Impact of Suspended Solids and Organic Matter on Chlorine and UV Disinfection Efficiency of Greywater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
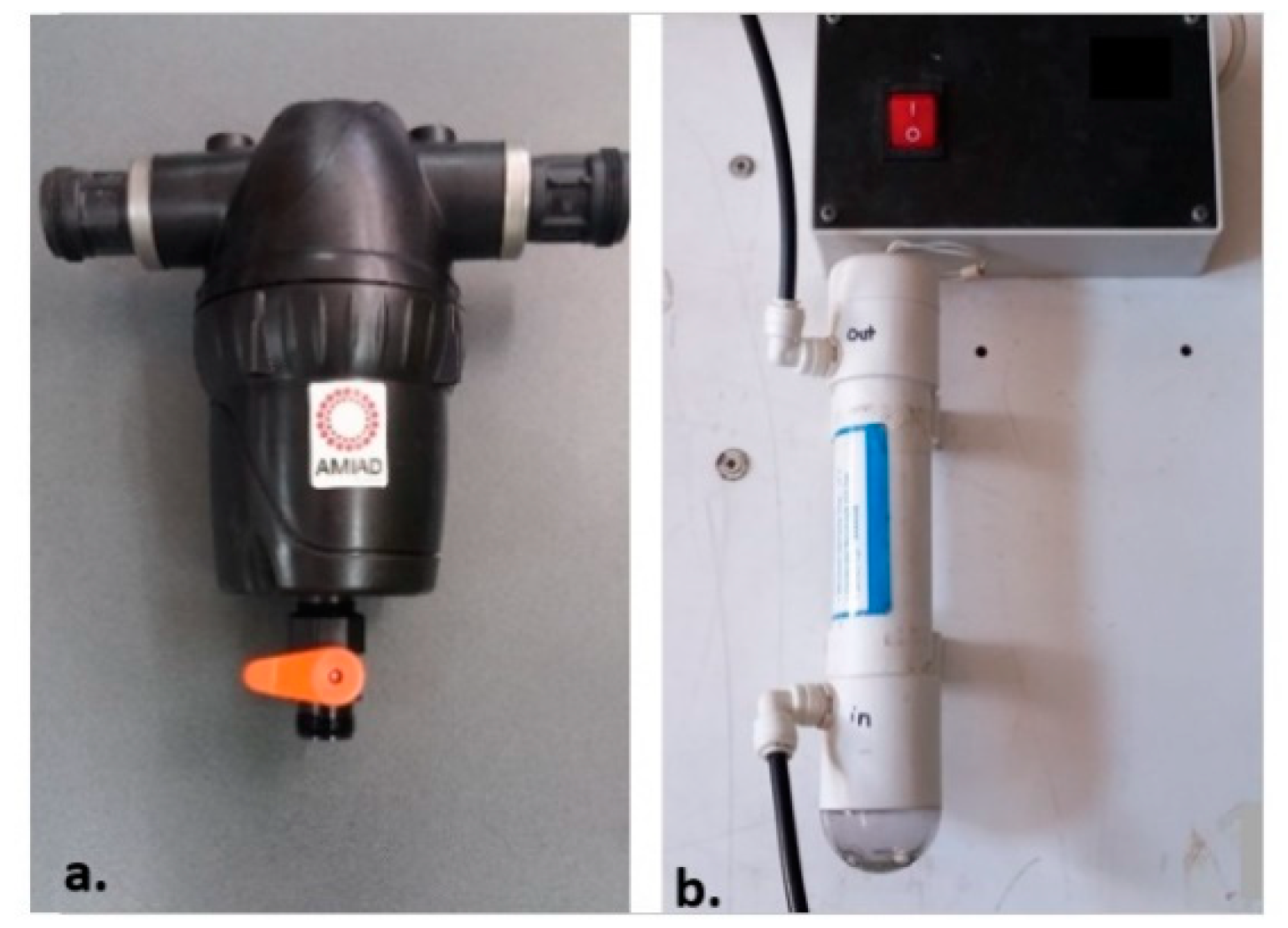
2.1. GW Treatment System
2.2. Batch Experiment
2.2.1. Chlorination Experiment
2.2.2. Collimated Beam Setup
2.3. Flow-Through Setups
2.3.1. Flow-Through Chlorination Chamber
2.3.2. Flow-Through UV Reactor
2.4. Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Batch Experiments
3.1.1. Chlorination
3.1.2. Collimated Beam
3.2. Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) Model
3.3. Flow-Through Setups and Model Verification
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| BOD5 | five-day biochemical oxygen demand |
| FC | fecal coliforms |
| GW | greywater |
| MLR | multiple linear regression |
| RVFCW | recirculating vertical flow constructed wetland |
| TSS | total suspended solids |
| UV | ultraviolet irradiation |
| β1–β8 | coefficients |
References
- Maimon, A.; Tal, A.; Friedler, E.; Gross, A. Safe on-site reuse of greywater for irrigation-a critical review of current guidelines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3213–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- March, J.G.; Gual, M. Studies on chlorination of greywater. Desalination 2009, 249, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems Manual; EPA 625-R- 00-008, Office of Water; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fenner, R.A.; Komvuschara, K. A new kinetic model for ultraviolet disinfection of greywater. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 850–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeren, K.M.; Hodgson, B.A.; Sharvelle, S.E.; De Long, S.K. Investigation of pathogen disinfection and regrowth in a simple graywater recycling system for toilet flushing. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 26174–26186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.S.; Leong, J.Y.C.; Poh, P.E.; Chong, M.N.; Von Lau, E. A review of greywater recycling related issues: Challenges and future prospects in Malaysia. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverenz, H.L.; Darby, J.; Tchobanoglous, G. Comparison of a commercially available chlorine and an ultraviolet disinfection unit for onsite wastewater systems. Small Flows Mag. 2007, 8, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Friedler, E.; Kovalio, R.; Ben-Zvi, A. Comparative study of the microbial quality of greywater treated by three on-site treatment systems. Environ. Technol. 2006, 27, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedler, E.; Yardeni, A.; Gilboa, Y.; Alfiya, Y. Disinfection of greywater effluent and regrowth potential of selected bacteria. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Ultraviolet Disinfection Guidance Manual for the Final Long Term 2 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule; EPA 815-R-06-007 Office of Water; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Benami, M.; Gillor, O.; Gross, A. The question of pathogen quantification in disinfected graywater. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winward, G.; Avery, L.; Stephenson, T.; Jefferson, B. Ultraviolet (UV) disinfection of grey water: Particle size effects. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrerova, Z.; Linden, K.G. Ultraviolet and chlorine disinfection of Mycobacterium in wastewater: Effect of aggregation. Water Environ. Res. 2006, 78, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virto, R.; Manas, P.; Alvarez, I.; Condon, S.; Raso, J. Membrane damage and microbial inactivation by chlorine in the absence and presence of a chlorine-demanding substrate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5022–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onga, Z.C.; Asadsangabifardb, M.; Ismailb, Z.; Tama, J.H.; Roushenasa, P. Design of a compact and effective greywater treatment system in Malaysia. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 146, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Linden, K.G. How particles affect UV light in the UV disinfection of unfiltered drinking water. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2003, 95, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carré, E.; Pérot, J.; Jauzein, V.; Lopez-Ferber, M. Impact of suspended particles on UV disinfection of activated-sludge effluent with the aim of reclamation. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 22, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.E.; Rodríguez, R.A.; Salveson, A.; Goel, N.; Rhodes, S.; Kehoe, P.; Linden, K.G. Disinfection methods for treating low TOC, light graywater to California title 22 water reuse standards. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madge, B.A.; Jensen, J.N. Ultraviolet disinfection of fecal coliform in municipal wastewater: Effects of particle size. Water Environ. Res. 2006, 78, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Shmueli, O.; Ronen, Z.; Raveh, E. Recycled Vertical Flow Constructed Wetland (RVFCW)—a novel method of recycling greywater for landscape irrigation in small communities and households. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfiya, Y.; Gross, A.; Sklarz, M.; Friedler, E. Reliability of on-site greywater treatment systems in Mediterranean and arid environments—A case study. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater—Volume 1 and Vol. 4—Excreta and Greywater Use in Agriculture Policy and Regulatory Aspects; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mamane, H.; Linden, K.G. UV disinfection of indigenous aerobic spores: Implications for UV reactor validation in unfiltered waters. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2898–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedler, E.; Gilboa, Y. Performance of UV disinfection and the microbial quality of greywater effluent along a reuse system for toilet flushing. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inbar, Y. New standards for treated wastewater reuse in Israel. In Wastewater Reuse-Risk Assessment, Decision-Making and Environmental Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, A.; Maimon, A.; Alfiya, Y.; Friedler, E. Greywater Reuse; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden, J.; Trussell, R.; Hand, D.; Howe, K.; Tchobanoglous, G. Water Treatment: Principles and Design, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mamane, H. Impact of particles on UV disinfection on water and wastewater effluents: A review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2008, 24, 65–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantwell, R.E.; Hofmann, R. Ultraviolet absorption properties of suspended particulate matter in untreated surface waters. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, H.E.; Liss, S.N.; Farnood, R.R.; Allen, D.G. Ultraviolet disinfection of sequencing batch reactor effluent: A study of physiochemical properties of microbial floc and disinfection performance. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2005, 4, S65–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaj, A.; Sommer, R.; Schoenen, D. Biodosimetry: Model calculations for UV water disinfection devices with regard to dose distributions. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.; Chen, C.L.; Nellor, M. Standardized collimated beam testing protocol for water/wastewater ultraviolet disinfection. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Explanatory Variable | Coefficient | Estimate | p-Value | LogWorth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Chlorination | Dissolved BOD5 (mg/L) | β1 | −0.016 | <0.0001 | 5.43 |
| TSS (mg/L) | β2 | −0.013 | <0.0001 | 10.8 | |
| Log FC raw (log(CFU/100 mL)) | β3 | 0.831 | <0.0001 | 22.8 | |
| Residual chlorine (mg/L) | β4 | 0.644 | <0.0001 | 2.83 | |
| UV irradiation Collimated beam | Dissolved BOD5 (mg/L) | β5 | 0.001 | 0.2211 * | 0.20 |
| TSS (mg/L) | β6 | −0.012 | <0.0001 | 23.0 | |
| Log FC raw (log(CFU/100 mL)) | β7 | 0.495 | <0.0001 | 43.5 | |
| UV dose (mJ/cm2) | β8 | 0.059 | <0.0001 | 38.2 |
| Range | Average | Median | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSS (mg/L) | 3.9–233 | 38 | 15 |
| Dissolved BOD5 (mg/L) | 0–107 | 41 | 37 |
| % Transmission254 nm | 39–85 | 64 | 67 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 1.47–512 | 87 | 18 |
| FC (CFU/100 mL) | 0–106 | 105 | 105 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Friedler, E.; F. Chavez, D.; Alfiya, Y.; Gilboa, Y.; Gross, A. Impact of Suspended Solids and Organic Matter on Chlorine and UV Disinfection Efficiency of Greywater. Water 2021, 13, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020214
Friedler E, F. Chavez D, Alfiya Y, Gilboa Y, Gross A. Impact of Suspended Solids and Organic Matter on Chlorine and UV Disinfection Efficiency of Greywater. Water. 2021; 13(2):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020214
Chicago/Turabian StyleFriedler, Eran, Diana F. Chavez, Yuval Alfiya, Yael Gilboa, and Amit Gross. 2021. "Impact of Suspended Solids and Organic Matter on Chlorine and UV Disinfection Efficiency of Greywater" Water 13, no. 2: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020214
APA StyleFriedler, E., F. Chavez, D., Alfiya, Y., Gilboa, Y., & Gross, A. (2021). Impact of Suspended Solids and Organic Matter on Chlorine and UV Disinfection Efficiency of Greywater. Water, 13(2), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020214







