Resilience in Complex Catchment Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
How can we use catchment resilience as a unifying concept in catchment management and regulation—particularly in light of climate risks, population growth and other pressures?
2. The Catchment as a Complex Natural-Social-Technical (NST) System
3. How to Be Resilient: Bounce Back, Absorb and Transform
3.1. Engineering Resilience
3.2. Systems Resilience
3.3. Complex Adaptive Systems Resilience
3.4. Resilience Frameworks
4. Catchment Resilience
4.1. Complexity Challenges for Catchment Resilience: A Review
- Natural-social-technical aspects: Acknowledging and accounting for the influence and feedback arising from human values, behaviour, culture, infrastructure and institutions;
- Interactions: Accounting for multiple interactions across natural, social, and technical systems; connecting global-scale dynamics to local realities and vice versa;
- Spatial scales: Coverage of multiple spatial scales; connecting contextual, place-based understandings (bottom-up) with theoretical and systemic knowledge (top-down);
- Time scales: Coverage of multiple temporal scales;
- Multiple forms of evidence; and
- Uncertainty: Recognitions of the uncertainty in future projections.
4.2. Studying Catchment Resilience
5. Future Catchment Resilience
5.1. The How of Future Catchment Resilience
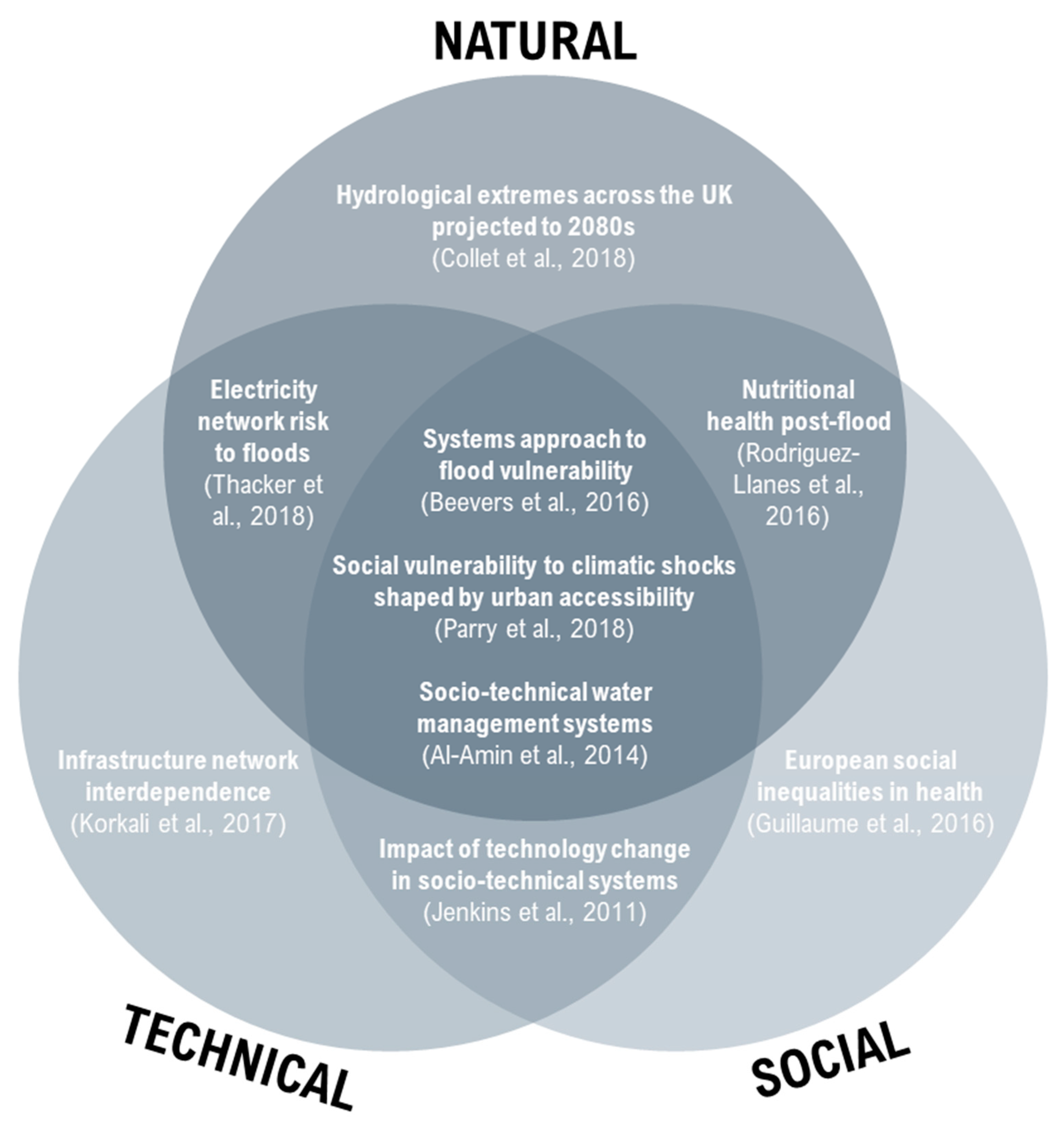
- Strategic overview of the contextual issues for a specific catchment to include the natural, social and technical components. This would set the framework for understanding the catchment and estimate where in the natural-social-technical Venn diagram those identified issues reside, which can then inform a deeper analysis and explore feedbacks between exposure, vulnerability and resilience (Figure 2). This could be completed using:
- ○
- Indicator methods, which are top-down approaches and may be useful at this broad exploratory stage (e.g., communication capacity as in [63]; or multiple livelihood sources [64]). However, indicators can miss deeper issues that could be picked up by also using community workshops or other participatory methods (i.e., bottom-up approaches).
- Natural aspects might be analysed (bearing in mind temporal and spatial scales of assessment) using:
- ○
- ○
- Methods to map and characterise ecological impacts, knock-on effects and feedbacks from within the natural catchment system [65].
- ○
- Methods to explore the efficacy, and feedbacks from building with nature for increasing resilience.
- Technical aspects might be analysed (bearing in mind temporal and spatial scales of assessment) using:
- Social aspects might be analysed (bearing in mind temporal and spatial scales of assessment) using:
- ○
- Human factors methods, such as the Event Analysis of Systemic Teamwork method [67], to study team operations within governance, or critical services such as emergency response.
- ○
- Capabilities Approach framework [68] to study what capacities are required for local neighbourhood-scale resilience.
- ○
- Agent-based modelling to study household-level decision making around the uptake of adaptation measures [69].
- Interaction analysis would use the domain information from above. However, it needs method development in order to recognise and build interactions. Methods may include
- ○
- Systems analysis [62]—where are the functional pinch points, risks, and high-level vulnerabilities within the existing interconnected system structure?
5.2. The Why of Future Catchment Resilience
6. Conclusions
We have argued for catchments to be considered as complex adaptive systems, consisting of interacting subsystems (natural, social, and technical), which are able to adapt and transform in response to shocks (such as hydrohazards). Our reviews suggest that research from this perspective is in its infancy. If approaches do not begin to acknowledge the “fluid frontiers” and interactions between the natural-social-technical realms, spatial and temporal scales, and bottom-up and top-down approaches, then future assessments may miss substantial opportunities to enhance catchment resilience. Understanding where parts of the system need to be strengthened or where redundancy may enhance or inhibit catchment resilience is critical to maximising its potential for managing climate risks, population growth and other pressures.How can we use catchment resilience as a unifying concept in catchment management and regulation—particularly in light of climate risks, population growth and other pressures?
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urban Population (% of Total Population)|Data (worldbank.org). Available online: https:\\data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.URB.TOTL.IN.ZS (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision (ST/ESA/SER.A/420); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bedinger, M.; Beevers, L.; Collet, L.; Visser, A. Are We Doing ‘Systems’ Research? A Review of Methods for Climate Change Adaptation to Hydro-Hazards in A Complex World. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClymont, K.; Morrison, D.; Beevers, L.; Carmen, E. Flood resilience: A systematic review. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2020, 63, 1151–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswami, A. Unpacking the Urban Infrastructure Nexus with Environment, Health, Livability, Well-Being, and Equity. One Earth 2020, 2, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNISDR (United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction). Terminology. 2017. Available online: https://www.unisdr.org/files/7817_UNISDRTerminologyEnglish) (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Beevers, L.; Walker, G.; Strathie, A. A systems approach to flood vulnerability. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2016, 33, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Innes, E.J.; Šakić Trogrlić, R.; Beevers, L. Chapter 1.4—Social vulnerability to drought in rural Malawi. In Understanding Disaster Risk; Pinto Santos, P., Chmutina, K., Von Meding, J., Raju, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 81–107. ISBN 9780128190470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, G.; Mijatović, D.; Rojas, W.; Flores, J.; Pinto, M.; Mamani, G.; Condori, E.; Hilaquita, D.; Gruberg, H.; Padulosi, S. Climate change and crop diversity: Farmers’ perceptions and adaptation on the Bolivian Altiplano. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 703–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, S.; Kelly, S.; Pant, R.; Hall, J.W. Evaluating the Benefits of Adaptation of Critical Infrastructures to Hydrometeorological Risks. Risk Anal. 2018, 38, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Llanes, J.M.; Ranjan-Dash, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Guha-Sapir, D. Looking upstream: Enhancers of child nutritional status in post-flood rural settings. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utete, B.; Phiri, C.; Mlambo, S.S.; Muboko, N.; Fregene, B.T. Vulnerability of fisherfolks and their perceptions towards climate change and its impacts on their livelihoods in a peri-urban lake system in Zimbabwe. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2019, 21, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crick, F.; Jenkins, K.; Surminski, S. Strengthening insurance partnerships in the face of climate change–Insights from an agent-based model of flood insurance in the UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, S.J.; Graham, S. (En)visioning place-based adaptation to sea-level rise. Geogr. Environ. 2016, 3, e00028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebbi, W.; Boulet, G.; Le Dantec, V.; Chabaane, Z.L.; Fanise, P.; Mougenot, B.; Ayari, H. Analysis of evapotranspiration components of a rainfed olive orchard during three contrasting years in a semi-arid climate. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256–257, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha-Sapir, D.; Hoyois, P.; Below, R. Database EM-DAT Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters. 2019. Available online: https://www.emdat.be/ (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Guerreiro, S.B.; Dawson, R.J.; Kilsby, C.; Lewis, E.; Ford, A. Future heat-waves, droughts and floods in 571 European cities. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 034009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, L.; Harrigan, S.; Prudhomme, C.; Formetta, G.; Beevers, L. Future hot-spots for hydro-hazards in Great Britain: A probabilistic assessment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5387–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser-Quinn, A.; Beevers, L.; Collet, L.; Formetta, G.; Smith, K.; Wanders, N.; Thober, S.; Pan, M.; Kumar, R. Spatio-temporal analysis of compound hydro-hazard extremes across the UK. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 130, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Baldassarre, G.; Viglione, A.; Carr, G.; Kuil, L.; Yan, K.; Brandimarte, L.; Blöschl, G. Debates-Perspectives on socio-hydrology: Capturing feedbacks between physical and social processes. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4770–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempels, B.; Hartmann, T. A co-evolving frontier between land and water: Dilemmas of flexibility versus robustness in flood risk management. Water Int. 2014, 39, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.J.; Bradford, R.A.; Bonaiuto, M.; De Dominicis, S.; Rotko, P.; Aaltonen, J.; Waylen, K.A.; Langan, S.J. Enhancing flood resilience through improved risk communications. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, M.; Kovats, S.; Matthies, F.; Few, R. Health impacts of flooding: A global systematic review. Epidemiology 2004, 15, S125–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, E.; Pornet, C.; Dejardin, O.; Launay, L.; Lillini, R.; Vercelli, M.; Mar-Dell’Olmo, M.; Fernndez Fontelo, A.; Borrell, C.; Ribeiro, A.I.; et al. Development of a cross-cultural deprivation index in five European countries. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2016, 70, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkali, M.; Veneman, J.G.; Tivnan, B.F.; Bagrow, J.P.; Hines, P.D.H. Reducing Cascading Failure Risk by Increasing Infrastructure Network Interdependence. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep44499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.P.; Stanton, N.A.; Salmon, P.M.; Walker, G.H. Using work domain analysis to evaluate the impact of technological change on the performance of complex socio-technical systems. Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci. 2011, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappin, E.; Van Der Lei, T. Adaptation of interconnected infrastructures to climate change: A socio-technical systems perspective. Util. Policy 2014, 31, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amin, S.; Berglund, E.Z.; Larson, K. Complex Adaptive System Framework to Simulate Adaptations of Human-Environmental Systems to Climate Change and Urbanization: The Verde River Basin. In World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2014: Water Without Borders-Proceedings of the 2014 World Environmental and Water Resources Congress; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 2014; pp. 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, L.; Davies, G.; Almeida, O.; Frausin, G.; De Moraés, A.; Rivero, S.; Filizola, N.; Torres, P. Social Vulnerability to Climatic Shocks Is Shaped by Urban Accessibility. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2018, 108, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.X.; Van Der Heijden, J.; Osmond, P. The city politics of an urban age: Urban resilience conceptualisations and policies. Palgrave Commun. 2018, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restemeyer, B.; Woltjer, J.; Van Den Brink, M. A strategy-based framework for assessing the flood resilience of cities–A Hamburg case study. Plan. Theory Pract. 2015, 16, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.V.; James, H. Measuring Household Resilience to Floods: A Case Study in the Vietnamese Mekong River Delta. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegger, D.L.T.; Driessen, P.P.J.; Wiering, M.; Van Rijswick, H.F.M.W.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Matczak, P.; Crabbé, A.; Raadgever, G.T.; Bakker, M.H.N.; Priest, S.J.; et al. Toward more flood resilience: Is a diversification of flood risk management strategies the way forward? Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Breen, P.; Anderies, J.M. Resilience: A Literature Review Bellagio Initiative; IDS: Brighton, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, L.; Dowds, G.; Currie, M. Long-Term Impacts of Flooding Following the Winter 2015/16 Flooding in North East Scotland: Comprehensive. 2020. Available online: https://www.crew.ac.uk/sites/www.crew.ac.uk/files/sites/default/files/publication/CRW2016_02_Summary_Report_1.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Fisher, L. Disaster Responses: More than 70 Ways to Show Resilience. Nature 2015, 518, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClymont, K.; Bedinger, M.; Beevers, L.; Walker, G.; Morrison, D. Chapter 2.2—Analyzing city-scale resilience using a novel systems approach. In Understanding Disaster Risk; Pinto Santos, P., Chmutina, K., Von Meding, J., Raju, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 179–201. ISBN 9780128190470. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Van Der Leeuw, S.; O’Brien, K.; Berkhout, F.; Biermann, F.; Brondizio, E.S.; Cudennec, C.; Dearing, J.; Duraiappah, A.; Glaser, M.; et al. Plausible and desirable futures in the Anthropocene: A new research agenda. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2016, 39, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brondizio, E.S.; O’Brien, K.; Bai, X.; Biermann, F.; Steffen, W.; Berkhout, F.; Cudennec, C.; Lemos, M.C.; Wolfe, A.; Palma-Oliveira, J.; et al. Re-conceptualizing the Anthropocene: A call for collaboration. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2016, 39, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Dearing, J.A.; Dyke, J.G.; van der Leeuw, S.; Seitzinger, S.; Steffen, W.; Syvitski, J. Methods and approaches to modelling the Anthropocene. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2016, 39, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson, G.; Szerszynski, B.; Sörlin, S.; Marks, J.; Avril, B.; Crumley, C.; Hackmann, H.; Holm, P.; Ingram, J.; Kirman, A.; et al. Reconceptualizing the ‘Anthropos’ in the Anthropocene: Integrating the social sciences and humanities in global environmental change research. Environ. Sci. Policy 2013, 28, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, A.C. Case Study of Institutional and Social Responses to Flooding; Reforming for Resilience? J. Flood Risk Manag. 2011, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavhura, E. Applying a systems-thinking approach to community resilience analysis using rural livelihoods: The case of Muzarabani district, Zimbabwe. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 25, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyeye, K.; Emmitt, S. Multi-Scale, Integrated Strategies for Urban Flood Resilience. Int. J. Disaster Resil. Built Environ. 2017, 6, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, R.A.; Shrestha, S.; Pandey, V.P. Groundwater vulnerability to climate change: A review of the assessment methodology. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 853–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toimil, A.; Losada, I.J.; Díaz-Simal, P.; Izaguirre, C.; Camus, P. Multi-sectoral, high-resolution assessment of climate change consequences of coastal flooding. Clim. Chang. 2017, 145, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahi, N.Z.; Dongo, K.; Koudou, A.; Badolo, M. Innovative approach to build a “no regret” framework for reinforcing agricultural water resilience under climate risks and change in Burkina Faso. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strategies Manag. 2017, 9, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedinger, M. Systematic literature review-Climate Change Adaptation to Hydrohazards [Data set]. Zenodo 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balica, S.; Popescu, I.; Beevers, L.; Wright, N. Parametric and physically based modelling techniques for flood risk and vulnerability assessment: A comparison. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 41, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsborough, A.; Borgomeo, E.; Hall, J.W. Adaptation pathways in practice: Mapping options and trade-offs for London’s water resources. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 27, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.-H. From flood control to flood adaptation: A case study on the Lower Green River Valley and the City of Kent in King County, Washington. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.-H.; Le, T.A.; Van Nguyen, K. Urban design principles for flood resilience: Learning from the ecological wisdom of living with floods in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 155, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshire, L. ‘Know your neighbours’: Disaster resilience and the normative practices of neighbouring in an urban context. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2015, 47, 1081–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Montano, B.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Rangecroft, S.; Van Loon, A.F. Hydrological change: Towards a consistent approach to assess changes on both floods and droughts. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 111, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, T.; Howden, N.; Worrall, F. The changing water cycle: Hydroclimatic extremes in the British Isles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2016, 3, 854–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.; McGuinness, M. Flood resilience in the context of shifting patterns of risk, complexity and governance: An exploratory case study. E3S Web Conf. 2016, 7, 21004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshtian, A.; Donaghy, K.P.; Rouhani, O.M. Flood-Resilient Deployment of Fueling Stations: Extension of Facility Location Problem. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2016, 2599, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zischg, J.; Rogers, B.; Gunn, A.; Rauch, W.; Sitzenfrei, R. Future trajectories of urban drainage systems: A simple exploratory modeling approach for assessing socio-technical transitions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, B.C.; Bertram, N.; Gersonius, B.; Gunn, A.; Löwe, R.; Murphy, C.; Pasman, R.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Urich, C.; Wong, T.H.F.; et al. An interdisciplinary and catchment approach to enhancing urban flood resilience: A Melbourne case. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadlou, M.; Karimi, M.; Alizadeh, S.; Shirzadi, A.; Parvinnejhad, D.; Shahabi, H.; Panahi, M. Flood susceptibility assessment using integration of adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and biogeography-based optimization (BBO) and BAT algorithms (BA). Geocarto Int. 2019, 34, 1252–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedinger, M.; Beevers, L.; Walker, G.H.; Visser-Quinn, A.; McClymont, K. Urban Systems: Mapping Interdependencies and Outcomes to Support Systems Thinking. Earth’s Future 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzee, I.; Reyers, B. Piloting a social-ecological index for measuring flood resilience: A composite index approach. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.; Qasim, M.; Shrestha, R.P.; Khan, A.N.; Tun, K.; Ashraf, M. Community resilience to flood hazards in Khyber Pukhthunkhwa province of Pakistan. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2016, 18, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momblanch, A.; Beevers, L.; Srinivasalu, P.; Kulkarni, A.; Holman, I.P. Enhancing production and flow of freshwater ecosystem services in a managed Himalayan river system under uncertain future climate. Clim. Chang. 2020, 162, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregnolato, M.; Ford, A.; Robson, C.; Glenis, V.; Barr, S.; Dawson, R. Assessing urban strategies for reducing the impacts of extreme weather on infrastructure networks. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, K.L.; Stanton, N.A. Distributed cognition in Search and Rescue: Loosely coupled tasks and tightly coupled roles. Ergonomics 2016, 59, 1353–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, A. Capability and Well-being. In The Quality of Life; Nussbaum, M., Sen, A., Eds.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; pp. 30–53. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.; Aitken, G.; Beevers, L.; Wright, G. ‘An Application of ‘Big Data’ in Flood Risk Management’, River Flow. Delft 7–10 July 2020; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 100 Resilient Cities—The Rockefeller Foundation. Available online: https://www.rockefellerfoundation.org/100-resilient-cities/ (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- WHO|Healthy Cities. Available online: https://www.who.int/healthpromotion/healthy-cities/en/ (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- THE 17 GOALS|Sustainable Development (un.org). Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Galderisi, A.; Limongi, G.; Salata, K.-D. Strengths and weaknesses of the 100 Resilient Cities Initiative in Southern Europe: Rome and Athens’ experiences. City Territ. Arch. 2020, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. A General Framework for Analyzing Sustainability of Social-Ecological Systems. Science 2009, 325, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazmierczak, A.; Cavan, G.; Connelly, A.; Lindley, S. Mapping Flood Disadvantage in Scotland 2015: Main Report; Scottish Government: Edinburgh, UK, 2015.
- Blair, P.; Buytaert, W. Socio-hydrological modelling: A review asking “why, what and how?”. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 443–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Concept | Current State of the Art | Future Next Steps | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Natural-Social-Technical Dimensions | This was the most frequently mentioned challenge to address; In particular, papers referred to infrastructure, ecological and economic aspects as critical challenges | More dimensions should be considered systematically within methods—this should become routine in assessments. Specifically, future assessments should consider community impacts and post-hazard infrastructure aspects. |
| 2 | Interactions | Only 1/5 [19%] studies claim to address interactions of any kind; Where interactions are considered, these tend to be in studies which consider short-term (hours or days or weeks) shocks | Future work must link short-term shocks and long-term stressors in assessments. This requires new methods which can explicitly link interactions across time scales. |
| 3 | Spatial Scale | Research has tended to have a strong emphasis on regional and community scale analysis; Most research which considered spatial scales explicitly had a physical emphasis, i.e., social dynamics and considerations less covered | Next steps must consider a finer level of scale (e.g., household level) to determine what scale of critical complexity dynamics are necessary to incorporate. Additionally, research is needed to incorporate social, behavioural, cognitive, and/or cultural aspects across spatial scales within assessments. |
| 4 | Time Scale | Most research reviewed focused (90% occurrence) on medium-term impacts rather than short-term or long-term impacts | In the future, more focus is needed on short-term (hours or days or weeks) and linking this to medium-term (months or years) as well as longer-term considerations (impacts and interactions). |
| 5 | Multiple Forms of Evidence | Most approaches used within recent research still relied on classic quantitative methods (e.g., physical measurement and statistical analysis) and simulations | Future work will require the research community to develop methods which integrate participatory methods (bottom-up) and decision-making analyses (top-down) better and more efficiently. |
| 6 | Uncertainty | Only 22% of research accounts for uncertainty; | Future research must include greater consideration of multiple possible futures. Methods must also consider and quantify how uncertainty cascades through different time scales, and across different spatial scales. |
| OVERALL |
| Future work:
| |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beevers, L.; Bedinger, M.; McClymont, K.; Visser-Quinn, A. Resilience in Complex Catchment Systems. Water 2021, 13, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040541
Beevers L, Bedinger M, McClymont K, Visser-Quinn A. Resilience in Complex Catchment Systems. Water. 2021; 13(4):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040541
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeevers, Lindsay, Melissa Bedinger, Kerri McClymont, and Annie Visser-Quinn. 2021. "Resilience in Complex Catchment Systems" Water 13, no. 4: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040541
APA StyleBeevers, L., Bedinger, M., McClymont, K., & Visser-Quinn, A. (2021). Resilience in Complex Catchment Systems. Water, 13(4), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040541








