Cyanobacterial Biomass as a Potential Biosorbent for the Removal of Recalcitrant Dyes from Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cyanobacterial Biomass: Preparation and Characterization
2.2. Adsorption Experiments
2.3. Kinetics Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biomass Characterization
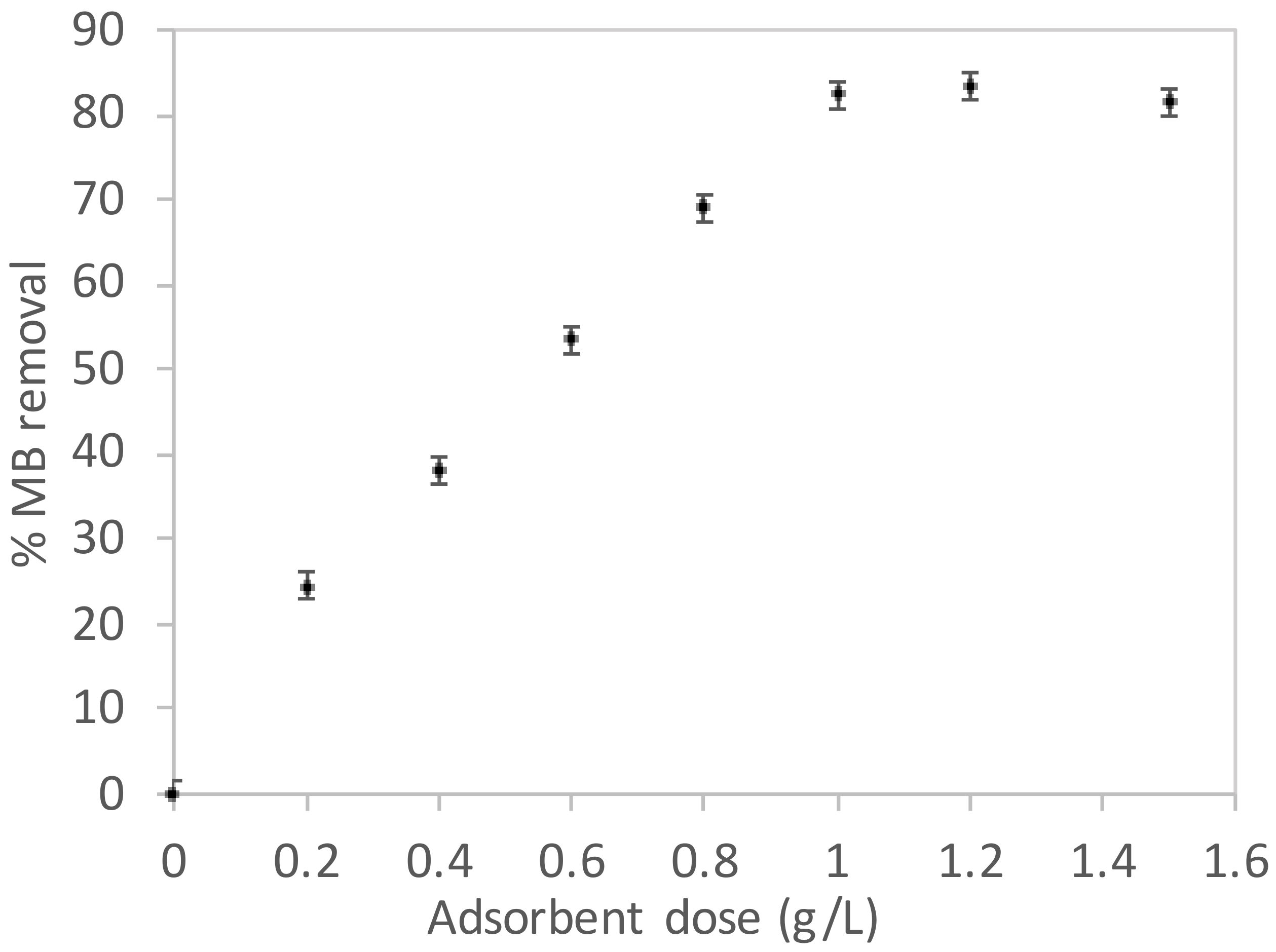
3.2. Adsorption Parameters Assay
3.3. Adsorption Parameters Assay
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adeel, M.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Francis, D.; Yang, Y. Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrbić, B.D.; Kadokami, K.; Antić, I. Survey on the micro-pollutants presence in surface water system of northern Serbia and environmental and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, M.F.; Sapawe, N. A review on the current techniques and technologies of organic pollutants removal from water/wastewater. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 31, A158–A165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.C.; Levy, R.C.; Da Silva, A.M.; Pryor, S.C. Developing and diagnosing climate change indicators of regional aerosol optical properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- W.M.O. State of the Global Climate 2020; WMO-No. 1264; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, A.E.; van Heuven, S.M.A.C.; de Bakker, D.M.; van Duyl, F.C.; Reichart, G.-J.; de Nooijer, L.J. Combined Effects of Experimental Acidification and Eutrophication on Reef Sponge Bioerosion Rates. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Govers, L.L.; Lamers, L.P.M.; Bouma, T.J.; de Brouwer, J.H.F.; van Katwijk, M.M. Eutrophication threatens Caribbean seagrasses—An example from Curaçao and Bonaire. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, P.M.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Sandrini, G.; Stal, L.J.; Matthijs, H.C.P.; Davis, T.W.; Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. How rising CO2 and global warming may stimulate harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management, 2nd ed.; Chorus, I., Welker, M., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, O.J.; Kim, H.; Chiang, P.C. Decolorization of wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 30, 449–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayomie, O.S.; Kandeel, H.; Shoeib, T.; Yang, H.; Youssef, N.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Novel approach for effective removal of methylene blue dye from water using fava bean peel waste. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zaban, M.I.; Mahmoud, M.A.; AlHarbi, M.A. Catalytic degradation of methylene blue using silver nanoparticles synthesized by honey. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2007–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krosuri, A.; Wu, S.; Bashir, M.A.; Walquist, M. Efficient degradation and mineralization of methylene blue via continuous-flow electrohydraulic plasma discharge. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemici, B.T.; Ozel, H.U.; Ozel, H.B. Removal of methylene blue onto forest wastes: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichour, A.; Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H.; Mohamed Zuki, F.B.; Kheireddine Aroua, M.; Ibbora, C.V. Low-cost, biodegradable and highly effective adsorbents for batch and column fixed bed adsorption processes of methylene blue. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshariani, F.; Roosta, A. Experimental study and mathematical modeling of biosorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution in a packed bed of microalgae Scenedesmus. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can-Terzi, B.; Goren, A.Y.; Okten, H.E.; Sofuoglu, S.C. Biosorption of methylene blue from water by live Lemna minor. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangabhashiyam, S.; Lata, S.; Balasubramanian, P. Biosorption characteristics of methylene blue and malachite green from simulated wastewater onto Carica papaya wood biosorbent. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 10, 197–215. [Google Scholar]
- De Carvalho, H.P.; Huang, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, G.; Dong, L.; Liu, X. Improvement of Methylene Blue removal by electrocoagulation/banana peel adsorption coupling in a batch system. Alex. Eng. J. 2015, 54, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, K.L.; Lee, X.J.; Ong, H.C.; Chen, W.H.; Chang, J.S.; Lin, C.S.; Show, P.L.; Ling, T.C. Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue and anionic Congo red dyes using wet-torrefied microalgal biochar: Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, R.; Kothari, R.; Singh, H.M.; Ahmad, S.; Ashokkumar, V.; Tyagi, V.V. Production of algal biomass for its biochemical profile using slaughterhouse wastewater for treatment under axenic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Masud, A.; Aich, N.; Atkinson, J.D. Phenol and Cr(VI) removal using materials derived from harmful algal bloom biomass: Characterization and performance assessment for a biosorbent, a porous carbon, and Fe/C composites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ani, J.U.; Akpomie, K.G.; Okoro, U.C.; Aneke, L.E.; Onukwuli, O.D.; Ujam, O.T. Potentials of activated carbon produced from biomass materials for sequestration of dyes, heavy metals, and crude oil components from aqueous environment. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vahabisani, A.; An, C. Use of biomass-derived adsorbents for the removal of petroleum pollutants from water: A mini-review. Environ. Syst. Res. 2021, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasundari, E.; Kumar, P.K. Adsorption isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamic analysis of Cu(II) ions onto the dried algal biomass (Spirulina platensis). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 56, 129–144. [Google Scholar]
- Nithya, K.; Sathish, A.; Pradeep, K.; Kiran Baalaji, S. Algal biomass waste residues of Spirulina platensis for chromium adsorption and modeling studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño-Camelo, K.; Diaz-Uribe, C.; Gallego-Cartagena, E.; Vallejo, W.; Martinez, V.; Quiñones, C.; Hurtado, M.; Schott, E. Cyanobacterial Biomass Pigments as Natural Sensitizer for TiO2 Thin Films. Int. J. Photoenergy 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saravanan, A.; Sundararaman, T.R.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Yaashikaa, P.R. Effective adsorption of Cu(II) ions on sustainable adsorbent derived from mixed biomass (Aspergillus campestris and agro waste): Optimization, isotherm and kinetics study. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayachi, F.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Aatrous, M.; Sakly, A.; Lamine, A.B. Evaluating the adsorption of Ni(II) and Cu(II) on spirulina biomass by statistical physics formalism. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 80, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the Adsorption in Solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–471. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, P.; Chowdhury, S.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, I. Insight into adsorption equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of Malachite Green onto clayey soil of Indian origin. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyinbor, A.A.; Adekola, F.A.; Olatunji, G.A. Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic modeling of liquid phase adsorption of Rhodamine B dye onto Raphia hookerie fruit epicarp. Water Resour. Ind. 2016, 15, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapoor, A.; Yang, R.T. Surface diffusion on energetically heterogeneous surfaces. AIChE J. 1989, 35, 1735–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjelloun, M.; Miyah, Y.; Akdemir Evrendilek, G.; Zerrouq, F.; Lairini, S. Recent Advances in Adsorption Kinetic Models: Their Application to Dye Types. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, T.; Yalçın, D.; Erkaya, I.A.; Udoh, A.U. Identification and Characterization of Some Species of Cyanobacteria, Chlorophyta and BacillariophytaUsing Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2016, 11, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Baxter, L.; Fonseca, F. Biomass fly ash in concrete: SEM, EDX and ESEM analysis. Fuel 2008, 87, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarín, J.R.; Moreno-Pirajan, J.C.; Giraldo, L. Kinetic Study of the Bioadsorption of Methylene Blue on the Surface of the Biomass Obtained from the Algae D. antarctica. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 2124845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, J.; Kaur, G. Freundlich, Langmuir adsorption isotherms and kinetics for the removal of malachite green from aqueous solutions using agricultural waste rice straw. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 4, 250–258. [Google Scholar]
- Ncibi, M.C.; Mahjoub, B.; Seffen, M. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of methylene blue biosorption by Posidonia oceanica (L.) fibres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghazy, R.M. Activated biomass of the green microalga chlamydomonas variabilis as an efficient biosorbent to remove methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions. Water SA 2019, 45, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hameed, B.H. Spent tea leaves: A new non-conventional and low-cost adsorbent for removal of basic dye from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.K.; Rastogi, A. Sorption and desorption studies of chromium(VI) from nonviable cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz, F.; Karaman, S. Removal of Basic Red 46 dye from aqueous solution by pine tree leaves. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, T.C.A.; da Silva, I.Z.; Rubio, A.J.; Bergamasco, R.; Gasparotto, F.; Paccola, E.A.S.; Yamaguchi, N.U. Sugarcane bagasse as an efficient biosorbent for methylene blue removal: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.K.; Nasar, A. Walnut shell powder as a low-cost adsorbent for methylene blue dye: Isotherm, kinetics, thermodynamic, desorption and response surface methodology examinations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, F.A.; Lima, E.C.; Dias, S.L.P.; Mazzocato, A.C. Methylene blue biosorption from aqueous solutions by yellow passion fruit waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozudogru, Y.; Merdivan, M.; Goksan, T. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by brown alga Cystoseira barbata. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 62, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Húmpola, P.D.; Odetti, H.S.; Fertitta, A.E.; Vicente, J.L. Thermodynamic analysis of adsorption models of phenol in liquid phase on different activated carbons. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2013, 58, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.H.; Xiong, S.; Wang, B.; Li, Q.; Yang, W.C. Cr(III) adsorption by sugarcane pulp residue and biochar. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 20, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, M.; Kirbiyik, Ç.; Çepelioǧullar, Ö.; Pütün, A.E. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by bio-char, a by-product of pyrolysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouei, A.I.; Amooey, A.A.; Asgharzadeh, F. Cadmium Removal from Aqueous Solution by Canola Residues: Adsorption Equilibrium and Kinetics; Iranian Association of Chemical Engineers (IAChE): Tehran, Iran, 2013; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, N.; Sundaram, M.M. Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons—A comparative study. Dye. Pigment. 2001, 51, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xian, Y.; He, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X.; Qi, H.; Ma, J.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Adsorption characteristics of pb(ii) using biochar derived from spent mushroom substrate. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uwamungu, J.Y.; Nartey, O.D.; Uwimpaye, F.; Dong, W.; Hu, C. Evaluating biochar impact on topramezone adsorption behavior on soil under no-tillage and rotary tillage treatments: Isotherms and kinetics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nworie, F.S.; Nwabue, F.I.; Oti, W.; Mbam, E.; Nwali, B.U. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using activated rice husk biochar: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and error analysis. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2019, 64, 4365–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Isotherm Model | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir 1 | qmax (mg g−1) 238.1 | KL (L mg−1) 0.024 | RL–R2 0.45–0.9412 | ARE (%) 12.5 |
| Freundlich 2 | KF (mg g−1)(L mg−1)1/n 14.23 | 1/n | R2 0.9913 | 4.8 |
| Temkin 3 | A (L mg−1) 0.416 | B (kJ/mol) | R2 0.9181 | 24.7 |
| Model | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order 1 | qe (mg g−1) 50.95 | k1 (min−1) 0.045 | R2 0.9483 | ARE (%) 24.8 |
| Pseudo-second-order 2 | qe (mg g−1) 46.51 | k2 (g.mg−1min−1) 0.013 | 0.9976 | 3.0 |
| Intraparticle diffusion 3 | C (mg g−1) 16.55 | kid (g.mg−1min−1) 2.1569 | 0.8079 | 9.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diaz-Uribe, C.; Angulo, B.; Patiño, K.; Hernández, V.; Vallejo, W.; Gallego-Cartagena, E.; Romero Bohórquez, A.R.; Zarate, X.; Schott, E. Cyanobacterial Biomass as a Potential Biosorbent for the Removal of Recalcitrant Dyes from Water. Water 2021, 13, 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223176
Diaz-Uribe C, Angulo B, Patiño K, Hernández V, Vallejo W, Gallego-Cartagena E, Romero Bohórquez AR, Zarate X, Schott E. Cyanobacterial Biomass as a Potential Biosorbent for the Removal of Recalcitrant Dyes from Water. Water. 2021; 13(22):3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223176
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiaz-Uribe, Carlos, Barni Angulo, Karen Patiño, Vincent Hernández, William Vallejo, Euler Gallego-Cartagena, Arnold R. Romero Bohórquez, Ximena Zarate, and Eduardo Schott. 2021. "Cyanobacterial Biomass as a Potential Biosorbent for the Removal of Recalcitrant Dyes from Water" Water 13, no. 22: 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223176
APA StyleDiaz-Uribe, C., Angulo, B., Patiño, K., Hernández, V., Vallejo, W., Gallego-Cartagena, E., Romero Bohórquez, A. R., Zarate, X., & Schott, E. (2021). Cyanobacterial Biomass as a Potential Biosorbent for the Removal of Recalcitrant Dyes from Water. Water, 13(22), 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223176







