Adsorption of Metals to Particles in Urban Stormwater Runoff—Does Size Really Matter?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
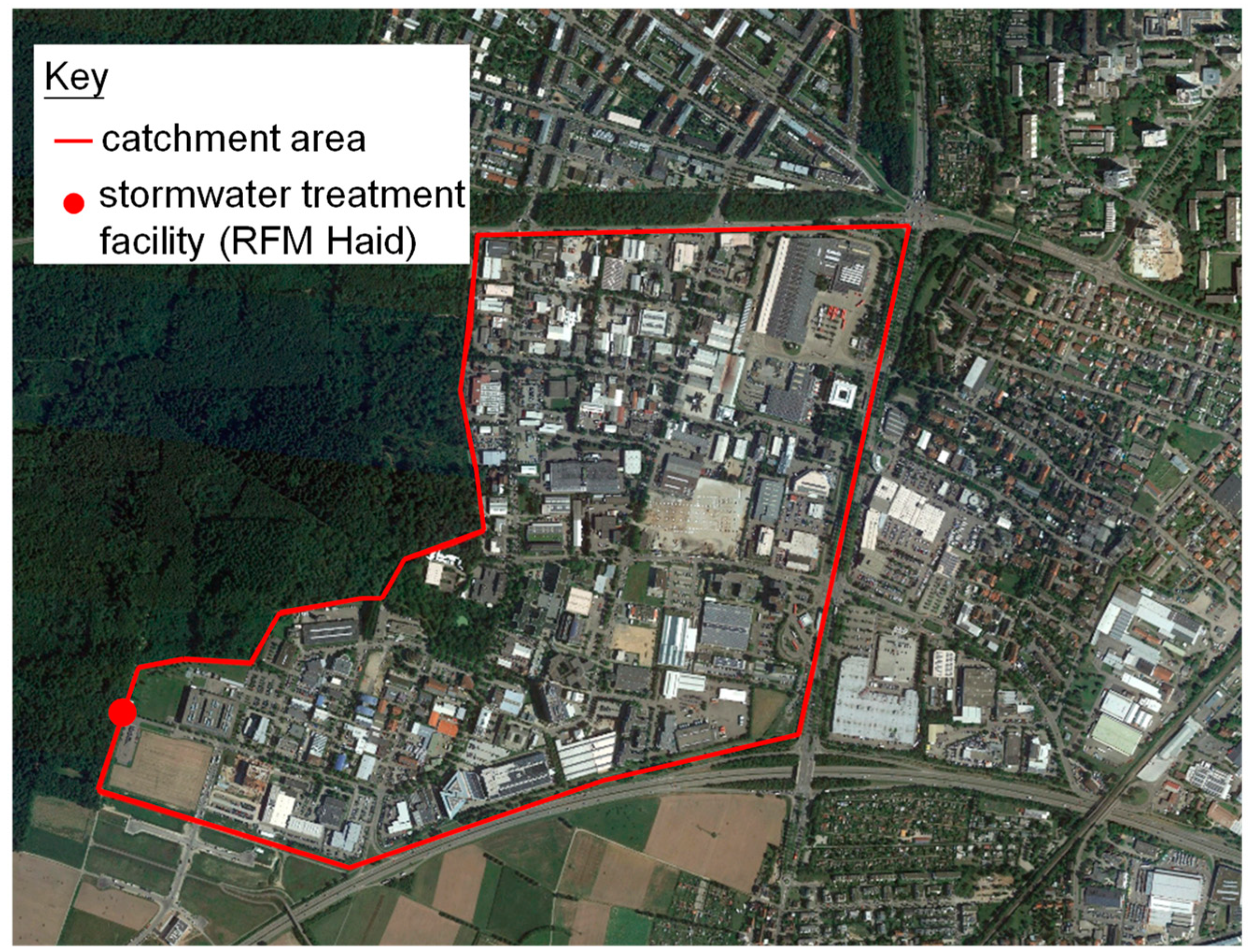
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Stormwater Treatment Facility
Functioning
2.3. Samples Collection
Emptying of Sampling Tanks
2.4. Laboratory Analyses and Methods
2.5. Evaluation Methods
2.5.1. Event Mean Concentration (EMC) and Event Load
2.5.2. Treatment Efficiency
2.5.3. Partitioning—Conceptual Model
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Data Presantation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size Distribution
3.2. Loss on Ignition
3.3. Event Mean Concentrations of TSS and Metals
3.4. Partitioning of Metals
3.5. Particle Size Relationship of Metals
3.6. Suitability of TSS as a Proxy for Metal Contamination
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larsen, T.A.; Hoffmann, S.; Lüthi, C.; Truffer, B.; Maurer, M. Emerging solutions to the water challenges of an urbanizing world. Science 2016, 352, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makepeace, D.K.; Smith, D.W.; Stanley, S.J. Urban stormwater quality: Summary of contaminant data. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 25, 93–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holten Lützhøft, H.-C.; Eriksson, E.; Donner, E.; Wickman, T.; Banovec, P.; Mikkelsen, P.S.; Ledin, A. Quantifying Releases of Priority Pollutants from Urban Sources. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2009, 2009, 5873–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Vollertsen, J.; Nielsen, A.H. Urban and Highway Stormwater Pollution. Concepts and Engineering; CRC Press; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 1439826854. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Ni, S. Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, E.R.; Money, J.E.; Green, P.G.; Young, T.M. Metals associated with stormwater-relevant brake and tire samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5855–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gromaire, M.C.; Garnaud, S.; Gonzalez, A.; Chebbo, G. Charecterisation of urban runoff pollution in Paris. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Welker, A.; Helmreich, B. Critical review of heavy metal pollution of traffic area runoff: Occurrence, influencing factors, and partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 895–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.B.; Rekhi, N.V.; Pise, N.R.; Reeves, R.L.; Matsumoto, M.; Wistrom, A.; Moussa, L.; Bay, S.; Kayhanian, M. A Review of the Contaminants and Toxicity Associated with Particles in Stormwater Runoff. Terminology 2003, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Gunawardana, C.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Role of particle size and composition in metal adsorption by solids deposited on urban road surfaces. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drapper, D.; Tomlinson, R.; Williams, P. Pollutant Concentrations in Road Runoff: Southeast Queensland Case Study. J. Environ. Eng. 2000, 126, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.; Li, L. Identification of traffic-related metals and the effects of different environments on their enrichment in roadside soils along the Qinghai-Tibet highway. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J. Magnetic Properties as Indicator of Heavy Metal Contaminations in Roadside Soil and Dust along G312 Highways. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabin, L.D.; Lim, J.H.; Stolzenbach, K.D.; Schiff, K.C. Contribution of trace metals from atmospheric deposition to stormwater runoff in a small impervious urban catchment. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3929–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Ge, R. Dry and wet deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and comparison with typical media in urban system of Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerman, R.T.; Owens, D.W.; Dodds, R.B.; Hornewer, N.J. Sources of pollutants in Wisconsin stormwater. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lygren, E.; Gjessing, E.; Berglind, L. Pollution transport from a highway. Sci. Total Environ. 1984, 33, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, B.; Zhu, W. Particle size distribution and pollutants in road-deposited sediments in different areas of Zhenjiang, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, A.; Zhang, X. Particle size distribution and characteristics of heavy metals in road-deposited sediments from Beijing Olympic Park. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 32, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardana, C.; Goonetilleke, A.; Egodawatta, P.; Dawes, L.; Kokot, S. Source characterisation of road dust based on chemical and mineralogical composition. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sansalone, J.J.; Buchberger, S.G. Partitioning and First Flush of Metals in Urban Roadway Storm Water. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charters, F.J.; Cochrane, T.A.; O’Sullivan, A.D. Particle size distribution variance in untreated urban runoff and its implication on treatment selection. Water Res. 2015, 85, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilliges, R.; Schriewer, A.; Helmreich, B. A three-stage treatment system for highly polluted urban road runoff. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniquiz-Redillas, M.; Kim, L.-H. Fractionation of heavy metals in runoff and discharge of a stormwater management system and its implications for treatment. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DWA/BWK. Arbeitsblatt DWA-A 102-2/BWK-A 3-2 Grundsätze zur Bewirtschaftung und Behandlung von Regenwetterabflüssen zur Einleitung in Oberflächengewässer–Teil 2: Emissionsbezogene Bewertungen und Regelungen; Deutsche Vereinigung für Wasserwirtschaft, Abwasser und Abfall: Hennef, Germany, 2020; ISBN 9783968620466. [Google Scholar]
- Garten- und Tiefbauamt der Stadt Freiburg—Abteilung Verkehrsplanung. Radverkehrskonzept Freiburg 2020. Anhang 3—Maßnahmenbeschreibungen. 2012. Available online: https://www.freiburg.de/pb/site/Freiburg/get/params_E-1121863396/431691/08b_Beschreibungen.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Schmiedgruber, M. Erstellung Eines Bilanzmodells für Eine Regenwasserbehandlunsanlage. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Charters, F.J.; Cochrane, T.A.; O’Sullivan, A.D. Characterising urban zinc generation to identify surface pollutant hotspots in a low intensity rainfall climate. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egodawatta, P.; Ziyath, A.M.; Goonetilleke, A. Characterising metal build-up on urban road surfaces. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; Chebbo, G.; Saget, A. Distribution of pollutant mass vs. volume in stormwater discharges and the first flush phenomenon. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2341–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deletic, A. The first flush load of urban surface runoff. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Bang, K.W.; Ketchum, L.H.; Choe, J.S.; Yu, M.J. First flush analysis of urban storm runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 293, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, W.C. Contaminant transport in surface water. In Handbook of Hydrology, 6th ed.; Maidment, D.R., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0070397325. [Google Scholar]
- Thomann, R.V.; Mueller, J.H. Principles of Surface Water Quality Modeling and Control; Harper & Row, Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1987; ISBN 9780060466770. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Bonhomme, C.; Le, M.-H.; Chebbo, G. New insights into the urban washoff process with detailed physical modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, X. Understanding the relationship between heavy metals in road-deposited sediments and washoff particles in urban stormwater using simulated rainfall. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 246–247, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaze, J.; Chiew, F.H. Experimental study of pollutant accumulation on an urban road surface. Urban Water 2002, 4, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelhardt, L.; Huber, M.; Welker, A. Development of a Laboratory Method for the Comparison of Settling Processes of Road-Deposited Sediments with Artificial Test Material. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M.; McKenzie, E.R.; Leatherbarrow, J.E.; Young, T.M. Characteristics of road sediment fractionated particles captured from paved surfaces, surface run-off and detention basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 439, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furumai, H.; Balmer, H.; Boller, M. Dynamic behavior of suspended pollutants and particle size distribution in highway runoff. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus associating with different size suspended solids in roof and road runoff in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 15788–15795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansalone, J.J.; Kim, J.-Y. Suspended particle destabilization in retained urban stormwater as a function of coagulant dosage and redox conditions. Water Res. 2008, 42, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anta, J.; Peña, E.; Suárez, J.; Cagiao, J. A BMP selection process based on the granulometry of runoff solids in a separate urban catchment. Water SA 2006, 32, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selbig, W.; Fienen, M.; Horwatich, J.; Bannerman, R.T. The Effect of Particle Size Distribution on the Design of Urban Stormwater Control Measures. Water 2016, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Droppo, I.G.; Irvine, K.N.; Jaskot, C. Flocculation/aggregation of cohesive sediments in the urban continuum: Implications for stormwater management. Environ. Technol. 2002, 23, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karickhoff, S.W.; Brown, D.S.; Scott, T.A. Sorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments. Water Res. 1979, 13, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepom, P.; Brown, B.; Hanke, G.; Loos, R.; Quevauviller, P.; Wollgast, J. Needs for reliable analytical methods for monitoring chemical pollutants in surface water under the European Water Framework Directive. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 August 2013 Amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as Regards Priority Substances in the Field of Water Policy. 2013. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2013/39/oj (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Jayarathne, A.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Geochemical phase and particle size relationships of metals in urban road dust. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, A. Schadstoffströme im Urbanen Wasserkreislauf—Aufkommen und Verteilung, Insbesondere in den Abwasserentsorgungssystemen. Habilitation; TU Kaiserslautern: Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brombach, H.; Weiss, G.; Fuchs, S. A new database on urban runoff pollution: Comparison of separate and combined sewer systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnecco, I.; Palla, A.; Sansalone, J.J. Partitioning of zinc, copper and lead in urban drainage from paved source area catchments. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardana, C.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Adsorption and mobility of metals in build-up on road surfaces. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xanthopoulos, C.; Hahn, H.H. Pollutants attached to particles from drainage areas. Sci. Total Environ. 1990, 93, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, J.D.; Boyd, G.B.; Agardy, F.J. Water Pollution Aspects of Street Surface Contaminants. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1974, 46, 458–467. [Google Scholar]
- Sansalone, J.J.; Buchberger, S.G. Characterization of solid and metal element distributions in urban highway stormwater. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, S.; Montrejaud-Vignoles, M.; Andral, M.; Herremans, L.; Fortune, J. Mineral, physical and chemical analysis of the solid matter carried by motorway runoff water. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Song, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Liana, J. Particle Size Dependent Heavy Metals in Road Dusts from Maanshan City, China. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andral, M.C.; Roger, S.; Montréjaud-Vignoles, M.; Herremans, L. Particle Size Distribution and Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Solid Matter Carried by Runoff from Motorways. Water Environ. Res. 1999, 71, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, S.M.; Lees, J.A. The distribution of heavy metals in deposited urban dusts and sediments, Coventry, England. Environ. Geochem. Health 1999, 21, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.; Taylor, K.; Hoon, S. Geochemical and mineral magnetic characterisation of urban sediment particulates, Manchester, UK. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lair, G.J.; Gerzabek, M.H.; Haberhauer, G. Sorption of heavy metals on organic and inorganic soil constituents. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2007, 5, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, P.; Benisch, J.; Blumensaat, F.; Dierschke, M.; Dittmer, U.; Gelhardt, L.; Gruber, G.; Grüner, S.; Heinz, E.; Hofer, T.; et al. AFS63—Harmonisierungsbedarf und Empfehlungen für die labortechnische Bestimmung des neuen Parameters. In Regenwasser in Urbanen Räumen; Aqua Urbanica Trifft RegenwasserTage: Landau in der Pfalz, Germany, 2018; ISBN 978-3-95974-086-9. [Google Scholar]
- Langeveld, J.G.; Liefting, H.J.; Boogaard, F.C. Uncertainties of stormwater characteristics and removal rates of stormwater treatment facilities: Implications for stormwater handling. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6868–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| TSS (mg L−1) | ||||||
| Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | ||
| <63 µm | 7.52 | 191 | 43.2 | 27.4 | 44.6 | 0.21 |
| 63–125 µm | 0.54 | 23.6 | 5.58 | 2.66 | 6.5 | 0.46 |
| 125–250 µm | 0.50 | 87.6 | 8.28 | 2.05 | 20.4 | 0.48 |
| 250–2000 µm | 0.39 | 108 | 16.1 | 4.10 | 31.3 | 0.71 |
| total | 8.95 | 237 | 63.4 | 33.4 | 66.9 | 0.28 |
| Cr (µg L−1) | ||||||
| min | max | mean | median | SD | ||
| <63 µm | 1.19 | 27.2 | 9.47 | 6.52 | 7.76 | 0.23 |
| 63–125 µm | <0.1 | 7.56 | 1.49 | 0.56 | 2.18 | 0.38 |
| 125–250 µm | <0.1 | 5.57 | 0.98 | 0.31 | 3.70 | 0.52 |
| 250–2000 µm | <0.1 | 9.05 | 0.90 | 0.30 | 2.06 | 0.83 |
| total | 1.60 | 41.9 | 13.4 | 8.82 | 12.2 | 0.28 |
| dissolved | <0.1 | 3.19 | 0.61 | 0.28 | 0.73 | 0.20 |
| Cu (µg L−1) | ||||||
| min | max | mean | median | SD | ||
| <63 µm | 1.75 | 65.4 | 17.9 | 13.2 | 15.2 | 0.27 |
| 63–125 µm | 0.16 | 19.2 | 3.48 | 1.33 | 5.33 | 0.44 |
| 125–250 µm | <0.1 | 13.0 | 2.00 | 0.81 | 3.70 | 0.46 |
| 250–2000 µm | <0.1 | 18.2 | 2.18 | 0.81 | 4.12 | 0.73 |
| total | 14.3 | 108 | 36.3 | 26.3 | 26.6 | 0.28 |
| dissolved | 3.00 | 19.1 | 10.8 | 10.7 | 3.97 | 0.16 |
| Zn (µg L−1) | ||||||
| min | max | mean | median | SD | ||
| <63 µm | 14.7 | 323 | 92.9 | 61.1 | 83.7 | 0.26 |
| 63–125 µm | 1.40 | 131 | 18.0 | 8.07 | 32.4 | 0.47 |
| 125–250 µm | 1.24 | 63.7 | 9.13 | 4.35 | 14.8 | 0.51 |
| 250–2000 µm | 0.96 | 105 | 13.1 | 4.95 | 24.0 | 0.80 |
| total | 157 | 835 | 350 | 276 | 180 | 0.21 |
| dissolved | 71.3 | 399 | 217 | 212 | 87.6 | 0.14 |
| Cd (µg L−1) | ||||||
| min | max | mean | median | SD | ||
| <63 µm | <0.1 | 0.21 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.24 |
| 63–125 µm | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.54 |
| 125–250 µm | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.49 |
| 250–2000 µm | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.72 |
| total | <0.1 | 0.58 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.23 |
| dissolved | <0.1 | 0.21 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.15 |
| Pb (µg L−1) | ||||||
| min | max | mean | median | SD | ||
| <63 µm | 0.20 | 18.7 | 4.64 | 3.11 | 4.69 | 0.28 |
| 63–125 µm | <0.1 | 6.64 | 0.99 | 0.37 | 1.72 | 0.44 |
| 125–250 µm | <0.1 | 3.90 | 0.57 | 0.19 | 1.03 | 0.45 |
| 250–2000 µm | <0.1 | 11.3 | 0.92 | 0.18 | 2.61 | 0.80 |
| total | 0.88 | 31.5 | 7.27 | 4.03 | 8.82 | 0.34 |
| dissolved | <0.1 | 1.28 | 0.15 | <0.1 | 0.29 | 0.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baum, P.; Kuch, B.; Dittmer, U. Adsorption of Metals to Particles in Urban Stormwater Runoff—Does Size Really Matter? Water 2021, 13, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030309
Baum P, Kuch B, Dittmer U. Adsorption of Metals to Particles in Urban Stormwater Runoff—Does Size Really Matter? Water. 2021; 13(3):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030309
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaum, Philipp, Bertram Kuch, and Ulrich Dittmer. 2021. "Adsorption of Metals to Particles in Urban Stormwater Runoff—Does Size Really Matter?" Water 13, no. 3: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030309
APA StyleBaum, P., Kuch, B., & Dittmer, U. (2021). Adsorption of Metals to Particles in Urban Stormwater Runoff—Does Size Really Matter? Water, 13(3), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030309







