Regional Hydrogeochemical Evolution of Groundwater in the Ring of Cenotes, Yucatán (Mexico): An Inverse Modelling Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Zone
2.2. Field Measurements and Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Hydrogeochemical Model of the RC
2.3.1. Hydrogeochemical Evolution of Groundwater in the RC
2.3.2. Determination of Saturation Indexes (SI)
2.3.3. Groundwater Mineral Precipitation/Dissolution Rate Modeling
2.4. Rainfall Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hydrogeochemical Evolution of the Groundwater of the RC
3.2. Groundwater-Rock Interaction in RC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartmann, A.; Goldscheider, N.; Wagener, T.; Lange, J.; Weiler, M. Karst water resources in a changing world: Review of hydrological modeling approaches. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 218–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, Z. Karst Aquifers—Characterization and Engineering; Stevanović, Z., Ed.; Professional Practice in Earth Sciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-12849-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, D.; Williams, P. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781118684986. [Google Scholar]
- Post, V.E.A.; Werner, A.D. Coastal aquifers: Scientific advances in the face of global environmental challenges. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, E.; Paytan, A.; Pedersen, B.; Velazquez-Oliman, G. Groundwater geochemistry of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico: Constraints on stratigraphy and hydrogeology. J. Hydrol. 2009, 367, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAGUA. Programa Hídrico Regional Visión 2030 (Regional Hydric Program: 2030 Vision); CDMX: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer-Gottwein, P.; Gondwe, B.R.N.; Charvet, G.; Marín, L.E.; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M.; Merediz-Alonso, G. Review: The Yucatan Peninsula karst aquifer, Mexico. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobierno del Estado de Yucatan. Decreto número 117-Reserva estatal geohidrológica del Anillo de Cenotes; Gobierno del Estado de Yucatan: Mérida, Yucatán, Mexico, 2013. Available online: https://sds.yucatan.gob.mx/areas-naturales/documentos/decreto-reserva-estatal-geohidrologica-anillo-de-cenotes.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2021).
- Pérez-Ceballos, R.; Pacheco-Ávila, J.; Euán-Ávila, J.I.; Hernández-Arana, H. Regionalization based on water chemistry and physicochemical traits in the ring of Cenotes, Yucatan, Mexico. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2012, 74, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, A.R.; Penfield, G.T.; Kring, D.A.; Pilkington, M.Z.; Camargo, A.; Stein, B.J.; Boynton, W.V. Chicxulub crater: A possible Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary impact crater on the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Geology 1991, 19, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, K.O.; Ocampo, A.C.; Duller, C.E. Surficial geology of the Chicxulub impact crater, Yucatan, Mexico. Earth Moon Planets 1993, 63, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia-Fucugauchi, J.; Camargo-Zanoguera, A.; Pérez-Cruz, L.; Pérez-Cruz, G. The chicxulub multi-ring impact crater, yucatan carbonate platform, Gulf of Mexico. Geofis. Int. 2011, 50, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaona Vizcayno, S.; Gordillo de Anda, T.; Villasuso Pino, M. Cenotes, karst característico en mecanismos de formación. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geológicas 1980, 4, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Young, M.B.; Gonneea, M.E.; Fong, D.A.; Moore, W.S.; Herrera-Silveira, J.; Paytan, A. Characterizing sources of groundwater to a tropical coastal lagoon in a karstic area using radium isotopes and water chemistry. Mar. Chem. 2008, 109, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoessell, R.K.; Coke, J.G. An Explanation for the Lack of a Dilute Freshwater Lens in Unconfined Tropical Coastal Aquifers: Yucatan Example. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans. 2006, 56, 785–792. [Google Scholar]
- Graniel-Castro, E.; Pacheco-Medina, A.; Coronado-Peraza, V. Origen de los sulfatos en el agua subterránea del sur de la sierrita de Ticul, Yucatán. Ingeniería 2009, 13, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, E.C.; Velazquez-Oliman, G.; Leal-Bautista, R.M.; Dunning, N. The Icaiche Formation: Major contributor to the stratigraphy, hydrogeochemistry and geomorphology of the northern Yucatán peninsula, Mexico. Boletín Soc. Geológica Mex. 2019, 71, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez, L. Aplicación de principios geoquímicos en la Hidrología Kárstica de la Península de Yucatán. Ing. Hidráulica México 1986, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Arcega-Cabrera, F.; Velázquez-Tavera, N.; Fargher, L.; Derrien, M.; Noreña-Barroso, E. Fecal sterols, seasonal variability, and probable sources along the ring of cenotes, Yucatan, Mexico. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2014, 168, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco Castro, R.; Pacheco Ávila, J.; Ye, M.; Cabrera Sansores, A. Groundwater Quality: Analysis of Its Temporal and Spatial Variability in a Karst Aquifer. Groundwater 2018, 56, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, M.; Cabrera, F.A.; Tavera, N.L.V.; Kantún Manzano, C.A.; Vizcaino, S.C. Sources and distribution of organic matter along the Ring of Cenotes, Yucatan, Mexico: Sterol markers and statistical approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, D.T.; Pearson, A.L.; Voice, T.C.; Polanco-Rodríguez, A.G.; Sanchez-Rodríguez, E.C.; Xagoraraki, I.; Concha-Valdez, F.G.; Puc-Franco, M.; Lopez-Cetz, R.; Rzotkiewicz, A.T. Influence of rainy season and land use on drinking water quality in a karst landscape, State of Yucatán, Mexico. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 98, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, E.; Velazquez-Oliman, G.; Marin, L. The Hydrogeochemistry of the Karst Aquifer System of the Northern Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Int. Geol. Rev. 2002, 44, 191–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villasuso-Pino, M.; Sanchez y Pinto, I.; Canul-Macario, C.; Baldazo Escobedo, G.; Casares Salazar, R.; Souza Cetina, J.; Poot Euan, P.; Pech, C. Hydrogeology And Conceptual Model Of The Karstic Coastal Aquifer In Northern Yucatan State, Mexico. Trop. Subtrop. Agroecosyst. 2011, 13, 243–260. [Google Scholar]
- De la Barreda, B.; Metcalfe, S.E.; Boyd, D.S. Precipitation regionalization, anomalies and drought occurrence in the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 4541–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterlin, J.; Bonet, F. Las Formaciones Cenozoicas de la parte Mexicana de la Península de Yucatán (The Cenozoic Formations of the Mexican part of the Yucatan Peninsula). Ing. Hidráulica México 1963, 17, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, E.; Velazquez-Oliman, G.; Leal-Bautista, R.M.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; Wagner, N. Aspects of the Hydrogeology of southern Campeche and Quintana Roo, Mexico. Boletín Soc. Geológica Mex. 2021, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SGM. Carta Geológico-Minera Calkiní: F15-9-12; Pachuca: Hidalgo, México, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- SGM. Carta Geológico-Minera Tizimín: F16-7; Pachuca: Hidalgo, México, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- SGM. Carta Geológico-Minera Mérida: F16-10; Pachuca: Hidalgo, México, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- APHA-AWWA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. In American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Plant Performance, 21st ed.; APHA-AWWA-WEF, Ed.; APHA-AWWA-WEF: Washignton, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. (Eds.) Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 9780429152320. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, D.E.; Bocanegra, E.M.; Manzano, M. La modelacion hidrogeoquimica como herramienta en estudios hidrogeologicos. Bol. Geol. Min. 2000, 111, 83–97. [Google Scholar]
- Custodio, E.; Llamas, M. Hidrología Subterránea; OMEGA, Ed.; OMEGA: Barcelona, España, 1976; ISBN 8428204462. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. PHREEQC (Version 3)-A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations. Model. Tech. B 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoessell, R.K. Yucatan Water Chemistry Collected by Ronald Stoessell and Co-Workers. Available online: http://www.ronstoessell.org/PublicationsandData/Yucatan_Data.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Canul-Macario, C.; González-Herrera, R.; Sánchez-Pinto, I.; Graniel-Castro, E. Contribution to the evaluation of solute transport properties in a karstic aquifer (Yucatan, Mexico). Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pytkowicz, R.; Kester, D. The Physical Chemistry of Seawater. In Oceanography Marine Biology: An Annual Review; Barnes, H., Ed.; George Allen y Unwin Ltd.: London, UK, 1971; pp. 11–60. [Google Scholar]
- Back, W.; Hanshaw, B.B. Comparison of aqueous geochemistry of the carbonate peninsulas of Florida and Yucatan. Geol. Soc. Am. 1963, 121, 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. Geological Survey Research 1970, Chapter A; USGS: Washington, DC, USA, 1970.
- Bischoff, J.L.; Juliá, R.; Shanks, W.C., III; Rosenbauer, R.J. Karstification without carbonic acid: Bedrock dissolution by gypsum-driven dedolomitization. Geology 1994, 22, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bąbel, M.; Schreiber, B.C. 9.17-Geochemistry of Evaporites and Evolution of Seawater. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 483–560. ISBN 978-0-08-098300-4. [Google Scholar]
- Canul-Macario, C.; Salles, P.; Hernández-Espriu, J.A.; Pacheco-Castro, R. Empirical relationships of groundwater head–salinity response to variations of sea level and vertical recharge in coastal confined karst aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 1679–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Levinson, A.; Mariño-Tapia, I.; Enriquez, C.; Waterhouse, A.F. Tidal variability of salinity and velocity fields related to intense point-source submarine groundwater discharges into the Coastal Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batllori Sampedro, E.; González Piedra, J.I.; Díaz Sosa, J.; Febles Patrón, J.L. Caracterización hidrológica de la región costera noroccidental del estado de yucatán, MÉXICO. Investig. Geogr. 2006, 59, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. IPCC Workshop on Sea Level Rise and Ice Sheet Instabilities; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; ISBN 978-92-9169-130-2. [Google Scholar]
- Church, J.A.; Clark, P.U.; Cazenave, A.; Gregory, J.; Jevrejava, S.; Lebermann, A.; Merrifield, M.; Milne, G.; Nerem, R.S.; Nunn, P.; et al. Sea Level Change. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Jouzel, J., van de Wal, R., Woodworth, P., Xiao, C., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 227. [Google Scholar]
- WHO-World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 9241546964. [Google Scholar]
- DOF, Diario Oficial de la Federación NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-127-SSA1-1994, Salud ambiental, agua para uso y consumo humano-Límites permisibles de calidad y tratamientos a que debe someterse el agua para su potabilización. Última reforma publicada DOF 03-02-1995. 2000. Available online: http://www.agrolab.com.mx/sitev002/sitev001/assets/nom-127-ssa1-1994.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2021).

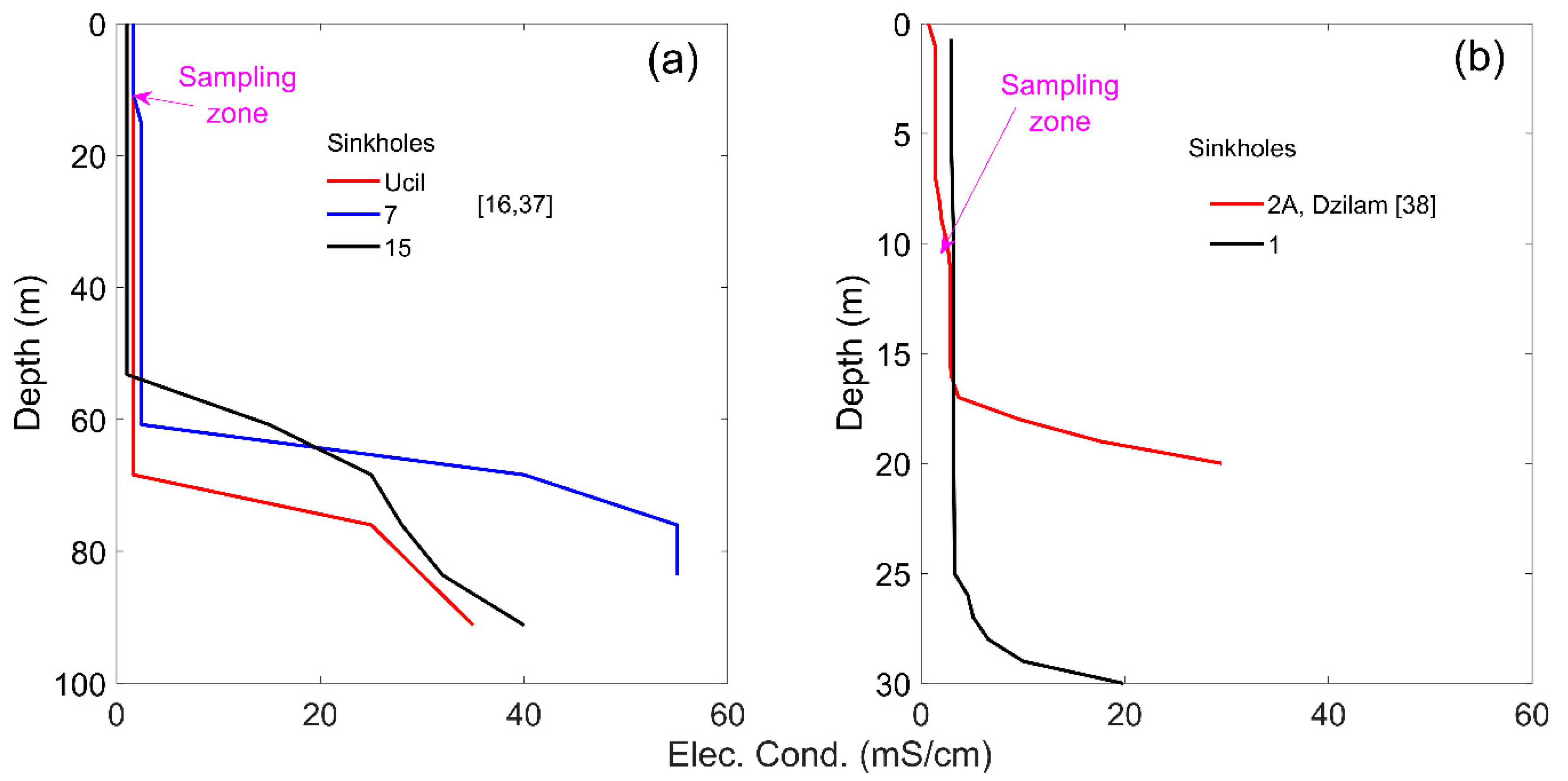


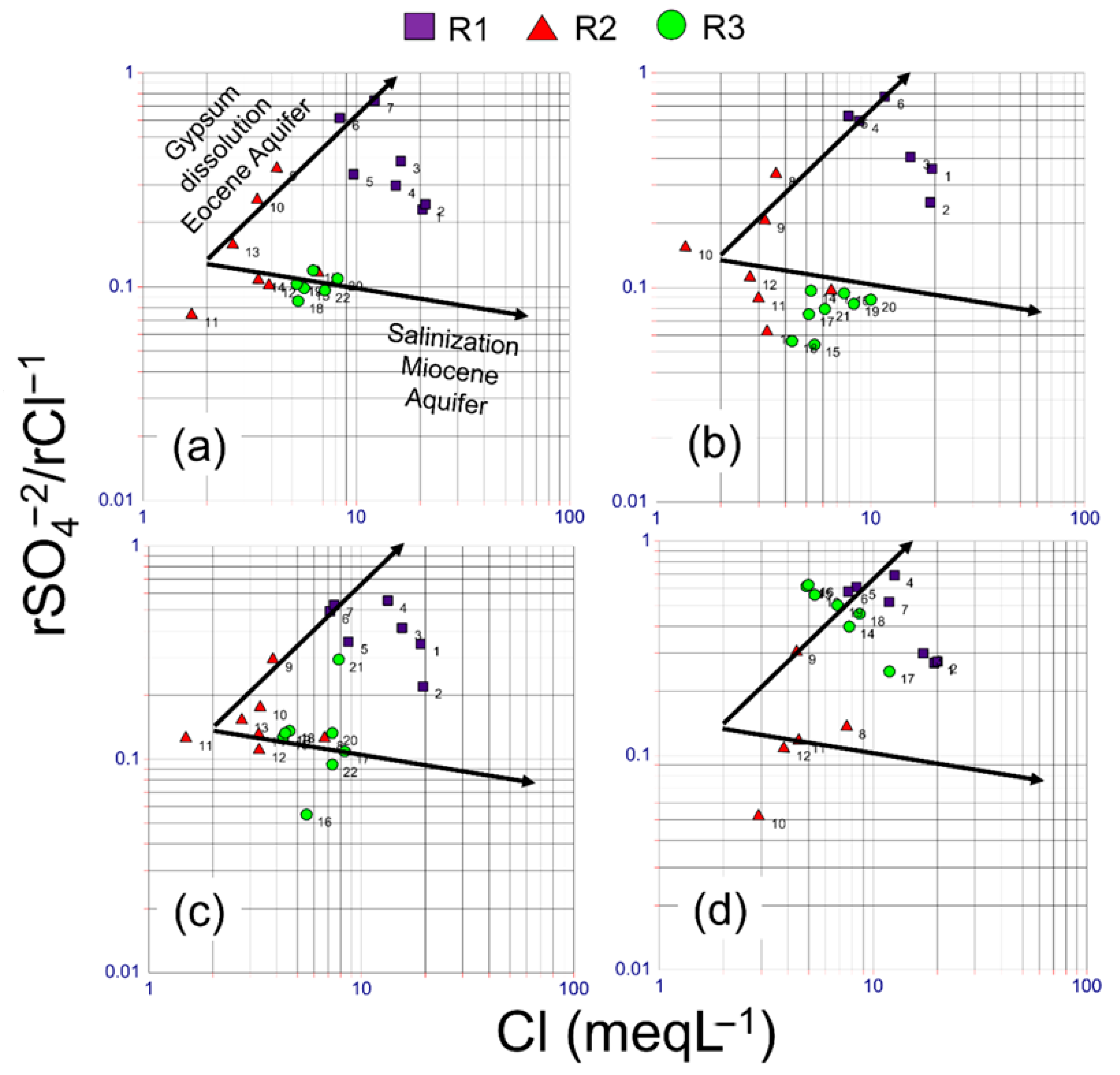


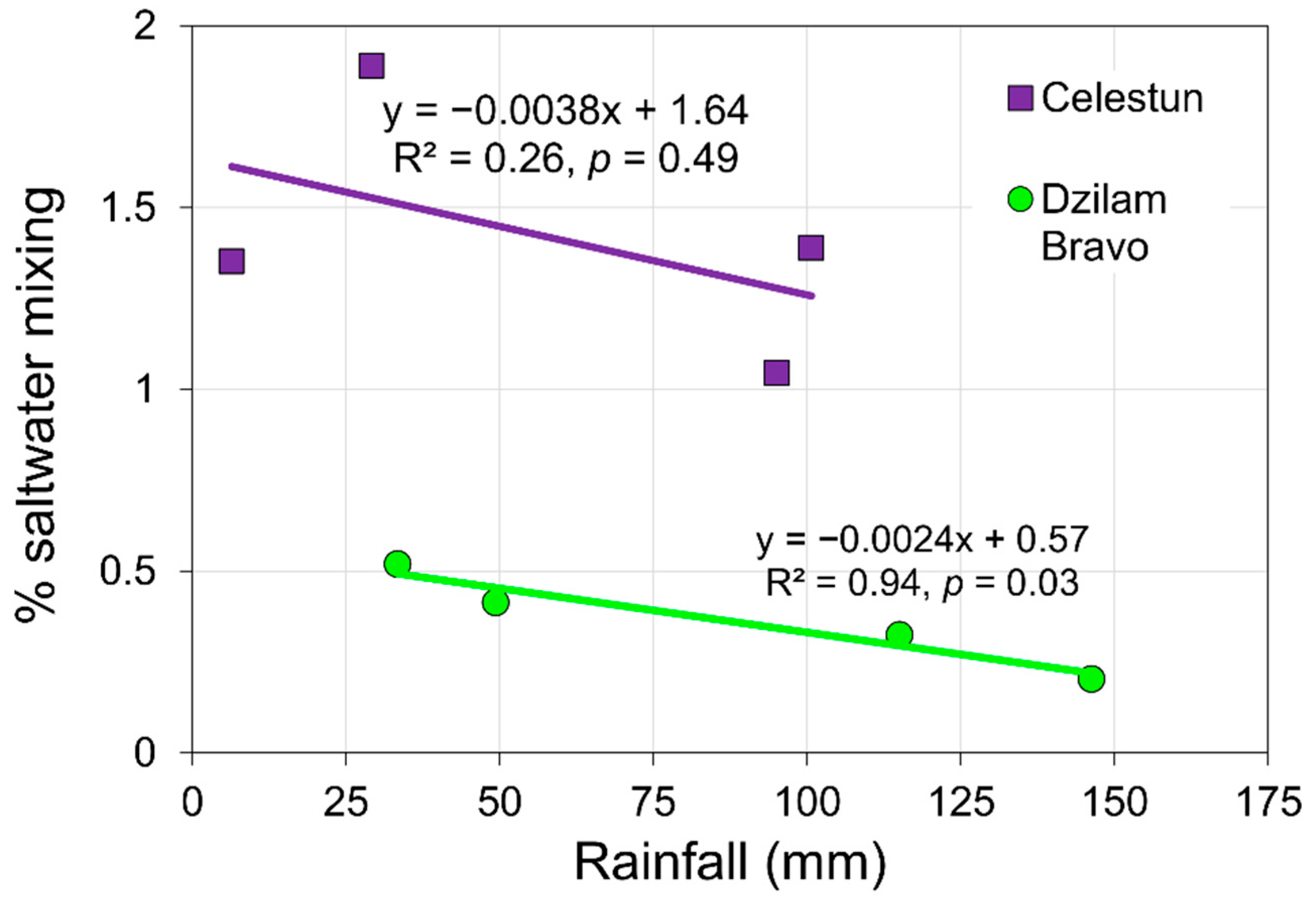

| SP | Region | T (°C) | pH | EC (µS cm−1) | O2 (mg L−1) | Ca+2 (mg L−1) | Mg+2 (mg L−1) | Na+ (mg L−1) | K+ (mg L−1) | HCO3− (mg L−1) | Cl− (mg L−1) | SO4−2 (mg L−1) | NO3− (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C | 26.9 | 6.79 | 2696 | 7.93 | 155.8 | 77.7 | 283.7 | 9.9 | 411.5 | 589.6 | 230.4 | 3.6 |
| MC | 27.4 | 6.63 | 1790 | 3.38 | 140.9 | 64.6 | 141.1 | 5.4 | 403.2 | 294.1 | 252.0 | 6.2 | |
| R | 25.9 | 6.71 | 1030 | 2.42 | 98.9 | 46.3 | 55.0 | 4.1 | 417.5 | 128.9 | 23.7 | 10.4 | |
| MD | 26.7 | 6.57 | 1278 | 0.65 | 105.2 | 86.3 | 88.5 | 3.1 | 570.9 | 202.8 | 27.0 | 0.6 | |
| D | 26.4 | 6.61 | 1350 | 0.71 | 112.4 | 44.1 | 113.7 | 5.1 | 417.2 | 244.3 | 34.0 | 0.8 | |
| 2 | C | 27.1 | 7.89 | 2764 | 1.03 | 131.3 | 87.5 | 264.0 | 9.5 | 423.5 | 539.7 | 312.0 | 10.2 |
| MC | 27.4 | 6.36 | 1812 | 3.36 | 120.8 | 74.1 | 137.7 | 5.1 | 432.0 | 274.2 | 242.8 | 5.5 | |
| R | 26.1 | 6.85 | 1058 | 3.07 | 88.3 | 46.9 | 53.8 | 4.0 | 432.6 | 119.3 | 18.2 | 13.0 | |
| MD | 26.8 | 6.57 | 1370 | 0.15 | 98.2 | 52.1 | 85.5 | 3.2 | 488.8 | 187.4 | 24.6 | 10.5 | |
| D | 26.7 | 8.24 | 1531 | 0.21 | 100.4 | 52.9 | 121.8 | 5.3 | 453.7 | 255.7 | 27.7 | 4.4 | |
| 3 | C | 26.7 | 7.11 | 2614 | 2.88 | 138.0 | 74.4 | 396.2 | 10.8 | 412.7 | 539.9 | 266.4 | 6.7 |
| MC | 27.2 | 7.06 | 1564 | 4.98 | 115.5 | 58.6 | 102.1 | 4.6 | 422.6 | 218.0 | 137.2 | 12.7 | |
| R | 25.6 | 7.08 | 1056 | 4.41 | 88.6 | 48.2 | 49.93 | 4.9 | 428.1 | 123.6 | 22.6 | 11.3 | |
| MD | 26.3 | 7.50 | 1326 | 5.98 | 91.8 | 51.5 | 67.8 | 3.2 | 464.9 | 151.9 | 26.0 | 11.6 | |
| D | 25.8 | 7.09 | 1630 | 0.96 | 97.2 | 56.3 | 106.7 | 7.0 | 417.9 | 238.5 | 54.6 | 6.6 | |
| 4 | C | 27.1 | 6.89 | 2736 | 2.6 | 203.2 | 86.1 | 295.0 | 10.1 | 443.5 | 550.4 | 284.8 | 13.7 |
| MC | 27.4 | 6.99 | 1794 | 3.2 | 165.8 | 74.9 | 143.5 | 5.4 | 405.8 | 282.9 | 191.2 | 17.7 | |
| R | 26.3 | 6.98 | 1083 | 3.4 | 119.8 | 66.6 | 61.7 | 2.5 | 435.3 | 166.3 | 25.4 | 13.9 | |
| MD | 26.8 | 6.82 | 1323 | 1.4 | 139.9 | 73.5 | 90.1 | 3.5 | 420.3 | 189.5 | 143.3 | 9.6 | |
| D | 26.2 | 7.68 | 1637 | 0.4 | 137.3 | 71.6 | 145.4 | 6.7 | 400.2 | 287.7 | 161.8 | 9.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Ceballos, R.; Canul-Macario, C.; Pacheco-Castro, R.; Pacheco-Ávila, J.; Euán-Ávila, J.; Merino-Ibarra, M. Regional Hydrogeochemical Evolution of Groundwater in the Ring of Cenotes, Yucatán (Mexico): An Inverse Modelling Approach. Water 2021, 13, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050614
Pérez-Ceballos R, Canul-Macario C, Pacheco-Castro R, Pacheco-Ávila J, Euán-Ávila J, Merino-Ibarra M. Regional Hydrogeochemical Evolution of Groundwater in the Ring of Cenotes, Yucatán (Mexico): An Inverse Modelling Approach. Water. 2021; 13(5):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050614
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Ceballos, Rosela, Cesar Canul-Macario, Roger Pacheco-Castro, Julia Pacheco-Ávila, Jorge Euán-Ávila, and Martín Merino-Ibarra. 2021. "Regional Hydrogeochemical Evolution of Groundwater in the Ring of Cenotes, Yucatán (Mexico): An Inverse Modelling Approach" Water 13, no. 5: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050614
APA StylePérez-Ceballos, R., Canul-Macario, C., Pacheco-Castro, R., Pacheco-Ávila, J., Euán-Ávila, J., & Merino-Ibarra, M. (2021). Regional Hydrogeochemical Evolution of Groundwater in the Ring of Cenotes, Yucatán (Mexico): An Inverse Modelling Approach. Water, 13(5), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050614







