Restoration of Seagrass Meadows in the Mediterranean Sea: A Critical Review of Effectiveness and Ethical Issues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Are Seagrasses on the Decline in the Mediterranean Sea?
2.1. Posidonia Oceanica
2.2. Zostera Marina
2.3. Zostera Noltei
2.4. Cymodocea Nodosa
2.5. Ruppia Maritima
2.6. Halophila Stipulacea
2.7. All Seagrasses
3. Concerning Natural Recolonization
4. The Techniques of Seagrass Restoration
4.1. Cement Slabs with Holes
4.2. Cement Frames around a Wire Mesh Retaining Cuttings
4.3. Metallic, Plastic, or Biodegradable Wire Grid, Laid Flat on the Bottom, Retaining Cuttings
4.4. Fixing the Cuttings to the Bottom by Means of Stakes or Staples
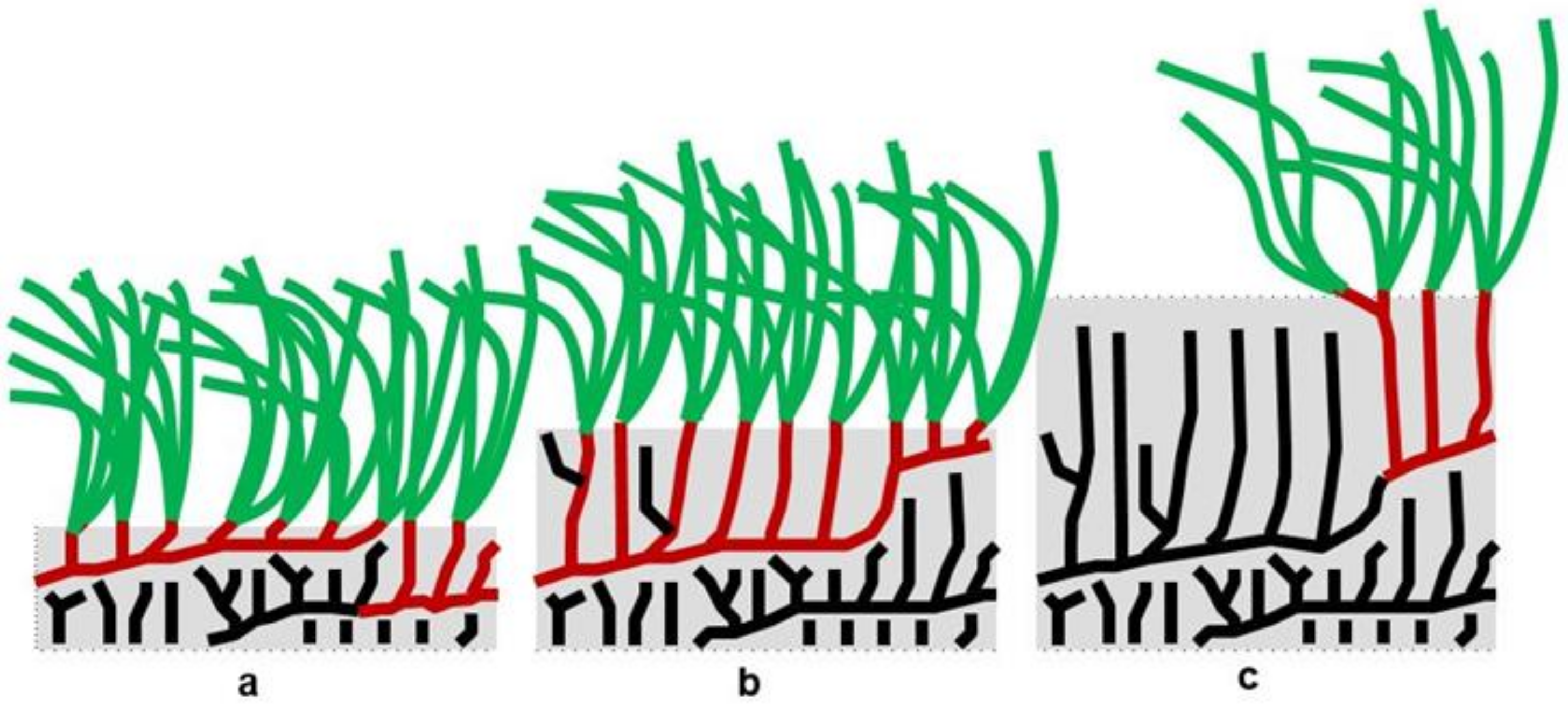
4.5. The Digging of Holes in which Blocks of Matte are Placed, and Similar Techniques
4.6. Planting of Seedlings, Germinated in the Laboratory
4.7. Planting Seeds
5. Seagrass Restoration: Where? When? Why?
5.1. The Diversity of Ecosystems Does Matter
5.2. Seagrass Restoration: Where?
5.3. Seagrass Restoration as a Pretext for Future Destruction?
5.4. Why Restore Seagrass Meadows and When?
- The exact site and the biotope where the transplanting will be done must have been occupied previously by P. oceanica.
- The causes of the disappearance of P. oceanica (pollution, trawling, anchorage, etc.) from the site where the transplanting will be done must have ceased to operate. Thus, before any transplanting is done, it must be demonstrated that the meadows or isolated clumps of P. oceanica that are nearest to the transplanting site have started a process of natural recolonization.
- Transplanting must not be done near very extensive meadows. It is useless to add several dozen or hundreds of square metres (0.001 to 0.01 ha) to a meadow consisting of several hundreds or thousands of hectares.
- Transplanting must not be done to compensate for the destruction of a meadow. To avoid such abuse, no transplanting must be done within a distance of 10 km from the site of deliberate destruction of a meadow (as part of coastal development) for a 10-year period.
- However, transplanting on the exact site of the temporary destruction of a meadow may be possible, at least in the countries where the legal protection of P. oceanica is not opposed to this. This is the case when an open trench for an archaeological dig is covered over, or a pipe (or cable) crossing a meadow is buried.
- With the exception of this special case above (point 5), any transplanting of P. oceanica must be undertaken after experimental transplanting of several hundred cuttings; scientific monitoring for at least 3 years must show that the experiment has been a success before a larger scale operation can be envisaged.
- The removal of cuttings for transplanting must not endanger existing meadows. Therefore, it must be spread over a large area of meadow (less than 2 cuttings/m2). The use of cuttings detached naturally, although giving less good results, or plantlets from seeds, can also be envisaged.
- Lastly, transplanting must be done within an overall strategy of P. oceanica meadow management of the concerned region.
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christenhusz, M.J.M.; Byng, J.W. The number of known plant species in the world and its annual increase. Phytotaxa 2016, 261, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chambers, P.A.; Lacoul, P.; Murphy, K.J.; Thomaz, S.M. Global diversity of aquatic macrophytes in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hartog, C.; Kuo, J. Taxonomy and biogeography of seagrasses. In Seagrass Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. Ruppia maritima. In AlgaeBase; World-Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland: Galway, Ireland, 2020; Available online: https://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Duarte, C.M.; Kennedy, H.; Marbà, N.; Holmer, M.; Mateo, M.A.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Kendrick, G.A.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Mcglathery, K.J.; et al. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Pergent, G.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Ruitton, S.; Thibaut, T.; Verlaque, V. The necromass of the Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadow: Fate, role, ecosystem services and vulnerability. Hydrobiologia 2016, 781, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johannessen, S.C.; Macdonald, R.W. Geoengineering with seagrasses: Is credit due where credit is given? Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nordlund, L.M.; Koch, E.W.; Barbier, E.B.; Creed, J.C. Seagrass ecosystem services and their variability across genera and geographical regions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Falco, G.; Molinaroli, E.; Conforti, A.; Simeone, S.; Tonielli, R. Biogenic sediments from coastal ecosystems to Beach-Dune Systems: Implications for the adaptation of mixed and carbonate beaches to future sea level rise. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 3191–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pergent-Martini, C.; Pergent, G.; Monnier, B.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Mori, C.; Valette-Sansevin, A. Contribution of Posidonia oceanica meadows in the context of climate change mitigation in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 165, 105236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Bernard, G.; Pergent, G.; Shili, A.; Verlaque, M. Regression of Mediterranean seagrasses caused by natural processes and anthropogenic disturbances and stress: A critical review. Bot. Mar. 2009, 52, 395–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz, J.M.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Enríquez, S. Mediterranean seagrasses. Bot. Mar. 2009, 52, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Verlaque, M. Does the seagrass Posidonia really occur in Madagascar? Phycologia 2008, 47, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shili, A.; Ben Maiz, N.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Trabelsi, E.B. Abrupt changes in Potamogeton and Ruppia beds in a Mediterranean lagoon. Aquat. Bot. 2007, 87, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Por, F.D. Lessepsian Migrations: The Influx of Red Sea Biota into the Mediterranean by Way of the Suez Canal; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978; pp. 8–228. [Google Scholar]
- Gerakaris, V.; Lardi, P.I.; Issaris, Y. First record of the tropical seagrass species Halophila decipiens Ostenfeld in the Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Bot. 2020, 160, 103151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, G.; Beer, S.; Willette, D.A.; Viana, I.G.; Chiquillo, K.L.; Beca-Carretero, P.; Villamayor, B.; Azcárate-García, T.; Shem-Tov, R.; Mwabvu, B.; et al. The tropical seagrass Halophila stipulacea: Reviewing what we know from its native and invasive habitats, alongside identifying knowledge gaps. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Dennison, W.B.; Duarte, C.M.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Hughes, A.R.; Hendrick, G.A.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Olyarnik, S.; et al. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. BioScience 2006, 56, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waycott, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Olyarnik, S.; Calladine, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Hughes, A.R.; et al. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12377–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coles, R.; Grech, A.; McKenzie, L. Seagrass under pressure. Seagrass Watch 2013, 47, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; van Keulen, M.; Coles, R.G. Seagrass meadows in a globally changing environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuya, F.; Vila, F.; Bergasa, O.; Zarranz, M.; Espino, F.; Robaina, R.R. Artificial seagrass leaves shield transplanted seagrass seedlings and increase their survivorship. Aquat. Bot. 2017, 136, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen-Unsworth, L.C.; Unsworth, R. A call for seagrass protection. Science 2018, 261, 446–447. [Google Scholar]
- de Los Santos, C.B.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Alcoverro, T.; Marbà, N.; Duarte, C.M.; van Katwijk, M.M.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J.; Sanchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Roca, G.; et al. Recent trend reversal for declining European seagrass meadows. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.M.; Dalby, O.; Kendrick, G.A.; Statton, J.; Sinclair, E.A.; Fraser, M.W.; MacReadie, P.I.; Gillies, C.L.; Coleman, R.A.; Waycott, M.; et al. Seagrass restoration is possible: Insights and lessons from Australia and New Zealand. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hartog, C. The Sea-Grasses of the World; North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1970; p. 275. [Google Scholar]
- Short, F.T.; Ibelings, B.W.; den Hartog, C. Comparison of a current eelgrass disease to the wasting disease in the 1930s. Aquat. Bot. 1988, 30, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesen, W.B.J.T.; van Katwijk, M.M.; den Hartog, C. Eelgrass condition and turbidity in the Dutch Wadden Sea. Aquat. Bot. 1990, 37, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hartog, C. Sudden declines of seagrass beds: ‘Wasting disease’ and other disasters. In Seagrass Biology: Proceedings of an International Workshop, Rottnest Island, Australia, 25–29 January 1996; Kuo, J., Phillips, R.C., Walker, D.I., Kirkman, H., Eds.; University Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 1996; pp. 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Ralph, P.J.; Short, F.T. Impact of the wasting disease pathogen, Labyrinthula zosterae, on the photobiology of eelgrass Zostera marina. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 226, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.L.; Orth, R.J. Genetic diversity and structure of natural and transplanted eelgrass populations in the Chesapeake and Chincoteague Bays. Estuaries 1998, 21, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Katwijk, M.M.; Bos, A.R.; de Jonge, V.N.; Hanssen, L.S.A.M.; Hermus, D.C.R.; de Jonge, D.J. Guidelines for seagrass restoration: Importance of habitat selection and donor population, spreading of risks, and ecosystem engineering effects. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, J.L.; Urra, J.; Marina, P.; Mateo, Á.; Salas, C.; Gofas, S. Loss of Zostera marina in southern Spain and effects on its associated molluscan assemblage. In Proceedings of the 4th Mediterranean Symposium on Marine Vegetation, Yasmine-Hammamet, Tunisia, 2–4 December 2010; El Asmi, S., Langar, H., Belkacem, W., Eds.; RAC/SPA Publications: Tunis, Tunisia, 2010; pp. 212–214. [Google Scholar]
- Auby, I.; Rigouin, L.; Trut, G.; Oger-Jeanneret, H.; Ganthy, F.; Trut, F.; Gouriou, L.; Bujan, S.; Devaux, L.; Gouillieux, B.; et al. Suivi Stationnel (2006–2015) des Herbiers de Zostères (Zostera noltei et Zostera marina) et Calcul de L’indicateur ‘Angiospermes’ (2015) Dans la Masse D’eau Côtière FRFC06—Arcachon Amont—Bassin Hydrographique Adour-Garonne; Ifremer Publications: Paris, France, 2016; p. 50. [Google Scholar]
- Lefcheck, J.S.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Wilcox, D.J.; Murphy, R.R.; Keisman, J.; Gurbisz, C.; Hannam, M.; Landry, J.B.; Moore, K.A.; et al. Long-term nutrient reductions lead to the unprecedented recovery of a temperate coastal region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3658–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulo, D.; Cunha, A.H.; Boavida, J.; Serrão, E.A.; Gonçalves, E.J.; Fonseca, M. Open coast seagrass restoration. Can we do it? Large scale seagrass transplants. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walter, R.K.; O’Leary, J.K.; Vitousek, S.; Taherkhani, M.; Geraghty, C.; Kitajima, A. Large-scale erosion driven by intertidal eelgrass loss in an estuarine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 243, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Correa, J.M.; Bayle-Sempere, J.T.; Sánchez-Jerez, P.; Valle, C. Posidonia oceanica meadows are not declining globally. Analysis of population dynamics in marine protected areas of the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 336, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonacorsi, M.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Bréand, N.; Pergent, G. Is Posidonia oceanica regression a general feature in the Mediterranean Sea? Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2013, 14, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leriche, A.; Pasqualini, V.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Bernard, G.; Bonhomme, P.; Clabaut, P.; Denis, J. Spatial, temporal and structural variations of a Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadow facing human activities. Aquat. Bot. 2006, 84, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boero, F. Scientists can be free, but only once they are tenured. Ethics Sci. Environ. Politics 2015, 15, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, C.M.; Fulweiler, R.W.; Lovelock, C.E.; Martinetto, P.; Saunders, M.I.; Pandolfi, J.M.; Gelcich, S.; Nixon, S.W. Reconsidering ocean calamities. BioScience 2015, 65, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvo, S.; Pirrotta, M.; Tomasello, A. Letter to the editor regarding the article “Taking advantage of seagrass recovery potential to develop novel and effective meadow rehabilitation methods” by Alagna et al., published in Marine Pollution Bulletin, 149: 2019 (110578). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeusne, C.; Chevaldonné, P.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Perez, T. Climate change effects on a miniature ocean: The highly diverse, highly impacted Mediterranean Sea. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leriche, A.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Bernard, G.; Bonhomme, P.; Denis, J. A one-century suite of seagrass bed maps: Can we trust ancient maps? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 59, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astruch, P.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Bonhomme, D.; Goujard, A.; Antonioli, P.A.; Bonhomme, P.; Perez, T.; Ruitton, S.; de Saint-Martin, T.; Verlaque, M. Mapping and state of conservation of benthic marine habitats and assemblages of Port-Cros National Park (Provence, France, Northwestern Mediterranean Sea). Sci. Rep. Port-Cros Natl. Park 2012, 26, 45–90. [Google Scholar]
- Pergent-Martini, C.; Valette, A.; Damier, É.; Pergent, G. L’évaluation surfacique des habitats est-elle un indicateur fiable de la dynamique spatio-temporelle en milieu marin? In Proceedings of the Colloque National de Cartographie des Habitats Marins: CARAMB’AR, Brest, France, 14–16 March 2017; pp. 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Valette-Sansevin, A.; Pergent, G.; Buron, K.; Damier, E.; Pergent-Martini, C. Continuous mapping of benthic habitats along the coast of Corsica: A tool for the inventory and monitoring of blue carbon ecosystems. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2019, 20, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualini, V.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Pergent, G. Mediterranean coastal resources management: The example of the Island of Corsica. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference: Remote Sensing for Marine and Coastal Environments, Technology and Applications, Orlando, FL, USA; 1997; Volume 1, pp. 632–640. [Google Scholar]
- Paillard, M.; Gravez, V.; Clabaut, P.; Walker, P.; Blanc, J.J.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Belsher, T.; Urscheler, F.; Poydenot, F.; Sinnassamy, J.M.; et al. Cartographie de L’herbier de Posidonie et des Fonds Marins Environnants de Toulon à Hyères (Var, France). Reconnaissance par Sonar Latéral et Photographie Aérienne. Notice de Présentation; IFREMER and GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 1993; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Andromede Oceanologie. La Méditerranée Dévoile ses Dessous—Cartographie Continue des Habitats Marins; Partenariat Agence de L’EAU RMC—Andromède: Marseille, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Astier, J.M.; Taillez, P. Pour un plan d’occupation des fonds marins: Inventaire des herbiers de posidonies du littoral du Var. Ann. Soc. Sci. Nat. Archéol. Toulon Var 1984, 36, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Belsher, T.; Houlgatte, E.; Boudouresque, C.F. Cartographie de la prairie à Posidonia oceanica et des principaux facies sédimentaires marins du Parc national de Port-Cros (Var, France, Méditerranée). Sci. Rep. Port-Cros Natl. Park 2005, 21, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Molinier, R.; Picard, J. Recherches sur les herbiers de Phanérogames marines du littoral méditerranéen français. Ann. Inst. Océanogr. 1952, 27, 157–234. [Google Scholar]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Bernard, G.; Bonhomme, P.; Charbonnel, E.; Diviacco, G.; Meinesz, A.; Pergent, G.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Ruitton, S.; Tunesi, L. Protection and Conservation of Posidonia oceanica Meadows; RAMOGE and RAC/SPA Publications: Tunis, Tunisia, 2012; p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- Libes, M.; Boudouresque, C.F. Uptake and long-distance transport of carbon in the marine phanerogam Posidonia oceanica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1987, 38, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, A.; Calvo, S.; Di Maida, G.; Lovison, G.; Pirrotta, M.; Sciandra, M. Shoot age as a confounding factor on detecting the effect of human-induced disturbance on Posidonia oceanica growth performance. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 343, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Jeudy de Grissac, A.; Meinesz, A. Un nouveau type d’herbier à Posidonia oceanica: L’herbier de colline. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Mediterr. 1985, 29, 173–175. [Google Scholar]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Thommeret, J.; Thommeret, Y. Sur la Découverte D’un Bioconcrétionnement Fossile Intercalé dans L’herbier à Posidonia oceanica de la Baie de Calvi (Corse); CIESM Publications: Monaco, Monaco, 1980; pp. 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Diviacco, G.; Virno-Lamberti, C.; Spada, E. Osservazioni sulla prateria di Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile di ‘Marina di Tarquinia’ (Lazzio settentrionale). Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 1999, 6, 496–499. [Google Scholar]
- Diviacco, G.; Spada, E.; Virno-Lamberti, C. Le Fanerogame marine del Lazio. Descrizione e Cartografia Delle Praterie di Posidonia oceanica e Dei Prati di Cymodocea Nodosa; ICRAM Publications: Rome, Italy, 2001; p. 113. [Google Scholar]
- Abadie, A.; Gobert, S.; Bonacorsi, M.; Lejeune, P.; Pergent, G.; Pergent-Martini, C. Marine space ecology and seagrasses. Does patch type matters in Posidonia oceanica seascape? Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, S.; Lepoint, G.; Pelaprat, C.; Remy, F.; Lejeune, P.; Richir, J.; Abadie, A. Temporal evolution of sand corridors in a Posidonia oceanica seascape: A 15-year study. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2016, 17, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pergent, G.; Calvo, S.; Cancemi, G.; Djellouli, A.; Dupuy de La Granrive, R.; Langar, H.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Tomasello, A. Nouvelles Connaissances sur les Herbiers Tigrés de Méditerranée. In Proceedings of the 4th Mediterranean Symposium on Marine Vegetation, Yasmine-Hammamet, Tunisia, 2–4 December 2010; El Asmi, S., Langar, H., Belkacem, W., Eds.; RAC/SPA Publications: Tunis, Tunisia, 2010; pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Coppa, S.; Quattrocchi, G.; Cucco, A.; de Lucia, G.A.; Vencato, S.; Camedda, A.; Domenici, P.; Conforti, A.; Satta, A.; Tonielli, R.; et al. Self-organisation in striped seagrass meadows affects the distributional pattern of the sessile bivalve Pinna nobilis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravez, V.; Nieri, M.; Boudouresque, C.F. Surveillance de L’herbier de Posidonie de La Baie du Prado (Marseille). Rapport de Synthèse 1986–1992; Direction Générale des Services Techniques de La Ville de Marseille et GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 1992; p. 80. [Google Scholar]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Astruch, P.; Goujard, A.; Rouanet, É.; Bonhomme, D.; Bonhomme, P. The withdrawal of the lower limit of the Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadow in the Bay of Hyères (NW Mediterranean): A combination of natural and human-induced recent and ancient phenomena? In Proceedings of the 6th Mediterranean Symposium on Marine Vegetation, Antalya, Turkey, 14–15 January 2019; Langar, H., Ouerghi, A., Eds.; RAC/SPA Publications: Tunis, Tunisia, 2019; pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, G.M. Coral clues to rapid sea-level change. Science 2005, 308, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichter, M.; Zviely, D.; Klein, M.; Sivan, D. Sea-level changes in the Mediterranean: Past, present and future—A review. In Seaweeds and Their Role in Globally Changing Environments; Israel, A., Einav, R., Seckbach, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Vacchi, M.; Ghilardi, M.; Spada, G.; Currás, A.; Robresco, S. New insights into the sea-level evolution in Corsica (NW Mediterranean) since the late Neolithic. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 12, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborel, J.; Morhange, C.; Lafont, R.; Le Campion, J.; Laborel-Deguen, F.; Sartoretto, S. Biological evidence of sea-level rise during the last 4500 years on the rocky coasts of continental southwestern France and Corsica. Mar. Geol. 1994, 120, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.G.; Kominz, M.A.; Browning, J.V.; Wright, J.D.; Mountain, G.S.; Katz, M.E.; Sugarman, P.J.; Cramer, B.S.; Christie-Blick, N.; Pekar, S.F. The Phanerozoic record of global sea-level change. Science 2005, 310, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanc, J.J.; Jeudy de Grissac, A. Recherches de Géologie Sédimentaire sur Les Herbiers à Posidonies du Littoral de la Provence; CNEXO Publications: Paris, France, 1978; p. 185. [Google Scholar]
- Deter, J.; Guibert, A.; Freschet, E.; Boissery, P.; Holon, F. Assessment on 90 years of coastal development in France and consequences for Posidonia oceanica beds. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Mediterr. 2013, 40, 520. [Google Scholar]
- Holon, F.; Boissery, P.; Guilbert, A.; Freschet, E.; Deter, J. The impact of 85 years of coastal development on shallow seagrass beds (Posidonia oceanica L. (Delile)) in South Eastern France: A slow but steady loss without recovery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 165, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Esplá, A.A.; Aranda, A.; Gras, D.; Guillen, J.E. Impactos sobre las praderas de Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile en el SE español: Necesidad de establecer herramientas de ordenamiento y gestión del litoral. In Pour Qui la Méditerranée au 21 Siècle ? Villes des Rivages et Environnement Littoral en Méditerranée; Ville de Montpellier Publications: Montpellier, France, 1994; pp. 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Peirano, A.; Damasso, V.; Montefalcone, M.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. Effects of climate, invasive species and anthropogenic impacts on the growth of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile in Liguria (NW Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, L.; Belluscio, A.; Criscoli, A.; Ardizzone, G.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Fraschetti, S.; Gristina, M.; Knittweis, L.; Martin, C.S.; Pergent, G.; et al. Seagrass meadows (Posidonia oceanica) distribution and trajectories of change. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgos, E.; Montefalcone, M.; Ferrari, M.; Paoli, C.; Vassallo, P.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. Ecosystem functions and economic wealth: Trajectories of change in seagrass meadows. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbà, N.; Díaz-Almela, E.; Duarte, C.M. Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) loss between 1842 and 2009. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 176, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, G.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Picon, P. Long term changes in Zostera meadows in the Berre lagoon (Provence, Mediterranean Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 73, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, G.; Bonhomme, P.; Boudouresque, C.F. Recovery of the seagrass Zostera marina in a disturbed Mediterranean lagoon (Etang de Berre, Bouches-du-Rhône, Southern France). Hydrobiologia 2005, 539, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plus, M.; Chapelle, A.; Lazure, P.; Auby, I.; Levavasseur, G.; Verlaque, M.; Belsher, T.; Deslous-Paoli, J.M.; Zaldívar, J.M.; Murray, C.N. Modelling of oxygen and nitrogen cycling as a function of macrophyte community in the Thau lagoon. Cont. Shelf Res. 2003, 23, 1877–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rismondo, A.; Curiel, D.; Scarton, F.; Mion, D.; Caniglia, G. A new seagrass map for the Venice Lagoon. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on the Mediterranean Coastal Environment, Ravenna, Italy, 7–11 October 2003; Middle East Technical University Publications: Ankara, Turkey, 2003; pp. 843–852. [Google Scholar]
- Sfriso, A.; Buosi, A.; Tomio, Y.; Juhmani, A.-S.; Facca, C.; Sfriso, A.A.; Franzoi, P.; Scapin, L.; Bonometto, A.; Ponis, E.; et al. Aquatic angiosperm transplantation: A tool for environmental management and restoring in transitional water systems. Water 2019, 11, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shili, A.; Trabelsi, E.B.; Ben Maiz, N. Benthic macrophyte communities in the Ghar El Melh Lagoon (North Tunisia). J. Coast. Conserv. 2002, 8, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergent-Martini, C. Protection des Habitats D’herbiers de Phanérogames Marines de Méditerranée. Les Etudes D’impacts en Milieu Marin; Centre d’Activités Régionales Aires Spécialement Protégées (Plan d’Action Pour La Méditerranée) Publications: Tunis, Tunisia, 2000; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Zaouali, J. Flore et faune benthiques de deux lagunes tunisiennes: Le lac de Bizerte, Tunisie septentrionale, et la mer de Bou Grara, Tunisie méridionale. Bull. Off. Natl. Pêche Tunis. 1980, 4, 169–200. [Google Scholar]
- Barrajón, A.; Moreno, D.; Pérez Lloréns, J.L. Las praderas de Zostera marina. Distribución en Andalucía. In Praderas y Bosques Marinos de Andalucía; Luque, A.A., Templado, J., Eds.; Consejería de Medio Ambiente: Sevilla, Spain, 2004; p. 336. [Google Scholar]
- Pergent, G.; Bazairi, H.; Bianchi, C.N.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Buia, M.C.; Clabaut, P.; Harmelin-Vivien, M.; Mateo, M.A.; Montefalcone, M.; Morri, C.; et al. Mediterranean Seagrass Meadows: Resilience and Contribution to Climate Change Mitigation. A Short Summary; IUCN Publications: Gland, Switzerland; Málaga, Spain, 2012; p. 40. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, A.H.; Assis, J.F.; Serrão, E.A. Seagrasses in Portugal: A most endangered marine habitat. Aquat. Bot. 2013, 104, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillas, P.; Charpentier, A.; Auby, I.; Lescuyer, F.; Coulet, E. Spatial dynamics of Zostera noltii over a 5-year period of fluctuating salinity in the Vaccarès Lagoon, France. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2000, 7, 377–380. [Google Scholar]
- Charpentier, A.; Grillas, P.; Lescuyer, F.; Coulet, E.; Auby, I. Spatio-temporal dynamics of a Zostera noltii dominated community over a period of fluctuating salinity in a shallow lagoon, Southern France. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petit, G.; Aleem, A.A. Caractéristiques et évolution de la végétation d’un étang des Pyrénées-Orientales. C.R. Hebd. Séances Acad. Sci. 1952, 235, 632–634. [Google Scholar]
- Hervé, P.; Bruslé, J. L’étang de Canet-Saint-Nazaire (P.O.). Ecologie générale et ichtyofaune. Life Environ. 1981, 31, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Scarton, F.; Curiel, D.; Rismondo, A. Aspetti della dinamica temporal di praterie a Fanerogame marine in laguna di Venezia. Lav. Soc. Venez. Sci. Nat. 1995, 20, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Meinesz, A.; Javel, F.; Cottalorda, J.M.; Thibaut, T. Disparition des Phanérogames Marines Cymodocea nodosa et Nanozostera Noltii Dans la Lagune de L’anse de Port-Cros (Var) et Transplantation Expérimentale de C. nodosa. Rapport Laboratoire Environnement Marin Littoral—Université de Nice-Sophia Antipolis; LEML-UNSA Publications: Nice, France, 2005; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Haritonidis, S.; Diapoulis, A.; Nikolaidis, G. First results on the localisation of the herbiers of marine phanerogams in the Gulf of Thermaikos. Posidonia Newsl. 1990, 3, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Maiz, N.; Shili, A. Les peuplements phytobenthiques du Lac Nord de Tunis de 1926 à 2006. In Proceedings of the 3rd Mediterranean Symposium on Marine Vegetation, Marseille, France, 27–29 March 2007; RAC/SPA Publications: Tunis, Tunisia, 2007; pp. 247–249. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Ros, J.; Marcos, C.; Ballester, R.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M. Distribution and biomass of the macrophyte beds in a hypersaline coastal lagoon (the Mar Menor, SE Spain), and its recent evolution following major environmental changes. In Second International Workshop on Posidonia Beds; Boudouresque, C.F., Fresi, E., Gravez, V., Eds.; GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 1989; pp. 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; García-Charton, J.A.; Barcala, E.; Marcos, D. Changes in benthic fish assemblages as a consequence of coastal works in a coastal lagoon: The Mar Menor (Spain, Western Mediterranean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 53, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguen, F.; Molinier, R. Études écologiques et biocénotiques dans la baie du Brusc (Var). Fascicule 1. Les sols phanérogamiques de la formation lagunaire du Brusc. Bull. Inst. Oceanogr. 1961, 58, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Francour, P. La lagune du Brusc. Synthèse Bibliographique et État Actuel; Ministère de l’Environnement and GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 1987; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, G.; Bonhomme, P.; Boudouresque, C.F. Relevé des Herbiers de Magnoliophytes Marines Dans la Lagune du Brusc (Commune de Six-Fours-les-Plages, Var). Dans le Cadre du Projet de Réorganisation des Mouillages Forains Dans la Lagune; GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 2004; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Rouanet, É.; Bonnefont, J.L.; Durand, R. Site Natura 2000 FR 9302001 ‘Lagune du Brusc’—Document D’objectifs—Tome 1: Diagnostics Ecologiques et Socioéconomiques, Enjeux et Objectifs de Conservation Hiérarchisés; Institut Océanographique Paul Ricard Publications: Marseille, France, 2009; p. 102. [Google Scholar]
- Couvray, S.; Simide, R.; Kirchhofer, D.; Vion, A.; Bonnefont, J.L. Projet SAR-LAB. Site Atelier de Restauration Ecologique Lagune du Brusc. Rapport Intermédiaire; Phase 2017–2018; Institut Océanographique Paul Ricard Publications: Six-Fours-la-Plage, France, 2020; p. 140. [Google Scholar]
- Simide, R.; Abello, C.; Marsac, R.; Couvray, S. A unique feature of lagoon along French Mediterranean coast. In Proceedings of the Gecomars 2020—International Workshop on Ecosystem Based Management, Marseille, France, 4–5 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Montefalcone, M.; Albertelli, G.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. Urban seagrass: Status of Posidonia oceanica facing Genoa city waterfront (Italy) and implications for management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefalcone, M.; Morri, C.; Peirano, A.; Albertelli, G.; Bianchi, C.N. Substitution and phase shift within the Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows of NW Mediterranean Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 75, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprandi, A.; Montefalcone, M.; Vacchi, M.; Coppo, S.; Diviacco, G.; Morri, C.; Ferrari, M.; Bianchi, C.N. Combining modelling and historical data to define the status of Posidonia oceanica meadows. In Proceedings of the 5th Mediterranean Symposium on Marine Vegetation, Portorož, Slovenia, 27–28 October 2014; Langar, H., Bouafif, C., Ouerghi, A., Eds.; RAC/SPA Publications: Tunis, Tunisia, 2014; pp. 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- den Hartog, C.; Priest, L. A profound view and discourse on the typification and status of three confused taxa: Ruppia maritima, R. spiralis and R. cirrhosa. Bot. Mar. 2020, 63, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, P. Recherches sur quelques étangs du litoral méditerranéen français et sur leurs faunes malacologiques. Life Environ. 1966, 20, 1–359. [Google Scholar]
- Chomerat, N. Patrons de Réponse du Phytoplancton à La Variabilité des Facteurs Abiotiques Dans un Etang Méditerranéen Hypereutrophe: Succès Ecologique de Planktothrix agardhii (Gom.) Anagn. & Kom. (Cyanoprocaryote) Dans un Ecosystème Saumâtre. Ph.D. Thesis, Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Acunto, S.; Maltagliati, F.; Rindi, F.; Rossi, F.; Cinelli, F. Osservazioni su Una Prateria di Halophila stipulacea (Forssk.) Aschers. (Hydrocharitaceae) nel Mar Tirreno Meridionale. Atti Soc. Tosc. Sci. Nat. Mem. Ser. B 1995, 102, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gambi, M.C.; Barbieri, F.; Bianchi, C.N. New record of the alien seagrass Halophila stipulacea (Hydrocharitaceae) in the western Mediterranean: A further clue to changing Mediterranean Sea biogeography. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2009, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, S.; Tomasello, A.; Di Maida, G.; Pirrotta, M.; Buia, M.C.; Cinelli, F.; Cormaci, M.; Furnari, G.; Giaccone, G.; Luzzu, F.; et al. Seagrasses along the Sicilian coasts. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 26, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, Y.R.; Zakhama-Sraieb, R.; Benamer, I.; Charfi-Cheikhrouha, F. Occurrence of the seagrass Halophila stipulacea (Hydrocharitaceae) in the southern Mediterranean Sea. Bot. Mar. 2011, 54, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambi, M.C.; Gaglioti, M.; Barbieri, F. Sometimes they come back: The re-colonization of the alien seagrass Halophila stipulacea (Forsskål) Ascherson, 1867 (Hydrocharitaceae) in the Palinuro Harbor (Tyrrenian Sea, Italy). BioInvasions Rec. 2018, 7, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefalcone, M.; Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C.; Peirano, A.; Albertelli, G. Lower limit typology and functioning of six Posidonia oceanica meadows in the Ligurian Sea (NW Mediterranean). Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2006, 13, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Meinesz, A.; Astier, J.M.; Bodoy, A.; Cristiani, G.; Lefèvre, J.R. Impact de l’aménagement du domaine maritime sur l’étage infralittoral des Bouches-du-Rhône (France, Méditerranée occidentale). Life Environ. 1982, 32, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Meinesz, A.; Lefèvre, J.R.; Astier, J.M. Impact of coastal development on the infralittoral zone along the southern Mediterranean shore of continental France. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 23, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganteaume, A.; Bonhomme, P.; Emery, E.; Hervé, G.; Boudouresque, C.F. Impact sur la prairie à Posidonia oceanica de l’amarrage des bateaux de croisière, au large du port de Porquerolles (Provence, France, Méditerranée). Sci. Rep. Port-Cros Natl. Park 2005, 21, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Andromede Oceanologie. Le Projet REPIC, Début D’une Politique de Restauration des Herbiers Sous-Marins à Posidonies en France? 2019. Available online: https://medtrix.fr/le-projet-repic-debut-dune-politique-de-restauration-des-herbiers-sous-marins-a-posidonie-en-france/ (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Bedini, R.; Bedini, M.; Salvadori, E. A new transplanting method of Posidonia oceanica (Linnaeus) Delile, 1813 plants. In Monitoring of Mediterranean Coastal Areas. Problems and Measurement Techniques; Bonora, L., Carboni, D., de Vicenzi, M., Eds.; Firenze University Press: Florence, Italy, 2020; pp. 492–500. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, A.H.; Marbá, N.N.; van Katwijk, M.M.; Pickerell, C.; Henriques, M.; Bernard, G.; Ferreira, M.A.; Garcia, S.; Garmendia, J.M.; Manent, P. Changing paradigms in seagrass restoration. Restor. Ecol. 2012, 20, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caye, G. Sur la Morphogénèse et le Cycle Végétatif de Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Ph.D. Thesis, Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France, 1980; p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Meinesz, A. Découverte de l’herbier de Posidonie. Parc national de Port-Cros. Cahier 1982, 4, 1–79. [Google Scholar]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Jeudy de Grissac, A.; Meinesz, A. Relations entre la sédimentation et l’allongement des rhizomes orthotropes de Posidonia oceanica dans la baie d’Elbu (Corse). In International Workshop on Posidonia Oceanica Beds, Porquerolles, France, 12–15 October 1983; Boudouresque, C.F., Jeudy de Grissac, A., Ollivier, J., Eds.; GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 1984; Volume 1, pp. 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Mossé, R.A. Recherches lépidochronologiques sur Posidonia oceanica: Rhizomes plagiotropes et orthotropes des herbiers profonds de Port-Cros (Mediterranée, France). Trav. Sci. Parc Natl. Port-Cros 1984, 10, 87–107. [Google Scholar]
- González-Correa, J.M.; Bayle-Sempere, J.T.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Valle, C.; Sánchez-Jerez, P.; Ruiz, J.M. Recovery of deep Posidonia oceanica meadows degraded by trawling. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 320, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, S.; Lovison, G.; Pirrotta, M.; Di Maida, G.; Tomasello, A.; Sciandra, M. Modelling the relationship between sexual reproduction and rhizome growth in Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Mar. Ecol. 2006, 27, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, A.; Sciandra, M.; Muggeo, V.M.R.; Pirrotta, M.; Di Maida, G.; Calvo, S. Reference growth charts for Posidonia oceanica seagrass: An effective tool for assessing growth performance by age and depth. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinesz, A.; Lefèvre, J.R. Régénération d’un herbier à Posidonia oceanica quarante années après sa destruction par une bombe dans la rade de Villefranche (Alpes Maritimes). In International Workshop on Posidonia oceanica Beds, Porquerolles, France, 12–15 October 1983; Boudouresque, C.F., Jeudy de Grissac, A., Olivier, J., Eds.; GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 1984; Volume 1, pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Marbà, N.; Duarte, C.M. Rhizome elongation and seagrass clonal growth. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 174, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, G.; Badalamenti, F.; Jensen, A.C.; Koch, E.W.; Riggio, S. Colonisation process of vegetative fragments of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile on rubble mounds. Mar. Biol. 2005, 147, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, G. Recensement des floraisons de Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile en Méditerranée. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Mediterr. 1977, 24, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Thélin, I.; Boudouresque, C.F. Posidonia oceanica flowering and fruiting: Recent data from an international inquiry. Posidonia Newsl. 1985, 1, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, J. Note sur la floraison de Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile dans les îles Medas (Gerona, Espagne). Posidonia Newsl. 1989, 2, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Balestri, E.; Piazzi, L.; Acunto, S.; Cinelli, F. Flowering and fruiting beds in Tuscany (Italy). In La Posidonia oceanica; Cinelli, F., Fresi, E., Lorenzi, C., Mucedola, A., Eds.; Revista Marittima Publications: Rome, Italy, 1995; Volume 12, pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Balestri, E.; Cinelli, F. Sexual reproductive success in Posidonia oceanica. Aquat. Bot. 2003, 75, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Almela, E.; Marbà, N.; Álvarez, E.; Balestri, E.; Ruiz-Fernández, J.M.; Duarte, C.M. Patterns of seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) flowering in the Western Mediterranean. Mar. Biol. 2006, 148, 723–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Almela, E.; Marbà, N.; Duarte, C.M. Consequences of Mediterranean warming events in seagrass (Posidonia oceania) flowering records. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergent, G. Recherches Lépidochronologiques Chez Posidonia oceanica (Potamogetonaceae). Fluctuations des Paramètres Anatomiques et Morphologiques des Écailles des Rhizomes. Ph.D. Thesis, Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France, 1987; p. 853. [Google Scholar]
- Pergent, G.; Ben Maiz, N.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Meinesz, A. The flowering of Posidonia oceanica over the past fifty years: A lepidochronological study. In International Workshop on Posidonia Beds; Boudouresque, C.F., Meinesz, A., Fresi, E., Gravez, V., Eds.; GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 1989; Volume 2, pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Pergent, G.; Pergent-Martini, C. Some applications of lepidochronological analysis in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Bot. Mar. 1990, 33, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.A.; Romero, J.; Pérez, M.; Littler, M.M.; Littler, D.S. Dynamics of millenary organic deposits resulting from the growth of the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 44, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmeier, M.; Caye, G.; Molenaar, H. Seed enzyme polymorphism and autogamy of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica from the western Mediterranean. Bot. Mar. 1999, 42, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Balestri, E.; Cinelli, E. Grazing of inflorescences of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Bot. Mar. 2000, 43, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L. Las praderas de FanerÓgamas marinas. ReproducciÓn sexual: FloraciÓn, fructificaciÓn y germinaciÓn. Estructura genética de las praderas. In Praderas y Bosques Marinos de Andalucía; Luque, A.A., Templado, J., Eds.; Consejería de Medio Ambiente, Junta de Andalucía Publications: Sevilla, Spain, 2004; pp. 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Vergés, A.; Becerro, M.A.; Alcoverro, T.; Romero, J. Variation in multiple traits of vegetative and reproductive seagrass tissues influences plant-herbivore interactions. Oecologia 2007, 151, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, B.; Raventos, N.; Planes, S. Assessing effects of fishing prohibition on Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows in the Marine Natural Reserve of Cerbère-Banyuls. Aquat. Bot. 2008, 88, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzen, D.H. Seed predation by animals. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1971, 2, 465–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, L.M.; Leighton, M. Vertebrate responses to spatiotemporal variation in seed production of mast-fruiting Dipterocarpaceae. Ecol. Monogr. 2000, 70, 101–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.J.; Allen, R.B.; Whitehead, D.; Carswell, F.E.; Ruscoe, W.A.; Platt, K.H. Climate and net carbon availability determine temporal patterns of seed production by Nothofagus. Ecology 2005, 86, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pergent-Martini, C. Impact D’un Rejet D’eaux Usées Urbaines sur L’herbier à Posidonia oceanica, Avant et Après La Mise en Service D’une Station D’épuration. Ph.D. Thesis, Pascal Paoli University of Corsica, Corsica, France, 1994; p. 191. [Google Scholar]
- Pergent-Martini, C.; Pergent, G. Spatio-temporal dynamics of Posidonia oceanica beds near a sewage outfall (Mediterranean—France). In Seagrass Biology: Proceedings of an International Workshop, Rottnest Island, Australia, 25–29 January 1996; Kuo, J., Phillips, R.C., Walker, D.I., Kirkman, H., Eds.; Faculty of Sciences, the University of Western Australia Publications: Nedlands, Australia, 1996; pp. 299–306. [Google Scholar]
- Pergent-Martini, C.; Pasqualini, V. Seagrass population dynamics before and after the setting up of a wastewater treatment plant. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2000, 7, 405–408. [Google Scholar]
- Gravez, V.; Gélin, A.; Charbonnel, E.; Francour, P.; Abellard, O.; Remonnay, L. Surveillance de L’herbier de Posidonie de La Baie du Prado (Marseille)—Suivi 1995; Ville de Marseille and GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 1995; p. 56. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, G.; Cadiou, G.; Escoffier, B.; Le Direach, L.; Bonhomme, P.; Charbonnel, E. Surveillance de L’herbier à Posidonia oceanica du Golfe de Giens (Var, France). Seconde Phase, Premier Suivi, Syndicat Intercommunal Hyères-Carqueiranne Pour L’assainissement de La Baie de Giens and GIS Posidonie; GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 2000; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Ragonese, S.; Rizzo, A. Dove cresce la Posidonia? Notizario SIBM 2013, 64, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
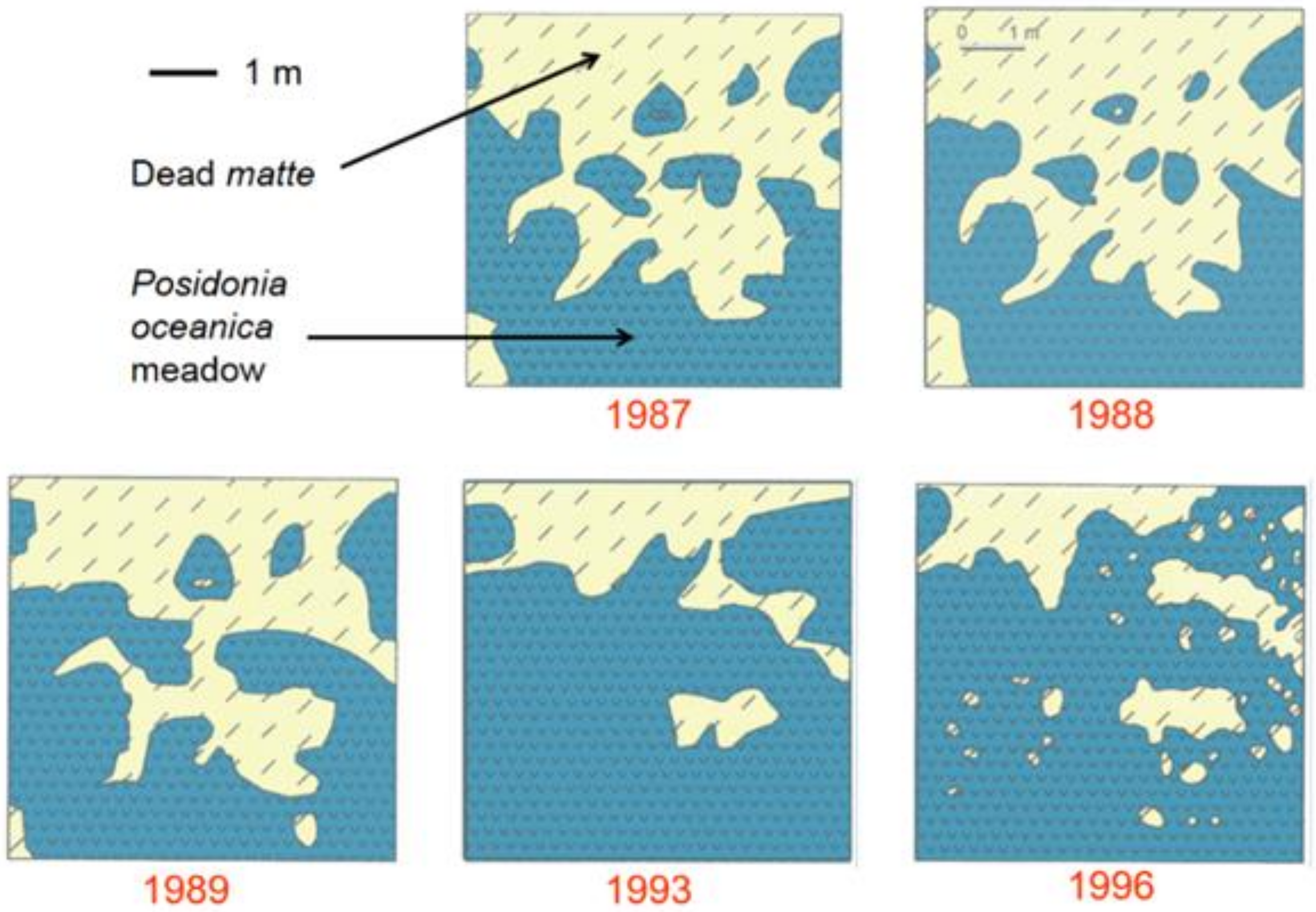
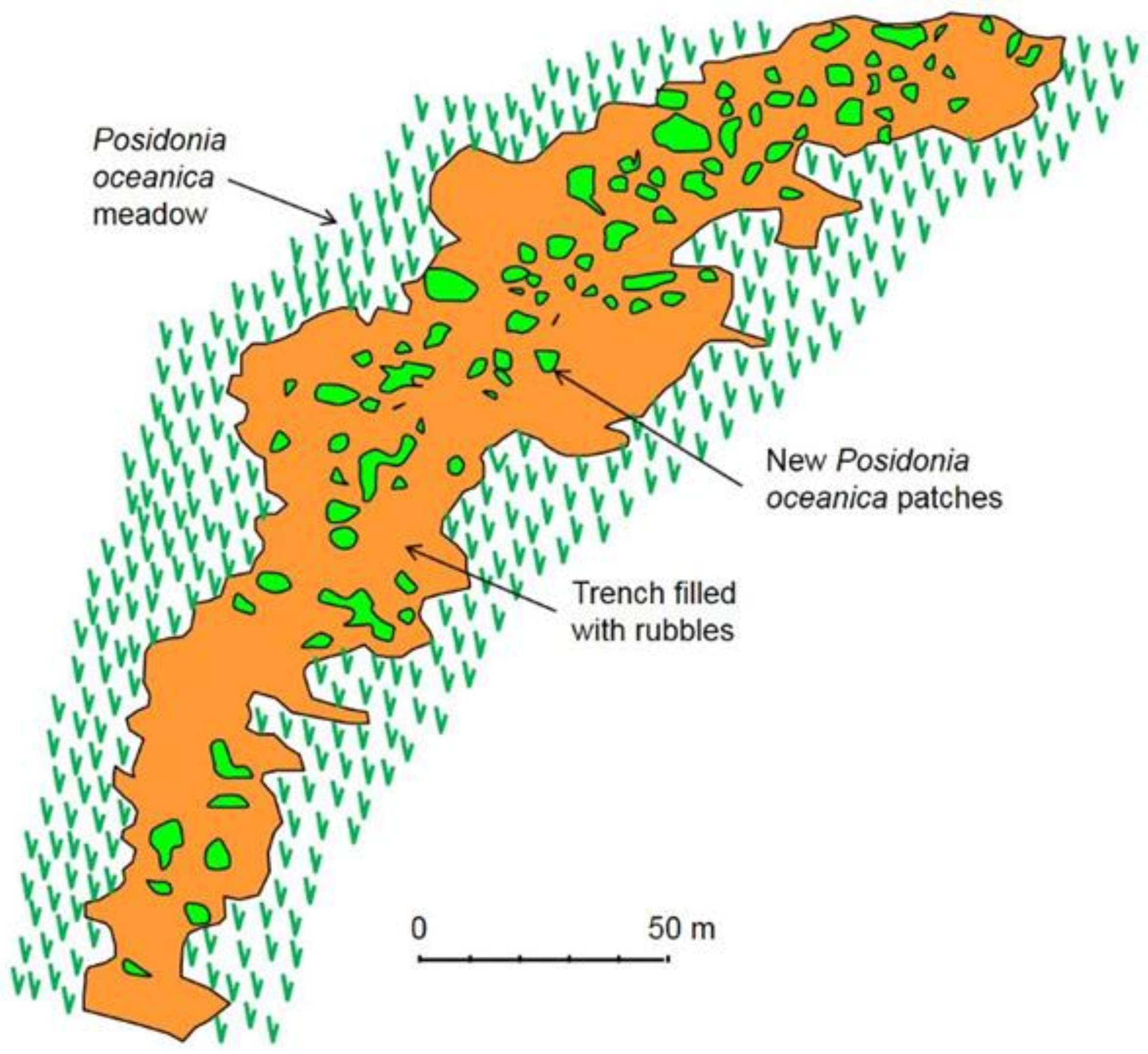
- Cotugno, M.; Lorenti, M.; Scipione, M.B.; Buia, M.C. Spontaneous Posidonia oceanica recovery. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International MEDCOAST Congress on Coastal and Marine Sciences Engineering, Management and Conservation, Marmaris, Turkey, 22–26 October 2019; pp. 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Di Carlo, G.; Badalamenti, F.; Terlizzi, A. Recruitment of Posidonia oceanica on rubble mounts: Substratum effects on biomass partitioning and leaf morphology. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2006, 13, 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Di Carlo, G.; Badalamenti, F.; Terlizzi, A. Recruitment of Posidonia oceanica on rubble mounts: Substratum effects on biomass partitioning and leaf morphology. Aquat. Bot. 2007, 87, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badalamenti, F.; Alagna, A.; D’Anna, G.; Terlizzi, A.; Di Carlo, G. The impact of dredge-fill on Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows: Regression and patterns of recovery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambi, M.C.; Guidetti, P. Morphological observations on seedlings of Posidonia oceanica (L) Delile germinated in situ. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 1998, 5, 549–552. [Google Scholar]
- Buia, M.C.; Piraino, S. Record of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile seedlings in the Egadi Islands (Sicily, Italy). Posidonia Newsl. 1989, 2, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Buia, M.C.; Mazzella, L. Reproductive phenology of the Mediterranean seagrasses Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile, Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Aschers., and Zostera noltii Hornm. Aquat. Bot. 1991, 40, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acunto, S.; Piazzi, L.; Balestri, E.; Cinelli, F. Segnalazioni Di Fioriture Di Posidonia Oceanica (L.) Delile Lungo Le Coste Toscane. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 1996, 3, 437–438. [Google Scholar]
- Gambi, M.C.; Buia, M.C.; Mazzella, L. Record of a diffuse germination of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile in the central Adriatic Sea (Croatia). Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 1996, 3, 467–470. [Google Scholar]
- Balestri, E.; Piazzi, L.; Cinelli, F. Survival and growth of transplanted and natural seedlings of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile in a damaged coastal area. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1998, 228, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Acunto, S.; Balestri, E.; Cinelli, F. Osservazioni preliminari sulla germinazione di semi e sviluppo in situ di piantine di Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Inf. Bot. Ital. 1996, 28, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Alagna, A.; Fernandez, T.V.; Di Carlo, G.; Terlizzi, A.; Badalamenti, F. Influence of substrate type and algal cover on seedlings recruitment and growth performances of the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica. In Proceedings of the 4th Mediterranean Symposium on Marine Vegetation, Yasmine-Hammamet, Tunisia, 2–4 December 2010; El Asmi, S., Langar, H., Belkacem, W., Eds.; RAC/SPA Publications: Tunis, Tunisia, 2010; pp. 149–150. [Google Scholar]
- Alagna, A.; Fernandez, T.V.; Terlizzi, A.; Badalamenti, F. Influence of microhabitat on seedling survival and growth of the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 119, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badalamenti, F.; Alagna, A.; Fici, S. Evidences of adaptative traits to rocky substrates undermine paradigm of habitat preference of the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep08804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alagna, A.; Vega Fernández, T.; D’Anna, G.; Magliola, C.; Mazzola, S.; Badalamenti, F. Assessing Posidonia oceanica seedling substrate preference: An experimental determination of seedling anchorage success in rocky vs. sandy substrates. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e125321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balestri, E.; Vallerini, F.; Lardicci, C. Recruitment and patch establishment by seed in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica: Importance and conservation implications. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Procaccini, G.; Mazzella, L. Genetic variability and reproduction in two Mediterranean seagrasses. In Seagrass biology: Proceedings of an International Workshop, Rottnest Island, Australia, 25–29 January 1996; Kuo, J., Phillips, R.C., Walker, D.I., Kirkman, H., Eds.; The University of Western Australia Publications: Perth, Australia, 1996; pp. 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Procaccini, G. Microsatellite DNA polymorphism in Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 1997, 4, 436–439. [Google Scholar]
- Micheli, C.; Cupido, R.; Lombardi, C.; Belmonte, A.; Peirano, A. Changes in genetic structure of Posidonia oceanica at Monterosso al Mare (Ligurian Sea) and its resilience over a decade (1998–2009). Environ. Manag. 2012, 50, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, C.; D’esposito, D.; Belmonte, A.; Peirano, A.; Valiante, L.M.; Procaccini, G. Genetic diversity and structure in two protected Posidonia oceanica meadows. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 109, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnisci, V.; de Martiis, S.C.; Belmonte, A.; Micheli, C.; Piermattei, V.; Bonamano, S.; Marcelli, M. Assessment of the ecological structure of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile on the northern coast of Lazio, Italy (central Tyrrhenian, Mediterranean). Ital. Bot. 2020, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IUCN. Translocation of Living Organisms; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 1987; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Boudouresque, C.F. La restauration des écosystèmes à phanérogames marines. In Restauration des Ecosystèmes Côtiers; Drévès, L., Chaussepied, M., Eds.; IFREMER: Paris, France, 2001; Volume 29, pp. 65–85. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, M.; Burdon, D.; Hemingway, K.L.; Apitz, S.E. Estuarine, coastal and marine ecosystem restoration: Confusing management and science—A revision of concepts. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 74, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinesz, A.; Caye, G.; Loquès, F.; Macaux, S. Analyse bibliographique sur la culture des Phanérogames marines. Posidonia Newsl. 1990, 3, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Cinelli, F. La riforestazione quale mezzo di ripristino e di controllo per les praterie di fanerogame marine. In Parchi Marini del Mediterraneo. Probleme e Perspective. Atti del 2 Convegno Internazionale. San Teodoro; Icimar: Sardegna, Italy, 1991; pp. 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Addy, C.E. Eelgrass planting guide. Md. Conserv. 1947, 24, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Thorhaug, A. The flowering and fruiting of restored Thalassia beds: A preliminary note. Aquat. Bot. 1979, 6, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.S.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Thayer, G.W. A Low-Cost Planting Technique for Eelgrass (Zostera marina L.); National marine Fisheries Service, Southeast Fisheries Center, Beaufort Laboratory: Beaufort, NC, USA, 1982; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, M.S.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Thayer, G.W. A low cost transplanting procedure for sediment stabilization and habitat development using eelgrass (Zostera marina). Wet Lands 1982, 2, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastyan, G.R.; Cambridge, M.L. Transplantation as a method for restoring the seagrass Posidonia australis. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addy, C.E. Germination of eelgrass seeds. J. Wildl. Manag. 1947, 11, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Katwijk, M.M.; Thorhaug, A.; Marbà, N.; Orth, R.J.; Duarte, C.M.; Kendrick, G.A.; Althuizen, I.H.J.; Balestri, E.; Bernard, G.; Cambridge, M.L.; et al. Global analysis of seagrass restoration: The importance of large-scale planting. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carannante, F. Monitoraggio a Lungo Termine di Trapianti di Posidonia oceanica su Vasta Scala. Ph.D. Thesis, Università di Viterbo, Viterbo, Italy, 2011; p. 175. [Google Scholar]
- Astruch, P.; Rouanet, É.; Boudouresque, C.F. Étude sur la Thématique de la Réintroduction D’espèces Dans le Milieu Naturel. Volet Scientifique. Contrat Direction de L’ENVIRONNEMENT de La Principauté de Monaco and GIS Posidonie; GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 2016; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Maggi, P. Le problème de la disparition des herbiers à posidonies dans le golfe de Giens (Var). Sci. Pêche 1973, 221, 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, G. Jardinier de la Mer. Association-Fondation, G. Cooper pour la reconquête des milieux naturels détruits. Cahier 1976, 1, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, G. Réimplantation de Posidonia oceanica. Protection des implants. Bull. Ecol. 1982, 13, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Giaccone, G.; Calvo, S. Restaurazione del manto vegetale mediante trapianto di Posidonia oceanica (Linneo) Delile. Risultati preliminari. Mem. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 1980, 10, 207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Eugène, C.; Sougy-Peuriere, A.; Augier, H.; Cabrerizo, A.; Harmand, J.M.; Sougy, M. Réhabilitation des Fonds Marins de la Réserve Marine de Monaco. Compte-Rendu du Premier Suivi (Effectué en Septembre 1993) Sur la Réimplantation par Bouturage (Réalisée en Juin 1993) de 2990 Tiges de Posidonies; CERIMER: Marseille, France, 1993; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Sougy, A. Les posidonies face aux attaques de la mer. Mer Littoral 1996, 15, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasello, A.; Pirrotta, M.; Calvo, S. Construction underwater landscape by using Posidonia oceanica transplanting combined with innovative artificial reefs. In Proceedings of the 6th Mediterranean Symposium on Marine Vegetation, Antalya, Turkey, 14–15 January 2019; Langar, H., Ouerghi, A., Eds.; RAC/SPA Publications: Tunis, Tunisia, 2019; pp. 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar, H.; Meinesz, A. Vegetative reproduction in Posidonia oceanica. II. Effects of depth changes on transplanted orthotropic shoots. Mar. Ecol. 1992, 13, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaar, H.; Meinesz, A.; Caye, G. Vegetative reproduction in Posidonia oceanica. Survival and development in different morphological types of transplanted cuttings. Bot. Mar. 1993, 36, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Cinelli, F. Restoration of the littoral sea bottom by means of transplantation of cuttings and sprouts. In Posidonia oceanica, a Contribution to the Preservation of a Major Mediterranean Marine Ecosystem; Cinelli, F., Fresi, E., Lorenzi, C., Mucedola, A., Eds.; Revista Marittima: Rome, Italy, 1995; pp. 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Piazzi, L.; Balestri, E.; Magri, M.; Cinelli, F. Experimental transplanting of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile into a disturbed habitat in the Mediterranean Sea. Bot. Mar. 1998, 41, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Balestri, E.; Balata, D.; Cinelli, F. Pilot transplanting experiment of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile to restore a damaged coastal area in the Mediterranean Sea. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2000, 7, 409–411. [Google Scholar]
- Vangeluwe, D.; Lepoint, G.; Bouquegneau, J.M.; Gobert, S. Effet de la transplantation sur les pousses de Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Life Environ. 2004, 54, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Gobert, S.; Lepoint, G.; Bouquegneau, J.M.; Vangeluwe, D.; Eisinger, M.; Paster, M.; Schuhmaker, H.; van Treeck, P. Restoration of seagrass meadows: Means and limitations. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on the Mediterranean Coastal Environment, MEDCOAST 05, Kusadasi, Turkey, 7–11 October 2005; Ozhan, E., Ed.; MEDCOAST Secretariat, Middle East Technical University: Ankara, Turkey, 2005; pp. 1323–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Vangeluwe, D. Effets de la Transplantation sur La Biométrie et La Dynamique des Nutriments, du Carbone et de La Chlorophylle de Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Liège, Liège, Belgium, 2006; p. 196. [Google Scholar]
- Meinesz, A.; Cottalorda, J.M.; Molenaar, H. Bilan sur L’évolution des Boutures et Plantules de Posidonies, Provenant du Bassin Méditerranéen, Transplantées en 1988–1995 Dans le Parc National de Port-Cros “Le Posidonium”; Report Université Nice Sophia Antipolis and GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 2013; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta, M.; Tomasello, A.; Scannavino, A.; Di Maida, G.; Luzzu, F.; Bellissimo, G.; Bellavia, C.; Costantini, C.; Orestano, C.; Sclafani, G.; et al. Transplantation assessment of degraded Posidonia oceanica habitats: Site selection and long-term monitoring. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larkum, A.W.D. Ecology of Botany Bay. I. Growth of Posidonia australis (Brown) Hook f. in Botany Bay and other bays of the Sidney Basin. Austr. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1976, 27, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.T.; Kopp, B.S.; Gaeckle, J.; Tamaki, H. Seagrass ecology and estuarine mitigation: A low-cost method for eelgrass restoration. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 1759–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bovina, G. Conservazione e restauro delle praterie di Posidonia oceanica. In Il Ripristino Degli Ecosistemi Marino-Costieri e La Difesa Delle Coste Sabbiose Nelle Aree Protette; Onori, L., Ed.; ISPRA: Rome, Italy, 2009; pp. 309–339. [Google Scholar]
- Acunto, S.; Piazzi, L.; Cinelli, F.L.; de Biasi, A.M.; Pacciardi, L.; Ceraudo, S.; Fersini, G. Transplantation of the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica through naturalistic engineering techniques: Value, weakness and further improvements. PeerJ Prepr. 2015, 3, e1051v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagna, A.; D’Anna, G.; Musco, L.; Fernandez, T.V.; Gresta, M.; Pierozzi, N.; Badalamenti, F. Taking advantage of seagrass recovery potential to develop novel and effective meadow rehabilitation methods. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagna, A.; D’Anna, G.; Musco, L.; Fernandez, T.V.; Gresta, M.; Pierozzi, N.; Badalamenti, F. Reply to “Letter to the editor regarding the article ‘Taking advantage of seagrass recovery potential to develop novel and effective meadow rehabilitation methods’ by Alagna et al., published in Marine Pollution Bulletin, 149: 2019 (110578)” by Calvo et al. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 158: 2020 (111395). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kenworthy, W.J.; Fonseca, M.S.; Homziak, J.; Thayer, G.W. Development of a transplanted seagrass (Zostera marina L) meadow in Back Sound, Carteret county, North Carolina. In Proceedings of the Seventh Annual Conference on the Restoration and Creation of Wetlands, Tampa, FL, USA, 16–17 May 1980; pp. 175–193. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.C.; Short, F.T. Restoring eelgrass, Zostera marina L., habitat using a new transplanting technique: The horizontal rhizome method. Aquat. Bot. 1997, 59, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaar, H. Étude de La Transplantation de Boutures de La Phanérogame Marine Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Modélisation de L’architecture et du Mode de Croissance. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Nice Sophia Antipolis, Nice, France, 1992; p. 221. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, E.A.; Meek, S.K.; Gordon, D.M.; Cameron, T.C.; Steer, M.D.; Smith, D.J.; Miliou, A.; Tsimpidis, T. The use of storm fragments and biodegradable replanting methods allows for a low-impact habitat restoration method of sragrass meadows, in the eastern Aegean Sea. Conserv. Evid. 2020, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rismondo, A.; Curiel, D.; Solazzi, A.; Marzocchi, M.; Chiozzotto, E.; Scattolin, M. Sperimentazione di trapianto di fanerogame marine in Laguna di Venezia: 1992–1994. Proc. Ital. Soc. Ecol. 1995, 16, 699–701. [Google Scholar]
- Scannavino, A.; Pirrotta, M.; Tomasello, A.; Di Maida, G.; Luzzu, F.; Bellavia, C.; Bellissimo, G.; Costantini, C.; Orestano, C.; Scalfani, G.; et al. Biodegradable anchor modular system for transplanting Posidonia oceanica cuttings. In Proceedings of the 5th Mediterranean Symposium on Marine Vegetation, Portorož, Slovenia, 27–28 October 2014; Langar, H., Bouafif, C., Ouerghi, A., Eds.; RAC/SPA Publications: Tunis, Tunisia, 2014; pp. 236–237. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, M.S.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Homziak, J.; Thayer, G.W. Transplanting of eelgrass and shoalgrass as a potential means of economically mitigating a recent loss of habitat. In Proceedings of the Sixth Annual Conference on Wetland Restoration and Creation, Tampa, FL, USA, 19 May 1979; Cole, D.P., Ed.; Environmental Studies Center, and Tampa Port Authority: Tampa, FL, USA, 1979; pp. 279–326. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, R.C. Planting guidelines for seagrasses. Coast. Eng. Tech. 1980, 80, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, R.C. Responses of transplanted and indigenous Thalassia testudinum Banks ex König and Halodule wrightii Aschers. to sediment loading and cold stress. Contrib. Mar. Sci. 1980, 23, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- de La Rosa, M.R.; García, N.; Zarranz, M.; Manent, P.; Domínguez, R.; Grimón, M.; Louzara, G.; González, N. Preliminary results of experimental evaluation about different methods of transplanting Cymodocea nodosa in the Canary Islands. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2006, 13, 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Meinesz, A.; Verlaque, M. Note préliminaire concernant quelques expériences de repiquage de Caulerpa prolifera et de Zostera noltii dans la zone de rejet de l’effluent thermique de la centrale électrique de Martigues-Ponteau (golfe de Fos, France). Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Mediterr. 1979, 25, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Jeudy de Grissac, A. Essais d’implantations d’espèces végétales marines: Les espèces pionnières, les posidonies. In International Workshop on Posidonia oceanica Beds, Porquerolles, France, 12–15 October 1983; Boudouresque, C.F., Jeudy de Grissac, A., Olivier, J., Eds.; GIS Posidonie Publications: Marseille, France, 1984; Volume 1, pp. 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, G.; Morancy, R.; Jouvenel, J.Y.; Javel, F.; Meinesz, A. Étude des possibilités de restauration des herbiers de Zostera dans l’étang de Berre par des réimplantations expérimentales. In Les Actes des Rencontres LAGUN’R. Rencontres Scientifiques Autour de L’étang de Berre; Aix-en-Provence, GIPREB: Berre-l’Étang, France, 2013; pp. 345–359. [Google Scholar]
- Curiel, D.; Rismondo, A.; Scarton, F.; Caniglia, G.; Marzocchi, M. Preliminary results on seagrass transplantation with Cymodocea nodosa and Zostera marina in Venice lagoon. G. Bot. Ital. 1995, 129, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Faccioli, F. The morphological restoration of he Venice Lagoon. Quad. Trimest. Consorzio Venezia Nuova 1996, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- da Ros, Z.; Corinaldesi, C.; Dell’Anno, A.; Gambi, C.; Torsani, F.; Danovaro, R. Restoration of Cymodocea nodosa seagrass meadows: Efficiency and ecological implications. Restor. Ecol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Fernández-Torquemada, Y.; González-Correa, J.M. Evaluation of the viability of Posidonia oceanica transplants associated with a marina expansion. Bot. Mar. 2009, 52, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Descamp, P.; Cornu, T.; Bougerol, M.; Boissery, P.; Ferlat, C.; Delaruelle, G.; Deter, J.; Gobert, S. Experimental transplantation of Posidonia oceanica. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on the Mediterranean Coastal Environment—MEDCOAST 2017, Melliha, Malta, 31 October–5 November 2017; Ozhan, E., Ed.; MEDCOAST Mediterranean Coastal Foundation: Mugla, Turkey, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 427–435. [Google Scholar]
- Gouvernement Princier. Projet D’extension en Mer: 500 m2 de Posidonies Transplantés. 2020. Available online: http://www.gouv.mc/Action-Gouvernementale/L-Environnement/Actualites/Projet-d-extension-en-mer-500-m2-de-posidonies-transplantes (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Paling, E.I.; van Keulen, M.; Wheeler, K.; Phillips, J.; Dyhrberg, R.; Lord, D.A. Improving mechanical seagrass transplantation. Ecol. Eng. 2001, 18, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.R.; Phillips, R.C. Experimental seagrass mitigation in the Florida Keys. In Proceedings of the Seventh Annual Conference on the Restoration and Creation of Wetlands, Tampa, FL, USA, 16–17 May 1980; pp. 155–173. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Iituka, T.; Goto, H.; Terawaki, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Kikuti, K. Study on the technique for Zostera bed creation. CRIEPI Annu. Res. Rep. U 1988, 14, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Zarranz, M.E.; González-Henríquez, N.; García-Jiménez, P.; Robaina, R.R. Restoration of Cymodocea nodosa seagrass meadows through seed propagation: Germination in vitro, seedling culture and field transplant. Bot. Mar. 2010, 53, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, R.; Nanneli, A.; Batistini, F. Restoration of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile meadows: Is there an effective methodology? J. Life Sci. 2013, 7, 722–726. [Google Scholar]
- Meinesz, A.; Caye, G.; Loquès, F.; Molenaar, H. Polymorphism and development of Posidonia oceanica transplanted from different parts of the Mediterranean into the National Park of Port-Cros. Bot. Mar. 1993, 36, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrados, J.; Marín, A.; Celdrán, D. Use of Posidonia oceanica seedlings from beach-cast fruits for seagrass planting. Bot. Mar. 2013, 56, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orth, R.J.; Lefcheck, J.S.; McGlathery, K.S.; Aoki, L.; Luckenbach, M.W.; Moore, K.A.; Oreska, M.P.J.; Snyder, R.; Wilcox, D.J.; Lusk, B. Restoration of seagrass habitats leads to rapid recovery of coastal ecosystem services. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudouresque, C.F. Insights into the diversity of the biodiversity concept. Sci. Rep. Port-Cros Natl. Park 2014, 28, 65–86. [Google Scholar]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, E.; Knowlton, N. Global marine biodiversity trends. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2006, 31, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, J.S. The measurement of marine species diversity, with an application to the benthic fauna of the Norwegian continental shelf. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 250, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, R.M. Scaling of marine biodiversity. Océanis 1998, 24, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ellingsen, K.E. Biodiversity of a continental shelf soft-sediment macrobenthos community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 218, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, K.J.; Whittaker, R.J. Species diversity—Scale matters. Science 2002, 295, 1245–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rubies, A.; Macpherson, E. Substrate use and temporal pattern of recruitment in juvenile fishes of the Mediterranean littoral. Mar. Biol. 1995, 124, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheminée, A.; Sala, E.; Pastor, J.; Bodilis, P.; Thiriet, P.; Mangialajo, L.; Cottalorda, J.M.; Francour, P. Nursery value of Cystoseira forests for Mediterranean rocky reef fishes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 442, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheminée, A.; Pastor, J.; Bianchimani, O.; Thiriet, P.; Sala, E.; Cottalorda, J.M.; Dominici, J.M.; Lejeune, P.; Francour, P. Juvenile fish assemblages in temperate rocky reefs are shaped by the presence of macro-algae canopy and its three-dimensional structure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morancy Conseil Environnement. Restauration des Herbiers de Zostera Dans L’étang de Berre par des Réimplantations Expérimentales de Zostera noltii & Z. marina. Suivi des Transplantations à 3 ans; Morancy Conseil Environnement: Marseille, France, 2012; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Pasqualini, V.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Clabaut, P.; Pergent, G. Mapping of Posidonia oceanica using aerial photographs and side scan sonar: Application off the Island of Corsica (France). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 47, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellissimo, G.; Sirchia, B.; Ruvolo, V. Monitoring of Posidonia oceanica meadows in the Sicilian coasts under the Water Framefork Directive (WFD). In Monitoring of Mediterranean Coastal Areas. Problems and Measurement Techniques; Bonora, L., Carboni, D., de Vicenzi, M., Eds.; Firenze University Press: Florence, Italy, 2020; pp. 510–518. [Google Scholar]
- Morhange, C.; Laborel, J.; Hesnard, A.; Prone, A. Variation of relative mean sea level during the last 4000 years on the northern shores of Lacydon, the ancient harbour of Marseilles (chantier J. Verne). J. Coast. Res. 1996, 12, 841–849. [Google Scholar]
- Pauly, D. Anecdotes and the shifting baseline syndrome of fisheries. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1995, 10, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz-Arroyo, A.; Roberts, C.M.; Torre, J.; Cariño-Olvera, M.; Enríquez-Andrade, R.R. Rapidly shifting environmental baselines among fishers of the Gulf of California. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lotze, H.K.; Worm, B. Historical baselines for large marine animals. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 24, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, L.; Ballesteros, E.; Linares, C.; Hereu, B. Spatial and temporal variability of deep-water algal assemblages in the Northwesten Mediterranean: The effects of an exceptional storm. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 95, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, R.; Serrano, E.; Linares, E.; Zabala, M.; Ribes, M. Effect of a severe storm event on the mortality rate of the gorgonian Paramuricea clavata on the Medes Islands Marine Reserve and the nearby Montgrí coast. In Assessment of the Ecological Impact of the Extreme Storm of Sant Esteve’s Day (26 December 2008) on the Littoral Ecosystems of the North Mediterranean, Spanish Coasts; Final Report (PIEC 200430E599); Centro de Estudios Avanzados de Blanes, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científica: Blanes, Spain, 2012; pp. 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hereu, B.; Garcia-Rubies, A.; Linares, C.; Navarro, L.; Teixidó, N.; Garrabou, J.; Cebrian, E. Impact of Sant Esteve’s storm (2008) in Paracentrotus lividus populations. In Assessment of the Ecological Impact of the Extreme Storm of Sant Esteve’s Day (26 December 2008) on the Littoral Ecosystems of the North Mediterranean, Spanish Coasts; Final Report (PIEC 200430E599); Centro de Estudios Avanzados de Blanes, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas: Blanes, Spain, 2012; pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Teixidó, N.; Casas, E.; Cebrián, E.; Linares, C.; Garrabou, J. Impacts on coralligenous outcrop biodiversity of a dramatic coastal storm. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gera, A.; Pagès, J.F.; Arthur, R.; Farina, S.; Roca, G.; Romero, J.; Alcoverro, T. The effect of a centenary storm on the long-lived seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 1910–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oprandi, A.; Mucerino, L.; de Leo, F.; Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C.; Azzola, A.; Benelli, F.; Besio, G.; Ferrari, M.; Montefalcone, M. Effects of a severe storm on seagrass meadows. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Astruch, P.; Bănaru, D.; Blanfuné, A.; Carlotti, F.; Faget, D.; Goujard, A.; Harmelin-Vivien, M.; Le Diréach, L.; Pagano, M.; et al. Global change and the management of Mediterranean coastal habitats: A plea for a socio-ecosystem-based approach. In Evolution of Marine Coastal Ecosystems under the Pressure of Global Change-Proceedings of Coast Bordeaux Symposium and of the 17th French-Japanese Oceanography Symposium; Ceccaldi, J.H., Hénocque, Y., Komatsu, T., Prouzet, P., Sautour, B., Yoshida, J., Eds.; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 297–320. [Google Scholar]
- Lepoint, G.; Vangeluwe, D.; Eisinger, M.; Paster, M.; van Treeck, P.; Bouquegneau, J.M.; Gobert, S. Nitrogen dynamics in Posidonia oceanica cuttings: Implications for transplantation experiments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, S.; Scannavino, A.; Luzzu, F.; Di Maida, G.; Pirrotta, M.; Orestano, C.; Paredes, F.; Montagnino, F.M.; Tomasello, A. Tecnica di reimpianto mediante supporto biodegradabile. In Conservazione e Gestione Della Naturalità Negli Ecosistemi Marino-costieri. Il Trapianto Delle Praterie di Posidonia oceanica; Manuali e Linee Guida n. 106/2014; Bacci, T., La Porta, B., Maggi, C., Nonnis, O., Paganelli, D., Rende, S.F., Polifrone, M., Eds.; ISPRA: Rome, Italy, 2014; pp. 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer, H. Posidonies. SM2 veut replanter les prairies méditerranéennes. Le Marin 2012, 3413, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, S.; Scannavino, A.; Luzzu, F.; Di Maida, G.; Pirrotta, M.; Orestano, C.; Tomasello, A. Recupero di fondali a matte morta nel Golfo di Palermo mediante riforestazione con Posidonia oceanica. In Conservazione e Gestione Della Naturalità Negli Ecosistemi Marino-Costieri. Il Trapianto Delle Praterie di Posidonia oceanica; Manuali e Linee Guida n. 106/2014; Bacci, T., La Porta, B., Maggi, C., Nonnis, O., Paganelli, D., Rende, S.F., Polifrone, M., Eds.; ISPRA: Rome, Italy, 2014; pp. 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jahnke, M.; Serra, L.A.; Bernard, G.; Procaccini, G. The importance of genetic make-up for restoration success—A case study of the seagrass Zostera noltii Hornem in a Mediterranean lagoon. In Proceedings of the 5th Mediterranean Symposium on Marine Vegetation, Portorož, Slovenia, 27–28 October 2014; Langar, H., Bouafif, C., Ouerghi, A., Eds.; RAC/SPA: Tunis, Tunisia, 2014; pp. 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Pergent, G. La protection légale de la Posidonie en France: Un outil efficace. Nécessité de son extension à d’autres pays méditerranéens. In Les Espèces Marines à Protéger en Méditerranée; Boudouresque, C.F., Avon, M., Gravez, V., Eds.; GIS Posidonie: Marseille, France, 1991; pp. 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Bianchi, C.N. Une idée neuve: La protection des espèces marines. In GIS Posidonie: Plus de 30 Ans au Service de La Protection et de La Gestion du Milieu Marin; Le Diréach, L., Boudouresque, C.F., Eds.; GIS Posidonie: Marseille, France, 2013; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, M.L. A decision-based framework to increase seagrass transplantation success. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2007, 10, 336–340. [Google Scholar]
- den Hartog, C. Procedures for the restoration of seagrass beds. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2000, 7, 353–356. [Google Scholar]
- Orth, R.J. Protection and restoration of seagrasses: Addressing global concerns from a local perspective in Chesapeake Bay, USA. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2000, 7, 401–404. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, C.; Buffard, A.; Pioch, S.; Thorin, S. Marine ecosystem restoration and biodiversity offset. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktarov, E.; Saunders, M.I.; Abdullah, S.; Mills, M.; Beher, J.; Possingham, H.P.; Mumby, P.J.; Lovelock, C.E. The cost and feasibility of marine coastal restoration. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 1055–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.S.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Thayer, G.W. Draft Guidelines for Mitigation and Restoration of Seagrasses in the United States and Adjacent Waters; NOAA Coastal Ocean Program Decision Analysis Series; National Fisheries Service: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1996; p. 222. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, M.S.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Thayer, G.W. Guidelines for Conservation and Restoration of Sea Grasses in the United States and Adjacent Waters; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1998; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Calumpong, H.P.; Fonseca, M.S. Seagrass transplantation and other seagrass restoration methods. In Global Seagrass Research Method; Short, F.T., Coles, R.G., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 425–443. [Google Scholar]
- Genot, I.; Caye, G.; Meinesz, A.; Orlandini, M. Role of chlorophyll and carbohydrate contents in survival of Posidonia oceanica cuttings transplanted to different depths. Mar. Biol. 1994, 119, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinesz, A.; Molenaar, H.; Bellone, E.; Loquès, F. Vegetative reproduction in Posidonia oceanica. II. Effects of rhizome length and transplantation season in orthotropic shoots. Mar. Ecol. 1992, 13, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, E.A.; Verduin, J.; Krauss, S.L.; Hardinge, J.; Anthony, J.; Kendrick, G.A. A genetic assessment of a successful seagrass meadow (Posidonia australis) restoration trial. Ecol. Manag. Restor. 2013, 14, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafratta, A.; Serrano, O.; Masqué, P.; Mateo, M.A.; Fernandes, M.; Gaylard, S.; Lavery, S. Challenges to select suitable habitats and demonstrate ‘additionality’ in Blue Carbon projects: A seagrass case study. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 197, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; McGlathery, K.J. Eelgrass recovery in the coastal bays of Virginia Coast Reserve. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 448, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezek, R.J.; Furman, B.T.; Jung, R.P.; Hall, M.A.; Bell, S.S. Long-term performance of seagrass restoration projects in Florida, USA. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matheson, F.E.; Reed, J.; dos Santos, V.M.; Mackay, G.; Cummings, V.J. Seagrass rehabilitation: Successful transplants and evaluation of methods at different spatial scales. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 51, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leakey, R.; Lewin, R. The Sixth Extinction. Patterns of Life and the Future of Humankind; Doubleday: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 271. [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzler, A.; Génot, J.C.; Wintz, M. Espaces protégés: De la gestion conservatoire vers la non-intervention. Courrier de l’Environnement de l’INRA 2008, 56, 29–44. [Google Scholar]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boudouresque, C.-F.; Blanfuné, A.; Pergent, G.; Thibaut, T. Restoration of Seagrass Meadows in the Mediterranean Sea: A Critical Review of Effectiveness and Ethical Issues. Water 2021, 13, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081034
Boudouresque C-F, Blanfuné A, Pergent G, Thibaut T. Restoration of Seagrass Meadows in the Mediterranean Sea: A Critical Review of Effectiveness and Ethical Issues. Water. 2021; 13(8):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081034
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoudouresque, Charles-François, Aurélie Blanfuné, Gérard Pergent, and Thierry Thibaut. 2021. "Restoration of Seagrass Meadows in the Mediterranean Sea: A Critical Review of Effectiveness and Ethical Issues" Water 13, no. 8: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081034
APA StyleBoudouresque, C.-F., Blanfuné, A., Pergent, G., & Thibaut, T. (2021). Restoration of Seagrass Meadows in the Mediterranean Sea: A Critical Review of Effectiveness and Ethical Issues. Water, 13(8), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081034






