare offers almost one and a half million datasets; 254 of them are related to tsunamis. Furthermore, it provides nearly 200 figures and more than 150 journal contributions related to tsunamis. | |||
| 10. | Science Data Bank | Computer Network Information Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences | https://www.scidb.cn/en |
| Note: Science Data Bank (ScienceDB) is a public, general-purpose data repository aiming to provide data services (e.g., data acquisition, long-term preservation, publishing, sharing, and access). ScienceDB is devoted to becoming a repository of long-term data sharing and data publishing in China. According to authors key features of ScienceDB, for example are data findability, open and sharing data, data traceability, and permanent accessibility. ScienceDB offers 484 datasets; one of them is related to tsunamis. | |||
| 11. | Kaggle | Kaggle | https://www.kaggle.com/datasets |
| Note: Kaggle was founded in 2010, and it is a subsidiary of Google LLC. Kaggle is an online platform for a community of data scientists. Focus on finding and publishing datasets and models. Kaggle offers more than 70,000 datasets; 14 of them are related to tsunamis. | |||
| 12. | Data World | data.world, Inc. | https://data.world/ |
| Note: Data World was founded in 2016, it is public benefit corporation, which aims at makes data easily understandable for the public. This company has three main goals: (1) build the most meaningful, collaborative and abundant data resource in the world in order to maximize data’s societal problem-solving utility. (2) advocate publicly for improving the adoption, usability, and proliferation of open data and linked data. (3) serve as an accessible historical repository of the world’s data. It offers more than 600 datasets related to the tsunami. | |||
| 13. | Harvard Dataverse | The President & Fellows of Harvard College | https://dataverse.harvard.edu/ |
| Note: The Harvard Dataverse Repository is a free data repository open to all researchers from any discipline, both inside and outside of the Harvard community, where you can share, archive, cite, access, and explore research data. Each individual Dataverse collection is a customizable collection of datasets (or a virtual repository) for organizing, managing, and showcasing datasets. Harvard Dataverse offers more than 110,000 datasets; 33 of them are related to tsunamis. | |||
| 14. | Google—Dataset Search | https://datasetsearch.research.google.com/ | |
| Note: Google—Dataset Search is a search engine for data sets created by Google, it was launched in 2018. Data Search has two main goal: (1) foster a data sharing ecosystem that will encourage data publishers to follow best practices for data storage and publication. (2) give scientists a way to show the impact of their work through citation of data sets that they have produced. | |||
| 15. | The World Bank Water Data catalog | The World Bank Group | https://wbwaterdata.org/organization/worldbank-data-catalog |
| Note: World Bank—Data catalog offers different types of data, e.g., geospatial, microdata, time series, and other types of datasets. Part of World Bank is World Bank Water data. | |||
| 16. | The World Bank Data catalog | The World Bank Group | https://datacatalog.worldbank.org/ |
| Note: World Bank Water data—Data catalog is a source for all water-related open data at the World Bank. It contains datasets and applications generated or compiled by the Water Global Practice. In to total it contains 2654 datasets, 26 of them are related to tsunamis. | |||
| 17. | PANGAEA | PANGAEA | https://www.pangaea.de/ |
| Note: PANGAEA is an information system, which operated as an Open Access library with aim on archive, publish and distribute georeferenced data from earth system research. PANGAEA is member of the World Data System (WDS) of the International Science Council (ISC). The search engine is powered by the open-source software Elasticsearch and metadata processing is provided by panFMP. PANGAEA offers more than 400,000 datasets; more than 3500 are related to tsunamis. | |||
| 18. | WHO data collections | WHO | https://www.who.int/data/collections |
| Note: WHO manages and maintains a wide range of data collections related to global health and well-being. WHO has 194 Member States across six regions, and from more than 150 offices, WHO staff are united in a shared commitment to achieve better health for everyone, everywhere. WHO offers 80 datasets; none of them is related to the tsunami. | |||
| 19. | Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction | United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction | https://www.desinventar.net/ |
| Note: Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction is built on two modules. The first one is Administration and Data Entry module, which is a relational and structural database through which the database is fed by filling in predefined fields (space and temporal data, types of events and causes, and sources) and by both direct and indirect effects (deaths, houses, infrastructure, and economic sectors). The second is The Analysis module, which allows access to the database by queries that may include relations among the diverse variables of effects, types of events, causes, sites, dates, etc. This module allows at the same time to represent those queries with tables, graphics, and thematic maps. | |||
| 20. | The Humanitarian Data Exchange | United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs | https://data.humdata.org/ |
| Note: The Humanitarian Data Exchange (HDX) is an open platform for sharing data across crises and organizations. Launched in July 2014, the goal of HDX is to make humanitarian data easy to find and use for analysis. HDX growing collection of datasets has been accessed by users in over 200 countries and territories. | |||
| 21. | Earth Online | European Space Agency | https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/ |
| Note: European Space Agency (ESA)—Earth Online. Earth Online is the entry point for scientific-technical information on Earth Observation activities by the European Space Agency (ESA). The web portal provides a vast amount of content, grown and collected over more than a decade: Detailed technical information on Earth Observation (EO) missions; satellites and sensors; EO data products and services; online resources such as catalogs and library; applications of satellite data; access to promotional satellite imagery. | |||
| 22. | EU Open Data Portal | Publications Office of the European Union in Luxembourg | https://data.europa.eu/data/datasets |
| Note: EU Open Data Portal was funded by the European Union, and it is managed by Publications Office of the European Union. This portal provides access to open data from international, EU, national, regional, local, and geo data portals. It replaces the EU Open Data Portal and the European Data Portal. This portal has four main sections: searching data, providing data, using data, and training and library. The portal offers more than 15,000 datasets; 9 of them are related to tsunamis. | |||
| 23. | Novosibirsk Tsunami Laboratory | Institute of Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Geophysics SB RAS, Tsunami Laboratory, Novosibirsk, Russia | http://tsun.sscc.ru/nh/list.html |
| Note: Novosibirsk Tsunami Laboratory was founded in 2004. It contains databases related to tsunamis, earthquakes, impacts events, volcanic activities, bolides and asteroids, and hurricanes. | |||
| 24. | InnovationLab GeoNode | Labs GeoNode | https://www.geonode-gfdrrlab.org/ |
| Note: InnovationLab GeoNode is a geospatial content management system, a platform for the management and publication of geospatial data. It brings together mature and stable open-source software projects under a consistent and easy-to-use interface allowing non-specialized users to share data and create interactive maps. Data management tools built into GeoNode allow for integrated creation of data, metadata, and map visualizations. Each dataset in the system can be shared publicly or restricted to allow access to only specific users. Social features such as user profiles and commenting and rating systems allow for the development of communities around each platform to facilitate the use, management, and quality control of the data the GeoNode instance contains. | |||
| 25. | STAR—Study of the Tsunami Aftermath and Recovery | None * | http://stardata.org/data.html |
| Note: The Study of the Tsunami Aftermath and Recovery (STAR) is a longitudinal survey of individuals, households, communities, and facilities in the provinces of Aceh and North Sumatra, Indonesia. The study is designed to provide evidence on the immediate and longer-term consequences of the 2004 Sumatran-Andaman earthquake and tsunami and recovery efforts. * STAR is a collaborative project involving investigators at Duke University; SurveyMETER (Indonesia); the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill; the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA); the University of Pennsylvania; the University of Southern California; the World Bank; Statistics Indonesia. | |||
| 26. | Mendeley Data | Elsevier Inc. | https://data.mendeley.com/ |
| Note: Mendeley Data was launched in 2015 by Elsevier. It is an open, cloud-based research data management (RDM) platform that empowers research institutions to manage the entire lifecycle of research data, and enables researchers to discover, collect, and share research data. It enables librarians and administrators to moderate, manage, report on, and showcase research data output regardless of which data repository researchers use. It contains more than seven million datasets; more than 2000 of them are related to the tsunami. | |||
| 27. | Dryad | Dryad | https://datadryad.org/search?q= |
| Note: Dryad is an open source, community driven project that takes a unique approach to data publication and digital preservation. Dryad focuses on search, presentation, and discovery and delegates the responsibility for the data preservation function to the underlying repository with which it is integrated. Dryad’s original iteration launched in 2009, in 2019, Dryad merged with Dash. | |||
| 28. | National Center for Biotechnology Information Support Center | National Library of Medicine | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/search/ |
| Note: NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information Support Center) was established in 1998. NCBI is now a leading source for public biomedical databases, software tools for analyzing molecular and genomic data, and research in computational biology. Today NCBI creates and maintains over 40 integrated databases for the medical and scientific communities as well as the general public. | |||
| 29. | Qualitative Data Repository | Qualitative Data Repository | https://data.qdr.syr.edu/ |
| Note: Qualitative Data Repository (QDR) is a dedicated archive for storing and sharing digital data (and accompanying documentation) generated or collected through qualitative and multi-method research in the social sciences. QDR provides search tools to facilitate the discovery of data, and, also, serves as a portal to material beyond its own holdings, with links to U.S. and international archives. The repository’s initial emphasis is on political science. | |||
| 30. | DataCite | DataCite | https://search.datacite.org/ |
| Note: Datacite is a leading global non-profit organization that provides persistent identifiers (DOIs) for research data and other research outputs. Organizations within the research community join DataCite as members to be able to assign DOIs to all their research outputs. This way, their outputs become discoverable and associated metadata is made available to the community. DataCite then develops additional services to improve the DOI management experience, making it easier for our members to connect and share their DOIs with the broader research ecosystem and to assess the use of their DOIs within that ecosystem. DataCite is an active participant in the research community and promotes data sharing and citation through community-building efforts and outreach activities. | |||
| 31. | Open data initiative of the Government of Spain | Government of Spain | https://datos.gob.es/en/catalogo |
| Note: The Aporta Initiative was launched in 2009 to promote the opening of public information and development of advanced services based on data. It is backed by the Ministry of Economy and Business, the Ministry of Territorial Policy and Civil Service, and the Public Corporate Entity Red.es. The main goal of the Aporta initiative, a key element in the Spanish government’s open data policy, is to harmonize and efficiently take advantage of the synergies between ongoing open data projects. It seeks to always drive and coordinate actions being carried out by different levels the administration, the private sector, and academic field, according to an integrating governance model. It does all of this in order to promote new products and services from the private sector and civil society to benefit society. | |||
| 32. | Malta Data Portal | Government of Malta | https://open.data.gov.mt/dashboard.html |
| Note: Malta Data Portal was founded by the Republic of Malta in 2014. It was financed by the Malta government and European Union. It offers 205 datasets related to the republic of Malta. | |||
| 33. | National Opendata Portal | Republic of Cyprus | https://www.data.gov.cy/ |
| Note: National Opendata Portal was founded by the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Cyprus in 2014, and it offers datasets related to the Republic of Cyprus. In total, it offers more than 1100 datasets. Most of them are related to the environment, economy and finance, population, government, and health. | |||
| 34. | Open Data From Public Administration | Agenzia per l’Italia Digitale | https://dati.gov.it/ |
| Note: Open Data From Public Administration was born as a project promoted in 2011 by the Italian government and since 2015 it has been managed by the Agency for Digital Italy. The data.gov.it Portal is the national catalog of metadata relating to open type data released by public administrations and constitutes the search tool and the access point to the data made available according to the open data paradigm, in accordance with the provisions from art. 9 of the legislative decree n. 36/2006 (transposition of the European Directive on the reuse of public sector information). Dati.gov.it is also the tool with which the Agency for Digital Italy promotes the policies for the enhancement of national public information assets. To this end, the portal makes available to administrations and developers a series of useful resources to deepen the topic of open data, to improve the quality of the data exposed and, ultimately, to encourage their reuse. | |||
| 35. | O catálogo central de dados abertos em Portugal | Agência para a Modernização Administrativa | https://dados.gov.pt/en/ |
| Note: O catálogo central de dados abertos em Portugal is the Portuguese Public Administration’s open data portal. Its function is to aggregate, reference and store open data from different Public Administration’s bodies and sectors, therefore creating the central catalogue of open data in Portugal. Besides working as a shared data storing and publication service, it may be used by any public body, also working as an indexing portal of contents in other open data portals/catalogues. It also provides several interaction mechanisms between data suppliers and re-users, such as the possibility to commend, submit complementary data versions and suggest improvements to the platform. | |||
| 36. | OECD Data | Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development | https://data.oecd.org/ |
| Note: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is an international organization that works to build better policies for better lives. OECD’s goal is to shape policies that foster prosperity, equality, opportunity, and well-being for all. OECD draws on 60 years of experience and insights to better prepare the world of tomorrow. Data OECD is part of OECD and offers more than 7500 datasets, two of them are related to tsunamis. Another part of OECD, which focuses on datasets, is OECD iLibrary. | |||
| 37. | OECD iLibrary | Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development | https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/ |
| Note: OECD iLibrary is the online library of the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) featuring its books, papers, and statistics and is the knowledge base of OECD’s analysis and data. | |||
| 38. | DesignSafe-CI | The Natural Hazards Engineering Research Infrastructure | https://www.designsafe-ci.org/data/browser/public/ |
| Note: DesignSafe-CI is supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency created by U.S. Congress in 1950. DesignSafe-CI is the web-based research platform of the NHERI Network that provides the computational tools needed to manage, analyze, and understand critical data for natural hazards research. | |||
| 39. | The official portal for European data | Publications Office of the European Union | https://data.europa.eu/en |
| Note: European Data Portal—the portal provides access to open data from international, EU, national, regional, local, and geo data portals. It replaces the EU Open Data Portal and the European Data Portal. The portal addresses the whole data value chain, from data publishing to data reuse. Going beyond collecting metadata (data about data), the strategic objective of the portal is to improve accessibility and increase the value of open data. The portal is divided into four sections: (1) searching data, (2) providing data, (3) using data, and (4) training and library. | |||
| 40. | SAGE Research methods | SAGE Publications | https://methods.sagepub.com/Datasets |
| Note: SAGE Research methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. Nearly everyone at a university is involved in research, from students learning how to conduct research to faculty conducting research for publication to librarians delivering research skills training and doing research on the efficacy of library services. SAGE Research Methods has the answer for each of these user groups, from a quick dictionary definition, a case study example from a researcher in the field, a downloadable teaching dataset, a full-text title from the Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences series, or a video tutorial showing research in action. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. The site is designed to guide users to the content they need to learn a little or a lot about their method. The Methods Map can help those less familiar with research methods to find the best technique to use in their research. Built upon SAGE’s researchers. | |||
| 41. | Gebco | British Oceanographic Data Centre | https://www.gebco.net/ |
| Note: Gebco is a non-profit making organization which relies largely on the voluntary contributions of an enthusiastic international team of geoscientists and hydrographers. GEBCO is continually working to improve its gridded data sets with the aim of providing the most authoritative publicly available bathymetric grids for the world’s oceans. | |||
| 42. | Irish National Seabed Survey Data Access | GSI Seabed Mapping | http://www.gsiseabed.ie/data.htm |
| Note: INFOMAR /Irish National Seabed Survey (INNS)—INFOMAR is a successor to the Irish National Seabed Survey (INSS) and concentrates on creating integrated mapping products of the physical, chemical and biological features of the seabed in the near-shore area. The INSS (1999–2005) involved mapping of more than 80% of Ireland’s seabed territory, supporting the delineation of the exclusive economic zone, and extending inshore coverage to the 200 m depth contour overall, with extension in to 50 m depth offshore. The INFOMAR program which was tasked with mapping the remaining coastal areas. This is being undertaken in two phases; Phase one (2006–2016) focusing on 26 inshore priority bays and 3 priority coastal areas, and Phase two (2016–2026) mapping the remaining unsurveyed coastal and shelf areas. | |||
| 43. | University of Hawaii Sea Level Center | University of Hawaii Sea Level Center | http://uhslc.soest.hawaii.edu/data/ |
| Note: University of Hawaii Sea Level Center maintains one of the largest global networks of tide gauges that feed the FD stream, but there are numerous other international agencies that contribute. These FD data are received from partner agencies on a monthly basis and incorporated into the FD stream. | |||
| 44. | European Marine Observation and Data Network | The European Marine Observation and Data Network | https://emodnet.eu/en/portals |
| Note: European Marine Observation and Data Network (EMODnet) is a network of organizations supported by the EU’s integrated maritime policy. These organizations work together to observe the sea, process the data according to international standards and make that information freely available as interoperable data layers and data products. EMODnet provides access to European marine data across seven discipline-based themes. For each of these themes, EMODnet has created a gateway to a range of data archives managed by local, national, regional, and international organizations. Through these gateways, users have access to standardized observations, data quality indicators, and processed data products, such as basin-scale maps. These data products are free to access and use. | |||
| 45. | Spanish National Center of Geographic Information | Centro Nacional de Información Geográfica | http://centrodedescargas.cnig.es/CentroDescargas/ |
| Note: Spanish National Center of Geographic Information—The Download Center (CdD) is a web site created by the National Center for Geographic Information (CNIG), aimed at serving users as a free tool for downloading geographic digital files generated by the Directorate General for the National Geographic Institute (IGN). It offers Geo-referenced images of maps with various scales of representation, to display on the computer screen or on mobile devices. These images do not contain neither marginal information (captions) nor framework of coordinates, Altimetric information that represents the landform of the national territory, and, in the case of Lidar data, of the elements that are found on it as well, and other geographic information. | |||
| 46. | The Centre for Environmental Data Analysis | Science and Technology Facilities Council | https://catalogue.ceda.ac.uk/ |
| Note: The original “CEDA” group followed the merger of two of NERC’s data centers—the BADC and NEODC—in 2005, originally being called the Centre for Environmental Data Archival. However, with greater support for users by analyzing the data with a slight name change from the A in CEDA from Archival to Analysis occurred in 2015 to reflect this growing and important role for CEDA. CEDA aims to support environmental science, further environmental data archival practices, and develop and deploy new technologies to enhance access to data. Additionally, they provide services to aid large scale data analysis. | |||
| 47. | Nasa—MODIS | NASA | https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/dataprod/ |
| Note: Nasa—MODIS—Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer is a key instrument aboard the Terra and Aqua satellites. Terra MODIS and Aqua MODIS are viewing the entire Earth’s surface every 1 to 2 days, acquiring data in 36 spectral bands, or groups of wavelengths (see MODIS Technical Specifications). These data will improve our understanding of global dynamics and processes occurring on the land, in the oceans, and in the lower atmosphere. MODIS is playing a vital role in the development of validated, global, interactive Earth system models able to predict global change accurately enough to assist policy makers in making sound decisions concerning the protection of our environment. | |||
| 48. | NASA—ASTER | NASA | https://asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov/gdem.asp |
| Note: ASTER (Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer) was founded by the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) of Japan and the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), and focus on spaceborne thermal emission and reflection. The first version of the ASTER GDEM, released in June 2009, was generated using stereo-pair images collected by the ASTER instrument onboard Terra. ASTER GDEM coverage spans from 83 degrees north latitude to 83 degrees south, encompassing 99 percent of Earth’s landmass. | |||
| 49. | Geospatial Information Authority of Japan | Geospatial Information Authority of Japan | https://fgd.gsi.go.jp/download/menu.php |
| Note: The Geospatial Information Authority of Japan is Japan’s national mapping organization and a special organization of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism. Part of The Geospatial Information Authority of Japan focus on collecting and providing disaster prevention information using the latest technology, and information about past disasters. | |||
| 50. | RadioCarbon—IntCal13 Supplemental Data | Radiocarbon | http://www.radiocarbon.org/IntCal13.htm |
| Note: RadioCarbon—IntCal13 Supplemental Data was published in Radiocarbon journal in 55th volume in 2013. Radiocarbon is the main international journal of record for research articles and date lists relevant to 14C and other radioisotopes and techniques used in archaeological, geophysical, oceanographic, and related dating. | |||
| 51. | Satellite Imaging Corporation | Satellite Imaging Corporation | https://www.satimagingcorp.com/gallery/ |
| Note: Satellite Imaging Corporation Satellite Imaging Corporation (SIC) was formed in the early 1990’s as a response to increasing demand for medium and high resolution 2D and 3D satellite image data. Management has over 40 years of experience in on/offshore survey, satellite remote sensing, and GIS industry. SIC has processed satellite image data for clients belonging to a variety of industries for their domestic and international mapping, GIS, environmental and design project needs. SIC have performed projects throughout Africa, Europe, Russia, North America, South America, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. SICs portfolio includes cadastre and GIS projects for the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), precision agriculture mapping, transportation and pipeline corridor surveys, near shore bathymetry, support for 2D/3D seismic data acquisition, and the planning of well locations and access roads located in rural, and remote areas around the world. | |||
| 52. | OpenTopography | https://portal.opentopography.org/datasets | OpenTopography Facility, San Diego Supercomputer Center, University of California San Diego |
| Note: OpenTopography Facility is based at the San Diego Supercomputer Center at the University of California, San Diego. Main missions of OpenTopography Facility is to democratize online access to high-resolution (meter to sub-meter scale), Earth science-oriented, topography data acquired with lidar and other technologies. Harness cutting edge cyberinfrastructure to provide Web service-based data access, processing, and analysis capabilities that are scalable, extensible, and innovative. Promote discovery of data and software tools through community populated metadata catalogs. Partner with public domain data holders to leverage OpenTopography infrastructure for data discovery, hosting and processing. Provide professional training and expert guidance in data management, processing, and analysis. Foster interaction and knowledge exchange in the Earth science lidar user community. | |||
| 53. | Sea Level Station Monitoring Facility | Flanders Marine Institute | http://www.ioc-sealevelmonitoring.org/list.php |
| Note: Sea Level Station Monitoring—The Global Sea Level Observing System (GLOSS) was established by the UNESCO Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) in 1985 to establish a well-designed, high-quality in situ sea level observing network to support a broad research and operational user base. The backbone of the global tide gauge network is the GLOSS Core Network (GCN), a global set of 300 tide gauge stations that provide optimal sampling of the global ocean. GCN gauges were allocated to each island or group of islands at intervals not closer than 500 km, and along continental coasts at intervals generally not less than 1000 km. Preference was given to islands in order to maximize exposure to the open ocean. | |||
| 54. | Open platform for French public data | Government of France | https://www.data.gouv.fr/en/datasets/ |
| Note: Open platform for French public data is a portal governed by the French government. Part of Data.Gouv.FR is Etalab, which supports the opening up of public data for the State and administrations. As such, Etalab develops and manages the open platform for public data data.gouv.fr, a platform which hosts the datasets and lists their reuse. | |||
| 55. | AVISO | AVISO CNES Data Center | https://aviso-data-center.cnes.fr/ |
| Note: AVISO from Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (Cnes), which is the government agency responsible for shaping and implementing France’s space policy in Europe, was founded in 1998. In recent years, AVISO has become a reference in international oceanographic and altimetric communities. In 2014 AVISO opens to wider applications than the ocean themes. Thus, becoming AVISO +, the portal opens to hydrology/coastal/ice and merges with the CTOH website to provide users with more operational and demonstration products, and expertise in an intuitive and modern web site. | |||
| 56. | Italian Tsunami Effects Database | Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia | https://tsunamiarchive.ingv.it/ited.1.0/ |
| Note: The Italian Tsunami Effects Database (ITED), the first database dealing with the tsunami effects observed along the Italian coasts from historical times. ITED was compiled starting from the Euro Mediterranean Tsunami Catalogue. ITED focuses on the propagation effects observed along the Italian coasts providing information on how each locality was interested by tsunamis effects over time. Currently ITED contains about 300 observations of tsunami effects referred to 184 localities of the Italian coasts and related to the 70 Italian tsunami events present in EMTC v2. Whenever a place experienced a tsunami effects more than once, details of each observation is supplied to allow the user to build the tsunami-history of the locality | |||
| 57. | WEBRITEC | European Commission | https://webritech.jrc.ec.europa.eu |
| Note: There are three section of the repository. TAD show the theorical Sea Levels Tide calculated by an algorithm and compare them with a real Measurements for each buoys in Database. TAT provides the tsunami analysis tool dealing with tsunami public calculations, a list of user calculations and ability to submit a new calculation. Sea levels at specific points on the Globe are also available. | |||
| 58. | European/NEAMTWS Tsunami Catalogue | UNESCO/IOC Project Office | http://www.ioc-tsunami.org/ |
| Note: A unified catalogue containing 290 tsunamis generated in the European and Mediterranean seas since 6150 B.C. to current days was developed based on the GITEC, GITEC-II, and TRANSFER projects. | |||
| 59. | Euro-Mediterranean Paleotsunami Database | Istituto Nazionale di Geofisi-ca e Vulcanologia | http://paleotsunami.rm.ingv.it/index.php |
| Note: Database was developed within the frame of the EC TRANSFER project with the aim to collect data on tsunami inundations occurred in the past. Evidence of paleotsunamis is derived from coastal stratigraphy because of the presence of peculiar sediments or boulders. Dating of the paleotsunami deposits helps in correlating events with historical tsunamis or previous ones. This Database provide mainly two types of information of use for developing tsunami scenarios and time dependent hazard calculations: locations of past inundations and their frequency. | |||
| 60 | Tsunami Measurement Data | IUGG Tsunami Commission | http://www.nda.ac.jp/~fujima/TMD/index.html |
| Note: IUGG Tsunami Commission requested to all researchers to provide the data of tsunami traces of Indian Ocean Tsunami. Provided data are written by the common definition with available tables and figures. IUGG Tsunami Commission collects and authorizes the data, makes small-scale maps and large-scale surveyed-area maps and distributes them to tsunami community. | |||
| Description | General Availability | Filter/Search Options | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Last Update | Repository Domain | Availability | Downloadable Data | Data Usability Rating | Metadata | Dataset Preview | Search | Dataset Filter | Location Filter | Field/Topic Filter | Format Filter | License Filter | Year/Date Filter | |
| 1. | 2021 | General | Free | Yes | No | Downloadable | Yes | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 2. | 2020 | General | Free | Yes | No | Downloadable | Yes | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| 3. | 2018 | General | Free | No | No | Downloadable | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| 4. | 2018 | General | Free | Yes | No | View only | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| 5. | 2013 | Tsunami | Free | No | No | No | N/A | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| 6. | N/A | Natural Hazards | Free | No | No | No | N/A | No | Datasets only section | No | No | No | No | No |
| 7. | 2021 | General | Free | Yes | Yes | Downloadable | No | Yes | Datasets only | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 8. | 2020 | Disasters | Registration needed | Yes | N/A | N/A | Yes | N/A | N/A | Yes | Yes | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| 9. | 2021 | General | Free | Yes | No | View only | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| 10. | 2018 | General | Free | Yes | No | Downloadable | No | Yes | Datasets only | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| 11. | 2021 | General | Free | Yes | Yes | View only | Yes | Yes | Datasets only section | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| 12. | 2021 | General | Paid | N/A | N/A | View only | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| 13. | 2020 | General | Free | Yes | No | Downloadable | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Limited | Yes |
| 14. | 2021 | General | Free | No | No | View only | No | Yes | Datasets only | No | Yes | Yes | Limited | Limited |
| 15. | 2020 | Water-related | Free | Yes | Yes | View only | No | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| 16. | 2017 | General | Free | Yes | Not rated | Downloadable | No | Yes | Datasets only section | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| 17. | 2021 | Environment | Free | Yes | No | View only | Yes | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| 18. | N/A | Health | Free | No | No | No | No | Yes | Datasets only section | No | No | No | No | No |
| 19. | N/A | Disasters | Free | Yes | No | No | No | No | Datasets only | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| 20. | 2021 | General | Free | Yes | No | View only | No | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| 21. | N/A | General | Free | No | No | No | No | Yes | Datasets only section | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| 22. | 2021 | General | Free | Yes | No | View only | No | Yes | Datasets only section | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 23. | 2020 | Natural Hazards | Free | No | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Yes | Yes | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| 24. | 2017 | Natural Hazards | Free | Yes | No | View only | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| 25. | 2015 | Tsunami | Registration | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A | No | Datasets only | No | No | No | No | No |
| 26. | 2021 | General | Free | Partially | No | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| 27. | 2020 | General | Free | Yes | No | View only | No | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| 28. | 2021 | Biotechnology | Free | Partially | No | Downloadable | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Limited |
| 29. | N/A | General | Free | Yes | No | Downloadable | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Limited | Limited | Yes |
| 30. | 2021 | General | Free | No | No | Downloadable | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| 31. | 2015 | General | Free | Yes | No | Downloadable | No | Yes | Datasets only section | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 32. | N/A | General | Free | No | No | View only | No | Yes | Datasets only section | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| 33. | N/A | General | Free | Yes | No | Downloadable | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 34. | N/A | General | Free | Yes | No | View only | No | Yes | Datasets only | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| 35. | 2019 | General | Free | Yes | No | View only | No | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 36. | 2010 | General | Free | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| 37. | N/A | General | Limited | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| 38. | 2021 | Natural Hazards | Free | Yes | No | View only | Yes | Yes | Datasets only | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 39. | 2020 | General | Free | Yes | Yes | Downloadable | Yes | Yes | Datasets only section | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 40. | N/A | General | Paid | N/A | No | View only | N/A | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| 41. | 2020 | Bathymetry | Free | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A | No | Datasets only section | No | No | No | No | No |
| 42. | 2010 | Bathymetry | Free | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A | No | Datasets only | No | No | No | No | No |
| 43. | 2021 | Sea Level | Free | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A | No | Datasets only | No | No | No | No | No |
| 44. | N/A | Water-related | Paid | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | No | Datasets only section | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| 45. | 2020 | Geography | Free | Yes | No | Downloadable | Yes | No | Datasets only | No | No | No | No | No |
| 46. | 2019 | Environment | Registration needed | Yes | No | Downloadable | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| 47. | N/A | Satellite Imaging | Free | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | No | Datasets only section | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| 48. | N/A | Geography | Free | Yes | N/A | N/A | Yes | No | Datasets only section | No | No | No | No | No |
| 49. | N/A | Geography | Registration needed | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A | No | Datasets only | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| 50. | N/A | Environment | Free | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A | No | Datasets only | No | No | No | No | No |
| 51. | N/A | Satellite Imaging | Free | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A | No | Datasets only | No | No | No | No | No |
| 52. | 2011 | Topography | Limited | Yes | No | Downloadable | Yes | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | Yes | Limited | No | No |
| 53. | 2021 | Sea Level | Free | Yes | N/A | N/A | Yes | No | Datasets only | No | No | No | No | No |
| 54. | 2020 | General | Free | Yes | Yes | View only | Yes | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 55. | 2021 | Geography | Limited | N/A | No | View only | No | Yes | Datasets only section | No | No | No | No | No |
| 56. | 2019 | Tsunami | Free | Yes | N/A | N/A | Yes | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | No | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| 57. | 2021 | Tsunami | Free | Yes | N/A | N/A | Yes | Yes | Datasets only | Yes | No | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| 58. | 2014 | Tsunami | Free | No | N/A | N/A | Yes | No | Datasets only | No | No | N/A | N/A | No |
| 59. | N/A | Tsunami | Free | Yes | N/A | N/A | No | Yes | Datasets only | No | No | N/A | N/A | No |
| 60. | 2010 | Tsunami | Free | Yes | No | No | No | No | Datasets only | No | No | No | No | No |
References
- Papadopoulos, G.; Lorito, S.; Løvholt, F.; Rudloff, A.; Schindele, F. Geophysical risk: Tsunami. In Science for Disaster Risk Management 2017: Knowing Better and Losing Less; Poljanšek, K., Marín Ferrer, M., De Groeve, T., Clark, I., Eds.; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; pp. 162–176. ISBN 978-92-79-60678-6. [Google Scholar]
- Harbitz, C.B.; Løvholt, F.; Bungum, H. Submarine Landslide Tsunamis: How Extreme and How Likely? Nat. Hazards 2014, 72, 1341–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, J.; Løvholt, F.; Jalayer, F.; Lorito, S.; Salgado-Gálvez, M.A.; Sørensen, M.; Abadie, S.; Aguirre-Ayerbe, I.; Aniel-Quiroga, I.; Babeyko, A.; et al. Probabilistic Tsunami Hazard and Risk Analysis—A Review of Research Gaps. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röbke, B.R.; Vött, A. The Tsunami Phenomenon. Prog. Oceanogr. 2017, 159, 296–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, T. Geochemical Approaches in Tsunami Research: Current Knowledge and Challenges. Geosci. Lett. 2021, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagué-Goff, C.; Szczuciński, W.; Shinozaki, T. Applications of Geochemistry in Tsunami Research: A Review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 165, 203–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anpalagan, A.; Woungang, I. Tsunami Prediction and Impact Estimation Using Classifiers on Historical Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Intelligent Data Science Technologies and Applications (IDSTA), Valencia, Spain, 19–22 October 2020; pp. 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Gràcia, E.; Urgeles, R.; Sallares, V.; De Martini, P.M.; Pantosti, D.; González, M.; Yalciner, A.C.; Mascle, J.; Sakellariou, D.; et al. Historical and Pre-Historical Tsunamis in the Mediterranean and Its Connected Seas: Geological Signatures, Generation Mechanisms and Coastal Impacts. Mar. Geol. 2014, 354, 81–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Ma, Y.; Yuan, C.; Xie, Z.; Dong, G. A Three-Dimensional Non-Hydrostatic Model for Tsunami Waves Generated by Submarine Landslides. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 96, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titov, V.; Moore, C. Meteotsunami Model Forecast: Can Coastal Hazard Be Quantified in Real Time? Nat. Hazards 2021, 106, 1545–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías, J.; Escalante, C.; Castro, M.J. Multilayer-HySEA Model Validation for Landslide-Generated Tsunamis-Part 2: Granular Slides. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, D. Numerical Modeling of Tsunami: Advances and Future Challenges after the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake and Tsunami. Earth Sci. Rev. 2021, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.; Yuliatmoko, R.S.; Sunardi, B.; Prayogo, A.S.; Muzli, M.; Rohadi, S. Tsunami Simulation for Disaster Mitigation Based on Earthquake Scenarios in the Molucca Subduction Zone (Case Study of the Molucca Sea Earthquake on 7 July 2019). AIP Conf. Proc. 2021, 2320, 040026-1–04006-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bosnic, I.; Costa, P.J.M.; Dourado, F.; La Selle, S.; Gelfenbaum, G. Onshore Flow Characteristics of the 1755 CE Lisbon Tsunami: Linking Forward and Inverse Numerical Modeling. Mar. Geol. 2021, 434, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Omira, R. The 6–7 July 2010 Meteotsunami along the Coast of Portugal: Insights from Data Analysis and Numerical Modelling. Nat. Hazards 2021, 106, 1397–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanelli, M.; Occhipinti, G.; Savastano, G.; Komjathy, A.; Shume, E.B.; Crespi, M. GNSS Total Variometric Approach: First Demonstration of a Tool for Real-Time Tsunami Genesis Estimation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulia, I.E.; Satake, K. Synthetic Analysis of the Efficacy of the S-Net System in Tsunami Forecasting. Earth Planets Space 2021, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pararas-Carayannis, G. Brief History of Early Pioneering Tsunami Research—Part A. Sci. Tsunami Hazards 2018, 37, 49–129. [Google Scholar]
- Trinaistich, W.C.; Mulligan, R.P.; Take, W.A. Runup of Landslide-Generated Waves Breaking on Steep Slopes Captured Using Digital Imagery and Hydrochromic Paint. Coast. Eng. 2021, 166, 103888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keet, M. Methodologies for Ontology Development. Available online: https://eng.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Computer_Science/Programming_and_Computation_Fundamentals/Book%3A_An_Introduction_to_Ontology_Engineering_(Keet)/06%3A_Methods_and_Methodologies/6.01%3A_Methodologies_for_Ontology_Development (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- Contreras, M.C.B.; Reyes, L.F.H.; Ortiz, J.A.R. Methodology for Ontology Design and Construction. Contad. Adm. 2019, 64, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Pérez, A.; Fernández, M.; Vicente, A. de Towards a Method to Conceptualize Domain Ontologies. In Proceedings Workshop: Ontological Engineering, Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI’96), Budapest, Rumanía, 13 August 1996; Facultad de Informática (UPM): Budapest, Rumanía, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Noy, N.F.; McGuinness, D.L. Ontology Development 101: A Guide to Creating Your First Ontology 2001. Available online: https://protege.stanford.edu/publications/ontology_development/ontology101.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- CRED EM-DAT: The International Disaster Database. Available online: https://www.emdat.be/classification (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- Library of Congress Recommended Formats Statement. Available online: https://www.loc.gov/preservation/resources/rfs/TOC.html (accessed on 26 April 2021).
- Gusiakov, V.K.; Dunbar, P.K.; Arcos, N. Twenty-Five Years (1992–2016) of Global Tsunamis: Statistical and Analytical Overview. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 2795–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, M.C. Data Archiving in Ecology and Evolution: Best Practices. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenopir, C.; Allard, S.; Douglass, K.; Aydinoglu, A.U.; Wu, L.; Read, E.; Manoff, M.; Frame, M. Data Sharing by Scientists: Practices and Perceptions. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, E.; Baldridge, E.; Brym, Z.; Locey, K.; McGlinn, D.; Supp, S. Nine Simple Ways to Make It Easier to (Re)Use Your Data. Ideas Ecol. Evol. 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.-W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for Scientific Data Management and Stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wernet, G.; Bauer, C.; Steubing, B.; Reinhard, J.; Moreno-Ruiz, E.; Weidema, B. The Ecoinvent Database Version 3 (Part I): Overview and Methodology. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnane, R.J.; Allegri, G.; Bushi, A.; Dabbeek, J.; de Moel, H.; Duncan, M.; Fraser, S.; Galasso, C.; Giovando, C.; Henshaw, P.; et al. Data Schemas for Multiple Hazards, Exposure and Vulnerability. Disaster Prev. Manag. Int. J. 2019, 28, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, S.; Bizer, C.; Kobilarov, G.; Lehmann, J.; Cyganiak, R.; Ives, Z. DBpedia: A Nucleus for a Web of Open Data. In Proceedings of the The Semantic Web, Busan, Korea, 11–15 November 2007; Aberer, K., Choi, K.-S., Noy, N., Allemang, D., Lee, K.-I., Nixon, L., Golbeck, J., Mika, P., Maynard, D., Mizoguchi, R., et al., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 722–735. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, K.; Cyganiak, R.; Hausenbals, M.; Zhao, J. Describing Linked Datasets with the VoID Vocabulary. Available online: https://www.w3.org/TR/void/ (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- Javed, Y.; Norris, T.; Johnston, D. Ontology-Based Inference to Enhance Team Situation Awareness in Emergency Management. In Proceedings of the 8th International ISCRAM Conference, Lisbon, Portugal, 8–11 May 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, D.; Sukhobok, D.; Nikolov, N.; Elvesæter, B.; Pultier, A. The InfraRisk Ontology: Enabling Semantic Interoperability for Critical Infrastructures at Risk from Natural Hazards. In Proceedings of the On the Move to Meaningful Internet Systems. OTM 2017 Conferences, Rhodes, Greece, 23–28 October 2017; Panetto, H., Debruyne, C., Gaaloul, W., Papazoglou, M., Paschke, A., Ardagna, C.A., Meersman, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 463–479. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Huang, Q. A Geo-Ontology-Based Approach to Decision-Making in Emergency Management of Meteorological Disasters. Nat. Hazards 2017, 89, 531–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermet, Y.; Demir, I. Towards an Information Centric Flood Ontology for Information Management and Communication. Earth Sci. Inform. 2019, 12, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannour, W.; Maalel, A.; Ben Ghezala, H.H. Ontology-Based Representation of Crisis Response Situations. In Proceedings of the Computational Collective Intelligence, Hendaye, France, 4–6 September 2019; Nguyen, N.T., Chbeir, R., Exposito, E., Aniorté, P., Trawiński, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Mehla, S.; Agarwal, A.G. An Ontology Based Earthquake Recommendation System. In Proceedings of the Advanced Informatics for Computing Research, Shimla, India, 15–16 June 2019; Luhach, A.K., Singh, D., Hsiung, P.-A., Hawari, K.B.G., Lingras, P., Singh, P.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J. Integration of a Geo-Ontology-Based Knowledge Model and Spatial Analysis into Emergency Response for Geologic Hazards. Nat. Hazards 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Act to Staunch Loss of Research Data. Nature 2015, 520, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrier, L.; Blondal, E.; Ayala, A.P.; Dearborn, D.; Kenny, T.; Lightfoot, D.; Reka, R.; Thuna, M.; Trimble, L.; MacDonald, H. Research Data Management in Academic Institutions: A Scoping Review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normile, D. Scientific Consensus on Great Quake Came Too Late. Science 2011, 332, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcos, N.P.; Dunbar, P.K.; Stroker, K.J.; Kong, L.S.L. The Impact of Post-Tsunami Surveys on the NCEI/WDS Global Historical Tsunami Database. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 2809–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Virmani, D.; Abraham, A. Tsunami in the Last 15 Years: A Bibliometric Analysis with a Detailed Overview and Future Directions. Nat. Hazards 2021, 106, 139–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilectin, H.D.; Mercy, R.B.V. Classification and Dynamic Class Detection of Real Time Data for Tsunami Warning System. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Recent Advances in Computing and Software Systems, Chennai, India, 27–27 April 2012; pp. 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Kusumah, Y.; Irawan, B.; Setianingsih, C. Sea Wave Detection System Using Web-Based Decision Tree Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 10th Electrical Power, Electronics, Communications, Controls and Informatics Seminar (EECCIS), Malang, Indonesia, 26–28 August 2020; pp. 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Pughazhendhi, G.; Raja, A.; Ramalingam, P.; Elumalai, D.K. Earthosys—Tsunami Prediction and Warning System Using Machine Learning and IoT. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Data Engineering, Chennai, India, 21–23 February 2019; Chaki, N., Devarakonda, N., Sarkar, A., Debnath, N.C., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Liliana, D.Y.; Priharsari, D. Tsunami Early Warning Detection Using Bayesian Classifier. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference of Computer and Informatics Engineering (IC2IE), Banyuwangi, Indonesia, 10–11 September 2019; pp. 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Igarashi, Y.; Murata, S.; Baba, T.; Hori, T.; Okada, M. A Nonlinear Parametric Model Based on a Power Law Relationship for Predicting the Coastal Tsunami Height. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2019, 40, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Format | NOAA_Tsunami | DATA.GOV_Tsunami |
|---|---|---|
| application/x-netcdf | 643 | 0 |
| HTML | 486 | 0 |
| WMS | 407 | 262 |
| WCS | 375 | 182 |
| CSV | 275 | 282 |
| Esri REST | 192 | 240 |
| 181 | 199 | |
| KML | 89 | 93 |
| ZIP | 10 | 78 |
| XML | 9 | 6 |
| WFS | 7 | 7 |
| KMZ | 3 | 0 |
| TIFF | 0 | 10 |
| JSON | 0 | 2 |
| TAR | 0 | 2 |
| RDF | 0 | 1 |
| Domain-Specific Property | Type of Property | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| hasAccess | object property | How is a data repository available (paid, free, or under registration)? |
| hasDomain | object property | Which application domain is a data repository interested in? |
| hasOwner | object property | Who is the owner of the data repository? |
| hasPart/isPartOf | object property | Relationship between whole and its parts. |
| providesFormatOfDataset | object property | Which data formats are available in the data repository? |
| providesLanguageOfDataset | object property | Which language is data sets expressed in? |
| areUsedForStudy | object property | Which data are used for the investigation of which disasters? |
| containsDataFrom | object property | Which location data are come from? |
| hasDataForDownloading | datatype property | Does a data repository provide datasets for downloading? |
| Types of properties for datasets filtering: hasDatasetFilter hasDomainFilter hasLicenseFilter hasLocationFilter | datatype property | Does a data repository provide filters for datasets, their domains, licenses, or locations? |
| hasMetadataForDownloading | datatype property | Is it possible to download the metadata of datasets? |
| hasSearchField | datatype property | Is there any search functionality? |
| hasTimeScaleFilter | datatype property | Is it possible to filter datasets according to a timescale? |
| hasUsabilityOfRating | datatype property | Is there information about the rating of usability? |
| offersPreviewOfDataset | datatype property | Is it possible to preview the datasets? |
| hasTotalDatasets | datatype property | How many datasets are in the data repository? |
| hasTsunamiDataset | datatype property | How many datasets related to the tsunami are in the data repository? |
| containsDataOfTimeScaleMin | datatype property | When were the data of datasets measured (min. year-month-day)? |
| containsDataOfTimeScaleMax | datatype property | When were the data of datasets measured (max. year-month-day)? |
| alternativeName | annotation property | Expression of an alternative name for the data repository. |
| description | annotation property | Specification of more details of data repository. |
| identifier | annotation property | Identifier of the data repository (if it is available). |
| url | annotation property | URL link to the data repository. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nacházel, T.; Babič, F.; Baiguera, M.; Čech, P.; Husáková, M.; Mikulecký, P.; Mls, K.; Ponce, D.; Salmanidou, D.; Štekerová, K.; et al. Tsunami-Related Data: A Review of Available Repositories Used in Scientific Literature. Water 2021, 13, 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162177
Nacházel T, Babič F, Baiguera M, Čech P, Husáková M, Mikulecký P, Mls K, Ponce D, Salmanidou D, Štekerová K, et al. Tsunami-Related Data: A Review of Available Repositories Used in Scientific Literature. Water. 2021; 13(16):2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162177
Chicago/Turabian StyleNacházel, Tomáš, František Babič, Marco Baiguera, Pavel Čech, Martina Husáková, Peter Mikulecký, Karel Mls, Daniela Ponce, Dimitra Salmanidou, Kamila Štekerová, and et al. 2021. "Tsunami-Related Data: A Review of Available Repositories Used in Scientific Literature" Water 13, no. 16: 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162177
APA StyleNacházel, T., Babič, F., Baiguera, M., Čech, P., Husáková, M., Mikulecký, P., Mls, K., Ponce, D., Salmanidou, D., Štekerová, K., Triantafyllou, I., Tučník, P., Zanker, M., & Bureš, V. (2021). Tsunami-Related Data: A Review of Available Repositories Used in Scientific Literature. Water, 13(16), 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162177










