Machine Learning Approach to Predict Quality Parameters for Bacterial Consortium-Treated Hospital Wastewater and Phytotoxicity Assessment on Radish, Cauliflower, Hot Pepper, Rice and Wheat Crops
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Treatment and Quality Parameters
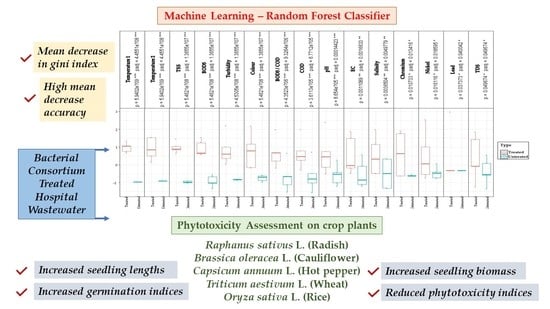
2.2. Machine Learning Approach
2.2.1. Kruskal–Wallis Test
2.2.2. Random Forest (RF) Classifier
2.3. Phytotoxicity Assessment
2.3.1. Germination Experiments
2.3.2. Germination Indices (GI)
2.3.3. Phytotoxicity Indices (PI)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Prediction of Quality Parameters
3.2. Phytotoxicity Assessment of the Re-Use of Treated Hospital Wastewater for Crop Irrigation
3.2.1. Radish Crop
3.2.2. Cauliflower Crop
3.2.3. Hot Pepper Crop
3.2.4. Wheat Crop
3.2.5. Rice Crop
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Minhas, P.S.; Saha, J.K.; Dotaniya, M.L.; Sarkar, A.; Saha, M. Wastewater irrigation in India: Current status, impacts and response options. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Ghosal, P.S.; Varma, M. A review on hospital wastewater treatment: A special emphasis on occurrence and removal of pharmaceutically active compounds, resistant microorganisms, and SARS-CoV-2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Maurya, N.S.; Tiwari, B. Hospital wastewater treatment scenario around the globe. Curr. Dev. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 549–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Aukidy, M.; Al Chalabi, S.; Verlicchi, P. Hospital Wastewater Treatments Adopted in Asia, Africa, and Australia. In Hospital Wastewaters. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Verlicchi, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; p. 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, E.; Bonetta, S.; Bertino, C.; Lorenzi, E.; Bonetta, S.; Gilli, G. Hospital effluents management: Chemical, physical, microbiological risks and legislation in different countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 168, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Chamorro, S.; Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Gros, M.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Borrego, C.M.; Barceló, D.; Balcázar, J.L. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Res. 2015, 69, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Zia, M.H. Wastewater Production, Treatment and Use in Pakistan, Final Country Report. UN-Water Activity Information System. In Proceedings of the Second Regional Workshop of the Project ‘Safe Use of Wastewater in Agriculture, New Delhi, India, 16–18 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Water and Power. Pakistan Water Sector Strategy (PWSS): National Water Sector Profile, 5; Ministry of Water and Power, Office of the Chief Engineering Advisor: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2002.
- Zafar, R.; Bashir, S.; Nabi, D.; Arshad, M. Occurrence and quantification of prevalent antibiotics in wastewater samples from Rawalpindi and Islamabad, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meo, M.I.; Haydar, S.; Nadeem, O.; Hussian, G.; Mian, H.R. Characterization of hospital wastewater, risk waste generation and management practices in Lahore. Proc. Pak. Acad. Sci. 2014, 51, 317–329. [Google Scholar]
- GoP/DoE. Hospital Waste Management Rules, 2005. S.R.O.1013 (1)/2005; Government of Pakistan (GoP), Ministry of Environment: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2005.
- National Environment Quality Standards (NEQS). The Gazette of Pakistan; Ministry of Environment, Local Government and Rural Development, Government of Pakistan (GoP): Islamabad, Pakistan, 2000; pp. 1289–1294.
- Qadir, M.; Wichelns, D.; Raschid-Sally, L.; McCornick, P.G.; Drechsel, P.; Bahri, A.; Minhas, P.S. The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabeen, A.; Huang, X.; Aamir, M. The Challenges of water pollution, threat to public health, flaws of water laws and policies in Pakistan. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2015, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muhammad, N.; Nafees, M.; Ge, L.; Khan, M.H.; Bilal, M.; Chan, W.P.; Lisak, G. Assessment of industrial wastewater for potentially toxic elements, human health (dermal) risks, and pollution sources: A case study of Gadoon Amazai industrial estate, Swabi, Pakistan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olicón-Hernández, D.R.; Gómez-Silván, C.; Pozo, C.; Andersen, G.L.; González-Lopez, J.; Aranda, E. Penicillium oxalicum XD-3.1 removes pharmaceutical compounds from hospital wastewater and outcompetes native bacterial and fungal communities in fluidised batch bioreactors. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 158, 105179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogwugwa, V.H.; Oyetibo, G.O.; Amund, O.O. Taxonomic profiling of bacteria and fungi in freshwater sewer receiving hospital wastewater. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovlatabadi, A.; Estiri, E.H.; Najafi, M.L.; Ghorbani, A.; Rezaei, H.; Behmanesh, M.; Momeni, E.; Gholizadeh, A.; Cristaldi, A.; Mancini, G.; et al. Bioaccumulation and health risk assessment of exposure to potentially toxic elements by consuming agricultural products irrigated with wastewater effluents. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Cheng, S.; Chen, G. Bioelectrochemical systems for efficient recalcitrant wastes treatment. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Sheng, L.; Wang, Y. Distribution and enrichment of heavy metals among sediments, water body and plants in Hengshuihu Wetland of Northern China. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, T.; Lin, M.; Lizhi, X.; Rizwanullah, L.; Nasrullah, M.; Xiuyuan, M.; Manzoor, Y.Z.; Elis, R.J. Farmers’ awareness about impacts of reusing wastewater, risk perception and adaptation to climate change in Faisalabad District, Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4663–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.S. Environmental contamination from health-care facilities. In Health Care and Environmental Contamination; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, B.S. Contaminant properties of hospital clinical laboratory wastewater: A physiochemical and microbiological assessment. J. Environ. Prot. 2016, 7, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Aukidy, M.; Verlicchi, P.; Voulvoulis, N. A framework for the assessment of the environmental risk posed by pharmaceuticals originating from hospital effluents. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand-Weaver, M.; Margiotta-Casaluci, L.; Patel, A.; Panter, G.H.; Owen, S.F.; Sumpter, J.P. The read-across hypothesis and environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11384–11395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malchi, T.; Maor, Y.; Tadmor, G.; Shenker, M.; Chefetz, B. Irrigation of root vegetables with treated wastewater: Evaluating uptake of pharmaceuticals and the associated human health risks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9325–9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Wong, C.K.C.; Chu, L.M. Distribution of antibiotics in wastewater-irrigated soils and their accumulation in vegetable crops in the Pearl River delta, Southern China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11062–11069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, R.S.; Sibley, P.K. Human health risk assessment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in plant tissue due to biosolids and manure amendments, and wastewater irrigation. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Agüera, A.; Bayona, J.M.; Cytryn, E.; Fotopoulos, V.; Lambropoulou, D.; Manaia, C.M.; Michael, C.; Revitt, M.; Schröder, P. The potential implications of reclaimed wastewater reuse for irrigation on the agricultural environment: The knowns and unknowns of the fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistant bacteria and resistance genes—A review. Water Res. 2017, 123, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.T.; Shah, I.A.; Ihsanullah, I.; Naushad, M.; Ali, S.; Shah, S.H.A.; Mohammad, A. Hospital wastewater as a source of environmental contamination: An overview of management practices, environmental risks, and treatment processes. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 41, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T.; Bilal, M.; Nabeel, F.; Adeel, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Environmentally-related contaminants of high concern: Potential sources and analytical modalities for detection, quantification, and treatment. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, I.B.; Simões, L.C.; Simões, M. The effects of emerging environmental contaminants on Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolated from drinking water in planktonic and sessile states. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raja, S.; Cheema, H.M.N.; Babar, S.; Khan, A.A.; Murtaza, G.; Aslam, U. Socio-economic background of wastewater irrigation and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in crops and vegetables. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 158, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Mahmood, Q.; Waseem, A.; Irshad, M.; Faridullah; Pervez, A. Assessment of heavy metals in wheat plants irrigated with contaminated wastewater. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Murtaza, G.; Ghafoor, A.; Qadir, M.; Owens, G.; Aziz, M.A.; Zia, M.H.; Saifullah. Disposal and Use of Sewage on Agricultural Lands in Pakistan: A Review. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.M.; Eugster, E.A. What is in our environment that effects puberty? Reprod. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rashid, A.; Mirza, S.A.; Keating, C.; Ali, S.; Campos, L.C. Hospital wastewater treated with a novel bacterial consortium (Alcaligenes faecalis and Bacillus paramycoides spp.) for phytotoxicity reduction in Berseem clover and tomato crops. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 1764–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Mirza, S.A.; Keating, C.; Ali, S.; Campos, L.C. Indigenous Bacillus paramycoides spp. and Alcaligenes faecalis: Sustainable solution for bioremediation of hospital wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkl, M.; Anthony, J.; Aymerich, E.; Brunner, N.; Chubilleau, C.; Das, S.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Kazmi, A.A.; Philip, L.; Singh, A. Interpreting best available technologies more flexibly: A policy perspective for municipal wastewater management in India and other developing countries. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2018, 71, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Dai, T.; Qiao, Z.; Sun, P.; Hao, J.; Yang, Y. Application of artificial intelligence to wastewater treatment: A bibliometric analysis and systematic review of technology, economy, management, and wastewater reuse. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 133, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, F.; Papirio, S.; Esposito, G.; Gargano, R.; De Marinis, G. Machine learning algorithms for the forecasting of wastewater quality indicators. Water 2017, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazhar, S.; Ditta, A.; Bulgariu, L.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmed, M.; Nadiri, A. Sequential treatment of paper and pulp industrial wastewater: Prediction of water quality parameters by Mamdani Fuzzy Logic model and phytotoxicity assessment. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Man, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Hong, M.; Cui, P. A deep learning based dynamic COD prediction model for urban sewage. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Ok, Y.S. The application of machine learning methods for prediction of metal sorption onto biochars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2346101 (accessed on 24 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrap, T.C.A. Public Available Specification 100—Specification for Composted Material. Annex D: Method Assess Contam. Weed Propagules Phytotoxins Compost. Mater. The Waste and Resources Action Program (WRAP). 2002. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=Public%20available%20specification%20100%20%20specification%20for%20composted%20material (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Hoekstra, N.J.; Bosker, T.; Lantinga, E.A. Effects of cattle dung from farms with different feeding strategies on germination and initial root growth of cress (Lepidium sativum L.). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 93, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.C.; de Souza, J.B.; Vidal, C.M.D.; Herbert, L.T.; de Souza, K.V.; Martins, K.G.; Young, B.J. Phytotoxicity indexes and removal of color, COD, phenols and ISA from pulp and paper mill wastewater post-treated by UV/H2O2 and photo-Fenton. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 202, 110939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiquia, S.M.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Hodgkiss, I.J. Effects of composting on phytotoxicity of spent pig-manure sawdust litter. Environ. Pollut. 1996, 93, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagur-González, M.G.; Estepa-Molina, C.; Martín-Peinado, F. Toxicity assessment using Lactuca sativa L. bioassay of the metal(loid)s As, Cu, Mn, Pb and Zn in soluble-in-water saturated soil extracts from an abandoned mining site. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusan, M.J.; Albalasmh, A.A.; Zuraiqi, S.; Bashabsheh, M. Evaluation of phytotoxicity effect of olive mill wastewater treated by different technologies on seed germination of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9127–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, M. Corrections: A Critical Approach, 3rd ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Thunéll, S.; Lindberg, U.; Jiang, L.; Trygg, J.; Tysklind, M.; Souihi, N. A machine learning framework to improve effluent quality control in wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arismendy, L.; Cárdenas, C.; Gómez, D.; Maturana, A.; Mejía, R.; Quintero M., C.G. Intelligent System for the Predictive Analysis of an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Process. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Gao, F.; Chen, G. Wastewater quality monitoring system using sensor fusion and machine learning techniques. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Rong, S.; Wang, R.; Yu, S. Recent advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning for nonlinear relationship analysis and process control in drinking water treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermet-Said, H.; Moulai-Mostefa, N. Optimization of Turbidity and COD Removal from Pharmaceutical Wastewater by Electrocoagulation. Isotherm Modeling and Cost Analysis. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icke, O.; van Es, D.M.; de Koning, M.F.; Wuister, J.J.G.; Ng, J.; Phua, K.M.; Koh, Y.K.K.; Chan, W.J.; Tao, G. Performance improvement of wastewater treatment processes by application of machine learning. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 2671–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Arshad, M.; Ditta, A.; Hussain, A.; Naveed, M.; Hasnain, M.; Nazir, Q. Combining textile effluent wastewater with organic fertilizer for improved growth and productivity of wheat and soil health. J. Environ. Agric. Sci. 2016, 8, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Blamey, F.P.C.; Asher, C.J.; Menzies, N.W. Trace metal phytotoxicity in solution culture: A review. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rana, S.; Kumar, K. Study of phytotoxic effect of textile wastewater on seed germination and seedling growth of T. aestivum. Int. J. Biosci. Technol. 2017, 10, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Raklami, A.; Oubane, M.; Meddich, A.; Hafidi, M.; Marchner, B.; Heinze, S.; Oufdou, K. Phytotoxicity and genotoxicity as a new approach to assess heavy metals effect on Medicago sativa L.: Role of metallo-resistant rhizobacteria. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, L.; George, J.; Midhun, G.; Magesh, S.B.; Suriyanarayanan, S. Impacts of treated sewage effluent on seed germination and vigour index of monocots and dicot seeds. Russ. Agric. Sci. 2015, 41, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviani, I.; Raviv, M.; Hadar, Y.; Saad, I.; Laor, Y. Original and residual phytotoxicity of olive mill wastewater revealed by fractionations before and after incubation with Pleurotus ostreatus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 11254–11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gal, A.; Borochov-Neori, H.; Yermiyahu, U.; Shani, U. Is osmotic potential a more appropriate property than electrical conductivity for evaluating whole-plant response to salinity? Environ. Exp. Bot. 2009, 65, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Papadavid, G.; Dalias, P.; Fotopoulos, V.; Michael, C.; Bayona, J.M.; Piña, B.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Ranking of crop plants according to their potential to uptake and accumulate contaminants of emerging concern. Environ. Res. 2019, 170, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, R.; Domínguez, C.; Matamoros, V.; Bayona, J.M.; Diez, S. Chemical characterization and phytotoxicity assessment of peri-urban soils using seed germination and root elongation tests. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34401–34411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fargasova, A. Phytotoxicity of chromium and nickel. Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2008, 15, 335–348. Available online: http://tchie.uni.opole.pl/freeECE/S_15_3/Fargasova_15(S3).pdf (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Fiansconaro, M.L.; Antolin, M.C.; Lovato, M.E.; Gervasio, S.; Martin, C.A. Study of fat compost from dairy industry wastewater as a new substrate for pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) crop. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 193, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Pérez, M.; Camacho-Ferre, F. Effect of composts in substrates on the growth of tomato transplants. Hort. Technol. 2010, 20, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Moral, R.; Moreno-Caselles, J.; Perez-Espinosa, A.; Paredes, C. Use of composted sewage sludge in growth media for broccoli. Bioresoure Technol. 2006, 97, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gómez, A.; Bernal, M.P.; Roig, A. Growth of ornamental plants in two composts prepared from agroindustrialwastes. Bioresoure Technol. 2002, 83, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.L.; Jia, Y.B.; Yang, X.E.; He, Z.L.; Stofella, P.J. Assessing lead thresholds for phytotoxicity and potential dietary toxicity in selected vegetable crops. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 80, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casa, R.; D’Annibale, A.; Pieruccetti, F.; Stazi, S.R.; Sermanni, G.G.; Cascio, B.L. Reduction of the phenolic components in olive-mill wastewater by an enzymatic treatment and its impact on durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) germinability. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, A.; Manzoor, M.; Gul, I.; Zafar, R.; Jamil, H.I.; Niazi, A.K.; Ali, M.A.; Park, T.J.; Arshad, M. Phytotoxicity of different antibiotics to rice and stress alleviation upon application of organic amendments. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, E.B.; Milla, O.V.; Huang, W.; Ho, Y.; Chiu, J.; Chang, H. Rice germination as a bioassay to test the phytotoxicity of MSWI bottom ash recycling wastewater. J. Hazard. Toxicradioact. Waste 2013, 17, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, S.D.; Rajan, M.R. Impact of dyeing industry effluent on ground water quality by water quality index and correlation analysis. Res. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 47–53. Available online: http://www.researchinbiotechnology.com/ (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Amin, H.; Arain, B.; Amin, F.; Surhio, M. Phytotoxicity of chromium on germination, growth and biochemical attributes of Hibiscus esculentus L. Am. J. Plant. Sci. 2013, 4, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, V.K.; Kaushik, P. Influence of textile mill wastewater irrigation on the growth of Sorghum cultivars. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2007, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, S.M.; Zayed, M.S.; Atta, H.M. Evaluation of phytotoxicity of compost during composting process. Nat. Sci. 2012, 10, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zwolak, A.; Sarzyńska, M.; Szpyrka, E.; Stawarczyk, K. Sources of soil pollution by heavy metals and their accumulation in vegetables: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceschin, S.; Bellini, A.; Scalici, M. Aquatic plants and ecotoxicological assessment in freshwater ecosystems: A review. Environ. Sci Pollut Res. 2021, 28, 4975–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, K.; Wang, F.; Liang, S.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; Chai, T. Improved Cd, Zn and Mn tolerance and reduced Cd accumulation in grains with wheat-based cell number regulator TaCNR2. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arif, N.; Sharma, N.C.; Yadav, V.; Ramawat, N.; Dubey, N.K.; Tripathi, D.K.; Chauhan, D.K.; Sahi, S. Understanding heavy metal stress in a rice crop: Toxicity, tolerance mechanisms, and amelioration strategies. J. Plant. Biol. 2019, 62, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, Y.N.; Lee, L.K.; Foo, K.Y. Scientific rationale of hospital discharge as a sustainable source of irrigation water: Detection, phytological assessment and toxicity verification. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Michael, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Fotopoulos, V. Can the pharmaceutically active compounds released in agroecosystems be considered as emerging plant stressors? Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. Turning food waste to energy and resources towards a great environmental and economic sustainability: An innovative integrated biological approach. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B. Towards environment-sustainable wastewater treatment and reclamation by the non-aerated microalgal-bacterial granular sludge process: Recent advances and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Quality Parameters | Units | Hospital Wastewater | NEQS [12] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | Treated | |||
| Temperature | °C | 25 | 4 | =<3 |
| Turbidity | NTU | 51 *** | 5 *** | 5 |
| BOD | mg/L | 246 **** | 78 **** | 80–250 |
| Colour | PCU | 188 | 55 | - |
| TSS | mg/L | 2300 **** | 483 **** | <500 |
| COD | mg/L | 396 **** | 260 **** | 150–400 |
| BI | - | 0.62 | 0.3 | - |
| EC | µs/cm | 444 **** | 267 **** | - |
| Salinity | pg/L | 0.2 ** | 0.1 ** | - |
| TDS | mg/L | 296 **** | 220 **** | 1000 |
| Chromium | mg/L | 1.8 | Nd | 0.05 |
| Nickel | mg/L | 1.8 | Nd | 0.02 |
| Lead | mg/L | 0.17 | Nd | 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashid, A.; Mirza, S.A.; Keating, C.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Ali, S.; Campos, L.C. Machine Learning Approach to Predict Quality Parameters for Bacterial Consortium-Treated Hospital Wastewater and Phytotoxicity Assessment on Radish, Cauliflower, Hot Pepper, Rice and Wheat Crops. Water 2022, 14, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010116
Rashid A, Mirza SA, Keating C, Ijaz UZ, Ali S, Campos LC. Machine Learning Approach to Predict Quality Parameters for Bacterial Consortium-Treated Hospital Wastewater and Phytotoxicity Assessment on Radish, Cauliflower, Hot Pepper, Rice and Wheat Crops. Water. 2022; 14(1):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010116
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashid, Aneeba, Safdar A. Mirza, Ciara Keating, Umer Z. Ijaz, Sikander Ali, and Luiza C. Campos. 2022. "Machine Learning Approach to Predict Quality Parameters for Bacterial Consortium-Treated Hospital Wastewater and Phytotoxicity Assessment on Radish, Cauliflower, Hot Pepper, Rice and Wheat Crops" Water 14, no. 1: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010116
APA StyleRashid, A., Mirza, S. A., Keating, C., Ijaz, U. Z., Ali, S., & Campos, L. C. (2022). Machine Learning Approach to Predict Quality Parameters for Bacterial Consortium-Treated Hospital Wastewater and Phytotoxicity Assessment on Radish, Cauliflower, Hot Pepper, Rice and Wheat Crops. Water, 14(1), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010116