Fabrication of Manganese-Supported Activated Alumina Adsorbent for Defluoridation of Water: A Kinetics and Thermodynamics Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Fabrication of MnOOH-Supported AA
2.2.1. Modification of AA
2.2.2. AA Coated with MnOOH
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
2.4. Mathematical Model and Basic Parameter Expression
2.4.1. Adsorption Kinetic Model
2.4.2. Adsorption Thermodynamic Model
2.4.3. Adsorption Thermodynamic Parameters
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results
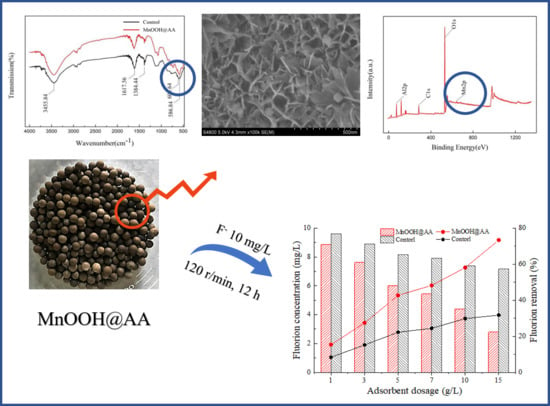
3.1. Characterization of MnOOH-Supported AA
3.1.1. Surface Morphology and Phase Composition
3.1.2. XPS Analysis
3.1.3. FTIR
3.2. Analysis of Influential Factors and Regeneration Effects
3.2.1. Effect of MnOOH-Supported AA on Fluoride Removal
3.2.2. Effect of pH on Fluoride Adsorption
3.2.3. Effect of Coexisting Anions on Fluoride Adsorption
3.2.4. Regeneration of MnOOH-Supported AA
3.3. Kinetic Study of Fluoride Adsorption
3.3.1. Quasi-First-Order Model and Quasi-Second-Order Model
3.3.2. Weber and Morris Model
3.4. Kinetic Study of Fluoride Adsorption
3.4.1. Adsorption Isotherms
3.4.2. Isosteric Enthalpies for Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ranasinghe, N.; Kruger, E.; Tennant, M. Spatial distribution of groundwater fluoride levels and population at risk for dental caries and dental fluorosis in Sri Lanka. Int. Dent. J. 2019, 69, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Ma, F. Determining fluoride distribution and influencing factors in groundwater in Songyuan, Northeast China, using hydrochemical and isotopic methods. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 217, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhou, K.; Yang, Y.; Du, H. A pilot-scale study of cryolite precipitation from high fluoride-containing wastewater in a reaction-separation integrated reactor. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhou, K.; Yang, Y.; Du, H. Growth kinetics of calcium fluoride at high supersaturation in a fluidized bed reactor. Environ. Technol. 2013, 35, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi; Maheshwari, R.C. Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Shuang, C.; Li, A. Performance evaluation of magnetic anion exchange resin removing fluoride. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 91, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, N.; Meenakshi, S. Role of metal ion incorporation in ion exchange resin on the selectivity of fluoride. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Bouchrit, R.; Hafiane, A.; Bouguecha, S.A.-T. Fluoride removal from aqueous solution by direct contact membrane distillation: Theoretical and experimental studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 10493–10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehn, P. Fluoride removal with extra low energy reverse osmosis membranes: Three years of large scale field experience in Finland. Desalination 2008, 223, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arahman, N.; Mulyati, S.; Lubis, M.R.; Takagi, R.; Matsuyama, H. The removal of fluoride from water based on applied current and membrane types in electrodialyis. J. Fluor. Chem. 2016, 191, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, L.; Stillings, L.L.; Decker, D.L. Assessing changes in the physico-chemical properties and fluoride adsorption capacity of activated alumina under varied conditions. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 76, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawane, S.H.; Khan, A.A.; Singh, K.; Tripathi, A.; Hasda, R.; Halder, G. Insight into Optimization, isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamics of fluoride adsorption onto activated alumina. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2017, 37, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A.; Purkait, M.K. The defluoridation of water by acidic alumina. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 2316–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, N.; Meenakshi, S. Enriched fluoride sorption using alumina/chitosan composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathy, S.S.; Bersillon, J.-L.; Gopal, K. Removal of fluoride from drinking water by adsorption onto alum-impregnated activated alumina. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 50, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, U.; Behera, S.K.; Siddiqi, H.; Meikap, B. Facile method to synthesize efficient adsorbent from alumina by nitric acid activation: Batch scale defluoridation, kinetics, isotherm studies and implementation on industrial wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, U.; Siddiqi, H.; Bal, M.; Meikap, B. Calcium and zirconium modified acid activated alumina for adsorptive removal of fluoride: Performance evaluation, kinetics, isotherm, characterization and industrial wastewater treatment. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 2045–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, L.; An, X.; Wan, G.; Zhu, W.; Luo, Y. Enhanced fluoride removal from water by rare earth (La and Ce) modified alumina: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.-X.; Wang, S.-G.; Gong, W.-X.; Liu, X.-W.; Gao, B.-Y. Removal of fluoride by hydrous manganese oxide-coated alumina: Performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliyekkal, S.M.; Sharma, A.K.; Philip, L. Manganese-oxide-coated alumina: A promising sorbent for defluoridation of water. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugya, A.Y.; Imam, T.S.; Hua, X.; Ma, J. Efficacy of Eichhornia Crassipes, Pistia Stratiotes and Nymphaea Lotus in the Biosorption of Nickel from Refinery Wastewater. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 13075–13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, S.; Mulugeta, E.; Zewge, F.; Chandravanshi, B.S. Water defluoridation by aluminium oxide–manganese oxide composite material. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Komarneni, S. Fluoride removal by ordered and disordered mesoporous aluminas. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 197, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, R.-L.; Wu, F.-C. Inferring the favorable adsorption level and the concurrent multi-stage process with the Freundlich constant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Duan, G.; Chen, S.-M.; Liu, X. Hydrothermally controlled synthesis of α-MnO2, γ-MnOOH, and Mn3O4 nanomaterials with enhanced electrochemical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 752, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.P.; Babu, A.T.; Babu, B.; Antony, R. Γ-Mnooh Nanorods: Efficient Adsorbent for Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.S.; Raichur, A.M. Abatement of fluoride from water using manganese dioxide-coated activated alumina. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullick, A.; Neogi, S. Ultrasound assisted synthesis of Mg-Mn-Zr impregnated activated carbon for effective fluoride adsorption from water. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 50, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Zhong, H.; Pan, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Huang, L. Removal of Fluoride from Wastewater Solution Using Ce-Alooh with Oxalic Acid as Modification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121373. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, L.; Yang, W.; He, Y.; Ren, L.; Wang, H. Enhanced surface hydroxyl groups by using hydrogen peroxide on hollow tubular alumina for removing fluoride. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 297, 110051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, K.; Singh, R.; Baruah, I.; Choudhury, H.; Sharma, M. Equilibrium and kinetics modeling of fluoride adsorption onto activated alumina, alum and brick powder. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, U.; Behera, S.K.; Meikap, B. A novel acid modified alumina adsorbent with enhanced defluoridation property: Kinetics, isotherm study and applicability on industrial wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, R.; Vairamuthu, R.; Ganapathy, A. Use of chemically activated cotton nut shell carbon for the removal of fluoride contaminated drinking water: Kinetics evaluation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, J.-P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saini, A.; Maheshwari, P.H.; Tripathy, S.S.; Waseem, S.; Dhakate, S. Processing of rice straw to derive carbon with efficient de-fluoridation properties for drinking water treatment. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 34, 101136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tian, X.; Ashraf, I.; Chen, B. Fluoride removal using a chelating resin containing phosphonic-sulfonic acid bifunctional group. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1613, 460697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Das, P.; Sengupta, S.; Manna, S. Calcium impregnated activated charcoal: Optimization and efficiency for the treatment of fluoride containing solution in batch and fixed bed reactor. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 109, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekka, B.; Dhaka, R.S.; Patel, R.K.; Dash, P. Fluoride removal in waters using ionic liquid-functionalized alumina as a novel adsorbent. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Technique | Category | Materials | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | Chemical precipitation | Calcium salt, etc. | Low cost, simple operation | High amount of retained water (sludge dewatering is required prior to disposal) |
| Coagulant sedimentation | Iron salt, aluminum salt, etc. | Low cost, simple operation | Can be expensive, efficiency depends on pH and the presence of co-existing ions in water, adjustment and readjustment of pH is required, elevated residual aluminum concentration, formation of sludge with a high amount of toxic aluminum fluoride complex | |
| Ion exchange | Ion exchange | Ion exchange resin | High efficiency | High cost of installation and regeneration |
| Separation membrane | Electrodialysis | Ion exchange membrane | High efficiency, no need to dosage agents | Expensive, vulnerable to interfering ions (sulfate, phosphate, chloride, bicarbonate, etc.), high operation cost, toxic concentrate generated |
| Reverse osmosis | Reverse osmosis membrane | High efficiency, suitable for treating high-fluoride water | High cost of installation and maintenance, replacement of media after multiple regenerations | |
| Ultrafiltration | Ultrafiltration membrane | No risk of secondary contamination, suitable for treating high-fluoride water | High cost, pre-processing complexity, strict technical requirements | |
| Nanofiltration | Nanofiltration membrane | |||
| Adsorption | Activated alumina | Activated alumina | Greater accessibility, low cost, simple operation, availability of wide range of adsorbents, produce high-quality water, environmentally friendly | Common ions interfere with fluoride adsorption, regeneration difficult, low adsorption efficiency under high fluoride concentration |
| S. No. | Adsorbent | Adsorption Capacity | Concentration Range | Contact Time | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fe-impregnated chitosan (Fe-CTS) | 1.97 mg/g | 10 mg/L | 6 h | - |
| 2 | Magnetic iron oxide fabricated hydrotalcite/chitosan (Fe3O4HTCS) | 5.03 mg/g | 10 mg/L | 20 min | 5 |
| 3 | Hydrous zirconium oxide-impregnated chitosan beads | 22.1 mg/g | 9.7–369.2 mg/L | 160 h | 5 |
| 4 | Sn(IV) chloride impregnated chitosan La3+ modified | 17.63 mg/g | 5–100 mg/L | 30 min | 6 |
| 5 | Lanthanum-aluminum loaded hydrothermal palygorskite (La-Al-HP) | 1.30 mg/g | 4.89 mg/L | 540 min | 7.5 |
| 6 | Fe3+-modified bentonite clay | 2.91 mg/g | 10 ppm | 30 min | 2~10 |
| 7 | MnO2 coated Na-bentonite | 2.4 mg/g | 5 mg/L | 30 min | 8 |
| 8 | Hydroxyapatite nanorods | 1.49 mg/g | 10 mg/L | 3 h | 7 |
| 9 | Sulfate-doped hydroxyapatite hierarchical hollow microspheres | 28.3 mg/g | 2–100 mg/L | 2 h | 3.0~10.0 |
| 10 | Hydroxyapatite decorated with carbon nanotube composite (CNT-HAP) | 11.05 mg/g | 15 mg/L | 300 min | 6 |
| 11 | Hydroxyapatite montmorillonite (HAP-MMT) | 16.7 mg/g | 30 mg/L | 30 min | 5 |
| 12 | Zirconium impregnated activated carbon (ZrAC) | 5.4 mg/g | 2.5–20 mg/L | 180 min | 4 |
| 13 | Mg-Mn-Zr impregnated activated carbon (ACMg-Mn-Zr) | 26.27 mg/g | 5–30 mg/L | 3 h | 4 |
| 14 | Alumina impregnated activated carbon | 2.86 mg/g | 10 mg/L | 3 h | 6.1 |
| 15 | Activated alumina | - | 2–20 mg/L | 24 h | 6~8 |
| 16 | Acid activated alumina | 69.52 mg/g | 10–60 mg/L | 3 h | 6.5 |
| 17 | Nitric acid activated alumina | 45.75 mg/g | 40 mg/L | 3 h | 3.5 |
| F− | Total Fe | |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration (mg/L) | 2 ± 0.5 | 2 ± 0.5 |
| 5 ± 0.5 | 2 ± 0.5 | |
| 10 ± 0.5 | 2 ± 0.5 |
| Test Item | Detection and Analysis Method | Standard Limits for Drinking Water (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| F− | Fluorometric spectrophotometry | 1.0 |
| Fe | Phenanthroline spectrophotometry | 0.3 |
| T | Direct-reading method | - |
| Regenerant Concentration (mg/L) | F− Concentration (mg/L) | Removal Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.48 | 50.40 |
| 2 | 1.32 | 73.60 |
| 2.5 | 1 | 80.16 |
| 5 | 0.98 | 80.56 |
| 7.5 | 0.97 | 80.75 |
| 10 | 0.96 | 80.95 |
| Regenerant Time (h) | F− Concentration (mg/L) | Removal Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.17 | 76.79 |
| 1.5 | 1.13 | 77.58 |
| 2 | 0.96 | 80.8 |
| 2.5 | 1.17 | 76.79 |
| 3 | 1.45 | 71.23 |
| C0 (mg/L) | 0~23 min1/2 | 23~67 min1/2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | k | C | R2 | k | C | |
| 2 | 0.9112 | 0.0212 | −0.0494 | 0.8294 | 0.0067 | 0.2738 |
| 5 | 0.9789 | 0.0347 | −0.0524 | 0.9658 | 0.0097 | 0.5357 |
| 10 | 0.9494 | 0.0318 | −0.0548 | 0.9648 | 0.0116 | 0.5372 |
| Temperature °C | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | qe (mg/g) | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | |
| 25 | 0.216 | 1.450 | 0.8968 | 0.274 | 0.5631 | 0.9614 |
| 35 | 0.188 | 1.676 | 0.8908 | 0.272 | 0.6243 | 0.9383 |
| 45 | 0.208 | 1.957 | 0.9522 | 0.335 | 0.6241 | 0.9852 |
| C0 (mg/L) | ΔH (J/mol) | ΔG (J/mol) | ΔS (J/(mol·K)) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 308 | 318 | 298 | 308 | 318 | ||
| 2 | 11,131.61 | −11,973.36 | −12,375.15 | −12,776.94 | 77.53 | 41.54 | 43.30 |
| 5 | 3004.26 | −1408.50 | −1455.76 | −1503.03 | 14.81 | 4.89 | 5.05 |
| 10 | 11,370.23 | −7110.14 | −7348.73 | −7587.33 | 62.01 | 24.67 | 25.52 |
| 15 | 8057.76 | −2433.97 | −2515.64 | −2597.32 | 35.21 | 8.45 | 8.72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, K.; Li, P.; Fu, J.; Kang, N.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Yu, F. Fabrication of Manganese-Supported Activated Alumina Adsorbent for Defluoridation of Water: A Kinetics and Thermodynamics Study. Water 2021, 13, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091219
You K, Li P, Fu J, Kang N, Gao Y, Cheng X, Yang Y, Yu F. Fabrication of Manganese-Supported Activated Alumina Adsorbent for Defluoridation of Water: A Kinetics and Thermodynamics Study. Water. 2021; 13(9):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091219
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Kun, Peijie Li, Jinxiang Fu, Ning Kang, Yujia Gao, Xiaoxiang Cheng, Yuehong Yang, and Furui Yu. 2021. "Fabrication of Manganese-Supported Activated Alumina Adsorbent for Defluoridation of Water: A Kinetics and Thermodynamics Study" Water 13, no. 9: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091219
APA StyleYou, K., Li, P., Fu, J., Kang, N., Gao, Y., Cheng, X., Yang, Y., & Yu, F. (2021). Fabrication of Manganese-Supported Activated Alumina Adsorbent for Defluoridation of Water: A Kinetics and Thermodynamics Study. Water, 13(9), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091219