Systematic Review of Flood and Drought Literature Based on Science Mapping and Content Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Using singular instead of plural (e.g., river instead of rivers);
- Using all caps or small caps (e.g., Climate Reanalysis, China);
- Choosing the abbreviated form (e.g., SPI instead of Standardized Precipitation Index; HDI instead of Human Development Index).
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Analysis of the Authors’ Keywords
3.1.1. Spatial Scale of Studies
3.1.2. Managing Risk
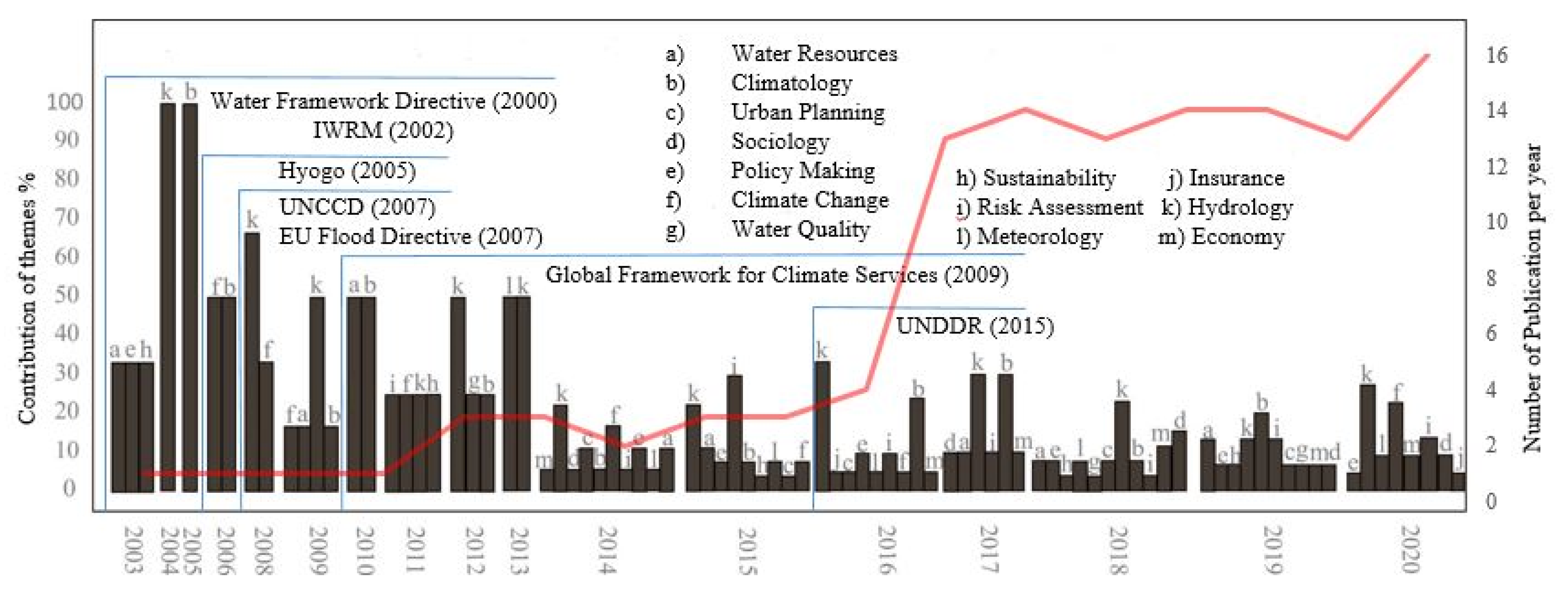
3.2. Analysis of the Research Themes
3.3. Methods and Indices Applied in Flood and Drought Research
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Best, J. Anthropogenic stresses on the world’s big rivers. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golnaraghi, M.; Surminski, S.; Mehryar, S.; Kousky, C.; Roezer, V. Building Flood Resilience in a Changing Climate. 2020. Available online: https://www.preventionweb.net/files/72437_buildingfloodresilienceinachangingc.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Van Loon, A.F.; Gleeson, T.; Clark, J.; Van Dijk, A.I.; Stahl, K.; Hannaford, J.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Teuling, A.J.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Uijlenhoet, R.; et al. Drought in the Anthropocene. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wens, M.; Johnson, J.M.; Zagaria, C.; Veldkamp, T.I. Integrating human behavior dynamics into drought risk assessment—A sociohydrologic, agent-based approach. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2019, 6, e1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindersson, S.; Brandimarte, L.; Mård, J.; Di Baldassarre, G. A review of freely accessible global datasets for the study of floods, droughts and their interactions with human societies. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2020, 7, e1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christenson, E.; Elliott, M.; Banerjee, O.; Hamrick, L.; Bartram, J. Climate-related hazards: A method for global assessment of urban and rural population exposure to cyclones, droughts, and floods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2169–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un.org. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/publications/world-urbanization-prospects-the-2011-revision.html (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Krysanova, V.; Buiteveld, H.; Haase, D.; Hattermann, F.F.; Van Niekerk, K.; Roest, K.; Martínez-Santos, P.; Schlüter, M. Practices and lessons learned in coping with climatic hazards at the river-basin scale: Floods and droughts. Ecol. Soc. 2008, 13, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinho, P.F.; Marengo, J.A.; Smith, M.S. Complex socio-ecological dynamics driven by extreme events in the Amazon. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.J.; de Ruiter, M.C.; Mård, J.; Schröter, K.; Van Loon, A.; Veldkamp, T.; von Uexkull, N.; Wanders, N.; AghaKouchak, A.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; et al. The need to integrate flood and drought disaster risk reduction strategies. Water Secur. 2020, 11, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreibich, H.; Blauhut, V.; Aerts, J.C.; Bouwer, L.M.; Van Lanen, H.A.; Mejia, A.; Mens, M.; Van Loon, A.F. How to improve attribution of changes in drought and flood impacts. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Baldassarre, G.; Wanders, N.; AghaKouchak, A.; Kuil, L.; Rangecroft, S.; Veldkamp, T.I.; Garcia, M.; van Oel, P.R.; Breinl, K.; Van Loon, A.F. Water shortages worsened by reservoir effects. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Baldassarre, G.; Martinez, F.; Kalantari, Z.; Viglione, A. Drought and flood in the Anthropocene: Feedback mechanisms in reservoir operation. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2015, 8, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marengo, J.A.; Alves, L.M.; Soares, W.R.; Rodriguez, D.A.; Camargo, H.; Riveros, M.P.; Pabló, A.D. Two contrasting severe seasonal extremes in tropical South America in 2012: Flood in Amazonia and drought in northeast Brazil. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 9137–9154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneralp, B.; Güneralp, İ.; Liu, Y. Changing global patterns of urban exposure to flood and drought hazards. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 31, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nation World Water Assessment Programme, 2009, Global Trends in Water-Related Disasters: An Insight for Folicymakers. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000181793 (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Brunner, M.I.; Slater, L.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Clark, M. Challenges in modeling and predicting floods and droughts: A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water. 2021, 8, e1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMartin, D.W.; Merino, B.H.H.; Bonsal, B.; Hurlbert, M.; Villalba, R.; Ocampo, O.L.; Upegui, J.J.V.; Poveda, G.; Sauchyn, D.J. Limitations of water resources infrastructure for reducing community vulnerabilities to extremes and uncertainty of flood and drought. Environ. Manage. 2018, 62, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Kwak, J.; Noh, H.S.; Kim, H.S. Evaluation of drought and flood risks in a multipurpose dam under climate change: A case study of Chungju Dam in Korea. Nat. Hazards 2014, 73, 1663–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, K.S.; Chung, E.S.; Sung, J.Y.; Lee, K.S. Development of spatial water resources vulnerability index considering climate change impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 5228–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Chun, H.; Song, J. New Strategies for Resilient Planning in response to Climate Change for Urban Development. Procedia Eng. 2018, 212, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Krysanova, V.; Hattermann, F. Projections of climate change impacts on floods and droughts in Germany using an ensemble of climate change scenarios. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassa, J.A.; Nugraha, E. Building Urban Resilience to Climate Change in the Secondary Cities in Indonesia; IRGSC: Kupang, Indonesia, 2014; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Masood, M.; Takeuchi, K. Climate Change Impact on the Manageability of Floods and Droughts of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna Basins Using Flood Duration Curves and Drought Duration Curves. J. Disaster Emerg. Res. 2015, 10, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhris, O.E.F. The impact of climate change on the hydrology in highly urbanised Belgian areas. In Water and Urban Development Paradigms; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Kanae, S.; Emori, S.; Oki, T.; Kimoto, M. Global projections of changing risks of floods and droughts in a changing climate. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 754–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, B.; Döll, P.; Alcamo, J.; Henrichs, T.; Kaspar, F. Estimating the impact of global change on flood and drought risks in Europe: A continental, integrated analysis. Clim. Chang. 2006, 75, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasham, C.F.; Korzenevica, M.; Charles, K.J. On considering climate resilience in urban water security: A review of the vulnerability of the urban poor in sub-Saharan Africa. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water. 2019, 6, e1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Head, B.W. Managing urban water crises: Adaptive policy responses to drought and flood in Southeast Queensland, Australia. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parasiewicz, P.; King, E.L.; Webb, J.A.; Piniewski, M.; Comoglio, C.; Wolter, C.; Buijse, A.D.; Bjerklie, D.; Vezza, P.; Melcher, A.; et al. The role of floods and droughts on riverine ecosystems under a changing climate. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2019, 26, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, N.T.; Vinh, N.Q. The notions of resilience in spatial planning for drought-flood coexistence (DFC) at regional scale. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 143, 012066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramyar, R.; Zarghami, E. Green infrastructure contribution for climate change adaptation in urban landscape context. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 1193–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelic, P.; Brindha, K.; Amarnath, G.; Eriyagama, N.; Muthuwatta, L.; Smakhtin, V.; Gangopadhyay, P.K.; Malik, R.P.S.; Mishra, A.; Sharma, B.R.; et al. Controlling Floods and Droughts Through Underground Storage: From Concept to Pilot Implementation in the Ganges River Basin; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Gujarat, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, M.M.G.T.; Kawasaki, A. Socioeconomic vulnerability to disaster risk: A case study of flood and drought impact in a rural Sri Lankan community. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 152, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markantonis, V.; Farinosi, F.; Dondeynaz, C.; Ameztoy, I.; Pastori, M.; Marletta, L.; Ali, A.; Carmona Moreno, C. Assessing floods and droughts in the Mékrou River basin (West Africa): A combined household survey and climatic trends analysis approach. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 1279–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bola Bosongo, G.; Ndembo Longo, J.; Goldin, J.; Lukanda Muamba, V. Socioeconomic impacts of floods and droughts in the middle Zambezi river basin. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2014, 6, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Doherty, M.; Coffee, J.; Wong, T.; Hellmann, J. Measuring the adaptation gap: A framework for evaluating climate hazards and opportunities in urban areas. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 66, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grobicki, A.; MacLeod, F.; Pischke, F. Integrated policies and practices for flood and drought risk management. Water Policy 2015, 17, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Weng, B.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, T.; Yan, D.; Ma, J. Evolution of drought–flood abrupt alternation and its impacts on surface water quality from 2020 to 2050 in the Luanhe River Basin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hrdinka, T.; Novický, O.; Hanslík, E.; Rieder, M. Possible impacts of floods and droughts on water quality. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2012, 6, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Li, N.; Wu, X. Threshold determination and hazard evaluation of the disaster about drought/flood sudden alternation in Huaihe River basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P.; Stults, M. Defining urban resilience: A review. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2016, 147, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, G.; Peduzzi, P. The PREVIEW Global Risk Data Platform: A geoportal to serve and share global data on risk to natural hazards. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Weng, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. Analysis of the Evolution of Drought, Flood, and Drought-Flood Abrupt Alternation Events under Climate Change Using the Daily SWAP Index. Water 2020, 12, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Networks: An Introduction; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Khirfan, L.; Mohtat, N.; Peck, M. A systematic literature review and content analysis combination to “shed some light” on stream daylighting (Deculverting). Water Secur. 2020, 10, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioana-Toroimac, G. Outcomes of the hydromorphology integration in the water framework directive: A review based on science mapping. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börner, K.; Chaomei, C.; Boyack, K. Visualizing Knowledge Domains. Annu. Rev. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 179–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Science Mapping: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veslava, O.; Malak, P. Maps and Mapping in Scientometrics. In Metody i Narzędzia BadaĔ Piśmiennictwa Cyfrowego i Jego Użytkowników [Methods and Tools for Researching Digital Writing and Its Users]; Góralska, M., Wandel, A., Eds.; Wrocław University: Wrocław, Poland, 2016; pp. 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. ‘Science Mapping Software Tools: Review, Analysis, and Cooperative Study among Tools’. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 62, 1382–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loet, L.; Goldstone, R.L. Interdisciplinary at the Journal and Specialty Level: The Changing Knowledge Bases of the Journal Cognitive Science. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2014, 65, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeman, L.C. Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc. Netw. 1987, 1, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodrich, M.; Tamassia, R.; Design, A. Foundations, Analysis, and Internet Examples; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mulrow, C.D. Systematic reviews: Rationale for systematic reviews. BMJ 1994, 309, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Lee, E.H. Reducing confusion about grounded theory and qualitative content analysis: Similarities and differences. Qual. Rep. 2014, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Page, C.P. Plan of Implementation of the World Summit on Sustainable Development. Sustain. Dev. 2002, 24, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Undrr.org. Available online: https://www.undrr.org/publication/hyogo-framework-action-2005-2015-building-resilience-nations-and-communities-disasters (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Unccd.int. Available online: https://www.unccd.int/sites/default/files/relevant-links/2017-01/Decision%203COP8%20adoption%20of%20The%20Strategy%20%281%29_0.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2021).



| Rank | Keyword | Degree | Keyword | Betweenness Centerality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Flood & Drought | 54 | Flood & Drought | 1413.917 |
| 2 | River Basin | 19 | River Basin | 126.833 |
| 3 | Climate Change | 10 | GDP | 34.250 |
| 4 | Exposure | 10 | ENSO | 18.083 |
| 5 | GRACE | 9 | tempo-spatial evolution | 18.083 |
| 6 | Resilience | 8 | HDI | 17.750 |
| 7 | Soil Moisture | 7 | States | 17.750 |
| 8 | ASCAT | 7 | Climate Change | 14.667 |
| 9 | Cyclone | 7 | ML | 12.750 |
| 10 | hazard events | 7 | PWM | 12.750 |
| Average Geodesic Distance | Average Clustering Coefficient | Graph Density | Average Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.66 | 0.935 | 0.06 | 7.19 |
| Rank | Method/Index | Degree | Method/Index | Betweenness Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Statistical Analysis | 30 | Statistical Analysis | 1874 |
| 2 | M-Kendall | 27 | M-Kendall | 1421.5 |
| 3 | RS | 23 | RS | 1081 |
| 4 | SPI | 17 | SPI | 901.5 |
| 5 | Hydrological Retrospective | 15 | Survey | 386 |
| 6 | MGB-IPH | 15 | SST | 158 |
| 7 | ERA-Interim | 15 | GEV | 24 |
| 8 | ERA20CM | 15 | HDI | 8 |
| 9 | CFSR | 15 | Hydrological Retrospective | 0 |
| 10 | JAR-55 | 15 | MGB-IPH | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fasihi, S.; Lim, W.Z.; Wu, W.; Proverbs, D. Systematic Review of Flood and Drought Literature Based on Science Mapping and Content Analysis. Water 2021, 13, 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192788
Fasihi S, Lim WZ, Wu W, Proverbs D. Systematic Review of Flood and Drought Literature Based on Science Mapping and Content Analysis. Water. 2021; 13(19):2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192788
Chicago/Turabian StyleFasihi, Siavash, Wen Zyn Lim, Wenyan Wu, and David Proverbs. 2021. "Systematic Review of Flood and Drought Literature Based on Science Mapping and Content Analysis" Water 13, no. 19: 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192788
APA StyleFasihi, S., Lim, W. Z., Wu, W., & Proverbs, D. (2021). Systematic Review of Flood and Drought Literature Based on Science Mapping and Content Analysis. Water, 13(19), 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192788







