Energy Exchange and Evapotranspiration over the Ejina Oasis Riparian Forest Ecosystem with Different Land-Cover Types
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
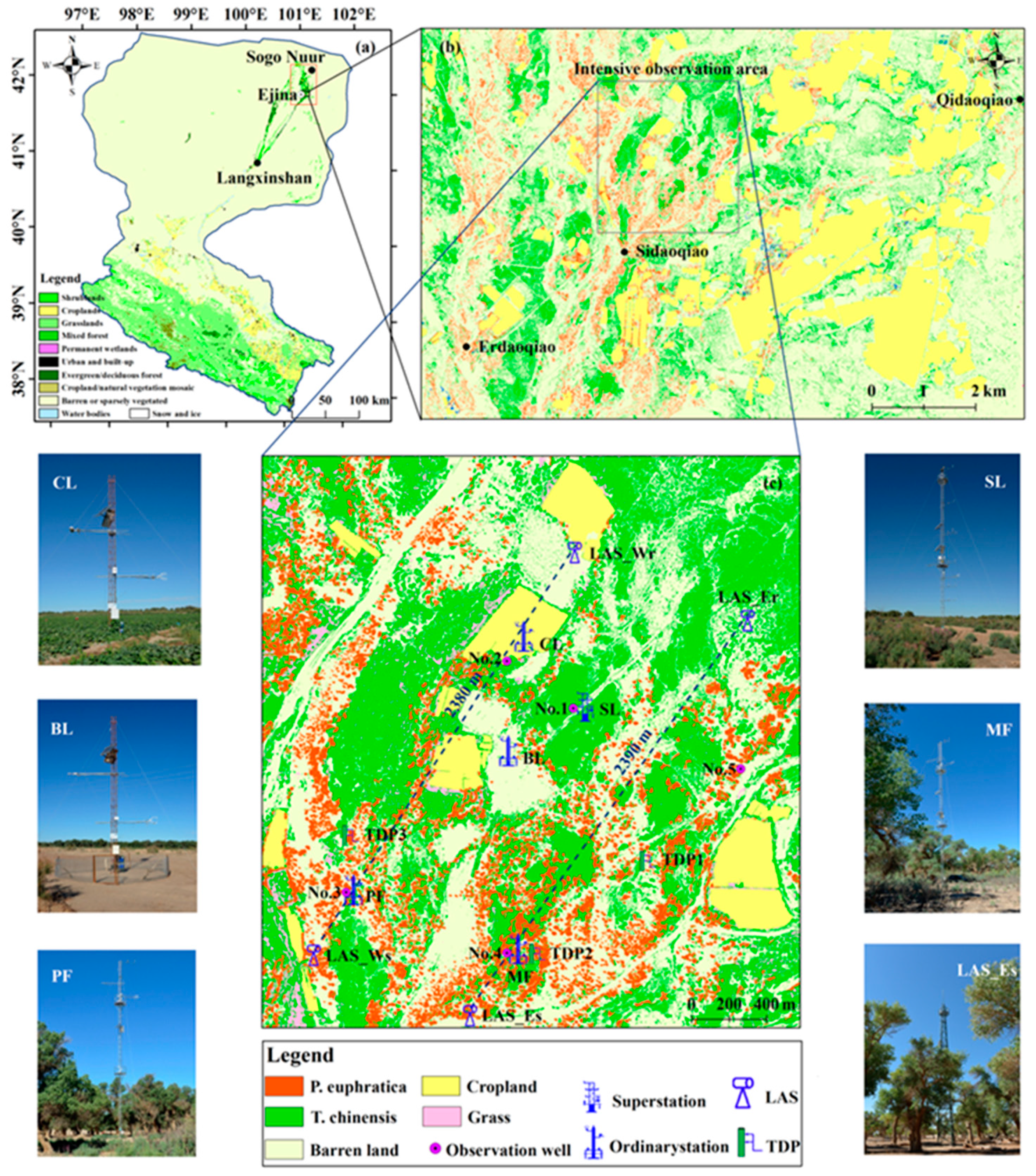
2.1. Study Area and Site Description
2.2. Data Processing
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Footprint Analysis of EC Flux Measurements
2.3.2. Energy Balance Closure Assessment
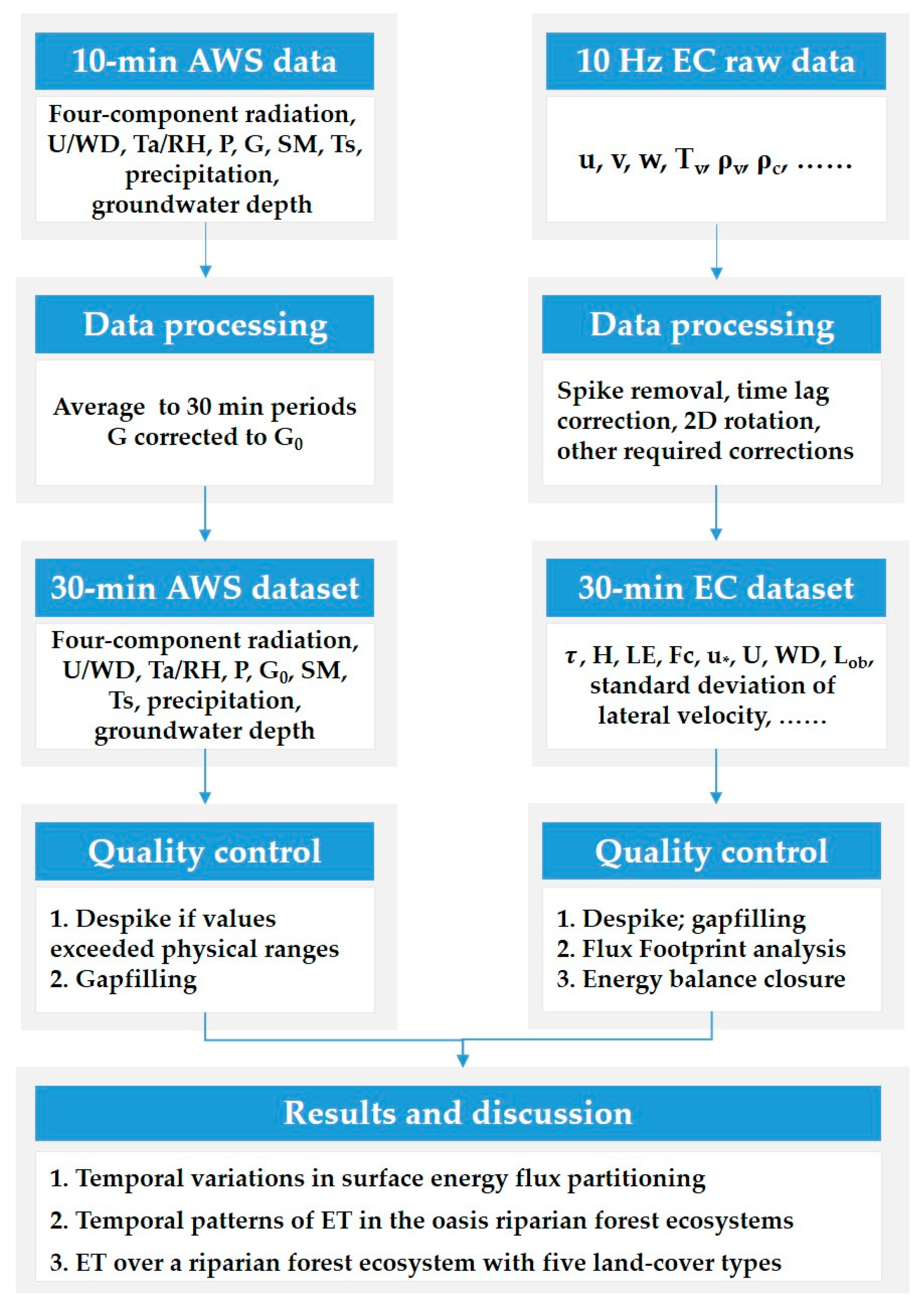
2.4. Flowchart of This Study
3. Results and Discussion
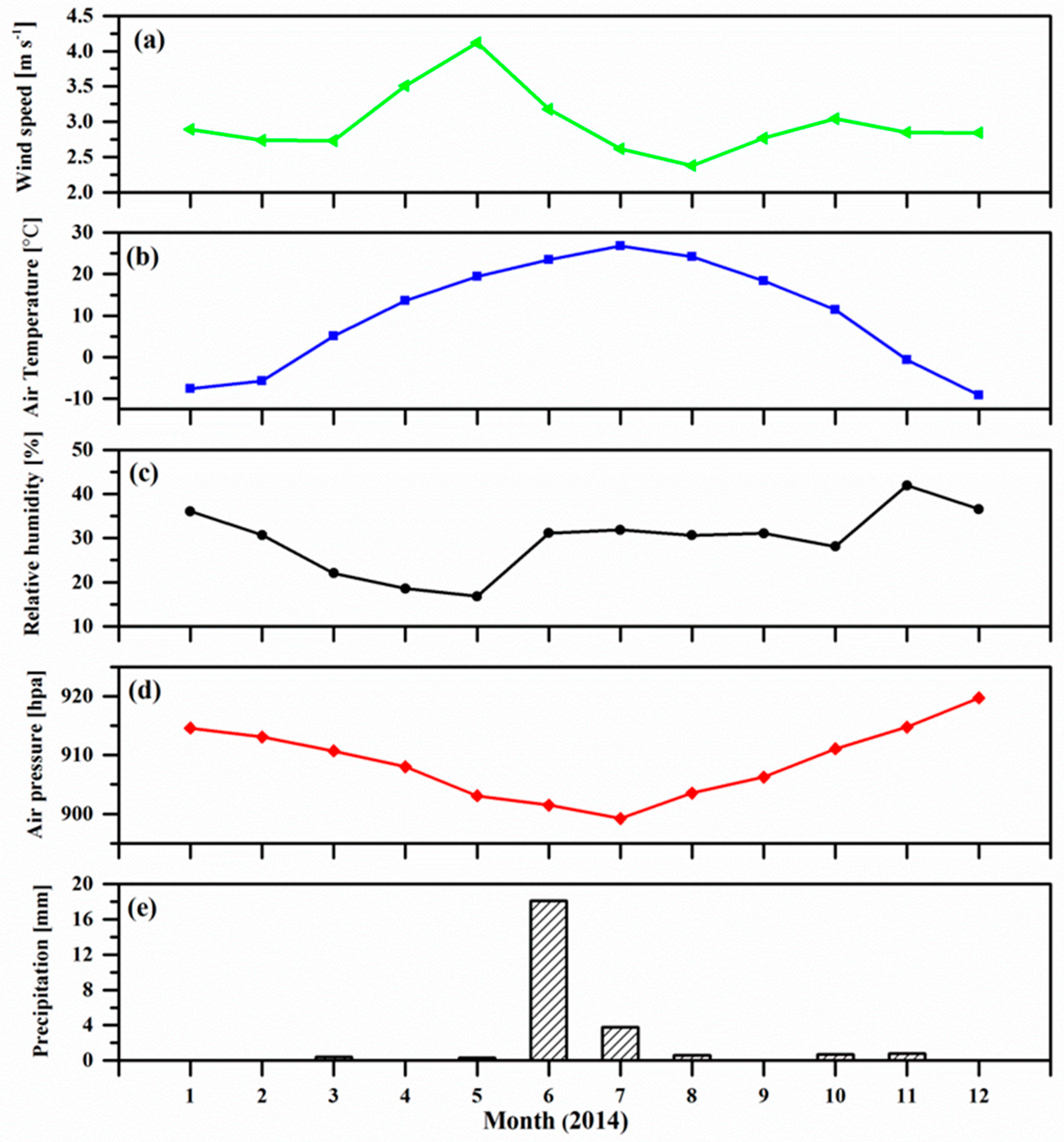
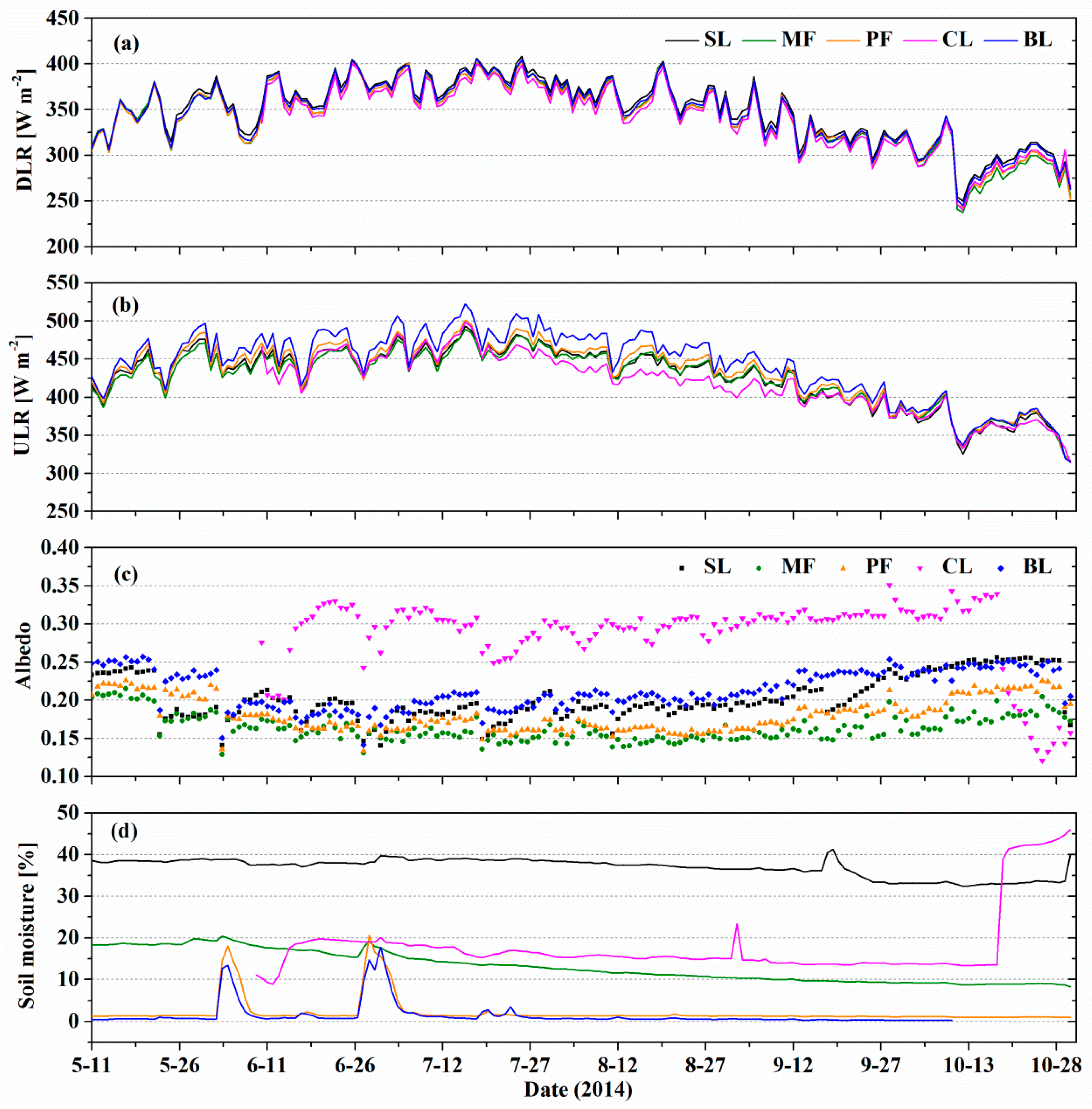
3.1. Meteorological Conditions
3.2. Representativeness of EC Flux Matrix Measurements
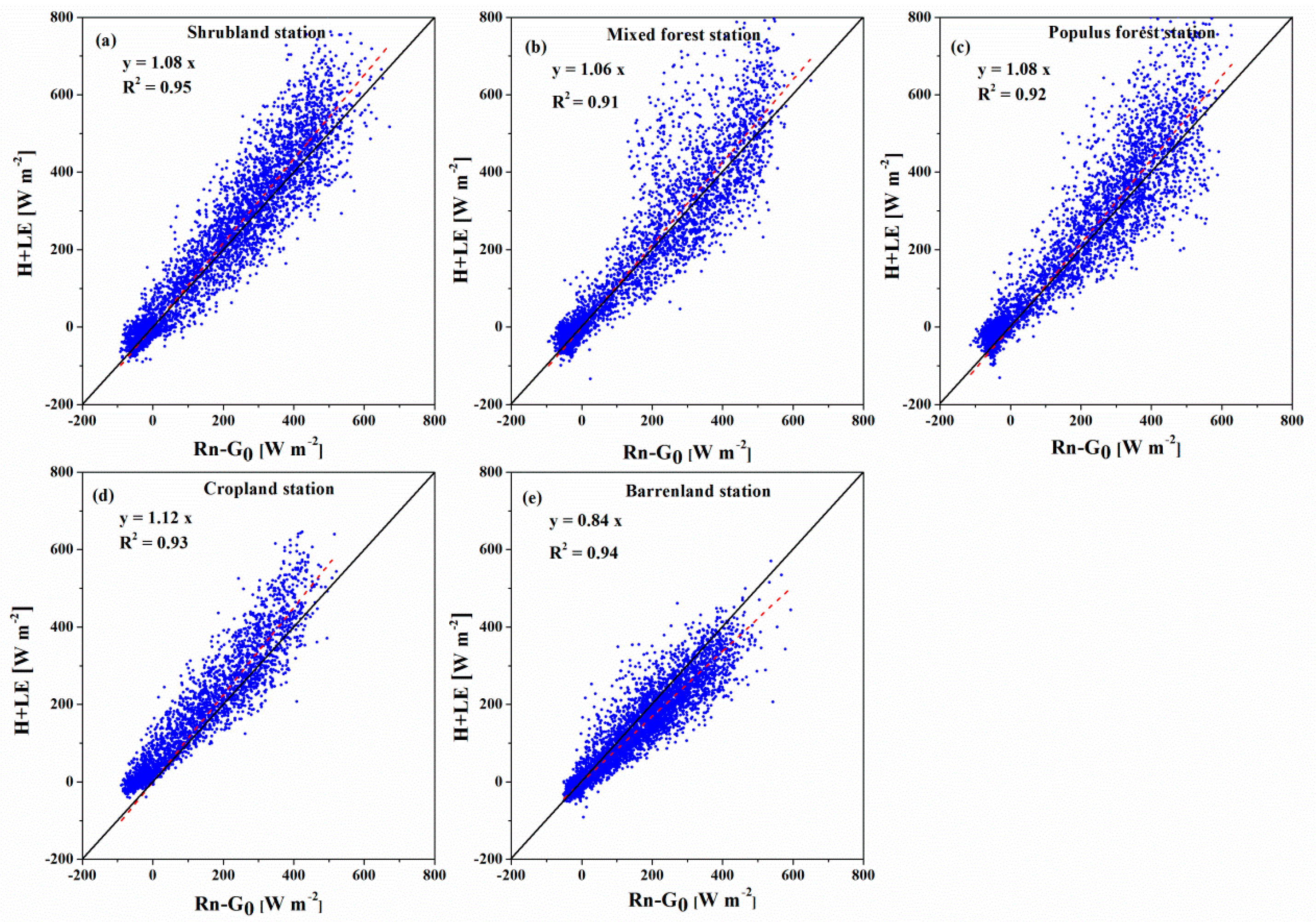
3.3. Energy Balance Closure of the EC Flux Measurements
3.4. Temporal Variations in Energy Flux Partitioning over a Riparian Forest Ecosystem
3.5. Temporal Patterns of Evapotranspiration in the Oasis Riparian Forest Ecosystems
3.6. Evapotranspiration over a Riparian Forest Ecosystem with Different Land-Cover Types
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Cui, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Niu, H.; Jiang, G. Seasonal and interannual variation in water vapor and energy exchange over a typical steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 146, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; He, J.; Zhang, K. Energy exchange and evapotranspiration over irrigated seed maize agroecosystems in a desert-oasis region, northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 223, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D.; Kelliher, F.; Black, T.A.; Jarvis, P. Climate and vegetation controls on boreal zone energy exchange. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2000, 6, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldocchi, D.D.; Xu, L.; Kiang, N. How plant functional-type, weather, seasonal drought, and soil physical properties alter water and energy fluxes of an oak–grass savanna and an annual grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 123, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burba, G.G.; Verma, S.B. Seasonal and interannual variability in evapotranspiration of native tallgrass prairie and cultivated wheat ecosystems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 135, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.; Kustas, W.; Prueger, J.; Diak, G. Surface flux estimation using radiometric temperature: A dual-temperature-difference method to minimize measurement errors. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Lu, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, C. Energy flux partitioning and evapotranspiration in a sub-alpine spruce forest ecosystem. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5093–5104. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; He, X.; Bateni, S.; Auligne, T.; Shaomin, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Mao, K. Mapping regional turbulent heat fluxes via variational assimilation of land surface temperature data from polar orbiting satellites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Lin, G.; Zhang, W.; Miao, H.; Wei, L.; Huang, J.; Han, X. Energy balance and partition in Inner Mongolia steppe ecosystems with different land use types. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Piao, S.; Huntingford, C.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; McVicar, T.R.; Peng, S.; Ottlé, C.; et al. Partitioning global land evapotranspiration using CMIP5 models constrained by observations. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Allen, R.G.; Morse, A.; Kustas, W.P. Use of Landsat thermal imagery in monitoring evapotranspiration and managing water resources. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with internalized calibration (METRIC)—Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.M.; Jacobs, J.M.; Sumner, D.M.; Ray, R.L. A comparison of models for estimating potential evapotranspiration for Florida land cover types. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Sahoo, B.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Singh, R. Evaluation of variable-infiltration capacity model and MODIS-Terra satellite-derived grid-scale evapotranspiration estimates in a river basin with tropical monsoon-type climatology. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration: Observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, 2011RG000373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Koirala, S.; Weber, U.; Ichii, K.; Gans, F.; Camps-Valls, G.; Papale, D.; Schwalm, C.; Tramontana, G.; Reichstein, M. The FLUXCOM ensemble of global land-atmosphere energy fluxes. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.M.; Liu, J. Evolution of evapotranspiration models using thermal and shortwave remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Development of a global evapotranspiration algorithm based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M. Validation of remotely sensed evapotranspiration over the Hai River Basin, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Song, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ge, Y.; Xu, T.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, F. Upscaling evapotranspiration measurements from multi-site to the satellite pixel scale over heterogeneous land surfaces. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D.D.; Hincks, B.B.; Meyers, T.P. Measuring biosphere-atmosphere exchanges of biologically related gases with micrometeorological methods. Ecology 1988, 69, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D.; Falge, E.; Gu, L.; Olson, R.; Hollinger, D.; Running, S.; Anthoni, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Davis, K.; Evans, R. FLUXNET: A new tool to study the temporal and spatial variability of ecosystem-scale carbon dioxide, water vapor, and energy flux densities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 2415–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D. Assessing the eddy covariance technique for evaluating carbon dioxide exchange rates of ecosystems: Past, present and future. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Fu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wen, X.; Zhang, L. Recent progress and future directions of ChinaFLUX. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2006, 49 (Suppl. II), 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubinet, M.; Grelle, A.; Ibrom, A.; Rannik, Ü.; Moncrieff, J.; Foken, T.; Kowalski, A.S.; Martin, P.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; et al. Estimates of the annual net carbon and water exchange of forests: The EUROFLUX methodology. In Advances in Ecological Research; Fitter, A., Raffaelli, D., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 30, pp. 113–175. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Wu, Y. Area-averaged evapotranspiration over a heterogeneous land surface: Aggregation of multi-point EC flux measurements with a high-resolution land-cover map and footprint analysis. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4037–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Law, B.E.; Falge, E.; Gu, L.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Bakwin, P.; Berbigier, P.; Davis, K.; Dolman, A.J.; Falk, M.; Fuentes, J.D.; et al. Environmental controls over carbon dioxide and water vapor exchange of terrestrial vegetation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCaughey, J.H.; Lafleur, P.M.; Joiner, D.W.; Bartlett, P.A.; Costello, A.M.; Jelinski, D.E.; Ryan, M.G. Magnitudes and seasonal patterns of energy, water, and carbon exchanges at a boreal young jack pine forest in the BOREAS northern study area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 28997–29007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Feng, J. Seasonal and interannual variations of evapotranspiration and energy exchange over different land surfaces in a semiarid area of China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 1875–1888. [Google Scholar]
- Trepekli, A.; Loupa, G.; Rapsomanikis, S. Seasonal evapotranspiration, energy fluxes and turbulence variance characteristics of a Mediterranean coastal grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 226, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, P.; Meyers, T.P.; Scott, R.L.; Kennedy, L.; Heuer, M. Energy exchange and evapotranspiration over two temperate semi-arid grasslands in North America. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 153, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, S.G.; Yu, G.R.; Asanuma, J.; Sugita, M.; Zhang, L.M.; Hu, Z.M.; Wei, Y.F. Seasonal and interannual variations in water vapor exchange and surface water balance over a grazed steppe in central Mongolia. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Yang, D. Interannual and seasonal variability in evapotranspiration and energy partitioning over an irrigated cropland in the North China Plain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Kang, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, L. Evapotranspiration measurement and estimation using modified Priestley–Taylor model in an irrigated maize field with mulching. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 168, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Su, C.; Zhang, Y. Research on the microclimate characteristics and cold island effect over a reservoir in the Hexi Region. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Qi, Y. A preliminary study of turbulence transfer characteristics in Gobi area with an eddy correlation technique. Plateau Meteorol. 1990, 9, 120–129, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zuo, H. The characters of energy budget on the Gobi and desert surface in Hexi region. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1992, 6, 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.D.; Devitt, D.A.; Sala, A.; Cleverly, J.R.; Busch, D.E. Water relations of riparian plants from warm desert regions. Wetlands 1998, 18, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Grinevsky, S.O.; Pozdniakov, S.P.; Yu, J.; Dautova, D.S.; Min, L.; Du, C.; Zhang, Y. Application of the water table fluctuation method for estimating evapotranspiration at two phreatophyte-dominated sites under hyper-arid environments. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2289–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy-Meir, I. Desert ecosystems: Environment and producers. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 25–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, H. Response of the accumulation of proline in the bodies of Populus euphratica to the change of groundwater level at the lower reaches of Tarim River. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 1995–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y.; et al. Heihe Watershed Allied Telemetry Experimental Research (HiWATER): Scientific Objectives and Experimental Design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chang, X.; He, Z. Responses of distribution pattern of desert riparian forests to hydrologic process in Ejina oasis. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2004, 47, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, P. Relationship between water and vegetation in the Ejina Delta. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2012, 26, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xiao, S.; Xiao, H. Integrated study of the water-ecosystem-economy in the Heihe River Basin. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Ge, Y.; Li, H.; Han, F.; Hu, X.; Tian, W.; Tian, Y.; Pan, X.; Nian, Y. Hydrological cycle in the Heihe River Basin and its implication for water resource management in endorheic basins. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 890–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Huang, W.; Chen, X. Impact of Ecological Water Diversion on temporal and spatial change of water resources in Heihe downstream. J. China Hydrol. 2011, 31, 52–56, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Si, J.; Qi, F.; Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y. Vegetation changes in the lower reaches of the Heihe River after its water import. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occidential Sin. 2005, 25, 631–640, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xi, H.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.; Chang, Z.; Su, Y. Response of NDVI to groundwater level change in the lower reaches of the Heihe River, China. J. Desert Res. 2013, 33, 574–582, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Nian, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, J. Landscape changes of the Ejin Delta in the Heihe River Basin in Northwest China from 1930 to 2010. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.L.; Lu, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.H.; Lu, X.G. Ejin oasis land use and vegetation change between 2000 and 2011: The role of the ecological water diversion project. Energies 2015, 8, 7040–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y. Growing season evapotranspiration from Tamarix ramosissima stands under extreme arid conditions in northwest China. Environ. Geol. 2005, 48, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Xiao, H.; Si, J.; Xiao, S.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Y. Evapotranspiration and crop coefficient of Populus euphratica Oliv forest during the growing season in the extreme arid region northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Zhang, P.; Shao, M.A.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, X. Energy and water exchanges over a riparian Tamarix spp. stand in the lower Tarim River basin under a hyper-arid climate. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 194, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, G.F.; Luo, Y.; Shao, M.A.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, X.C. Evapotranspiration and its main controlling mechanism over the desert riparian forests in the lower Tarim River Basin. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C. Tamarix ramosissima stand evapotranspiration and its association with hydroclimatic factors in an arid region in northwest China. J. Arid Environ. 2017, 138, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.Y. Evapotranspiration of a Populus euphratica Oliv. forest and its controlling factors in the lower Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2017, 9, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.F.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xi, H.Y.; Zhao, C.Y. Comparable water use of two contrasting riparian forests in the lower Heihe River basin, Northwest China. J. For. Res. 2018, 29, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.F.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.H.; Xi, H.Y.; O’Grady, A.P.; Pinkard, E.A. Responses of riparian forests to flood irrigation in the hyper-arid zone of NW China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, F.; Zhang, J. Vegetation coverage classification and vegetation structure parameters of Populus euphratica forest in Ejina Oasis by LiDAR. J. Desert Res. 2017, 37, 689–697, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W. Characteristics of Phenology and Physiological Ecology of Populus euphratica Olive in Ejina. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Ren, Z. Aggregation of area-averaged evapotranspiration over the Ejina Oasis based on a flux matrix and footprint analysis. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, Y. HiWATER: Dataset of Leaf Area Index by LAI2200 in the Lower Reaches of the Heihe River Basin. A Big Earth Data Platform for Three Poles. 2015. Available online: http://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en/data/d6584b27-1e02-4bc7-90d1-8b360d9c69ab/ (accessed on 12 October 2021). [CrossRef]
- Liebethal, C.; Huwe, B.; Foken, T. Sensitivity analysis for two ground heat flux calculation approaches. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 132, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, W.; Wang, J. Assessment of the Energy balance closure under advective conditions and its impact using remote sensing data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z. Assessment of uncertainties in eddy covariance flux measurement based on intensive flux matrix of HiWATER-MUSOEXE. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, T.; Wang, W.; Ma, M. Intercomparison of surface energy flux measurement systems used during the HiWATER-MUSOEXE. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2013, 118, 13140–13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, W.; Jia, Z.; Zhu, M.; Bai, J.; Wang, J. A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauder, M.; Foken, T. Documentation and Instruction Manual of the Eddy-Covariance Software Package TK3 (Update); Universität Bayreuth, Abt. Mikrometeorologie: Bayreuth, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Horst, T.; Weil, J. Footprint estimation for scalar flux measurements in the atmospheric surface layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1992, 59, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Guo, Q.; Baldocchi, D.; Leclerc, M.; Xu, L.; Schmid, H. Upscaling fluxes from tower to landscape: Overlaying flux footprints on high-resolution (IKONOS) images of vegetation cover. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 136, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kljun, N.; Calanca, P.; Rotach, M.; Schmid, H. A simple two-dimensional parameterisation for Flux Footprint Prediction (FFP). Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 3695–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chehbouni, A.; Watts, C.; Lagouarde, J.-P.; Kerr, Y.; Rodriguez, J.-C.; Bonnefond, J.-M.; Santiago, F.; Dedieu, G.; Goodrich, D.; Unkrich, C. Estimation of heat and momentum fluxes over complex terrain using a large aperture scintillometer. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 105, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, T.; Schaaf, C.L.; Kljun, N.; Munger, J.W. Seasonal variation of source contributions to eddy-covariance CO2 measurements in a mixed hardwood-conifer forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 253, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moene, A.F.; Dam, J.C.V. Transport in the Atmosphere-Vegetation-Soil Continuum; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 436. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, S.; Mendes, K.R.; da Silva, L.L.; Mutti, P.R.; Medeiros, S.S.; Amorim, L.B.; dos Santos, C.A.C.; Perez-Marin, A.M.; Ramos, T.M.; Marques, T.V.; et al. Closure and partitioning of the energy balance in a preserved area of a Brazilian seasonally dry tropical forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 271, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majozi, N.P.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Ramoelo, A.; Mathieu, R.; Nickless, A.; Verhoef, W. Analysing surface energy balance closure and partitioning over a semi-arid savanna FLUXNET site in Skukuza, Kruger National Park, South Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3401–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGloin, R.; Šigut, L.; Havránková, K.; Dušek, J.; Pavelka, M.; Sedlák, P. Energy balance closure at a variety of ecosystems in Central Europe with contrasting topographies. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 248, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncley, S.P.; Foken, T.; Vogt, R.; Kohsiek, W.; DeBruin, H.; Bernhofer, C.; Christen, A.; Van Gorsel, E.; Grantz, D.; Feigenwinter, C. The energy balance experiment EBEX-2000. Part I: Overview and energy balance. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2007, 123, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foken, T. The energy balance closure problem: An overview. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 1351–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foken, T.; Mauder, M.; Liebethal, C.; Wimmer, F.; Beyrich, F.; Leps, J.-P.; Raasch, S.; DeBruin, H.A.; Meijninger, W.M.; Bange, J. Energy balance closure for the LITFASS-2003 experiment. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 101, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Li, X. Diurnal variations of the flux imbalance over homogeneous and heterogeneous landscapes. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2018, 168, 417–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, F.; De Roo, F.; Rotenberg, E.; Yakir, D.; Schmid, H.P.; Mauder, M. Secondary circulations at a solitary forest surrounded by semi-arid shrubland and their impact on eddy-covariance measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 211, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agam, N.; Kustas, W.P.; Evett, S.R.; Colaizzi, P.D.; Cosh, M.H.; McKee, L.G. Soil heat flux variability influenced by row direction in irrigated cotton. Adv. Water Resour. 2012, 50, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Horton, R.; Liu, H. Impact of wave phase difference between soil surface heat flux and soil surface temperature on soil surface energy balance closure. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyrich, F.; Herzog, H.J.; Neisser, J. The LITFASS project of DWD and the LITFASS-98 experiment: The project strategy and the experimental setup. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2002, 73, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauder, M.; Liebethal, C.; Göckede, M.; Leps, J.P.; Beyrich, F.; Foken, T. Processing and quality control of flux data during LITFASS. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 121, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Goldstein, A.; Falge, E.; Aubinet, M.; Baldocchi, D.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Ceulemans, R.; Dolman, H.; Field, C. Energy balance closure at FLUXNET sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Yu, G.-R.; Wen, X.; Zhang, L.M.; Ren, C.Y.; Fu, Y.L. Energy balance closure ChinaFLUX sites. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2005, 48, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Zhu, Z.L.; Jia, Z.Z.; Zhu, M.J. Measurements of evapotranspiration from eddy-covariance systems and large aperture scintillometers in the Hai River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 487, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twine, T.E.; Kustas, W.; Norman, J.; Cook, D.; Houser, P.; Meyers, T.; Prueger, J.; Starks, P.; Wesely, M. Correcting eddy-covariance flux underestimates over a grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 103, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. Characteristics of Energy Balance of Riparian Tamarix Shrubs in Desert. J. Desert Res. 2014, 34, 108–117, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y. Research advance about the energy budget and transportation of water vapor in the HEIFE area. Adv. Earth Sci. 1994, 9, 30–34, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ward, H.C. Scintillometry in urban and complex environments: A review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 064005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Land surface process experiments and interaction study in China: From HEIFE to IMGRASS and GAME-Tibet/TIPEX. Plateau Meteorol. 1999, 18, 280–294, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Si, J.; Feng, Q.; Cao, S.; Yu, T.; Zhao, C. Water use sources of desert riparian Populus euphratica forests. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5469–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cui, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y. Utilization of water resources and ecological protection in the Tarim River. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 215–222, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Ren, L.; Skaggs, T.H.; Lü, H.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Fang, X. Simulation of Populus euphratica root uptake of groundwater in an arid woodland of the Ejina Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.M.; Schaepman, M.E.; Clevers, J.G.; Su, Z.B.; Hu, G. Groundwater depth and vegetation in the Ejina area, China. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2011, 25, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Y. Photosynthesis of Populus euphratica in relation to groundwater depths and high temperature in arid environment, northwest China. Photosynthetica 2010, 48, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Si, J.; Li, J.; Xi, H. Feature of root distribution of Populus euphratica and its water uptake model in extreme arid region. Adv. Earth Sci. 2008, 23, 765–772, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fu, A.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. Water use strategies of the desert riparian forest plant community in the lower reaches of Heihe River Basin, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, S.; Kustas, W.P.; Nieto, H.; Sun, L.; Xu, Z.; Skaggs, T.H.; Yang, Y.; Ma, M.; Xu, T.; et al. Monitoring and validating spatially and temporally continuous daily evaporation and transpiration at river basin scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, K.; Zhou, J. Assessing the impacts of an ecological water diversion project on water consumption through high-resolution estimations of actual evapotranspiration in the downstream regions of the Heihe River Basin, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Z.; Su, Y.; Xi, H. Sap flow of Populus euphratica in a desert riparian forest in an extreme arid region during the growing season. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2007, 49, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Site Name (Abbreviations) | Longitude, Latitude | Altitude (m) | Turbulence Sensors, Manufacturers | Sensor Height (m) | Surface Type | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shrubland station a (SL) | 101°08′14″ E, 42°00′04″ N | 873 | CSAT3&LI7500, Campbell/LI-COR, USA | 8 | T. chinensis | 2013.7– |
| Mixed forest station (MF) | 101°08′00″ E, 41°59′28″ N | 874 | CSAT3&Li7500, Campbell/LI-COR, USA | 22 | P. euphratica and T. chinensis | 2013.7– |
| Populus forest station (PF) | 101°07′26″ E, 41°59′35″ E | 876 | CSAT3&LI7500, Campbell/LI-COR, USA | 22 | P. euphratica and sparse T. chinensis | 2013.7–2016.4 |
| Cropland station (CL) | 101°08′01″ E, 42°00′17″ N | 875 | CSAT3&LI7500A, Campbell/LI-COR, USA | 3.5 | Cantaloupe | 2013.7–2015.11 |
| Barren-land station (BL) | 101°07′57″ E, 41°59′57″ N | 878 | CSAT3&LI7500, Campbell/LI-COR, USA | 3 | Bare land | 2013.7–2016.3 |
| Observation Items b | Sensor | Manufacturers | Height/Depth (m) | Site Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air pressure | CS100 AV-410BP | Campbell, Logan, UT, USA Avalon, Atlanta, GA, USA | 10 1.0 | SL MF |
| Precipitation | TR-525M | Texas Electronics, Dallas, TX, USA | 28 | SL, MF |
| Wind speed/direction | 010C/020C | Met One, Grants Pass, OR, USA | 5/7/10/15/20/28;15 | SL |
| WS03001 | R.M. Young, Traverse City, MI, USA | 28 | MF, PF | |
| Air temperature/ relative humidity | HC2S3 | Campbell, Logan, UT, USA | 5/7/10/15/20/28 | SL |
| HMP45C | Vaisala, Vantaa, Finland | 28 | MF, PF | |
| Four-component radiation | CNR4 | Kipp & Zonen, The Netherland | 10(SL);24 (PF) | SL, PF |
| CNR1 | Kipp & Zonen, The Netherland | 24 | MF | |
| CNR4 | Kipp & Zonen, The Netherland | 6 | CL, BL, PF | |
| Soil temperature | 109-L | Campbell, Logan, UT, USA | 0/−0.02/−0.04/−0.1/ −0.2/−0.4/−0.8/−1.2/−1.6 | SL |
| AV-10T | Avalon, Atlanta, GA, USA | 0/−0.02/−0.04/−0.1/ −0.2/−0.4/−0.6/−1 | MF | |
| −0.02/−0.04 | PF, BL, CL | |||
| Soil moisture | ML2X | Delta−T Devices, Cambridge, UK | −0.02/−0.04/−0.1/ −0.2/−0.4/−0.8/−1.2/−1.6 | SL |
| −0.02/−0.04/−0.1/ −0.2/−0.4/−0.6/−1 | MF | |||
| −0.02/−0.04 | PF, BL, CL | |||
| Soil heat flux | HFP01SC | Hukseflux, Delft, The Netherlands Campbell, Logan, UT, USA | −0.06 | SL, MF, PF, BL, CL |
| HFP01 |
| Surface Type | Southeasterly Winds (Frequency: 2.5%) | Northwesterly Winds (Frequency: 3%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL | MF | PF | CL | BL | SL | MF | PF | CL | BL | |
| P. euphratica | – | 0.46 | 0.27 | – | – | – | 0.36 | 0.35 | – | – |
| T. chinensis | 0.92 | 0.28 | 0.26 | – | 0.02 | 0.62 | 0.45 | 0.12 | – | – |
| cantaloupe | – | – | – | 1.00 | – | – | – | 0.01 | 1.00 | – |
| barren-land | 0.08 | 0.26 | 0.47 | – | 0.98 | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.52 | – | 1.00 |
| Sites | May | June | July | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL | H/Rn | 0.78 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.37 | 0.65 |
| LE/Rn | 0.19 | 0.48 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.57 | 0.25 | |
| MF | H/Rn | 0.60 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.55 |
| LE/Rn | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.9 | 0.80 | 0.57 | 0.24 | |
| PF | H/Rn | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.36 | 0.59 |
| LE/Rn | 0.40 | 0.68 | 0.81 | 0.71 | 0.50 | 0.27 | |
| CL | H/Rn | – | 0.40 | 0.25 | −0.04 | 0.28 | – |
| LE/Rn | – | 0.47 | 0.74 | 1.24 | 0.83 | – | |
| BL | H/Rn | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.35 |
| LE/Rn | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.22 | |
| Surface Type c | ET (mm) | May | June | July | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL | Mean | 1.1 | 3.2 | 5.2 | 4.8 | 2.9 | 0.8 | 3.1 |
| Sum | 23.7 | 95.1 | 161.3 | 149.5 | 86.2 | 25.2 | 541.0 | |
| MF | Mean | 2.8 | 5.6 | 6.9 | 5.3 | 3.2 | 0.9 | 4.2 |
| Sum | 58.6 | 166.7 | 215.6 | 163.7 | 96.5 | 30.2 | 731.4 | |
| PF | Mean | 2.6 | 4.4 | 6.2 | 4.3 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 3.6 |
| Sum | 54.1 | 131.9 | 193.3 | 133.9 | 76.5 | 32.6 | 622.4 | |
| CL | Mean | – | 2.3 | 3.8 | 5.6 | 3.1 | – | 3.8 |
| Sum | – | 47.5 | 118.3 | 173.3 | 92.4 | – | 431.5 | |
| BL | Mean | 0.7 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.1 |
| Sum | 14.6 | 36.7 | 52.2 | 45.1 | 20.6 | 25.3 | 194.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Xu, F.; Wang, J. Energy Exchange and Evapotranspiration over the Ejina Oasis Riparian Forest Ecosystem with Different Land-Cover Types. Water 2021, 13, 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233424
Wang W, Xu F, Wang J. Energy Exchange and Evapotranspiration over the Ejina Oasis Riparian Forest Ecosystem with Different Land-Cover Types. Water. 2021; 13(23):3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233424
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Weizhen, Feinan Xu, and Jiemin Wang. 2021. "Energy Exchange and Evapotranspiration over the Ejina Oasis Riparian Forest Ecosystem with Different Land-Cover Types" Water 13, no. 23: 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233424
APA StyleWang, W., Xu, F., & Wang, J. (2021). Energy Exchange and Evapotranspiration over the Ejina Oasis Riparian Forest Ecosystem with Different Land-Cover Types. Water, 13(23), 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233424





