Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs and Their Short-Term Seismic Precursor Anomalies along the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southeast Tibet Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
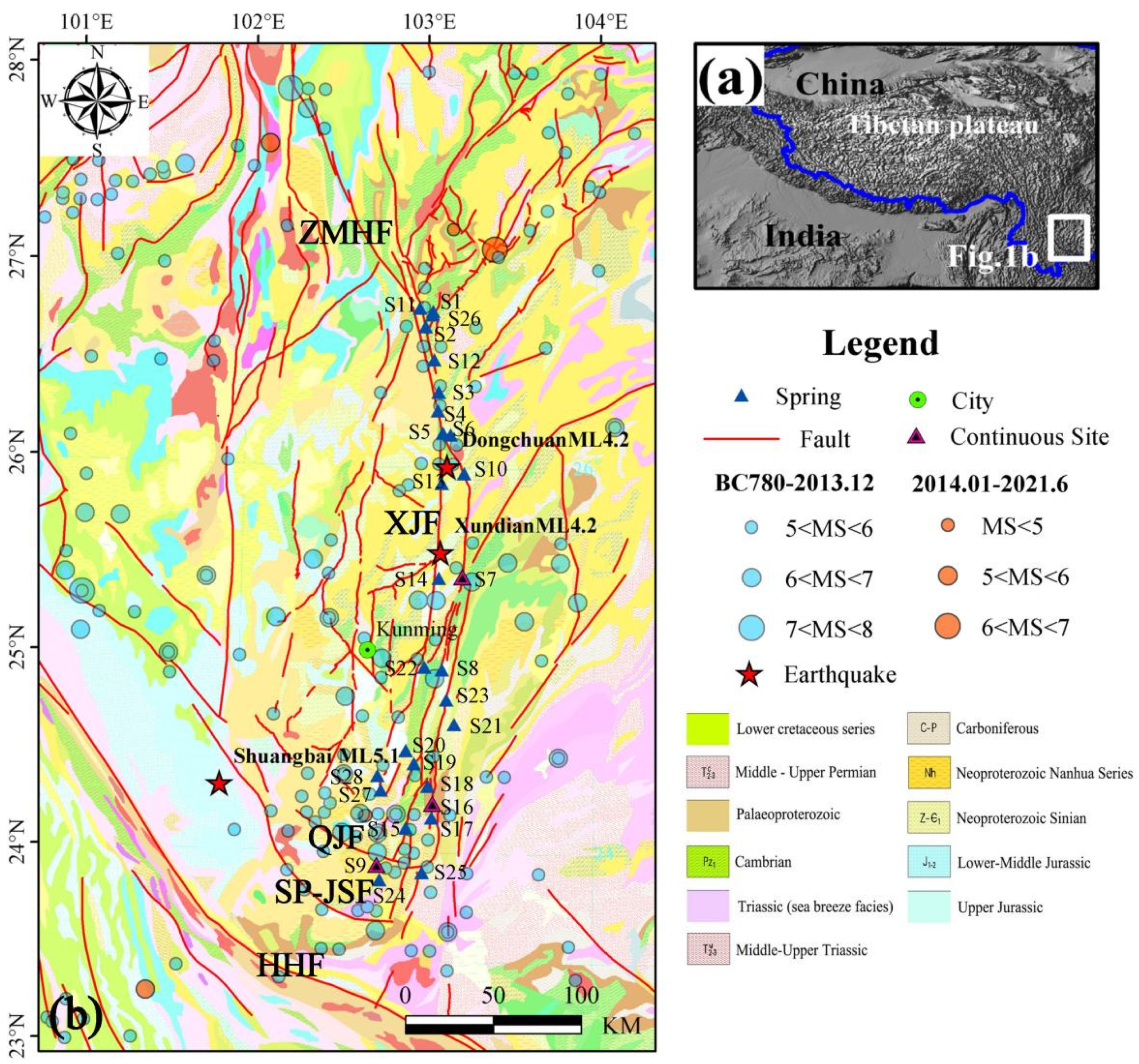
2. Geological Setting
3. Sampling and Analyzing Methods
4. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Origin of Hot Spring Water
5.2. Origin of Water-Soluble Ions in Hot Springs
5.2.1. Origin of Major Elements
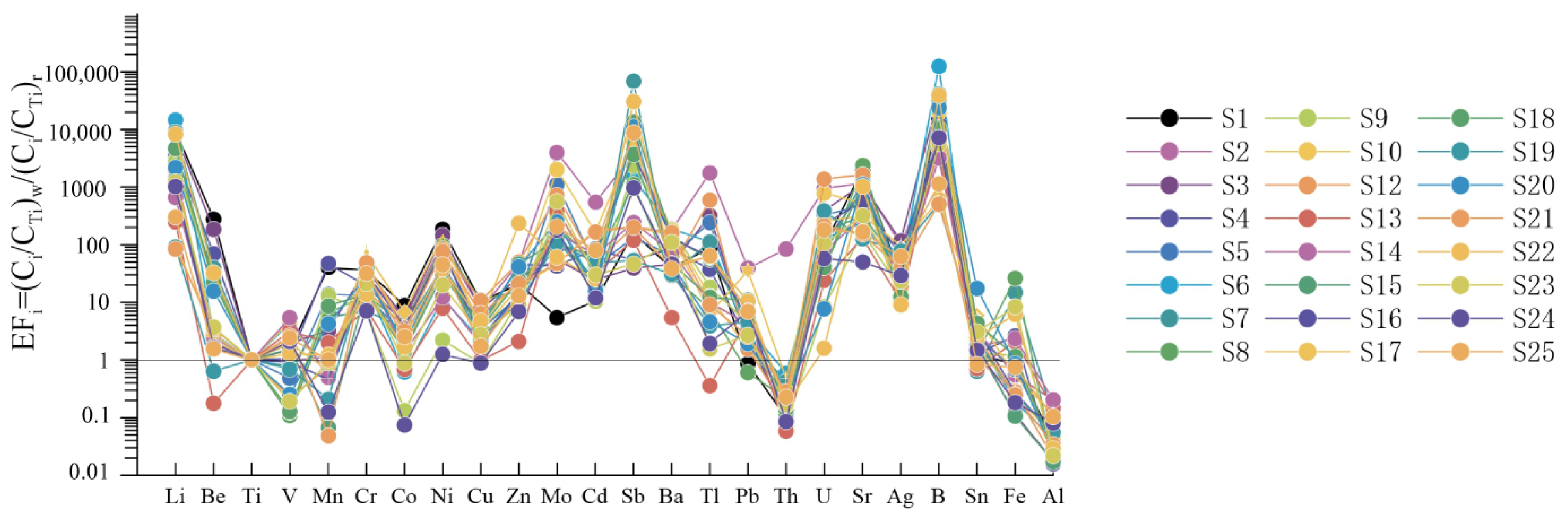
5.2.2. Origin of Trace Elements
5.3. Water–Rock Interaction of Hot Springs When Circulating inside the Fault
5.3.1. The Water–Rock Reaction Equilibrium
5.3.2. Reservoir Temperature and Circulation Depth
5.3.3. Mineral Saturation States
5.4. Correlation between Hydrogeochemical Changes and Earthquakes
5.4.1. Precursory and Postseismic Anomalies
5.4.2. The Hydrogeochemical Circulation Model of Hot Spring Waters in Xiaojiang Fault
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skelton, A.; Andrén, M.; Kristmannsdóttir, H.; Stockmann, G.; Mörth, C.M.; Sveinbjörnsdóttir, Á.; Jónsson, S.; Sturkell, E.; Guõrúnardóttir, H.R.; Hjartarson, H.; et al. Changes in groundwater chemistry before two consecutive earthquakes in Iceland. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Shi, Z.; Yin, G.; Liang, J. Travertine deposits, deep thermal metamorphism and tectonic activity in the Longmenshan tectonic region, southwestern China. Tectonophysics 2014, 633, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, S.; Horton, T.W.; Oze, C. Origin of warm springs in Banks Peninsula, New Zealand. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Singh, R.P. Coseismic Groundwater Temperature Response Associated with the Wenchuan Earthquake. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 177, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, T.; Masaki, Y. Post-seismic hydrochemical changes in regional groundwater flow systems in response to the 2016 Mw 7.0 Kumamoto earthquake. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, T.; Yamada, C.; Shibata, T.; Tawara, Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Manga, M.; Rahman, A.T.M.S.; Shimada, J. Coseismic groundwater drawdown along crustal ruptures during the 2016 Mw 7.0 Kumamoto earthquake. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 5891–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, K.; Yu, Z.Q.; Berndtsson, R.; Hosono, T. Temporal characteristics of groundwater chemistry affected by the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake using self-organizing maps. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G. Groundwater trace elements change induced by M5.0 earthquake in Yunnan. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y.; Takahata, N.; Igarashi, G.; Koizumi, N.; Sturchio, N.C. Helium degassing related to the Kobe earthquake. Chem. Geol. 1998, 150, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, H.; Hilton, D.R.; Güleç, N.; Mutlud, H. Post-earthquake anomalies in He–CO2, isotope and relative abundance systematics of thermal waters: The case of the 2011 Van earthquake, eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Chem. Geol. 2015, 411, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.-Y.; Koizumi, N.; Kitagawa, Y. Hydrogeochemical Anomalies and the 1995 Kobe Earthquake. Science 1995, 269, 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jie, C.; Guan, Z.; Liu, W.; Bai, L. Helium and carbon isotopic compositions of thermal springs in the earthquake zone of Sichuan, Southwestern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2006, 26, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Du, F.; Long, F.; Zhu, H. Tectonic dynamics and correlation of major earthquake sequences of the Xiaojiang and Qujiang-Shiping fault systems, Yunnan, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Du, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Xie, C.; Cui, Y. Continuously observation of fault fluid geiochemistry after Yushu Ms7.1 earthquake. Prog. Geophys. 2012, 27, 888–893. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen, S.E.; Manga, M. Hydrogeochemical precursors. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 697–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Cui, Y.; Du, J. Gas geochemistry of the hot spring in the Litang fault zone, Southeast Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 79, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tang, Q.; Cao, C.; Li, W.Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.P. The origin of Permian Pobei ultramafic complex in the northeastern Tarim craton, western China: Evidences from chemical and C-He-Ne-Ar isotopic compositions of volatiles. Chem. Geol. 2017, 469, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, D.; Ma, X.; Chen, Y.; Varentsov Ivan, M.; Xue, G.; Xue, S.; Lozovsky, I. Electrical resistivity structure of the Xiaojiang strike-slip fault system (SW China) and its tectonic implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 176, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Boschetti, T.; Barberio, M.D.; Billi, A.; Franchini, S.; Iacumin, P.; Selmo, E.; Petitta, M. Tracing deep fluid source contribution to groundwater in an active seismic area (central Italy): A combined geothermometric and isotopic (δ13C) perspective. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberio, M.D.; Gori, F.; Barbieri, M.; Billi, A.; Caracausi, A.; De Luca, G.; Franchini, S.; Petitta, M.; Doglioni, C. New observations in Central Italy of groundwater responses to the worldwide seismicity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttitta, D.; Caracausi, A.; Chiaraluce, L.; Favara, R.; Sulli, A. Continental degassing of helium in an active tectonic setting (northern Italy): The role of seismicity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.; Facca, G.; Genzano, N.; Gherardi, F.; Lisi, M.; Pierotti, L.; Tramutoli, V. Earthquake-related signals in central Italy detected by hydrogeochemical and satellite techniques. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 584716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.; Ciolini, R.; Facca, G.; Fazio, F.; Gherardi, F.; Heinicke, J.; Pierotti, L. Tectonic-Related Geochemical and Hydrological Anomalies in Italy during the Last Fifty Years. Minerals 2021, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrén, M.; Stockmann, G.; Skelton, A.; Sturkell, E.; Mörth, C.M.; Guðrúnardóttir, H.R.; Keller, N.S.; Odling, N.; Dahrén, B.; Broman, C.; et al. Coupling between mineral reactions, chemical changes in groundwater, and earthquakes in Iceland. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 2315–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppola, M.; Correale, A.; Barberio, M.D.; Billi, A.; Cavallo, A.; Fondriest, M.; Nazzari, M.; Paonita, A.; Romano, C.; Stagno, V.; et al. Meso-to nano-scale evidence of fluid-assisted co-seismic slip along the normal Mt. Morrone Fault, Italy: Implications for earthquake hydrogeochemical precursors. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2021, 568, 117010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberio, M.D.; Barbieri, M.; Billi, A.; Doglioni, C.; Petitta, M. Hydrogeochemical changes before and during the 2016 Amatrice-Norcia seismic sequence (central Italy). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Person, M.; Baumgartner, L.; Bos, B.; Connolly, J.; Gratier, J.P.; Gueydan, F.; Miller, S.A.; Rosenberg, C.L.; Urai, J.L.; Yardley, B.W.D. Group report: Fluids, geochemical cycles, and mass transport in fault zones. In Tectonic Faults—Agents of Change on a Dynamic Earth. Report of the 95th Dahlem Workshop on The Dynamics of Fault Zones Berlin, 16–21 January 2005; Handy, M.R., Hirth, G., Hovius, N., Eds.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 403–425. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/230561302 (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Martinelli, G.; Dadomo, A. Factors constraining the geographic distribution of earthquake geochemical and fluid-related precursors. Chem. Geol. 2017, 469, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, A.; Claesson, L.L.; Wästeby, N.; Andrén, M.; Stockmann, G.; Sturkell, E.; Mörth, C.M.; Stefansson, A.; Tollefsen, E.; Siegmund, H.; et al. Hydrochemical changes before and after earthquakes based on long term measurements of multiple parameters at 2 sites in northern Iceland—A review. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 2702–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geological Ministry of China. 1:500,000 Geologic Map of Yunnan Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1966. (In Chinese)
- Wang, E.; Burchfiel, B.C. Late Cenozoic to Holocene deformation in southwestern Sichuan and adjacent Yunnan, China, and its role in formation of the southeastern part of the Tibetan Plateau. GSA Bull. 2000, 112, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, F. Characteristics of the active Xiaojiang fault zone in Yunnan, China: A slip boundary for the southeastward escaping Sichuan–Yunnan Block of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2003, 21, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Fang, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. Soil Degassing From the Xianshuihe–Xiaojiang Fault System at the Eastern Boundary of the Chuan–Dian Rhombic Block, Southwest China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, F.; Chen, K.; Ran, H. Research on Relationship between Geochemical Characteristics of Thermal Springs and Seismic Activity in Xiaojiang Fault Zone and its Adjacent Area. J. Seismol. Res. 2014, 37, 228–243. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, Z.; Xu, S.; Barry, P.H.; Sano, Y.; Zhang, L.; Halldórsson, S.A.; Chen, A.-T.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, C.-Q.; et al. Linking deeply-sourced volatile emissions to plateau growth dynamics in southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4157. (In press) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.R.; Luo, Z.; Qian, H.; Wen, X.Z.; Zhou, H.; Huang, W. Field study of a highly active fault zone; the Xianshuihe Fault of Southwestern China. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1991, 103, 1178–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.R.; Gillespie, A.R.; Han, Y.; Sieh, K.E.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, C. Red River and associated faults, Yunnan Province, China; Quaternary geology, slip rates, and seismic hazard. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1984, 95, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; Cao, Z.; Shen, X.; Shen, J. The Xiaojiang Active Fault Zone; Seismological Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 1–237. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.Z. The uniform-slip method for estimating mean slip-rate of strike-slip fault. J. Earthq. Pred. Res. 1998, 7, 170–182. [Google Scholar]
- Tapponnier, P.; Peltzer, G.; Le Dain, A.Y.; Armijo, R.; Cobbold, P. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology 1982, 10, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M. Study on relationship between earthquake and Hydro-Geochemistry of groundwater in southern part of North-South earthquake belt in China. J. Geomech 2003, 9, 21–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- BGMRSP. Regional Geology of Xizang (Tibet) Autonomous Region; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Du, J.; Xie, C.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Yi, L.; Liu, H.; Cui, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics of hot spring waters in the Kangding district related to the Lushan MS = 7.0 earthquake in Sichuan, China. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.W. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA): Camden, NJ, USA; Water Environment Federation (WEF): Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Guo, D. Determining Trace Elements in Rock Samples Containing Refractory Minerals by Pressurize-microwave Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Uranium Geol. 2018, 34, 105–111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Song, X.; Han, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. A study of root water uptake of crops indicated by hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes: A case in Shanxi Province, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Franchini, S.; Barberio, M.D.; Billi, A.; Boschetti, T.; Giansante, L.; Gori, F.; Jónsson, S.; Petitta, M.; Skelton, A.; et al. Changes in groundwater trace element concentrations before seismic and volcanic activities in Iceland during 2010–2018. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 793, 148635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, P.; Zhou, S.; Han, Z.; Tu, H.; Zhang, S. Seasonal variability of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in a wetland system of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, southwest China: A quantitative assessment of groundwater inflow fluxes. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Isotopic shifts in waters from geothermal and volcanic systems along convergent plate boundaries and their origin. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1992, 113, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Guan, Z.; Liu, Y. Hot spring water observations and its anomalies before the Lushan MS7.0 earthquake in the western Sichuan region. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2015, 37, 347–356. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Yuan, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Characteristics of atmospheric precipitation δ18O in Eastern China and the origin of water vapor. Sci. China Press 2009, 54, 3521–3531. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti, T.; Cifuentes, J.; Iacumin, P.; Selmo, E. Local meteoric water line of Northern Chile (18 S–30 S): An application of error-in-variables regression to the oxygen and hydrogen stable isotope ratio of precipitation. Water 2019, 11, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apollaro, C.; Vespasiano, G.; Muto, F.; De Rosa, R.; Barca, D.; Marini, L. Use of mean residence time of water, flowrate, and equilibrium temperature indicated by water geothermometers to rahnk geothermal resources. Application to the thermal water circuits of Northern Calabria. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2016, 328, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Jang, G.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Brief analysis of the reasons of CO2 Degassing from hot springs on main faults within the east of Yunnan. Earth Environ. 2005, 33, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Aiuppa, A.; Dongarra, G.; Capasso, G.; Allard, P. Trace elements in the thermal groundwaters ofVulcano Island (Sicily). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2000, 98, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, S.; Wen, H.; Lan, J.; Luo, C. A Preliminary Study on the Possible Mechanism of Enrichment and Occurrence State of Nb-Ga-REE in the Emeishan Basalts from the Diandong Qianxi Region. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2020, 39, 1256–1277. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Franks, S.G.; Aagaard, P. Origin and migration of brines from Paleozoic strata in Central Tarim, China: Constraints from 87Sr/86Sr, δD, δ18O and water chemistry. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Geothermal solute equilibria: Derivationof Na–K–Ma–Ca geoindicators. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, R.O.; Truesdel, A.H. Empirical Na-K-Ca geothermometer for natural waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1973, 37, 1255–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proceedings of the Second United Nations symposium on the development and use of geothermal resources. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/7315693-proceedings-second-united-nations-symposium-development-use-geothermal-resources-volume (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Fournier, R.O.; Potter, R.W. Magnesium correction to the Na-K-Ca chemical geothermometer. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta. 1979, 43, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonani, F. Some remarks on the application of geochemical techniques in geothermal exploration. In Advances in European Geothermal Research; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1980; pp. 428–443. [Google Scholar]
- Fouillac, C.; Micard, G. Sodium/Lithium ratios in water applied to geothermetry of geothermal reservoirs. Geothermics 1981, 10, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, R.O.; Potter, R.W. A revised and expanded silica (quartz) geothermometer. Geoth. Res. Counc. Bull. 1982, 11, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Arnórsson, S. Chemical equilibria in icelandic geothermal systems-Implications for chemical geothermometry investigations. Geothermics 1983, 12, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodini, G.; Frondini, F.; Marini, L. Theoretical geothermometers and pCO2 indicators for aqueous solutions coming from hydrothermal systems of medium-low temperature hosted in carbonate-evaporite rocks. Application to the thermal springs of the Etruscan Swell. Italy. Appl. Geochem. 1995, 10, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Guo, J. Silica geothermal temperature scale and its related problems. Ground Water 1996, 18, 85–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z. Used the SiO2 mixing model to calculate Zhangzhou geothermal heat storage temperature. Chin. Sciense Bull. 1990, 35, 57–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, W.J. Groundwater Geochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications to Contamination; Lewis Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Rouabhia, A.; Djabri, L.; Hadji, R.; Baali, F.; Fahdi, C.; Hanni, A. Geochemical characterization of groundwater from shallow aquifer surrounding Fetzara Lake NE Algeria. Arab. J. Geosci. 2012, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Manga, M. Hydrologic responses to earthquakes and a general metric. Geofluid 2010, 10, 206–216. [Google Scholar]
- Toutain, J.P.; Munoz, M.; Poitrasson, F.; Lienard, A.C. Springwater chloride ion anomaly prior to a ML=5.2 Pyrenean earthquake. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1997, 149, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shi, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, C. Earthquake-related hydrochemical changes in thermal springs in the Xianshuihe Fault zone. West. China J. Hydrol. 2020, 579, 124175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D. Geochemical precursors to seismic activity. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1988, 126, 241–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, S.C.; Menzies, C.D.; Sutherland, R.; Denys, P.H.; Teagle, D.A.H. Changes in hot spring temperature and hydrogeology of the Alpine Fault hanging wall, New Zealand, induced by distal South Island earthquakes. Geofluids 2015, 15, 216–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjram, M.; Gleeson, T.; Uijendijk, E. Is the permeability of crystalline rock in the shallow crust related to depth, lithology or tectonic setting? Geofluids 2015, 15, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claesson, L.; Skelton, A.; Graham, C.; Moerth, C.M. The timescale and mechanisms of fault sealing and water-rock interaction after an earthquake. Geofluids 2007, 7, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchi, F.; Pik, R.; Pizzino, L.; Guerra, M.; Lombardi, S. Geochemical changes at the Bagni di Triponzo thermal spring during the Umbria-Marche 1997–1998 seismic sequence. J. Seism. 2000, 4, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, N.; Nakhaei, M.; Porhemmat, J. Assessment of hydrogeochemistry and contamination of Varamin deep aquifer, Tehran Province, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shen, Z.K. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J. On “whether earthquake precursors help for prediction do exist”. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 409–414. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cicerone, R.D.; Ebel, J.E.; Britton, J. A systematic compilation of earthquake precursors. Tectonophysics 2009, 476, 371–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crampin, S.; Gao, Y.; Bukits, J. A review of retrospective stress-forecasts of earthquakes and eruptions. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2015, 24, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yan, Y.; Fang, W.; Wang, W.; Shi, H.; Li, P. Short-Term Seismic Precursor Anomalies of Hydrogen Concentration in Luojishan Hot Spring Bubbling Gas, Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 8, 586279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.; Tamburello, G. Geological and Geophysical Factors Constraining the Occurrence of Earthquake Precursors in Geofluids: A Review and Reinterpretation. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 596050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Unsworth, M.J.; Meju, M.A.; Ma, X.; Teng, J.; Kong, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.; et al. Crustal deformation of the eastern Tibetan plateau revealed by magnetotelluric imaging. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Yi, L.; Liu, L.; Xie, C.; Cui, Y.; Du, J.; Cheng, J.; Yang, L. Hot Spring Gas Geochemistry in Western Sichuan Province, China After the Wenchuan Ms 8.0 Earthquake. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2015, 26, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Caracausi, A.; Sano, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zheng, G.; Lang, Y.; Liu, C. Deciphering a mantle degassing transect related with India-Asia continental convergence from the perspective of volatile origin and outgassing. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 310, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| NO. | Temperature (°C) | SiO2 (mg/L) | Reservoir Temperature (°C) | Circulation Depth (km) | Temperature Difference between Spring Vent and Reservoir (°C) | Structural Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S11 | 46.6 | 19.10 | 61.7 | 2.33 | 15.1 | Northern Segment |
| S1 | 43.0 | 16.80 | 57.0 | 2.09 | 14.0 | |
| S2 | 33.7 | 8.56 | 34.3 | 0.96 | 0.6 | |
| S12 | 40.8 | 12.10 | 45.6 | 1.52 | 4.8 | Middle eastern branch Segment |
| S3 | 37.0 | 14.70 | 52.3 | 1.85 | 15.3 | |
| S4 | 40.1 | 15.20 | 53.4 | 1.91 | 13.3 | |
| S6 | 45.2 | 13.50 | 49.3 | 1.70 | 4.1 | |
| S10 | 23.6 | 6.15 | 24.3 | 0.45 | 0.7 | |
| S7 | 58.5 | 33.70 | 84.3 | 3.45 | 25.8 | |
| S13 | 37.0 | 14.80 | 52.5 | 1.86 | 15.5 | Middle western branch Segment |
| S14 | 31.2 | 11.70 | 44.4 | 1.46 | 13.2 | |
| S20 | 53.2 | 19.80 | 63.1 | 2.39 | 9.9 | Southern Segment |
| S18 | 48.2 | 22.40 | 67.8 | 2.63 | 19.6 | |
| S16 | 30.1 | 8.65 | 34.6 | 0.97 | 4.5 | |
| S15 | 40.0 | 16.50 | 56.4 | 2.06 | 16.4 | |
| S9 | 61.8 | 44.10 | 96.0 | 4.04 | 34.2 |
| Continuous Site | a (Xundian spring S7) | b (Panxi spring S16) | c (Qujiang spring S9) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date (yyyy/mm/dd) | Earthquake | Na+ | Cl- | SO42- | TDS | d | Na+ | Cl− | SO42− | TDS | d | Na+ | Cl− | SO42− | TDS | d |
| (Day) | (km) | (Day) | (km) | (Day) | (km) | |||||||||||
| 2021/6/10 | ML5.1 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 21 | 179.3 | - | 24 | 24 | 24 | 120.2 | - | 12 | 8 | 35 | 100.4 |
| 2020/7/8 | ML4.2 | - | - | - | - | 63.8 | 4 | 28 | 17 | - | 192.8 | - | - | - | - | 231.0 |
| 2020/1/15 | ML4.2 | 13 | - | 10 | - | 19.1 | - | 12 | - | - | 143.8 | - | - | - | - | 182.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Zhou, X.; Yan, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Liu, F. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs and Their Short-Term Seismic Precursor Anomalies along the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southeast Tibet Plateau. Water 2021, 13, 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192638
Li C, Zhou X, Yan Y, Ouyang S, Liu F. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs and Their Short-Term Seismic Precursor Anomalies along the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southeast Tibet Plateau. Water. 2021; 13(19):2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192638
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chenhua, Xiaocheng Zhou, Yucong Yan, Shupei Ouyang, and Fengli Liu. 2021. "Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs and Their Short-Term Seismic Precursor Anomalies along the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southeast Tibet Plateau" Water 13, no. 19: 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192638
APA StyleLi, C., Zhou, X., Yan, Y., Ouyang, S., & Liu, F. (2021). Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs and Their Short-Term Seismic Precursor Anomalies along the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southeast Tibet Plateau. Water, 13(19), 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192638





