Evolution of Surface Drainage Network for Spoil Heaps under Simulated Rainfall
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
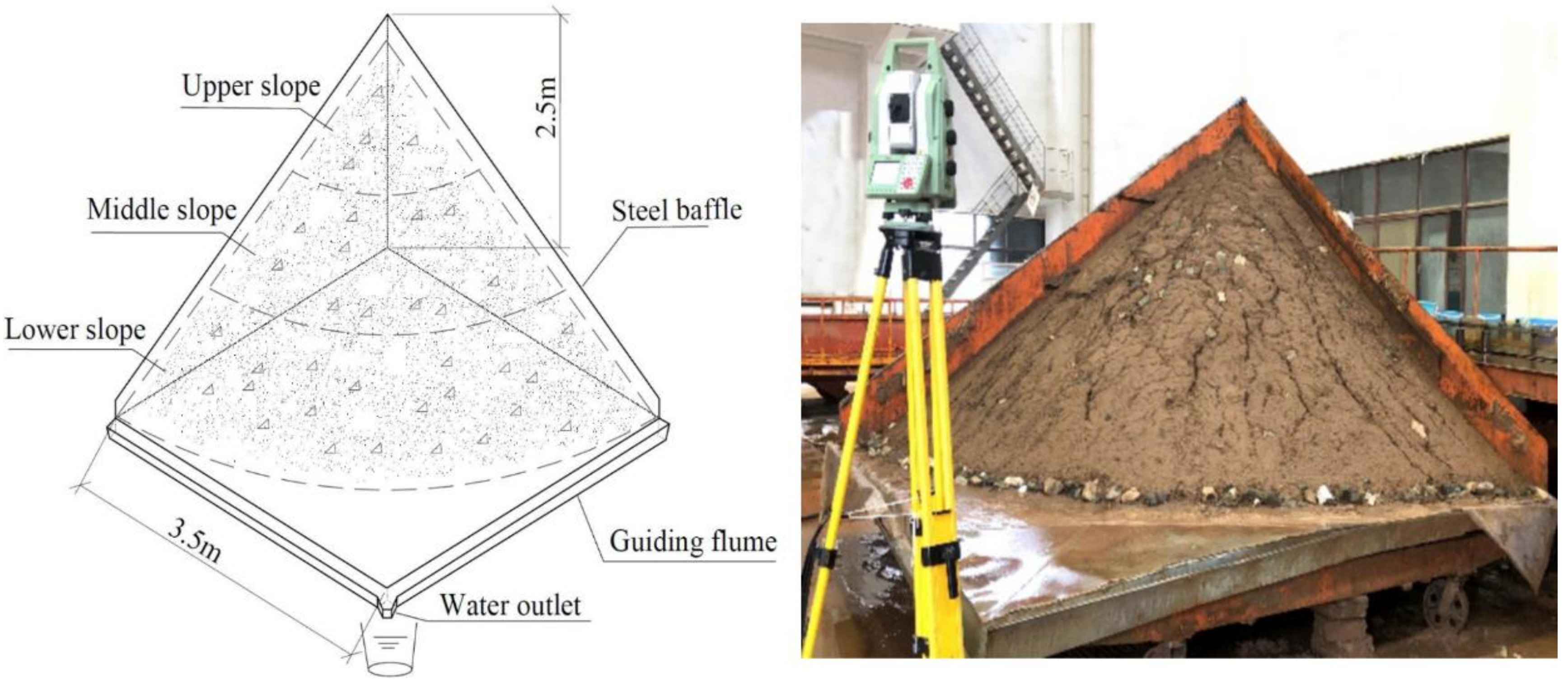
2.2. Spoil Heap Simulation
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Surface Elevation Sampling
2.5. Drainage Network Delineation
2.6. Drainage Network Characterization
2.6.1. Network Configuration
2.6.2. Stream Characteristics
2.6.3. Fractal Dimension
2.7. Hydrodynamic Parameters of Runoff
3. Results
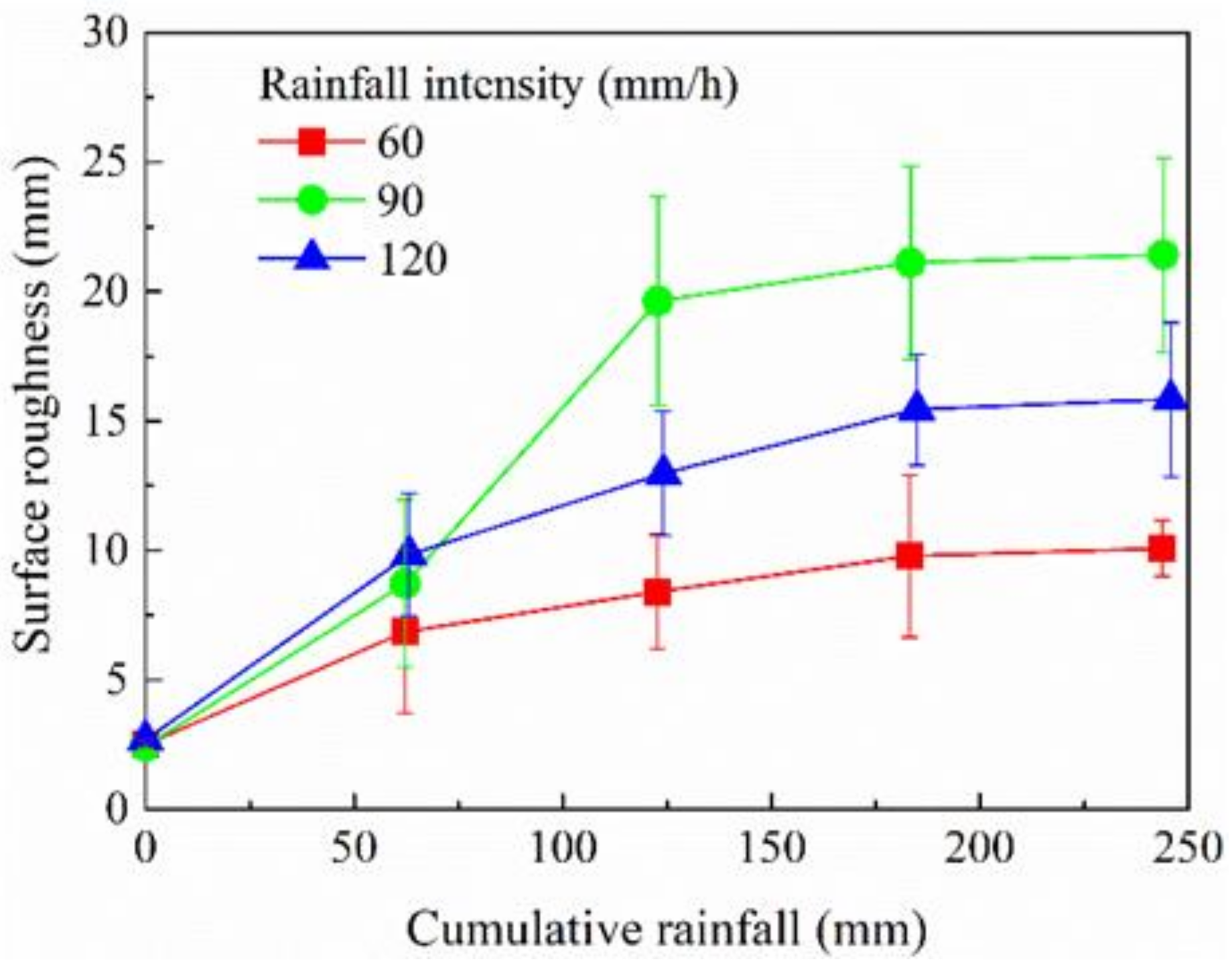
3.1. Soil Surface Roughness
3.2. Relationship between the Total Stream Length and Critical Flow Accumulation Area
3.3. Characteristics of a Developing Drainage Network
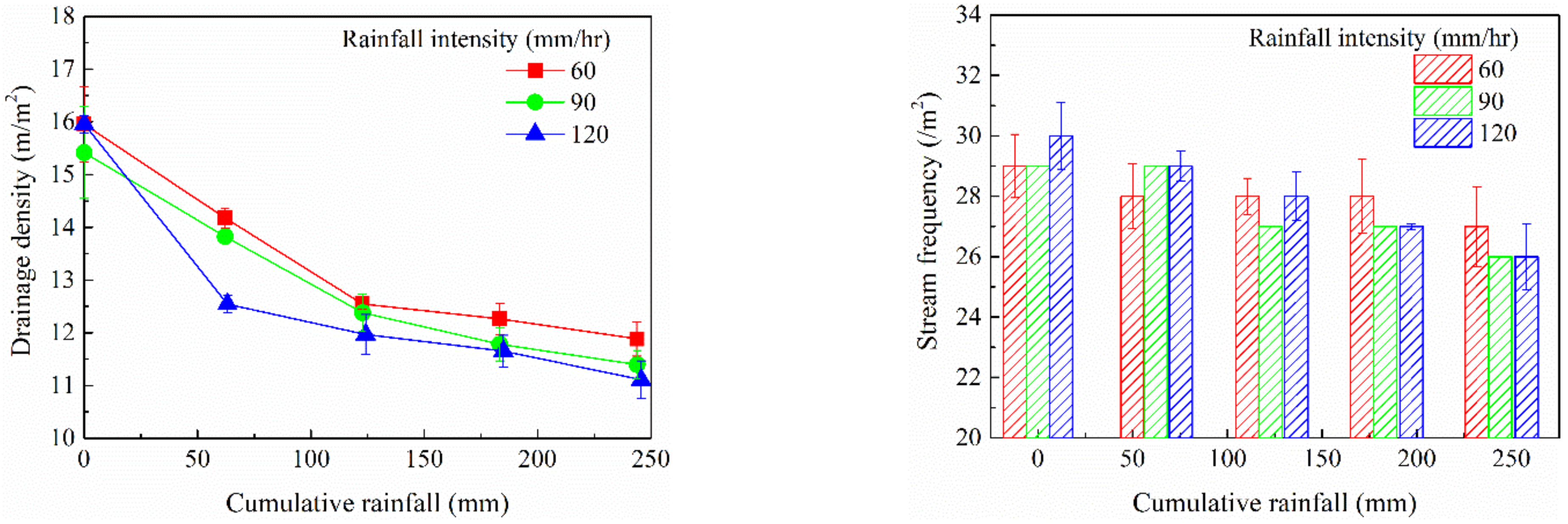
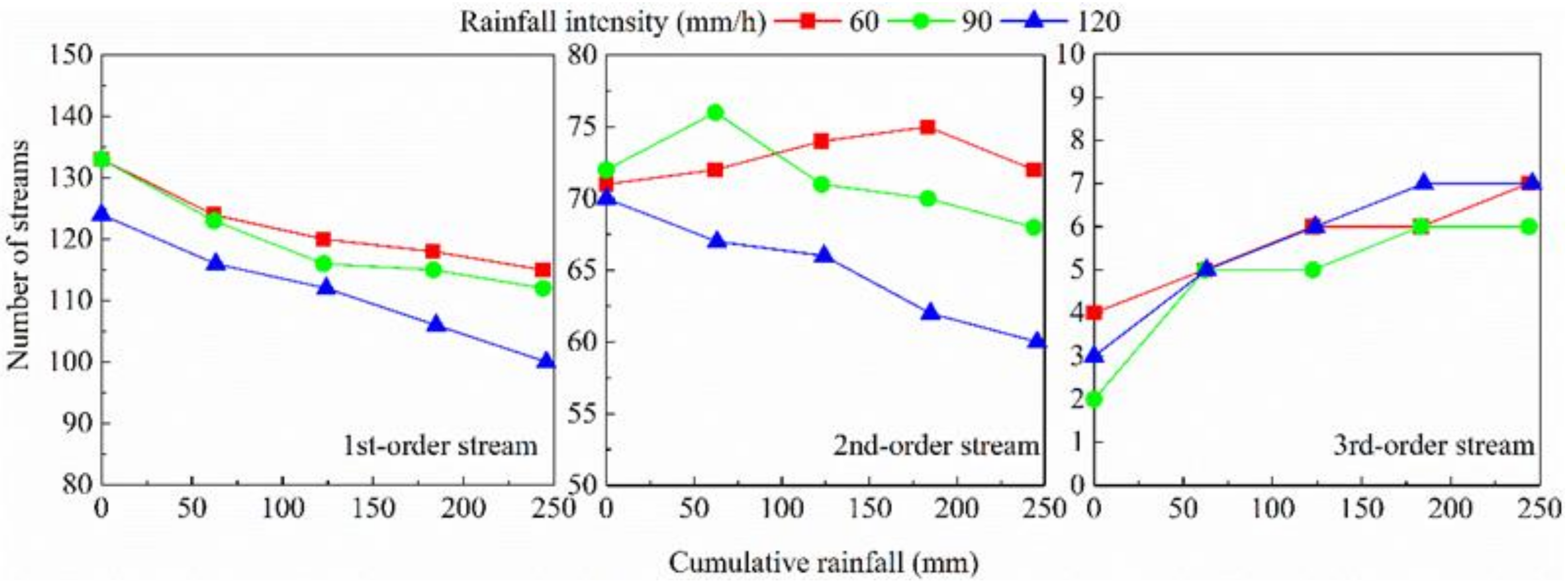
3.3.1. Drainage Density and Stream Frequency
3.3.2. Relationship between Roughness and Drainage Density and Stream Frequency
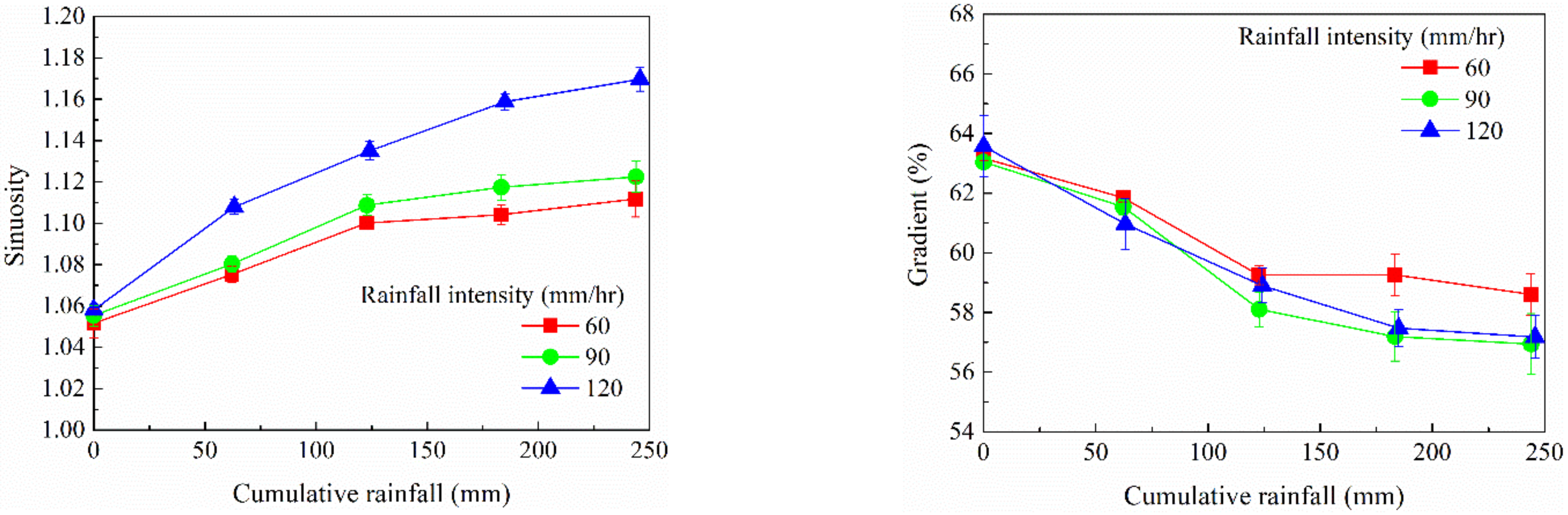
3.3.3. Flow Path Sinuosity and Gradient
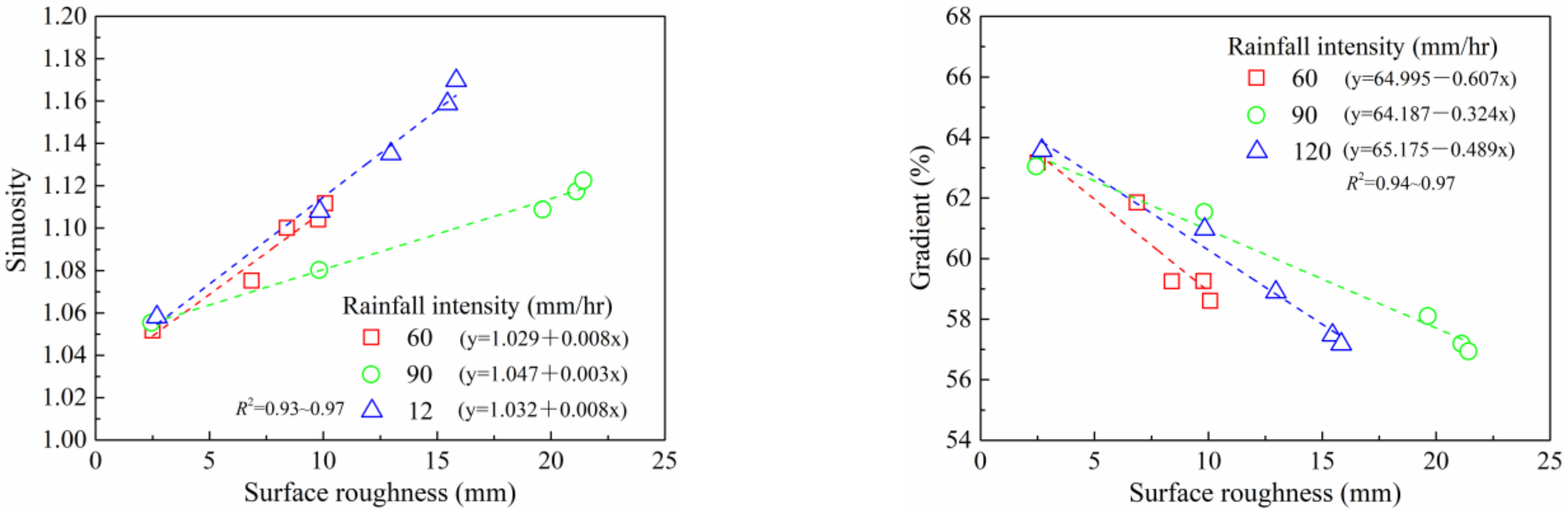
3.3.4. Relationship between Roughness and Stream Sinuosity and Gradient
3.4. Fractal Dimension of the Drainage Network
3.5. Relationship between Hydrodynamic Parameters and Drainage Network Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, H.; Rong, Y.; Lv, J.; Xie, Y. Runoff erosion processes on artificially constructed conically-shaped overburdened stockpiles with different gravel contents: Laboratory experiments with simulated rainfall. Catena 2019, 175, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda, A. Soil water erosion on road embankments in eastern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 378, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.C.; Silva, T.I. Dam Construction and Loss of Geodiversity in the Araguari River Basin, Brazil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.S.; Jing, M.X.; Yang, Y.L.; Li, W.H. Standardization parameter for spoilbank underlying surface simulation of development construction project. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 26, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Innes, J.; Yusheng, Y.; Shanmu, C.; Krzyzanowski, J.; Jingsheng, X.; Wenlian, L. Extent of soil erosion and surface runoff associated with large-scale infrastructure development in Fujian Province, China. Catena 2012, 89, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Shi, D.; Jiang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. Runoff erosion process on different underlying surfaces from disturbed soils in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Catena 2014, 123, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Basha, B.M. Slope Stability of Waste Dumps and Landfills: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges. In Proceedings of the Indian Geotechnical Conference, Kakinada, India, 18–20 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, M.D.; Ruiz-Capillas, P.; Mola, I.; Pérez-Corona, E.; Casado, M.A.; Balaguer, L. Soil Development at the Roadside: A Case Study of a Novel Ecosystem. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Ye, Y. Natural and anthropogenic rates of soil erosion. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wang, W.; Jiang, G.; Peng, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, W. Effects of disturbed landforms on the soil water retention function during urbanization process in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Catena 2016, 144, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Foster, G.R.; Lane, L.J.; Finkner, S.C. A Process-Based Soil Erosion Model for USDAWater Erosion Prediction Project Technology. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1989, 32, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuela, A.; Darboux, F.; Javaux, M.; Bielders, C.L. Evolution of overland flow connectivity in bare agricultural plots. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 1595–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, M.; Shi, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Welbourne, D.; Lin, Q. Digital close range photogrammetry for the study of rill development at flume scale. Catena 2016, 143, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q. Measurement of the connectivity of runoff source areas on a bare soil surface in a laboratory experiment. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 74, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martz, L.W.; Garbrecht, J. Automated extraction of drainage network and watershed from digital elevation models. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1993, 29, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helming, K.; Römkens, M.J.; Prasad, S.N.; Sommer, H. Erosional development of small scale drainage networks. Process. Model. Landf. Evol. 1999, 78, 123–145. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R. Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins: Hydrological approach to quantitative morphology. GSA Bull. 1945, 56, 275–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvajal, F.; Aguilar, M.A.; Agüera, F.; Aguilar, F.J.; Giraldez, J.V. Maximum Depression Storage and Surface Drainage Network in Uneven Agricultural Landforms. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 95, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, T.; He, S. Spatial heterogeneity of microtopography and its influence on the flow convergence of slopes under different rainfall patterns. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, J.A.; Darboux, F.; Nearing, M.A. Development and evolution of rill networks under simulated rainfall. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, J.; Luo, H.; Xie, Y. Impact of rock fragment size on erosion process and micro-topography evolution of cone-shaped spoil heaps. Geomorphology 2020, 350, 106936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.J.; Gordon, L.M.; Neroni, V.; Wells, R.R. Emergence, persistence, and organization of rill networks on a soil-mantled experimental landscape. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, S7–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps. In World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.; Zhao, J. A brief introduction on the rainfall simulation laboratory and equipment. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 11, 177–178. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Yao, W.; Tang, H.; Wei, G.; Wang, L. Laboratory investigations of rill dynamics on soils of the Loess Plateau of China. Geomorphology 2017, 293, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheaton, J.M.; Brasington, J.; Darby, S.E.; Sear, D.A. Accounting for uncertainty in DEMs from repeat topographic surveys: Improved sediment budgets. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 136–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, J.F.; Mark, D.M. The extraction of drainage networks from digital elevation data. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1984, 27, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaya, V.; Raghukanth, S.T.G.; Mohan, S.S. Estimating fractal dimension of lineaments using box counting method for the Indian landmass. Geocarto Int. 2014, 29, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.T.; Gao, Z.L.; Yang, S.W.; Li, Y.H.; Tian, H.W. Dynamic processes of soil erosion by runoff on engineered landforms derived from expressway construction: A case study of typical steep spoil heap. Catena 2015, 128, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, G.; Liu, P.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, J.; Hu, F. Response of soil detachment rate to the hydraulic parameters of concentrated flow on steep loessial slopes on the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 2613–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Wu, L. Sediment and solute transport on soil slope under simultaneous influence of rainfall impact and scouring flow. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xingming, Z.; Tao, J.; Xiaofeng, L.; Yanling, D.; Kai, Z. The temporal variation of farmland soil surface roughness with various initial surface states under natural rainfall conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 170, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, T.; Strauss, P.; Grims, M.; Kamptner, E.; Mansberger, R.; Spiegel, H. Long-term agricultural management effects on surface roughness and consolidation of soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 151, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, F. Soil surface roughness effects on infiltration process of a cultivated slopes on the Loess Plateau of China. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4759–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, C.; Wu, F. Effect of microrelief on water erosion and their changes during rainfall. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Luo, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, A. Effect of rainfall intensity on erosion and rill evolution of engineering piles. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 6, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhlisin, M.; Naam, S.I. Effect of rock fragments on pore water pressure and slope stability at a hillslope. J. Geol. Soc. India 2015, 86, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.C.; Kosugi, K.I.; Lee, T.H.; Misuyama, T. The effects of rock fragments on hydrologic and hydraulic responses along a slope. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romkens, M.J.M.; Helming, K.; Prasad, S.N. Soil erosion under different rainfall intensities, surface roughness, and soil water regimes. Catena 2001, 46, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.D.; Abrantes, J. Can infrared thermography be used to estimate soil surface microrelief and rill morphology? Catena 2014, 113, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tang, H.; Yao, W.; Zhang, N.; Xizhi, L. Experimental investigation of morphological characteristics of rill evolution on loess slope. Catena 2016, 137, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Scan Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall Intensity (mm/h) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 60 | 1.454a | 1.400b | 1.375b | 1.364b | 1.350b |
| 90 | 1.459a | 1.387b | 1.315a | 1.309a | 1.305a |
| 120 | 1.455a | 1.333a | 1.305a | 1.304a | 1.292a |
| Ds (m/m2) | F (/m2) | S | G (%) | Average Runoff Rate (mm/min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v (m/s) | −0.851 **1 | −0.881 ** | 0.704 * | 0.940 ** | 0.483 ns |
| τ (N/m2) | 0.480 ns | −0.062 ns | 0.589 ns | −0.461 ns | 0.960 ** |
| e (m) | −0.388 ns | −0.683 * | 0.509 ns | −0.482 ns | 0.934 ** |
| ω (N/(m·s)) | −0.644 * | −0.453 ns | 0.832 ** | −0.719 * | 0.932 ** |
| Regression Equation | R-Square | F-Value | Sig. | n | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a 1 | b | c | Equation | ||||
| ω = 0.503R − 0.019Ds + 0.204 | 0.961 | 111.020 | 0.032 | 0.000 | 0.150 | 0.000 | 12 |
| ω = 0.306R + 1.703S − 1.794 | 0.979 | 214.539 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 12 |
| ω = 0.537R − 0.011G + 0.590 | 0.968 | 135.324 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.030 | 0.000 | 12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.; Lv, J.; Luo, H.; Xie, Y. Evolution of Surface Drainage Network for Spoil Heaps under Simulated Rainfall. Water 2021, 13, 3475. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233475
Chen D, Lv J, Luo H, Xie Y. Evolution of Surface Drainage Network for Spoil Heaps under Simulated Rainfall. Water. 2021; 13(23):3475. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233475
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Dongkai, Jiaorong Lv, Han Luo, and Yongsheng Xie. 2021. "Evolution of Surface Drainage Network for Spoil Heaps under Simulated Rainfall" Water 13, no. 23: 3475. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233475
APA StyleChen, D., Lv, J., Luo, H., & Xie, Y. (2021). Evolution of Surface Drainage Network for Spoil Heaps under Simulated Rainfall. Water, 13(23), 3475. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233475





