Trophic Niche Overlap between Invasive and Indigenous Fish in a Northwest Reservoir of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
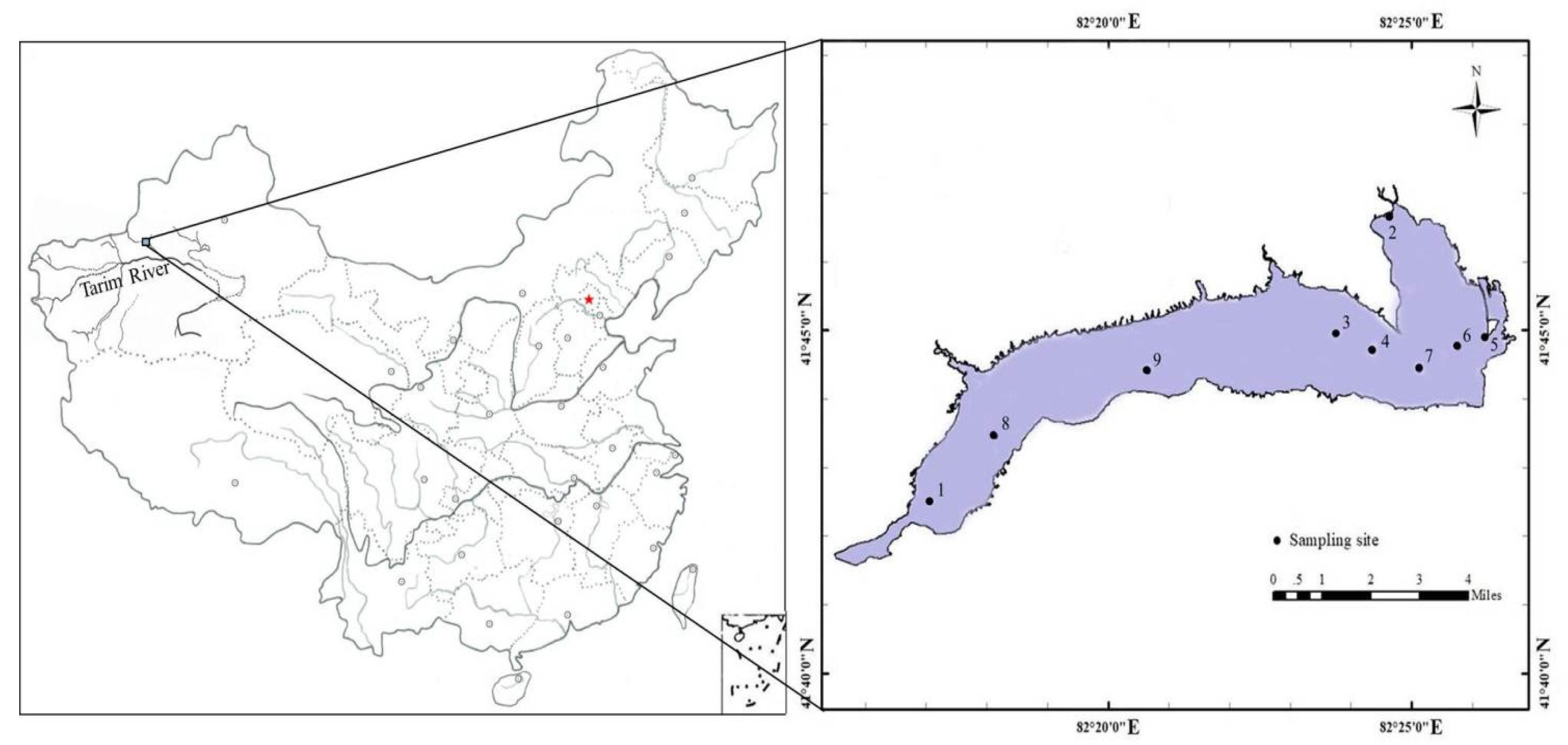
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.3. Stable-Isotope Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strayer, D.L. Alien species in fresh waters: Ecological effects, interactions with other stressors, and prospects for the future. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 152–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadye, W.T.; Booth, A.J. An invader within an altered landscape: One catfish, two rivers and an inter-basin water transfer scheme. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, K.S.; Townsend, C.R. Impacts of freshwater invaders at different levels of ecological organisation, with emphasis on salmonids and ecosystem consequences. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cucherousset, J.; Olden, J.D. Ecological Impacts of Nonnative Freshwater Fishes. Fisheries 2011, 36, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudmore, B.; Mandrak, N.E. Biological synopsis of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Can. Manuscr. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 2705, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kolar, C.S.; Chapman, D.C.; Courtenay, W.R., Jr.; Housel, C.M.; Williams, J.D.; Jennings, D.P. Asian Carps of the Genus Hypophthalmichthys (Pisces, Cyprinidae)—A Biological Synopsis and Environmental Risk Assessment. Natl. Invasive Species Counc. Mater. 2005, 5, 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- Schofield, P.J. Foreign Nonindigenous Carps and Minnows (Cyprinidae) in the United States: A Guide to Their Identification, Distribution, and Biology; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Reston, WV, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Chen, Y. Investigation and protection strategies of fishes of Lhasa River. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2010, 34, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yan, G.W.; Wang, Z.C.; Jiang, Z.F.; Liang, Z.H. Investigation and compilation of bracketed keys for invasive fishes in upstream of Tarim River. J. Tarim Univ. 2011, 23, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.J.; Zhang, F.F.; Qiu, Y.P.; Chen, G.Z. A new record of invasive fish from the Dian Lake in Yunnan Province—Silurus asotus. Sichuan J. Zool. 2018, 37, 260. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, D. First record of exotic Amur catfish, Silurus asotus (Actinopterygii: Siluriformes: Siluridae), in the Tibet stretch of the Lancang River, China. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2018, 48, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miranda, N.A.F.; Perissinotto, R. Stable Isotope Evidence for Dietary Overlap between Alien and Native Gastropods in Coastal Lakes of Northern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcagni, M.; Rizzo, A.; Campbell, L.M.; Arribére, M.A.; Juncos, R.; Reissig, M.; Kyser, K.; Barriga, J.P.; Battini, M.; Guevara, S.R. Stable isotope analysis of trophic structure, energy flow and spatial variability in a large ultraoligotrophic lake in Northwest Patagonia. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, J.P.; Elliott Smith, E.A.; Besser, A.C.; Newsome, S.D. A Guide to Using Compound-Specific Stable Isotope Analysis to Study the Fates of Molecules in Organisms and Ecosystems. Diversity 2019, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Layman, C.A.; Araujo, M.S.; Boucek, R.; Hammerschlag-Peyer, C.M.; Harrison, E.; Jud, Z.R.; Matich, P.; Rosenblatt, A.E.; Vaudo, J.J.; Yeager, L.A.; et al. Applying stable isotopes to examine food-web structure: An overview of analytical tools. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Zanden, H.B.; Soto, D.X.; Bowen, G.J.; Hobson, K.A. Expanding the Isotopic Toolbox: Applications of Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotope Ratios to Food Web Studies. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hladyz, S.; Cook, R.A.; Petrie, R.; Nielsen, D.L. Influence of substratum on the variability of benthic biofilm stable isotope signatures: Implications for energy flow to a primary consumer. Hydrobiologia 2011, 664, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Lin, L.; Tu, T.; Jeng, M.; Chikaraishi, Y.; Wang, P. Trophic structure and energy flow in a shallow-water hydrothermal vent: Insights from a stable isotope approach. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e204753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, S.F.; Colombo, F. How picky can you be? Temporal variations in trophic niches of co-occurring suspension-feeding species. Food Webs 2014, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschke, N.; Everett, J.D.; Suthers, I.M.; Smith, J.A.; Hunt, B.P.V.; Doblin, M.A.; Taylor, M.D. Zooplankton trophic niches respond to different water types of the western Tasman Sea: A stable isotope analysis. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2015, 104, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, M.J.; Hussey, N.E.; Fisk, A.T.; Tobin, A.J.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Communal or competitive? Stable isotope analysis provides evidence of resource partitioning within a communal shark nursery. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 439, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogloff, W.R.; Yurkowski, D.J.; Davoren, G.K.; Ferguson, S.H. Diet and isotopic niche overlap elucidate competition potential between seasonally sympatric phocids in the Canadian Arctic. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschlag-Peyer, C.M.; Yeager, L.A.; Araújo, M.S.; Layman, C.A. A Hypothesis-Testing Framework for Studies Investigating Ontogenetic Niche Shifts Using Stable Isotope Ratios. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swanson, H.K.; Lysy, M.; Power, M.; Stasko, A.D.; Johnson, J.D.; Reist, J.D. A new probabilistic method for quantifying n-dimensional ecological niches and niche overlap. Ecology 2015, 96, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A.; Montaña, C.G.; Post, D.M. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 2007, 88, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.L.; Inger, R.; Parnell, A.C.; Bearhop, S. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER—Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Tuerxun, E.; Xie, C.; Liu, J.; Li, L. Fauna composition and distribution of aboriginal fish in the Tarim River of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. J. Fish. China 2009, 6, 949–956. [Google Scholar]
- Karjan, A. Research on Fishery Ecology and Development of Xinjiang Weigan River Basin-Kizil Reservoir; Xinjiang Science and Technology Press: Urumqi, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.J.; Hu, G.F. Threatened fishes of the world: Schizothorax (Schizopyge) biddulphi Günther, 1876 (Cyprinidae). Environ. Biol. Fish. 2009, 85, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhenyu, L.; Gregg, W.P.; Dianmo, L. Invasive species in China—An overview. Biodivers. Conserv. 2001, 10, 1317–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, M.B. The conservation status of large migratory cyprinids including Aspiorhynchus laticeps of Xinjiang China. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2011, 27, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, C.J.; Kryskalla, J.R. Methods of Analysis by the US Geological Survey National Water Quality Laboratory: Evaluation of Alkaline Persulfate Digestion as an Alternative to Kjeldahl Digestion for Determination of Total and Dissolved Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Water; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Reston, WV, USA, 2003; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Hosomi, M.; Sudo, R. Simultaneous determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in freshwater samples using persulfate digestion. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1986, 27, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Gu, X.; Zeng, Q. Food sources and trophic relationships of three decapod crustaceans: Insights from gut contents and stable isotope analyses. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2888–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, C.P.; Prepas, E.E.; Tonn, W.M.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Kotak, B.G. A stable carbon and nitrogen isotope study of lake food webs in Canada’s Boreal Plain. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Gu, X.; Zeng, Q.; Pan, G. Seasonal and spatial variations of the food web structure in a shallow eutrophic lake assessed by stable isotope analysis. Fish. Sci. 2014, 80, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ute, J.; Katja, M.; Thomas, B.; Rainer, K.; Kerstin, B. Stable isotope food web studies: A case for standardized sample treatment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 287, 251–253. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, W.; Shi, L.; Chen, Y. Stable isotopes in aquatic food web of an artificial lagoon in the Hangzhou Bay, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2010, 28, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: Models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 2002, 83, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M.; Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A.; Takimoto, G.; Quattrochi, J.; Montaña, C.G. Getting to the fat of the matter: Models, methods and assumptions for dealing with lipids in stable isotope analyses. Oecologia 2007, 152, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.C.; Donohue, I.; Jackson, A.L.; Britton, J.R.; Harper, D.M.; Grey, J. Population-Level Metrics of Trophic Structure Based on Stable Isotopes and Their Application to Invasion Ecology. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnell, A.C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L. Source Partitioning Using Stable Isotopes: Coping with Too Much Variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, P.; Reichwaldt, E.S.; Harrod, C.; Rossberg, A.G. Determining trophic niche width: An experimental test of the stable isotope approach. Oikos 2012, 121, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, B.; Sherr, E.B. δ13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems. In Stable Isotopes in Ecological Research; Rundel, P.W., Ehleringer, J.R., Nagy, K.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 196–229. [Google Scholar]
- Minagawa, M.; Wada, E. Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chains: Further evidence and the relation between δ15N and animal age. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabana, G.; Rasmussen, J.B. Modelling food chain structure and contaminant bioaccumulation using stable nitrogen isotopes. Nature 1994, 372, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, J.; Roques, L.; Hamel, F. Success rate of a biological invasion in terms of the spatial distribution of the founding population. Bull. Math. Biol. 2012, 74, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, J.J.; Chen, P.; Qi, F.; Feng, Y.H.; Dili, A.; Hu, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, L.G.; Zhang, R.M. Situations of Fish Stocks in Weigan River in Xinjiang. Fish. Sci. 2021, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Rothhaupt, K.; Hanselmann, A.J.; Yohannes, E. Niche differentiation between sympatric alien aquatic crustaceans: An isotopic evidence. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2014, 15, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cody, M.L. Optimization in ecology. Science 1974, 183, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.N.Q.; Jackson, M.C.; Sheath, D.; Verreycken, H.; Britton, J.R. Patterns of trophic niche divergence between invasive and native fishes in wild communities are predictable from mesocosm studies. J. Anim. Ecol. 2015, 84, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barley, S.C.; Meekan, M.G.; Meeuwig, J.J. Species diversity, abundance, biomass, size and trophic structure of fish on coral reefs in relation to shark abundance. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 565, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, O.N.R.I.; Abe, S.; Matsuzaki, K.; Iguchi, K. Interspecific interactions between ayu, Plecoglossus altivelis, and pale chub, Zacco platypus, in artificial streams. Fish. Sci. 2000, 66, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, F.G.; John, H.H.; Ladd, E.J. Effect of intra- and interspecific interactions on the feeding behavior of two subtidal sea stars. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 232, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Gunckel, S.L.; Hemmingsen, A.R.; Li, J.L. Effect of Bull Trout and Brook Trout Interactions on Foraging Habitat, Feeding Behavior, and Growth. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2002, 131, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhrov, A.A.; Artamonova, V.S.; Karabanov, D.P. Finding of topmouth gudgeon Pseudorasbora parva (Temminck et Schlegel) (Actinopterygii: Cyprinidae) in the Brahmaputra River basin (Tibetan Plateau, China). Russ. J. Biol. Invasions 2013, 4, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Xie, S.; Cheng, F. Broad Diet Composition and Seasonal Feeding Variation Facilitate Successful Invasion of the Shimofuri Goby (Tridentiger bifasciatus) in a Water Transfer System. Water 2020, 12, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Liang, X.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Wen, Z.; Cheng, X.; Li, A.; Cai, W.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of food habit transition from carnivory to herbivory in a typical vertebrate herbivore, grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bissattini, A.M.; Vignoli, L. Let’s eat out, there’s crayfish for dinner: American bullfrog niche shifts inside and outside native ranges and the effect of introduced crayfish. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 2633–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, K.; Stenroth, P.; Nystrom, P.; Graneli, W. Invasions and niche width: Does niche width of an introduced crayfish differ from a native crayfish? Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | August | October | February | June |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (m) | 2.17 ± 1.61 n = 5 | 6.91 ± 3.72 n = 9 | 7.41 ± 4.66 n = 9 | 5.38 ± 3.96 n = 9 |
| SD (m) | 0.40 ± 0.34 n = 5 | 2.21 ± 1.12 n = 9 | 1.00 ± 0.26 n = 9 | 0.77 ± 0.61 n = 9 |
| pH | 7.68 ± 0.14 n = 5 | 8.79 ± 0.06 n = 9 | 7.99 ± 0.32 n = 9 | 8.73 ± 0.13 n = 9 |
| T (°C) | 23.94 ± 2.54 n = 5 | 14.72 ± 0.99 n = 9 | 0.34 ± 0.41 n = 9 | 22.23 ± 1.85 n = 9 |
| SAL (ppt) | - | - | 0.33 ± 0.04 n = 9 | 0.28 ± 0.04 n = 9 |
| DO (mg/L) | 7.43 ± 0.30 n = 5 | 10.26 ± 0.36 n = 9 | 9.86 ± 0.46 n = 9 | 7.52 ± 0.62 n = 9 |
| TDS (mg/L) | - | - | 447.47 ± 55.55 n = 9 | 377.66 ± 56.63 n = 9 |
| ORP (mv) | - | - | 157.06 ± 40.34 n = 9 | 173.16 ± 23.60 n = 9 |
| TN (mg/L) | 1.04 ± 0.51 n = 5 | 1.43 ± 0.16 n = 9 | 1.58 ± 0.19 n = 9 | 1.61 ± 0.23 n = 9 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.06 ± 0.05 n = 6 | 0.02 ± 0.01 n = 9 | 0.05 ± 0.02 n = 9 | 0.03 ± 0.02 n = 9 |
| Species | n | TL | NRb | CRb | CD | MNND | SDNND | TA | SEAc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native species | |||||||||
| Aspiorhynchus laticeps | 6 | 2.69 ± 0.37 | 3.90 | 5.77 | 1.71 | 1.24 | 1.83 | 4.94 | 5.20 |
| Schizothorax biddulphi | 5 | 1.89 ± 0.08 | 0.75 | 2.83 | 1.19 | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.94 | 1.55 |
| Schizothorax eurystomus | 4 | 2.49 ± 0.86 | 5.11 | 1.09 | 2.58 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1.31 | 1.67 |
| Schizothorax intermedius | 4 | 2.08 ± 0.19 | 1.22 | 0.48 | 0.57 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.25 |
| Schizothorax barbatus | 7 | 2.16 ± 0.18 | 1.35 | 1.96 | 0.72 | 0.25 | 0.42 | 1.32 | 1.53 |
| Non-native species | |||||||||
| Silurus asotus | 10 | 2.87 ± 0.43 | 5.36 | 1.87 | 1.17 | 0.65 | 0.54 | 4.11 | 1.92 |
| Ctenopharynagodon idellus | 11 | 1.82 ± 0.44 | 4.74 | 3.70 | 1.82 | 0.82 | 0.50 | 10.71 | 6.57 |
| Rhinogobius giurinus | 11 | 3.00 ± 0.13 | 1.24 | 3.19 | 0.81 | 0.44 | 0.57 | 2.17 | 1.38 |
| Pseuderasbora parva | 12 | 3.02 ± 0.25 | 2.62 | 3.46 | 0.98 | 0.55 | 0.26 | 3.58 | 1.69 |
| Cyprinus carpio | 27 | 2.45 ± 0.25 | 3.94 | 4.98 | 1.18 | 0.41 | 0.30 | 11.36 | 3.05 |
| Carassius auratus | 24 | 2.71 ± 0.14 | 1.50 | 3.71 | 0.86 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 3.25 | 1.15 |
| Hemiculter leacisculus | 12 | 2.87 ± 0.24 | 3.13 | 2.69 | 0.83 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 4.08 | 1.96 |
| Abbottina rivularis | 7 | 2.84 ± 0.18 | 1.97 | 2.24 | 0.87 | 0.79 | 0.12 | 2.48 | 1.85 |
| Species | A. laticeps | S. biddulphi | S. eurystomus | S. intermedius | S. barbatus | S. asotus | C. idellus | R. giurinus | P. parva | C. carpio | C. auratus | H. leacisculus | A. rivularis |
| A. laticeps | 3 | 1 | 1 | 15 | 39 | 42 | 31 | 17 | 51 | 30 | 41 | 38 | |
| S.biddulphi | 17 | 1 | 2 | 28 | 7 | 76 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. eurystomus | 29 | 11 | 0 | 23 | 2 | 46 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 14 | 1 | |
| S.intermedius | 25 | 35 | 0 | 88 | 53 | 98 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 0 | 10 | 1 | |
| S. barbatus | 40 | 24 | 1 | 8 | 47 | 96 | 0 | 0 | 61 | 1 | 15 | 2 | |
| S. asotus | 59 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 16 | 43 | 43 | 22 | 55 | 36 | 63 | 52 | |
| C.idellus | 14 | 19 | 1 | 2 | 24 | 18 | 2 | 1 | 32 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| R. giurinus | 74 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 53 | 17 | 62 | 44 | 34 | 49 | 69 | |
| P. parva | 58 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 14 | 70 | 47 | 27 | 23 | 49 | |
| C. carpio | 40 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 34 | 71 | 13 | 12 | 40 | 14 | 37 | |
| C. auratus | 68 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 40 | 46 | 42 | 28 | 92 | 30 | 80 | |
| H. leacisculus | 68 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 70 | 32 | 48 | 12 | 42 | 40 | 55 | |
| A. rivularis | 79 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 61 | 37 | 66 | 32 | 75 | 73 | 51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Nie, Z.; Ji, F.; Qiu, L.; Shen, J. Trophic Niche Overlap between Invasive and Indigenous Fish in a Northwest Reservoir of China. Water 2021, 13, 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233459
Wei J, Nie Z, Ji F, Qiu L, Shen J. Trophic Niche Overlap between Invasive and Indigenous Fish in a Northwest Reservoir of China. Water. 2021; 13(23):3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233459
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jie, Zhulan Nie, Fenfen Ji, Longhui Qiu, and Jianzhong Shen. 2021. "Trophic Niche Overlap between Invasive and Indigenous Fish in a Northwest Reservoir of China" Water 13, no. 23: 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233459
APA StyleWei, J., Nie, Z., Ji, F., Qiu, L., & Shen, J. (2021). Trophic Niche Overlap between Invasive and Indigenous Fish in a Northwest Reservoir of China. Water, 13(23), 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233459






