Large-Volume Samplers for Efficient Composite Sampling and Particle Characterization in Sewer Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
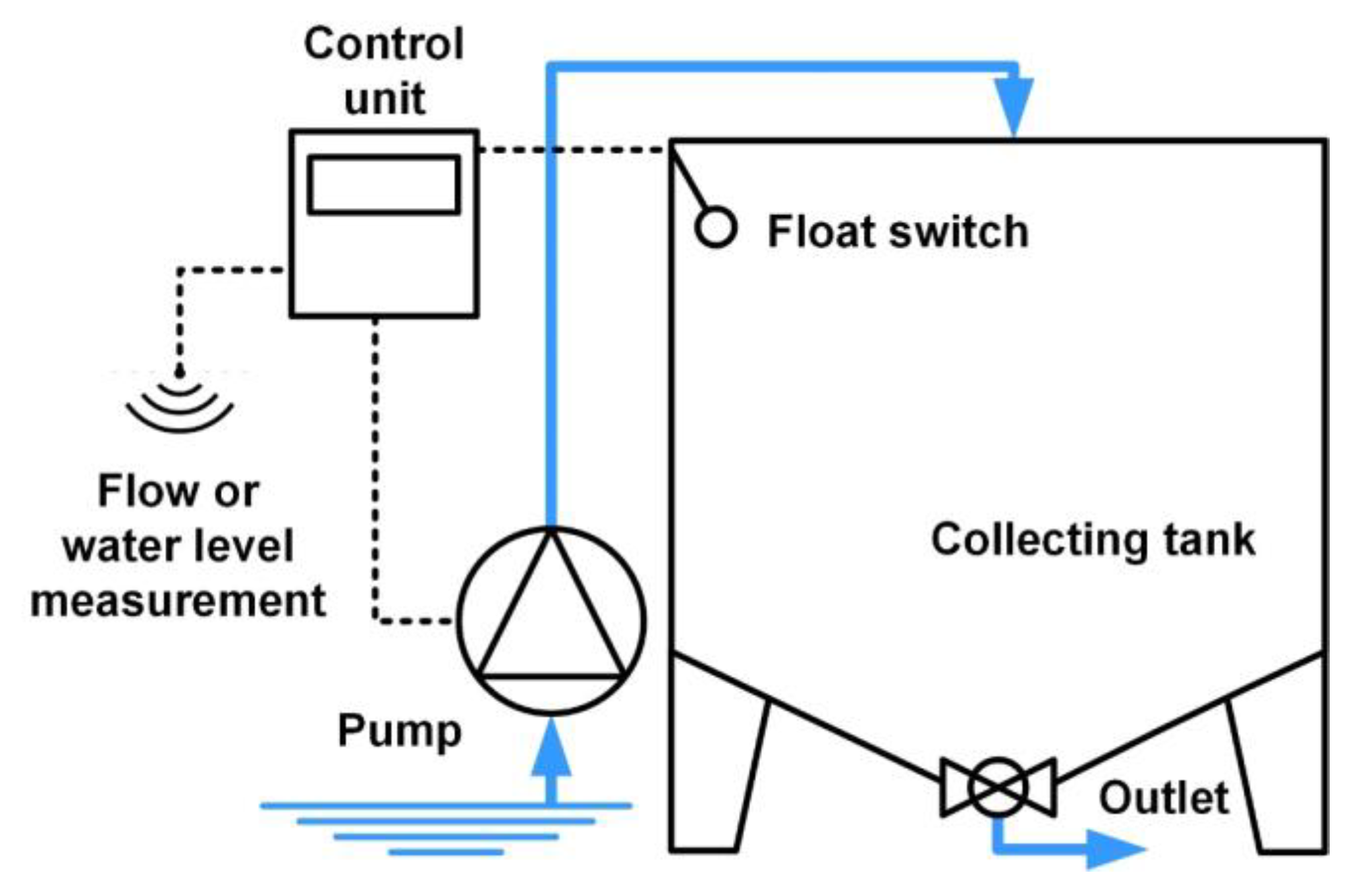
2.1. Large-Volume Samplers
2.2. Subsampling Methods
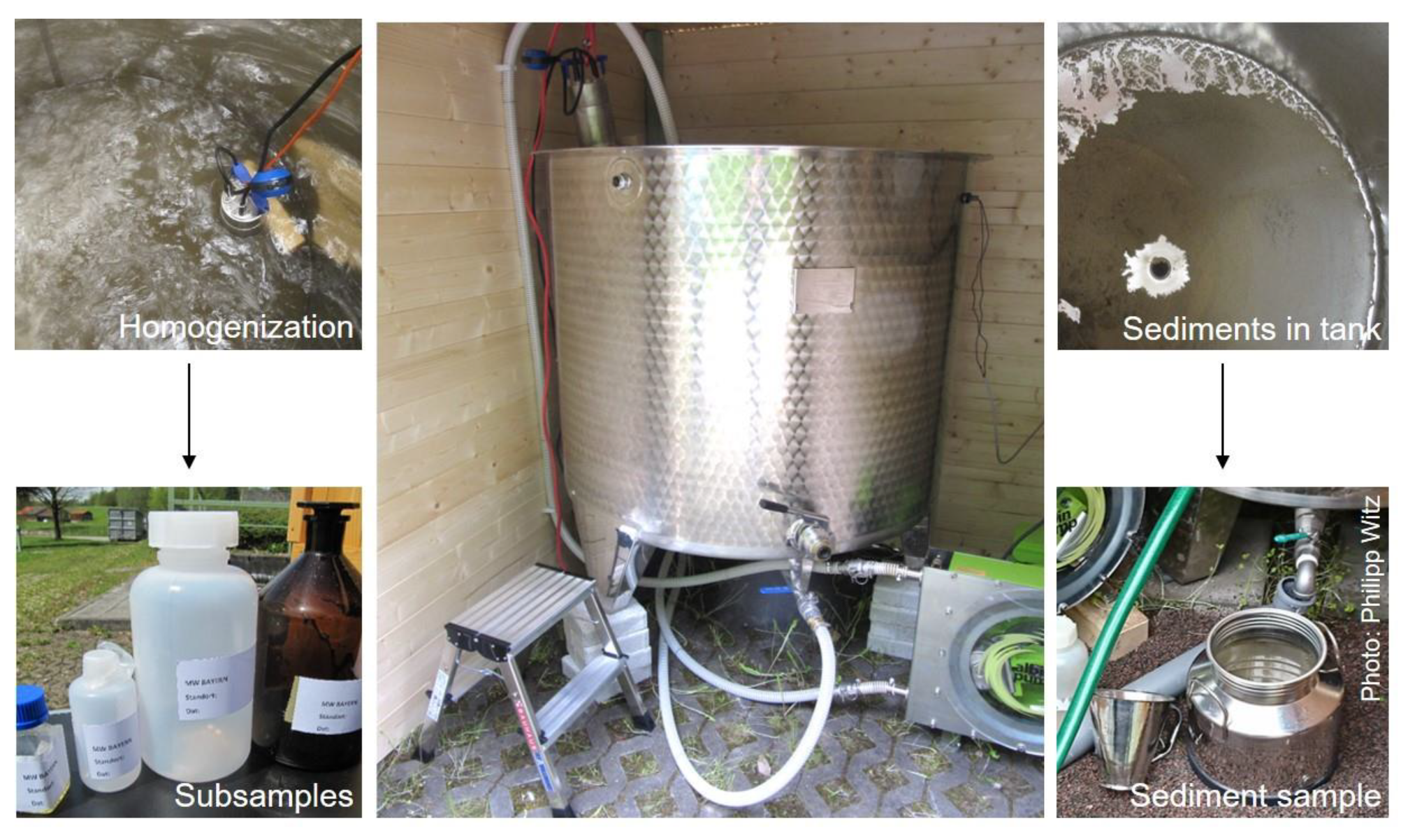
2.2.1. Homogenized Sample
2.2.2. Sedimented Sample with Supernatant Sample
2.3. Sampling Campaign
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Standard Water Quality Parameters
2.4.2. Particle Size Fractionation and Loss on Ignition
2.4.3. Particle-Bound Phosphorus and Metals
2.5. Quality Assurance
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. Calculation of Event Mean Concentrations from Sedimented LVS Samples
2.6.2. Calculation of Event Mean Concentrations from Autosampler Pollutographs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sampled Events
3.2. Comparability of LVS and Autosamplers
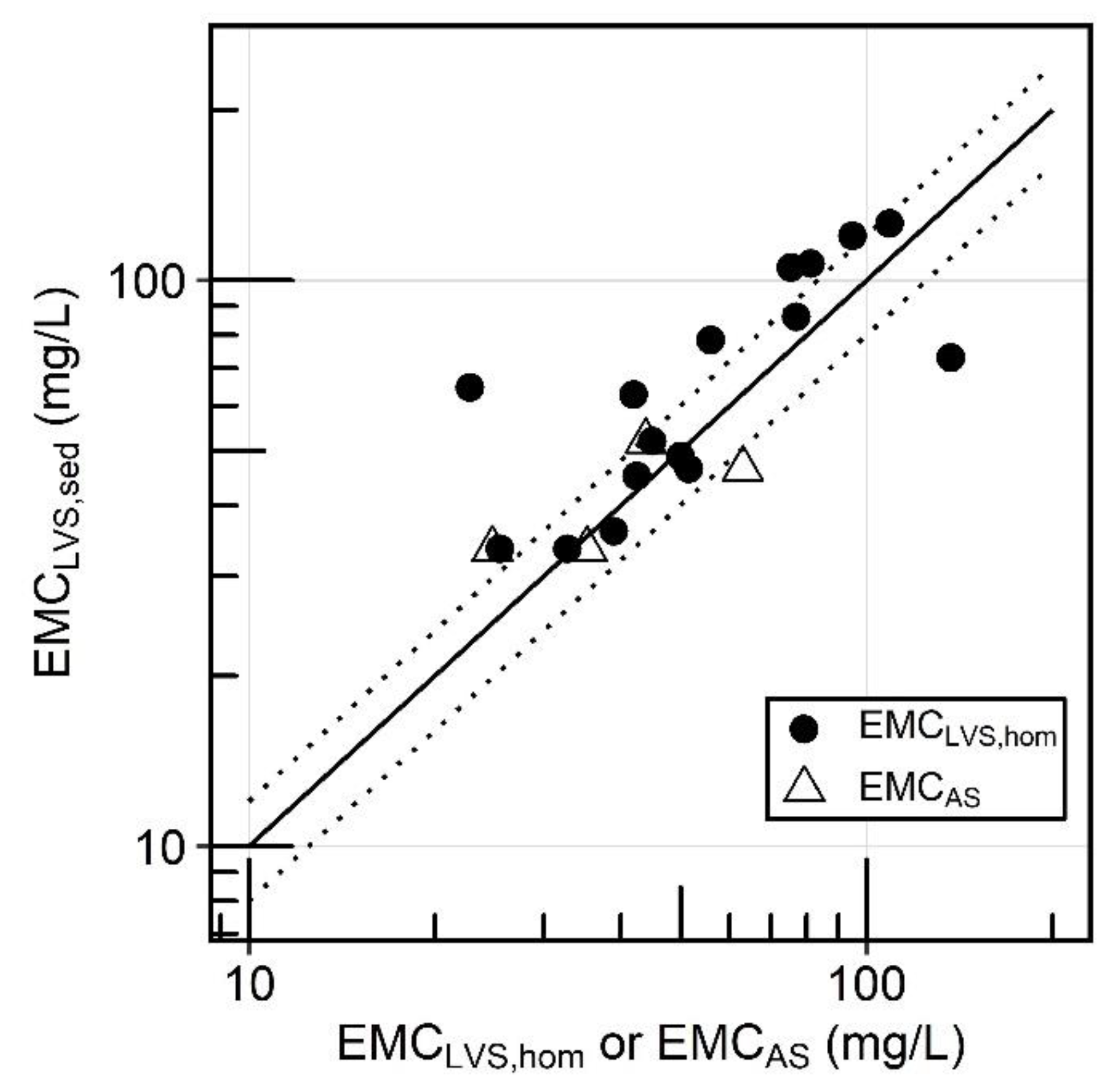
3.3. Differences between Homogenized and Sedimented LVS Samples
3.3.1. Subsampling Bias
3.3.2. Size Fractionation at 63 µm
3.3.3. Differences in Sample Processing
3.3.4. Differences in Analytics
3.4. Characterization of Solids in CSOs
3.4.1. Concentration Levels Lower than Previously Reported
3.4.2. Particle Size and Organic Matter Content
3.4.3. Pollutant Loading
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Launay, M.; Dittmer, U.; Steinmetz, H. Organic micropollutants discharged by combined sewer overflows-Characterisation of pollutant sources and stormwater-related processes. Water Res. 2016, 104, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becouze-Lareure, C.; Dembélé, A.; Coquery, M.; Cren-Olivé, C.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L. Assessment of 34 dissolved and particulate organic and metallic micropollutants discharged at the outlet of two contrasted urban catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, S.; Scherer, U.; Wander, R.; Behrendt, H.; Venohr, M.; Opitz, D.; Hillenbrand, T.; Marscheider-Weidemann, F.; Götz, T. Calculation of Emissions into Rivers in Germany Using the MONERIS Model: Nutrients, Heavy Metals and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons; Texte 46/2010; Umweltbundesamt (UBA): Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2010.
- Paijens, C.; Bressy, A.; Frère, B.; Tedoldi, D.; Mailler, R.; Rocher, V.; Neveu, P.; Moilleron, R. Urban pathways of biocides towards surface waters during dry and wet weathers: Assessment at the Paris conurbation scale. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicke, D.; Matzinger, A.; Sonnenberg, H.; Caradot, N.; Schubert, R.-L.; Dick, R.; Heinzmann, B.; Dünnbier, U.; von Seggern, D.; Rouault, P. Micropollutants in Urban Stormwater Runoff of Different Land Uses. Water 2021, 13, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotta, G.S.; Brazier, R.E. Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, R.E.; Clark, S.; Eppakayala, V.K.; Sileshi, R. Don’t Throw the Baby Out with the Bathwater-Sample Collection and Processing Issues Associated with Particulate Solids in Stormwater. J. Water Manag. Modeling 2017, 25, C416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todeschini, S.; Papiri, S.; Ciaponi, C. Placement Strategies and Cumulative Effects of Wet-weather Control Practices for Intermunicipal Sewerage Systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 2885–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Sansalone, J.J. Event-based size distributions of particulate matter transported during urban rainfall-runoff events. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2756–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, S.; Lambert, B.; Grotehusmann, D. Neue Aspekte in der Behandlung von Siedlungsabflüssen. Umweltwiss. Schadst. Forsch. 2010, 22, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selbig, W.; Fienen, M.; Horwatich, J.; Bannerman, R. The Effect of Particle Size Distribution on the Design of Urban Stormwater Control Measures. Water 2016, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Swamikannu, X.; Radulescu, D.; Kim, S.; Stenstrom, M.K. Design of stormwater monitoring programs. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4186–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madoux-Humery, A.-S.; Dorner, S.; Sauvé, S.; Aboulfadl, K.; Galarneau, M.; Servais, P.; Prévost, M. Temporal variability of combined sewer overflow contaminants: Evaluation of wastewater micropollutants as tracers of fecal contamination. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4370–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, J.; Papiri, S.; Stenstrom, M.K. First flush in a combined sewer system. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Bang, K.W.; Ketchum, L.H.; Choe, J.S.; Yu, M.J. First flush analysis of urban storm runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 293, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmer, I.K.; Bader, H.-P.; Scheidegger, R.; Singer, H.; Luck, A.; Hanke, I.; Carlsson, C.; Stamm, C. Significance of urban and agricultural land use for biocide and pesticide dynamics in surface waters. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2850–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-S.; Kang, J.-H.; Kayhanian, M.; Stenstrom, M.K. Sampling Issues in Urban Runoff Monitoring Programs: Composite versus Grab. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, D.T.; Zhang, K.; Westerlund, C.; Viklander, M.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A. Assessment of sampling strategies for estimation of site mean concentrations of stormwater pollutants. Water Res. 2018, 129, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.; Harmel, D. Quality assurance/quality control in stormwater sampling. In Quality Assurance & Quality Control of Environmental Field Sampling; Zhang, C., Mueller, J.F., Mortimer, M.R., Eds.; Future Science Ltd.: London, UK, 2014; pp. 98–127. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, S.; Mayer, I.; Haller, B.; Roth, H. Lamella settlers for storm water treatment-performance and design recommendations. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotehusmann, D.; Lambert, B.; Fuchs, S.; Graf, J. Konzentrationen und Frachten Organischer Schadstoffe im Straßenabfluss: Schlussbericht zum BASt Forschungsvorhaben FE-Nr; 05.152/2008/GRB; Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen (BASt): Bergisch Gladbach, Germany, 2014.
- Eyckmanns-Wolters, R.; Fuchs, S.; Maus, C.; Sommer, M.; Voßwinkel, N.; Mohn, R.; Uhl, M. Reduktion des Feststoffeintrags durch Niederschlagswassereinleitungen (REFENI). Phase 1: Projektbericht. 2013. Available online: http://isww.iwg.kit.edu/medien/Abschlussbericht_ReduktionFeststoffeintragPhase1.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2019).
- Baum, P.; Kuch, B.; Dittmer, U. Adsorption of Metals to Particles in Urban Stormwater Runoff—Does Size Really Matter? Water 2021, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, M.; Eyckmanns-Wolters, R.; Fuchs, S.; Ebbert, S.; Maus, C.; Uhl, M.; Weiß, G.; Nichler, T.; Engelberg, M.; Gillar, M.; et al. Analyse der Leistungsfähigkeit von Regenüberlaufbecken und Überwachung durch Online Messtechnik. Abschlussbericht. 2015. Available online: https://isww.iwg.kit.edu/download/2015_12_16_Schlussbericht_Monitoring.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Nickel, J.P.; Fuchs, S. Micropollutant emissions from combined sewer overflows. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, S.; Kaiser, M.; Reid, L.; Toshovski, S.; Nickel, J.P.; Gabriel, O.; Clara, M.; Hochedlinger, G.; Trautvetter, H.; Hepp, G.; et al. Grenzüberschreitende Betrachtung des Inn-Salzach-Einzugsgebietes als Grundlage für ein transnationales Gewässermanagement. Unpublished Report. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, S.; Rothvoß, S.; Toshovski, S. Ubiquitäre Schadstoffe–Eintragsinventare, Umweltverhalten und Eintragsmodellierung; Texte 52/2018; Umweltbundesamt (UBA): Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2018.
- Wagner, A. Event-Based Measurement and Mean Annual Flux Assessment of Suspended Sediment in Meso Scale Catchments; Dissertation; Institut für Wasser und Gewässerentwicklung, Fachbereich Siedlungswasserwirtschaft und Wassergütewirtschaft: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nickel, J.P.; Fuchs, S. Qualitative Untersuchung von Mischwasserentlastungen in Bayern: Schlussbericht; Karlsruher Institut für Technologie (KIT): Karlsruhe, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- DWA-A 102-2/BWK-A 3-2. Arbeitsblatt DWA-A 102-2/BWK-A 3-2 Grundsätze zur Bewirtschaftung und Behandlung von Regenwetterabflüssen zur Einleitung in Oberflächengewässer: Teil 2: Emissionsbezogene Bewertungen und Regelungen; Deutsche Vereinigung für Wasserwirtschaft, Abwasser und Abfall: Hennef, Germany, 2020; ISBN 9783968620466. [Google Scholar]
- Droppo, I.G.; Irvine, K.N.; Jaskot, C. Flocculation/aggregation of cohesive sediments in the urban continuum: Implications for stormwater management. Environ. Technol. 2002, 23, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, Q.; Xie, W.; Li, X.; Yin, C. Role of urban surface roughness in road-deposited sediment build-up and wash-off. J. Hydrol. 2018, 560, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, S.; Kemper, M.; Nickel, J.P. Feststoffe in der Regenwasserbehandlung. In 52. Essener Tagung für Wasserwirtschaft vom 20.-22. März 2019 in Aachen, Wasser und Gesundheit; Pinnekamp, J., Ed.; Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Siedlungswasserwirtschaft an der RWTH Aachen e.V.: Aachen, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-3-938996-56-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sansalone, J.J.; Buchberger, S.G. Characterization of solid and metal element distributions in urban highway stormwater. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaze, J.; Chiew, F.H.S. Nutrient Loads Associated with Different Sediment Sizes in Urban Stormwater and Surface Pollutants. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardana, C.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Role of particle size and composition in metal adsorption by solids deposited on urban road surfaces. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boogaard, F.C.; van de Ven, F.; Langeveld, J.G.; Kluck, J.; van de Giesen, N. Removal efficiency of storm water treatment techniques: Standardized full scale laboratory testing. Urban Water J. 2016, 14, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelbach, S.; Wöhrle, C. Settleable Solids from Combined Sewers: Settling, Stormwater Treatment, and Sedimentation Rates in Rivers. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugate, D.; Chant, B. Aggregate settling velocity of combined sewage overflow. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN 872. Wasserbeschaffenheit-Bestimmung Suspendierter Stoffe-Verfahren Durch Abtrennung Mittels Glasfaserfilter; Deutsche Fassung EN 872:2005; Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V.: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, P.; Benisch, J.; Blumensaat, F.; Dierschke, M.; Dittmer, U.; Gelhardt, L.; Gruber, G.; Grüner, S.; Heinz, E.; Hofer, T.; et al. AFS63-Harmonisierungsbedarf und Empfehlungen für die labortechnische Bestimmung des neuen Parameters. In Regenwasser in Urbanen Räumen. Aqua Urbanica Trifft Regenwassertage, Landau in der Pfalz, 18.-19.06.2018; Schmitt, T.G., Ed.; Technische Universität Kaiserslautern: Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2018; pp. 153–168. ISBN 978-3-95974-086-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger, J.; Tondera, K.; Linnemann, V. Determining fine suspended solids in combined sewer systems: Consequences for laboratory analysis. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Planning and Technologies for Sustainable Management of Water in the City (NOVATECH 2016), Lyon, France, 28 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, S.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; Caradot, N.; Hofer, T.; Gruber, G. Performance and uncertainties of TSS stormwater sampling strategies from online time series. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selbig, W.R.; Bannerman, R.T. Ratios of Total Suspended Solids to Suspended Sediment Concentrations by Particle Size. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.R.; Glysson, G.D.; Turcios, L.M.; Schwarz, G.E. Comparability of Suspended-Sediment Concentration and Total Suspended Solids Data; U.S. Department of the Interior: Reston, VA, USA, 2000.
- Galloway, J.M.; Evans, D.A.; Green, W.R. Comparability of Suspended-Sediment Concentration and Total Suspended-Solids Data for Two Sites on the L’Anguille River, Arkansas, 2001 to 2003: Scientific Investigations Report 2005-5193; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2005.
- Clark, S.E.; Siu, C.Y.S. Measuring Solids Concentration in Stormwater Runoff: Comparison of Analytical Methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseen, R.M.; Ballestero, T.P.; Fowler, G.D.; Guo, Q.; Houle, J. Sediment Monitoring Bias by Automatic Sampler in Comparison with Large Volume Sampling for Parking Lot Runoff. J. Irrig. Drain Eng. 2011, 137, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, J.M.; Walling, D.E. An assessment of the effects of sample collection, storage and resuspension on the representativeness of measurements of the effective particle size distribution of fluvial suspended sediment. Water Res. 1995, 29, 2498–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lau, S.-L.; Kayhanian, M.; Stenstrom, M.K. Particle Size Distribution in Highway Runoff. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, A.; Dierschke, M.; Gelhardt, L. Methodische Untersuchungen zur Bestimmung von AFS63 (Feine Abfiltrierbare Stoffe) in Verkehrsflächenabflüssen. Wasser Abwasser 2019, 4, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Rusydi, A.F. Correlation between conductivity and total dissolved solid in various type of water: A review. IOP Conf. Ser.Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 118, 12019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, J.P.; Sacher, F.; Fuchs, S. Up-to-date monitoring data of wastewater and stormwater quality in Germany. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clara, M.; Gruber, G.; Humer, F.; Hofer, T.; Kretschmer, F.; Ertl, T. SCHTURM-Spurenstoffemissionen aus Siedlungsgebieten und von Verkehrsflächen; Austrian Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management: Vienna, Austria, 2014.
- Brombach, H.; Weiss, G.; Fuchs, S. A new database on urban runoff pollution: Comparison of separate and combined sewer systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smullen, J.T.; Shallcross, A.L.; Cave, K.A. Updating the U.S. nationwide urban runoff quality data base. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francey, M.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A.; Duncan, H. New Insights into the Quality of Urban Storm Water in South Eastern Australia. J. Environ. Eng. 2010, 136, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piro, P.; Carbone, M.; Garofalo, G.; Sansalone, J. Size Distribution of Wet Weather and Dry Weather Particulate Matter Entrained in Combined Flows from an Urbanizing Sewershed. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 206, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Welker, A.; Helmreich, B. Critical review of heavy metal pollution of traffic area runoff: Occurrence, influencing factors, and partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 895–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Property | Large-Volume Sampler | Autosampler |
|---|---|---|
| Sampling strategy | Volume-proportional | Time-proportional |
| Sampling interval | 40–350 m3 | 3 min |
| Subsample volume | 8–10 L | 150–200 mL |
| Sample containers | Stainless steel, 1000 L | PE, 12–24 × 1 L |
| Samples per container | 10–100 | 5–6 |
| Pumping system | Peristaltic | Vacuum |
| Pump capacity | 1090 L∙h−1 | No data available |
| Pumping speed | ~0.62 m∙s−1 | >0.5 m∙s−1 |
| Suction height | Max. 8 m | Max. 8 m |
| Max. particle size | 5 mm | No data available |
| Suction hose | PVC, Ø 25 mm | PVC, Ø 12–16 mm |
| Active cooling | No | Yes |
| CSO Facility | Date (MM-dd-yyyy) | Total Overflow Duration (h) | Total Overflow Volume (m3) | Share of Total Volume Represented in the Composite Sample or Pollutograph (%) * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVS Overflow | LVS Inlet | AS Overflow | AS Inlet | ||||
| SED06 | 09-04-2018 | 1.5 | 4504 | 100 I,II | - | - | - |
| SED06 | 09-23-2018 | 2.6 | 7215 | 100 I,II | 100 I,II | - | - |
| SED06 | 05-20-2019 | 24.2 | 43,880 | - | 100 I,II | - | - |
| SED06 | 06-22-2019 | 4.1 | 10,167 | 100 I,II | - | - | - |
| SED06 | 07-01-2019 | 1.4 | 6282 | 100 I,II | - | - | - |
| SED06 | 07-28-2019 | 6.3 | 15,173 | 100 I,II | - | - | - |
| SED02 | 12-02-2018 | 8.8 | 2807 | 100 I,II | 100 I,II | - | - |
| SED02 | 05-11-2019 | 5.1 | 1657 | 100 I,II | 100 I,II | 76 | 82 |
| SED02 | 10-01-2019 | 8.9 | 2721 | 100 I,II | 100 I,II | 46 | 53 |
| SED05 | 10-09-2019 | 7.5 | 2481 | 100 I | - | 33 | - |
| FFR02 | 09-23-2018 | 4.8 | 8474 | 99 I,II | - | - | - |
| FFR02 | 12-02-2018 | 4.7 | 4306 | 100 I,II | - | - | - |
| FFR02 | 10-05-2019 | 1.7 | 2054 | 100 I,II | - | - | - |
| SES02 | 05-20-2019 | 46.0 | 71,054 | 11 I | - | 7 | - |
| SES02 | 05-28-2019 | 12.4 | 9353 | 81 I | - | 51 | - |
| SES02 | 07-01-2019 | 5.2 | 5827 | 100 I | - | 100 | - |
| SES02 | 07-27-2019 | 12.8 | 20,777 | 36 I | - | 40 | - |
| SES02 | 08-02-2019 | 4.1 | 6227 | 100 I | - | 100 | - |
| SES02 | 08-20-2019 | 11.8 | 9890 | 77 I | - | 43 | - |
| SES02 | 10-04-2019 | 11.8 | 9015 | 86 I | - | 40 | - |
| SES02 | 10-30-2019 | 12.7 | 8255 | 94 I | - | 53 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nickel, J.P.; Fuchs, S. Large-Volume Samplers for Efficient Composite Sampling and Particle Characterization in Sewer Systems. Water 2021, 13, 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202831
Nickel JP, Fuchs S. Large-Volume Samplers for Efficient Composite Sampling and Particle Characterization in Sewer Systems. Water. 2021; 13(20):2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202831
Chicago/Turabian StyleNickel, Jan Philip, and Stephan Fuchs. 2021. "Large-Volume Samplers for Efficient Composite Sampling and Particle Characterization in Sewer Systems" Water 13, no. 20: 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202831
APA StyleNickel, J. P., & Fuchs, S. (2021). Large-Volume Samplers for Efficient Composite Sampling and Particle Characterization in Sewer Systems. Water, 13(20), 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202831







