Numerical Study on the Hydrologic Characteristic of Permeable Friction Course Pavement
Abstract
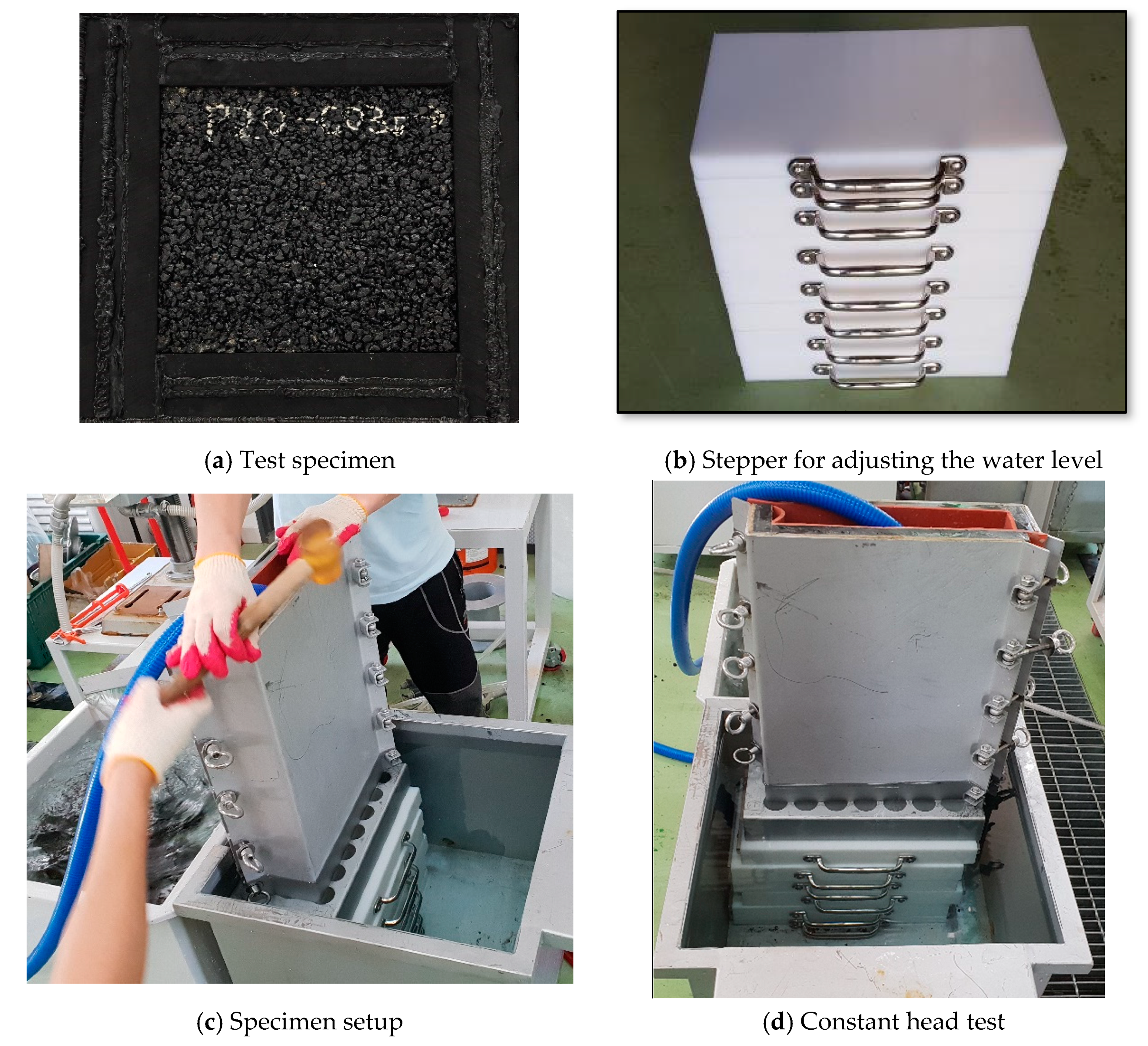
:1. Introduction
2. Water Flow in a PFC Pavement
3. Modeling of Water Flow in a PFC Pavement and Analysis Parameters
3.1. Transient Unsaturated/Saturated Seepage
3.2. Geometric Dimensions
3.3. Boundary Conditions
3.4. Analysis Cases
3.5. Material Parameters
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Time Taken for Water Flow over the PFC Pavement Surface
4.2. Effect of Geometric Design
4.3. Allowable Rainfall Intensity for the PFC Pavement
4.4. Effects of Thickness and Porosity
4.5. Design Charts for PFC Pavement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, L.; Tang, B.; Fwa, T. Evaluation of functional characteristics of laboratory mix design of porous pavement materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 191, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yu, J.; Song, W.; Zou, J.; Song, Q.; Zhou, L. A critical state-of-the-art review of durability and functionality of open-graded friction course mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, Z.; Shibata, S. Assessment of Rain Garden Effects for the Management of Urban Storm Runoff in Japan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B.K. Porous Pavements; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Manrique-Sanchez, L.; Caro, S. Numerical assessment of the structural contribution of porous friction courses (PFC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, B.J.; Winston, R.J.; Hunt, W.F.; Barrett, M.E. Water quality of drainage from permeable friction course. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 138, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbee, R.; Rijs, G.; De Brouwer, R.; van Velzen, L. Characterization and treatment of runoff from highways in the Netherlands paved with impervious and pervious asphalt. Water Environ. Res. 1999, 71, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseen, R.M.; Ballestero, T.P.; Houle, J.J.; Avellaneda, P.; Briggs, J.; Fowler, G.; Wildey, R. Seasonal performance variations for storm-water management systems in cold climate conditions. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Fwa, T.; Chai, K. Drainage considerations for porous asphalt surface course design. Transp. Res. Rec. 2004, 1868, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V. Runoff control in porous pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. 2002, 1789, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Feng, S.; Huo, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, S. Experimental study on rainfall-runoff relation for porous pavements. Hydrol. Res. 2008, 39, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charbeneau, R.J.; Barrett, M.E. Drainage hydraulics of permeable friction courses. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Shen, C. Coupled two-dimensional surface flow and three-dimensional subsurface flow modeling for drainage of permeable road pavement. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 04016051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRCS, U. Urban Hydrology for Small Watersheds-Technical Release 55; US Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation: Washington, DC, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- LeFevre, N.-J.B.; Watkins, D.W., Jr.; Gierke, J.S.; Brophy-Price, J. Hydrologic performance monitoring of an underdrained low-impact development storm-water management system. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2010, 136, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.-G.; Sandoval, N.; Lin, W.; Kim, H.; Cho, Y.-H. A case study: Evaluation of water storage capacity in permeable block pavement. KSCE J. Civil Eng. 2014, 18, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Valeo, C.; He, J.; Chu, A. Three types of permeable pavements in cold climates: Hydraulic and environmental performance. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, G. Seepage Hydraulics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Thode, R.; Gitirana, G. Theory Manual of Saturated/Unsaturated Finite Element. 2D/3D Seepage Modeling; SVFlux, SoilVision Systems Ltd: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fredlund, M. User’s Manual for SVFlux, Saturated-Unsaturated Numerical Modeling; SoilVision Systems: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- AASHTO, A. Policy on geometric design of highways and streets. Am. Assoc. State Highw. Transp. Off. Wash. DC 2001, 1, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.; Nguyen, T.H.; Lee, E.; Lee, Y.; Ahn, J. Measurement of Permeability in Horizontal Direction of Open-Graded Friction Course with Rutting. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Marcaida, A.K.; Lee, Y.; Jung, J. Development of Test Equipment for Evaluating Hydraulic Conductivity of Permeable Block Pavements. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, B.K.; Kim, Y.T.; (Department of Ocean Engineering, Pukyong National University, Busan, Korea). Personal Communication, 2012.
- Fredlund, D.G.; Xing, A. Equations for the soil-water characteristic curve. Can. Geotech. J. 1994, 31, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GCTS Testing System. Available online: https://www.gcts.com/ (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Si, C.; Chen, E.; You, Z.; Zhang, R.; Qiao, P.; Feng, Y. Dynamic response of temperature-seepage-stress coupling in asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V.; Colonna, P.; Sansalone, J.J.; Sciddurlo, A. Measurement of hydraulic conductivity in porous mixes. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012, 2295, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Equivalent Length, LR (m) | Equivalent Slope, SR (%) | Rainfall Intensity, I (mm/h) |
|---|---|---|
| 10, 15, 20, 30 | 0.5, 2, 4, 6, 8 | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120 |
| Volumetric Water Content, θs (%) | Residual Volumetric Water Content, θr (%) | Material Parameters, | Soil Suction, Ψ (kPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | n | |||
| 20 | 0.001 | 2.23 | 1.63 | 0.01 |
| LR (m) | SR (%) | Time Taken for Water Flow over PFC Pavement Surface, tp (min) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I = 10 (mm/h) | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 | ||
| 10 | 0.5 | 60 | 30 | 20 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| 2 | 85 | 35 | 22 | 15.5 | 12.5 | 10 | 8.5 | 7.5 | 6.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5 | |
| 4 | - | 49 | 26 | 18 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5.5 | 5 | |
| 6 | - | - | 35 | 21 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 5 | |
| 8 | - | - | - | 26 | 18 | 13.5 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5.5 | |
| 15 | 0.5 | 60 | 30 | 19 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| 2 | 75 | 33.5 | 21 | 15.5 | 12 | 10 | 8.5 | 7.5 | 6 | 5.5 | 5 | 4.5 | |
| 4 | - | 41 | 24 | 17 | 13 | 10.5 | 9 | 7.5 | 6.5 | 6 | 5.5 | 4.5 | |
| 6 | - | 55.5 | 28 | 19 | 14 | 11.5 | 9.5 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5.5 | 5 | |
| 8 | - | - | 34 | 21 | 15.5 | 12 | 10 | 8.5 | 7.5 | 6.5 | 6 | 5 | |
| 20 | 0.5 | 60 | 30 | 19 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| 2 | 71 | 33 | 21 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| 4 | 104 | 38 | 23 | 16 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| 6 | - | 45 | 25 | 17 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| 8 | - | 59 | 29 | 19 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | |
| 30 | 0.5 | 59 | 30 | 19 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| 2 | 67 | 32 | 20 | 15 | 12 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| 4 | 84 | 35 | 21 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| 6 | 115 | 39 | 23 | 16 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| 8 | - | 45 | 25 | 17 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| Length, LR (m) | Slope, SR (%) | Allowable Rainfall Intensity, Ia (mm/h) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 7.5 | |
| 4 | 15 | |
| 6 | 22.5 | |
| 8 | 30 | |
| 15 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 5 | |
| 4 | 10 | |
| 6 | 15 | |
| 8 | 20 | |
| 20 | 0.5 | 1 |
| 2 | 2.5 | |
| 4 | 5 | |
| 6 | 10 | |
| 8 | 15 |
| Thickness, T (m) | Porosity, n (%) | Time Taken for Water Flow over PFC Pavement Surface, tp (min) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 10 | 6 |
| 20 | 12.5 | |
| 0.1 | 10 | 13.5 |
| 20 | 27.5 |
| Thickness, T (m) | Porosity, n (%) | Time Taken for Water Flow over PFC Pavement Surface, tp (min) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 10 | 2.5 |
| 20 | 5.5 | |
| 0.1 | 10 | 6 |
| 20 | 12 |
| SR (%) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I/k = 0.0003 | 0.0006 | 0.0008 | 0.0011 | 0.0014 | 0.0017 | 0.0019 | 0.0022 | 0.0025 | 0.0028 | 0.0031 | 0.0033 | ||
| 200 | 0.5 | 3.6 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 0.84 | 0.66 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.24 |
| 2 | 5.1 | 2.1 | 1.32 | 0.93 | 0.75 | 0.6 | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.3 | |
| 4 | - | 2.94 | 1.56 | 1.08 | 0.84 | 0.66 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.3 | |
| 6 | - | - | 2.1 | 1.26 | 0.9 | 0.72 | 0.6 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.3 | |
| 8 | - | - | - | 1.56 | 1.08 | 0.81 | 0.66 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.33 | |
| 300 | 0.5 | 1.8 | 0.9 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.12 |
| 2 | 2.25 | 1.005 | 0.63 | 0.465 | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.255 | 0.225 | 0.18 | 0.165 | 0.15 | 0.135 | |
| 4 | - | 1.23 | 0.72 | 0.51 | 0.39 | 0.315 | 0.27 | 0.225 | 0.195 | 0.18 | 0.165 | 0.135 | |
| 6 | - | 1.665 | 0.84 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 0.345 | 0.285 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.165 | 0.15 | |
| 8 | - | - | 1.02 | 0.63 | 0.465 | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.255 | 0.225 | 0.195 | 0.18 | 0.15 | |
| 400 | 0.5 | 1.8 | 0.9 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.12 |
| 2 | 2.13 | 0.99 | 0.63 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| 4 | 3.12 | 1.14 | 0.69 | 0.48 | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| 6 | - | 1.35 | 0.75 | 0.51 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| 8 | - | 1.77 | 0.87 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.15 | |
| 600 | 0.5 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.08 |
| 2 | 1.34 | 0.64 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.08 | |
| 4 | 1.68 | 0.7 | 0.42 | 0.3 | 0.24 | 0.2 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.08 | |
| 6 | 2.3 | 0.78 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.2 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.08 | |
| 8 | - | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.2 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.08 | |
| Slope, SR (%) | Time, tp (h) | Time, tp (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.44 | 0.183 | 11 |
| 2 | 0.48 | 0.2 | 12 |
| 4 | 0.50 | 0.217 | 12.5 |
| 6 | 0.52 | 0.233 | 13 |
| 8 | 0.60 | 0.25 | 15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.H.; Ahn, J. Numerical Study on the Hydrologic Characteristic of Permeable Friction Course Pavement. Water 2021, 13, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13060843
Nguyen TH, Ahn J. Numerical Study on the Hydrologic Characteristic of Permeable Friction Course Pavement. Water. 2021; 13(6):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13060843
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Tan Hung, and Jaehun Ahn. 2021. "Numerical Study on the Hydrologic Characteristic of Permeable Friction Course Pavement" Water 13, no. 6: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13060843






