Natural Organic Matter Removal from Raw Surface Water: Benchmarking Performance of Chemical Coagulants through Excitation-Emission Fluorescence Matrix Spectroscopy Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Raw Surface Water
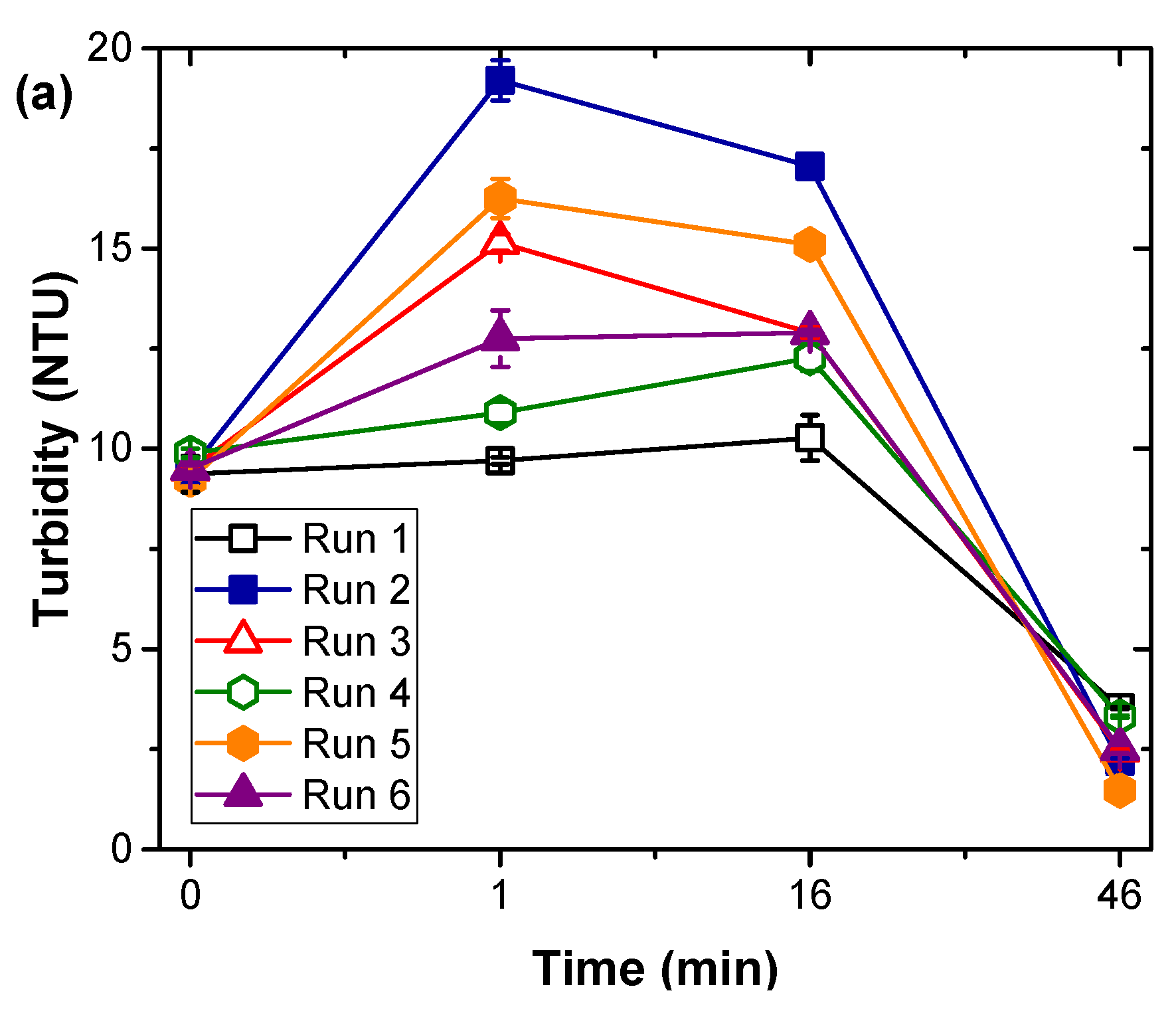
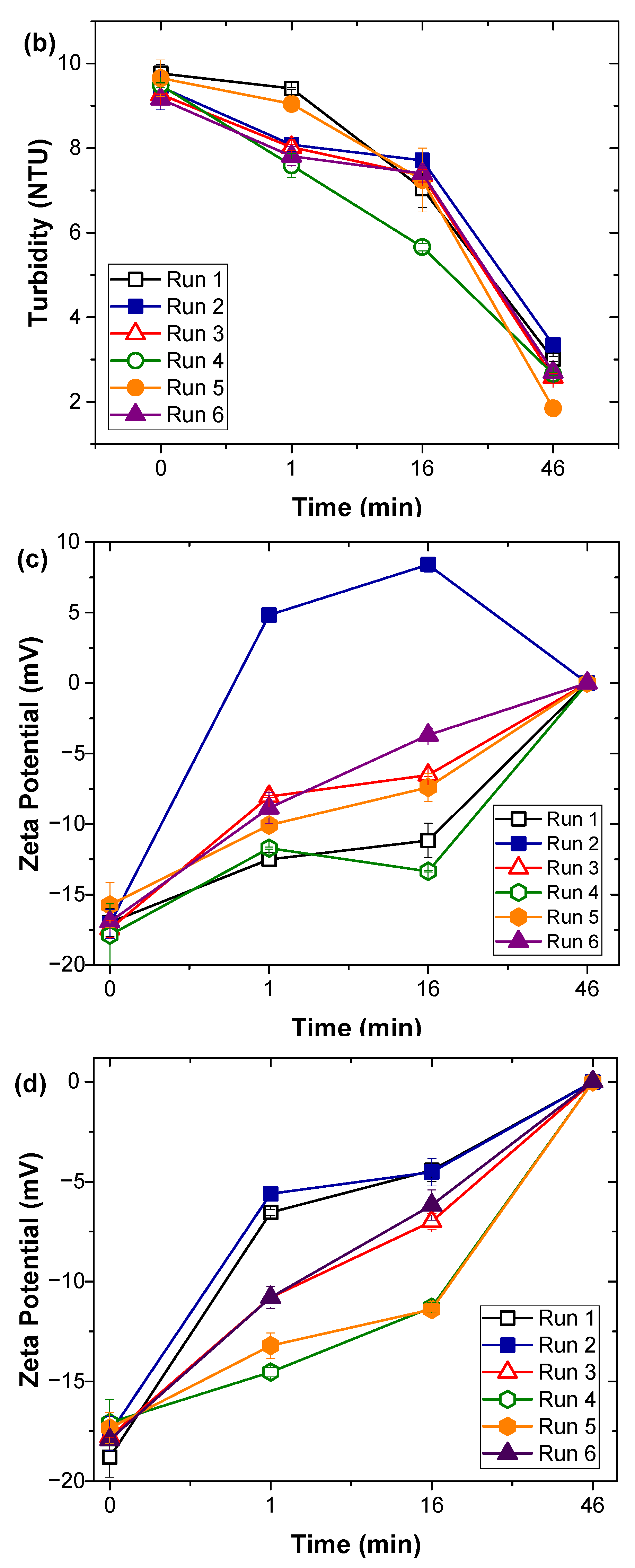
2.2. Coagulation Experiments
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Natural Organic Matter Fractions Removal by Coagulation Treatment
3.2. Model Fitting and Statistical Analyses
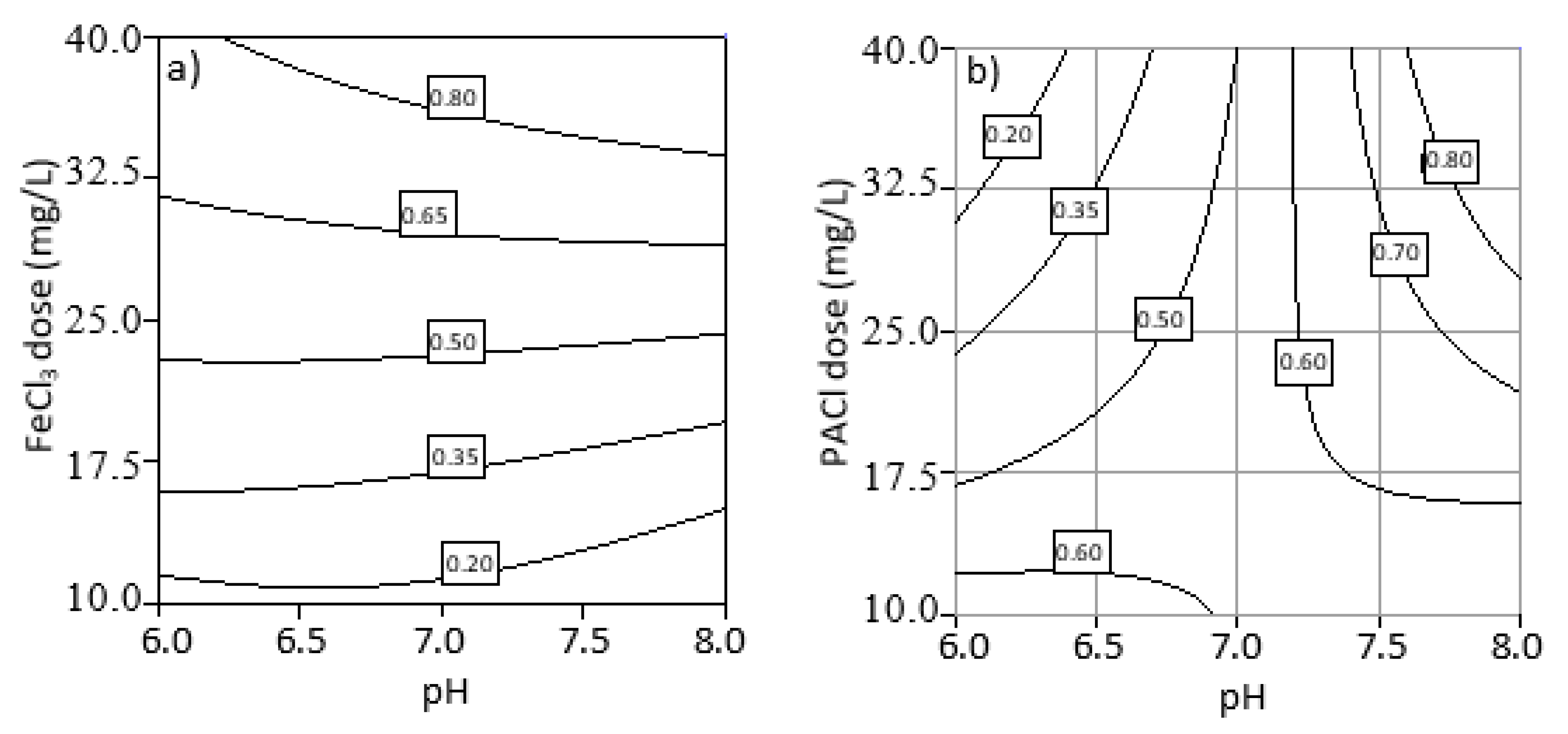
3.3. Effect of Initial pH, Coagulant Dosage, and Their Interaction
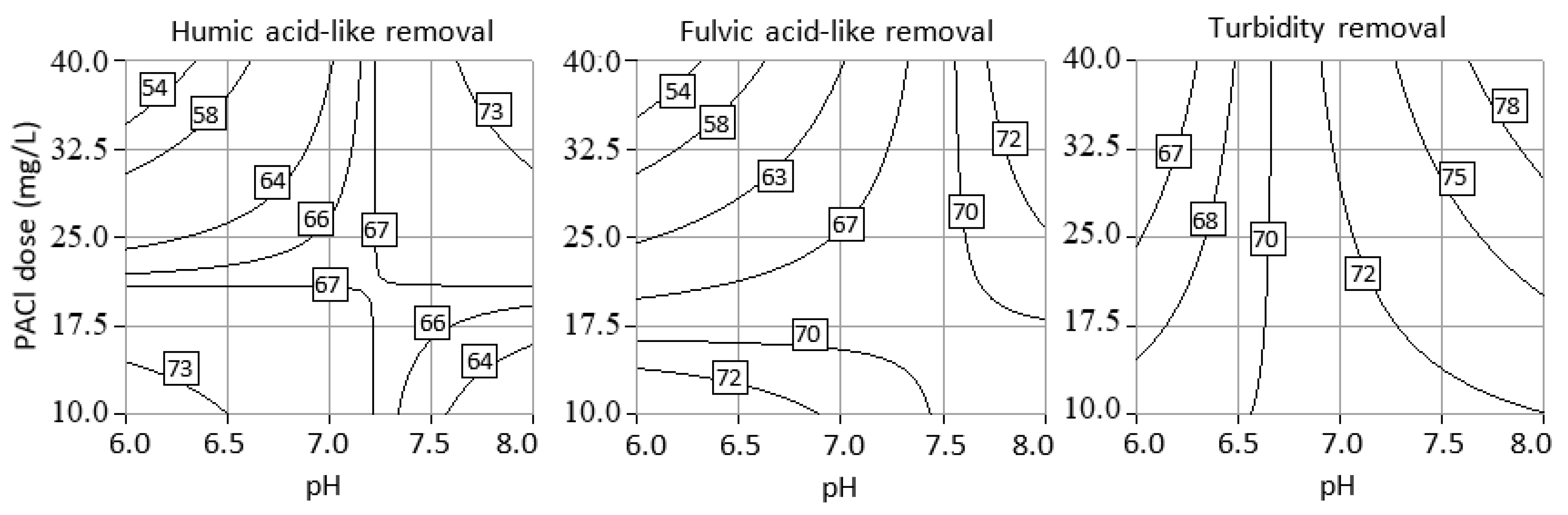
3.4. Optimization of Process Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; LeBoeuf, E.J.; Dai, S.; Gu, B. Fluorescence spectroscopic studies of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.C.; Genuino, D.A.D.; Rivera, K.K.P.; de Luna, M.D.G. Ultrasonic cleaning of polytetrafluoroethylene membrane fouled by natural organic matter. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 497, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongcharee, S.; Aravinthan, V.; Erdei, L. Removal of natural organic matter and ammonia from dam water by enhanced coagulation combined with adsorption on powdered composite nano-adsorbent. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Chao, P.; Mash, H. Reactivity of natural organic matter with aqueous chlorine and bromine. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1502–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Segura, S.; Mostafa, E.; Baltruschat, H. Electrogeneration of inorganic chloramines on boron-doped diamond anodes during electrochemical oxidation of ammonium chloride, urea and synthetic urine matrix. Water Res. 2019, 160, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Wang, D.; Ni, J.; Qu, J.; Ni, W.; Van Leeuwen, J. Natural organic matter (NOM) removal in a typical North-China water plant by enhanced coagulation: Targets and techniques. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 68, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensano, B.M.B.; Borea, L.; Naddeo, V.; Belgiorno, V.; de Luna, M.D.G.; Ballesteros, F.C. Removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater by intermittent electrocoagulation. Water 2017, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.B.; Huy, B.T.; Ray, S.K.; Lee, Y.I.; Cho, J.; Hur, J. H2O2-assisted photocatalysis for removal of natural organic matter using nanosheet C3N4-WO3 composite under visible light and the hybrid system with ultrafiltration. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Segura, S.; Ocon, J.D.; Chong, M.N. Electrochemical oxidation remediation of real wastewater effluents—A review. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 113, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.A.; Parsons, S.A. Removal of NOM from drinking water: Fenton’s and photo-Fenton’s processes. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of natural organic matter (NOM) and its constituents from water by adsorption—A review. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levchuk, I.; Rueda Márquez, J.J.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of natural organic matter (NOM) from water by ion exchange—A review. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayarathne, H.N.P.; Angove, M.J.; Aryal, R.; Abuel-Naga, H.; Mainali, B. Removal of natural organic matter from source water: Review on coagulants, dual coagulation, alternative coagulants, and mechanisms. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, C.; Bell, K.; Ibrahim, E.; Verges, D.; Amy, G.; Lechevallier, M. Impact of enhanced and optimized coagulation on removal of organic matter and its biodegradable fraction in drinking water. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3247–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Segura, S.; Eiband, M.M.S.G.; de Melo, J.V.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A. Electrocoagulation and advanced electrocoagulation processes: A general review about the fundamentals, emerging applications and its association with other technologies. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 801, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, P.; Campo, R.; Giustra, M.G.; De Marchis, M.; Di Bella, G. Bench scale continuous coagulation-flocculation of saline industrial wastewater contaminated by hydrocarbons. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 34, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Guha, B.; Lippincott, L.; Cach, S.; Wei, J.; Su, T.L.; Meng, X. Challenges of arsenic removal from municipal wastewater by coagulation with ferric chloride and alum. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Bian, Y.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Xu, S.; Xiong, N.; Wan, P. The role of magnetic MOFs nanoparticles in enhanced iron coagulation of aquatic dissolved organic matter. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Vepsäläinen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Natural organic matter removal by coagulation during drinking water treatment: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 159, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, W.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Sun, S.; Jia, R. Characteristics and mechanism of chitosan in flocculation for water coagulation in the Yellow River diversion reservoir. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 34, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Wei, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Z.; Tang, H. Coagulation of humic acid: The performance of preformed and non-preformed Al species. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 296, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Liu, S.; Chow, C.W.K.; Drikas, M.; Amal, R.; Lim, M. Understanding effects of water characteristics on natural organic matter treatability by PACl and a novel PACl-chitosan coagulants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Luna, M.D.G.; Warmadewanthi; Liu, J.C. Combined treatment of polishing wastewater and fluoride-containing wastewater from a semiconductor manufacturer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 347, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setareh, P.; Khezri, S.M.; Hossaini, H.; Pirsaheb, M. Coupling effect of ozone/ultrasound with coagulation for improving NOM and turbidity removal from surface water. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 37, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.; Flora, J.R.V.; Park, Y.G.; Badawy, M.; Saleh, H.; Yoon, Y. Removal of natural organic matter from potential drinking water sources by combined coagulation and adsorption using carbon nanomaterials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 95, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, N.; Yenugadhati, N.; Birkett, N.J.; Lindsay, J.; Turner, M.C.; Willhite, C.C.; Krewski, D. Association between aluminum in drinking water and incident Alzheimer’s disease in the Canadian Study of Health and Aging cohort. Neurotoxicology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luna, M.D.G.; Sablas, M.M.; Hung, C.M.; Chen, C.W.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Dong, C. Di Modeling and optimization of imidacloprid degradation by catalytic percarbonate oxidation using artificial neural network and Box-Behnken experimental design. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, L.T.; Lima, E.C.; dos Santos, A.A.; Vaghetti, J.C.P.; Costa, T.M.H.; Benvenutti, E.V. Use of statistical design of experiments to evaluate the sorption capacity of 1,4-diazoniabicycle[2.2.2]octane/silica chloride for Cr(VI) adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 297, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, Y.; Seyhan, S.; Yurdakoc, M. Removal of boron from aqueous solution by adsorption on Al2O3based materials using full factorial design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottipati, R.; Mishra, S. Process optimization of adsorption of Cr(VI) on activated carbons prepared from plant precursors by a two-level full factorial design. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenher, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, S.; Marín, J.M.; Restrepo, G.; Frimmel, F.H. Application of excitation-emission fluorescence matrices and UV/Vis absorption to monitoring the photocatalytic degradation of commercial humic acid. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lu, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zong, Y.; She, Z. Three-dimensional fluorescence excitation-emission matrix (EEM) spectroscopy with regional integration analysis for assessing waste sludge hydrolysis treated with multi-enzyme and thermophilic bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieroza, M.; Baker, A.; Bridgeman, J. Relating freshwater organic matter fluorescence to organic carbon removal efficiency in drinking water treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Yin, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Fan, G.; Hua, B.; Ren, B.; Zheng, H.; Deng, B. DOM removal by flocculation process: Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy (EEMs) characterization. Desalination 2014, 346, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyed Shahabadi, S.M.; Reyhani, A. Optimization of operating conditions in ultrafiltration process for produced water treatment via the full factorial design methodology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luna, M.D.G.; Murniati; Budianta, W.; Rivera, K.K.P.; Arazo, R.O. Removal of sodium diclofenac from aqueous solution by adsorbents derived from cocoa pod husks. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangli, F.; Wei, W.; Chen, Y.; Jin, W.; Xu, N. Optimization of preparation conditions for polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)/ceramic composite pervaporation membranes using response surface methodology. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 311, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuino, D.A.D.; de Luna, M.D.G.; Capareda, S.C. Improving the surface properties of municipal solid waste-derived pyrolysis biochar by chemical and thermal activation: Optimization of process parameters and environmental application. Waste Manag. 2018, 72, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cao, B. Coagulation behavior of polyferric chloride for removing NOM from surface water with low concentration of organic matter and its effect on chlorine decay model. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigobello, E.S.; Dantas, A.D.B.; Di Bernardo, L.; Vieira, E.M. Influence of the apparent molecular size of aquatic humic substances on colour removal by coagulation and filtration. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, X.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q. Coagulation efficiency of polyaluminum chloride for natural organic matter removal from low specific UV absorbance surface water and the subsequent effects on chlorine decay. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 161, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suquet, J.; Godo-Pla, L.; Valentí, M.; Verdaguer, M.; Martin, M.J.; Poch, M.; Monclús, H. Development of an environmental decision support system for enhanced coagulation in drinking water production. Water 2020, 12, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keucken, A.; Heinicke, G.; Persson, K.M.; Köhler, S.J. Combined coagulation and ultrafiltration process to counteract increasing NOM in brown surface water. Water 2017, 9, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Philippe, L.; Perreault, F.; Garcia-Segura, S. Photocatalytic treatment of natural waters. Reality or hype? The case of cyanotoxins remediation. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Westerhoff, P.; Crittenden, J. Impact of natural organic matter and divalent cations on the stability of aqueous nanoparticles. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4249–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Cui, F.; Shi, W. The impact of recycling alum-humic-floc (AHF) on the removal of natural organic materials (NOM): Behavior of coagulation and adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ding, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J. Coagulation behaviors of aluminum salts towards humic acid: Detailed analysis of aluminum speciation and transformation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 118137. [Google Scholar]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 4.8 ± 0.1 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 9.5 ± 0.2 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −17.6 ± 0.6 |
| Fulvic acid-like substances: Ex/Em = 200 − 250/380 − 550 (au) | 2830 ± 60 |
| Humic acid-like substances: Ex/Em = 250 − 400/380 − 550 (au) | 2260 ± 50 |
| Variables | Coded Symbols | Coded Levels | |
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 1 | ||
| Initial pH | A | 6 | 8 |
| Coagulant dose (mg L−1 Al or Fe) | B | 10 | 40 |
| Removal% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run | Coded Values | HLS | FLS | Turbidity | ||||
| pH | Coagulant Dose (mg L−1) | FeCl3 | PACl | FeCl3 | PaCl | FeCl3 | PACl | |
| 1 | 6 | 10 | 64.90 | 77.02 | 53.51 | 75.27 | 63.45 | 69.23 |
| 2 | 6 | 40 | 62.70 | 48.97 | 72.00 | 49.97 | 76.87 | 64.52 |
| 3 | 7 | 25 | 51.74 | 67.91 | 64.34 | 58.64 | 73.94 | 72.12 |
| 4 | 8 | 10 | 40.54 | 60.47 | 46.00 | 67.94 | 66.56 | 71.96 |
| 5 | 8 | 40 | 69.55 | 78.46 | 73.87 | 75.63 | 84.05 | 80.98 |
| 6 | 7 | 25 | 50.49 | 69.37 | 63.08 | 60.14 | 74.13 | 71.98 |
| Response | Factor | RC | SS | SE | F-Value | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeCl3 | PACl | FeCl3 | PACl | FeCl3 | PACl | FeCl3 | PACl | FeCl3 | PACl | ||
| A | −4.38 | 3.19 | 76.65 | 40.70 | 0.44 | 0.52 | 98.11 | 38.19 | 0.064 | 0.102 | |
| HLS | B | 6.70 | −2.56 | 179.68 | 26.21 | 0.44 | 0.52 | 230.01 | 24.69 | 0.042 | 0.127 |
| Removal | AB | 7.80 | 11.56 | 243.52 | 534.07 | 0.44 | 0.52 | 311.70 | 504.10 | 0.036 | 0.028 |
| Curvature | 92.02 | 7.46 | 0.77 | 0.89 | 117.78 | 7.00 | 0.059 | 0.230 | |||
| A | −1.41 | 4.58 | 7.95 | 84.00 | 0.45 | 0.53 | 10.02 | 74.66 | 0.195 | 0.070 | |
| FLS | B | 11.59 | −4.40 | 537.31 | 77.53 | 0.45 | 0.53 | 676.89 | 68.91 | 0.025 | 0.070 |
| Removal | AB | 2.34 | 8.25 | 22.00 | 272.09 | 0.45 | 0.53 | 27.71 | 241.85 | 0.120 | 0.041 |
| Curvature | 7.46 | 61.38 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 9.39 | 72.34 | 0.201 | 0.075 | |||
| A | 2.57 | 4.79 | 26.47 | 91.45 | 0.067 | 0.057 | 1466.54 | 7183.51 | 0.017 | 0.008 | |
| Turbidity | B | 7.73 | 1.08 | 238.36 | 4.65 | 0.067 | 0.057 | 13233.08 | 363.49 | 0.005 | 0.033 |
| Removal | AB | 1.02 | 3.43 | 4.14 | 47.10 | 0.067 | 0.057 | 229.43 | 3679.75 | 0.042 | 0.011 |
| Curvature | 2.26 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.098 | 125.32 | 15.72 | 0.057 | 0.157 | |||
| Responses | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistics | HLS Removal | FLS Removal | Turbidity Removal | |||
| FeCl3 | PACl | FeCl3 | PACl | FeCl3 | PACl | |
| R2 | 0.9988 | 0.9987 | 0.9965 | 0.9912 | 0.9995 | 0.9985 |
| R2adj | 0.9953 | 0.9948 | 0.9858 | 0.9647 | 0.9978 | 0.9940 |
| Adeq. Precision | 59.06 | 42.30 | 29.14 | 15.36 | 119.09 | 54.21 |
| CV (%) | 1.15 | 1.23 | 1.42 | 1.64 | 0.27 | 0.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Go, R.J.C.; Yang, H.-L.; Kan, C.-C.; Ong, D.C.; Garcia-Segura, S.; de Luna, M.D.G. Natural Organic Matter Removal from Raw Surface Water: Benchmarking Performance of Chemical Coagulants through Excitation-Emission Fluorescence Matrix Spectroscopy Analysis. Water 2021, 13, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020146
Go RJC, Yang H-L, Kan C-C, Ong DC, Garcia-Segura S, de Luna MDG. Natural Organic Matter Removal from Raw Surface Water: Benchmarking Performance of Chemical Coagulants through Excitation-Emission Fluorescence Matrix Spectroscopy Analysis. Water. 2021; 13(2):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020146
Chicago/Turabian StyleGo, Raymond John C., Hui-Ling Yang, Chi-Chuan Kan, Dennis C. Ong, Sergi Garcia-Segura, and Mark Daniel G. de Luna. 2021. "Natural Organic Matter Removal from Raw Surface Water: Benchmarking Performance of Chemical Coagulants through Excitation-Emission Fluorescence Matrix Spectroscopy Analysis" Water 13, no. 2: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020146
APA StyleGo, R. J. C., Yang, H.-L., Kan, C.-C., Ong, D. C., Garcia-Segura, S., & de Luna, M. D. G. (2021). Natural Organic Matter Removal from Raw Surface Water: Benchmarking Performance of Chemical Coagulants through Excitation-Emission Fluorescence Matrix Spectroscopy Analysis. Water, 13(2), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020146








