Optimization of Magnetic Nanoparticles Draw Solution for High Water Flux in Forward Osmosis
Abstract
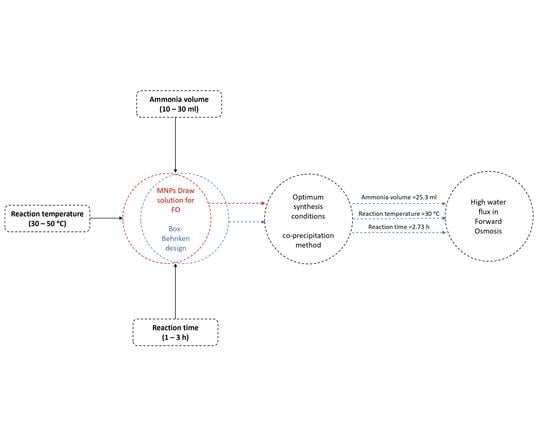
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Nanoparticles Preparation and Characterization
2.3. Membrane Filtration Setup
2.4. Box-Behnken Design
3. Results
3.1. ANOVA Analysis and Adequacy of the Regression Model
3.2. Effect of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesis Conditions on the Water Flux
3.3. Optimization and Model Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parlar, I.; Hacıfazlıoğlu, M.; Kabay, N.; Pek, T.; Yüksel, M. Performance comparison of reverse osmosis (RO) with integrated nanofiltration (NF) and reverse osmosis process for desalination of MBR effluent. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 29, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaee, A.; Zaragoza, G.; van Tonningen, H.R. Comparison between Forward Osmosis-Reverse Osmosis and Reverse Osmosis processes for seawater desalination. Desalination 2014, 336, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giagnorio, M.; Ricceri, F.; Tiraferri, A. Desalination of brackish groundwater and reuse of wastewater by forward osmosis coupled with nanofiltration for draw solution recovery. Water Res. 2019, 153, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouzaam, A.; Qiblawey, H. Functional GO-based membranes for water treatment and desalination: Fabrication methods, performance and advantages. A review. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matin, A.; Rahman, F.; Shafi, H.Z.; Zubair, S.M. Scaling of reverse osmosis membranes used in water desalination: Phenomena, impact, and control; future directions. Desalination 2019, 455, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Laoui, T.; Falath, W.; Farooque, A.M. Fouling control in reverse osmosis for water desalination & reuse: Current practices & emerging environment-friendly technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, M.; Hawari, A.H.; Alfahel, R.; Hassan, M.K.; Altaee, A. Comparison of Nanofiltration with Reverse Osmosis in Reclaiming Tertiary Treated Municipal Wastewater for Irrigation Purposes. Membranes 2021, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, M.; Hawari, A.H.; Alfahel, R. Treatment of Wastewater Using Reverse Osmosis for Irrigation Purposes. In International Conference on Civil Infrastructure and Construction (CIC 2020); Qatar University Press: Doha, Qatar, 2020; pp. 724–728. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.-P.; Li, H.-Q. A review of forward osmosis membrane fouling: Types, research methods and future prospects. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2017, 6, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, M.A.; Hawari, A.H.; Das, P.; Khan, S.; Altaee, A. Comparison of dual stage ultrafiltration and hybrid ultrafiltration-forward osmosis process for harvesting microalgae (Tetraselmis sp.) biomass. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2020, 157, 108112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouzaam, A.; Qiblawey, H. Synergetic effects of dodecylamine-functionalized graphene oxide nanoparticles on antifouling and antibacterial properties of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 42, 102120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Yang, L.; Cai, J.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q.; Liu, M. Hydroacid magnetic nanoparticles in forward osmosis for seawater desalination and efficient regeneration via integrated magnetic and membrane separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.; Yang, S.; Lee, S. Evaluation of citrate-coated magnetic nanoparticles as draw solute for forward osmosis. Desalination 2014, 347, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X. Forward osmosis technology for water treatment: Recent advances and future perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Mulcahy, D. Recent developments in forward osmosis: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizani, M.; Endo, T.; Ito, R.; Funamizu, N. Polyethylene Glycol-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles-Based Draw Solution for Forward Osmosis. Sanit. Value Chain. 2020, 4, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Nikiema, B.C.W.-Y.; Ito, R.; Guizani, M.; Funamizu, N. Estimation of Water Flux and Solute Movement during the Concentration Process of Hydrolysed Urine by Forward Osmosis. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2017, 15, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attallah, O.A.; Al-Ghobashy, M.; Nebsen, M.; El-Kholy, R.; Salem, M.Y. Assessment of pectin-coated magnetite nanoparticles in low-energy water desalination applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18476–18483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabani, Z.; Rahimpour, A. Chitosan- and dehydroascorbic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and their potential as draw solute in forward osmosis process. Iran. Polym. J. 2016, 25, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, F.; Karimi-Jashni, A.; Zerafat, M.M. Desalination of brackish water by gelatin-coated magnetite nanoparticles as a novel draw solute in forward osmosis process. Environ. Technol. 2020, 42, 2885–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zufia-Rivas, J.; Morales, P.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S. Effect of the Sodium Polyacrylate on the Magnetite Nanoparticles Produced by Green Chemistry Routes: Applicability in Forward Osmosis. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Chai, P.V.; Takriff, M.S.; Benamor, A.; Mohammad, A.W. Optimization of nickel oxide nanoparticle synthesis through the sol–gel method using Box-Behnken design. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewis, D.; Benamor, A.; Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Nasser, M.; El-Naas, M.; Qiblawey, H. Removal of Oil Content from Oil-Water Emulsions Using Iron Oxide/Bentonite Nano Adsorbents. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 38, 101583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, C.L.; Basri, M.; Lye, F.F.; Masoumi, H.R.F.; Tripathy, M.; Karjiban, R.A.; Abdul-Malek, E. Comparison of Box-Behnken and central composite designs in optimization of fullerene loaded palm-based nano-emulsions for cosmeceutical application. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 59, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Su, J.; Chung, T.-S.; Amy, G. Hydrophilic Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Performance in Forward Osmosis Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 50, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Ström, V.; Olsson, R.T.; Belova, L.; Rao, K.V. Particle size and magnetic properties dependence on growth temperature for rapid mixed co-precipitated magnetite nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 145601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaminger, S.; Syhr, C.; Berensmeier, S. Controlled Synthesis of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Magnetite or Maghemite? Crystals 2020, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, H.-C.; Schwaminger, S.; Schindler, M.; Wagner, F.E.; Berensmeier, S. Influencing factors in the CO-precipitation process of superparamagnetic iron oxide nano particles: A model based study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 377, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanaprakash, G.; Mahadevan, S.; Jayakumar, T.; Kalyanasundaram, P.; Philip, J.; Raj, B. Effect of initial pH and temperature of iron salt solutions on formation of magnetite nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 103, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.; Mansoor, M.A.; Haider, B.; Nasir, R.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Abdulrahman, A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nano particles with high selectivity using in-situ precipitation method. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samrot, A.V.; Sahithya, C.S.; Selvarani, J.; Purayil, S.K.; Ponnaiah, P. A review on synthesis, characterization and potential biological applications of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayssieres, L.; Chanéac, C.; Tronc, E.; Jolivet, J.P. Size Tailoring of Magnetite Particles Formed by Aqueous Precipitation: An Example of Thermodynamic Stability of Nanometric Oxide Particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 205, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guizani, M.; Maeda, T.; Ito, R.; Funamizu, N. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Candidate Draw Solution for Forward Osmosis. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2018, 16, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrinic, I.; Stergar, J.; Bukšek, H.; Drofenik, M.; Gyergyek, S.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Ban, I. Superparamagnetic Fe3O4@Ca Nanoparticles and Their Potential as Draw Solution Agents in Forward Osmosis. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, M.M.; Chung, T.-S. Desalination process using super hydrophilic nanoparticles via forward osmosis integrated with ultrafiltration regeneration. Desalination 2011, 278, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Factors | Levels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | +1 | ||
| Ammonia (mL) | ×1 | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Time (h) | ×2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Temperature (C) | ×3 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| StdOrder | X1 | X2 | X3 | YActual | YPredicted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 1 | 40 | 0.733 | 0.740 |
| 2 | 30 | 1 | 40 | 0.559 | 0.488 |
| 3 | 10 | 3 | 40 | 0.569 | 0.639 |
| 4 | 30 | 3 | 40 | 1.369 | 1.361 |
| 5 | 10 | 2 | 30 | 0.942 | 0.897 |
| 6 | 30 | 2 | 30 | 1.609 | 1.642 |
| 7 | 10 | 2 | 50 | 0.99 | 0.956 |
| 8 | 30 | 2 | 50 | 0.637 | 0.681 |
| 9 | 20 | 1 | 30 | 0.898 | 0.935 |
| 10 | 20 | 3 | 30 | 1.884 | 1.857 |
| 11 | 20 | 1 | 50 | 0.992 | 1.018 |
| 12 | 20 | 3 | 50 | 0.907 | 0.870 |
| 13 | 20 | 2 | 40 | 1.81 | 1.803 |
| 14 | 20 | 2 | 40 | 1.7 | 1.803 |
| 15 | 20 | 2 | 40 | 1.9 | 1.803 |
| Source | DF | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9 | 3.39357 | 0.37706 | 46.47 | 0.000 |
| Linear | 3 | 0.81776 | 0.27259 | 33.59 | 0.001 |
| X1 | 1 | 0.11045 | 0.11045 | 13.61 | 0.014 |
| X2 | 1 | 0.29915 | 0.29915 | 36.87 | 0.002 |
| X3 | 1 | 0.40816 | 0.40816 | 50.30 | 0.001 |
| Square | 3 | 1.79179 | 0.59726 | 73.60 | 0.000 |
| X1 X1 | 1 | 1.16118 | 1.16118 | 143.10 | 0.000 |
| X2 X2 | 1 | 0.69881 | 0.69881 | 86.12 | 0.000 |
| X3 X3 | 1 | 0.14481 | 0.14481 | 17.85 | 0.008 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 3 | 0.78403 | 0.26134 | 32.21 | 0.001 |
| X1 X2 | 1 | 0.23717 | 0.23717 | 29.23 | 0.003 |
| X1 X3 | 1 | 0.26010 | 0.26010 | 32.05 | 0.002 |
| X2 X3 | 1 | 0.28676 | 0.28676 | 35.34 | 0.002 |
| Error | 5 | 0.04057 | 0.00811 | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 3 | 0.02051 | 0.00684 | 0.68 | 0.641 |
| Total | 14 | 3.43415 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hafiz, M.; Talhami, M.; Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Hawari, A.H. Optimization of Magnetic Nanoparticles Draw Solution for High Water Flux in Forward Osmosis. Water 2021, 13, 3653. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243653
Hafiz M, Talhami M, Ba-Abbad MM, Hawari AH. Optimization of Magnetic Nanoparticles Draw Solution for High Water Flux in Forward Osmosis. Water. 2021; 13(24):3653. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243653
Chicago/Turabian StyleHafiz, MhdAmmar, Mohammed Talhami, Muneer M. Ba-Abbad, and Alaa H. Hawari. 2021. "Optimization of Magnetic Nanoparticles Draw Solution for High Water Flux in Forward Osmosis" Water 13, no. 24: 3653. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243653
APA StyleHafiz, M., Talhami, M., Ba-Abbad, M. M., & Hawari, A. H. (2021). Optimization of Magnetic Nanoparticles Draw Solution for High Water Flux in Forward Osmosis. Water, 13(24), 3653. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243653