Hydrochemical Assessment of the Irrigation Water Quality of the El-Salam Canal, Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Field Measurements
2.4. Laboratory Measurements
2.5. Irrigation Water Quality
2.6. Data Treatments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Characteristics
3.1.1. Chemical Composition
| Sites | pH | EC dS m−1 | TDS | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | CO32− | HCO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg L−1 | |||||||||||
| S1 | 7.82 | 0.72 | 292.00 | 71.88 | 29.56 | 115.19 | 65.19 | 54.54 | 384.92 | 0.00 | 122.73 |
| S2 | 7.94 | 0.97 | 895.00 | 135.46 | 32.69 | 126.59 | 88.66 | 67.54 | 657.24 | 0.03 | 192.24 |
| S3 | 8.12 | 2.24 | 1098.00 | 171.54 | 39.56 | 137.21 | 97.07 | 73.43 | 763.74 | 0.06 | 205.96 |
| S4 | 8.42 | 2.34 | 1124.00 | 371.55 | 37.60 | 193.32 | 82.48 | 131.18 | 991.84 | 0.01 | 346.30 |
| S5 | 7.78 | 2.1 | 854.00 | 353.16 | 40.34 | 233.40 | 131.10 | 240.03 | 1144.22 | 0.00 | 315.79 |
| Mean | 8.02 | 1.67 | 852.60 | 220.72 | 35.95 | 161.14 | 92.90 | 113.34 | 788.39 | 0.02 | 236.61 |
| ±SE | 0.05 | 0.15 | 67.08 | 26.86 | 0.93 | 10.07 | 4.87 | 15.33 | 59.04 | 0.01 | 18.49 |
| CV% | 3.26 | 45.80 | 39.34 | 60.84 | 12.93 | 31.24 | 26.21 | 67.65 | 37.44 | 127.48 | 39.07 |
| LSD0.05 | 2.58 * | 0.14 * | 3.18 * | 5.79 * | 1.72 * | 6.8 * | 2.63 * | 3.92 * | 10.28 * | 0.82 * | 5.47 * |
| Permissible limits worldwide | |||||||||||
| WHO [43] | 6.5–8.5 | 1.5 | 500 | 200 | 12 | 75 | 50 | 250 | 250 | - | 500 |
| FAO [45] | 6.5–8.5 | 0.7-˂3 | 0–2000 | 0–920 | 0–2 | 0–400 | 9.4–13.5 | 70 | 575 | - | - |
3.1.2. Hydrochemical Facies
3.1.3. Heavy Metals Assessment
3.1.4. Correlation between Water Chemical Parameters and Heavy Metals
3.2. Irrigation Suitability Assessment
3.2.1. Permeability Index (PI)
3.2.2. Sodium Percentage (Na%)
3.2.3. Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR)
3.2.4. Kelly’s Index (KI)
3.2.5. Magnesium Hazard (MH)
3.2.6. Potential Salinity (PS)
3.2.7. Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC)
3.2.8. Total Hardness (TH)
3.2.9. Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhuyan, M.; Bakar, M.; Sharif, A.S.M.; Hasan, M.; Islam, M. Water quality assessment using water quality indicators and multivariate analyses of the old Brahmaputra River. Pollution 2018, 4, 481–493. [Google Scholar]
- Bano, I.; Arshad, M. Climatic changes impact on water availability. In Perspectives on Water Usage for Biofuels Production; Arshad, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yıldız, S.; Karakuş, C.B. Estimation of irrigation water quality index with development of an optimum model: A case study. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2019, 22, 4771–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkel, J.; Aerts, J.C.; Brown, S.; Jiménez, J.A.; Lincke, D.; Nicholls, R.J.; Scussolini, P.; Sanchez-Arcilla, A.; Vafeidis, A.; Addo, K.A. The ability of societies to adapt to twenty-first-century sea-level rise. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Amier, Y.A.; El-Zeiny, A.; El-Halawany, E.-S.F.; Elsayed, A.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Noureldeen, A.; Darwish, H.; Al-Barty, A.; Elagami, S.A. Environmental and stress analysis of wild plant habitat in River Nile Region of Dakahlia Governorate on basis of geospatial techniques. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.; El Attar, S.; Rafaat, Y.; Mohamed, M. Water resources management in Egypt. J. Eng. Sci. 2009, 37, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Gawad, S. Water quality challenges facing Egypt. In Comparative Risk Assessment and Environmental Decision Making; Linkov, I., Ramadan, A.B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 335–347. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elmabod, S.K.; Fitch, A.C.; Zhang, Z.; Ali, R.R.; Jones, L. Rapid urbanisation threatens fertile agricultural land and soil carbon in the Nile delta. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 252, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Alfy, M.A.; El-Amier, Y.A.; El-Eraky, T.E. Land use/cover and eco-toxicity indices for identifying metal contamination in sediments of drains, Manzala Lake, Egypt. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Kamel, A.H. Groundwater in Egypt issue: Resources, location, amount, contamination, protection, renewal, future overview. Egypt. J. Chem. 2016, 59, 321–362. [Google Scholar]
- Loutfy, N.M. Reuse of wastewater in Mediterranean region, Egyptian experience. In Waste Water Treatment and Reuse in the Mediterranean Region; Barceló, D., Petrovic, M., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 183–213. [Google Scholar]
- Omran, E.-S.E.; Negm, A.M. Egypt’s Environment from Satellite. In Environmental Remote Sensing in Egypt; Elbeih, S.F., Negm, A.M., Kostianoy, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 23–91. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, A.A.; Rabeh, S.A.; Fayez, M.; Monib, M.; Hegazi, N.A. El-Salam canal is a potential project reusing the Nile Delta drainage water for Sinai desert agriculture: Microbial and chemical water quality. J. Adv. Res. 2012, 3, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assar, W.; Ibrahim, M.G.; Mahmod, W.; Fujii, M. Assessing the agricultural drainage water with water quality indices in the El-Salam Canal mega project, Egypt. Water 2019, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalifa, W. Simulation of water quality for the El-Salam canal in Egypt. In Water Pollution; Brebbia, C.A., Ed.; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2014; pp. 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.; Tajsabreen, B.; Yaashikaa, P.; Reshma, B. Effective water/wastewater treatment methodologies for toxic pollutants removal: Processes and applications towards sustainable development. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Amier, Y.A.; Elsayed, A.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Noureldeen, A.; Darwish, H.; Fakhry, H. Optimizing the biosorption behavior of Ludwigia stolonifera in the removal of lead and chromium metal ions from synthetic wastewater. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat, S.T.; Rozana, M.; Kian, T.W.; Kawamura, G.; Matsuda, A.; Lockman, Z. One-dimensional α-Fe2O3 nanowires formation by high temperature oxidation of iron and their potential use to remove Cr (VI) ions. In 1-Dimensional Metal Oxide Nanostructures; Lockman, Z., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 115–142. [Google Scholar]
- El-Amier, Y.A.; Bonanomi, G.; Al-Rowaily, S.L.; Abd-ElGawad, A.M. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals along three main drains in Nile Delta and potential phytoremediation by macrophyte plants. Plants 2020, 9, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Shahid, S.A.; Heng, L. Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques Null; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pesce, S.F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquía River. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shil, S.; Singh, U.K.; Mehta, P. Water quality assessment of a tropical river using water quality index (WQI), multivariate statistical techniques and GIS. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mostafa, A. Development of Water Quality Indicators and Atlas of Drainage Water Quality Using GIS Tools; Technical report submitted to the NAWQAM project-Egypt; CIDA-DRTPC-MWRI: Giza, Egypt, 2002; p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Assar, W.; Ibrahim, M.G.; Mahmod, W.; Allam, A.; Tawfik, A.; Yoshimura, C. Effect of water shortage and pollution of irrigation water on water reuse for irrigation in the Nile Delta. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2020, 146, 05019013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, C.S. Soil and Plant Analysis; Interscience Publishers, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Constable and Co Ltd.: London, UK, 1962; Volume 497. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, W.C.; Haenisch, E.L.; Sawyer, D.T. Quantitative Analysis; Wiley Toppen: Tokyo, Japan, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Doneen, L.D. Notes on Water Quality in Agriculture; Department of Water Science and Engineering, University of California: Oakland, CA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; United State Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; Volume 78.
- Wilcox, L. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; United State Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955.
- Ravikumar, P.; Somashekar, R.; Angami, M. Hydrochemistry and evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in the Markandeya River basin, Belgaum District, Karnataka State, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 459–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, K. Irrigation With Saline Water; IARI: New Delhi, India, 1972; Volume 198. [Google Scholar]
- Durfor, C.N.; Becker, E. Public Water Supplies of the 100 Largest Cities in the United States, 1962; US Government Printing Office: Boston, MA, USA, 1964.
- Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Gopinath, M.; Chidambaram, S.; Vasanthavigar, M.; Sarma, V. Hydrochemical characterization and quality appraisal of groundwater from Pungar sub basin, Tamilnadu, India. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2014, 26, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, W. Permissible composition and concentration of irrigated waters. In Proceedings of the American Society of Civil Engineers 1940, Reston, VA, USA, January 1940; Volume 66, pp. 607–613. [Google Scholar]
- Şener, Ş.; Şener, E.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Mondal, G.C.; Kumar, S.; Singh, T.B.; Tewary, B.K.; Sinha, A. Major ion chemistry, weathering processes and water quality assessment in upper catchment of Damodar River basin, India. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Nag, S. Deciphering groundwater quality for irrigation and domestic purposes–a case study in Suri I and II blocks, Birbhum District, West Bengal, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 124, 965–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, F.M. Significance of carbonates in irrigation waters. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Nath, B. Spatio-seasonal variations of salinity and associated chemical properties in the middle section of Karnaphuli river water, Chittagong, Bangladesh using laboratory analysis and GIS technique. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2020, 11, 372–382. [Google Scholar]
- Vincy, M.; Brilliant, R.; Pradeepkumar, A. Hydrochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater for drinking and irrigation purposes: A case study of Meenachil River Basin, Western Ghats, Kerala, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines For Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 38, pp. 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, L.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ge, Y.; Issanova, G.; Saparov, G. Hydrochemical characteristics and irrigation suitability of surface water in the Syr Darya River, Kazakhstan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FAO. Water Quality for Agriculture. Irrigation and Drainage; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tume, P.; González, E.; King, R.W.; Monsalve, V.; Roca, N.; Bech, J. Spatial distribution of potentially harmful elements in urban soils, city of Talcahuano, Chile. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, P.; Mahmudy-Gharaie, M.H.; Ghassemzadeh, F.; Karouyeh, A.K.J. Assessment of groundwater suitability for irrigation in a gold mine surrounding area, NE Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.J. An assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes around brick kilns in three districts of Balochistan province, Pakistan, through water quality index and multivariate statistical approaches. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 197, 14–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; Jing, L.; Yu, P.J. Major ion chemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in and around a mountainous tourist town of China. Expos. Health 2016, 8, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Qian, H.; Wu, H.J. Environmental background values of shallow groundwater in the Guanzhong Basin. Water Divers. Water Conserv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 14, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, F.; Nardone, A.; Fasano, E.; Scognamiglio, G.; Esposito, D.; Agrelli, D.; Ottaiano, L.; Fagnano, M.; Adamo, P.; Beccaloni, E. A systematic risk characterization related to the dietary exposure of the population to potentially toxic elements through the ingestion of fruit and vegetables from a potentially contaminated area. A case study: The issue of the “Land of Fires” area in Campania region, Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Screening Level Ecological Risk Assessment Protocol for Hazardous Waste Combustion Facilities; Appendix E: Toxicity Reference Values; EPA530-D99-001C; USA EPA: Dallas, TX, USA, 1999; Volume 3.
- EU. Heavy Metals in Wastes, European Commission on Environment. 2002. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/studies/pdf/heavy_metalsreport.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2002).
- He, Y.; Men, B.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, D. Relationship between heavy metals and dissolved organic matter released from sediment by bioturbation/bioirrigation. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 75, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Baky, T.; Hagras, A.; Hassan, S.; Zyadah, M. Environmental impact assessment of pollution in Lake Manzala, I-Distribution of some heavy metals in water and sediment. J. Egypt. Ger. Soc. Zool. 1998, 26, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, P.; Gu, X.; Lin, C.; Xin, M.; Zhang, H.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, X.; He, M.; Wang, B. Distribution, sources, and ecological risks of potentially toxic elements in the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: Under the long-term impact of the Yellow River input. J. Hazard. Mat. 2021, 413, 125429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Hron, K.; Kynčlová, P.; Garrett, R. A new method for correlation analysis of compositional (environmental) data—A worked example. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Sa, E.J.; DiMarco, S.F. Seasonal variability and controls on chromophoric dissolved organic matter in a large river-dominated coastal margin. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2233–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiguchía, C.; Moreno, C.; García-Vargas, M. Evaluation of natural and anthropogenic influences on the Guadalquivir River (Spain) by dissolved heavy metals and nutrients. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, F.; Hu, J. Distribution and partitioning of heavy metals in water and sediments of a typical estuary (Modaomen, South China): The effect of water density stratification associated with salinity. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.; Titus, R.; Pietersen, K.; Tredoux, G.; Harris, C. Hydrochemical characteristics of aquifers near Sutherland in the Western Karoo, South Africa. J. Hydrol. 2001, 241, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, F.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, F. Spatial distribution and correlation characteristics of heavy metals in the seawater, suspended particulate matter and sediments in Zhanjiang Bay, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kierczak, J.; Pędziwiatr, A.; Waroszewski, J.; Modelska, M. Mobility of Ni, Cr and Co in serpentine soils derived on various ultrabasic bedrocks under temperate climate. Geoderma 2016, 268, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragović, S.; Mihailović, N.; Gajić, B. Heavy metals in soils: Distribution, relationship with soil characteristics and radionuclides and multivariate assessment of contamination sources. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, N.J. Hydrogeochemical parameters for assessment of groundwater quality in the upper Gunjanaeru River basin, Cuddapah District, Andhra Pradesh, South India. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Feng, W.; Qian, H.; Zhang, Q. Hydrogeochemical characterization and irrigation quality assessment of shallow groundwater in the Central-Western Guanzhong Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fipps, G. Irrigation Water Quality Standards and Salinity Management Strategies. 2003. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/87829 (accessed on 30 April 2003).
- Heras, J.D.L.; Mañas, P. Reclaimed wastewater to irrigate olive groves and vineyards: Effects on soil properties. Agronomy 2020, 10, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, S.; Srikantaswamy, S. Analysis of agricultural impact on the Cauvery river water around KRS dam. World Appl. Sci. J. 2009, 6, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazaryan, K.; Chen, Y. Hydrochemical assessment of surface water for irrigation purposes and its influence on soil salinity in Tikanlik oasis, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
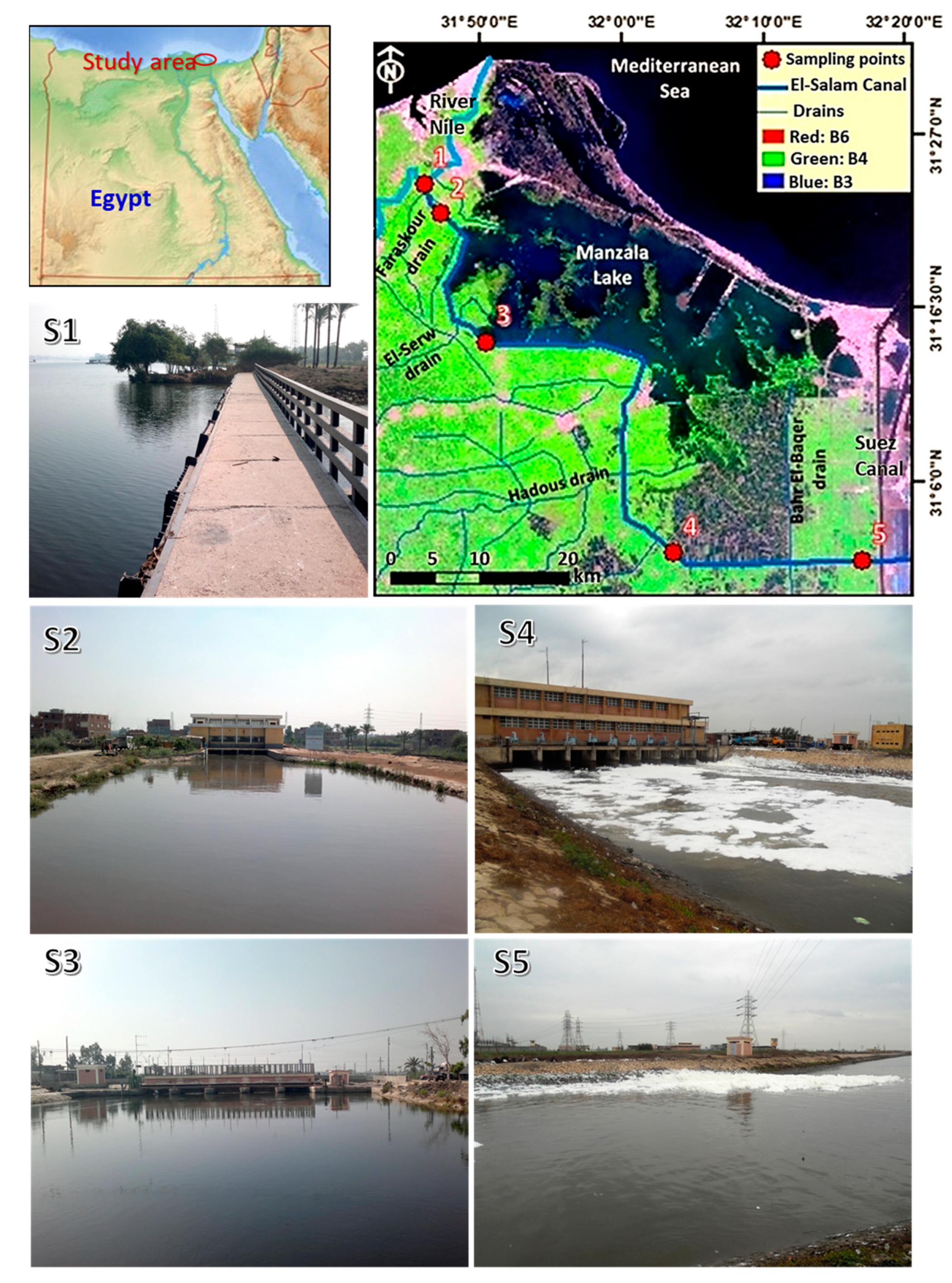




| Sites | Location | Coordinates | Characterization | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | |||
| S1 | Intake of the canal | 31.3954 | 31.7690 | River Nile (Reference station) |
| S2 | After mixing with Faraskour drain | 31.3669 | 31.7890 | Agriculture drain serves about 44.48 km2 |
| S3 | After mixing with El-Serw drain | 31.2356 | 31.8446 | Agriculture drain serves about 152.8 km2 |
| S4 | After mixing with Hadous drain | 31.0254 | 32.0672 | The largest drain in the eastern delta, serving a total area of 1756.96 km2 |
| S5 | Before El-Sahara | 31.0184 | 32.2882 | End of El-Salam Canal at east Nile Delta |
| Index | Formula | References |
|---|---|---|
| Permeability Index (PI) | [29] | |
| Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) | [30] | |
| Sodium percent (Na%) | [31] | |
| Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC) | [30] | |
| Magnesium Hazard (MH) | [32,33] | |
| Total Hardness (TH) | TH = | [34] |
| Kelly’s Index (KI) | [35,36] | |
| Potential Salinity (PS) | [29,32] | |
| Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI) | [37,38] |
| Index | Value | Water Quality | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Permeability Index (PI) | PI > 75% | Suitable | [39] |
| PI = 25–75% | Moderate | ||
| PI < 25% | Unsuitable | ||
| Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) | SAR < 10 | Excellent | [30,31] |
| SAR = 10–18 | Good | ||
| SAR = 19–26 | Doubtful/Fair Poor | ||
| SAR > 26 | Unsuitable | ||
| Sodium percent (Na%) | Na% < 20 | Excellent/Safe | [32,40] |
| Na% = 20–40 | Good/Safe | ||
| Na% = 40–60 | Permissible/Safe | ||
| Na% = 60–80 | Doubtful/unsafe | ||
| Na% > 80 | Unsuitable/unsafe | ||
| Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC) (meq L−1) | RSC < 1.25 | Good | [40] |
| RSC = 1.25–2.50 | Medium | ||
| RSC > 2.50 | Unsuitable | ||
| Magnesium Hazard (MH) | MH < 50% | Suitable | |
| MH > 50% | Unsuitable | ||
| Kelly’s Index (KI) | KI < 1 | Suitable | [36] |
| KI > 1 | Unsuitable | ||
| Potential Salinity (PS) (meq L−1) | PS < 3.0 | Excellent to good | [29] |
| PS = 3.0–5.0 | Good to injurious | ||
| PS > 5.0 | Injurious to unsatisfactory | ||
| Total Hardness (TH) (meq L−1) | 0–60 | Soft | [34] |
| 61–120 | Moderate | ||
| 121–180 | Hard | ||
| >181 | Very | ||
| Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI) | WQI = 0–25 | Excellent | [37,38] |
| WQI = 26–50 | Good | ||
| WQI = 51–75 | Poor | ||
| WQI = 76–100 | Very poor | ||
| WQI > 100 | Unsuitable |
| Sites | Fe | Mn | Pb | Cu | Co | Ni | Cr | Cd | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg L−1 | |||||||||
| S1 | 0.875 | 0.688 | 4.660 | 2.330 | 0.354 | 0.274 | 0.179 | 0.051 | 0.212 |
| S2 | 1.610 | 1.950 | 7.730 | 5.030 | 3.471 | 1.447 | 0.882 | 0.087 | 0.017 |
| S3 | 1.861 | 1.770 | 6.480 | 6.440 | 4.675 | 1.724 | 1.020 | 0.224 | 0.353 |
| S4 | 1.714 | 0.960 | 5.274 | 4.120 | 5.594 | 2.045 | 1.474 | 0.479 | 0.229 |
| S5 | 1.440 | 3.000 | 5.100 | 4.880 | 4.037 | 1.525 | 0.772 | 2.070 | 0.479 |
| Mean | 1.500 | 1.674 | 5.849 | 4.560 | 3.626 | 1.403 | 0.865 | 0.582 | 0.258 |
| ±SE | 0.076 | 0.182 | 0.250 | 0.300 | 0.398 | 0.134 | 0.094 | 0.170 | 0.034 |
| CV% | 25.44 | 54.48 | 21.36 | 32.94 | 54.93 | 47.90 | 54.03 | 145.74 | 66.83 |
| LSD0.05 | 1.47 * | 1.37 * | 2.65 * | 1.27 * | 0.08 * | 0.05 * | 0.98 * | 0.03 * | 0.008 * |
| Permissible limits worldwide | |||||||||
| US EPA [53] | 5 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 2 |
| EU [54] | 0.2 | 0.05 | - | 0.2 | - | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.005 | - |
| Sites | PI (%) | SAR | KI | MH (%) | Na (%) | PS (meq L−1) | RSC (meq L−1) | TH (meq L−1) | IWQI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 32.89 | 7.57 | 0.40 | 36.14 | 35.99 | 5.54 | −9.10 | 11.11 | 40.26 |
| S2 | 42.58 | 13.06 | 0.63 | 41.19 | 43.86 | 8.74 | −10.46 | 13.61 | 56.46 |
| S3 | 45.81 | 15.85 | 0.73 | 41.43 | 47.40 | 10.01 | −11.46 | 14.84 | 82.04 |
| S4 | 60.27 | 31.64 | 1.35 | 29.91 | 59.73 | 14.01 | −10.76 | 16.43 | 114.82 |
| S5 | 51.69 | 26.16 | 0.97 | 35.97 | 51.91 | 18.67 | −17.26 | 22.44 | 96.23 |
| Mean | 46.65 | 18.85 | 0.82 | 36.93 | 47.78 | 11.40 | −11.81 | 15.69 | 77.96 |
| ±SE | 2.04 | 1.97 | 0.07 | 0.94 | 1.77 | 1.01 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 5.99 |
| LSD0.05 | 6.49 * | 5.95 * | 1.15 * | 6.56 * | 7.33 * | 1.23 * | 1.17 * | 1.64 * | 3.05 * |
| Sites | PI | SAR | KI | MH | Na | PS | RSC | TH | IWQI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Moderate | Excellent | Suitable | Suitable | Good/Safe | Injurious to unsatisfactory | Good | Soft | Good |
| S2 | Moderate | Good | Suitable | Suitable | Permissible/Safe | Injurious to unsatisfactory | Good | Soft | Poor |
| S3 | Moderate | Good | Suitable | Suitable | Permissible/Safe | Injurious to unsatisfactory | Good | Soft | Very poor |
| S4 | Moderate | Unsuitable | Unsuitable | Suitable | Permissible/Safe | Injurious to unsatisfactory | Good | Soft | Unsuitable |
| S5 | Moderate | Unsuitable | Suitable | Suitable | Permissible/Safe | Injurious to unsatisfactory | Good | Soft | Very poor |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Amier, Y.A.; Kotb, W.K.; Bonanomi, G.; Fakhry, H.; Marraiki, N.A.; Abd-ElGawad, A.M. Hydrochemical Assessment of the Irrigation Water Quality of the El-Salam Canal, Egypt. Water 2021, 13, 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172428
El-Amier YA, Kotb WK, Bonanomi G, Fakhry H, Marraiki NA, Abd-ElGawad AM. Hydrochemical Assessment of the Irrigation Water Quality of the El-Salam Canal, Egypt. Water. 2021; 13(17):2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172428
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Amier, Yasser A., Wafaa K. Kotb, Giuliano Bonanomi, Hala Fakhry, Najat A. Marraiki, and Ahmed M. Abd-ElGawad. 2021. "Hydrochemical Assessment of the Irrigation Water Quality of the El-Salam Canal, Egypt" Water 13, no. 17: 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172428
APA StyleEl-Amier, Y. A., Kotb, W. K., Bonanomi, G., Fakhry, H., Marraiki, N. A., & Abd-ElGawad, A. M. (2021). Hydrochemical Assessment of the Irrigation Water Quality of the El-Salam Canal, Egypt. Water, 13(17), 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172428









