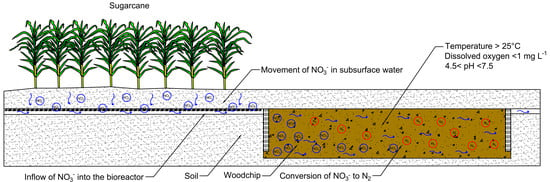
Nitrate Removal Performance of Denitrifying Woodchip Bioreactors in Tropical Climates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
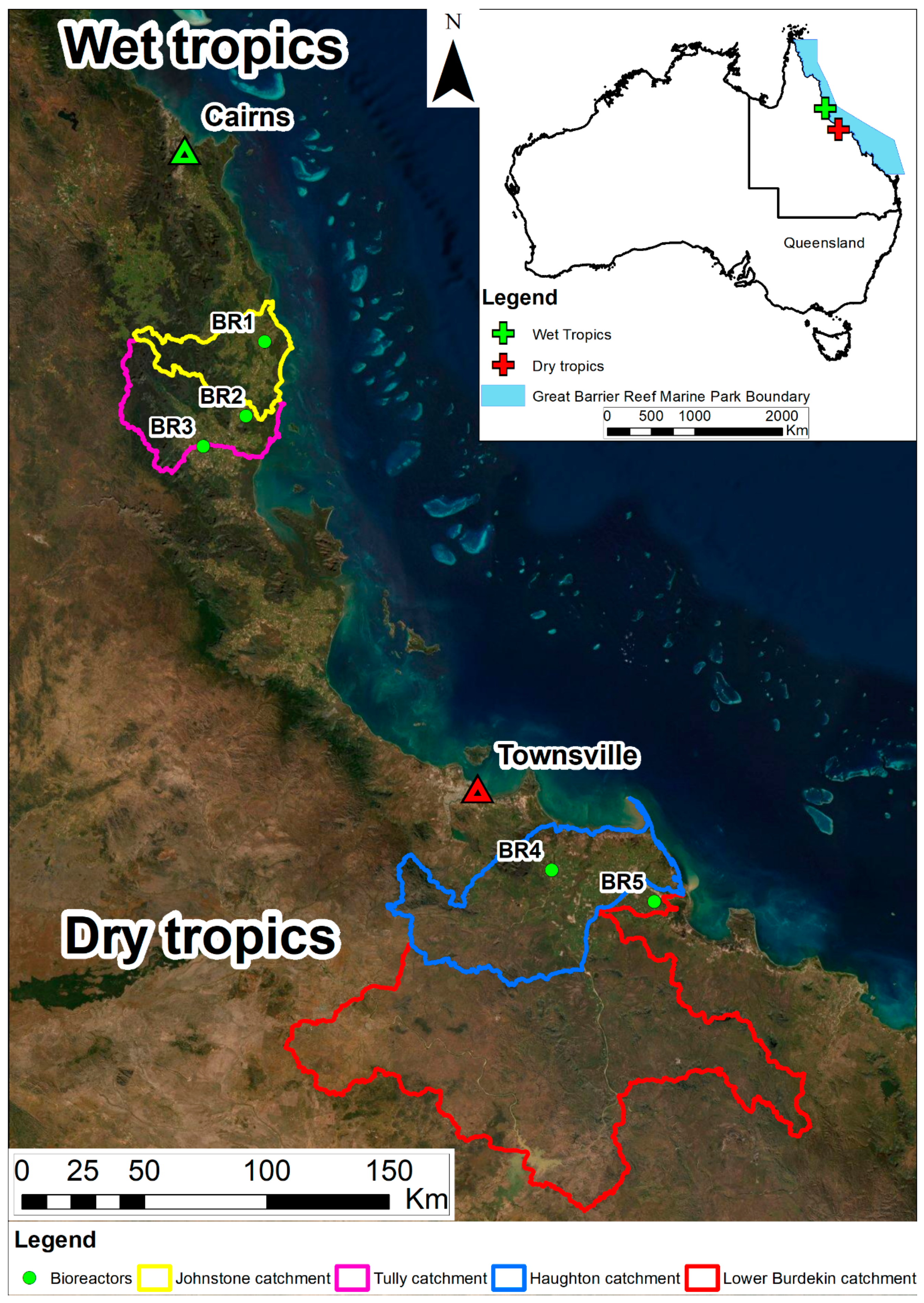
2.1. Wet Tropics Bioreactors
2.1.1. Study Area
2.1.2. BR1
2.1.3. BR2
2.1.4. BR3
2.2. Dry Tropics Bioreactors
2.2.1. Study Area
2.2.2. BR4
2.2.3. BR5
2.3. Water Sampling
2.3.1. Wet Tropics
2.3.2. Dry Tropics
2.3.3. Comparability of Analytical Results
2.4. Nitrate Removal Calculation
2.5. Woodchip Saturation, Bed Flow Rate and Hydraulic Residence Time
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influent Nitrate and Removal Performance
3.2. Nitrate Removal Processes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schipper, L.A.; Robertson, W.D.; Gold, A.J.; Jaynes, D.B.; Cameron, S.G. Denitrifying bioreactors—An approach for reducing nitrate loads to receiving waters. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisman, J.W.; Galloway, J.N.; Seitzinger, S.; Bleeker, A.; Dise, N.B.; Petrescu, A.M.R.; Leach, A.M.; de Vries, W. Consequences of human modification of the global nitrogen cycle. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2013, 368, 20130116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howarth, R.W. Coastal nitrogen pollution: A review of sources and trends globally and regionally. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, J.; Brodie, J.; Tracey, D.; Smith, R.; Vandergragt, M.; Collier, C.; Petus, C.; Baird, M.; Kroon, F.; Mann, R.; et al. Chapter 3: The risk from anthropogenic pollutants to Great Barrier Reef coastal and marine ecosystems. In Scientific Consensus Statement 2017: A Synthesis of the Science of Land-Based Water Quality Impacts on the Great Barrier Reef; State of Queensland: Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2017; p. 186. [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn, P.J.; Biggs, J.S.; Attard, S.J.; Kemei, J. Environmental impacts of irrigated sugarcane production: Nitrogen lost through runoff and leaching. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, J.; Brodie, J.; Lewis, S.; Mitchell, A. Quantifying the sources of pollutants in the Great Barrier Reef catchments and the relative risk to reef ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoey, J.; Campbell, M.L.; Hewitt, C.L.; Gould, B.; Bird, R. Acanthaster planci invasions: Applying biosecurity practices to manage a native boom and bust coral pest in Australia. Manage. Biol. Invasion. 2016, 7, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De’ath, G.; Fabricius, K.E.; Sweatman, H.; Puotinen, M. The 27–year decline of coral cover on the Great Barrier Reef and its causes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17995–17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christianson, L.E.; Cooke, A.C.; Hay, C.; Helmers, M.; Feyereisen, G.; Ranaivoson, A.; McMaine, J.; McDaniel, R.; Rosen, T.; Pluer, W.; et al. Effectiveness of denitrifying bioreactors on water pollutant reduction from agricultural areas. Trans. ASABE 2021, 64, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffman, P.M.; Rosi-Marshall, E.J. The Nitrogen Cycle. In Fundamentals of Ecosystem Science; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 137–158. [Google Scholar]
- Christianson, L.E.; Helmers, M.J. Woodchip Bioreactors for Nitrate in agricultural Drainage; Agriculture and Environment Extension Publications: Ames, IA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- DES. Bioreactors. Available online: https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/management/treatment-systems/for-agriculture/treatment-sys-nav-page/bioreactors/ (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Manca, F.; De Rosa, D.; Reading, L.P.; Rowlings, D.W.; Scheer, C.; Schipper, L.A.; Grace, P.R. Effect of soil cap and nitrate inflow on nitrous oxide emissions from woodchip bioreactors. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 166, 106235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addy, K.; Gold, A.J.; Christianson, L.E.; David, M.B.; Schipper, L.A.; Ratigan, N.A. Denitrifying bioreactors for nitrate removal: A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, N.L.; Bhandari, A.; Soupir, M.L.; Moorman, T.B. Woodchip denitrification bioreactors: Impact of temperature and hydraulic retention time on nitrate removal. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braker, G.; Schwarz, J.; Conrad, R. Influence of temperature on the composition and activity of denitrifying soil communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 73, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.G.; Schipper, L.A. Nitrate removal and hydraulic performance of organic carbon for use in denitrification beds. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1588–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, B.; Giri, S.; Pluer, W.T.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Geohring, L.D. Seasonal performance of denitrifying bioreactors in the Northeastern United States: Field trials. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Northern Gulf of Mexico Hypoxic Zone. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ms-htf/northern-gulf-mexico-hypoxic-zone (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Woli, K.P.; David, M.B.; Cooke, R.A.; McIsaac, G.F.; Mitchell, C.A. Nitrogen balance in and export from agricultural fields associated with controlled drainage systems and denitrifying bioreactors. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E.; Cooke, R.A.; Herbstritt, S.M. Temperature and substrate control woodchip bioreactor performance in reducing tile nitrate loads in east-central Illinois. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christianson, L.E.; Bhandari, A.; Helmers, M.J.; Kult, K.J.; Sutphin, T.; Wolf, R. Performance evaluation of four field-scale agricultural drainage denitrification bioreactors in Iowa. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christianson, L.E.; Helmers, M.J.; Bhandari, A.; Moorman, T.B. Internal hydraulics of an agricultural drainage denitrification bioreactor. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranaivoson, A.; Rice, P.; Moncrief, J.; Feyereisen, G.; Dittrich, M. Acetochlor and atrazine dissipation in a woodchip denitrifying bioreactor: A comparison of experimental results with model estimates. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 3, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaivoson, A.; Moncrief, J.; Venterea, R.; Rice, P.; Dittrich, M. Report to the Minnesota Department of Agriculture: Anaerobic Woodchip Bioreactor for Denitrification, Herbicide Dissipation, and Greenhouse Gas Mitigation. MDA Bioreactor Report 2012. pp. 1–17. Available online: https://www.mda.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/inline-files/bioreactor2012.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Partheeban, C. Demonstrating the Effectiveness of Nitrate-Nitrogen Removal of Denitrifying Bioreactors in South Dakota for Improved Drainage Water Management; Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering Department, South Dakota State University: Brookings, SD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, T.; Christianson, L. Performance of denitrifying bioreactors at reducing agricultural nitrogen pollution in a humid subtropical coastal plain climate. Water 2017, 9, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bock, E.M.; Coleman, B.S.L.; Easton, Z.M. Performance of an under-loaded denitrifying bioreactor with biochar amendment. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 217, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christianson, L.E.; Collick, A.S.; Bryant, R.B.; Rosen, T.; Bock, E.M.; Allen, A.L.; Kleinman, P.J.A.; May, E.B.; Buda, A.R.; Robinson, J. Enhanced Denitrification Bioreactors Hold Promise for Mid-Atlantic Ditch Drainage. Agric. Environ. Lett. 2017, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schipper, L.A.; Vojvodić-Vuković, M. Nitrate removal from groundwater using a denitrification wall amended with sawdust: Field trial. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, A.; Barkle, G.; Stenger, R.; Moorhead, B.; Clague, J. Nitrate removal and secondary effects of a woodchip bioreactor for the treatment of subsurface drainage with dynamic flows under pastoral agriculture. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 148, 105786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, L.A.; Cameron, S.G.; Warneke, S. Nitrate removal from three different effluents using large-scale denitrification beds. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrner, S. Groundwater Nitrate Removal using a Bioremediation Trench. Honours Thesis, University of Western Australia, Crawley, WA, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Manca, F.; De Rosa, D.; Reading, L.P.; Rowlings, D.W.; Scheer, C.; Layden, I.; Irvine-Brown, S.; Schipper, L.A.; Grace, P.R. Nitrate removal and greenhouse gas production of woodchip denitrification walls under a humid subtropical climate. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 156, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegscheidl, C.; Robinson, R.; Manca, F. Using Denitrifying Bioreactors to Improve Water Quality on Queensland Farms; Queensland Government, Department of Agriculture and Fisheries: Townsville, QLD, Australia, 2021.
- QDAF. Bioreactors: Key aspects for Effective Design, Operation and Monitoring—Interim Guideline for Bioreactor Trials July 2018; QDAF: Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2018.
- Rasiah, V.; Armour, J.D.; Cogle, A.L. Assessment of variables controlling nitrate dynamics in groundwater: Is it a threat to surface aquatic ecosystems? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.; Reading, L. Nitrate dynamics in groundwater under sugarcane in a wet-tropics catchment. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasiah, V.; Armour, J.D.; Nelson, P.N. Nitrate in shallow fluctuating groundwater under sugarcane: Quantifying the lateral export quantities to surface waters. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 180, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenahan, M.; Bristow, K. Understanding sub-surface solute distributions and salinization mechanisms in a tropical coastal floodplain groundwater system. J. Hydrol. 2010, 390, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayalakumaran, T.; Bristow, K.; Charlesworth, P.; Fass, T. Geochemical conditions in groundwater systems: Implications for the attenuation of agricultural nitrate. Agric. Water Manage. 2008, 95, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorburn, P.J.; Biggs, J.S.; Weier, K.L.; Keating, B.A. Nitrate in groundwaters of intensive agricultural areas in coastal Northeastern Australia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 94, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.E.; Wegener, M.K.; Bristow, K.L.; Harrison, S.R. Economic evaluation of alternative irrigation systems for sugarcane in the Burdekin delta in north Queensland, Australia. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2001, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; Mcmahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- BoM. Regional Weather and Climate Guide—The Wet Tropics. 2019. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/climate-guides/guides/027-Wet-Tropics-QLD-Climate-Guide.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- BOM. Johnstone Catchment Water Quality Targets. Available online: https://www.reefplan.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0018/46062/catchment-targets-wet-tropics-johnstone.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- BOM. Tully Catchment Water Quality Targets. Available online: https://www.reefplan.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0022/46066/catchment-targets-wet-tropics-tully.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- McInnes, K.; Abbs, D.; Bhend, J.; Chiew, F.; Church, J.; Ekstrm, M.; Kirono, D.; Lenton, A.; Lucas, C.; Moise, A. Wet Tropics Cluster Report; CSIRO and Bureau of Meteorology: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2015; p. 54.
- BoM. Regional Weather and Climate Guide—The Burdekin. 2019. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/climate-guides/guides/022-Burdekin-QLD-Climate-Guide.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- BOM. Burdekin Catchment Water Quality Targets. Available online: https://www.reefplan.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0015/46032/catchment-targets-burdekin-burdekin.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- BOM. Haughton Catchment Water Quality Targets. Available online: https://www.reefplan.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0017/46034/catchment-targets-burdekin-haughton.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Petheram, C.; Tickell, S.; O’Gara, F.; Bristow, K.L.; Smith, A.; Jolly, P. Analysis of the Lower Burdekin, Ord and Katherine-Douglas-Daly Irrigation Areas: Implications to Future Design and Management of Tropical Irrigation; CSIRO and CRC for Irrigation Futures: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2008.
- Holden, J.; McGuire, P. Irrigation of Sugarcane Manual; Sugar Research Australia: Indooroopilly, QLD, Australia, 2014; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- ANZECC; ARMCANZ. Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality; Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council and Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2000; Volume 2, p. 678.
- Weiss, R.F. The solubility of nitrogen, oxygen and argon in water and seawater. Deep Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1970, 17, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, L.A.; Vojvodić-Vuković, M. Nitrate removal from groundwater and denitrification rates in a porous treatment wall amended with sawdust. Ecol. Eng. 2000, 14, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.G.; Schipper, L.A. Hydraulic properties, hydraulic efficiency and nitrate removal of organic carbon media for use in denitrification beds. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.; Salo, M.W.; Schmit, C.G.; Hay, C.H. Nitrate and phosphate removal from agricultural subsurface drainage using laboratory woodchip bioreactors and recycled steel byproduct filters. Water Res. 2016, 102, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darcy, H. Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon: Exposition et Application; Victor Dalmont: Batignolles, France, 1856. [Google Scholar]
- Cheesman, A.; Bithin, D.; Nelson, P. Johnstone Bioreactor Site 01 Initial Data Assessment; James Cook University: Douglas, QLD, Australia, 2019; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Ohio-EPA. Characterization of Site Hydrogeology. Tech. Guid. Ground Water Investig. 2006, 3, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Rawls, W.J.; Brakensiek, D.L.; Miller, N. Green-Ampt infiltration parameters from soils data. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warneke, S.; Schipper, L.A.; Bruesewitz, D.A.; Baisden, W.T. A comparison of different approaches for measuring denitrification rates in a nitrate removing bioreactor. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4141–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.A.; Cooke, R.A. Calibrating Agridrain water level control structures using generalized weir and orifice equations. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2008, 24, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.A.; Cooke, R.A.; Eheart, J.W.; Cho, J. Estimation of flow and transport parameters for woodchip-based bioreactors: II. field-scale bioreactor. Biosys. Eng. 2010, 105, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, L.E.; Bhandari, A.; Helmers, M.J. Pilot-scale evaluation of denitrification drainage bioreactors: Reactor geometry and performance. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; Team, R.C. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R Package version 3.1–140. 2019. Available online: https://svn.r-project.org/R-packages/trunk/nlme/ (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Schipper, L.A.; Barkle, G.F.; Vojvodic-Vukovic, M. Maximum rates of nitrate removal in a denitrification wall. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, W.D.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Cherry, J.A. Long-term performance of in situ reactive barriers for nitrate remediation. Groundwater 2000, 38, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.A.; Clark, M.W. Efficacy of a denitrification wall to treat continuously high nitrate loads. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 42, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Congdon, R.; Lukacs, G. Water quality aspects of irrigation runoff from the Burdekin River irrigation area. In Downstream Effects of Land Use; Department of Natural Resources: Townsville, QLD, Australia, 1996; pp. 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Elgood, Z.; Robertson, W.D.; Schiff, S.L.; Elgood, R. Nitrate removal and greenhouse gas production in a stream-bed denitrifying bioreactor. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, M.O.; Buss, S.R.; Morgan, P.; Smith, J.W.N.; Bemment, C.D. Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: A review of biogeochemical controlling processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4215–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manca, F. Nitrate removal and nitrous oxide production of denitrifying woodchip bioreactors under subtropical and tropical climates. Ph.D. Thesis, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Lin, L.; Ye, Y.; Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Jin, Y.; Ru, Q.; Tian, G. Nutrient removal efficiency in a rice-straw denitrifying bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlan, R.G.; Al-Mashaqbeh, O. Effect of media type and particle size on dissolved organic carbon release from woody filtration media. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warneke, S.; Schipper, L.A.; Bruesewitz, D.A.; McDonald, I.; Cameron, S. Rates, controls and potential adverse effects of nitrate removal in a denitrification bed. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Dai, X.; Chai, X. Effect of influent pH on biological denitrification using biodegradable PHBV/PLA blends as electron donor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 131, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepine, C.; Christianson, L.E.; Sharrer, K.; Summerfelt, S. Optimizing hydraulic retention times in denitrifying woodchip bioreactors treating recirculating aquaculture system wastewater. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, M.G.; Barrett, M.; Lanigan, G.J.; Serrenho, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.G.; Thornton, S.F.; Rolfe, S.A.; Huang, W.E.; Fenton, O. Optimizing nitrate removal and evaluating pollution swapping trade-offs from laboratory denitrification bioreactors. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, P.; Kuypers, M.M.M. Microbial Nitrogen Cycling Processes in Oxygen Minimum Zones. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 317–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, O.; Healy, M.G.; Brennan, F.P.; Thornton, S.F.; Lanigan, G.J.; Ibrahim, T.G. Holistic evaluation of field-scale denitrifying bioreactors as a basis to improve environmental sustainability. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Bioreactor Name | Region and Agricultural Practice | Bioreactor Type | Catchment | Soil Type | Installation Date | Monitoring Period | Drainage Catchment Area (ha) | Woodchip Type | Bioreactor Length × Depth × Width (m) | Woodchip Volume (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR1 | Wet tropics—rainfed | Wall | Johnstone | Kandosol (Brosnan) | August 2018 | January 2019–March 2021 | 7.0 | Hardwood | 30.0 × 1.5 × 0.6 (at the bottom) × 2.1 (at the top) | 60.8 |
| BR2 | Off-line bed connected to tile-drainage | Tully | Hydrosol (Timara) | October 2019 | January 2020–March 2021 | 9.5 | Softwood | 10.0 × 1.0 × 1.5 | 15.0 | |
| BR3 | Off-line bed connected to tile-drainage | Tully | Kandosol (Urchee) | October 2019 | January 2020–March 2021 | 2.6 | Softwood | 10.0 × 1.0 × 1.5 | 15.8 | |
| BR4 | Dry tropics—irrigated | In-line bed downslope of a collection drain | Haughton River | Dermosol | June 2018 | September 2018–January 2019 (7 irrigations) | 25.6 | Softwood | 25.0 × 0.5 m × 2.9 | 36.3 |
| BR5 | Off-line bed downslope of a collection drain | Lower Burdekin | Vertosol | May 2019 | May 2019–March 2020 (13 irrigations | 25.7 | Softwood | 26.0 × 0.7 × 2.0 | 33.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manca, F.; Wegscheidl, C.; Robinson, R.; Argent, S.; Algar, C.; De Rosa, D.; Griffiths, M.; George, F.; Rowlings, D.; Schipper, L.; et al. Nitrate Removal Performance of Denitrifying Woodchip Bioreactors in Tropical Climates. Water 2021, 13, 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243608
Manca F, Wegscheidl C, Robinson R, Argent S, Algar C, De Rosa D, Griffiths M, George F, Rowlings D, Schipper L, et al. Nitrate Removal Performance of Denitrifying Woodchip Bioreactors in Tropical Climates. Water. 2021; 13(24):3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243608
Chicago/Turabian StyleManca, Fabio, Carla Wegscheidl, Rhianna Robinson, Suzette Argent, Christopher Algar, Daniele De Rosa, Matthew Griffiths, Fiona George, David Rowlings, Louis Schipper, and et al. 2021. "Nitrate Removal Performance of Denitrifying Woodchip Bioreactors in Tropical Climates" Water 13, no. 24: 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243608
APA StyleManca, F., Wegscheidl, C., Robinson, R., Argent, S., Algar, C., De Rosa, D., Griffiths, M., George, F., Rowlings, D., Schipper, L., & Grace, P. (2021). Nitrate Removal Performance of Denitrifying Woodchip Bioreactors in Tropical Climates. Water, 13(24), 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243608