Assessing the Removal of Arsenite and Arsenate Mixtures from the Synthetic Bangladesh Groundwater (SBGW) Using Combined Fe(VI)/Fe(III) Treatments and Local Regression Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthetic Bangladesh Groundwater (SBGW) Preparation
2.2. Ferrate(VI) Quantification
2.3. Ferrate(VI) Electrochemical Synthesis
2.4. Treatment Tests
2.5. Determination of Total Concentrations of Arsenic and its Species
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Ferrate(VI) Ions Combined with Fe(III) Ions in the Removal of Arsenic(III)
3.2. Effects of Ferrate(VI) Ions Combined with Fe(III) Ions in the Removal of As(V)
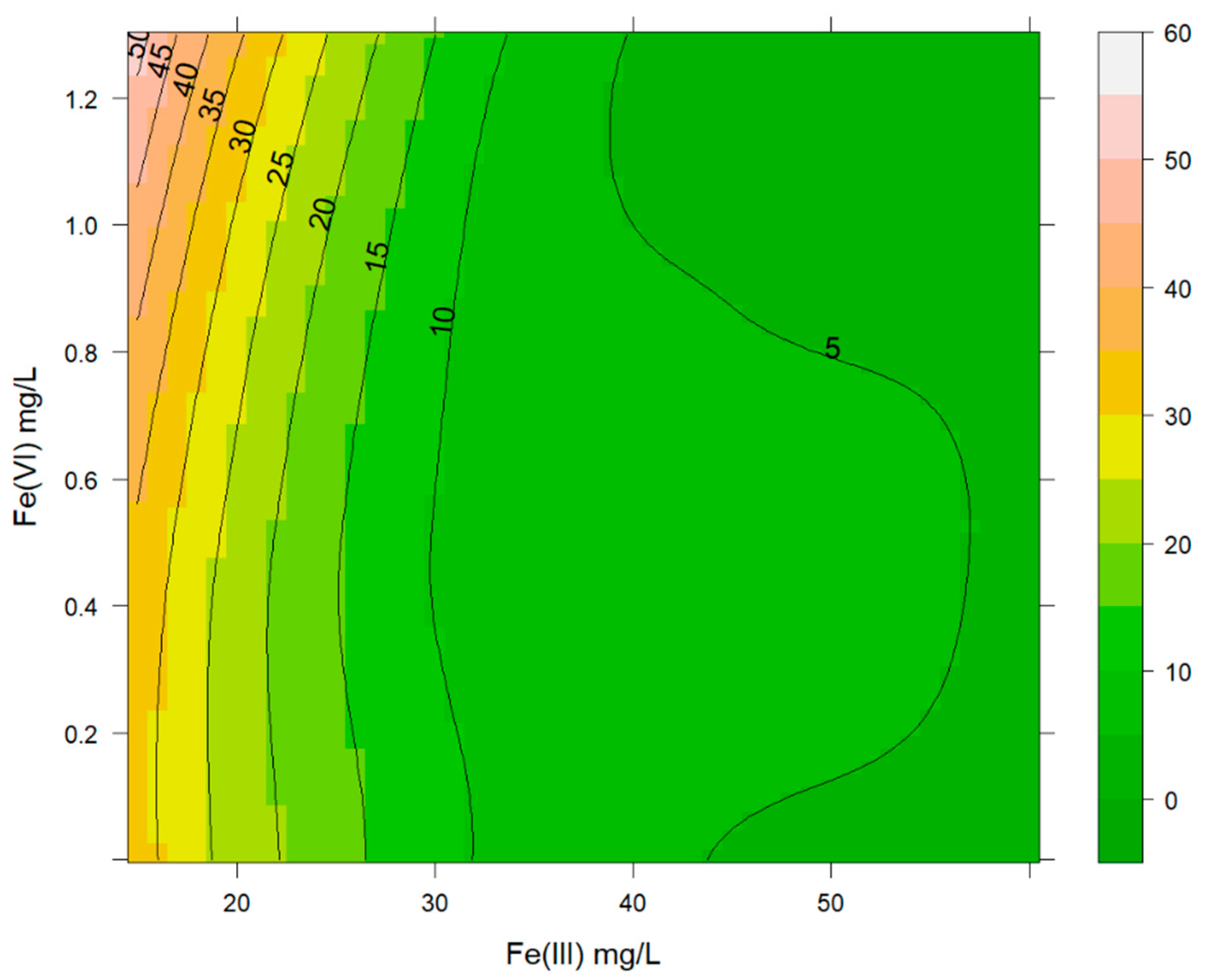
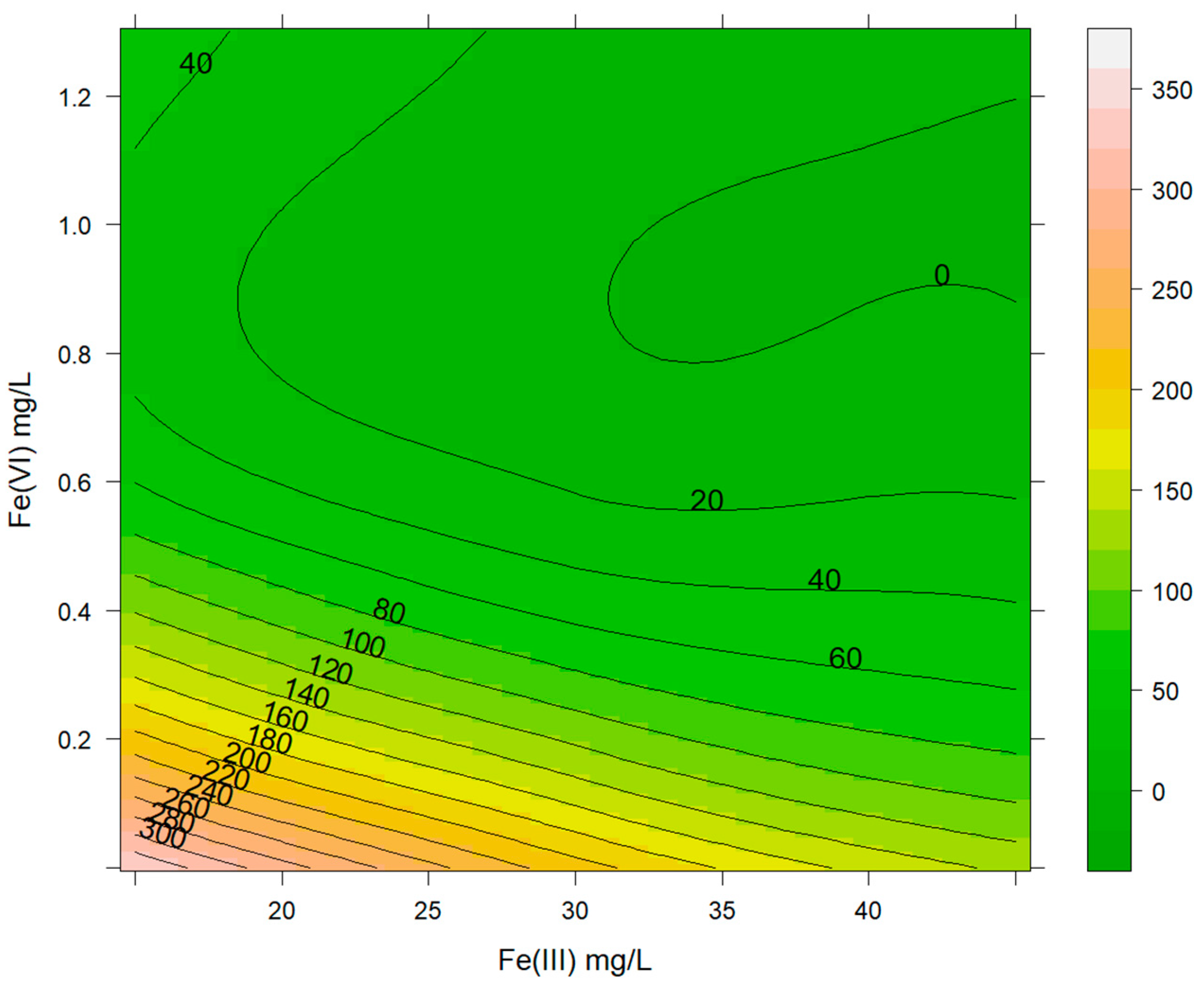
3.3. Effects of Ferrate(VI) Ions Combined with Fe(III) Ions in the Removal of As(III) Combined with As(V)
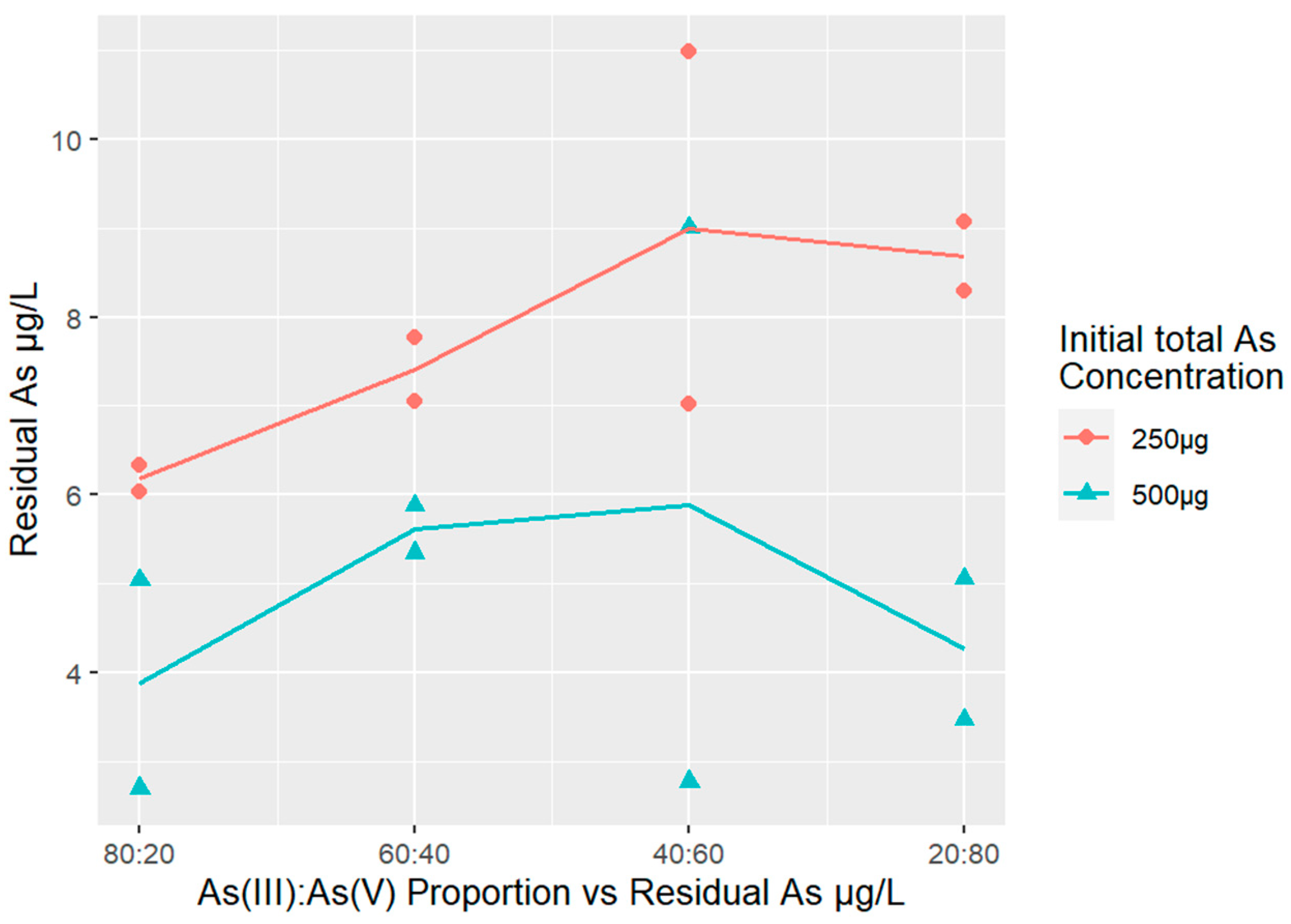
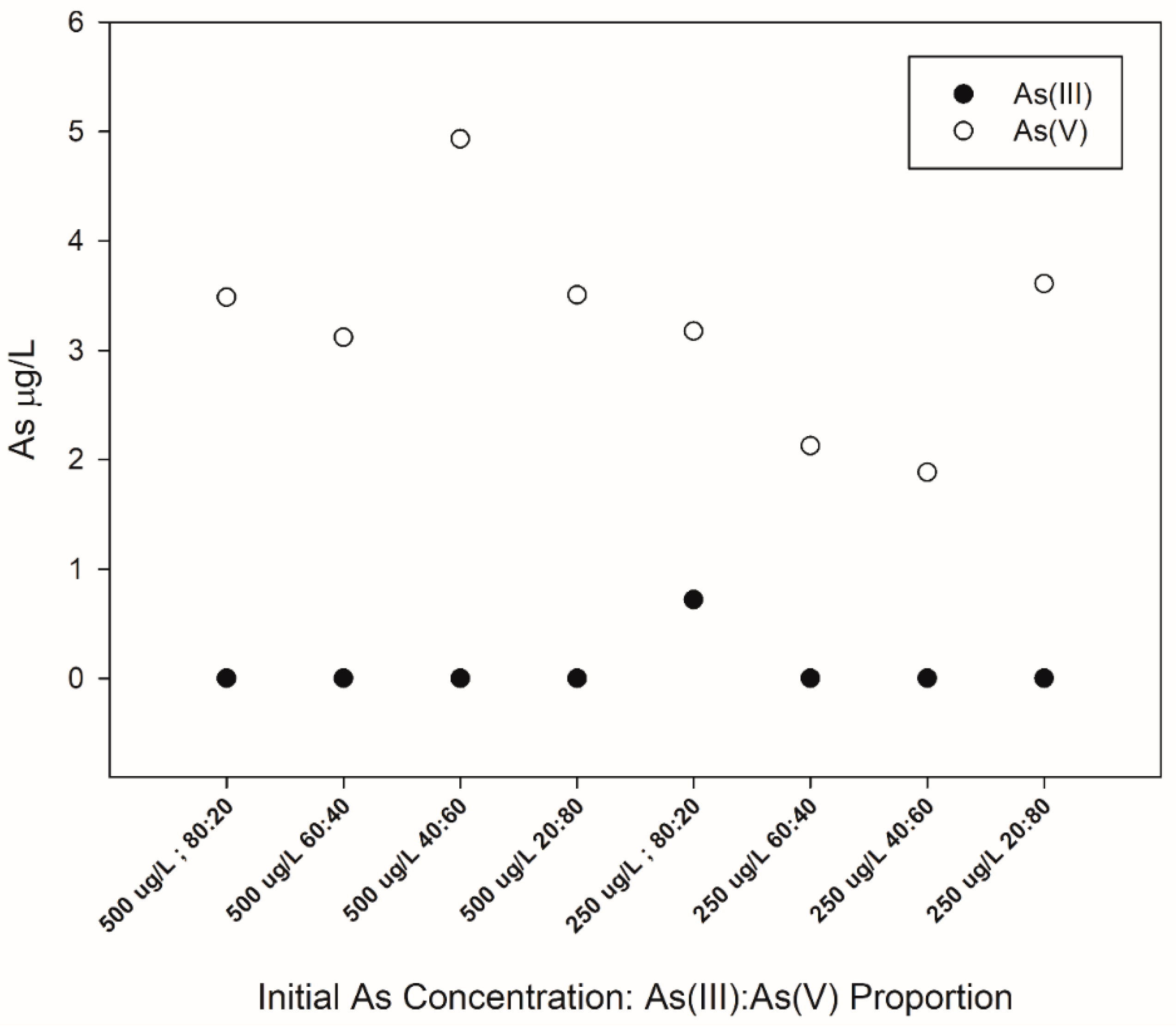
3.4. Arsenic Removal Using Different As(III) and As(V) Proportions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, C.K.; Ali, I. Arsenic: Occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Res. 2000, 34, 4304–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmett, R.E.R.; McIntosh, I.G. Occurrence of arsenic in soils and waters in the Waiotapu Valley, and its relation to stock health. N. Z. J. Sci. Technol. Sect. A 1939, 21, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Arsenic contamination, consequences and remediation techniques: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Exposure to Arsenic: A Major Public Health Concern; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, U.K.; Biswas, B.K.; Chowdhury, T.R.; Samanta, G.; Mandal, B.K.; Basu, G.C.; Chanda, C.R.; Lodh, D.; Saha, K.C.; Mukherjee, S.K.; et al. Groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh and West Bengal, India. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomova, K.; Jenisova, Z.; Feszterova, M.; Baros, S.; Liska, J.; Hudecova, D.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Arsenic: Toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, K.K.; Guha Mazumder, D.N. Effect of drinking arsenic-contaminated water in children. Indian J. Public Health 2012, 56, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J. Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 713–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Khan, M.I.; Amjad, M.; Hussain, M. Natasha Arsenic uptake, toxicity, detoxification, and speciation in plants: Physiological, biochemical, and molecular aspects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.M.; Arnold, L.L.; Eldan, M.; Lewis, A.S.; Beck, B.D. Methylated arsenicals: The implications of metabolism and carcinogenicity studies in rodents to human risk assessment. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 99–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, J.; Litter, M.I.; Parvez, F.; Román-Ross, G.; Nicolli, H.B.; Jean, J.S.; Liu, C.W.; López, D.; Armienta, M.A.; Guilherme, L.R.; et al. One century of arsenic exposure in Latin America: A review of history and occurrence from 14 Countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 429, 2–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, N.; Li, G. A critical review on arsenic removal from water using iron-based adsorbents. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 39545–39560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.P.; Kerrich, R.; Hendry, M.J. Distribution of arsenic(III), arsenic(V) and total inorganic arsenic in porewaters from a thick till and clay-rich aquitard sequence, Saskatchewan, Canada. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 2637–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, N.E.; Fernando, Q. A review of arsenic (III) in groundwater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 1991, 21, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissen, M.; Frimmel, F.H. Arsenic—A review. Part II: Oxidation of arsenic and its removal in water treatment. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2003, 31, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Nin, C.; Gong, Y.; Ma, J.; Bi, X.; Jiang, B. A Full-Wave Rectified Alternating Current Wireless Electrocoagulation Strategy for the Oxidative Remediation of As(III) in Simulated Anoxic Groundwater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Genuchten, C.M.; Addy, S.E.A.; Peña, J.; Gadgil, A.J. Removing Arsenic from Synthetic Groundwater with Iron Electrocoagulation: An Fe and As K-Edge EXAFS Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addy, S.E.A.; Ashok, G.J.; Kowolik, K.; Kostecki, R. Electro Chemical Arsenic Removal (ECAR) for Rural, Bangladesh Merging Technology with Sustainable Implementation; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009.
- Amrose, S.; Gadgil, A.; Srinivasan, V.; Kowolik, K.; Muller, M.; Huang, J.; Kostecki, R. Arsenic removal from groundwater using iron electrocoagulation: Effect of charge dosage rate. J. Environ. Sci. Health Toxic Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2013, 48, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, J.; Kailasa, S.K.; Kwon, E.E.; Tsang, Y.F.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, K.H. A critical review of ferrate(VI)-based remediation of soil and groundwater; Academic Press. Environ. Res. 2018, 160, 420–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maohong, F.; Robert, B.C.; Pao, H.C. Preliminary studies of the oxidation of arsenic (III) by potassium ferrate. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 18, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Um, I.H.; Yoon, J. Arsenic(III) oxidation by iron(VI) (Ferrate) and subsequent removal of arsenic(V) by iron(III) coagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5750–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Sharma, V.K.; Mbuya, O.S. Removal of arsenite by Fe(VI), Fe(VI)/Fe(III), and Fe(VI)/Al(III) salts: Effect of pH and anions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larroca, F.P.; Olschewski, E.S.; Quino-Favero, J.; Huamaní, J.R.; Castillo Sequera, J.L. Water Treatment Plant Prototype with pH Control Modeled on Fuzzy Logic for Removing Arsenic Using Fe(VI) and Fe(III). Water 2020, 12, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeloju, S.B.; Khan, S.; Patti, A.F. Arsenic contamination of groundwater and its implications for drinking water quality and human health in under-developed countries and remote communities—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, M.E.; Beldoménico, H.R. Determination of inorganic arsenic species by flow injection hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry with variable sodium tetrahydroborate concentrations. Spectrochim. Acta B 2004, 59, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaduzzaman, M.; Rietveld, L.C.; Hoque, B.A.; Bari, M.N.; van Halem, D. Arsenic removal from iron-containing groundwater by delayed aeration in dual-media sand filters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 124823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, G.; Xiong, X.; Guan, X.; Li, L.; Bao, H. Enhanced arsenite removal from water by Ti(SO4)2 coagulation. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4340–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Xu, M.; Zhou, B.; Liang, J.; Zhou, L. High-efficient removal of arsenite by coagulation with titanium xerogel coagulant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 118047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of solution chemistry on aqueous As(III) removal by titanium salts coagulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Guha, B.; Lippincott, L.; Cach, S.; Wei, J.; Su, T.L.; Meng, X. Challenges of arsenic removal from municipal wastewater by coagulation with ferric chloride and alum. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, C.; Xiao, L.; Fu, G.; Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; Chen, Y. Arsenic removal from alkaline leaching solution using Fe (III) precipitation. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 1714–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskan, M.B.; Pala, A. Determination of arsenic removal efficiency by ferric ions using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Li, G.; Chen, M.; Qin, F.; Li, H.; Qiang, Y. Effect Factor of Arsenite and Arsenate Removal by a Manufactured Material: Activated Carbon-Supported Nano-TiO2. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 6724157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, F. Removal of Arsenic by Bead Cellulose Loaded with Iron Oxyhydroxide from Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6808–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, L.N.; Melnikov, F.; Yamani, J.S.; Zimmerman, J.B. Multifunctional photoactive and selective adsorbent for arsenite and arsenate: Evaluation of nano titanium dioxide-enabled chitosan cross-linked with copper. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 358, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, L.N.; Petrović, P.V.; Gonzalez, I.S.; Stavitski, E.; Fishman, Z.S.; Rudel, H.E.; Anastas, P.T.; Zimmerman, J.B. Selective adsorption of arsenic over phosphate by transition metal cross-linked chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Geographical Survey and Department of Public Health and Engineering. Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater in Bangladesh; British Geological Survey Technical Report WC/00/19; British Geographical Survey: Keyworth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Licht, S.; Naschitz, V.; Halperin, L.; Halperin, N.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Ghosh, S.; Liu, B. Analysis of ferrate (VI) compounds and super-iron Fe (VI) battery cathodes: FTIR, ICP, Titrimetric, XRD, UV/VIS, and electrochemical characterization. J. Power Sources 2001, 101, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quino-Favero, J.; Eyzaguirre, R.; Mogrovejo, P.; Prieto, P.; Flores del Pino, L. Electrochemical synthesis of Ferrate(VI): Optimization of parameters and evaluation of their impact in production cost. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 113, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, G.; Clifford, D.A. Preservation of inorganic arsenic species in groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8877–8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welz, B.; He, Y.; Sperling, M. Flow injection on-line acid digestion and pre-reduction of arsenic for hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry—A feasibility study. Talanta 1993, 40, 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Groose, E.; Shyu, W.M. Local regression models. In Statistical Models in S; Wadsworth & Brooks; Chambers, J.M., Hastie, T.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Prucek, R.; Tuček, J.; Kolařík, J.; Filip, J.; Marušák, Z.; Sharma, V.K.; Zbořil, R. Ferrate(VI)-induced arsenite and arsenate removal by in situ structural incorporation into magnetic iron(iii) oxide nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3283–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Bang, S.; Korfiatis, G.P. Effects of silicate, sulfate, and carbonate on arsenic removal by ferric chloride. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartinen, E.O.; Martin, C.J. An overview of arsenic removal processes. Desalination 1995, 103, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio, I.; Scarlino, A.; Bloise, E.; Mele, G.; Santoro, O.; Pastore, T.; Santoro, D. Efficient removal of low-arsenic concentrations from drinking water by combined coagulation and adsorption processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PO43− | SiO32− | SO42− | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | Na+ | HCO3− | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentrations in mg L−1 | 1.3 | 19.5 | 8 | 61 | 8 | 125 | 138 | 275 | 0 |
| Factors | Estimated Coefficient | Standard Error | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe(III) | −0.017683 | 0.002826 | −6.258 | 0.0001 |
| Fe(VI) | −0.684623 | 0.068568 | −9.985 | 0.0000 |
| Fe(III)2 | 0.000114 | 0.000036 | 3.161 | 0.0101 |
| Fe(VI)2 | 0.120680 | 0.042542 | 2.837 | 0.0176 |
| Fe(III):Fe(VI) | 0.006892 | 0.001003 | 6.870 | 0.0000 |
| Factors | Estimated Coefficient | Standard Error | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe(III) | −0.002775 | 0.000441 | −6.288 | 0.0001 |
| Fe(VI) | 0.011415 | 0.010710 | 1.066 | 0.3116 |
| Fe(III)2 | 0.000030 | 0.000006 | 5.359 | 0.0003 |
| Fe(VI)2 | 0.003330 | 0.006645 | 0.501 | 0.6272 |
| Fe(III):Fe(VI) | −0.000320 | 0.000157 | −2.042 | 0.0685 |
| Factors | Estimated Coefficient | Standard Error | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe(III) | −0.008022 | 0.003044 | −2.636 | 0.0249 |
| Fe(VI) | −0.504883 | 0.073853 | −6.836 | 0.0000 |
| Fe(III)2 | 0.000054 | 0.000039 | 1.394 | 0.1936 |
| Fe(VI)2 | 0.199681 | 0.045822 | 4.358 | 0.0014 |
| Fe(III):Fe(VI) | 0.003098 | 0.001081 | 2.867 | 0.0168 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quino-Favero, J.; Eyzaguirre Perez, R.; Prieto Veramendi, P.; Mogrovejo García, P.; Flores del Pino, L. Assessing the Removal of Arsenite and Arsenate Mixtures from the Synthetic Bangladesh Groundwater (SBGW) Using Combined Fe(VI)/Fe(III) Treatments and Local Regression Analysis. Water 2021, 13, 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091134
Quino-Favero J, Eyzaguirre Perez R, Prieto Veramendi P, Mogrovejo García P, Flores del Pino L. Assessing the Removal of Arsenite and Arsenate Mixtures from the Synthetic Bangladesh Groundwater (SBGW) Using Combined Fe(VI)/Fe(III) Treatments and Local Regression Analysis. Water. 2021; 13(9):1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091134
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuino-Favero, Javier, Raúl Eyzaguirre Perez, Patricia Prieto Veramendi, Paloma Mogrovejo García, and Lisveth Flores del Pino. 2021. "Assessing the Removal of Arsenite and Arsenate Mixtures from the Synthetic Bangladesh Groundwater (SBGW) Using Combined Fe(VI)/Fe(III) Treatments and Local Regression Analysis" Water 13, no. 9: 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091134
APA StyleQuino-Favero, J., Eyzaguirre Perez, R., Prieto Veramendi, P., Mogrovejo García, P., & Flores del Pino, L. (2021). Assessing the Removal of Arsenite and Arsenate Mixtures from the Synthetic Bangladesh Groundwater (SBGW) Using Combined Fe(VI)/Fe(III) Treatments and Local Regression Analysis. Water, 13(9), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091134






