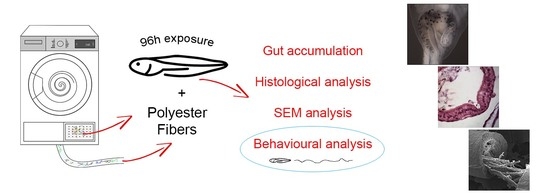
The Toxicity of Polyester Fibers in Xenopuslaevis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Characterization of PEFs
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Microscopical Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mortality, Malformations, and PEF Effects
3.2. Effects of PEFs on Swimming Behavior
4. Discussion
4.1. The Digestive System: The Main Target for PEFs
4.2. PEFs in the Gut: Physical Effects
4.3. Side Effects due to PEFs
4.4. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arthur, C.; Baker, J.; Bamford, H. Proceedings of the International Research Workshop on the Occurrence, Effects and Fate of Microplastic Marine Debris. In Proceedings of the International Research Workshop on the Occurrence, Effects and Fate of Microplastic Marine Debris, Tacoma, WA, USA, 9–11 September 2008; NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-30. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): Washington, DC, USA, 2009; p. 530. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; Wang, C.; Fu, L.; Tang, J. Environmental Distribution, Transport and Ecotoxicity of Microplastics: A Review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Gao, T.; Sillanpää, M. Atmospheric Microplastics: A Review on Current Status and Perspectives. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duis, K.; Coors, A. Microplastics in the Aquatic and Terrestrial Environment: Sources (with a Specific Focus on Personal Care Products), Fate and Effects. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Kang, S.; Sillanpää, M. Importance of Atmospheric Transport for Microplastics Deposited in Remote Areas. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, B.; Raffael, B.; Angers-Loustau, A.; Gilliland, D.; Kestens, V.; Petrillo, M.; Rio-Echevarria, I.M.; Van den Eede, G. Review of Micro- and Nanoplastic Contamination in the Food Chain. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 639–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shruti, V.C.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Elizalde-Martínez, I.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. First Study of Its Kind on the Microplastic Contamination of Soft Drinks, Cold Tea and Energy Drinks—Future Research and Environmental Considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; Mason, S.A. Plastic Debris in 29 Great Lakes Tributaries: Relations to Watershed Attributes and Hydrology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.Z.; Watts, A.J.R.; Winslow, B.O.; Galloway, T.S.; Barrows, A.P.W. Mountains to the Sea: River Study of Plastic and Non-Plastic Microfiber Pollution in the Northeast USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.; Laitala, K.; Klepp, I.G. Microfibres from Apparel and Home Textiles: Prospects for Including Microplastics in Environmental Sustainability Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelein, A.; Int-Veen, I.; Kammann, U.; Scharsack, J.P. Microplastic Fibers—Underestimated Threat to Aquatic Organisms? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belzagui, F.; Gutiérrez-Bouzán, C.; Álvarez-Sánchez, A.; Vilaseca, M. Textile Microfibers Reaching Aquatic Environments: A New Estimation Approach. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, F.; Gullo, M.P.; Gentile, G.; Di Pace, E.; Cocca, M.; Gelabert, L.; Brouta-Agnésa, M.; Rovira, A.; Escudero, R.; Villalba, R.; et al. Evaluation of Microplastic Release Caused by Textile Washing Processes of Synthetic Fabrics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Release of Synthetic Microplastic Plastic Fibres from Domestic Washing Machines: Effects of Fabric Type and Washing Conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, S.; Okoffo, E.D.; O’Brien, J.W.; Ribeiro, F.; Wang, X.; Wright, S.L.; Samanipour, S.; Rauert, C.; Toapanta, T.Y.A.; Albarracin, R.; et al. Airborne Emissions of Microplastic Fibres from Domestic Laundry Dryers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, K.J.; Miller, R.Z. Electric Clothes Dryers: An Underestimated Source of Microfiber Pollution. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyero, L.; López-Rojo, N.; Bosch, J.; Alonso, A.; Correa-Araneda, F.; Pérez, J. Microplastics Impair Amphibian Survival, Body Condition and Function. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Araújo, A.P.; Gomes, A.R.; Malafaia, G. Hepatotoxicity of Pristine Polyethylene Microplastics in Neotropical Physalaemus cuvieri Tadpoles (Fitzinger, 1826). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, B.; Bacchetta, R.; Santo, N.; Tremolada, P.; Parolini, M. Polystyrene Microplastics Did Not Affect Body Growth and Swimming Activity in Xenopus laevis Tadpoles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34644–34651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Chernick, M.; Hinton, D.E.; Shi, H. Microplastics in Small Waterbodies and Tadpoles from Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8885–8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Su, L.; Xue, Y.; Mu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Shi, H. Uptake, Accumulation and Elimination of Polystyrene Microspheres in Tadpoles of Xenopus tropicalis. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, S.N.; Chanson, J.S.; Cox, N.A.; Young, B.E.; Rodrigues, A.S.L.; Fischman, D.L.; Waller, R.W. Status and Trends of Amphibian Declines and Extinctions Worldwide. Science 2004, 306, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bacchetta, R.; Santo, N.; Fascio, U.; Moschini, E.; Freddi, S.; Chirico, G.; Camatini, M.; Mantecca, P. Nano-Sized CuO, TiO2 and ZnO Affect Xenopus laevis Development. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantle, J.A.; Fort, D.J.; Rayburn, J.R.; Deyoung, D.J.; Bush, S.J. Further Validation of FETAX: Evaluation of the Developmental Toxicity of Five Known Mammalian Teratogens and Non-Teratogens. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 1990, 13, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, J.N.; Schultz, T.W.; Buchanan, M.V.; Kao, G.L. Frog Embryo Teratogenesis Assay: Xenopus (FETAX)—A Short-Term Assay Applicable to Complex Environmental Mixtures. In Short-Term Bioassays in the Analysis of Complex Environmental Mixtures III; Waters, M.D., Sandhu, S.S., Lewtas, J., Claxton, L., Chernoff, N., Nesnow, S., Eds.; Environmental Science Research; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1983; pp. 393–405. ISBN 978-1-4613-3611-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hoke, R.A.; Ankley, G.T. Application of Frog Embryo Teratogenesis Assay-Xenopus to Ecological Risk Assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 2677–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwkoop, P.D.; Faber, J. Normal Table of Xenopus Laevis (Daudin): A Systematical and Chronological Survey of the Development from the Fertilized Egg till the End of Metamorphosis; Garland Pub.: New York, NY, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-8153-1896-5. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, A.; Santo, N.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Bolzoni, E.; Bacchetta, R.; Tremolada, P. Does Mechanical Stress Cause Microplastic Release from Plastic Water Bottles? Water Res. 2019, 166, 115082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Kumar, R.; Yang, S.; Büttner, O. Microplastic Particle Emission from Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents into River Networks in Germany: Loads, Spatial Patterns of Concentrations and Potential Toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Yang, L.; Shi, H.; Tripathee, L.; Gao, T. Research Progresses of Microplastic Pollution in Freshwater Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.; von Randow, M.; Voigt, A.-L.; von der Au, M.; Fischer, E.; Meermann, B.; Wagner, M. Ingestion and Toxicity of Microplastics in the Freshwater Gastropod Lymnaea stagnalis: No Microplastic-Induced Effects Alone or in Combination with Copper. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulyás, M.; Bencsik, N.; Pusztai, S.; Liliom, H.; Schlett, K. AnimalTracker: An ImageJ-Based Tracking API to Create a Customized Behaviour Analyser Program. Neuroinformatics 2016, 14, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, R.H.; Harris, R.M.; Mitchell, S.C. Plastic Contamination of the Food Chain: A Threat to Human Health? Maturitas 2018, 115, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemec, A.; Horvat, P.; Kunej, U.; Bele, M.; Kržan, A. Uptake and Effects of Microplastic Textile Fibers on Freshwater Crustacean Daphnia Magna Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, R.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wolosker, M.B.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Accumulation of Different Shapes of Microplastics Initiates Intestinal Injury and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in the Gut of Zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, S.Y.; Lee, C.M.; Weinstein, J.E.; Hurk, P.; van den Klaine, S.J. Trophic Transfer of Microplastics in Aquatic Ecosystems: Identifying Critical Research Needs. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blarer, P.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Microplastics Affect Assimilation Efficiency in the Freshwater Amphipod Gammarus fossarum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 23522–23532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, A.D.; Weinstein, J.E. Size- and Shape-Dependent Effects of Microplastic Particles on Adult Daggerblade Grass Shrimp (Palaemonetes pugio). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tussellino, M.; Ronca, R.; Formiggini, F.; Marco, N.D.; Fusco, S.; Netti, P.A.; Carotenuto, R. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Affect Xenopus laevis Development. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosetto, L.; Brown, C.; Williamson, J.E. Microplastics on Beaches: Ingestion and Behavioural Consequences for Beachhoppers. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gundlach, M.; Yang, S.; Jiang, J.; Velki, M.; Yin, D.; Hollert, H. Quantitative Investigation of the Mechanisms of Microplastics and Nanoplastics toward Zebrafish Larvae Locomotor Activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lackmann, C.; Wang, W.; Seiler, T.-B.; Hollert, H.; Shi, H. Microplastics Lead to Hyperactive Swimming Behaviour in Adult Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 224, 105521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, M.; Bauer, A.L.; Valiati, V.H.; Schulz, U.H. Microplastic Concentrations in Raw and Drinking Water in the Sinos River, Southern Brazil. Water 2020, 12, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, X.; Sheng, D.; Xu, Z.; Rong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylene Microplastics Affect the Distribution of Gut Microbiota and Inflammation Development in Mice. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaseyed, T.; Bergström, J.H.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Ermund, A.; Birchenough, G.M.H.; Schütte, A.; van der Post, S.; Svensson, F.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, A.M.; Nyström, E.E.L.; et al. The Mucus and Mucins of the Goblet Cells and Enterocytes Provide the First Defense Line of the Gastrointestinal Tract and Interact with the Immune System. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacchetta, R.; Tremolada, P.; Di Benedetto, C.; Santo, N.; Fascio, U.; Chirico, G.; Colombo, A.; Camatini, M.; Mantecca, P. Does Carbon Nanopowder Threaten Amphibian Development? Carbon 2012, 50, 4607–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gies, E.A.; LeNoble, J.L.; Noël, M.; Etemadifar, A.; Bishay, F.; Hall, E.R.; Ross, P.S. Retention of Microplastics in a Major Secondary Wastewater Treatment Plant in Vancouver, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, S.; Binelli, A.; Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Della Torre, C.; Parenti, C.C.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. The Fate of Microplastics in an Italian Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Treatment | Total Time | Immobilization Time | Distance Travelled | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Inner Part | Outer Part | Time | Inner Part | Outer Part | Distance | Inner Part | Outer Part | |||||||
| Sec | N | % | N | % | Sec | N | % | N | % | mm | N | % | N | % | |
| CTRL | 0–10 | 19 | 95 | 0 | 0 | 0–10 | 20 | 100 | 9 | 45 | 0–100 | 20 | 100 | 12 | 60 |
| >10–20 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5.0 | >10–20 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 20 | >100–200 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5.0 | |
| >20–30 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 95 | >20–30 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 35 | >200 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 35 | |
| Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | |
| 1 μg mL−1 | 0–10 | 20 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0–10 | 20 | 100 | 5 | 25 | 0–100 | 20 | 100 | 12 | 60 |
| >10–20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | >10–20 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 35 | >100–200 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 15 | |
| >20–30 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 100 | >20–30 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 40 | >200 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 25 | |
| Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | |
| 10 μg mL−1 | 0–10 | 17 | 85 | 0 | 0 | 0–10 | 20 | 100 | 5 | 25 | 0–100 | 18 | 90 | 14 | 70 |
| >10–20 | 3 | 15 | 3 | 15 | >10–20 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 25 | >100–200 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 15 | |
| >20–30 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 85 | >20–30 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 50 | >200 | 0 | 25 | 3 | 15 | |
| Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | |
| 50 μg mL−1 | 0–10 | 18 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 0–10 | 19 | 95 | 4 | 20 | 0–100 | 20 | 100 | 17 | 85 |
| >10–20 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 10 | >10–20 | 1 | 5 | 6 | 30 | >100–200 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 10 | |
| >20–30 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 90 | >20–30 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 50 | >200 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | |
| Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | Total | 20 | 100 | 20 | 100 | |
| Total | 0–10 | 74 | 92.5 | 0 | 0 | 0–10 | 79 | 98.7 | 23 | 28.8 | 0–100 | 78 | 97.5 | 55 | 68.8 |
| >10–20 | 6 | 7.5 | 6 | 7.5 | >10–20 | 1 | 1.3 | 22 | 27.5 | >100–200 | 2 | 2.5 | 9 | 11.2 | |
| >20–30 | 0 | 0 | 74 | 92.5 | >20–30 | 0 | 0 | 35 | 43.7 | >200 | 4 | 10.5 | 16 | 20 | |
| Total | 80 | 100 | 80 | 100 | Total | 80 | 100 | 80 | 100 | Total | 38 | 100 | 80 | 100 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bacchetta, R.; Winkler, A.; Santo, N.; Tremolada, P. The Toxicity of Polyester Fibers in Xenopuslaevis. Water 2021, 13, 3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233446
Bacchetta R, Winkler A, Santo N, Tremolada P. The Toxicity of Polyester Fibers in Xenopuslaevis. Water. 2021; 13(23):3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233446
Chicago/Turabian StyleBacchetta, Renato, Anna Winkler, Nadia Santo, and Paolo Tremolada. 2021. "The Toxicity of Polyester Fibers in Xenopuslaevis" Water 13, no. 23: 3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233446
APA StyleBacchetta, R., Winkler, A., Santo, N., & Tremolada, P. (2021). The Toxicity of Polyester Fibers in Xenopuslaevis. Water, 13(23), 3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233446