Effect of the Particle Size of Clinoptilolite Zeolite on Water Content and Soil Water Storage in a Loamy Sand Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2. Clinoptilolite Zeolite
2.3. Laboratory Column Experiment
2.4. Measurement of the Soil Hydraulic Properties
2.5. Modeling of Water Movement
2.6. Statistical Evaluations
3. Results and Discussion
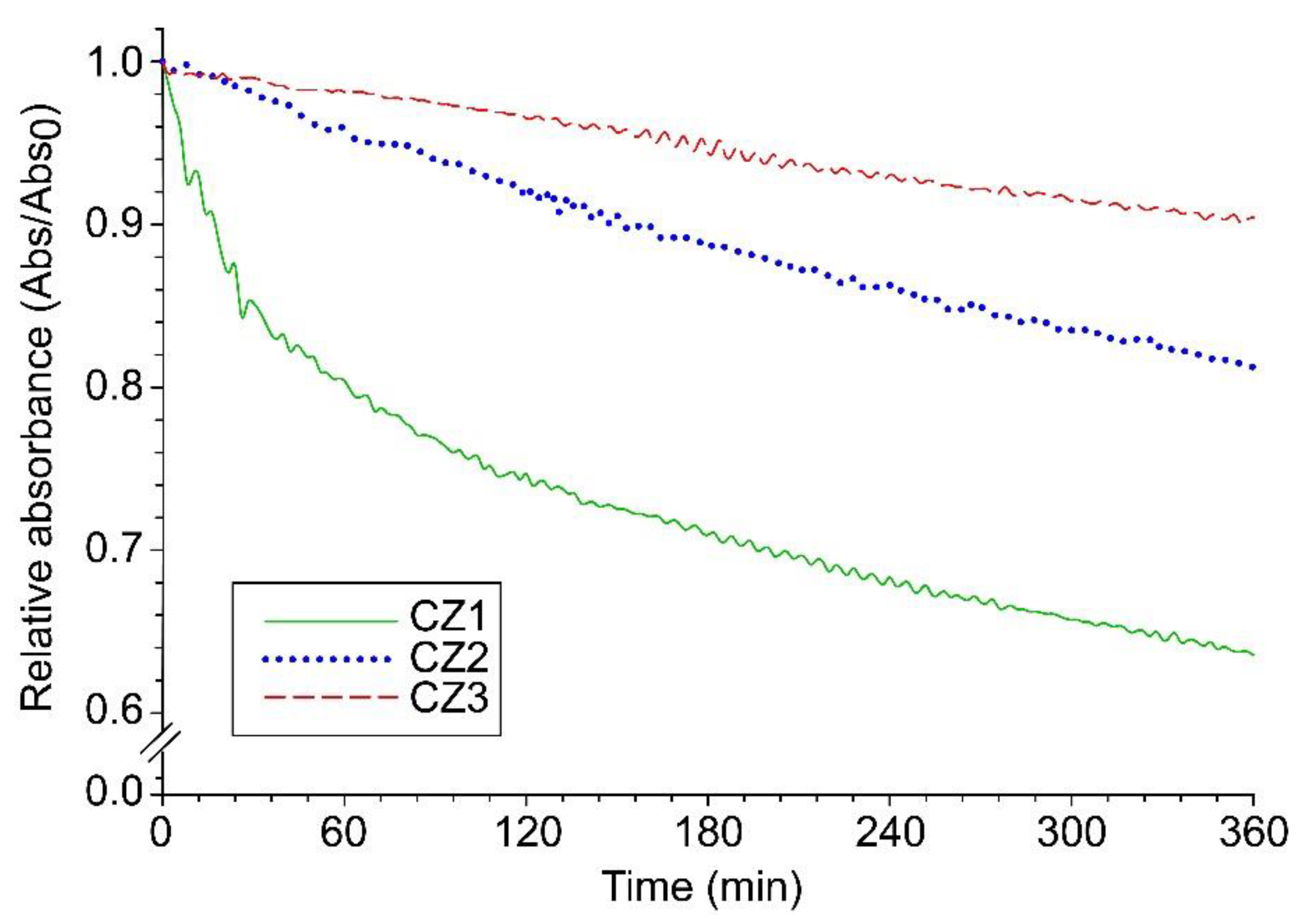
3.1. Characterization of Clinoptilolite Zeolite
3.2. Effect of CZ on Water Retention and Availability
3.3. Effect of CZ on Infiltration Rate and Hydraulic Conductivity
3.4. Simulation of Volumetric Water Content
3.5. Soil Water Storage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akhtar, M.; Ahmed, M.; Hayat, R.; Stöckle, C.O.; Hassan, F. Is Rainwater Harvesting an Option for Designing Sustainable Cropping Patterns for Rainfed Agriculture? Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 27, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Busaidi, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Inoue, M.; Eneji, A.E.; Mori, Y.; Irshad, M. Effects of Zeolite on Soil Nutrients and Growth of Barley Following Irrigation with Saline Water. J. Plant Nutr. 2008, 31, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepaskhah, A.R.; Barzegar, M. Yield, water and nitrogen-use response of rice to zeolite and nitrogen fertilization in a semi-arid environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiubin, H.; Zhanbin, H. Zeolite application for enhancing water infiltration and retention in loess soil. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2001, 34, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghani, M.; Nakhli, S.A.A.; Aghajani, M.; Rostami, M.H.; Borghei, S.M. Adsorption and oxidation study on arsenite removal from aqueous solutions by polyaniline/polyvinyl alcohol composite. J. Water Process. Eng. 2016, 14, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, J.; Frankl, A.; Zenebe, A.; Poesen, J.; Deckers, J. Environmental Conservation for Food Production and Sustainable Livelihood in Tropical Africa. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 26, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamedov, A.I.; Bar-Yosef, B.; Levkovich, I.; Rosenberg, R.; Silber, A.; Fine, P.; Levy, G.J. Amending Soil with Sludge, Manure, Humic Acid, Orthophosphate and Phytic Acid: Effects on Infiltration, Runoff and Sediment Loss. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierfelder, C.; Wall, P.C. Effects of conservation agriculture techniques on infiltration and soil water content in Zambia and Zimbabwe. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltz, F.C.; Quisenbrry, V.L.; McCart, L.B. Physical and hydraulic properties of root zone mixes amended with inorganics for golf putting green. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, E.L. Quantitative physical assessment of organic materials used in sports turf root zone mixes. Agron. J. 1992, 84, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigelow, C.A.; Bowman, D.C.; Cassel, K. Germination and establishment with root-zone amendments. Golf Course Manag. 1999, 67, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.T.; Petrovic, A.M. Physical Properties of Sand as Affected by Clinoptilolite Zeolite Particle Size and Quantity. J. Turfgrass Manag. 1994, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Faccini, B.; Coltorti, M. Variation of the hydraulic properties and solute transport mechanisms in a silty-clay soil amended with natural zeolites. Catena 2014, 123, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, C.-H.; Anderson, S.H.; Ervin, E.H. Amendments and Construction Systems for Improving the Performance of Sand-Based Putting Greens. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebnezhad, R.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Effects of bentonite on water infiltration in a loamy sand soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2013, 59, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh-Sarabi, S.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Effect of zeolite and saline water application on saturated hydraulic conductivity and infiltration in different soil textures. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2013, 59, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, G.; Camerlingo, C. Kinetic investigation of water physisorption on natural clinoptilolite at room temperature. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 302, 110238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mier, M.V.; Callejas, R.L.; Gehr, R.; Cisneros, B.E.J.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Heavy metal removal with Mexican clinoptilolite: Multi-component ionic exchange. Water Res. 2001, 35, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Golembiewski, R.; Trykowski, G.; Buszewski, B. Heterogeneity and hierarchy of clinoptilolite porosity. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githinji, L.J.M.; Dane, J.H.; Walker, R.H. Physical and hydraulic properties of inorganic amendments and modeling their effects on water movement in sand-based root zones. Irrig. Sci. 2010, 29, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azooz, R.H.; Arshad, M.A. Soil infiltration and hydraulic conductivity under long-term no-tillage and conventional tillage systems. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 76, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmi, Z.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Effect of zeolite on saturated hydraulic conductivity and crack behavior of silty clay paddled soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2011, 58, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahabadi, A.A.; Hajabbasi, M.; Khademi, H.; Kazemian, H. Soil cadmium stabilization using an Iranian natural zeolite. Geoderma 2007, 137, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Damodar, D.; Kumar, A.; Subba, A. Zeolites and their potential uses in agriculture. Adv. Agron. 2011, 113, 215–236. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.L.; Calvert, D.V.; Alva, A.K.; Li, Y.; Banks, D.J. Clinoptilolite zeolite and cellulose amendments to reduce ammonia volatilization in a calcareous sandy soil. Plant Soil 2002, 247, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigelow, C.A.; Bowman, D.C.; Cassel, D.; Rufty, T.W. Creeping Bentgrass Response to Inorganic Soil Amendments and Mechanically Induced Subsurface Drainage and Aeration. Crop. Sci. 2001, 41, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nus, J.; Brauen, S. Clinoptilolitic zeolite as an amendment for establishment of creeping bentgrass on sandymedia. Hortscience 1991, 26, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Physiological response of Bermuda grass grown in soil amendments during drought stress. Hortscience 2000, 35, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, A.C.D.C.; Oliviera, P.P.A.; Monte, M.B.D.M.; Souza-Barros, F. Brazilian sedimentary zeolite use in agriculture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 167, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudejani, H.T.; Heidarpour, M.; Shayannejad, M.; Shariatmadari, H.; Kazemian, H.; Afyuni, M. Composts Containing Natural and Mg-Modified Zeolite: The Effect on Nitrate Leaching, Drainage Water, and Yield. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2019, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Leoppert, R.H.; Soltanpour, P.N.; Tabatabai, M.A.; Johnston, G.T.; Sumner, M.E. Methods of Soil Analysis; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015: International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vladimir, A.H.; Chen-Yuan, D.; Feng-Jie, L.; Nan-Shan, C.; Shean-Jen, C. Natural zeolite for adsorbing and release of functional materials. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 091411. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T.; Leij, F.J.; Yates, S.R. The RETC Code for Quantifying the Hydraulic Functions of Unsaturated Soils; EPA/600/2-91/065–U. S. Salinity Laboratory; USDA ARS: Riverside, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bootlink, H.W.G.; Bouma, J. Saturated and field-saturated water flow parameters: 3.4.2.4 steady flow soil column method. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 812–814. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, J.R. The theory of infiltration: 1. The infiltration equation and its solution. Soil Sci. 1957, 83, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.; Sejna, M.; Saito, H.; Sakai, M.; van Genuchten, M.T. The HYDRUS-1D Software Package for Simulating the One-Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably-Saturated Media Version 4.17; University of California Riverside: Riverside, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–342. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. Physics 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loague, K.; Green, R.E. Statistical and graphical methods for evaluating solute transport models: Overview and application. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1991, 7, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River forecasting through conceptual models, part I, a discussion of principle. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacy, M.M.J.; Higgins, J.B. Collection of Simulated XRD Powder Patterns for Zeolites, 4th ed.; Revised; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Charkhi, A.; Kazemian, H.; Kazemeini, M. Optimized experimental design for natural clinoptilolite zeolite ball milling to produce nano powders. Powder Technol. 2010, 203, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeliz, Y.A. Characterization of two natural zeolites for geotechnical and geoenvironmental applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Korkuna, O.; Leboda, R.; Skubiszewska-Zie, J.; Vrublevs’Ka, T.; Gun’Ko, V.; Ryczkowski, J. Structural and physicochemical properties of natural zeolites: Clinoptilolite and mordenite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 87, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Bride, M.B. Surface chemistry of soil minerals. In Minerals in Soil Environments; Dixon, J.B., Weed, S.B., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madson, WI, USA, 1989; pp. 35–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ersoy, B.; Celik, M.S. Electrokinetic properties of clinoptilolite with mono- and multivalent electrolytes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2002, 55, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, A.; Sener, A.; Ucbeyiay, H. Investigation of coagulation and electrokinetic behaviors of clinoptilolite suspension with multivalent cations. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 53, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnola, N.B.; Dutta, P.K. Nanometer-Sized Zeolite X Crystals: Use as Photochemical Hosts. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Ariafar, S. The effect of water deficit and zeolite application on Growth Traits and Oil Yield of Medicinal Pep-permint (Mentha piperita L.). Int. J. Med. Arom. Plants 2013, 3, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Amin, M.S.M.; Anuar, A.R.; Saberioon, M.M. Water stress and natural zeolite impacts on phisiomorphological characteristics of moldavian balm (Dracocephalum moldavica l.). Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 4, 5184–5190. [Google Scholar]
- Voroney, R.P.; Van Straaten, P. Use of natural zeolites in sand root zones for putting greens. Greenmaster Mag. 1988, 8, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Schwen, A.; Bodner, G.; Scholl, P.; Buchan, G.D.; Loiskandl, W. Temporal dynamics of soil hydraulic properties and the water-conducting porosity under different tillage. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 113, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touma, J.; Voltz, M.; Albergel, J. Determining soil saturated hydraulic conductivity and sorptivity from single ring infiltration tests. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudejani, H.T.; Shayannejada, M.; Kazemianc, H.; Heidarpoura, M.; Rutherford, M. Effect of co-composting municipal solid waste with Mg-modified zeolite on soil water balance components using HYDRUS-1D. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 176, 105637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, V.; Coquet, Y.; Pot, V.; Houot, S.; Benoit, P. Modeling water and isoproturon dynamics in a heterogeneous soil profile under different urban waste compost applications. Geoderma 2016, 268, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Soil/ Clinoptilolite | Size | Surface Area 1 | Micropore Area 2 | Pore Volume 3 | Pore Size 4 | Zeta Potential 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (µm) | (m2 g−1) | (m2 g−1) | (cm³ g−1) | (Å) | (mV) | |
| CZ0 (Control) | <2000 | 3.559 ± 0.004 a | 0.114 ± 0.001 a | 0.0126 a | 141.6 a | −28.3 ± 0.6 a |
| CZ1 | 20 ± 1.5 | 34.722 ± 0.291 b | 7.074 ± 0.095 b | 0.1121 b | 129.1 b | −29.3 ± 0.6 a |
| CZ2 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 35.001 ± 0.185 b | 8.301 ± 0.131 b | 0.1128 b | 128.9 b | −31.1 ± 0.4 b |
| CZ3 | 0.2 ± 0.05 | 37.296 ± 0.443 c | 12.514 ± 0.184 c | 0.1153 b | 123.7 c | −33.9 ± 0.5 c |
| Soil Depth (cm) | Clinoptilolite | Statistical Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | MRE | D-Index | NSCE | ||
| 10 | CZ0 | 0.765 | 0.023 | −0.280 | 0.932 | 0.726 |
| CZ1 | 0.731 | 0.027 | −0.240 | 0.920 | 0.721 | |
| CZ2 | 0.788 | 0.024 | 0.533 | 0.933 | 0.776 | |
| CZ3 | 0.835 | 0.026 | 1.451 | 0.937 | 0.752 | |
| 20 | CZ0 | 0.752 | 0.025 | −0.521 | 0.901 | 0.715 |
| CZ1 | 0.764 | 0.026 | 0.821 | 0.923 | 0.695 | |
| CZ2 | 0.801 | 0.024 | 1.241 | 0.935 | 0.712 | |
| CZ3 | 0.795 | 0.025 | 1.534 | 0.925 | 0.724 | |
| 30 | CZ0 | 0.821 | 0.023 | 1.025 | 0.904 | 0.756 |
| CZ1 | 0.785 | 0.025 | 0.954 | 0.926 | 0.801 | |
| CZ2 | 0.805 | 0.026 | 0.846 | 0.920 | 0.795 | |
| CZ3 | 0.815 | 0.023 | 1.235 | 0.915 | 0.812 | |
| 40 | CZ0 | 0.855 | 0.028 | 2.045 | 0.912 | 0.784 |
| CZ1 | 0.905 | 0.032 | 1.864 | 0.925 | 0.804 | |
| CZ2 | 0.895 | 0.029 | 2.315 | 0.948 | 0.820 | |
| CZ3 | 0.915 | 0.028 | 2.125 | 0.938 | 0.815 | |
| 50 | CZ0 | 0.884 | 0.032 | 2.215 | 0.944 | 0.781 |
| CZ1 | 0.904 | 0.028 | 1.876 | 0.956 | 0.825 | |
| CZ2 | 0.909 | 0.033 | 2.386 | 0.940 | 0.786 | |
| CZ3 | 0.925 | 0.031 | 2.381 | 0.950 | 0.814 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, H.M.; Alghamdi, A.G. Effect of the Particle Size of Clinoptilolite Zeolite on Water Content and Soil Water Storage in a Loamy Sand Soil. Water 2021, 13, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050607
Ibrahim HM, Alghamdi AG. Effect of the Particle Size of Clinoptilolite Zeolite on Water Content and Soil Water Storage in a Loamy Sand Soil. Water. 2021; 13(5):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050607
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Hesham M., and Abdulaziz G. Alghamdi. 2021. "Effect of the Particle Size of Clinoptilolite Zeolite on Water Content and Soil Water Storage in a Loamy Sand Soil" Water 13, no. 5: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050607
APA StyleIbrahim, H. M., & Alghamdi, A. G. (2021). Effect of the Particle Size of Clinoptilolite Zeolite on Water Content and Soil Water Storage in a Loamy Sand Soil. Water, 13(5), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050607






