A Hypogene Karst Development Pattern Controlled by the Deep-Cycle of Groundwater in the Syncline in Huanjiang, Guangxi, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geologic Setting
3. Methods and Test
3.1. Deep Karstification of Well and Groundwater Sampling
3.2. Regional Hydrogeological Survey and Groundwater Sampling
3.3. Test Methods forf Hydrochemistry
3.4. Test Methods for Stable Isotopes
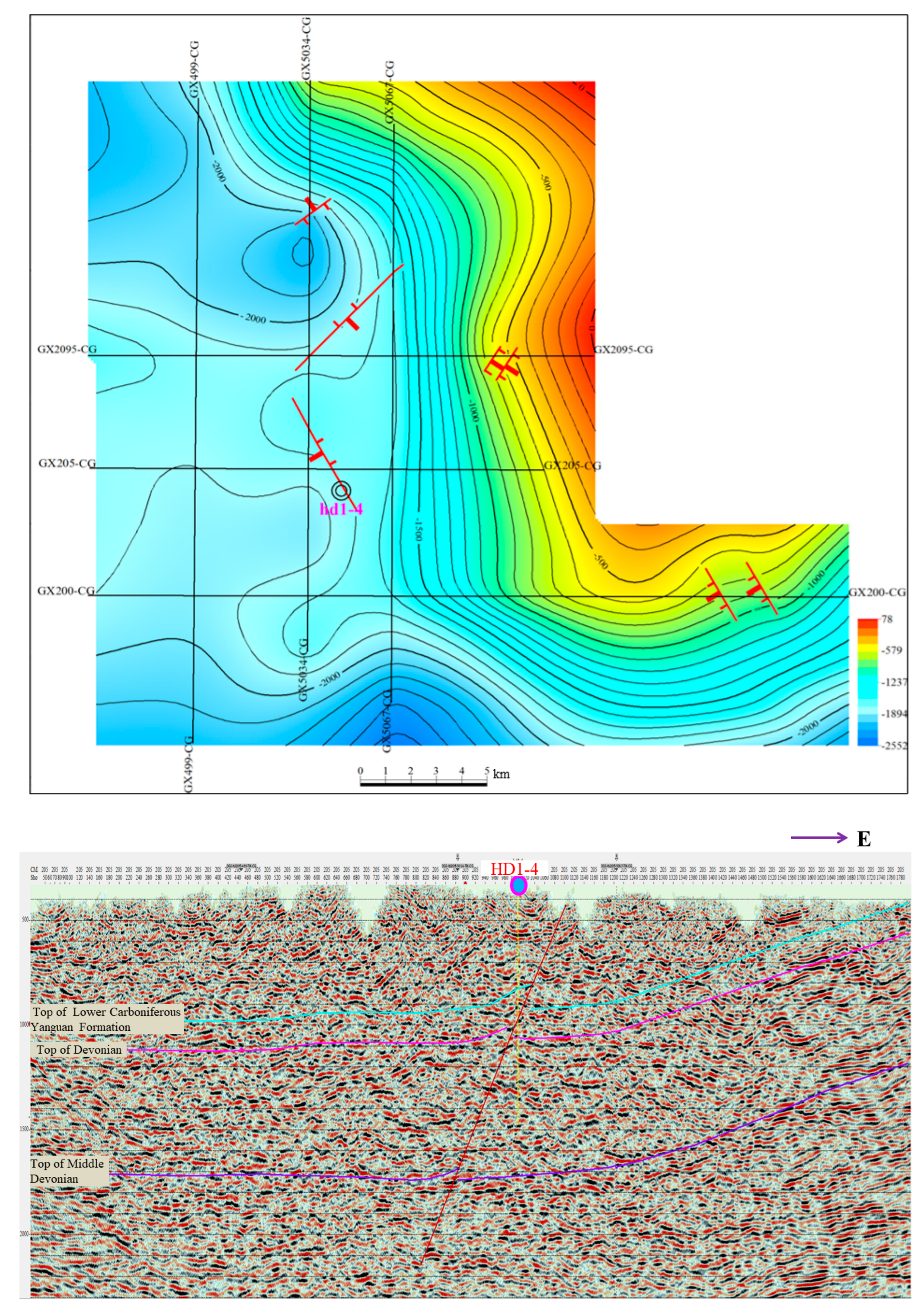
3.5. Geophysical Interpretation Methods
4. Results
4.1. Hydrogeological Characteristics of Sampling Points
4.2. Geochemistry of Deep Karst Groundwater
4.3. δ2H and δ18O Characteristics of Deep Groundwater
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparative Analysis of Physical Characteristics of Sampling Points
5.2. Hydrochemistry Evolution of Deep Karst Water
5.3. Isotopic Characteristics and Indications of Karst Groundwater
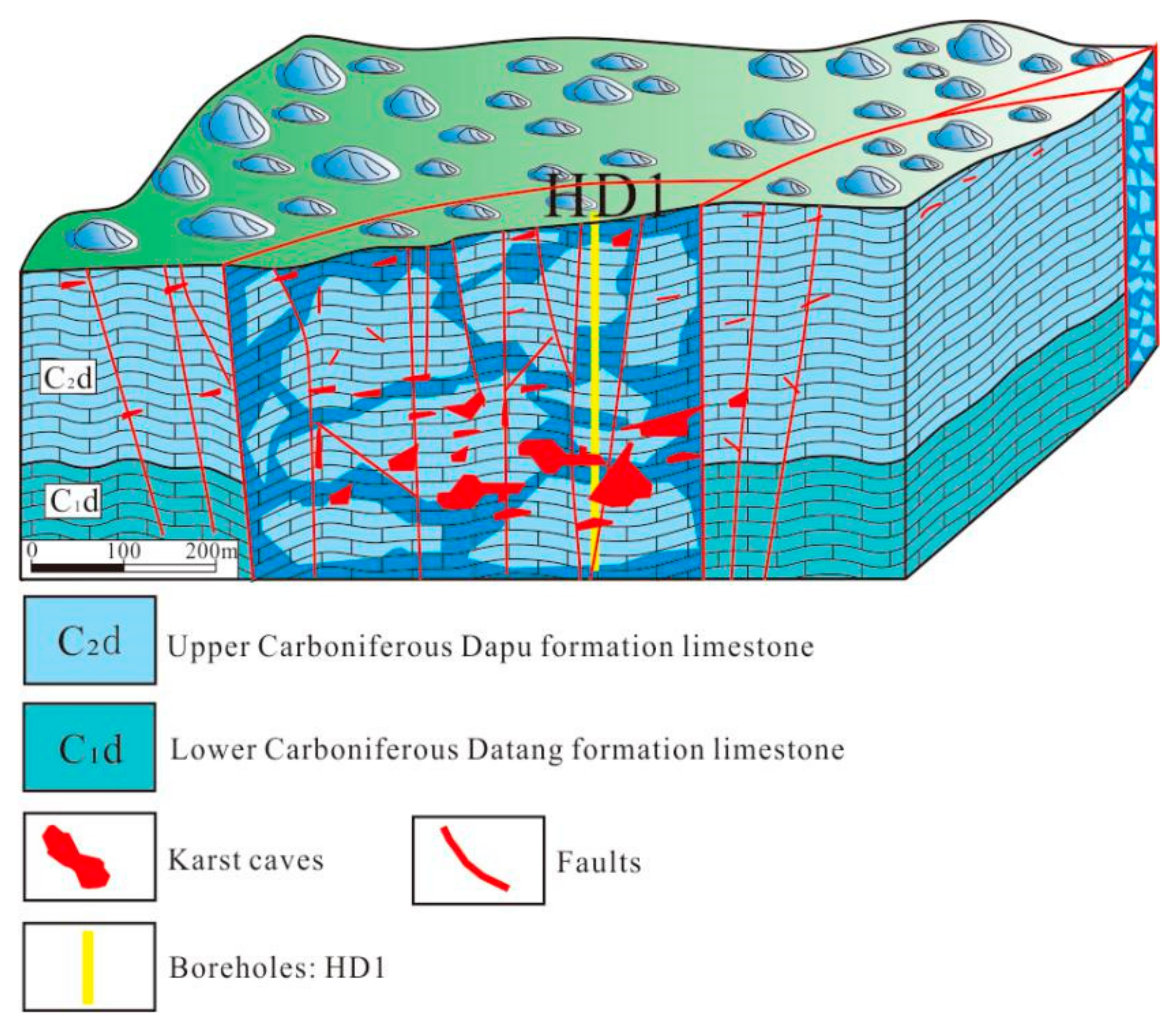
5.4. Hypogene Groundwater Circulation and Hypogene Karst Development Pattern
5.4.1. Bottom of Deep Karst Groundwater Circulation
5.4.2. Hydrodynamic Analysis of Hypogene Karst
5.4.3. Runoff Channels of Hypogene Karst Groundwater
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palmer, A.N. Origin and morphology of limestone caves. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1991, 103, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunsky, J. Thermomineral karst and caves of Zbrasov, Northern Moravia. Proc. Czechoslov. Soc. Geol. 1957, 62, 306–351. [Google Scholar]
- Dublyansky, Y.N. Hydrothermal karst in the Alpine folded region of the South of the USSR. Kras i Speleologia 1980, 3, 18–36. [Google Scholar]
- Dublyansky, Y.V. Speleogenetic History of the Hungarian Hydrothermal Karst. Environ. Geol. 1995, 25, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dublyansky, Y.V. Speleogenesis: Evolution of Karst Aquifers; National Speleological Society: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2000; pp. 298–303. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, D.C.; Williams, P.W. Karst Geomorphology and Hydrology; Unwin Hyman: London, UK, 1989; p. 601. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, D.C. Karst geomorphology, caves and cave deposits: A review of North American contributions during the past half century. In Perspectives on Karst Geomorphology, Hydrology and Geochemistry; Harmon, R.S., Wicks, C.W., Eds.; Paper 404; GSA Special: Boulder, CO, USA, 2006; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, D.C.; Williams, P.W. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Egemeier, S.J. Cavern development by thermal waters. Natl. Speleol. Soc. Bull. 1981, 49, 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.A. Geology of Carlsbad Cavern and other caves in the Guadalupe Mountains, New Mexico and Texas. N. Mex. Bu. Mines and Min. Res. Bull. 1987, 117, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Anette, S.E.; Libby, A.S. Microbial contributions to cave formation: New insights into sulfuric acid speleogenesis. Geology 2004, 32, 369–372. [Google Scholar]
- Harmon, R.S.; Wicks, C.M.; Ford, D.C.; White, W.B. Perspectives on Karst Geomorphology, Hydrology, and Geochemistry—A Tribute Volume to Derek C. Ford and William B. White, 2nd ed.; Geological Society of America: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, A.N. Distinction between epigenic and hypogenic maze caves. Geomorphology 2011, 134, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onac, B.P.; Hess, J.W.; White, W.B. The relationship between the mineral composition of speleothems and mineralization of breccia pipes: Evidence from corkscrew cave, Arizona, USA. Can. Mineral. 2007, 45, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audra, P.; D’antoni-Nobecourt, J.C. Hypogenic caves in France. Speleogenesis and morphology of the cave systems. Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 2010, 181, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, P.L. Syndepositional architecture of the northern Athabasca Oil Sands Deposit, northeastern Alberta. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 52, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Almasi, I.; Potma, K.; O’Keefe, J. Hypogenic karst beneath the Athabasca Oil Sands: Implications for oil sands mining operations. Bull. Can. Petrol. Geol. 2017, 65, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumkin, A.; Langford, B.; Lisker, S.; Amrani, A. Hypogenic karst at the Arabian platform margins: Implications for far-field groundwater systems. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 2017, 129, 1636–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumkin, A.; Langford, B. Arid hypogene karst in a multi-aquifer system: Hydrogeology and speleogenesis of Ashalim Cave, Negev Desert, Israel. In Advances in Karst Research: Theory, Fieldwork and Applications; Parise, M., Gabrovšek, F., Kaufmann, G., Ravbar, N., Eds.; Geological Society, Special Publications: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bertotti, G.; Audra, P.; Auler, A.; Bezerra, F.H.; de Hoop, S.; Pontes, C.; Prabhakaran, R.; Lima, R. The Morro Vermelho hypogenic karst system (Brazil): Stratigraphy, fractures, and flow in a carbonate strike-slip fault zone with implications for carbonate reservoirs. AAPG Bull. 2020, 104, 2029–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.C. Deep and Ultra-Deep Karst. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 1982, S1, 117–119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, M.E.; Liu, Z.Z.; Wang, F.Y. Karst Introduction, 2nd ed.; Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 1983; pp. 26–49. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J. Deep Karst. Eng. Investig. 1987, 1, 47–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fei, Y.L. The issue of development on karst deep valley. Water Power 1980, 5, 21–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Klimchouk, A.B. Hypogene Speleogenesis: Hydrogeological and Morphogenetic Perspective; Special Paper, 1; National Cave and Karst Research Institute: Carlsbad, NM, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.J. Application of tritium analysis to the study of deep karst and seepage problems at reservoir and dam sites. Carsol. Sin. 1988, 7, 132–138. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.C.; Han, B.P. Deep karst periods and types in the Tengxian and Peixian coal bearing basin. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 1993, 11, 59–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, R.Y. New progress in the study of paleokarst and deep karst in oil and gas fields. Carsol. Sin. 2001, 1, 20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.Y.; Song, H.R. Deep karstification of gas-oil reservoir. Carsol. Sin. 1997, 16, 189–198. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lolcama, J.L.; Cohen, H.A.; Tonkin, M.J. Deep karst conduits, flooding, and sinkholes; lessons for the aggregates industry. Eng. Geol. 2002, 65, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Mao, B.Y.; Zhang, Q. Evolvement and ecpectation of research on the modern deep karst. Adv. Earth Sci. 2008, 23, 495–501. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Q. The Simulation Study Deep karst Formation Conditions. In Karat Caves and Physiognomy; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1985. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, B.Y.; Xu, M.; Bai, A.Z. Study on the Karst Development Law and Mechanism of Heshan Coal Field in Guangxi Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 1, 205–208. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, W.Q.; Liu, Y.Y.F.; Dickson, J.A.D.; Shen, A.J.; Han, J.; Ye, Y.; Gao, H.L.; Guan, P.; Zheng, X.P. The Geological Model of Hydrothermal Activity in Outcrop and the Characteristics of Carbonate Hydrothermal Karst of Lower Paleozoic in Tarim Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2009, 27, 983–994. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Regional Geological Survey Report of Luocheng Sheet (scale, 1:200000); The Geological Survey of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region; Guangxi Geological Bureau Press: Nanning, China, 1968. (In Chinese)
- Regional Geological Survey Report of Donglan Sheet (scale, 1:200000); The Geological Survey of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region; Guangxi Geological Bureau Press: Nanning, China, 1971. (In Chinese)
- Wu, G.G.; Yao, G.S.; Xu, Z.Y.; Guo, Q.X.; Chen, Z.L. Structural patterns and origin of tectonic reformation in guizhong depression. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2009, 14, 33–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Li, S.Z.; Zhou, Y.G.; Jin, C.; Dai, L.M.; Liu, L.P.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Hao, Y.; Liu, E.S. Structural features and evolution of the Hechi-Yizhou fault zone, northern Guangxi-insights from shallow to deep structures of its Liucheng segment. Geotecton. Metallog. 2009, 33, 488–496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, P.X.; Jin, A.M.; Lou, Z.H. Investigation of pore structure and fractal characteristics of marine shale reservoirs of the Upper Paleozoic in Huanjiang sag, Guizhong depression. Chin. J. Geol. 2019, 54, 130–144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric water. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. Responses of Stormflow to Rainfall in a Typical Karst Catchment Based on Stable Isotopes and Hydrogeochemistry. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China, 2015. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Li, B.Z. Hydrochemical and isotopic analysis of groundwater in the Huize Lead-Zinc mining district, Yunnan. Acta Geol. 2018, 92, 1081–1089. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Schoen, R.; Ladouche, B.; Aquilina, L.; Bakalowicz, M.; Cubizolles, J. Hydro-chemical investigation of karstic systems (southern France); 2; Hydrodynamic and chemical monitoring of springs. J. Conf. Abs. 1999, 4, 562. [Google Scholar]
- Bakalowicz, M. The infiltration zone of karst aquifers; investigation methods; structure and behavior. Hydrogeologie 1995, 4, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bakalowicz, M. Geochemistry of Water Applied to the Study of Karst Aquifers and Karstification. Ph.D. Thesis, Universite Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris VI, Paris, France, 1979; p. 269. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.W.; Li, R.X.; Chen, Y.L. Geochemical behaviors and genesis of formation water in 8th Member of Xiashihezi Formation in western Sulige gas field, Ordos Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2013, 34, 625–631. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.C.; Ji, B.C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhang, S.Y. Isotopic and hydro-chemical evidence on the origin of groundwater through deep-circulation ways in Lake Daihai region, Inner Mongolia plateau. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 521–530. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kortatsi, B.K. Hydrochemical framework of groundwater in the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. Aquat. Geochem. 2007, 13, 41–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.X. Hydro-geochemistry and genesis of major ions in the Yangtze River, China. Geol. Bull. China 2010, 29, 46–456. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, B.; Wang, S.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Meng, X. Investgating hydrochemical groundwater processes in an Inland agricultrural area with limited data: A clustering approach. Water 2017, 9, 723. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Zhao, Y.F.; Tang, J.L.; Lu, W.; Luo, Z.X. Hydrochemistry characteristics and recharge source of groundwater in typical watersheds of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 1314–1325. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; He, J.; Li, J.J.; Cao, Y.T.; Gong, L.; Liu, J.W.; Bian, C.; Cai, Y.M. Major ipnic features and possible controls in the groundwater in the Hamatong River basin. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 4981–4991. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Li, C.S.; Jia, C. Spatiotemporal difference study of karst hydrochemical characteristics in the Baotu Spring area of Jinan. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 61–70. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.M. Environmental isotope studies on shallow groundwater in the lower Tarim River, Xinjiang. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. 1997, 24, 89–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Brijraj, K.D.; Moser, H. Application of environment isotopes to groundwater study in arid region. J. Hydrol. 1988, 98, 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Galvao, P.; Hirata, R.; Halihan, T.; Tarada, R. Recharge sources and hydrochemical evolution of an urban karst aquifer, Sete Lagoas, M.G. Brazil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 158–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Geochemistry of Clayey Aquitard Pore Water and Its Implication on Environment-a Case Study in the Coastal Plain of Northwest Bohai Bay; China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Mao, B.Y.; Yang, Y.N.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, L.W. The Formation Mechanism and Suitability for Engineering of Modern Deep Karst, 3rd ed.; Sci. Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 42–46. [Google Scholar]
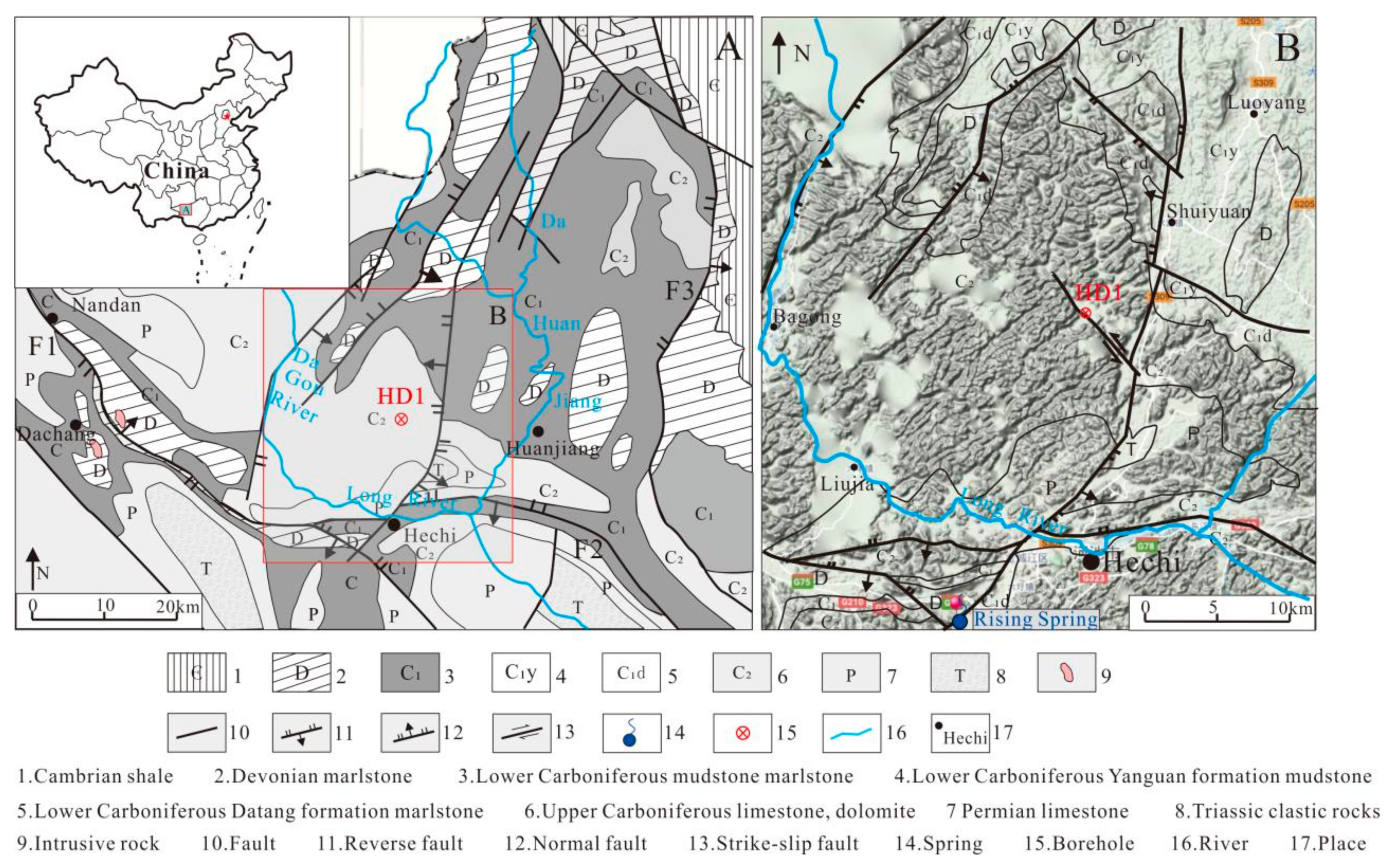
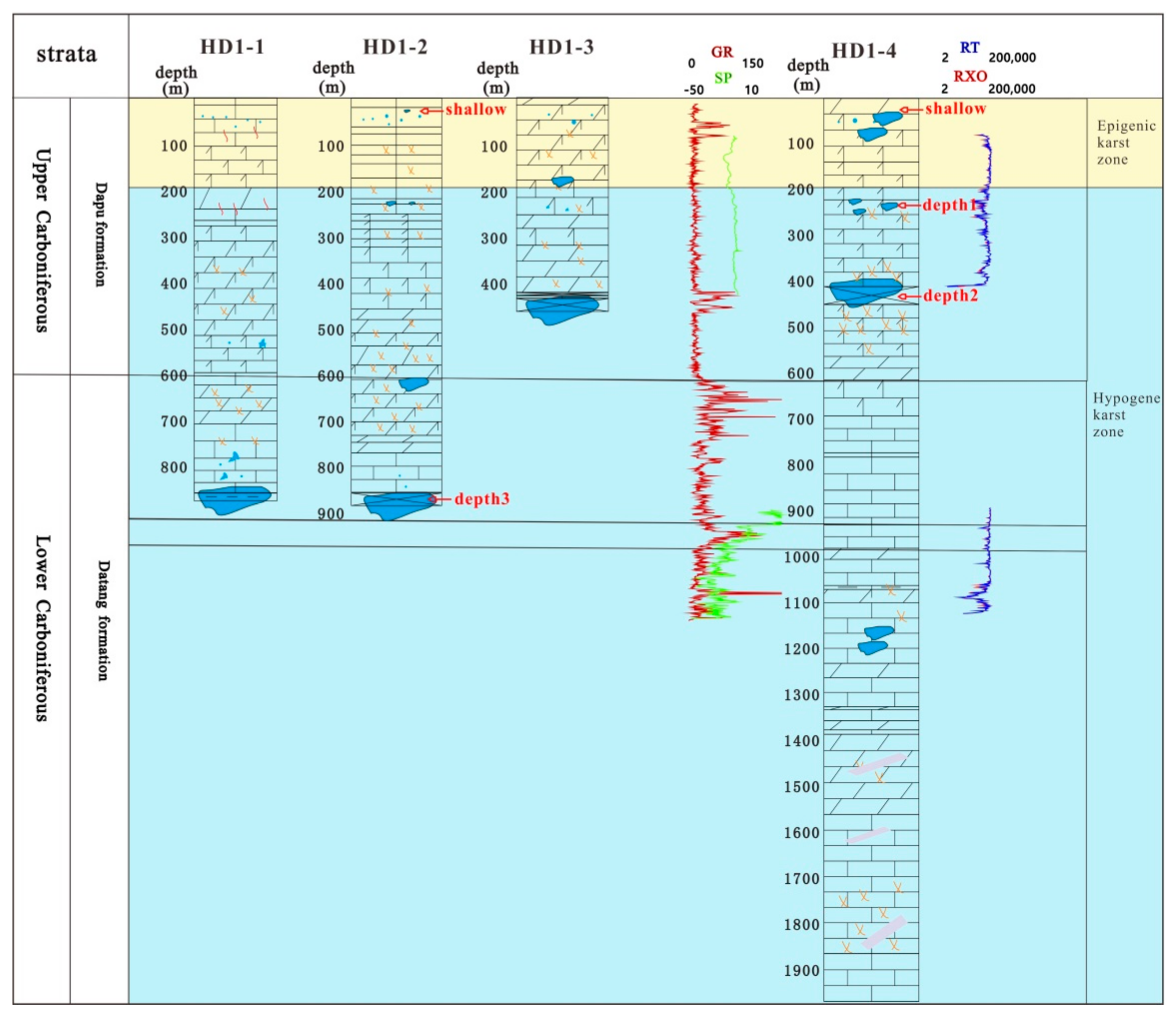




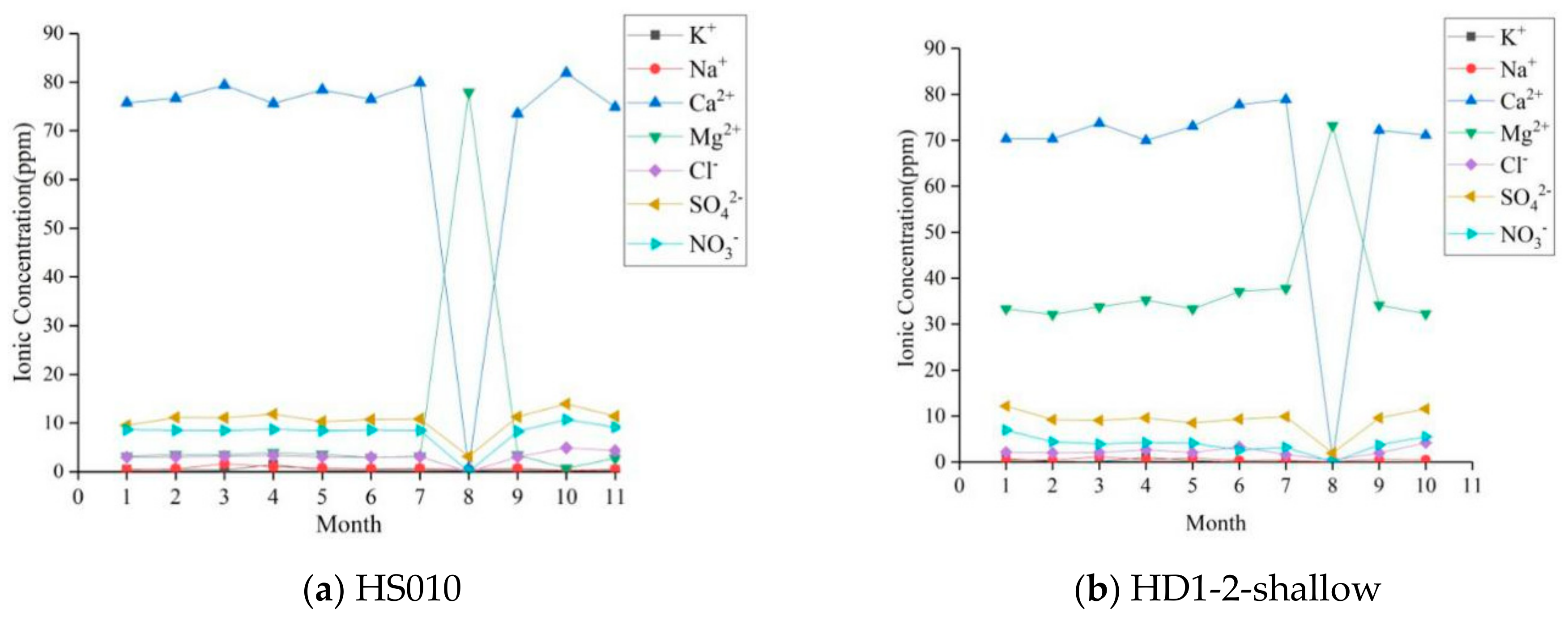

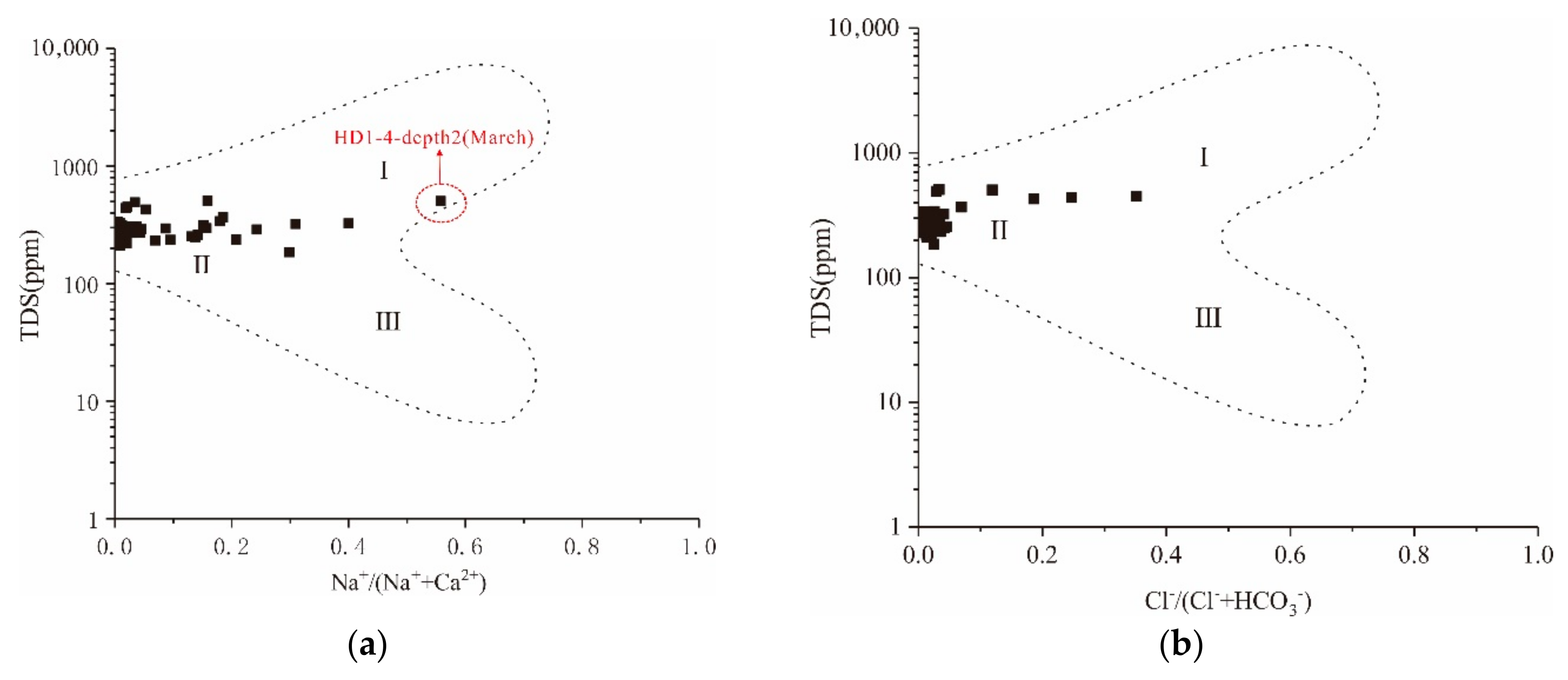


| ID | Elevation(m) | Type | Exposed Condition | Temperature (°C)/January | Average Flow in Dry Season (L/s) | Average Flow in Rainy Season (L/s) | Water Table (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD1-2 | 200 | well | C2d/Near the fault | 20~33/depth: 0–850 m | / | / | 7~20 |
| HD1-4 | 200 | well | C2d/Near the fault | 20~42/depth: 0–1100 m | / | / | 7~20 |
| HS001 | 193 | descending spring | C2h | 21.2 | 5.5 | 30.5 | 0 |
| HS002 | 187 | descending spring | C2h | 20.3 | 31 | 70 | 0 |
| HS003 | 172 | descending spring | C2h | 21.2 | 20.5 | 69 | 0 |
| HS004 | 176 | descending spring | C2h | 19.2 | 62.1 | 115 | 0 |
| HS005 | 183 | descending spring | C1d | 19.8 | 2 | 15 | 0 |
| HS006 | 252 | ponor | C2d | 16.1 | 10.5 | 80.7 | 1.2 |
| HS007 | 334 | puddle | C2d | 19.8 | / | / | 1 |
| HS008 | 135 | descending spring | C2d | 20.2 | 93.1 | 174.8 | 0 |
| HS009 | 100 | skylight | P1m | 21.2 | / | / | 30 |
| HS010 | 113 | ascending spring | Fault | 24.1 | 310.5 | 360.9 | 0 |
| HS011 | 92 | skylight | C2m | 20.8 | / | / | 19 |
| HS012 | 194 | skylight | C2h | 21.2 | / | / | 21 |
| HS013 | 365 | skylight | C1d | 21.6 | / | / | 1.5 |
| HS014 | 399 | descending spring | C2d/C1d/On the stratigraphic boundary | 19.6 | 18 | 47 | 0 |
| HS015 | 382 | puddle | C1d | 21.3 | / | / | 1.5 |
| HS016 | 417 | descending spring | C2h | 20.6 | 0.1 | 1.9 | 0 |
| HS017 | 191 | skylight | C2h | 21.2 | 173.1 | 246.7 | 0.9 |
| HS018 | 100 | descending spring | C1d | 20.2 | 0.01 | 1.8 | 0 |
| HS019 | 122 | pumping well | D3 | 22 | / | / | 18 |
| HS020 | 190 | ascending spring | C2d/C1d/On the stratigraphic boundary | 21.8 | 1.8 | 13.9 | 0 |
| HS021 | 217 | descending spring | C2h | 20.8 | 20.3 | 48.2 | 0 |
| HS022 | 183 | ponor | C2h | 17.3 | 1.1 | 10.5 | 1.3 |
| Long River | 110 | river | / | 17.2 | / | / | 0 |
| Parameters | Sampling ID | pH | TDS | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | NO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppm | |||||||||||
| MIN | HD1-2-shallow | 7.12 | 522.45 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.52 | 32.09 | 0.41 | 1.96 | 11.99 | 0.00 |
| HD1-2-depth3 | 7.52 | 508.23 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 1.18 | 30.44 | 0.34 | 2.12 | 11.52 | 0.00 | |
| HD1-4-shallow | 7.38 | 418.94 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 4.10 | 23.92 | 1.99 | 1.54 | 8.72 | 0.00 | |
| HD1-4-depth1 | 7.45 | 459.55 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 6.37 | 25.01 | 2.52 | 3.70 | 7.28 | 0.00 | |
| HD1-4-depth2 | 7.43 | 448.41 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 7.44 | 24.28 | 2.63 | 4.69 | 8.02 | 0.00 | |
| HS010 | 7.44 | 346.15 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 3.14 | 11.13 | 0.00 | |
| Other springs | 7.12 | 485.58 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 62.65 | 5.20 | 1.38 | 5.92 | 227.23 | 0.04 | |
| MAX | HD1-2-shallow | 7.82 | 750.88 | 1.04 | 1.19 | 78.84 | 73.19 | 4.17 | 12.17 | 413.51 | 6.94 |
| HD1-2-depth3 | 7.99 | 732.08 | 1.05 | 1.11 | 77.29 | 69.56 | 4.12 | 11.78 | 402.91 | 6.12 | |
| HD1-4-shallow | 7.81 | 650.88 | 1.22 | 9.01 | 67.25 | 54.86 | 8.53 | 10.69 | 355.18 | 16.12 | |
| HD1-4-depth1 | 7.84 | 667.46 | 0.96 | 10.38 | 68.00 | 57.35 | 9.16 | 10.88 | 363.42 | 15.49 | |
| HD1-4-depth2 | 8.02 | 868.21 | 2.96 | 66.72 | 63.58 | 54.84 | 49.08 | 97.36 | 371.09 | 18.47 | |
| HS010 | 7.88 | 459.38 | 1.47 | 1.64 | 81.87 | 77.93 | 4.92 | 13.92 | 236.02 | 10.71 | |
| Other springs | 7.65 | 644.74 | 2.39 | 19.63 | 88.28 | 29.50 | 16.91 | 97.83 | 336.41 | 18.46 | |
| MEAN | HD1-2-shallow | 7.57 | 672.33 | 0.28 | 0.53 | 65.78 | 38.22 | 2.24 | 9.09 | 339.60 | 3.86 |
| HD1-2-depth3 | 7.68 | 671.16 | 0.21 | 0.54 | 65.99 | 37.71 | 2.08 | 9.21 | 339.82 | 3.80 | |
| HD1-4-shallow | 7.59 | 561.53 | 0.50 | 2.82 | 50.41 | 33.60 | 4.13 | 7.83 | 282.21 | 6.14 | |
| HD1-4-depth1 | 7.65 | 584.47 | 0.20 | 3.31 | 53.92 | 33.90 | 4.49 | 7.97 | 294.41 | 4.59 | |
| HD1-4-depth2 | 7.66 | 632.73 | 0.79 | 14.51 | 52.37 | 32.39 | 11.85 | 22.33 | 303.11 | 5.63 | |
| HS010 | 7.58 | 437.76 | 0.46 | 0.65 | 70.71 | 9.32 | 3.09 | 10.40 | 209.56 | 8.05 | |
| Other springs | 7.38 | 552.39 | 0.86 | 1.55 | 75.53 | 17.47 | 4.74 | 15.69 | 288.46 | 3.63 | |
| STD | HD1-2-shallow | 0.19 | 62.29 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 23.14 | 12.43 | 1.00 | 2.75 | 116.88 | 1.81 |
| HD1-2-depth3 | 0.15 | 62.39 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 22.93 | 11.35 | 0.96 | 2.68 | 116.36 | 1.64 | |
| HD1-4-shallow | 0.15 | 80.39 | 0.40 | 2.72 | 20.28 | 7.61 | 1.83 | 2.92 | 98.24 | 4.92 | |
| HD1-4-depth1 | 0.11 | 68.53 | 0.28 | 3.27 | 18.20 | 8.14 | 1.90 | 2.57 | 100.88 | 4.35 | |
| HD1-4-depth2 | 0.17 | 108.20 | 0.88 | 18.52 | 15.81 | 7.98 | 12.91 | 25.40 | 103.17 | 5.72 | |
| HS010 | 0.11 | 30.43 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 22.17 | 21.62 | 1.15 | 2.56 | 62.72 | 2.62 | |
| Other springs | 0.15 | 42.89 | 0.70 | 4.30 | 7.96 | 7.31 | 4.12 | 19.93 | 29.87 | 5.03 | |
| C.V | HD1-2-shallow | 0.02 | 0.09 | 1.23 | 0.57 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.47 |
| HD1-2-depth3 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 1.63 | 0.62 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.46 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.43 | |
| HD1-4-shallow | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.80 | 0.96 | 0.40 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 0.80 | |
| HD1-4-depth1 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 1.38 | 0.99 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.95 | |
| HD1-4-depth2 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 1.11 | 1.28 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 1.09 | 1.14 | 0.34 | 1.02 | |
| HS010 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 1.38 | 1.71 | 3.19 | 0.43 | 2.68 | 4.07 | 3.34 | 3.08 | |
| Other springs | 0.02 | 10.76 | 0.61 | 1.61 | 2.88 | 3.32 | 2.15 | 3.44 | 2.92 | 2.31 | |
| Index | Parameters | HS010 (‰) | HD1-2 -shallow (‰) | HD1-2 -depth3 (‰) | HD1-4 -shallow (‰) | HD1-4 -depth1 (‰) | HD1-4 -depth2 (‰) | Other Springs (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ2H | min | −48.20 | −53.80 | −52.70 | −48.40 | −48.10 | −47.80 | −59.10 |
| max | −44.50 | −44.70 | −45.70 | −46.20 | −44.40 | −45.40 | −35.40 | |
| mean | −46.21 | −48.81 | −48.77 | −47.21 | −46.72 | −46.70 | −46.28 | |
| STD | 1.28 | 3.20 | 2.50 | 0.69 | 1.25 | 0.84 | 5.29 | |
| C.V | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.03 | −0.02 | 0.11 | |
| δ18O | min | −7.34 | −8.05 | −7.96 | −7.44 | −7.37 | −7.35 | −8.80 |
| max | −6.95 | −6.95 | −7.09 | −7.07 | −7.20 | −7.03 | −6.36 | |
| mean | −7.21 | −7.45 | −7.44 | −7.26 | −7.30 | −7.24 | −7.35 | |
| STD | 0.13 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.70 | |
| C.V | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.009 | –0.01 | 0.09 |
| Ionic Name | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | CO32− | NO3− | TDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | 1 | 0.58 | 0.16 | -0.25 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.09 | −0.22 | 0.11 | 0.12 |
| Na+ | 0.58 | 1 | −0.13 | 0.00 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.12 | −0.10 | 0.06 | 0.34 |
| Ca2+ | 0.16 | −0.13 | 1 | −0.75 | −0.02 | 0.20 | 0.68 | −0.82 | 0.29 | 0.29 |
| Mg2+ | −0.25 | 0.00 | −0.75 | 1 | −0.12 | −0.21 | −0.21 | 0.66 | −0.42 | 0.28 |
| Cl− | 0.66 | 0.95 | −0.02 | −0.12 | 1 | 0.82 | 0.11 | −0.15 | 0.20 | 0.28 |
| SO42− | 0.66 | 0.78 | 0.20 | −0.21 | 0.82 | 1 | 0.11 | −0.18 | 0.30 | 0.29 |
| HCO− | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.68 | −0.21 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 1 | −0.82 | 0.03 | 0.78 |
| CO32− | −0.22 | −0.10 | −0.82 | 0.66 | −0.15 | −0.18 | −0.82 | 1 | −0.32 | 0.33 |
| NO− | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.29 | −0.42 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.03 | −0.32 | 1 | 0.17 |
| TDS | 0.12 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.78 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, H.; Dan, Y.; Liang, J.; Liang, B.; Nie, G.; Ji, S. A Hypogene Karst Development Pattern Controlled by the Deep-Cycle of Groundwater in the Syncline in Huanjiang, Guangxi, China. Water 2021, 13, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020199
Dong H, Dan Y, Liang J, Liang B, Nie G, Ji S. A Hypogene Karst Development Pattern Controlled by the Deep-Cycle of Groundwater in the Syncline in Huanjiang, Guangxi, China. Water. 2021; 13(2):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020199
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Hongqi, Yong Dan, Jiapeng Liang, Bin Liang, Guoquan Nie, and Shaocong Ji. 2021. "A Hypogene Karst Development Pattern Controlled by the Deep-Cycle of Groundwater in the Syncline in Huanjiang, Guangxi, China" Water 13, no. 2: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020199
APA StyleDong, H., Dan, Y., Liang, J., Liang, B., Nie, G., & Ji, S. (2021). A Hypogene Karst Development Pattern Controlled by the Deep-Cycle of Groundwater in the Syncline in Huanjiang, Guangxi, China. Water, 13(2), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020199




