Abstract
Human pressures on water resources have been suggested as a driver of biological traits that induce changes in native fish populations. This study highlighted the interplay between environmental stress factors, mostly related to flow regulation, and the longitudinal river gradient in biological traits such as the growth, size structure and somatic condition of a sentinel fish, Luciobarbus sclateri. We found an increase in size-related metrics and somatic condition at population levels associated with downstream reaches, although fragmentation and habitat alteration, flow regime alteration and the abundance of non-native fish were also significantly involved in their variability. Age-related parameters and growth were only explained by flow regime alterations and the abundance of non-native fish species. The high plasticity observed in L. sclateri population traits suggests that this is a key factor in the species adaptability to resist in a strongly altered Mediterranean river basin. However, the interplay of multiple stressors plays an important role in fish population dynamics and could induce complex responses that may be essential for long-term monitoring in sentinel species.
1. Introduction
Freshwater ecosystems are considered among the most altered as a consequence of the historical pressure of human activities [1,2]. Hydraulic management to take advantage of water resources and the effects of climate change are inducing quantitative and qualitative changes in river systems [3,4]. These changes imply hydro-morphological, chemical and biological alterations which affect the freshwater fauna [2,5]. Hydraulic management is especially intense in Mediterranean regions where water resources are scarce [6]. Rivers in semi-arid regions, such as the Iberian Peninsula, are heavily impacted by the construction of a large number of dams and weirs [7,8].
Mediterranean regions are characterized by marked seasonality and inter-annual variability with severe periods of floods and droughts [9,10]. The native freshwater fauna is adapted to such natural variability and displays great resistance and resilience [11,12,13]; however, it is considered especially sensitive to human impacts [14,15]. Human pressures are particularly severe in Mediterranean regions and they coincide with high natural variability, causing severe alterations to fluvial ecosystems [8,16,17]. Despite the high adaptability of freshwater fauna, the expected increase in human impacts under future scenarios of global climate change could increase its vulnerability to such pressure, especially in Mediterranean regions [11,18,19].
The flow regime is considered one of the main driving forces of freshwater ecosystems, determining the structure and ecological dynamic of rivers [19,20]. In the Iberian Peninsula, the alteration of the natural flow regime by dam regulation is one of the most important stress factors that negatively affects the native fish fauna [21,22,23]. The effects of flow regime alteration have been widely documented in Mediterranean fish populations [24,25,26,27]. In addition, flow management infrastructures cause loss of connectivity and habitat alterations related to the fragmentation process (e.g., increase in lentic habitats, changes in water quality), which could facilitate the establishment and spread of non-native fish species, altering the composition of the community [28,29]. However, the effects of these stress factors have been poorly studied in Mediterranean rivers [30,31,32].
The Segura River basin is located in the southeast of the Iberian Peninsula and is characterized by a marked environmental variability and displays a wide variety of human impacts along its longitudinal gradient [33,34]. Furthermore, this basin shows a well-documented range of impacts on the natural flow regime [35,36] and is considered one of the most regulated Mediterranean river systems [37]. Therefore, the Segura River offers an opportunity to study the effect of multiple human-induced stressors along an intensively altered basin. The fish assemblage in the Segura River basin is characterized by a low number of species where Luciobarbus sclateri (Günther, 1868) appears to be dominant [38]. This native species is an endemic potamodromous fish considered a sentinel species in the southern Iberian Peninsula [12], and its biology and ecology have been well documented [39,40,41], being the unique native fish widely distributed in the Segura River basin [42]. Therefore, L. sclateri populations in the Segura River could be considered a useful tool through which to assess the intra-specific variability along a wide longitudinal gradient strongly affected by environmental alterations mainly related to flow regulation. However, few authors have described the effects of multiple stressors on its populations, and nothing is known about its intra-specific variability along longitudinal gradients [43,44,45].
The main objective of the present study was to assess the variability of L. sclateri population traits in relation to different environmental stressors along the longitudinal gradient of a highly regulated river system. Our hypothesis was that L. sclateri would exhibit high phenotypic plasticity that enables populations to survive along the longitudinal gradient of a highly impacted river basin. L. sclateri has been evaluated as near threatened (NT) on a regional scale due to the intensification of human pressures which caused a decrease in habitat quality (mainly pollution and flow regime alteration) and an increase in the establishment and spread of several non-native fish species [46]. Furthermore, in recent years, a severe decline in L. sclateri populations has been documented in the Segura River basin [38,47]. The use of different biological traits provides ecological insights into how populations respond to multiple stress factors, allowing us to understand how species’ traits could predispose species to local extinctions [48] and to establish more successful management and recovery programs [8,49].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Design
This study was conducted in the Segura River basin, situated in the semi-arid Mediterranean climatic zone in the southeast of the Iberian Peninsula (Figure 1). The river basin drains an area of 18,870 km2 and is characterized by a strong climatic and altitudinal gradient, and significant annual and inter-annual natural variation in the flow regime [6]. Multiple human activities—primarily related to agriculture, but also to electricity generation and human supply—have developed in the study area [33,34,37]. Irrigation accounts for 90% of the water demand and is considered the main pressure on the water resources. A total of 33 dams (>10 m height and >1 hm3 of reservoir) and 170 smaller obstacles exist along the longitudinal gradient of the river with a capacity of regulation of approximately 1200 hm3. Since 1979, this basin has received an external water transfer from the Tajo River with an average of 350 hm3year−1, so the storage capacity increased by around 140% of the natural input (871 hm3year−1) [37,50]. Furthermore, local agricultural practices add an artificial source of pollutant discharge (mainly phosphates and nitrates) into the river [51,52]. As a result, the fluvial and riparian habitats of the Segura River basin have been severely altered [33,53], in addition to strong modifications in the natural flow regime [54].
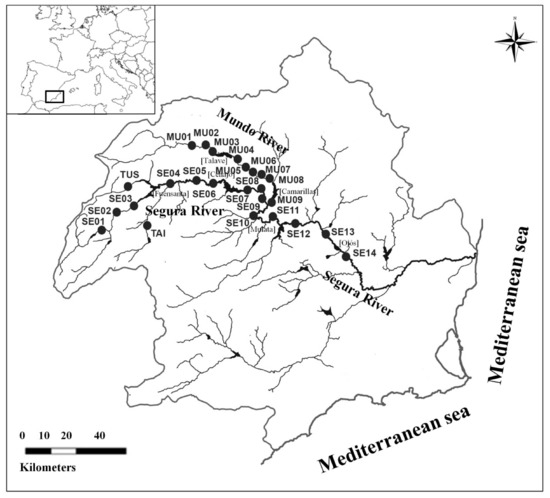
Figure 1.
Study area. Location of the Segura River basin in the southeast of the Iberian Peninsula. Sampling sites are marked (●): TAI (Taibilla River), TUS (Tus River), MU (Mundo River) and SE (Segura River). Names of large reservoirs are between parentheses [].
We sampled a total of 25 sites in fluvial reaches distributed along upstream–downstream gradients from the upper Segura main stem (SE) to the middle Segura (195 km), from the upper Mundo River (MU) to the Mundo–Segura confluence (51 km) and in two upper tributaries (Tus and Taibilla) (Figure 1). The range in altitude is 112–809 m.a.s.l. in the study area; the water conductivity ranged from 316 to 1303 µs cm−1 and the range of the mean annual water temperature was 13.9–16.9 °C during the study period. The distribution of sampling sites reflects the different hydrological flow regimes present in the study area. Sampling sites placed in areas with the most natural flow regime (e.g., MU01 and SE01; Figure 1) were characterized by a strong seasonal variation, alternating summer droughts and spring/autumn short-time flow peaks (Figure 2a). An impact gradient on the natural flow regime in the study area was described by Amat-Trigo [35] and Amat-Trigo et al. [36]. Impacted areas exhibit a seasonal inversion of the natural flow pattern (high flow levels in spring and summer, low flow levels in autumn and winter) due to the water demand for agricultural practices. Furthermore, impacted areas can be characterized by two extreme flow impacts: reaches downstream of the Cenajo reservoir (sampling sites SE06, SE07 and SE09; Figure 1) showed a high level of contingency and low variability, but also low predictability (Impact 1, Figure 2b), while other reaches (e.g., sampling sites MU09, SE12 and SE13; Figure 1) were characterized by more stable and high levels of base flow throughout the year, high values of temperature and spell peaks, in addition to the inversion in flow seasonality (Impact 2, Figure 2c).
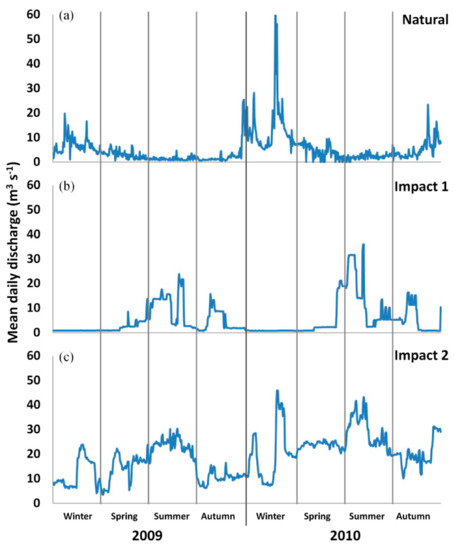
Figure 2.
Flow variation (mean daily discharge; m3 s−1) at three representative fluvial sectors in the study area. Repre-sentative flow regimes were measured at three gauging stations: (a) Natural flow regime at the upper part of the Mundo River, (b) Impact 1 just downstream of the Cenajo reservoir, and (c) Impact 2 downstream of the La Mulata dam (see location in Figure 1). Flow discharge data were obtained from the Segura Hydrographic Confederation.
The fish assemblage in the study area is composed of both native and non-native species [38]. Non-native species are dominant (90% of total species richness) and L. sclateri is the only widely distributed native species in the study area. The most abundant species are cyprinids: the native L. sclateri and the non-native species Pseudochondrostoma polylepis (Steindachner, 1864), Gobio lozanoi (Doadrio and Madeira, 2004) and Alburnus alburnus (Linnaeus, 1758). The non-natives Cyprinus carpio (Linnaeus, 1758) and Lepomis gibbosus (Linnaeus, 1758) are locally abundant. Furthermore, the natives Squalius pyrenaicus (Günther, 1868) and Salmo trutta (Linnaeus, 1758), as well as the non-natives Gambusia holbrooki Girard 1859, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792), Micropterus salmoides (Lacépède, 1802), Sander lucioperca (Linnaeus, 1758) and Esox lucius (Linnaeus, 1758), are present in the study area.
2.2. Environmental Variables
We described a total of ten environmental variables and gradient descriptors in the study area (Table 1). Water conductivity was measured in situ using a multi-parameter (340i WTW), and ecological status was assessed according to the EU Water Framework Directive, Fluvial Habitat Index (IHF) [55], Riparian Quality Index (RQI) [56] and altitude [57]. The Longitudinal Connectivity Index (ICL) [58] and free reach (length of reach available for free movement) were calculated using databases available online from the official monitoring service of the Segura Hydrographic Confederation (CHS) (https://www.chsegura.es/chs/cuenca/restauracionderios/obstaculos/visorjs.html; accessed on 12 September 2018). Water temperature and daily river discharge data were also obtained from the CHS online databases with data gathered by gauging stations distributed in the study area (https://www.chsegura.es/chs/cuenca/redesdecontrol/estadisticashidrologicas/; accessed on 12 September 2018). Mean monthly values of water temperature for 2009 and 2010 were calculated. Mean daily discharge (m3 s−1) over a 16-year period (1994–2010) was used to calculate the mean daily base flow (MDBF) as the total base flow component of the hydrograph divided by the number of recording days, and flow variability as the daily range between Q10% and Q90% discharge divided by the median value. These two flow metrics (MDBF and flow variability) were calculated using time series analysis (TSA) of the River Analysis Package (RAP version 3.0.7) [59].

Table 1.
Environmental variables and gradient descriptors measured or calculated at sampling sites. Altitude (meters above sea level), ecological status (categorized as: 1 = high; 2 = good; 3 = moderate; 4 = poor), Fluvial Habitat Index (IHF) and Riparian Quality Index (RQI) (%), conductivity (µS cm−1), free reach (km), Longitudinal Connectivity Index (ICL), water temperature (°C), mean daily base flow (MDBF) (m3 s−1) and flow variability ((Q10% − Q90%)/median).
2.3. Fish Sampling and Population Traits
Sites were sampled using electrofishing (working voltage between 200 and 350 V, 2–3 A), following the CEN standard protocol [60]. Each sampling site was considered an independent population, taking into account the distance between sampling sites, the presence of non-passable barriers (dams and weirs) and the biological characteristics of L. sclateri. Fish were collected in 100-m-long wadable sections blocked by nets that acted as barriers. Fish sampling sessions were carried out in 30–45 min. Sampling was conducted during October–November 2009 to prevent the capture of spawning fish [45] and to avoid variation in body condition due to gonad development [39,43,61]. Fish manipulation was carried out following the European Union Directive 2010/63/UE on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes and it was not necessary to obtain authorization from the research ethics commission. In concordance with administrative permits, a total of 1529 specimens of L. sclateri were caught, processed in the field and returned to their habitat. Fork length (FL ± 0.1 cm) and weight (TW ± 0.1 g) were measured. A subsample of scales (611 specimens) was taken and cleaned later in a laboratory to determine the age according to Herrera et al. [40] and Torralva et al. [45].
L. sclateri populations were evaluated at sampling sites to assess intra-specific variability. The fish population traits we studied were relative abundance, size-related parameters, age-related parameters, relative growth rates and somatic condition. Relative abundance was measured as the number of L. sclateri individuals caught per hour (catch per unit effort, CPUE) in a standardized sample area without significant differences in habitat complexity and, thus, assuming that catch efficiency remains constant. Size-related parameters included mean, maximum and range of fork length (FL), and a size diversity index calculated as a Shannon-Wiener modification using the number of size classes grouped in 2 cm length ranges. Age-related parameters included mean, maximum and range of age, determined for a subsample of L. sclateri scales. Back-calculated lengths were estimated by the Fraser-Lee equation following the methodology used by Torralva et al. [45] and Miñano et al. [62] based on the counting and measuring of scales’ annuli, and checked according to Musk et al. [63]. Proportions (%) of back-calculated lengths for each age class were obtained from the Walford method [64] and used to calculate the mean individual growth index (GI). Relative growth rates at the site level were estimated from the mean individual growth index (GI). The methodology used to calculate the growth index (GI) is detailed in Masó et al. [65] and Amat-Trigo et al. [66], which followed the Hickley and Dexter procedure [67]. We used the mean values of GI at age 1 year, age 2 years and maturity (individuals older than 2 years) according to the age of maturity previously established for the species in the Segura River basin [43,45,61]. Somatic condition was expressed as predicted values of log-transformed weight (mean value at sampling site) obtained from the application of univariate analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) using total weight (WT) as the dependent variable and fork length (FL) as the covariate; differences in variation were tested by ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD post hoc tests [68]. Individuals with an FL less than 75 mm were considered juveniles [43]. Bivariate relationships between population traits were analyzed using Spearman’s rank correlations. Statistical analysis was performed with the SPSS software package v. 24.
2.4. Effect of Environmental Stress Factors on Population Traits
We conducted a model selection analysis based on the Akaike Information Criterion with a correction for small samples sizes (AICc) [69] to determine the stressors associated with the variability in L. sclateri population traits. To establish model ranking, the MuMIn (Multi-Model Inference) R Package was used [70]. Stress factors were obtained by the reduction in transformed environmental variables and gradient descriptors (log for numeric variables, arcsine square root for proportions) using principal component analysis (PCA) with varimax rotation [71] using R package psych. Spearman’s rank correlation analysis was used to test the redundancy between the variables. Principal component axes scores were used as stressors. The ratio of the abundance of non-native fish species (abundance of non-native species/total abundance) was also considered a stressor. General linear model results (GLMs) for the best models (ΔAICc < 2.0) were used to describe the response of L. sclateri biological traits to the stress factors. These analyses were performed in the R statistical environment (Version 1.40.4).
3. Results
3.1. Relative Abundance and Population Traits
The abundance of L. sclateri showed high spatial variation, ranging from 13.33 to 150.00 catches per unit of effort (CPUE, Supplementary Table S1). The highest value was found in the Taibilla tributary (sampling site TAI) and the lowest was found at SE04, downstream of the Fuensanta reservoir (Figure 1).
The mean size fork length in the whole study area was 18.3 ± 6.55 cm FL, with the maximum value detected at MU03 (58.2 cm). The maximum validated age was 15+ years, with individuals this old detected at sampling sites SE04, SE07 and SE09; however, the mean age at the population level was 4.9 ± 1.43 years. The population size/structure differed among sampling sites, although a polymodal distribution pattern was evident in most sampling sites along the longitudinal gradient (Figure 3). Both size and age parameters displayed lower values in headwaters (Figure 3 and Table S1), with maximum fish sizes below 30 cm (FL), lower size ranges and lower size diversity index values (Figure 3a,b,c). The other sampling sites had specimens longer than 40 cm (FL), with higher values at sampling sites just downstream of non-passable obstacles (e.g., SE07, Figure 3) and upstream of large reservoirs (e.g., MU03, Figure 3).
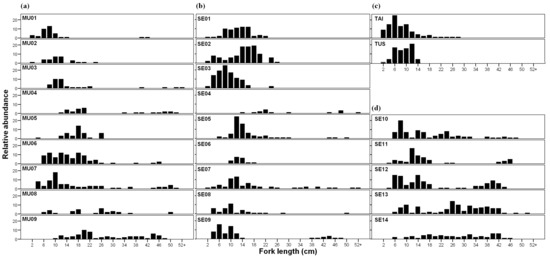
Figure 3.
Size distribution (2 cm fork length (FL) groups) of L. sclateri at sampling site. Plot distribution: (a) Mundo River (MU) sampling sites, (b) sampling sites placed from Segura (SE) riverbed to Mundo River confluence, (c) sampling sites at tributaries Tus and Taibilla (TAI) Rivers and (d) sampling sites from Segura–Mundo confluence to the latest downstream sampling site (SE14).
The growth index (GI) displayed high variability for individuals of each age class between sampling sites. The mean GI value at age 1 year across the study area was 66.74 ± 1.28, with a maximum value of 82.47 detected at sampling site SE01, while the mean value of GI at age 2 years was 39.34 ± 1.13, with a maximum of 53.52 at sampling site MU09. For mature fish, the mean GI value in the study area was 17.69 ± 1.57, with a maximum of 32.53 detected at site MU05. The lowest GI values were detected in the TUS tributary (age 1 year = 45.72; age 2 years = 19.26; mature = 0.03).
Somatic condition was higher in mature individuals and also showed greater variability among sampling sites. The mean of predicted values of log-transformed weight for mature individuals was 1.87 ± 0.03, with a maximum value of 2.43 at sampling site MU04, whereas the mean value for immature individuals was 0.63 ± 0.03, with a maximum of 0.90 at sampling site SE10. Generally, lower values of somatic condition were detected in headwaters for both mature (TUS = 1.28) and immature (SE01 = 0.44) individuals. Population traits at the site level are shown in Table S1 (Supplementary Material). The relationships among population traits are presented in Table S2 (Supplementary Material).
3.2. Environmental Factors
The first three PC axes obtained from the dimension reduction of environmental variables and gradient descriptors explained 79.7% of the total variance (Table 2). PC1 was associated with habitat alteration and fragmentation, which were directly related to poor ecological status and low RQI, high values of conductivity and water temperature and low connectivity (high values for ICL and low values of free reach). PC2 was associated with the longitudinal gradient, which was directly related to high altitude, IHF and low water temperatures. PC3 was associated with flow regime alteration, which was directly related to flow variability and MDBF.

Table 2.
Loadings and proportions of variance extracted by PCA of environmental variables with varimax rotation. Loadings > 0.50 are marked in bold.
3.3. Effects of Environmental Factors on Population Traits
Table 3 displays the best models obtained from the model selection analysis based on AICc. The longitudinal gradient (PC2) was significantly linked with size-related parameters and somatic condition metrics. The gradient from the upper sampling sites to the downstream sites was associated with increment in population traits including the size range, mean and maximum size, size diversity index and somatic condition metric (longitudinal gradient axis, Figure 4). The longitudinal gradient interplayed with other stressors such as the non-native fish species, showing a significant effect on size range and maximum size (size-related parameters, Table 3). In addition, this environmental factor interplayed with the flow regime alteration (PC3), displaying a significant effect on mean size (size-related parameters, Table 3) and somatic condition for mature individuals (somatic condition, Table 3). Finally, the longitudinal gradient also interplayed with habitat alteration and fragmentation (PC1), displaying a significant effect on the size diversity index (size-related parameters, Table 3) and somatic condition in immature individuals (somatic condition, Table 3).

Table 3.
General linear models (GLM) results for the best models obtained by model selection analysis based on the Akaike Information Criterion with a correction for small samples sizes (AICc). GLM analysis was conducted for each population trait: CPUE, size- and age-related parameters, growth and somatic condition. (• p < 0.1; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).
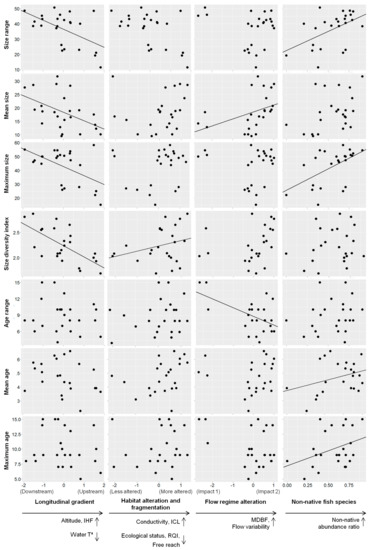
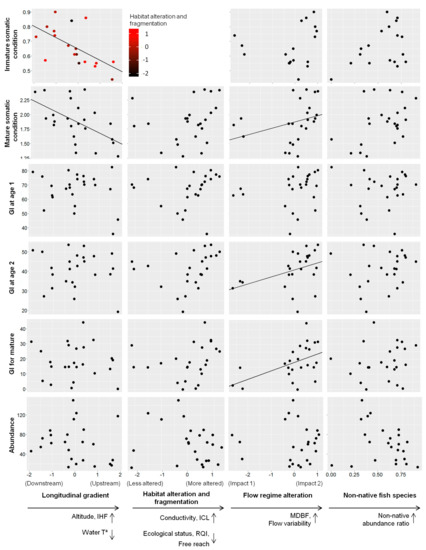
Figure 4.
Relationship between environmental factors (longitudinal gradient, habitat alteration and fragmentation, flow regime alteration and non-native fish species) and L. sclateri population traits. Significant results (GLM p-value < 0.05) are represented with marked trend line on the plot. In x-axes, arrows pointing down indicate decrease in environmental variables (i.e., water temperature), and arrows pointing up indicate increase in environmental variables (i.e., altitude) and also increase in non-native abundance ratio.
In addition to the interplay with the longitudinal gradient, the flow regime alteration (PC3) was linked to variability in the age range (age-related parameters, Table 3) and the growth index (GI) for mature fish and fish aged 2 years (growth, Table 3). An increase in the PC3 axis implied high flow variability and base flow (Impact 2, Figure 2c) and was associated with increased mean size and somatic condition of mature individuals, and GI at age 2 years and for mature individuals (flow regime axis, Figure 4). In contrast, a decrease in the PC3 axis implied low base flow and variability (Impact 1, Figure 2b) and was associated with a decreased age range (flow regime alteration axis, Figure 4).
In addition to the interplay with the longitudinal gradient, non-native fish species were linked to the variability in the mean and maximum age (age-related parameters, Table 3). An increased relative abundance of non-native fish species was associated with an increase in these two age-related parameters (non-native fish species axis; Figure 4).
Finally, habitat alteration and fragmentation (PC1) were linked to the size diversity index (size-related parameters, Table 3) and somatic condition of immature individuals (somatic condition, Table 3) and always exhibited an interplay with the longitudinal gradient. An increase in habitat alteration and fragmentation was associated with increased size diversity index (habitat alteration and fragmentation axis, Figure 4). Furthermore, the only interaction found in this study occurred between this stressor and the longitudinal gradient, which was associated with increased somatic condition for immature individuals (longitudinal gradient axis, Figure 4). Finally, the model selection analysis did not find any stress factors among those considered in this study to explain the variability in the growth index (GI) of fish at age 1 year or abundance (CPUE).
4. Discussion
In this study, we analyzed the variation in population traits of L. sclateri in response to environmental factors in the fluvial reaches of the Segura River basin. Our results confirm significant variability in population traits along the longitudinal gradient due to the effect of human impacts, mostly those related to flow regulation such as fragmentation and habitat alteration, flow regime alteration and the relative abundance of non-native fish species. The use of biological traits related to size and age, relative abundance, growth and somatic condition allowed us to identify the population-level responses of this sentinel Iberian fish to different stressors and to verify the complex effect of multiple stressors in a heavily modified Mediterranean-type river.
The longitudinal gradient is a key factor in the structure and dynamic of freshwater ecosystems, so it is essential to consider its effects in the assessment of multiple stressors in river systems [72,73,74,75]. Environmental conditions along the longitudinal gradient determine the availability of resources such as food, refuges and breeding areas [34,76]. Consequently, a marked effect of the spatial variation on fish populations was expected, especially in Mediterranean-type rivers which exhibit a strong climatic and altitudinal gradient [10,77,78]. The increment of resources downstream along natural river systems promotes large sizes and a wider range of size classes in the fish fauna [73,76,79]. We found significant variability in the size parameters and somatic condition of L. sclateri populations associated with spatial variation, with an increase in these biological traits along the longitudinal gradient. The size population structure displayed a polymodal pattern, with high variability among sampling sites. The size distribution results highlighted a lack of some size groups, and this was more evident in sampling sites downstream of reservoirs. Small and medium-sized individuals were scarce downstream of operational dams (i.e., at sites MU09, SE04, SE09 and SE11). The GLM results (Table 3) showed that size and somatic condition parameters were significantly associated with the longitudinal gradient. In fact, habitat alteration and fragmentation, flow regime alteration and relative abundance of non-native fish species were all related to the variability of population parameters, reflecting the severe alterations that have affected the Segura River basin [34,37].
Human impacts increase along the longitudinal gradient as a consequence of the greater accessibility to water resources [77]. As a result, the interplay among spatial variation and human stress factors shaped the environmental conditions that act as a “filter” of biological traits [80]. The selected traits determine the biological responses of freshwater fauna to cope with altered conditions [18,75,81]. The Segura River basin shows a strong influence of human alterations mainly related to agricultural supply [33,37]. Agricultural practices involve strong hydraulic management that results in a loss of connectivity (habitat fragmentation), flow regime alteration and water quality and habitat degradation and encourages the establishment of non-native fish species [18,32,82,83]. Our results show the interplay between environmental stress factors, mostly those related to flow regulation, and the longitudinal gradient in some biological traits such as size and somatic condition. In addition, we found that age and growth variations were significantly associated with the isolated effect of the flow regime alteration and the relative abundance of non-native fish species. This finding suggests that the magnitude of human impacts in the study area could be masking some ecological responses to longitudinal gradients [84,85].
The flow regime is considered the main driver of freshwater ecosystems, defining the structure, function and dynamic of rivers, and affecting the individual fitness and growth rate of fish populations [80,86,87]. We found significant relationships between flow regime alteration and some population traits of L. sclateri including mean size, age range, somatic condition for mature individuals and growth variability. Our results show an increase in these population traits associated with fluvial sectors that had a high level of base flow throughout the year (reflected as Impact 2 in Figure 2) and a flow regime pattern that reduced the strong seasonal variability of Mediterranean-type rivers. Although these fluvial sectors display an inversion in flow seasonality related to agricultural water demands, they also provide an increased availability of water, refuge and food resources [25,76,88]. Furthermore, high flow levels promote changes in body shape and muscle development, which induce better swimming performance and increased somatic condition [89,90], a finding that was previously documented in the Segura River basin [43]. In contrast, we observed a decrease in population traits (mean size, age range, somatic condition for matures and growth variability) associated with strong inversion in flow seasonality and base flow reduction (Impact 1 in Figure 2). We found this flow pattern in sampling sites downstream of the Cenajo reservoir, a consequence of the operating characteristics of its dam [34,35,54]. The extreme hydrological conditions caused by this type of water regulation result in a poor-quality habitat, especially for adult barbels [91], and are considered a limiting factor for the growth of barbel species in the Iberian Peninsula [25,92]. These two contrasting results in the response of fish populations under different hydrological flow patterns have been described in other Iberian rivers as well [25,93].
Non-native fish species tend to be dominant in human-altered ecosystems, such as the Mediterranean rivers, where more stable environmental conditions that result from flow regulation measures encourage their establishment and spread [82,83,94]. Iberian fish communities have exhibited significant changes over recent decades as a consequence of the introduction of a wide range of non-native fish species [95,96,97], and these changes are especially evident in the Segura River basin [38]. The negative responses of native fish populations associated with the presence and abundance of non-native species in the fish assemblage are well documented [75,98,99]. Our results show an increase in the maximum size and size range, and the mean and maximum age of L. Sclateri populations associated with a higher ratio of non-native fish abundance. The proliferation of non-native species is generally a result of changes in the environmental conditions caused by flow regulation [4,8]. The lack of small size classes of fish at sampling sites placed downstream of reservoirs where the presence of non-natives is favored (i.e., SE04 in Figure 3) suggests an effect of the fish assemblage composition on the structure of L. sclateri populations. In general, predation by non-native fish could affect the population structures and dynamics of native fish species in the Iberian Peninsula [95]. Some studies from other Iberian rivers confirmed the inclusion of different barbel species in the diet of top predator fish such as E. lucius [100,101] and S. Lucioperca [102]. Predatory fish (E. lucious, S. lucioperca and M. salmoides) showed a higher occurrence in the lower reaches of the study area. They could be inducing higher predation pressure on certain size classes of L. sclateri and therefore affecting the population size structure as Bravo et al. [103] showed in the Palancar River, where M. salmoides predation was directly related to the lack of 0+ individuals of dominant species such as L. sclateri.
The results of this study highlight relevant associations between human impacts, most of which were related to flow regulation, and the population traits of L. sclateri along a longitudinal gradient, providing insights into the population-level responses of this sentinel Iberian fish to environmental conditions at the site level. The key role of the longitudinal gradient in driving the increase in human impacts as a result of greater accessibility related to the lower reaches of rivers is evident, since most of the stressors were related to the spatial variation, so this dependence makes it difficult to interpret the effect of isolated stressors. In addition, there is a wide variety of human impacts present in the study area that were not considered in this study. For example, pollution could be driving the response of L. sclateri to environmental conditions [32], or predatory mammals (Lutra lutra), whose predation on L. sclateri in the Segura River basin was recently confirmed [104].
The ability of this species to adapt to changes in local conditions has been shown by the variation in population size/structure along the longitudinal gradient. Although human impacts exerted significant effects on the biological traits we evaluated, our findings also suggest that the wide inter-population plasticity displayed by L. sclateri may be a mechanism for this species to successfully inhabit a highly modified Mediterranean-type river. Cyprinids in general show great adaptability to environmental alterations [12,25,92,105], and L. sclateri showed a tolerance to the effects of flow regulation previously studied in the same river basin [45,61].
In recent decades, declines in fish populations have been documented for several Iberian fish species and there have been drastic reductions in fish species that were previously widely distributed in the study area. Native fish species are vulnerable to the rapid increase in human pressure on the water resource; this is especially so in Mediterranean areas where an increase in the magnitude of extreme weather events is expected under climate change scenarios [106]. Therefore, the use of well-known and widely distributed sentinel species, such as L. sclateri, may prove a useful tool to increase the knowledge of the adaptability and population responses to gradients of single and multiple stressors, which is essential to establish and improve management actions to protect native fish species.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/13/6/747/s1, Table S1: Population traits of L. sclateri at sampling site. Table S2. Coefficients of Spearman rank correlation between population traits.
Author Contributions
Project administration, F.J.O.-P. and M.T.; conceptualization, A.S.-P., F.J.O.-P. and M.T.; methodology and data collection, A.S.-P., F.J.O.-P., F.A.-T. and M.T.; formal analysis, A.S.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.-P.; writing—review and editing, A.S.-P., F.J.O.-P., F.A.-T. and M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support was provided by the Fundación Séneca (project 08728/PI/08); Regional Agency of Science and Technology, Autonomous Government of Murcia. A.S.P. was supported by a pre-doctoral contract (FPU14/03994) from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Education.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article or supplementary material.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the members of the UMU research group for their help and support with the field surveys.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. They have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could influence this paper. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Srinivasan, V.; Lambin, E.F.; Gorelick, S.M.; Thompson, B.H.; Rozelle, S. The Nature and Causes of the Global Water Crisis: Syndromes from a Meta-Analysis of Coupled Human-Water Studies. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W10516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, S.; Bregoli, F.; Acuña, V.; Barceló, D.; Elosegi, A.; Ginebreda, A.; Marcé, R.; Muñoz, I.; Sabater-Liesa, L.; Ferreira, V. Effects of Human-Driven Water Stress on River Ecosystems: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, T.I.E.; Wada, Y.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Döll, P.; Gosling, S.N.; Liu, J.; Masaki, Y.; Oki, T.; Ostberg, S.; Pokhrel, Y.; et al. Water Scarcity Hotspots Travel Downstream Due to Human Interventions in the 20th and 21st Century. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R.B. Global Water Resources: Vulnerability from Climate Change and Population Growth. Science. 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater Biodiversity: Importance, Threats, Status and Conservation Challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooke, J.M. Human Impacts on Fluvial Systems in the Mediterranean Region. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, K.; Gough, P.; Royte, J.; Schollema, P.P.; Wanningen, H. From Sea to Source: Protection and Restoration of Fish Migration in Rivers Worldwide; World Fish Migration Foundation: Groningen, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Maceda-Veiga, A. Towards the Conservation of Freshwater Fish: Iberian Rivers as an Example of Threats and Management Practices. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2013, 23, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Abarca, M.R.; Suárez, M.L.; Ramírez-Díaz, L. Ecology of Spanish Semiarid Streams. Limnetica 1992, 8, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Gasith, A.; Resh, V.H. Streams in Mediterranean Climate Regions: Abiotic Influences and Biotic Responses to Predictable Seasonal Events. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1999, 30, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershkovitz, Y.; Gasith, A. Resistance, Resilience, and Community Dynamics in Mediterranean-Climate Streams. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encina, L.; Rodríguez, A.; Granado-Lorencio, C. The Iberian Ichthyfauna: Ecological Contributions. Limnetica 2006, 25, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, C.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Almeida, P.R. Fish Assemblages in Non-Regulated and Regulated Rivers from Permanent and Temporary Iberian Systems. River Res. Appl. 2012, 29, 1042–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormerod, S.J. Current Issues with Fish and Fisheries: Editor’s Overview and Introduction. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M.; Freyhof, J. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes; Publications Kottelat: Cornol, Switzerland, 2007; ISBN 978-2-8399-0298-4. [Google Scholar]
- Clavero, M.; Hermoso, V.; Levin, N.; Kark, S. Geographical Linkages between Threats and Imperilment in Freshwater Fish in the Mediterranean Basin. Divers. Distrib. 2010, 16, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonada, N.; Resh, V.H. Mediterranean-Climate Streams and Rivers: Geographically Separated but Ecologically Comparable Freshwater Systems. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, S.E.; Arthington, A.H. Basic Principles and Ecological Consequences of Altered Flow Regimes for Aquatic Biodiversity. Environ. Manage. 2002, 30, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poff, N.L.; Zimmerman, J.K.H. Ecological Responses to Altered Flow Regimes: A Literature Review to Inform the Science and Management of Environmental Flows. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, D.A.; Poff, N.L. Adaptation to Natural Flow Regimes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M. Threatening Processes and Conservation Management of Endemic Freshwater Fish in the Mediterranean Basin: A Review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaroli, R.; Muñoz-Mas, R.; Martínez-Capel, F. Fish Community Responses to Antecedent Hydrological Conditions Based on Long-Term Data in Mediterranean River Basins (Iberian Peninsula). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belletti, B.; Leaniz, C.G.D.; Jones, J.; Bizzi, S.; Börger, L.; Segura, G.; Castelletti, A.; van de Bund, W.; Aarestrup, K.; Barry, J.; et al. More than One Million Barriers Fragment Europe’s Rivers. Nature 2020, 7838, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, P.; Amaral, S.D.; Ferreira, M.T.; Santos, J.M. Do Small Barriers Affect the Movement of Freshwater Fish by Increasing Residency? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, C.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Almeida, P.R. Life History of a Cyprinid Species in Non-Regulated and Regulated Rivers from Permanent and Temporary Mediterranean Basins. Ecohydrology 2014, 8, 1137–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merciai, R.; Bailey, L.L.; Bestgen, K.R.; Fausch, K.D.; Zamora, L.; Sabater, S.; García-Berthou, E. Water Diversion Reduces Abundance and Survival of Two Mediterranean Cyprinids. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2017, 27, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, J.M.; Ilhéu, M.; Matono, P.; Costa, A.M. Interannual Variation of Fish Assemblage Structure in a Mediterranean River: Implications of Streamflow on the Dominance of Native or Exotic Species. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhéu, M.; Matono, P.; Bernardo, J.M. Invasibility of Mediterranean-Climate Rivers by Non-Native Fish: The Importance of Environmental Drivers and Human Pressures. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinegger, R.; Palt, M.; Segurado, P.; Schmutz, S. Untangling the Effects of Multiple Human Stressors and Their Impacts on Fish Assemblages in European Running Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segurado, P.; Almeida, C.; Neves, R.; Ferreira, M.T.; Branco, P. Understanding Multiple Stressors in a Mediterranean Basin: Combined Effects of Land Use, Water Scarcity and Nutrient Enrichment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colin, N.; Villéger, S.; Wilkes, M.; de Sostoa, A.; Maceda-Veiga, A. Functional Diversity Measures Revealed Impacts of Non-Native Species and Habitat Degradation on Species-Poor Freshwater Fish Assemblages. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Colin, N.; Torralva, M.; Górski, K. Functional Response of Fish Assemblage to Multiple Stressors in a Highly Regulated Mediterranean River System. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, D.; Belmar, O.; Sánchez-Fernández, D.; Guareschi, S.; Millán, A.; Velasco, J. Responses of Mediterranean Aquatic and Riparian Communities to Human Pressures at Different Spatial Scales. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmar, O.; Bruno, D.; Martínez-Capel, F.; Barquín, J.; Velasco, J. Effects of Flow Regime Alteration on Fluvial Habitats and Riparian Quality in a Semiarid Mediterranean Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 30, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amat-Trigo, F. Biological Response of Invasive Fish in a Highly Regulated Mediterranean River Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Univerisity of Murcia, Murcia, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Amat-Trigo, F.; Torralva, M.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Oliva-Paterna, F.J. Effects of Flow Regulation along Longitudinal Gradient on Size-Related Metrics of Fish Populations from a Mediterranean Basin. Fishes Mediterr. Environ. 2016, 2016.010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindlay, A.L.; Zamorano, M.; Rodríguez Muñoz, I.; Molero, E.; Urrea, M.A. Implementation of the European Water Framework Directive: Integration of Hydrological and Regional Planning at the Segura River Basin, Southeast Spain. Land use policy 2011, 28, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Verdiell-Cubedo, D.; Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Torralva, M. La Ictiofauna Continental de La Cuenca Del Río Segura (S.E. Península Ibérica): Décadas Después de Mas (1986). An. Biol. 2014, 36, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encina, L.; Granado-Lorencio, C. Seasonal Changes in Condition, Nutrition, Gonad Maturation and Energy Content in Barbel, Barbus Sclateri, Inhabiting a Fluctuating River. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1997, 50, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Hernando, J.A.; Fernández-Delgado, C.; Bellido, M. Age, Growth and Reproduction of the Barbel, Barbus Sclateri (Günther, 1868), in a First-Order Stream in Southern Spain. J. Fish. Biol. 1988, 33, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralva, M. Biología de Babus Sclateri Günther, 1868 (Pisces, Cyprinidae) En Dos Cursos de Agua Con Distinto Grado de Regulación En La Cuenca Del Río Segura (S.E. de España). Ph.D. Thesis, Univerisity of Murcia, Murcia, Spain, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Morales, I.; José Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Verdiell-Cubedo, D.; Torralva, M. Inventario y Estado de Conservación de La Fauna Piscícola En La Cuenca Alta Del Río Segura (SE Península Ibérica). An. Biol. 2010, 32, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Miñano, P.A.; Torralva, M. Habitat Quality Affects the Condition of Barbus Sclateri in Mediterranean Semi-Arid Streams. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2003, 67, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, R.J.; Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Gálvez-Bravo, L.; Fernández-Delgado, C. Habitat Quality Affects the Condition of Luciobarbus Sclateri in the Guadiamar River (SW Iberian Peninsula): Effects of Disturbances by the Toxic Spill of the Aznalcóllar Mine. Hydrobiologia 2013, 700, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Torralva, M.; Angeles Puig, M.; Fernández-Delgado, C. Effect of River Regulation on the Life-History Patterns of Barbus Sclateri in the Segura River Basin (South-East Spain). J. Fish. Biol. 1997, 51, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralva, M.; Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Andreu-Soler, A.; Verdiell-Cubedo, D.; Miñano, P.A.; Egea-Serrano, A. Atlas de Distribución de Los Peces Epicontinentales de La Región de Murcia; Dirección General del Medio Natural (CARM): Murcia, Spain, 2005; ISBN MU-2362-2005. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Zamora-Marín, J.M.; Franco Galera, J.M.; Zamora-López, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Amat-Trigo, F.; Guillén Beltrán, A.; Guerrero Gómez, A.; Torralva, M. Peces Dulceacuícolas de La Cuenca Del Río Segura; Asociación de Naturalistas del Sureste (ANSE): Murcia, Spain, 2019; ISBN 978-84-09-07845-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bergerot, B.; Hugueny, B.; Belliard, J. Relating Life-History Traits, Environmental Constraints and Local Extinctions in River Fish. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Paukert, C.; Hogan, Z. Endangered River Fish: Factors Hindering Conservation and Restoration. Endanger. Species Res. 2012, 17, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHS (Confederación Hidrográfica del Segura). Plan. Hidrológico de La Cuenca Del Segura 2009-2015. Anejo 7: Inventario de Presiones; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, 2013. Available online: https://www.chsegura.es/export/sites/chs/descargas/planificacionydma/planificacion/docsdescarga/Anejo_07_Inventario_de_presiones.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2018).
- CHS (Confederación Hidrográfica del Segura). Plan. Hidrológico de La Demarcación Del Segura 2015/21. 2015. Available online: https://www.chsegura.es/export/sites/chs/descargas/planificacionydma/planificacion15-21/docsdescarga/docplan1521/01_MEMORIA/Memoria_PHDS2015_21.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2018).
- Pellicer-Martínez, F.; Martínez-Paz, J.M. Probabilistic Evaluation of the Water Footprint of a River Basin: Accounting Method and Case Study in the Segura River Basin, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmar, O.; Velasco, J.; Martínez-Capel, F. Hydrological Classification of Natural Flow Regimes to Support Environmental Flow Assessments in Intensively Regulated Mediterranean Rivers, Segura River Basin (Spain). Environ. Manage. 2011, 47, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piqué, G.; Batalla, R.J.; Sabater, S. Hydrological Characterization of Dammed Rivers in the NW Mediterranean Region. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1691–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, I.; Alvarez, M.; Casas, J.; Moreno, J.L.; Vivas, S.; Bonada, N.; Alba-Tercedor, J.; Jaimez-Cuellar, P.; Moya, G.; Prat, N.; et al. El Hábitat de Los Ríos Mediterráneos. Diseño de Un Índice de Diversidad de Hábitat. Limnetica 2002, 21, 115–133. [Google Scholar]
- González del Tánago, M.; García de Jalón, D. Riparian Quality Index (RQI): A Methodology for Characterising and Assessing the Environmental Conditions of Riparian Zones. Limnetica 2011, 30, 235–254. [Google Scholar]
- CHS (Confederación Hidrográfica del Segura). Estudio General Sobre La Demarcación Hidrográfica Del Segura. 2007. Available online: https://www.chsegura.es/export/sites/chs/descargas/planificacionydma/planificacion/docsdescarga/Proyecto_de_participacion_publica_v4.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2018).
- González Fernández, G.; Rodríguez Muñoz, I.; Seisdedos Fidalgo, P.; Pérez Cardenal, D.; Miguélez Carbajo, D.; Gallego García, R. Diseño de Índices Para El Análisis de La Conectividad Longitudinal En La Cuenca Del Duero. In Proceedings of the Actas del I Congreso Ibérico de Restauración Fluvial (RESTAURARÍOS), León, Spain, 2011; pp. 378–385. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, N.A.; Stewardson, M.J.; Kennard, M.J. River Analysis Package; Monash University: Melbourne, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- CEN (Comité Européen de Normaliation). Water Quality: Sampling of Fish with Electricity. European Standard EN—14011:2003; European Committee for Standarization: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Vila-Gispert, A.; Torralva, M. Condition of Barbus Sclateri from Semi-Arid Aquatic Systems: Effects of Habitat Quality Disturbances. J. Fish. Biol. 2003, 63, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miñano, P.A.; Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Fernández-Delgado, C.; Torralva, M. Edad y Crecimiento de Barbus Graellsii Steindachner, 1866 y Chondrostoma Miegii, Steindachner, 1866 (Pisces, Cyprinidae) En El Río Cinca (Cuenca Hidrográfica Del Ebro, NE España). Misc. Zool. 2000, 23, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Musk, R.S.; Britton, J.R.; Axford, S.N. The Effect of Subjective Fish Scale Ageing on Growth and Recruitment Analyses: A Case Study from the UK. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2006, 36, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Masó, G.; Latorre, D.; Tarkan, A.S.; Vila-Gispert, A.; Almeida, D. Inter-Population Plasticity in Growth and Reproduction of Invasive Bleak, Alburnus Alburnus (Cyprinidae, Actinopterygii), in Northeastern Iberian Peninsula. Folia Zool. 2016, 65, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amat-Trigo, F.; Torralva, M.; Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Oliva-Paterna, F.J. Colonization and Plasticity in Population Traits of the Invasive Alburnus Alburnus along a Longitudinal River Gradient in a Mediterranean River Basin. Aquat. Invasions 2019, 14, 310–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickley, P.; Dexter, K.F. A Comparative Index for Quantifying Growth in Length of Fish. Fish. Manag. 1979, 10, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walford, L.A. A New Graphic Method of Describing the Growth of Animals. Biol. Bull. 1946, 90, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Berthou, E.; Moreno-Amich, R. Multivariate Analysis of Covariance in Morphometric Studies of Reproductive Cycle. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 0-387-95364-7. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, K. MuMIn: Multi-Model Inference. R Package. 2018. Available online: http://Mumin.r-Forge.r-Project.Org/ (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Quinn, G.P.; Keough, M.J. Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologists; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; ISBN 978-0-511-07812-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pringle, C.M. Hydrologic Connectivity and the Management of Biological Reserves: A Global Perspective. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, M.F.; Batalha, D.C.; Collares-Pereira, M.J. Gradients in Stream Fish Assemblages across a Mediterranean Landscape: Contributions of Environmental Factors and Spatial Structure. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radinger, J.; Alcaraz-Hernández, J.D.; García-Berthou, E. Environmental and Spatial Correlates of Hydrologic Alteration in a Large Mediterranean River Catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M.; Blanco-Garrido, F.; Prenda, J. Assessing Freshwater Fish Sensitivity to Different Sources of Perturbation in a Mediterranean Basin. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2009, 18, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Martí, E.; García-Berthou, E.; Sabater, S.; Tomanova, S.; Muñoz, I. Comparing Fish Assemblages and Trophic Ecology of Permanent and Intermittent Reaches in a Mediterranean Stream. Hydrobiologia 2010, 657, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.J.; Santos, J.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Mendes, A. Evaluating the Response of Biological Assemblages as Potential Indicators for Restoration Measures in an Intermittent Mediterranean River. Environ. Manage. 2010, 46, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootton, R.J. Ecology of Teleost Fishes; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandre, C.M.; Sales, S.; Ferreira, M.T.; Almeida, P.R. Food Resources and Cyprinid Diet in Permanent and Temporary Mediterranean Rivers with Natural and Regulated Flow. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2014, 24, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L. Landscape Filters and Species Traits: Towards Mechanistic Understanding and Prediction in Stream Ecology. J. North. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1997, 16, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Richter, B.D.; Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E.; Naiman, R.J.; Kendy, E.; Acreman, M.; Apse, C.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Freeman, M.C.; et al. The Ecological Limits of Hydrologic Alteration (ELOHA): A New Framework for Developing Regional Environmental Flow Standards. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Elvira, B.; Collares-Pereira, M.J.; Moyle, P.B. Life-History Traits of Non-Native Fishes in Iberian Watersheds across Several Invasion Stages: A First Approach. Biol. Invasions 2008, 10, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M.; Hermoso, V.; Aparicio, E.; Godinho, F.N. Biodiversity in Heavily Modified Waterbodies: Native and Introduced Fish in Iberian Reservoirs. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, P.A.; Sagnes, P.; Laroche, J. Variability in the Growth Rate of Chub Leuciscus Cephalus along a Longitudinal River Gradient. J. Fish. Biol. 2009, 74, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M.; Blanco-Garrido, F.; Prenda, J. Invasive Species and Habitat Degradation in Iberian Streams: An Analysis of Their Role in Freshwater Fish Diversity Loss. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytle, D.A. Disturbance Regimes and Life-History Evolution. Am. Nat. 2001, 157, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mims, M.C.; Olden, J.D. Life History Theory Predicts Fish Assemblage Response to Hydrologic Regimes. Ecology 2012, 93, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Gispert, A.; Moreno-Amich, R. Mass-Length Relationship of Mediterranean Barbel as an Indicator of Environmental Status in South-West European Stream Ecosystems. J. Fish. Biol. 2001, 59, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerhans, R.B. Predictability of Phenotypic Differentiation across Flow Regimes in Fishes. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2008, 48, 750–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, C.M.; Quintella, B.R.; Ferreira, A.F.; Romão, F.A.; Almeida, P.R. Swimming Performance and Ecomorphology of the Iberian Barbel Luciobarbus Bocagei (Steindachner, 1864) on permanent and temporary rivers. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2014, 23, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, I.; Santos, J.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Pinheiro, A. Barbel Habitat Alterations Due to Hydropeaking. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2015, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.M.; Ferreira, A.P.; Ferreira, M.T. Intrabasin Variations in Age and Growth of Barbus Bocagei Populations. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2002, 18, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merciai, R.; Molons-Sierra, C.; Sabater, S.; García-Berthou, E. Water Abstraction Affects Abundance, Sizestructure and Growth of Two Threatened Cyprinid Fishes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marr, S.M.; Olden, J.D.; Leprieur, F.; Arismendi, I.; Ćaleta, M.; Morgan, D.L.; Nocita, A.; Šanda, R.; Serhan Tarkan, A.; García-Berthou, E. A Global Assessment of Freshwater Fish Introductions in Mediterranean-Climate Regions. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leunda, P.M. Impacts of Non-Native Fishes on Iberian Freshwater Ichthyofauna: Current Knowledge and Gaps. Aquat. Invasions 2010, 5, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández, V.; Solana-Gutiérrez, J.; García de Jalón, D.; Alonso, C. Sign, Strength and Shape of Stream Fish-Based Metric Responses to Geo-Climatic and Human Pressure Gradients. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M.; García-Berthou, E. Homogenization Dynamics and Introduction Routes of Invasive Freshwater Fish in the Iberian Peninsula. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucherousset, J.; Olden, J.D. Ecological Impacts of Non-Native Freshwater Fishes. Fisheries 2011, 36, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Berthou, E.; Almeida, D.; Benejam, L.; Magellan, K.; Bae, M.J.; Casals, F.; Merciai, R. Impacto Ecológico de Los Peces Continentales Introducidos En La Península Ibérica. Ecosistemas 2015, 24, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, P.A.; Velasco, J.C.; González-Sánchez, N.; Pollo, C. Fish Assemblages in Small Streams in Western Spain: The Influence of an Introducer Predator. Arch. Fur Hydrobiol. 1990, 118, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez, J.; Pena, J.C. Alimentación de Lucio Exos Lucius En Un Área de Reciente Colonización (Cuenca Del Esla, Noroeste de España). Variaciones En Función de La Talla. Ecología 2001, 15, 293–308. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Bote, J.L.; Roso, R. Diet of the Introduced Pikeperch Sander Lucioperca (L.) (Osteichthyes, Percidae) in a Recent Colonised Reservoir in South-Western Iberian Peninsula. Ital. J. Zool. 2012, 79, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, R.; Soriguer, M.C.; Villar, N.; Hernando, J.A. The Dynamics of Fish Populations in the Palancar Stream, a Small Tributary of the River Guadalquivir, Spain. Acta Oecologica 2001, 22, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettori, E.E.; Balestrieri, A.; Zapata-Pérez, V.M.; Bruno, D.; Rubio-Saura, N.; Robledano-Aymerich, F. Distribution and Diet of Recovering Eurasian Otter (Lutra Lutra) along the Natural-to-Urban Habitat Gradient (River Segura, SE Spain). Urban Ecosyst. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Gillingham, P.K.; Robert Britton, J. Shifts in the Climate Space of Temperate Cyprinid Fishes Due to Climate Change Are Coupled with Altered Body Sizes and Growth Rates. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3221–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Shukla, P.R., Skea, J., Calvo Buendia, E., Masson-Delmotte, V., Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D.C., Zhai, P., Slade, R., Connors, S., van Diemen, R., et al., Eds.; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).