Laboratory Analysis of Debris Flow Characteristics and Berm Performance
Abstract
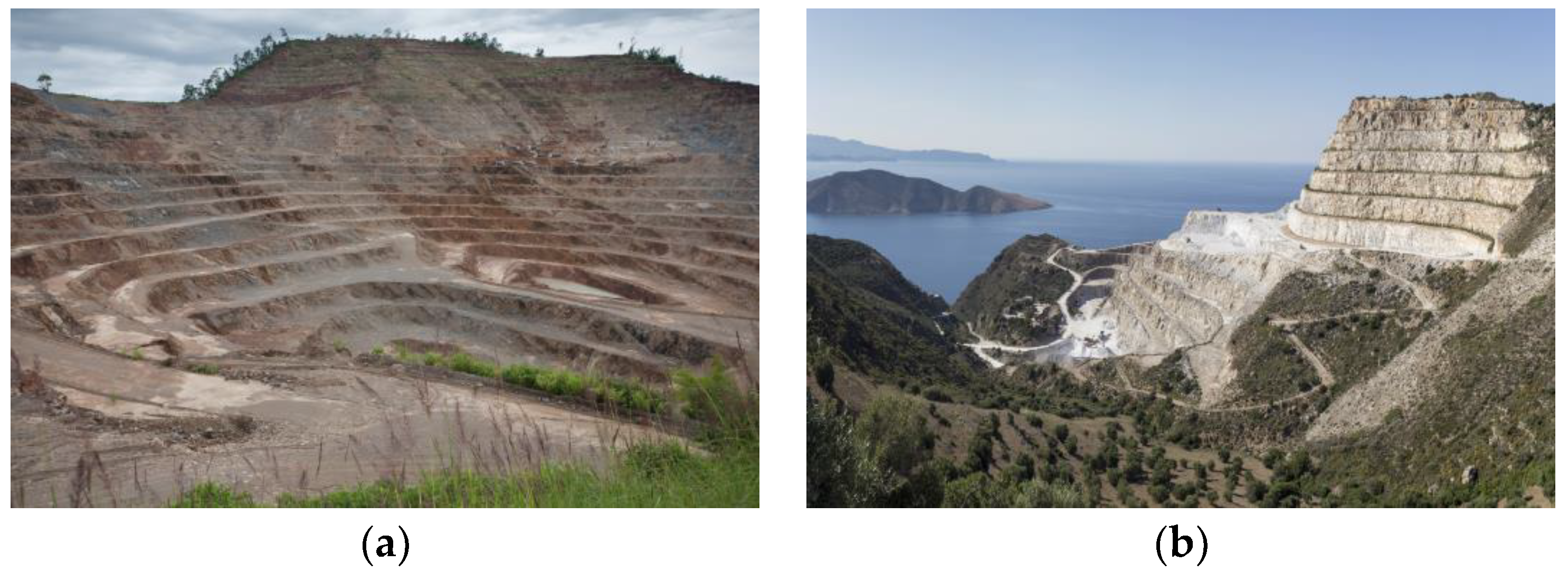
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
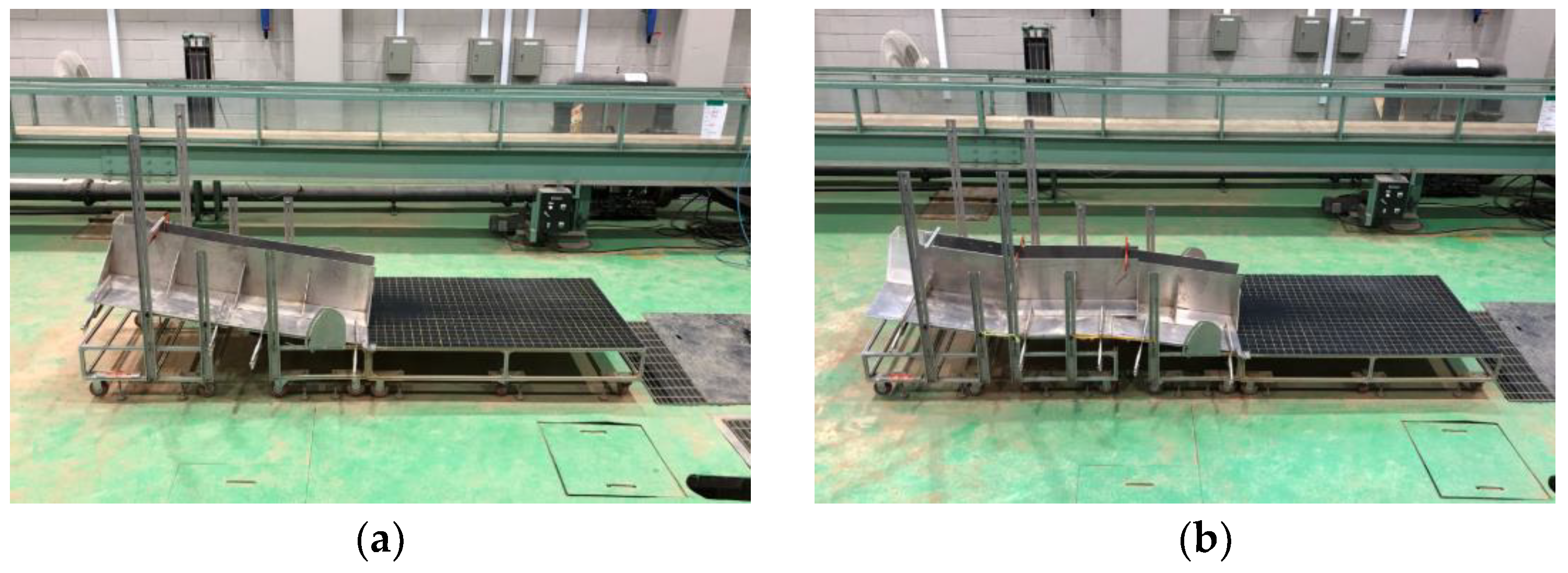
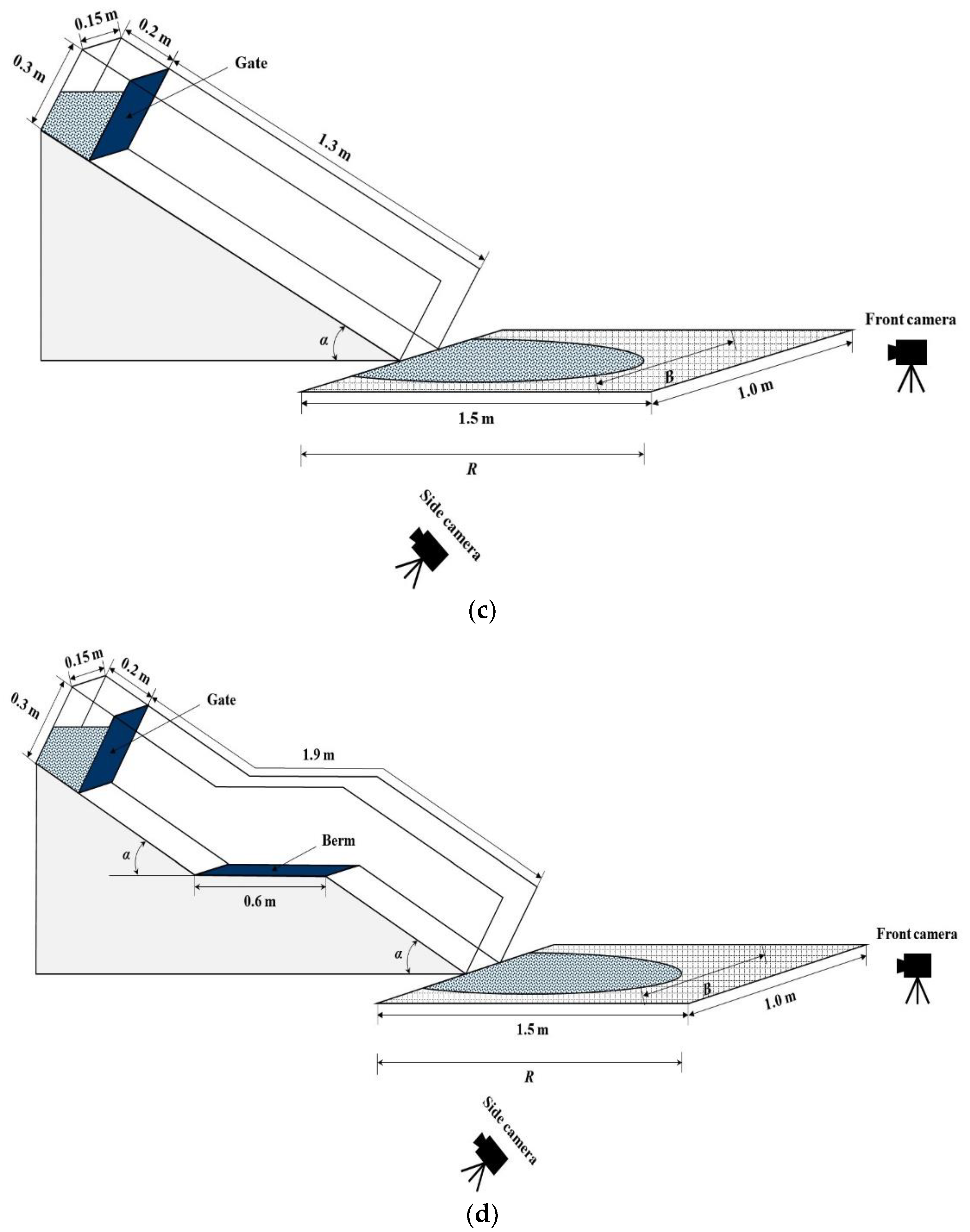
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Experimental Conditions
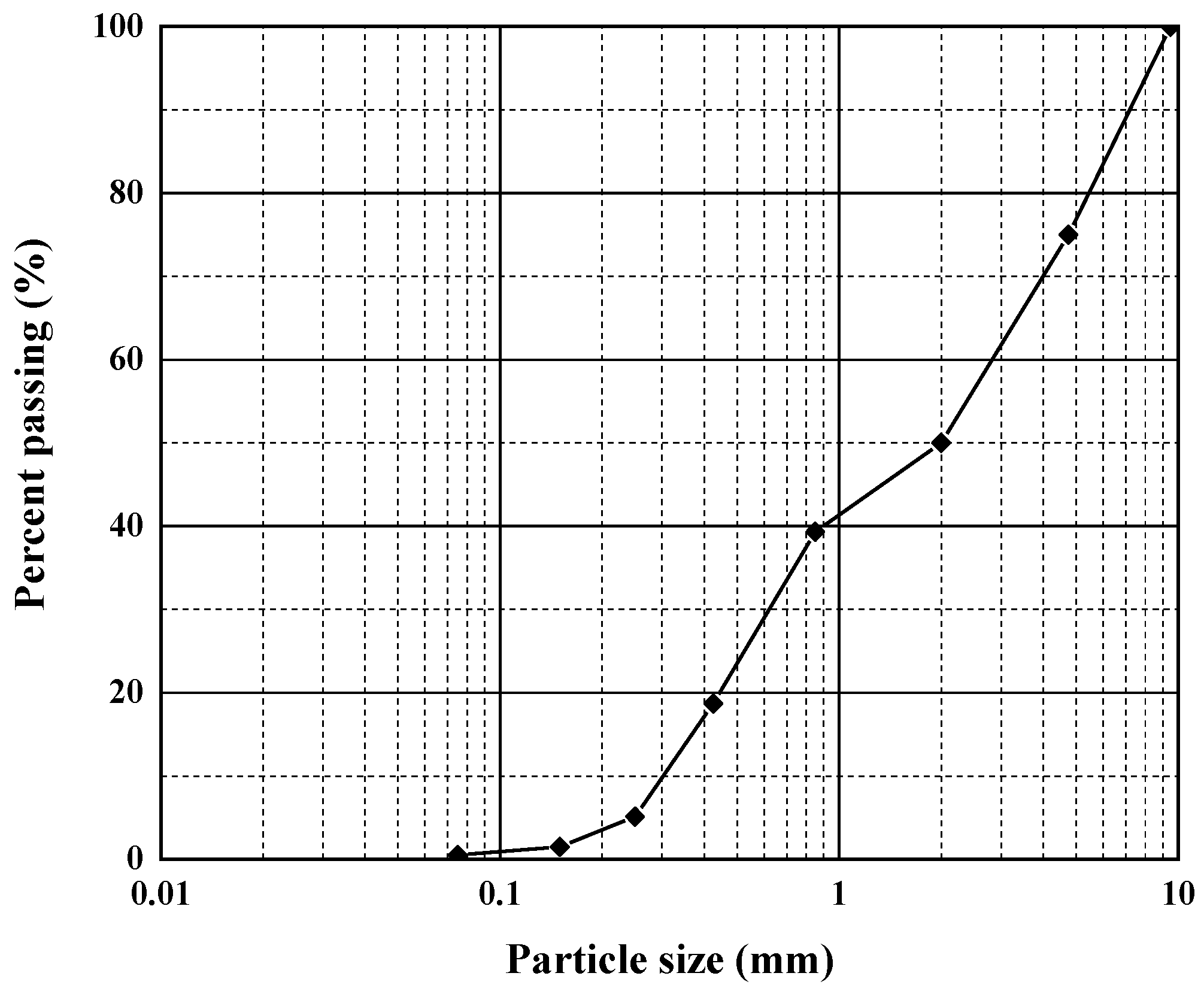
2.3. Sample Properties
2.4. Experimental Method
2.5. Methods for Assessing Debris Flow Characteristics
2.5.1. Flow Velocity
2.5.2. Froude Number
3. Results
3.1. Deposition Characteristics of Debris Flow
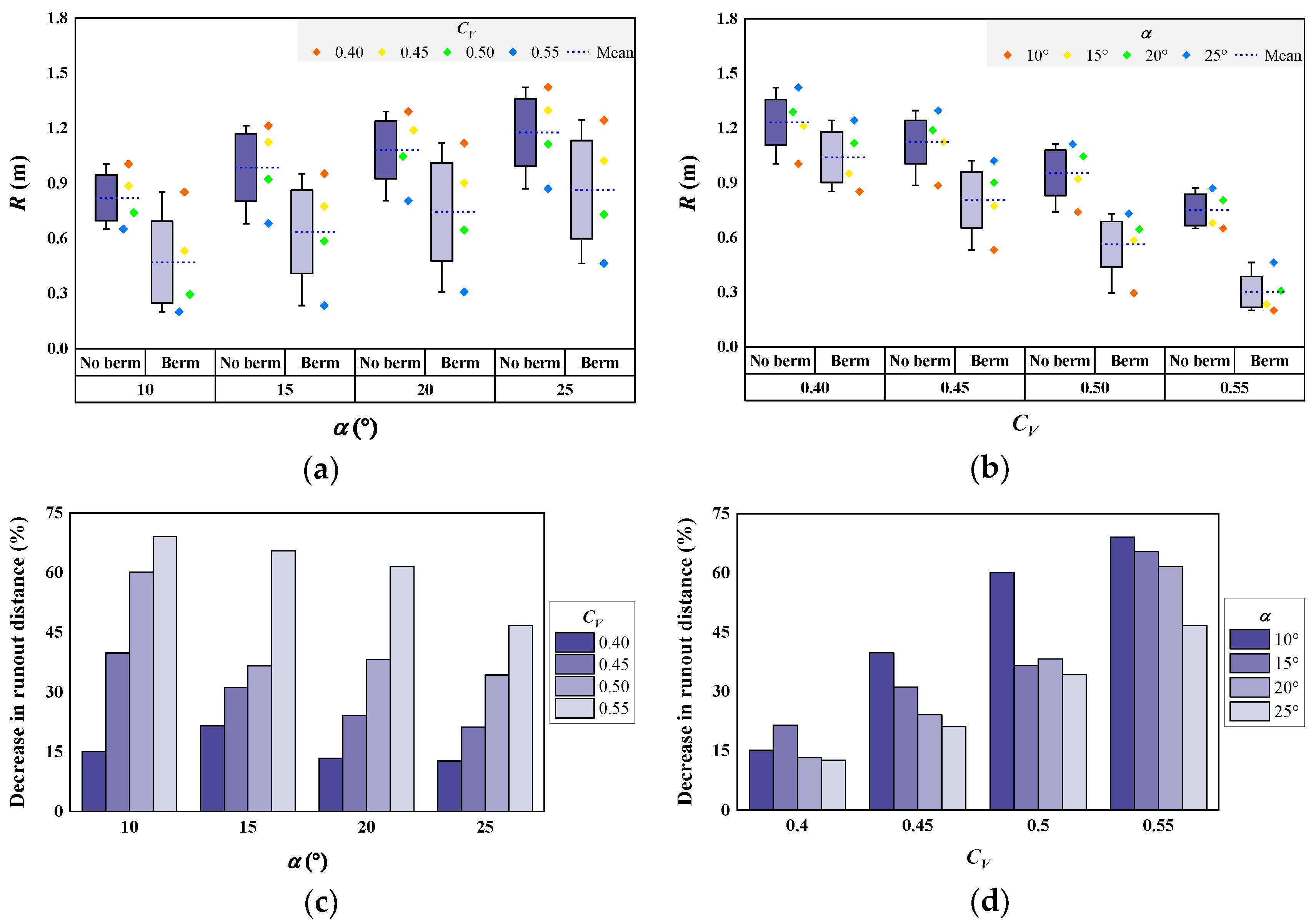
3.1.1. Runout Distance
3.1.2. Lateral Width
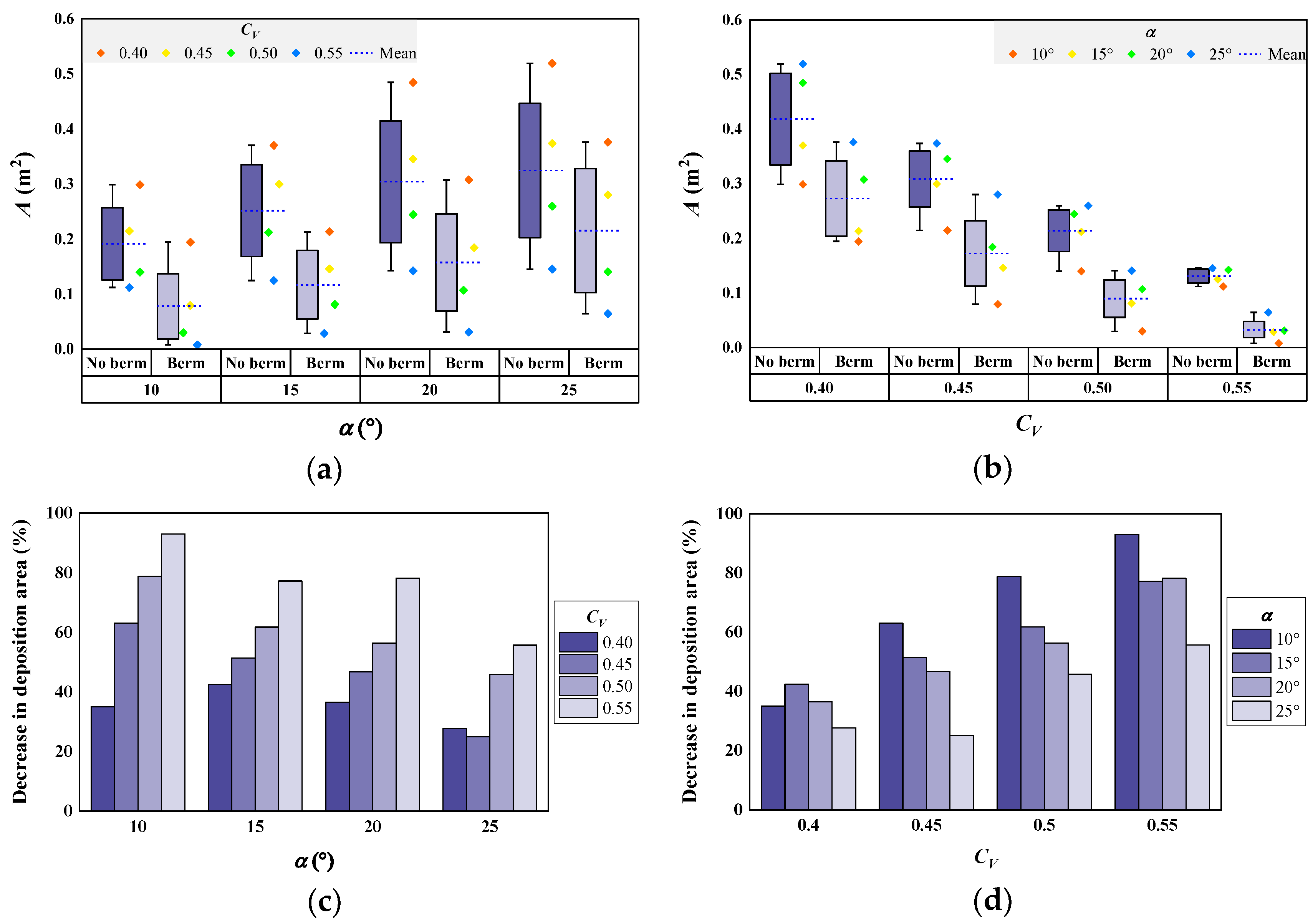
3.1.3. Deposition Area
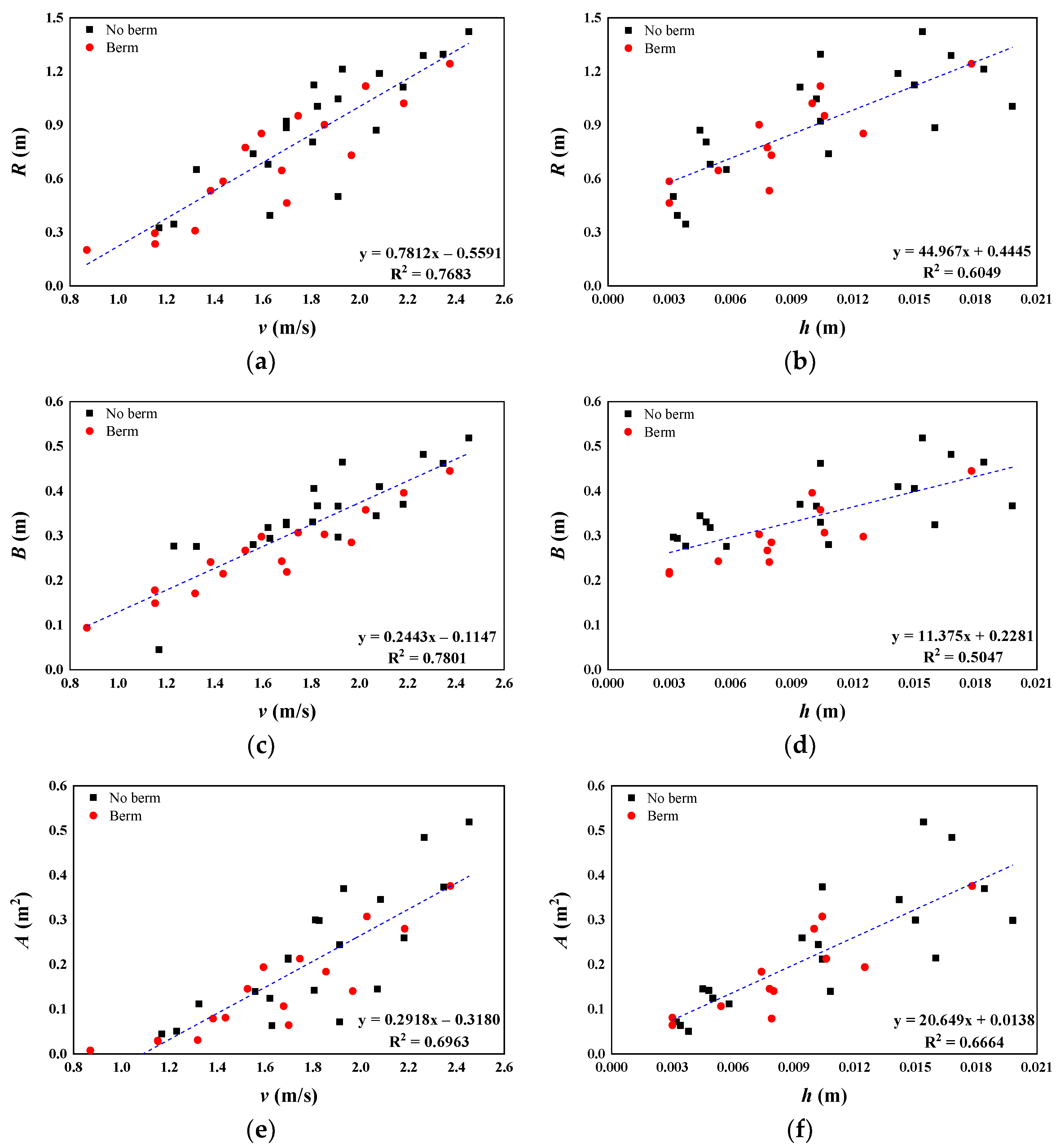
3.2. Relationships between Flow Characteristics and Deposition Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eu, S.; Im, S.; Kim, D.; Chun, K.W. Flow and deposition characteristics of sediment mixture in debris flow flume experiments. For. Sci. Technol. 2017, 13, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eu, S.; Im, S. Examining the impact force of debris flow in a check dam from small-flume experiments. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation, Golden, CO, USA, 10–13 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Kwon, T. Effect of rheological properties on debris-flow intensity and deposition in large scale flume experiment. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation, Golden, CO, USA, 10–13 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Ryou, K.; Lee, H. Debris flow characteristics in flume experiments considering berm installation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Paik, J. Depositional characteristics of debris flows in a rectangular channel with an abrupt change in slope. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eu, S.; Im, S.; Kim, D. Development of debris flow impact force models based on flume experiments for design criteria of soil erosion control dam. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungr, O.; Morgan, G.C.; Kellerhals, R. Quantitative analysis of debris torrent hazards for design of remedial measures. Can. Geotech. J. 1984, 21, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, R. Debris-flow mechanics. In Debris-flow Hazards and Related Phenomena; Jakob, M., Hungr, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 105–134. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.E. Physical geomorphology of debris flows. In Developments and Applications of Geomorphology; Costa, J.E., Fleisher, P.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 268–317. [Google Scholar]
- Highland, L.M.; Bobrowsky, P. The Landslide Handbook: A Guide to Understanding Landslides; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Kim, Y. The physical vulnerability of different types of building structure to debris flow events. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1475–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, V.; Cesca, M.; Marchi, L. Field and laboratory investigations of runout distances of debris flows in the Dolomites (Eastern Italian Alps). Geomorphology 2010, 115, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proske, D.; Suda, J.; Hübl, J. Debris flow impact estimation for breakers. Georisk 2011, 5, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, R.M. The physics of debris flows. Rev. Geophys. 1997, 35, 245–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, T. Testing various constitutive equations for debris flow modelling. In Hydrology, Water Resources and Ecology in Headwaters; Kovar, K., Tappeiner, U., Peters, N.E., Craig, R.G., Eds.; IAHS Press: Wallingford, UK, 1998; pp. 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Bettella, F.; Bisantino, T.; D’Agostino, V.; Gentile, F. Debris-flow runout distance: Laboratory experiments on the role of Bagnold, Savage and friction numbers. In Monitoring, Stimulation, Prevention and Remediation of Dense and Debris Flows Ⅳ; De Wrachien, D., Brebbia, C.A., Mambretti, S., Eds.; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2012; pp. 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, D.O.K. Review of Natural Terrain Landslide Debris-Resisting Barrier Design: Geo Report No. 104; Geotechnical Engineering Office, Civil Engineering Department, The Government of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region: Hong Kong, China, 2000; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- D’Agostino, V.; Bettella, F.; Cesca, M. Basal shear stress of debris flow in the runout phase. Geomorphology 2013, 201, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Ni, J.C.; Arulrajah, A.; Huang, H. A simple approach for characterizing tunnel bore conditions based upon pipe-jacking data. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 71, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Wang, L.; Xue, Z.; Ni, J.C.; Rahman, M.M.; Arulrajah, A. Lubrication performance of pipejacking in soft alluvial deposits. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 91, 102991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Cheng, W.; Wang, L.; Song, G. Improvement of the shearing behaviour of loess using recycled straw fiber reinforcement. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 3319–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungr, O. A review of landslide hazard and risk assessment methodology. In Landslides and Engineered Slopes. Experience, Theory and Practice; Aversa, S., Cascini, L., Picarelli, L., Scavia, C., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yifru, A.L.; Laache, E.; Norem, H.; Nordal, S.; Thakur, V. Laboratory investigation of performance of a screen type debris-flow countermeasure. HKIE Trans. 2018, 25, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddy, B.; Howard, E. Hydrological function of berms within a waste landform design. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Mine Closure, Perth, Australia, 15–17 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Huang, H.; Wang, Z.; Brierley, G.; Zhang, K. Rehabilitation of a debris-flow prone mountain stream in southwestern China-strategies, effects and implications. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Cao, T.; Yang, F.; Zhou, H. An experimental study on controlling post-earthquake debris flows using slit dams. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; You, Y. Experimental study on a debris-flow drainage channel with different types of energy dissipation baffles. Eng. Geol. 2017, 220, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; You, Y. Debris flow drainage channel with energy dissipation structures: Experimental study and engineering application. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 144, 06018012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Fei, W.; Zhou, H.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J. Experimental and numerical study on the load and deformation mechanism of a flexible net barrier under debris flow impact. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 2213–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Yin, J.; Qin, J.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, W. Experimental study on impact and deposition behaviours of multiple surges of channelized debris flow on a flexible barrier. Landslides 2020, 17, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, H. A study of the debris flow activity on the one-stepped channel slope. Soil Water Res. 2015, 10, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Stefano, M.; Gharabaghi, B.; Clemmer, R.; Jahanfar, M.A. Berm design to reduce risks of catastrophic slope failures at solid waste disposal sites. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; You, Y. Characteristics of a debris-flow drainage channel with a step-pool configuration. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, Z. Stability of extended earth berm for high landfill. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Peng, C.; Wu, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Zhou, G.G.D.; Chitneedi, B.K. Role of baffle shape on debris flow impact in step-pool channel: An SPH study. Landslides 2020, 17, 2099–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haas, T.; Braat, L.; Leuven, J.R.F.W.; Lokhorst, I.R.; Kleinhans, M.G. Effects of debris flow composition on runout, depositional mechanisms, and deposit morphology in laboratory experiments. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2015, 120, 1949–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanzoni, S.; Gregoretti, C.; Stancanelli, L.M. Coarse-grained debris flow dynamics on erodible beds. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 592–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, R.M.; Logan, M.; LaHusen, R.G.; Berti, M. The perfect debris flow? Aggregated results from 28 large-scale experiments. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, F03005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, R.M. Scaling and design of landslide and debris-flow experiments. Geomorphology 2015, 244, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.; Eu, S.; Kim, D. Understanding debris flow characteristics using flume experiments. In Advancing Culture of Living with Landslides; Mikos, M., Tiwari, B., Yin, Y., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhou, G.G.D.; Chen, X.; Song, D. Debris-flow deposition: Effects of fluid viscosity and grain size. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation, Golden, CO, USA, 10–13 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, B.; Nan, Y. A qualitative study of the critical conditions for the initiation of mine waste debris flows. Water 2020, 12, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T. Debris flow: Mechanics, Prediction, and Countermeasures, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2014; p. 572. [Google Scholar]
- Fairfield, G. Assessing the Dynamic Influences of Slope Angle and Sediment Composition on Debris Flow Behaviour: An Experimental Approach. Master’s Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T. Debris flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1981, 13, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickenmann, D. Debris flows 1987 in Switzerland: Modelling and fluvial sediment transport. In Hydrology in Mountainous Regions II; Sinniger, R.O., Monbaron, M., Eds.; IAHS: Lausanne, Switzerland, 1990; pp. 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Rickenmann, D. Empirical relationships for debris flows. Nat. Hazards 1999, 19, 47–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.G.D.; Li, S.; Song, D.; Choi, C.E.; Chen, X. Depositional mechanisms and morphology of debris flow: Physical modelling. Landslides 2019, 16, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.; Park, S. Numerical simulation of flood and debris flows through drainage culvert. Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2011, 11, 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, B. Numerical simulation of the topographical change in Korea mountain area by intense rainfall and consequential debris flow. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frank, F.; McArdell, B.W.; Huggel, C.; Vieli, A. The importance of entrainment and bulking on debris flow runout modeling: Examples from the Swiss Alps. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 2569–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Haas, T.; van Woerkom, T. Bed scour by debris flows: Experimental investigation of effects of debris-flow composition. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 1951–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, X.; Hou, T. An analysis of the supply process of loose materials to mountainous rivers and gullies as a result of dry debris avalanches. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Test Type | α (°) | CV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straight channel test | 10 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.60 |
| 15 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.60 | |
| 20 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.60 | |
| 25 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.60 | |
| Single-berm channel test | 10 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.60 |
| 15 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.60 | |
| 20 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.60 | |
| 25 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.60 | |
| CV | Wtotal (kg) | SP | SP | GP | WW (kg) | ρ (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <2 mm (kg) | 2–4.75 mm (kg) | 4.75–9.5 mm (kg) | ||||
| 0.40 | 7.100 | 2.200 | 1.100 | 1.100 | 2.700 | 1578 |
| 0.45 | 7.425 | 2.475 | 1.238 | 1.238 | 2.475 | 1650 |
| 0.50 | 7.750 | 2.750 | 1.375 | 1.375 | 2.250 | 1722 |
| 0.55 | 8.075 | 3.025 | 1.513 | 1.513 | 2.025 | 1794 |
| 0.60 | 8.400 | 3.300 | 1.650 | 1.650 | 1.800 | 1867 |
| Test Type | α (°) | v (m/s) [4] | h (m) [4] | Fr [4] | R (m) | B (m) | A (m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straight channel | 10 | 1.169–1.829 | 0.0058–0.0198 | 4.14–5.55 | 0.326–1.005 | 0.045–0.367 | 0.0450–0.2988 |
| 15 | 1.231–1.929 | 0.0038–0.0184 | 4.54–7.32 | 0.346–1.213 | 0.277–0.465 | 0.0506–0.3701 | |
| 20 | 1.629–2.265 | 0.0034–0.0168 | 5.58–8.92 | 0.394–1.290 | 0.294–0.482 | 0.0637–0.4846 | |
| 25 | 1.912–2.453 | 0.0032–0.0154 | 6.31–10.79 | 0.501–1.423 | 0.297–0.519 | 0.0718–0.5192 | |
| Single-berm channel | 10 | 0.870–1.594 | 0.0079–0.0125 | 4.55–4.97 | 0.201–0.853 | 0.094–0.298 | 0.0078–0.1943 |
| 15 | 1.153–1.746 | 0.0030–0.0106 | 5.41–8.36 | 0.235–0.952 | 0.149–0.307 | 0.0284–0.2131 | |
| 20 | 1.319–2.026 | 0.0054–0.0104 | 6.34–7.29 | 0.309–1.118 | 0.171–0.358 | 0.0310–0.3076 | |
| 25 | 1.699–2.375 | 0.0030–0.0178 | 5.68–9.90 | 0.464–1.243 | 0.219–0.445 | 0.0644–0.3759 |
| Deposition Characteristics | Range of Values | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R (m) | No berm | 0.326–1.423 | 0.891 | 0.323 |
| Berm | 0.201–1.243 | 0.679 | 0.314 | |
| All | 0.201–1.423 | 0.797 | 0.336 | |
| B (m) | No berm | 0.045–0.519 | 0.348 | 0.099 |
| Berm | 0.094–0.445 | 0.261 | 0.089 | |
| All | 0.045–0.519 | 0.309 | 0.104 | |
| A (m2) | No berm | 0.045–0.519 | 0.226 | 0.138 |
| Berm | 0.008–0.376 | 0.142 | 0.107 | |
| All | 0.008–0.519 | 0.189 | 0.132 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryou, K.; Chang, H.; Lee, H. Laboratory Analysis of Debris Flow Characteristics and Berm Performance. Water 2021, 13, 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162223
Ryou K, Chang H, Lee H. Laboratory Analysis of Debris Flow Characteristics and Berm Performance. Water. 2021; 13(16):2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162223
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyou, Kukhyun, Hyungjoon Chang, and Hojin Lee. 2021. "Laboratory Analysis of Debris Flow Characteristics and Berm Performance" Water 13, no. 16: 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162223
APA StyleRyou, K., Chang, H., & Lee, H. (2021). Laboratory Analysis of Debris Flow Characteristics and Berm Performance. Water, 13(16), 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162223







