Fish Response to Multiple Anthropogenic Stressors in Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: A Comparative Study of the Role of Different Management Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Fish Data
2.2.2. Anthropogenic Pressures
2.2.3. Multi-Metric Index Development
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthropogenic Pressures
3.2. Fish Assemblages of the Circeo Coastal Lagoons
3.2.1. Composition of Fish Assemblage
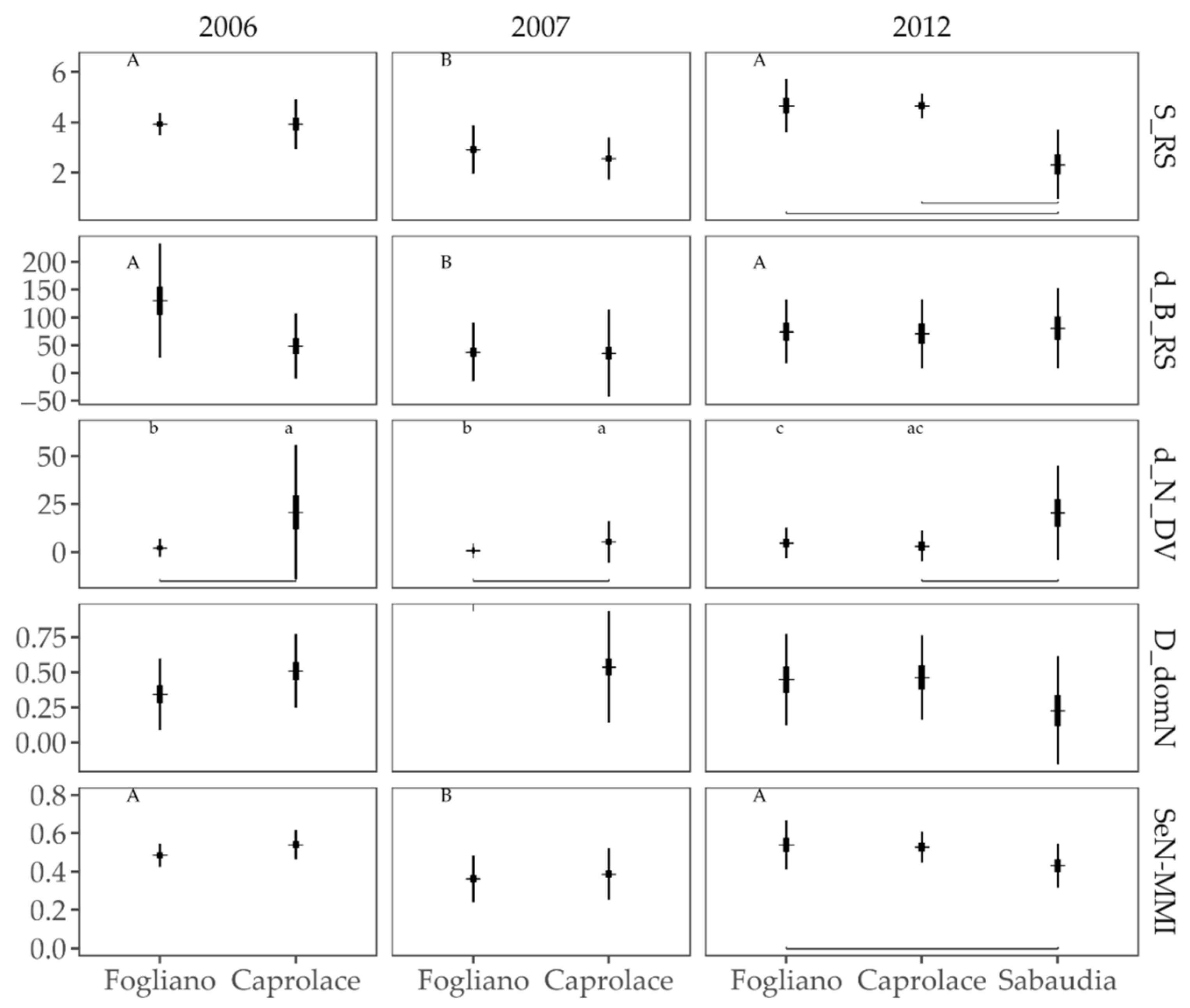
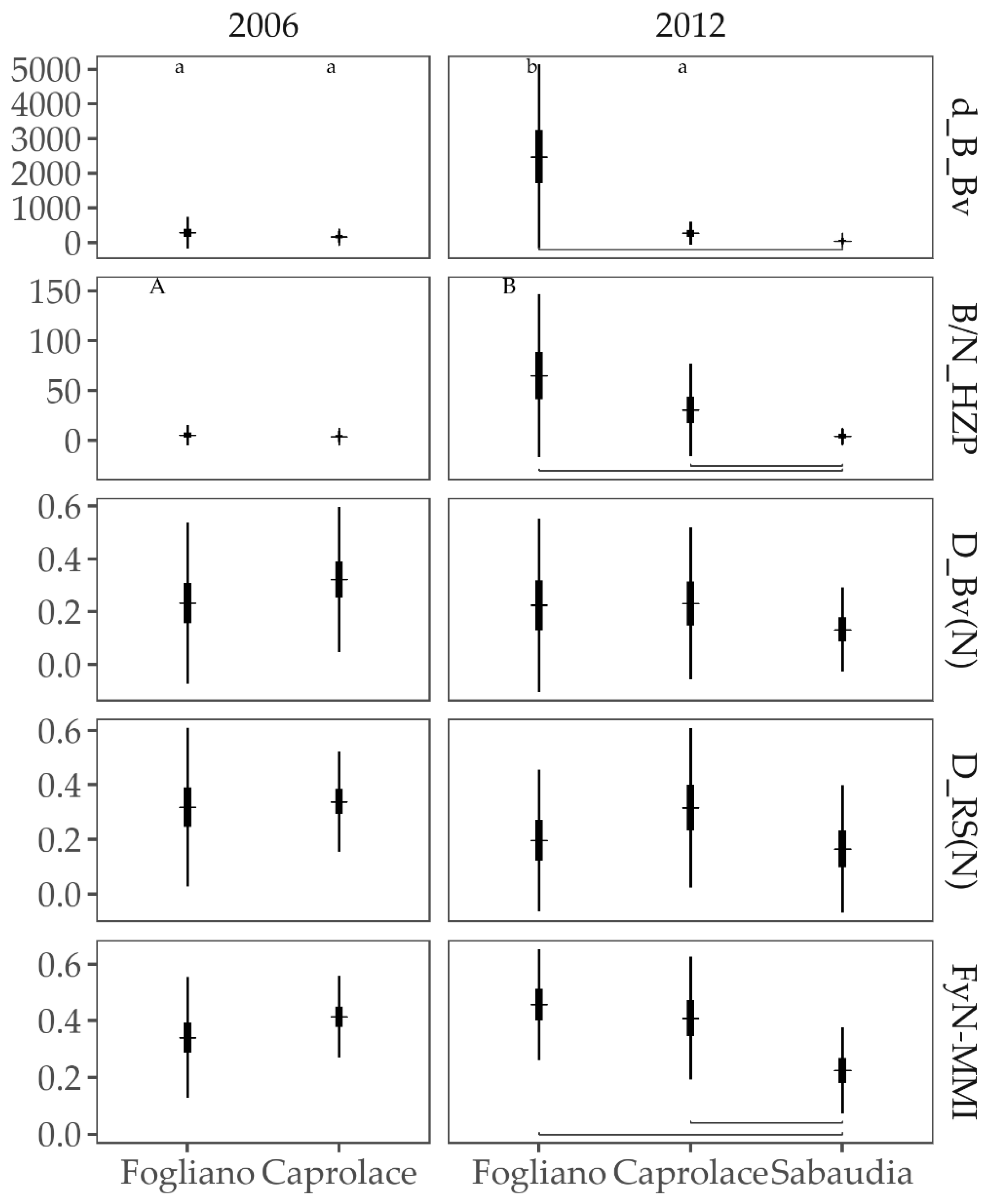
3.2.2. Multi-Metric Indices
3.2.3. Responses to the Anthropogenic Pressures
3.2.4. Comparison of Fish Assemblages among Lagoons and Years
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Newton, A.; Marcos, C. Coastal Lagoons: Environmental Variability, Ecosystem Complexity, and Goods and Services Uniformity. In Coasts and Estuaries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 253–276. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.; Day, J.W.; Ramachandran, R.; Wolanski, E. A synthesis: What is the future for coasts, estuaries, deltas and other transitional habitats in 2050 and beyond? In Coasts and Estuaries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, A.; Icely, J.; Cristina, S.; Brito, A.; Cardoso, A.C.; Colijn, F.; Riva, S.D.; Gertz, F.; Hansen, J.W.; Holmer, M.; et al. An overview of ecological status, vulnerability and future perspectives of European large shallow, semi-enclosed coastal systems, lagoons and transitional waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 140, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.; Brito, A.C.; Icely, J.D.; Derolez, V.; Clara, I.; Angus, S.; Schernewski, G.; Inácio, M.; Lillebø, A.I.; Sousa, A.I.; et al. Assessing, quantifying and valuing the ecosystem services of coastal lagoons. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 44, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, R.P.; Batista, M.I.; Henriques, S. Current limitations of global conservation to protect higher vulnerability and lower resilience fish species. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichert, N.; Lepage, M.; Lobry, J. Beyond classic ecological assessment: The use of functional indices to indicate fish Assemblages sensitivity to human disturbance in estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EU Water Framework Directive. Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council 2000/60/EC Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, 327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Domínguez, R.; Maci, S.; Courrat, A.; Lepage, M.; Borja, A.; Uriarte, A.; Neto, J.M.; Cabral, H.; Raykov, V.S.; Franco, A.; et al. Current developments on fish-based indices to assess ecological-quality status of estuaries and lagoons. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, G.B.G.; Vianna, M. Fish-based indices for assessing ecological quality and biotic integrity in transitional waters: A systematic review. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R. Assessment of Biotic Integrity Using Fish Communities. Fish. Mag. 1981, 6, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R.; Fausch, K.D.; Angermeier, P.L.; Yant, P.R.; Schlosser, I.J. Assessing biological integrity in running waters: A method and its rationale. Ill. Nat. Hist. Surv. Spec. Publ. 1986, 5, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, H.N.; Fonseca, V.F.; Gamito, R.; Gonçalves, C.I.; Costa, J.L.; Erzini, K.; Gonçalves, J.; Martins, J.; Leite, L.; Andrade, J.P.; et al. Ecological quality assessment of transitional waters based on fish assemblages in Portuguese estuaries: The Estuarine Fish Assessment Index (EFAI). Ecol. Indic. 2012, 19, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, F.; Nyitrai, D.; Crespo, D.; Pardal, M.A. Efficacy of single and multi-metric fish-based indices in tracking anthropogenic pressures in estuaries: An 8-year case study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoolmaster, D.R.; Grace, J.B.; Schweiger, E.W. A general theory of multimetric indices and their properties. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpech, C.; Courrat, A.; Pasquaud, S.; Lobry, J.; Le Pape, O.; Nicolas, D.; Boët, P.; Girardin, M.; Lepage, M. Development of a fish-based index to assess the ecological quality of transitional waters: The case of French estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, V.F.; Vasconcelos, R.P.; Gamito, R.; Pasquaud, S.; Gonçalves, C.I.; Costa, J.L.; Costa, M.J.; Cabral, H.N. Fish community-based measures of estuarine ecological quality and pressure–impact relationships. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 134, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capoccioni, F.; Leone, C.; Belpaire, C.; Malarvannan, G.; Poma, G.; De Matteis, G.; Tancioni, L.; Contò, M.; Failla, S.; Covaci, A.; et al. Quality assessment of escaping silver eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) to support management and conservation strategies in Mediterranean coastal lagoons. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, C.; Capoccioni, F.; Belpaire, C.; Malarvannan, G.; Poma, G.; Covaci, A.; Tancioni, L.; Contò, M.; Ciccotti, E. Evaluation of environmental quality of Mediterranean coastal lagoons using persistent organic pollutants and metals in thick-lipped grey mullet. Water 2020, 12, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Torricelli, P.; Franzoi, P. A habitat-specific fish-based approach to assess the ecological status of Mediterranean coastal lagoons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1704–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchetta, M.; Scapin, L.; Cavraro, F.; Pranovi, F.; Franco, A.; Franzoi, P. Can the Effects of Anthropogenic Pressures and Environmental Variability on Nekton Fauna Be Detected in Fishery Data? Insights from the Monitoring of the Artisanal Fishery Within the Venice Lagoon. Estuaries Coasts 2016, 39, 1164–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchetta, M.; Scapin, L.; Franco, A.; Franzoi, P. Uncertainty in developing fish based multi-metric indices. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavraro, F.; Bettoso, N.; Zucchetta, M.; D’Aietti, A.; Faresi, L.; Franzoi, P. Body condition in fish as a tool to detect the effects of anthropogenic pressures in transitional waters. Aquat. Ecol. 2019, 53, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, A.; Borja, A. Assessing fish quality status in transitional waters, within the European Water Framework Directive: Setting boundary classes and responding to anthropogenic pressures. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, M.; Harrison, T.; Breine, J.; Cabral, H.; Coates, S.; Galván, C.; García, P.; Jager, Z.; Kelly, F.; Mosch, E.C.; et al. An approach to intercalibrate ecological classification tools using fish in transitional water of the North East Atlantic. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poikane, S.; Zampoukas, N.; Borja, A.; Davies, S.P.; van de Bund, W.; Birk, S. Intercalibration of aquatic ecological assessment methods in the European Union: Lessons learned and way forward. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 44, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapin, L.; Zucchetta, M.; Facca, C.; Sfriso, A.; Franzoi, P. Using fish assemblage to identify success criteria for seagrass habitat restoration. Web Ecol. 2016, 16, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Catalano, B.; Penna, M.; Riccato, F.; Fiorin, R.; Franceschini, G.; Antonini, C.; Zucchetta, M.; Cicero, A.M.; Franzoi, P. Manuale per la Classificazione dell’Elemento di Qualità Biologica “Fauna Ittica” Nelle Lagune Costiere Italiane; Applicazione Dell’indice Nazional HFBI (Habitat Fish Bio-Indicator) ai Sensi del D. Lgs 152/2006; ISPRA: Roma, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, A.; Franzoi, P.; Malavasi, S.; Riccato, F.; Torricelli, P. Fish assemblages in different shallow water habitats of the Venice Lagoon. In Marine Biodiversity; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 159–174. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, A.; Franzoi, P.; Torricelli, P. Structure and functioning of Mediterranean lagoon fish assemblages: A key for the identification of water body types. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataudella, S.; Crosetti, D.; Ciccotti, E.; Massa, F. Sustainable management in Mediterranean coastal lagoons: Interactions among capture fisheries, aquaculture and environment. In Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: Sustainable Management and Interactions Among Aquaculture, Capture Fisheries and Environment; Cataudella, S., Crosetti, D., Massa, F., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 7–49. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.rewetland.eu/life/news/150423_final_report_ITA.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2020).
- Manzo, C. Fish Assemblages in Three Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: Structure, Functioning and Spatial-Temporal Dynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Rome “Tor Vergata”, Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, C. Fish Assemblages as Sensitive Tools in Describing Ecological Change in Coastal Lagoons, with Focus on the Role of European Eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) as a Qualifying Species in These Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Rome “Tor Vergata”, Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, I.C.; Tweedley, J.R.; Elliott, M.; Whitfield, A.K. The ways in which fish use estuaries: A refinement and expansion of the guild approach. Fish Fish. 2015, 16, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, A.; Elliott, M. The use of environmental integrative indicators to assess seabed disturbance in estuaries and coasts: Application to the Humber Estuary, UK. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 53, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.D.; Whitfield, A.K. A multi-metric fish index to assess the environmental condition of estuaries. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 65, 683–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjerfve, B. Chapter 1 Coastal Lagoons. In Elsevier Oceanography Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarin, C.; Zaggia, L.; Paschini, E.; Scirocco, T.; Lorenzetti, G.; Bajo, M.; Penna, P.; Francavilla, M.; D’Adamo, R.; Guerzoni, S. Hydrological Regime and Renewal Capacity of the Micro-tidal Lesina Lagoon, Italy. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, P.; Ghiozzi, E.; Malatesta, A.; Zarlenga, F. Seminario Informativo Sui Risultati Del Progetto “Laghi Costieri”; Edizione Università Degli Studi “La Sapienza” Di Roma-Provincia Di Latina: Terracina, Italy, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gardi, C.; Bosco, C.; Rusco, E.; Montanerella, L. An analysis of the Land Use Sustainability Index (LUSI) at territorial scale based on Corine Land Cover. Manag. Environ. Qual. 2010, 21, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, B.S.; Noon, B.R. A gentle introduction to quantile regression for ecologists. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 1, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian Hartig (DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level Mixed) Regression Models. R Package Version 0.3.3.0. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.project.org/package=DHARM (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Lenth, R.V. Least-Squares Means: The R Package lsmeans. J. Stat. Softw. Found. Open Access Stat. 2016, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoolmaster, D.R.; Grace, J.B.; Schweiger, E.W.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Mitchell, B.R.; Miller, K.M.; Little, A.M. An algorithmic and information-theoretic approach to multimetric index construction. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 26, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, Á.; Franco, J.; Valencia, V.; Bald, J.; Muxika, I.; Jesús Belzunce, M.; Solaun, O. Implementation of the European water framework directive from the Basque country (northern Spain): A methodological approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoolmaster, D.R.; Grace, J.B.; Schweiger, E.W.; Mitchell, B.R.; Guntenspergen, G.R. A causal examination of the effects of confounding factors on multimetric indices. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breine, J.J.; Maes, J.; Quataert, P.; Van den Bergh, E.; Simoens, I.; Van Thuyne, G.; Belpaire, C. A fish-based assessment tool for the ecological quality of the brackish Schelde estuary in Flanders (Belgium). Hydrobiologia 2007, 575, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Drouineau, H.; Franzoi, P.; Koutrakis, E.T.; Lepage, M.; Verdiell-Cubedo, D.; Bouchoucha, M.; López-Capel, A.; Riccato, F.; et al. Assessment of fish assemblages in coastal lagoon habitats: Effect of sampling method. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 112, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, S.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Brucet, S.; Courrat, A.; Poikane, S.; Solimini, A.; van de Bund, W.; Zampoukas, N.; Hering, D. Three hundred ways to assess Europe’s surface waters: An almost complete overview of biological methods to implement the Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontolan, G.; Pillon, S.; Bezzi, A.; Villalta, R.; Lipizer, M.; Triches, A.; D’Aietti, A. Human impact and the historical transformation of saltmarshes in the Marano and Grado Lagoon, northern Adriatic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, C.; Umgiesser, G.; Roland, A.; Bajo, M.; De Pascalis, F.; Ghezzo, M.; Scroccaro, I. Sediment dynamics and budget in a microtidal lagoon—A numerical investigation. Mar. Geol. 2016, 381, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaroli, E.; Guerzoni, S.; Sarretta, A.; Masiol, M.; Pistolato, M. Thirty-year changes (1970 to 2000) in bathymetry and sediment texture recorded in the Lagoon of Venice sub-basins, Italy. Mar. Geol. 2009, 258, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarretta, A.; Pillon, S.; Molinaroli, E.; Guerzoni, S.; Fontolan, G. Sediment budget in the Lagoon of Venice, Italy. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 934–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umgiesser, G.; Ferrarin, C.; Cucco, A.; De Pascalis, F.; Bellafiore, D.; Ghezzo, M.; Bajo, M. Comparative hydrodynamics of 10 Mediterranean lagoons by means of numerical modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 2212–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Marcos, C. Fisheries in coastal lagoons: An assumed but poorly researched aspect of the ecology and functioning of coastal lagoons. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 110, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, C.; Torres, I.; López-Capel, A.; Pérez-Ruzafa, A. Long term evolution of fisheries in a coastal lagoon related to changes in lagoon ecology and human pressures. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 689–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranovi, F.; Link, J.S. Ecosystem exploitation and trophodynamic indicators: A comparison between the Northern Adriatic Sea and Southern New England. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 81, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.; Whitfield, A.K.; Potter, I.C.; Blaber, S.J.M.; Cyrus, D.P.; Nordlie, F.G.; Harrison, T.D. The guild approach to categorizing estuarine fish assemblages: A global review. Fish. Fish. 2007, 8, 241–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Fernández, A.I.; Marcos, C.; Gilabert, J.; Quispe, J.I.; García-Charton, J.A. Spatial and temporal variations of hydrological conditions, nutrients and chlorophyll a in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, Spain). Hydrobiologia 2005, 550, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranford, P.J.; Hargrave, B.T.; Doucette, L.I. Benthic organic enrichment from suspended mussel (Mytilus edulis) culture in Prince Edward Island, Canada. Aquaculture 2009, 292, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartstein, N.D.; Stevens, C.L. Deposition beneath long-line mussel farms. Aquac. Eng. 2005, 33, 192–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardi, D. Effects of Bivalve Aquaculture on the Environment and Their Possible Mitigation: A Review. Fish. Aquac. J. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.I. Ecosystem influences of natural and cultivated populations of suspension-feeding bivalve molluscs: A review. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ardizzone, G.D.; Cataudella, S.; Rossi, R. Management of Coastal Lagoon Fisheries and Aquaculture in Italy; FAO Fisher.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Mompeán, M.C.; Marcos, C. Hydrographic, geomorphologic and fish assemblage relationships in coastal lagoons. In Lagoons and Coastal Wetlands in the Global Change Context: Impacts and Management Issues; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 107–125. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; De Pascalis, F.; Ghezzo, M.; Quispe-Becerra, J.I.; Hernández-García, R.; Muñoz, I.; Vergara, C.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Umgiesser, G.; Marcos, C. Connectivity between coastal lagoons and sea: Asymmetrical effects on assemblages’ and populations’ structure. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 216, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Oliva, M.; Pérez-Ruzafa, Á.; Umgiesser, G.; McKiver, W.; Ghezzo, M.; De Pascalis, F.; Marcos, C. Assessing the Hydrodynamic Response of the Mar Menor Lagoon to Dredging Inlets Interventions through Numerical Modelling. Water 2018, 10, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale (ARPA) della Regione Lazio. Available online: http://www.arpalazio.gov.it/ambiente/acqua/dati.htm# (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- LegAmbiente Lazio. Available online: https://www.legambientelazio.it/goletta-dei-laghi-2018-presenta-i-risultati-nel-lazio/ (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- De Wit, R.; Mostajir, B.; Troussellier, M.; Do Chi, T. Environmental Management and Sustainable Use of Coastal Lagoons Ecosystems. In Lagoons: Biology Management and Environmental Impact Series; Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 333–350. [Google Scholar]
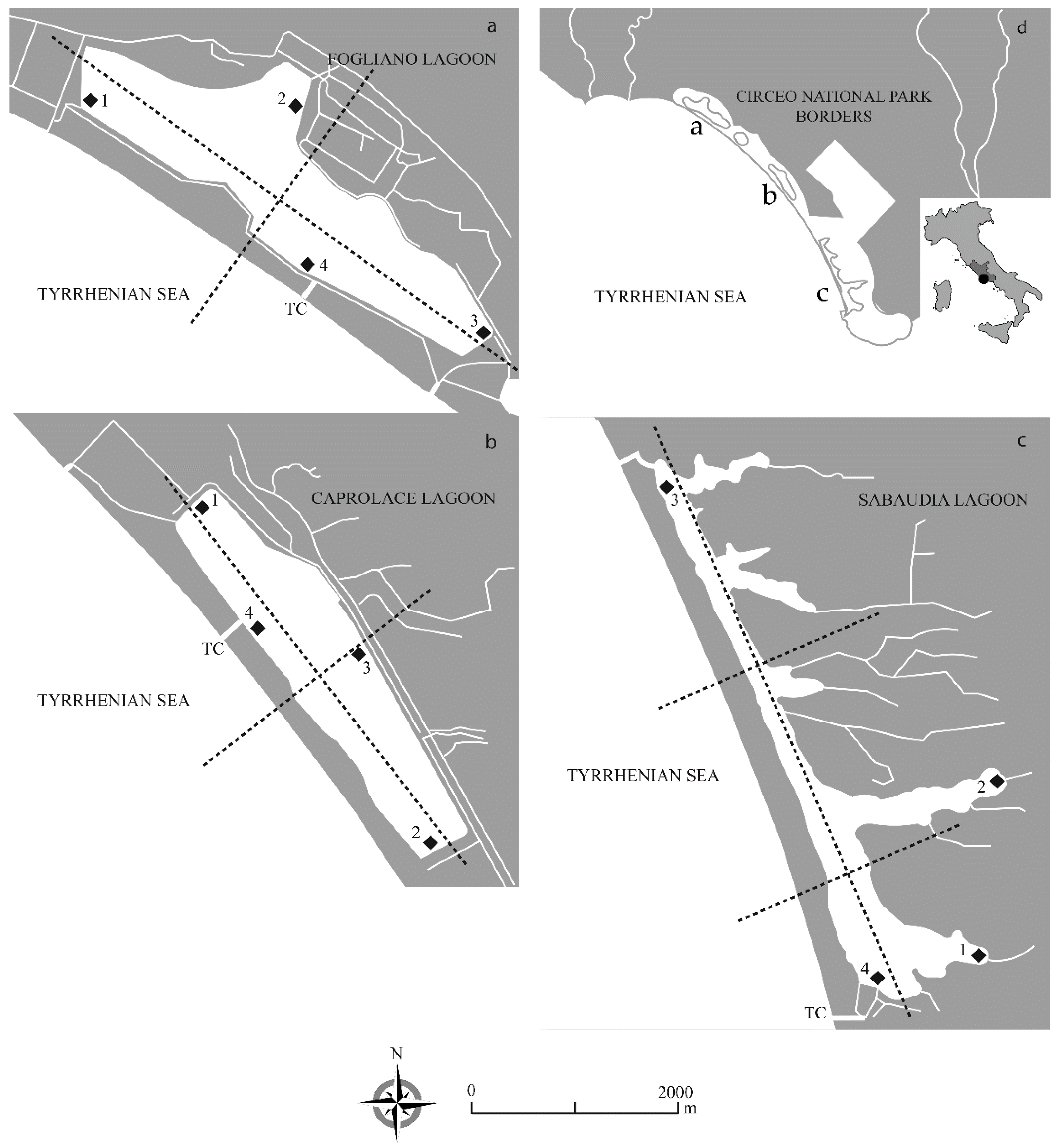



| Fogliano | Caprolace | Sabaudia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | 41°24’ | 41°21′ | 41°16′ |
| Longitude | 12°54′ | 12°58′ | 13°02′ |
| Perimeter (km) | 11.2 | 8.4 | 20.1 |
| Surface (ha) | 404 | 226 | 400 |
| Max depth (m) | 2.0 | 2.9 | 10.0 |
| Mean depth (m) | 0.9 | 1.3 | 4.5 |
| Volume (m3) | 3,616,000 | 2,923,783 | 14,000,000 |
| Inlet (n) | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Tributary (n) | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Tidal range (m) | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.20 |
| Water exchange rate (days) | 60 | 90 | 300 |
| Average water temperature (°C) | 20.3 | 19.4 | 23.5 |
| Average salinity (PSU) | 40.6 | 39.1 | 28.9 |
| Year | Gear | Season | FOG | CAP | SAB | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | SeN | WIN-SPR-SUM-AUT | * | * | - | [33] |
| FyN | WIN-SPR-SUM-AUT | * | * | - | ||
| 2007 | SeN | WIN-SPR-SUM-AUT | * | * | - | [33] |
| FyN | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2012 | SeN | SPR-SUM-AUT | * | * | * | [34]; present study |
| FyN | SPR-SUM-AUT | * | * | * |
| Pressure Category | Indicator | Periodicity of Evaluation | Dimension of Evaluation | Reference | Source of Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPI Morphology | EXCHANGE—Geomorphic types according to mean water renewal time | Fixed in time | Whole lagoon | [4,38,39] | [40] |
| BANKS—Percentage of natural banks | Fixed in time | Sectors | Modified after [25]; [23] | Field observations; GIS instruments | |
| INLET—Status and efficiency | Fixed in time | Whole lagoon | Expert judgment | Field observations; [40]; Consorzio Bonifica, personal communication, 2013 | |
| FW SUPPLY—Surface freshwater tributaries | Fixed in time | Sectors | Expert judgment | Present study; Consorzio Bonifica, personal communication, 2013 | |
| CPI Use | LANDSCAPE—Percentage of anthropogenically affected land | Fixed in time | Sectors | [41] | Present study; Corine Land Cover |
| AQUACULTURE—Mussel farming | Annual | Sectors | Expert judgment | Present study | |
| FISHERY—Fyke net density | Annual | Whole lagoon | Modified after [22,23] | Present study; National Fisheries Data Collection (2007–2012) | |
| FIXED BARRIER—Closed months per year | Annual | Whole lagoon | Expert judgment | Present study; National Fisheries Data Collection (2007–2012) | |
| CPI Quality | DO—Dissolved Oxygen | Seasonal | Whole lagoon | Legislative Decree (L.D.) no. 152/06 [24] | Agenzia Regionale Protezione Ambientale (ARPA) Lazio data set (2005–2012) |
| Chl-a—Chlorophyll | Seasonal | Whole lagoon | L.D. no. 152/06 | ARPA Lazio data set (2005–2012) | |
| DIN—Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen | Seasonal | Whole lagoon | L.D. no. 152/06 | ARPA Lazio data set (2005–2012) | |
| RP—Reactive Phosphorus | Seasonal | Whole lagoon | L.D. no. 152/06 | ARPA Lazio data set (2005–2012) |
| Species | HUFG | FMFG | 2006 | 2007 | 2012 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOG | CAP | FOG | CAP | FOG | CAP | SAB | |||
| Anguilla anguilla | C | BMa,HP | ✓ | -/7 | -/5 | ✓ | |||
| Gambusia affinis * | F | OV | ✓ | ||||||
| Aphanius fasciatus | RS | OV | 22/20 | 11/5 | 62/43 | 22/13 | 46/45 | 41/41 | ✓ |
| Atherina boyeri | RS | HZ | 66/74 | 24/3 | 26/26 | 30/30 | 23/32 | 44/48 | 89/57 |
| Gobius cobitis | RS | Bmi,BMa,HZ | |||||||
| Gobius niger | RS | Bmi,BMa,HZ | ✓ | -/6 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Knipowitschia panizzae | RS | Bmi,HZ | 4/ | ✓ | ✓ | 12/3 | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Nerophis ophidion | RS | Bmi,HZ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Salaria pavo | RS | Bmi,OV | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Syngnathus abaster | RS | Bmi,HZ | ✓ | 14/7 | ✓ | 6/- | 6/- | 7/- | ✓ |
| Aphia minuta | MM | PL | ✓ | ||||||
| Chelon labrosus | MM | OV,DV | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Dicentrarchus labrax | MM | HZ,HP | ✓ | 4/- | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Diplodus annularis | MM | Bmi,BMa,HZ | ✓ | 4/- | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Diplodus puntazzo | MM | OV | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Diplodus sargus | MM | OV | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Diplodus vulgaris | MM | Bmi,BMa,HZ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Engraulis encrasicolus | MM | PL | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Liza aurata | MM | OV,DV | ✓ | 6/22 | 3/- | ✓ | -/4 | 7/33 | |
| Liza ramada | MM | OV,DV | ✓ | 23/17 | ✓ | 13/4 | ✓ | -/3 | |
| Liza saliens | MM | OV,DV | ✓ | 4/4 | -/19 | 17/26 | 3/- | -/3 | ✓ |
| Mugil cephalus | MM | OV,DV | ✓ | 3/- | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Solea solea | MM | Bmi,BMa | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Sparus aurata | MM | Bmi,BMa,HZ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Apogon imberbis | MS | ||||||||
| Belone belone | MS | HP | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Dentex dentex | MS | ||||||||
| Epinephelus marginatus | MS | ||||||||
| Hippocampus guttulatus | MS | Bmi,HZ | |||||||
| Lithognathus mormyrus | MS | Bmi,BMa,HZ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Mullus barbatus | MS | Bmi,BMa | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Mullus surmuletus | MS | ||||||||
| Pagellus acarnae | MS | Bmi,BMa | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Parablennius sanguinolentus | MS | HV | ✓ | ||||||
| Sardina pilchardus | MS | PL | -/7 | ||||||
| Sarpa salpa | MS | Bmi,HV | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Sciaena umbra | MS | HP | |||||||
| Scorpaena porcus | MS | BMa,HP | ✓ | ||||||
| Serranus cabrilla | MS | BMa,HP | ✓ | ||||||
| Spicara maena | MS | HZ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Symphodus tinca | MS | Bmi,BMa | -/12 | ||||||
| Trachinotus ovatus | MS | Bmi,BMa | ✓ | ||||||
| Species | HUFG | FMFG | 2006 | 2012 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOG | CAP | FOG | CAP | SAB | |||
| Anguilla anguilla | C | BMa,HP | /43 | /46 | 10/81 | 6/85 | /7 |
| Gambusia affinis * | F | OV | |||||
| Aphanius fasciatus | RS | OV | 28/25 | 12/ | 25/ | 52/6 | ✓ |
| Atherina boyeri | RS | HZ | 70/30 | 78/36 | 46/ | 35/ | 97/72 |
| Gobius cobitis | RS | Bmi,BMa,HZ | ✓ | ||||
| Gobius niger | RS | Bmi,BMa,HZ | ✓ | /8 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Knipowitschia panizzae | RS | Bmi,HZ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Nerophis ophidion | RS | Bmi,HZ | |||||
| Salaria pavo | RS | Bmi,OV | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Syngnathus abaster | RS | Bmi,HZ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Aphia minuta | MM | PL | |||||
| Chelon labrosus | MM | OV,DV | ✓ | ||||
| Dicentrarchus labrax | MM | HZ,HP | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Diplodus annularis | MM | Bmi,BMa,HZ | ✓ | ✓ | 11/13 | ✓ | /5 |
| Diplodus puntazzo | MM | OV | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Diplodus sargus | MM | OV | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Diplodus vulgaris | MM | Bmi,BMa,HZ | |||||
| Engraulis encrasicolus | MM | PL | ✓ | ||||
| Liza aurata | MM | OV,DV | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Liza ramada | MM | OV,DV | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Liza saliens | MM | OV,DV | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Mugil cephalus | MM | OV,DV | |||||
| Solea solea | MM | Bmi,BMa | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Sparus aurata | MM | Bmi,BMa,HZ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Apogon imberbis | MS | ✓ | |||||
| Belone belone | MS | HP | ✓ | ||||
| Dentex dentex | MS | ✓ | |||||
| Epinephelus marginatus | MS | ✓ | |||||
| Hippocampus guttulatus | MS | Bmi,HZ | ✓ | ||||
| Lithognathus mormyrus | MS | Bmi,BMa,HZ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Mullus barbatus | MS | Bmi,BMa | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Mullus surmuletus | MS | ✓ | |||||
| Pagellus acarnae | MS | Bmi,BMa | ✓ | ||||
| Sardina pilchardus | MS | PL | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Sarpa salpa | MS | Bmi,HV | ✓ | ||||
| Sciaena umbra | MS | HP | ✓ | ✓ | /3 | ||
| Scorpaena porcus | MS | BMa,HP | /5 | ||||
| Serranus cabrilla | MS | BMa,HP | ✓ | ||||
| Spicara maena | MS | HZ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Symphodus tinca | MS | Bmi,BMa | ✓ | ||||
| Trachinotus ovatus | MS | Bmi,BMa | ✓ | ||||
| Pressures | SeN-MMI | FyN-MMI | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeN-MMI | FyN-MMI | S_RS | D_domN | d_N_DV | d_B_RS | D_RS(N) | d_B_Bv | B/N_HZP | D_Bv(N) | |
| Exchange | −0.000 | −0.345 ** | −0.224 ** | −0.183 * | 0.258 ** | 0.094 | −0.199 | −0.182 | −0.163 | −0.171 |
| Banks | −0.067 | 0.164 | 0.141 | 0.050 | −0.224 ** | −0.073 | 0.040 | 0.362 ** | 0.198 | 0.231 |
| Inlet | −0.089 | 0.087 | 0.146 | −0.066 | −0.263 *** | 0.100 | −0.026 | 0.373 ** | 0.209 | −0.016 |
| FW supply | −0.114 | 0.000 | 0.036 | 0.033 | −0.176 * | −0.060 | −0.059 | 0.134 | 0.140 | 0.039 |
| CPI Morphology | −0.112 | 0.013 | 0.082 | −0.005 | −0.214 ** | −0.034 | −0.071 | 0.305 * | 0.184 | 0.105 |
| Aquaculture | −0.011 | −0.323 ** | −0.192 * | −0.143 | 0.216 ** | 0.107 | −0.180 | 0.153 | −0.131 | −0.175 |
| Fishery | −0.077 | −0.318 ** | −412 *** | −0.072 | 0.325 *** | −0.034 | −0.124 | −0.303 * | −0.304 * | −0.093 |
| Barrier | −0.326 *** | −0.375 ** | -0.236 ** | 0.111 | −0.069 | −0.316 *** | −0.167 | −0.244 * | −0.252 * | −0.211 |
| Landscape | −0.117 | −0.105 | −0.050 | −0.032 | −0.082 | −0.100 | −0.114 | −0.084 | 0.101 | −0.085 |
| CPI Use | −0.277 *** | −0.482 *** | −361 *** | −0.027 | 0.090 | −0.215 ** | −0.257 * | −0.350 ** | −0.239 * | −0.243 * |
| DO | −0.181 * | −0.248 * | −0.103 | −0.184 * | −0.024 | −0.086 | −0.227 | −0.001 | −0.040 | −0.092 |
| Chl-a | 0.059 | −0.020 | 0.040 | −0.125 | 0.035 | 0.147 | −0.043 | 0.164 | 0.144 | −0.147 |
| DIN | −0.076 | −0.236 | −0.239 ** | −0.175 * | 0.263 *** | −0.006 | −0.218 | −0.017 | 0.086 | −0.268 * |
| RP | −0.271 *** | 0.006 | −0.143 | 0.096 | −0.145 | −0.164 * | 0.174 | −0.066 | −0.113 | 0.026 |
| CPI Quality | −0.133 | −0.188 | −0.126 | −0.190 * | 0.054 | −0.001 | −0.163 | 0.066 | 0.068 | −0.193 |
| Pressure Index | −0.270 *** | −0.354 ** | −0.200 * | −0.110 | −0.049 | −0.129 | −0.264 * | 0.007 | 0.005 | −0.179 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zucchetta, M.; Capoccioni, F.; Franzoi, P.; Ciccotti, E.; Leone, C. Fish Response to Multiple Anthropogenic Stressors in Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: A Comparative Study of the Role of Different Management Strategies. Water 2021, 13, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020130
Zucchetta M, Capoccioni F, Franzoi P, Ciccotti E, Leone C. Fish Response to Multiple Anthropogenic Stressors in Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: A Comparative Study of the Role of Different Management Strategies. Water. 2021; 13(2):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020130
Chicago/Turabian StyleZucchetta, Matteo, Fabrizio Capoccioni, Piero Franzoi, Eleonora Ciccotti, and Chiara Leone. 2021. "Fish Response to Multiple Anthropogenic Stressors in Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: A Comparative Study of the Role of Different Management Strategies" Water 13, no. 2: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020130
APA StyleZucchetta, M., Capoccioni, F., Franzoi, P., Ciccotti, E., & Leone, C. (2021). Fish Response to Multiple Anthropogenic Stressors in Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: A Comparative Study of the Role of Different Management Strategies. Water, 13(2), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020130







