The Significance of Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes in the Water Vapor Source in Dingxi Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
2.1. Sampling Sites and Acquired Dataset
2.1.1. Sampling Network
2.1.2. Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Calculation of d-excess Value
2.2.2. Backward Trajectory Analysis
2.2.3. Potential Source Contribution Factor Analysis
2.2.4. Concentration Weight Trajectory Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Vapor Source Information Indicated by δ18O and d-excess
3.2. Tracing Water Vapor Source with Lagrange Algorithm
3.2.1. Backward Trajectory Analysis
3.2.2. PSCF
3.2.3. CWT
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, M.Y.; Wang, L.; Parkes, S.D.; Strauss, J.; McCabe, M.F.; Evans, J.P.; Griffiths, A.D. Stable water isotope and surface heat flux simulation using ISOLSM: Evaluation against in-situ measurements. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.F.; Li, J.F.; Shi, P.J.; He, Y.Q.; Cai, A.L.; Tong, H.L. Relationship between sub-cloud secondary evaporation and stable isotope in precipitation indifferent regions of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Qi, F.; Wang, Q.J.; Kong, Y.L.; Cheng, A.F.; Yong, S.; Li, Y.G.; Li, J.G.; Guo, X.Y. Contributions of local terrestrial evaporation and transpiration to precipitation using δ18O and d-excess as a proxy in Shiyang inland river basin in China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 146, 140–151. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Zhang, M.J.; Che, Y.J.; Chen, F.L.; Qiang, F. Contribution of recycled moisture to precipitation in oases of arid central Asia: A stable isotope approach. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 3246–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jean, C.C.H.; Oliver, A.C.; Eugene, F.K.; Samuel, M.S. Oxygen isotopic composition of soil water: Quantifying evaporation and transpiration. Geoderma 1998, 82, 269–293. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, G.J.; Good, S.P. Incorporating water isoscapes in hydrological and water resource investigations. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews Water 2015, 2, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.D.; Mayer, B.; Harris, S.; Krouse, H.R. A 10-year record of stable isotope ratios of hydrogen and oxygen in precipitation at Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Tellus B 2004, 56, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, X.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Xia, J.; Zhang, X.C.; Yu, J.J.; Long, D.; Li, F.D.; Zhang, B. Spatio-temporal variations of δ2H and δ18O in precipitation and shallow groundwater in the Hilly Loess Region of the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 63, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrier, C.U.; Babu, M.P. A study on the spatial variations in stable isotopic composition of precipitation in a semiarid region of Southern India. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.J.; Yu, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.Y. Slope distribution of water vapor and its source in Chinese mainland. Groundwater 2017, 39, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, F.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, M.J.; Jin, S.; Dong, Z.W. Deuterium and oxygen 18 in precipitation and atmospheric moisture in the upper Urumqi River Basin, eastern Tianshan Mountains. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Stohl, A.; Trigo, R.M.; Dominguez, F.; Yoshimura, K.; Yu, L.; Drumond, A.; Durán-Quesada, M.A.; Nieto, R. Oceanic and terrestrial sources of continental precipitation. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, D.Q.; Xu, Q.; Hao, Y.G.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, B.B. Hydrogen and oxygen isotope characteristics and water vapor sources of summer precipitation in the desert of Western Ordos. For. Sci. Res. 2016, 29, 911–918. [Google Scholar]
- Voelker, A.H.L.; Colman, A.; Olack, G.; Waniek, J.J.; Hodell, D. Oxygen and hydrogen isotope signatures of Northeast Atlantic water masses. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2015, 116, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.D.; Yao, T.D.; MacClune, K.; White, J.W.C.; Schilla, A.; Vaughn, B. Stable isotopic variations in west China: A consideration of moisture sources. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Pan, Y.H.; Li, J.G.; Chen, A.F.; Wang, T.T.; Han, C.T.; Song, Y.X.; Theakstone, W.H. Can monsoon moisture arrive in the Qilian Mountains in summer? Quat. Int. 2015, 358, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Masayoshi, N.; Akiko, S.; Yoshihiro, M. Water isotope variations in the snow pack and summer precipitation at July 1 Glacier, Qilian Mountains in northwest China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 21, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.J.; Huang, Y.X.; Tao, J.H.; Li, D.L.; Wang, P.X. Regional distribution and variation of atmospheric water vapor in Northwest China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2006, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, M.J.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.L.; Li, F.; Chen, F.L. An investigation of moisture sources and secondary evaporation in Lanzhou, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3375–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.L.; Zhang, M.J.; Argiriou, A.A.; Wang, S.J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.Y. Deuterium Excess in Precipitation Reveals Water Vapor Source in the Monsoon Margin Sites in Northwest China. Water 2020, 12, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.R.; Song, X.F.; Yuan, G.F.; Sun, X.M.; Liu, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.M.; Wang, S.Q. Characteristics of Atmospheric Precipitation δ18O and Water Vapor Sources in Northwest China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 1, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Salamalikis, V.; Argiriou, A.A.; Dotsika, E. Stable isotopic composition of atmospheric water vapor in Patras, Greece: A concentration weighted trajectory approach. Atmos. Res. 2015, 152, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.F.; Zhang, M.J.; Wang, S.J.; Qiu, X.; Du, M.X.; Zhang, Y.N.; Yu, X.X.; Zhou, S.E. Analysis of diurnal water vapor isotope characteristics and water vapor sources in summer in the middle reaches of Heihe River. Arid Land Geogr. 2020, 43, 360–370. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.F.; Zhang, M.J.; Wang, S.J.; Qiu, X.; Zhou, S.E.; Zhang, Y.N.; Yu, X.X.; Wang, W. Isotopic characteristics of precipitation in the upper reaches of Heihe River and analysis of its water vapor source. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2020, 42, 937–951. [Google Scholar]
- Begum, B.A.; Kim, E.; Jeong, C.H.; Lee, D.W.; Hopke, P.K. Evaluation of the potential source contribution function using the 2002 Quebec forest fire episode. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3719–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, Y.H.; Zhou, J.H. Study on the impact of Tao River Diversion Project on the ecological carrying capacity of water resources in Dingxi. Water Resour. Dev. Manag. 2020, 12, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Su, B.G. Discussion on construction and management of rural safe drinking water project in Anding District of Dingxi City. Agric. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2017, 18, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Gao, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, D.; Wang, J. Optimization of stepwise clustering algorithm in backward trajectory analysis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 32, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wong, M.S.; Lee, K.H. Estimation of potential source regions of PM2.5 in Beijing using backward trajectories. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Chiang, H.C.; Lin, S.L.; Chen, M.J.; Lin, T.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Elemental characterization and source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in the western coastal area of central Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 541, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, L. A Lagrangian Analysis of Water Vapor Sources and Pathways for Precipitation in East China in Different Stages of the East Asian Summer Monsoon. J. Clim. 2019, 33, 977–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Gone, H.; Zhang, Q. Summer Water Vapor Sources in Northeast Asia and East Siberia Revealed by a Moisture-Tracing Atmospheric Model. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 3883–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.F.; Zhang, M.J.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, S.J.; Huang, X.Y.; Ma, Q.; Ma, X.N. Characteristics of δ18O in Precipitation and Moisture Transports over the Arid Region in Northwest China. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modelling system for trajectories. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Draxler, R.R. TrajStat: GIS-based software that uses various trajectory statistical analysis methods to identify potential sources from long-term air pollution measurement data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Hopke, P.K. A study of the sources of acid precipitation in Ontario, Canada. Atmos. Environ. 1989, 23, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Cheng, M.D.; Hopke, P.K. Potential source contribution function analysis and source apportionment of sulfur species measured at Rubidoux, CA during the Southern California Air Quality Study. Anal. Chim. Acta 1987, 277, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Argiriou, A.A.; Song, Y.; Lei, S. Isotopic evidence in modern precipitation for the westerly meridional movement in Central Asia. Atmos. Res. 2021, 259, 105698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.F. Isotopic characteristics of precipitation and analysis of water vapor sources in the middle Qilian Mountains. China Environ. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshrestha, U.C.; Raman, R.S.; Kulshrestha, M.J.; Rao, T.N.; Hazarika, P.J. Secondary aerosol formation and identification of regional source locations by PSCF analysis in the Indo-Gangetic region of India. J. Atmos. Chem. 2009, 63, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.P.; Zhu, B.; Yin, Y.; Jin, L.J.; Zhang, L. Characteristics of aerosol number concentration and its potential source area in summer at the top of Huangshan Mountain. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 852–861. [Google Scholar]
- Polissar, A.V.; Hopke, P.K.; Paatero, P.; Kaufmann, Y.J.; Hall, D.K. Bodhaine, B.A.; Dutton, E.G.; Harris, J.M. The aerosol at Barrow, Alaska: Long-term trends and source locations. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2441–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, L.J.; Zhu, B.; Yin, Y. Influence of advection transportation on pollutant concentration at the top of Huangshan Mountain from June to August 2011. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 969–978. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, Y.K.; Holsen, T.M.; Hopke, P.K. Comparison of hybrid receptor models to locate PCB sources in Chicago. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.F.; Zhang, M.J.; Wang, S.J.; Qiu, X.; Du, M.X.; Ma, R. Application of CWT Method in Identifying Water Vapor Sources of Summer Precipitation in China. Arid Area Res. 2018, 35, 872–881. [Google Scholar]
- Strauch, G.; Al-Mashaikhi, K.S.; Bawain, A.; Knöller, K.; Friesen, J.; Müller, T. Stable H and O isotope variations reveal sources of recharge in Dhofar, Sultanate of Oman. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2014, 50, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, P.D.; Kopec, B.G.; Mattingly, K.S.; Klein, E.S.; Welker, J.M. Baffin Bay sea ice extent and synoptic moisture transport drive water vapor isotope (δ18O, δ2H, and deuterium excess) variability in coastal northwest Greenland. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 13929–13955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA/WMO. Global Network for Isotopes in Precipitation (EB/OL). Available online: http://isohis.iaea.org (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Meng, Y.C.; Liu, G.D. Secondary evaporation effect of stable isotopes of precipitation in the Yangtze River Basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2010, 21, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, B.R. Isotope hydrology. Adv. Hydrosci. 1972, 8, 95–138. [Google Scholar]
- Araguás-Araguás, L.; Froehlich, K.; Rozanski, K. Stable isotope composition of precipitation over southeast Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 28721–28742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L.; Trigo, R.M. A Lagrangian identification of major sources of Sahel moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimelow, J.C.; Reuter, G.W. Transport of Atmospheric Moisture during Three Extreme Rainfall Events over the Mackenzie River Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cui, X. Moisture sources of an extreme precipitation event in Sichuan, China, based on the Lagrangian method. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2015, 16, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Huang, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, J.F.; Song, Y.; Cai, X.H.; Xie, S.D. Analysis of the transport pathways and potential sources of PM10 in Shanghai based on three methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.F.; Guo, H.W.; Qin, D.H.; Pan, H.X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.X. Contribution of recycled moisture to precipitation in the monsoon marginal zone: Estimate based on stable isotope data. J. Hydrol. 2018, 569, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Yue, S.L.; Ding, S.C.; Liu, S.H.; Ding, S.C. Cultivation technology of broad bean covered with double ridge and full film in semi-arid and two Yin areas. Gansu Agric. Technol. 2007, 12, 43–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, N.; Deng, F.R.; Khan, R.; Kumaret, K.R.; Hu, K.; Yu, X.N.; Wang, X.L.; Latha Devi, N.S.M.P. Temporal variations of PM concentrations, and its association with AOD and meteorology observed in Nanjing during the autumn and winter seasons of 2014–2017. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2020, 203, 105273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
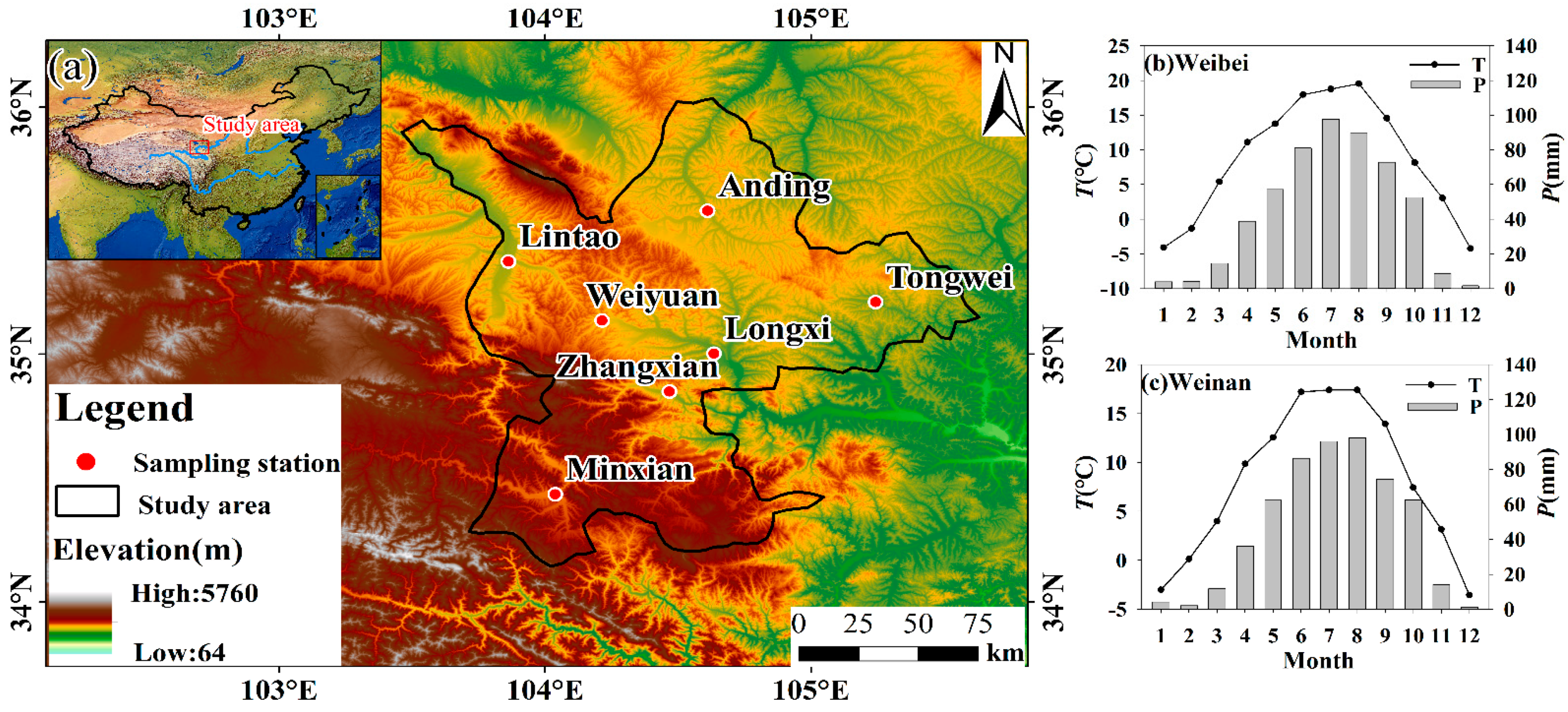





| Station | Latitude | Longitude | Alt (m) | Number of Samples | Annual Climatology | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | P (mm) | e (hPa) | h (%) | |||||
| Anding | 35°58′ | 104°61′ | 1898.83 | 62 | 7.2 | 377 | 8.1 | 63 |
| Longxi | 35°00′ | 104°63′ | 1731.29 | 84 | 8.2 | 414.8 | 8.3 | 68 |
| Weiyuan | 35°14′ | 104°21′ | 2111.34 | 73 | 6.1 | 504.3 | 7.9 | 68 |
| Tongwei | 35°21′ | 105°24′ | 1770.92 | 87 | 7.2 | 390.6 | 8.2 | 70 |
| Lintao | 35°38′ | 103°86′ | 1887.82 | 56 | 7.5 | 493.9 | 8.1 | 67 |
| Zhangxian | 34°85′ | 104°47′ | 1887.53 | 55 | 7.8 | 433.5 | 8.1 | 67 |
| Minxian | 34°43′ | 104°04′ | 2317.85 | 103 | 6.1 | 556.3 | 7.8 | 68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J. The Significance of Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes in the Water Vapor Source in Dingxi Area. Water 2021, 13, 2374. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172374
Wu X, Chen F, Liu X, Wang S, Zhang M, Zhu G, Zhou X, Chen J. The Significance of Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes in the Water Vapor Source in Dingxi Area. Water. 2021; 13(17):2374. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172374
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xixi, Fenli Chen, Xueyuan Liu, Shengjie Wang, Mingjun Zhang, Guofeng Zhu, Xin Zhou, and Jufan Chen. 2021. "The Significance of Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes in the Water Vapor Source in Dingxi Area" Water 13, no. 17: 2374. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172374
APA StyleWu, X., Chen, F., Liu, X., Wang, S., Zhang, M., Zhu, G., Zhou, X., & Chen, J. (2021). The Significance of Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes in the Water Vapor Source in Dingxi Area. Water, 13(17), 2374. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172374








